1. Introduction
Despite being curable, hepatitis C virus (HCV) is still a global major public health concern. The World Health Organization (WHO) set an ambitious goal to eliminate HCV by 2030 with specific targets to diagnose 90% of people living with HCV and treat 80% of diagnosed people [
1]. However, as of 2024, only 36% of the 50 million people living with HCV had been diagnosed, and just 20% had received curative treatment [
2].
People who inject drugs (PWID) are profoundly and disproportionately affected by HCV. HCV prevalence among PWID is estimated at 39% compared to the general population prevalence of just 1% [
3,
4], and HCV incidence is estimated at 12.1 per 100 person-years [
5]. Globally, there are 15.6 million PWID, of which an estimated 6.1 million people are living with HCV, accounting for 9% of all infections [
4]. Given the high burden, PWID are a priority population to accelerate access to prevention, testing, diagnosis, and treatment services to eliminate HCV by 2030.
Vietnam estimates about one million people living with HCV, but 85% of them remain undiagnosed and 70% of the diagnosed people remain untreated [
6,
7]. The country estimates 161,000 PWID, of which 44% are living with HCV and 17% are living with HIV [
8]. Barriers to access to HCV testing and treatment among PWID include restrictive drug policies, stigma and discrimination, poor access to health services, low hepatitis C testing, linkage to care and treatment, restrictions for accessing direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy, and the lack of government investment to support WHO elimination goals [
3]. In addition, lack of choice for HCV testing options, centralization of HCV viral load testing and treatment, low awareness of the disease, out-of-pocket payments, and high cost of HCV viral load testing and DAA treatment also act as barriers to accessing HCV services among PWID in Vietnam. As per standard of care in Vietnam, HCV testing is currently only available at health facilities where methadone maintenance treatment (MMT), antiretroviral therapy (ART) and pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is provided. HCV viral load testing is centralized at tertiary hospitals and paid for by social health insurance (SHI). DAAs are covered partially (50%) by national social health insurance (SHI), with patients expected to pay for the rest (50% of
$963 for Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir or
$879 for Sofosbuvir/Daclatasvir), but DAA costs remain too high and unaffordable for many people, particularly PWID [
9].
Evidence from previous studies [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14] shows that HCVST is acceptable and feasible among key populations (KPs) including PWID and different settings including Vietnam, and lay people can perform the self-test with minimal support. HIV self-testing (HIVST) has been proven to be effective in increasing the uptake of HIV testing, resulting in more people diagnosed and treated [
23,
24]. In July 2024, WHO pre-qualified the first HCV self-test (i.e., OraQuick HCV self-test) which is an important step to expand access to testing and diagnosis, accelerating the attainment of the 2030 hepatitis elimination goals [
25]. However, there is a lack of direct evidence on the effectiveness of HCVST. The remaining challenge lies in effectively implementing and scaling up HCVST to complement other HCV testing strategies and addressing gaps in current coverage. A first critical step towards HCVST introduction and scale-up is to determine where and how to implement HCVST or optimal approaches to deliver HCVST to support scale-up of this intervention among PWID population.
Drawing from the experiences of established HIVST services and leveraging existing HIVST systems [
15], we implemented three HCVST service delivery models: (1) Facility-based HCVST through ART outpatient clinics, MMT facilities, and private KP-led clinics providing PrEP in distribution of HCVST kits to people living with HIV (PLHIV) and key populations (KPs) including PWID; (2) Community-based HCVST through engagement of community-based organizations (CBO) to distribute HCVST kits to KPs including PWID; and (3) Secondary distribution (social network approaches), where clients who received HCVST at CBOs distributed HCVST kits to their sexual partners and/or injecting partners.
With this study in Vietnam, we investigate the effectiveness of three HCVST service delivery models compared to provider-led HCV testing (PL-HCVT). The PL-HCVT refers to the standard of care facility-based HCV testing (SOC-HCVT) at clinics and community-based HCV testing offered by CBOs (CBO-HCVT).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
We designed an implementation research study to assess the effectiveness of three HCVST service delivery models (facility-based, community-based, and secondary distribution) compared to PL-HCVT (SOC-HCVT and CBO-HCVT). HCVST distribution models were integrated into existing HIV and harm reduction services, such as community HIV testing, ART, MMT, and PrEP. We generated data on PWID from a larger implementation science study. Quantitative data were collected through: (1) a cross-sectional survey administered with PWID who opted for HCVST or SOC-HCVT/CBO-HCVT; (2) an e-logbook maintained client records when using HCV services.
2.2. Overview of the Intervention and Implementation Approach
We engaged a total of 18 intervention sites, including 10 clinics (3 MMT, 3 ART, and 4 KP-led clinics) and eight CBOs to provide HCVST through three service delivery models (community-based and facility-based distribution, and secondary distribution). The clinics offered a choice of facility-based HCVST or SOC-HCVT for PWID clients seeking or using MMT, ART and/or PrEP services, while the CBOs offered a choice of community-based HCVST or CBO-HCVT for PWID clients receiving needles & syringes and/or community HIV testing. HCVST secondary distribution was implemented through engagement of primary HCVST clients at CBOs. Each primary HCVST client distributed up to three kits to their sexual and/or injecting partners who they thought would benefit from HCVST. CBO service providers followed-up secondary distribution clients via telephone for up to four weeks to check if they performed the self-test and/or visited the designated clinics for HCV confirmatory testing and/or treatment initiation.
The linkage to care pathways included active referral from CBOs, which offered accompanied referrals for those who tested with the provider using assisted HCVST. Those who used unassisted HCVST across all three testing models were followed up by phone within four weeks of the client obtaining the kit. Clients who had a reactive test result were offered accompanied referrals or assistance with scheduling appointments if they preferred to go for confirmation testing alone. The linkage pathways also included passive referrals from clinics, where clients with a reactive test result were referred to HCV confirmatory testing and treatment using a standard referral slip. The cascade of care models was employed to track and visualize the results of linkage to care.
2.3. HCV Test Kits
In this study we used OraQuick HCV Rapid Antibody Test (OraSure Technologies, PA, USA) as an oral fluid-based assay to distribute to study participants who opted for HCVST. The OraQuick HCV Rapid Antibody Test has a sensitivity of 98% (95% CI 97%-99%) and a specificity of 100% (95% CI 90%-100%) [
16], is prequalified by WHO and the Conformitè Europëenne and marked for professional use that provides a result in 20-40 minutes [
17,
18]. Modified Instructions for Use developed by the manufacturer was used to adapt the professional use kit to a self-test. The test was packaged for single use as a self-test for the study in Vietnam.
We used Bioline HCV rapid test (Abbott Diagnostics, IL, USA) for study participants who opted for SOC-HCVT and CBO-HCVT. The Bioline HCV rapid test has a sensitivity of 95% (95% CI 93–96%) and a specificity of 100% (95% CI 99– 100%) [
19].
2.4. Study Population
The study population consisted of PWID seeking HIV and/or harm reduction services at the study sites and clients receiving HCVST kits distributed by primary HCVST clients at CBOs (secondary distribution). HIV-negative and HIV status-unknown individuals who self-identified as a person who injects drugs (PWID) and reported injecting drugs at least once in the past month, using MMT and/or receiving ART or PrEP were included in this study. Study participants were required to be 18 years or older, have an unknown HCV status or not have been tested for HCV in the past six months, provide written consent for participation in the study, and have access to a reliable phone for follow-up. PWID clients were excluded if they had been diagnosed with chronic HCV or on HCV treatment.
2.5. Study Procedures and Data Collection
PWID clients seeking HIV and/or harm reduction services at CBOs and clinics in the study sites were invited to participate in the study. The recruitment of study participants varied by primary distribution directly implemented by CBOs and clinics and secondary distribution indirectly administered by CBOs through engagement of primary HCVST clients.
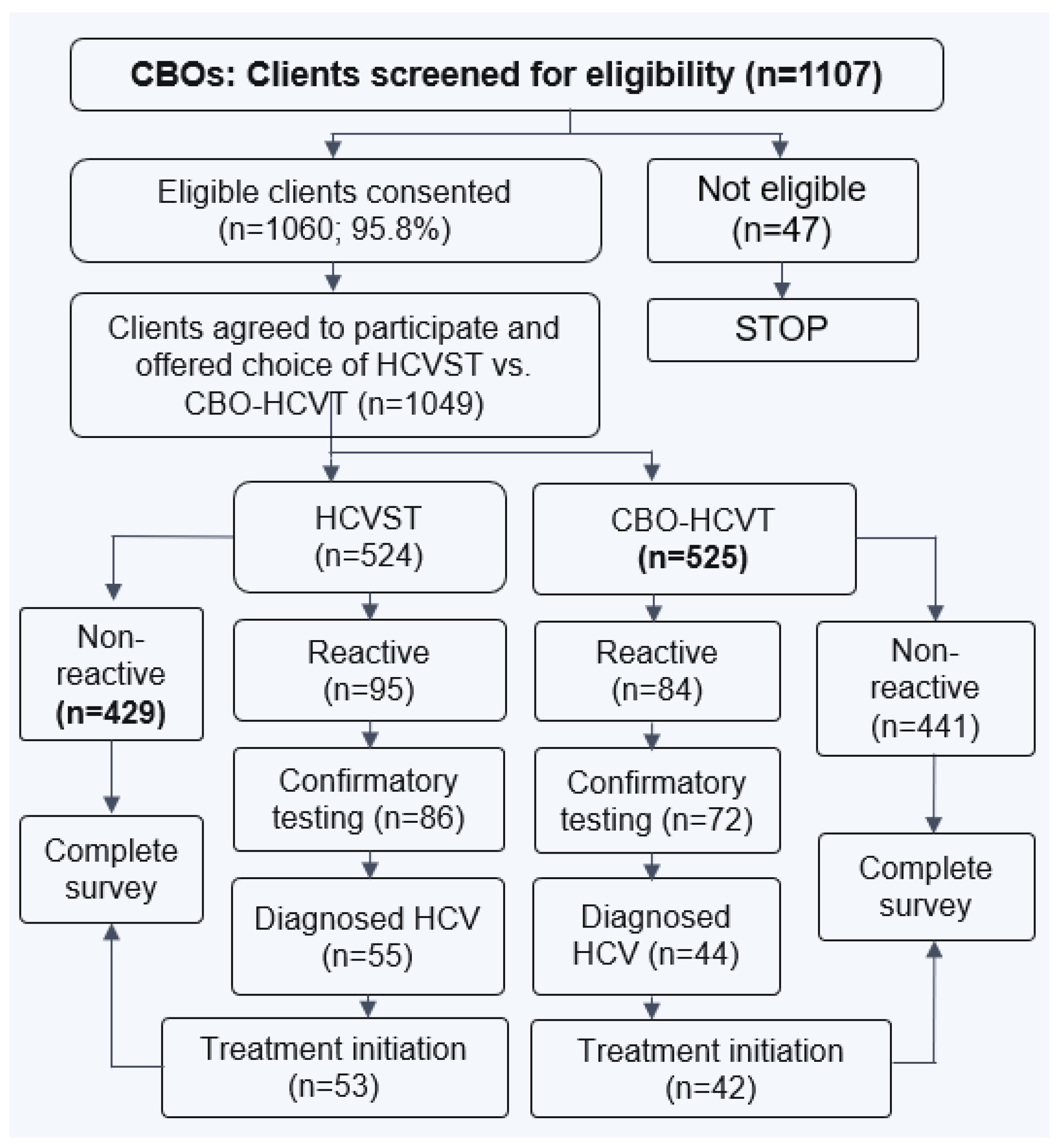
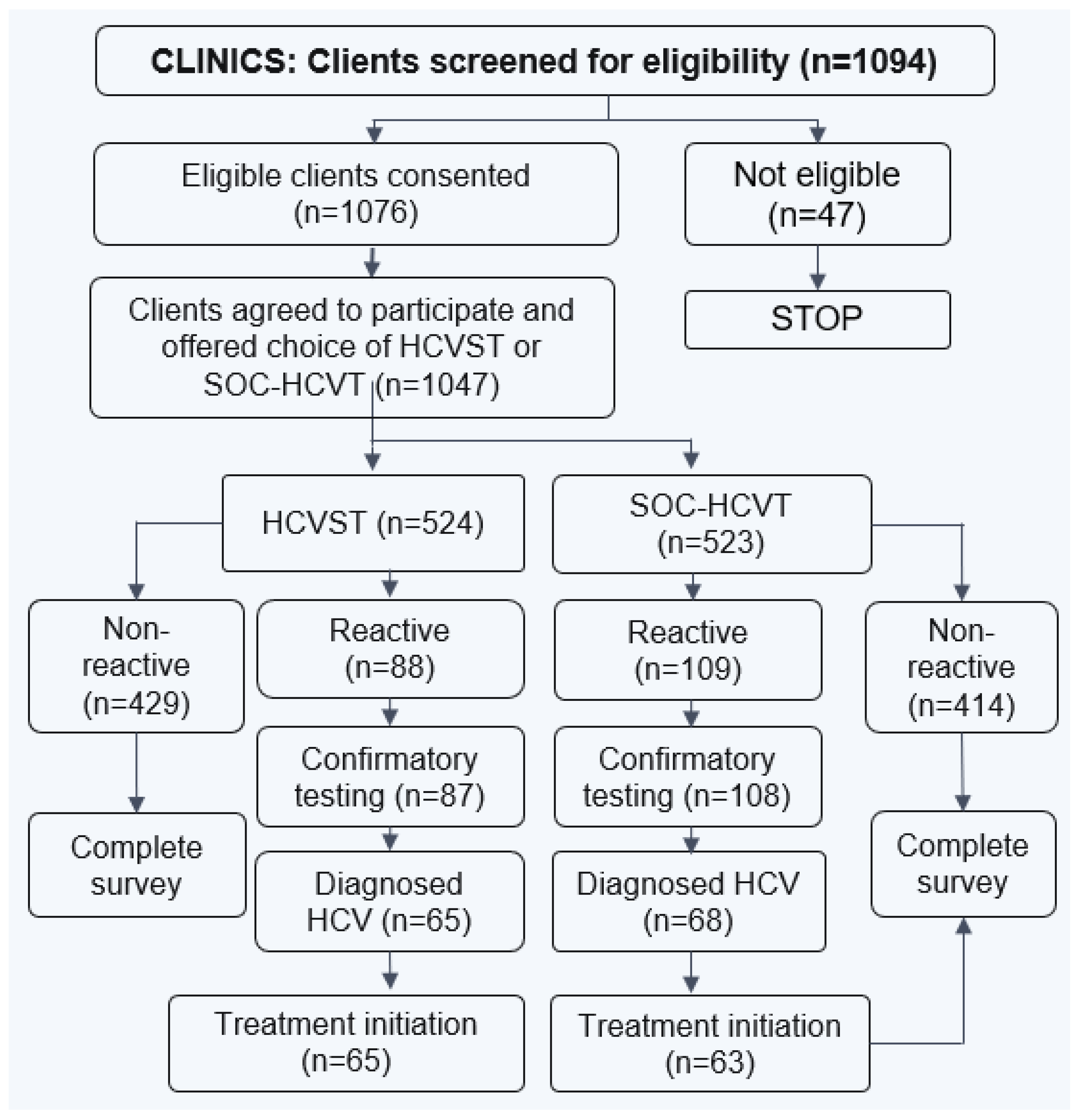
Figure 1 and
Figure 2 display the process of recruitment and enrollment of study participants at CBOs and clinics employed in the larger implementation science study.
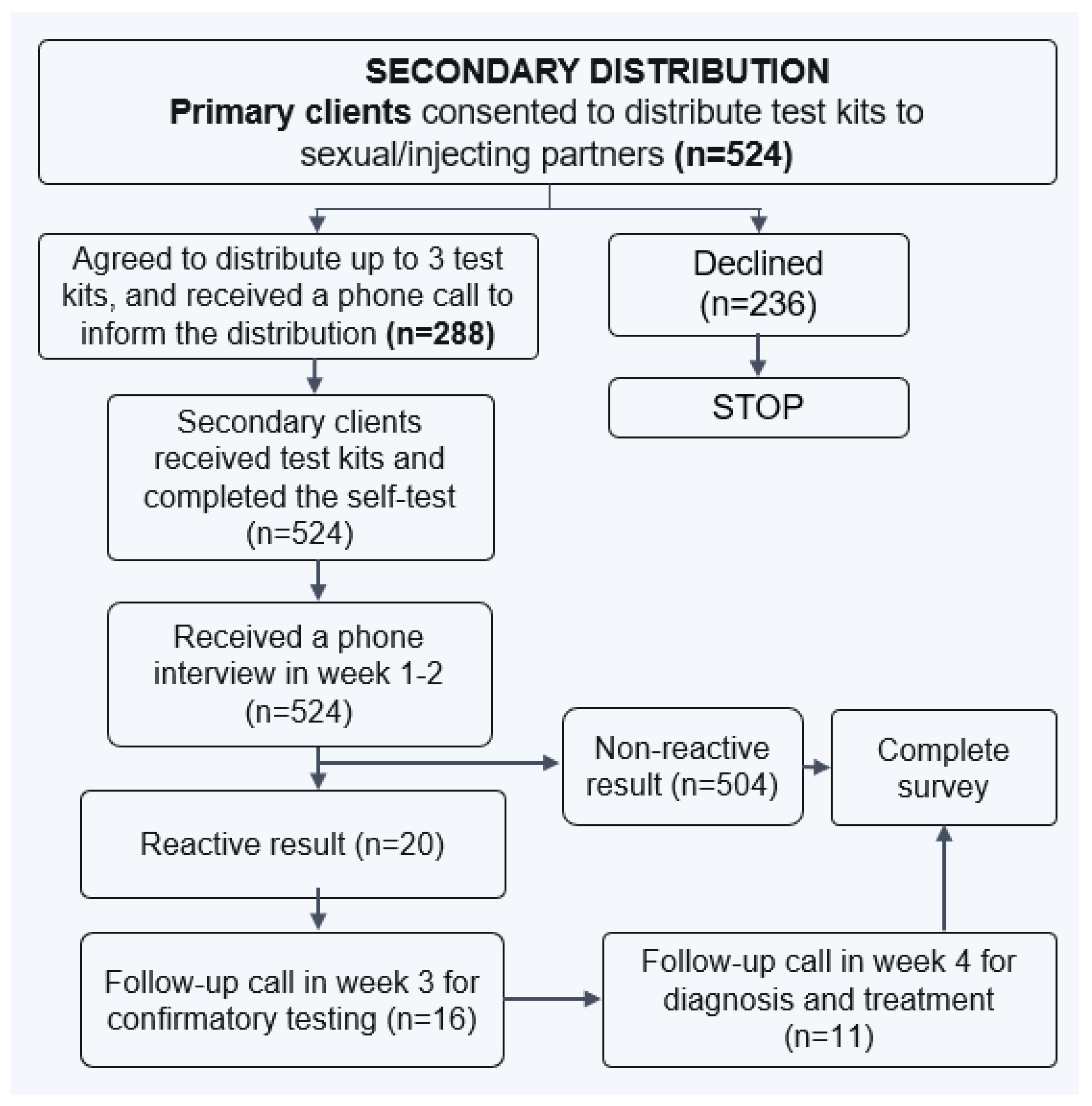
PWID clients who opted for HCVST at CBOs were invited to take part in secondary distribution of HCVST kits to their injecting and/or sexual partners (as distributors). The study staff obtained another written informed consent from the distributors. Each distributor received up to three HCVST kits to deliver to their partners.
Figure 3 displays study procedures for recruitment of study participants through HCVST secondary distribution model.
2.6. Analysis Approach
The primary outcome of interest was the proportion of first-time HCV testers reached by delivery model. The main analysis measured first-time testers by model and by dependent factors (age, gender, education, occupation, income, KP group, and testing model). In this study we evaluated the effectiveness of HCVST service delivery models by the ability to reach unreached populations or first-time testers, find people with HCV, and link them to care compared to PL-HCVT (SOC-HCVT and CBO-HCVT) among PWID.
Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and multivariable logistic regression models in SPSS Version 22.0. We conducted univariable and multivariable logistic regression to investigate factors associated with first-time HCV testing and/or HCV seropositivity. Variables adjusted in the logistic regression models included age, marital status, education, occupation, income, KP group, and testing model. Variables found to be statistically significant at a p-value of less than 0.05 are included in the multivariable logistic regression models. Multivariable logistic regression models were used to examine the factors associated with the outcome indicator. The analysis results were presented and interpreted as an odds ratio with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI). The programmatic monitoring data were analyzed to measure HCV seropositivity rate and success rate of the linkage to HCV confirmatory testing and treatment initiation.
3. Results
Demographic Characteristics of Study Participants
In total, 1161 PWID were included in this analysis, of which 689 opted for HCVST and 472 opted for PL-HCVT. There was no significant difference between HCVST and PL-HCVT clients in age, education, and income. The median age of the participants was 42 (IQR: 37-48); a great majority (88.2%) completed secondary school and higher education; and the vast majority (95.8%) had a monthly income of 10 million VND (
$417) or lower (
Table 1). However, the proportion of male and married PWID HCVST clients was lower than PL-HCVT (58.9% and 53% vs. 84.1% and 62.3%, respectively), while the proportion of employed PWID HCVST clients was higher than PL-HCVT (18.1% vs. 12.7%, respectively).
First-Time HCV Testers
Overall, the proportion of first-time HCV testers was higher in HCVST than in PL-HCVT (72% vs. 62.3%, respectively). There was a significant higher proportion of first-time testers among PWID who opted for HCVST secondary distribution and community-based distribution as well as CBO-HCVT compared to HCVST facility-based distribution and SOC-HCVT (93.3%, 87.1% and 82.7% vs. 35.7% and 41.9%, respectively; p < 0.001) (
Table 2).
Factors Associated with First-Time HCV Testing
Univariate analysis comparison between first-time HCV testing and having ever tested for HCV revealed that PWID who opted for HCVST secondary distribution and community-based distribution and CBO-HCVT were more likely to be first-time testers (
Table 3). A multivariable logistic regression analysis confirmed a significant association between first-time HCV testing and opting for HCVST secondary distribution (adjusted odds ratio [aOR]: 23; 95%CI: 11.92-44.39), HCVST community-based distribution (aOR: 9.65; 95%CI: 6.02-15.47) in addition to CBO-HCVT (aOR: 6.57; 95%CI: 4.19-10.32).
HCV Seropositivity Yield
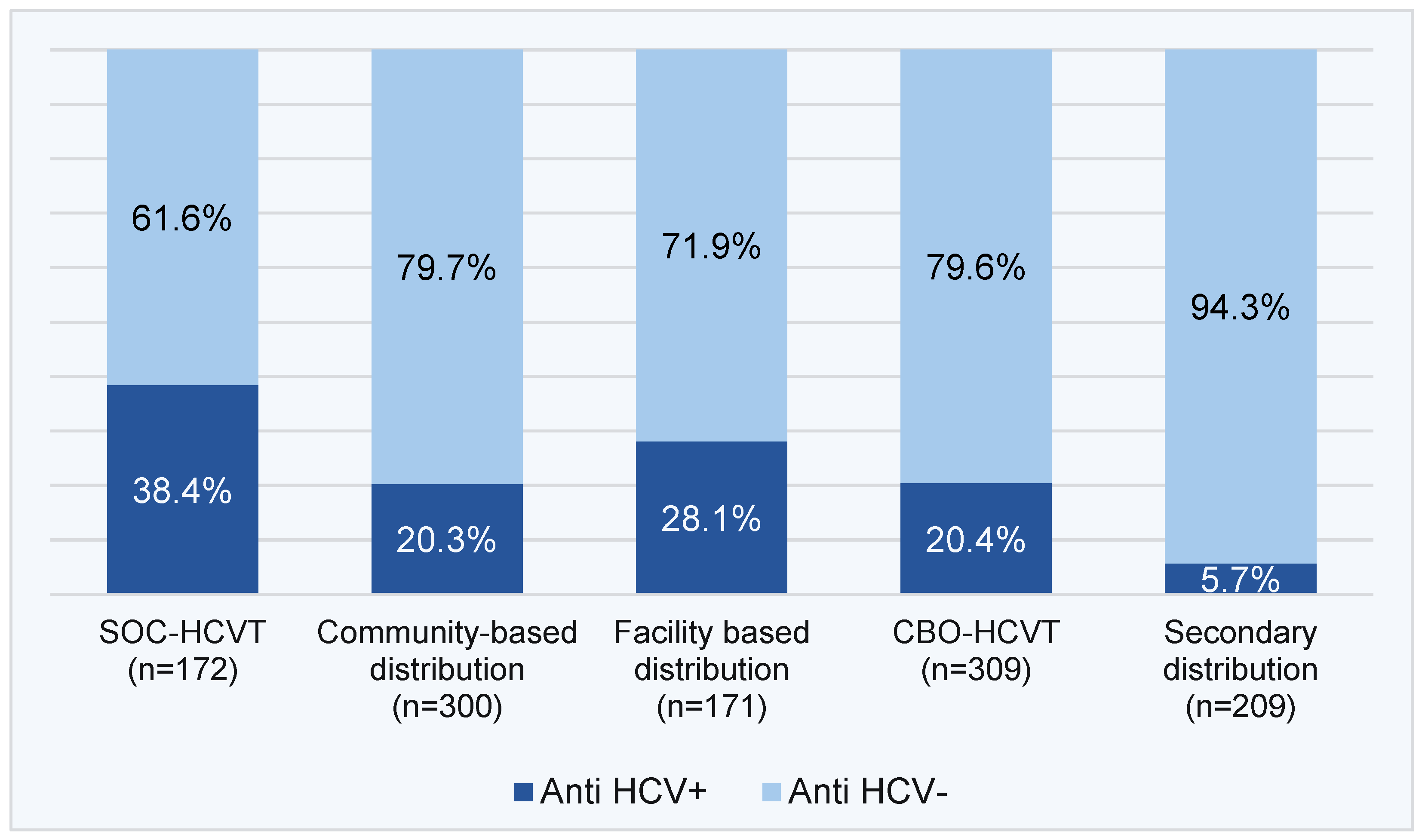
The HCV seropositivity yield was higher among clients who opted for PL-HCVT than HCVST, but higher through HCVST facility-based and community-based distribution compared to HCVST secondary distribution (38.4% and 20.3%; 28.1% and 20.4% vs. 5.7%, respectively) (
Figure 4).
Factors Associated with HCV Seropositivity
Univariate analysis comparison between HCV seropositive and negative results revealed that PWID aged 30 years and older and those being unemployed were more likely to have an HCV seropositive result (
Table 4). A multivariable logistic regression analysis confirmed a significant association between HCV seropositivity and being a PWID aged 30 years and older (aOR: 9.57; 95%CI: 2.25-40.7), but the association between being unemployed and HCV seropositivity was no longer significant when being adjusted with other factors. There was a significant association between HCV seropositivity and opting for HCV testing models in which SOC-HCVT achieved the highest yield of HCV seropositivity, followed by CBO-HCVT, HCVST community-based distribution and secondary distribution. HCV seropositivity rate in HCVST community-based distribution and secondary distribution was 52% and 89% lower than the SOC-HCVT (aOR: 0.48; 95%CI: 0.31-0.73 and aOR: 0.11; 95%CI: 0.06-0.2, respectively).
HCV Cascade of Care
Overall, SOC-HCVT and HCVST facility-based distribution yielded a higher rate of HCV seropositivity than CBO-HCVT and HCVST community-based distribution (38.4% and 28.1% vs. 20.3% and 20.4%, respectively) (
Table 5). HCV seropositivity rate in HCVST community-based distribution was compatible with CBO-HCVT. Notably, the success rate of linkage to care from HCVST facility-based distribution was as high as from SOC-HCVT (97.9% and 98.5%, respectively). The success rate of linkage to care from HCVST community-based distribution was like CBO-HCVT (88.9% and 80.3%, respectively). Interestingly, all PWID diagnosed HCV (100%) initiated DAA treatment that was offered free of charge by the study or the Global Fund.
Ranking the Effectiveness of HCVST Service Delivery Models Compared to PL-HCVT
To compare the effectiveness across five testing models we provided a score from 1 to 5 for each criterion (i.e., reaching unreached populations, detection of people with HCV, and linkage to care) in which 1 was the most effective and 5 was the least effective. Then, the total score was summed up to rank in order of the testing model effectiveness (
Table 6). Results of the ranking show that in addition to SOC-HCVT, HCVST community-based and facility-based distribution were more effective than CBO-HCVT and HCVST secondary distribution.
4. Discussion
This study evaluated the effectiveness of HCVST service delivery models compared to SOC-HCVT and CBO-HCVT as an additional approach to increase the uptake of HCV testing and linkage to care among PWID in Vietnam. Our results indicate that HCVST increases the uptake of HCV testing among PWID first-time testers and results in more people diagnosed and treated with HCV. This finding is consistent with previous multi-country randomized clinical trial study in Malaysia, Georgia, and Pakistan among key populations (PWID and men who have sex with men) and the general population that reported increasing uptake of HCV testing and resulting in high linkage to further care compared to the standard of care [
22].
We found a significantly higher proportion of first-time testers among PWID who opted for HCVST, particularly through HCVST community-based distribution and secondary distribution, compared to PL-HCVT (SOC HCVT and CBO-HCVT). This implies that HCVST community-based distribution and secondary distribution are optimal models to reach unreached PWID or those who may not otherwise test in existing HCV testing services. A previous study in China also reports first-time testers accounted for over half (58.6%) of HCV self-testers among men who have sex with men [
11]. Similar to community-based testing approach [
20], HCVST community-based distribution and secondary distribution are implemented by CBOs that reach and distribute test kits as an active testing approach. The active testing approach has proven to be more effective than the SOC passive testing approach in increasing the uptake of HCV testing among hard-to-reach populations such as PWID. This suggests that HCVST can be an effective strategy to accelerate the coverage of HCV testing among the PWID population that currently has poor access to health services [
3].
Although HCVST community-based and secondary distribution and CBO-HCVT have lower rates of HCV seropositivity than SOC-HCVT and HCVST facility-based distribution, the ability to reach more first-time testers of HCVST community-based and secondary distribution would ultimately result in more people diagnosed and treated with HCV. Evidence from previous studies on HIVST showed that the proportion of people diagnosed with HIVST is greater than facility-based testing [
15]. A cost-effective study of HCVST in four countries including Vietnam also indicated that HCVST increases the number of people tested, diagnosed, and cured [
21]. SOC-HCVT and HCVST facility-based distribution have the advantage of reaching PWID who are most at-risk and frequently visit health facilities for MMT, ART or PrEP services and obtaining a higher rate of HCV seropositivity but are limited in reaching first-time HCV testers who are not yet in the health systems. This finding suggests that HCVST could be used as a case finding strategy to accelerate elimination of hepatitis C among PWID.
This study provides direct evidence on the effectiveness of HCVST service delivery models in PWID. We found that in addition to the SOC-HCVT, HCVST community-based distribution is the most effective model, followed by HCVST facility-based distribution, CBO-HCVT, and HCVST secondary distribution. This is the first study measuring the effectiveness of HCVST service delivery models based on criteria for reaching first-time testers, finding people with HCV, and linking them to care. HCVST community-based distribution that is highly effective to reach first-time testers and detect people with HCV can be an optimal service delivery model. This suggests that HCVST can be an additional approach to the SOC- HCVT in which priority is given to HCVST community-based distribution, followed by facility-based and secondary distribution.
Due to co-location of the services, SOC-HCVT and HCVST facility-based distribution had a higher success rate of linking people with HCV to care than HCVST community-based and secondary distribution as well as CBO-HCVT. Linkage to care from the community to health facility requires setting up a functional referral system and supporting its operations. CBOs played a key role in offering active referral or linkage to clients opting for HCVST community-based and secondary distribution by accompanying or making appointments with the designated clinics for clients.
Limitations: This study has several limitations. Convenience sampling with “take all” method may create a selection bias in recruiting a sample of study participants that may not be representative of the entire PWID population. The study sample of PWID generated from a larger implementation science study may have limitations in obtaining comprehensive and in-depth data on HCVST among PWID. The short period of time for data collection (i.e., six months instead of 12 months as designed in the study) did not enable us to collect data on sustained virus response at 12 weeks after treatment (SVR12) to evaluate cure rate of HCV treatment.
5. Conclusions
Our study confirms that HCVST is an effective approach to increase the uptake of HCV testing and treatment among PWID. In addition to the standard of care facility-based HCV testing, HCVST community-based distribution is most effective, followed by facility-based distribution and secondary distribution. Evidence from the study informs guidelines on the design and implementation of HCVST services on a larger scale in Vietnam and other low- and middle-income countries. Given the availability of WHO-prequalified HCV self-test kits, scaling-up HCVST can become a reality to accelerate micro-elimination of hepatitis C among PWID.
Funding
This study was supported by Unitaid through the STAR project, implemented by Population Service International (PSI), PATH, and Jhpiego.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study obtained ethical approval from the World Health Organization Ethics Review Committee (reference number ERC 0003830 dated 15 September 2022), the local Institutional Review Board at Center for Creative Initiatives in Health and Population – CCIHP (reference number 011223/HDPB-CCIHP dated 30 November 2022) and the National Research Ethics Committee (reference number 235/CN-HDDD dated 22 December 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
All study participants provided written informed consent except for consent waivers for the recipients of HCVST through the secondary distribution delivery model. There were no refusals.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Center for Disease Control, district health centers, public and private clinics, and community-based organizations in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City for their support of the study. We thank all the study participants for their contributions. Thanks to Vietnam Administration of Medical Services (VAMS) and Vietnam Administration of HIV/AIDS Control (VAAC), Ministry of Health for their interest in innovation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The sponsors had no role in the design, execution, interpretation, or writing of the study.
References
- World Health Organization. Global Health Sector Strategy on Viral Hepatitis 2016–2021. June 2016. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/246177/WHO-HIV-2016.06-eng.pdf.
- World Health Organization. Global hepatitis report 2024: action for access in low- and middle- income countries. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2024. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240091672.
- Day, E.; Hellard, M.; Treloar, C.; Bruneau, J.; Martin, N.K.; Øvrehus, A.; et al. Hepatitis C elimination among people who inject drugs: Challenges and recommendations for action within a health systems framework. Liver International. 2019; 39:20–30. [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, L.; Peacock, A.; College, S.; Leung, J, Grebely J., Vickerman, P.; et al. Global prevalence of injecting drug use and sociodemographic characteristics and prevalence of HIV, HBV, and HCV in people who inject drugs: a multistage systematic review. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5(12): e1192–e207. Published Online October 23, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Artenie, A.; Stone, J.; Fraser, H.; Stewart, D.; Arum, C.; Lim, A.G.; et al. Incidence of HIV and hepatitis C virus among people who inject drugs, and associations with age and sex or gender: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2023; 8: 533–52 Published Online March 27, 2023. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Regional Officer for the Western Pacific. Viral hepatitis situation and response in Vietnam. 2018. Manila, Philippines.
- Ministry of Health and US-CDC. HBV and HCV seroprevalence surveillance in Vietnam. 2018. Hanoi, Vietnam.
- Vietnam Administration of HIV/AIDS Control. HIV sentinel surveillance 2021 results. Hanoi, Vietnam.
- Clinton Health Access Initiative. HCV market intelligence report 2023. Issue 3. https://www.clintonhealthaccess.org/report/2023-hepatitis-c-market-intelligence-report/.
- Xu, W.; Reipold, E.I.; Zhao, P.; Tang, W.; Tucker, J.D.; Ong, J.J.; et al. HCV Self-Testing to Expand Testing: A Pilot Among Men Who Have Sex with Men in China. Frontiers in Public Health. 2022,10:903747. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, P.; Weideman, A.M.; Xu, W.; Ong, J.J.; Jamil, M.S.; et al. Expanding hepatitis C virus test uptake using self-testing among men who have sex with men in China: two parallel randomized controlled trials. BMC Medicine. 2023, 21:279. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Nguyen, V.T.T.; Le, A.K.A.; Truong, M.B.; Tran, T.T.M.; Jamil, M.S.; et al. Acceptability and Usability of HCV Self-Testing in High-Risk Populations in Vietnam. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):377. [CrossRef]
- Reipold, E.I.; Farahat, A.; Elbeeh, A.; Soliman, R.; Aza, E.B.; Jamil, M.S.; et al. Usability and acceptability of self-testing for hepatitis C virus infection among the general population in the Nile Delta region of Egypt. BMC Public Health. 2021,21:1188. [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, E.; Watson, V.; Kumwenda, M.; Usharidze, D.; Gogochashvili, S.; Kakhaberi, D.; et al. Usability and Acceptability of Oral-Based HCV Self-Testing Among Key Populations: A Mixed-Methods Evaluation in Tbilisi, Georgia. Research Square. 2021. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Recommendation on guidance on hepatitis C virus self-testing. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240031128.
- Cha, Y.J. ; Park, Q. ; Kang, E.S. ; et al. Performance evaluation of the OraQuick® hepatitis C virus rapid antibody test. Ann Lab Med. 2013;33(3):184-189. [CrossRef]
- Kimble, M.M.; Stafylis, C.; Treut, P.; Saab, S.; Klausner, J.D. Clinical evaluation of a hepatitis C antibody rapid immunoassay on self-collected oral fluid specimens. Diagnostic Microbiology & Infectious Disease. 2019;95(2):149-51.
- Liu, L. ; Zhang, M. ; Hang, L. ; Kong, F. ; Yan, H. ; Zhang, Y. ; et al. Evaluation of a new point-of-care oral anti-HCV test for screening of hepatitis C virus infection. Virology Journal. 2020;17(1):14.
- Vetter,. B.N.; Reipold, E.I.; Ongarello, S.; Audu, R.; Ige, F.A.; Alkhazashvili, M.; et al. Sensitivity and specificity of rapid diagnostic tests for hepatitis C virus with or without HIV coinfection: a multicentre laboratory evaluation study. J Infect Dis. 2020.
- Vu, B.N.; Tuan, K.D.; Tran, A.K.; Tran, L.K.; Green, K.; Nguyen, K.T.; et al. Community-based and HIV integrated testing for hepatitis B and C among key populations in Vietnam. Clinical Liver Disease. 2022; 19:131–137. [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.G.; Ivanova, E.; Jamil, M.S.; Ong, J.J.; Easterbrook, P.; Fajardo, E.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of Hepatitis C virus self-testing in four settings. PLOS Glob Public Health 2023; 3(4): e0001667. [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.G.; Easterbrook, P.; Fajardo, E.; Ivanova, E.; Jamil, M.S.; Johnson, C.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of hepatitis C virus self-testing. In: Recommendations and guidance on hepatitis C virus self-testing. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- Shilton, S.; Hamid, S.; Hassan, M.R.A.; Stvillia, K.; Hasnain, A.; Japaridze, M.; et al. Uptake and linkage to care for HCV self-testing: results from a multi-country RCT. Poster at CROI, 19-22 February 2023, Seatle, Washington. https://www.croiconference.org/abstract/uptake-and-linkage-to-care-for-hcv-self-testing-results-from-a-multi-country-rct/.
- Empringham, B.; Karellis, A.; Kashkary, A.; D’Silva, O.; Carmona, S.; Suarez, M.F.; et al. How much does HIV self-testing cost in low- and middle-income countries? A systematic review of evidence from economic studies. Front. Public Health. 2023; 11:1135425. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO prequalifies the first self-test for hepatitis C virus. 10 July 2024. New release. https://www.who.int/news/item/10-07-2024-who-prequalifies-the-first-self-test-for-hepatitis-c-virus.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).