Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
22 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
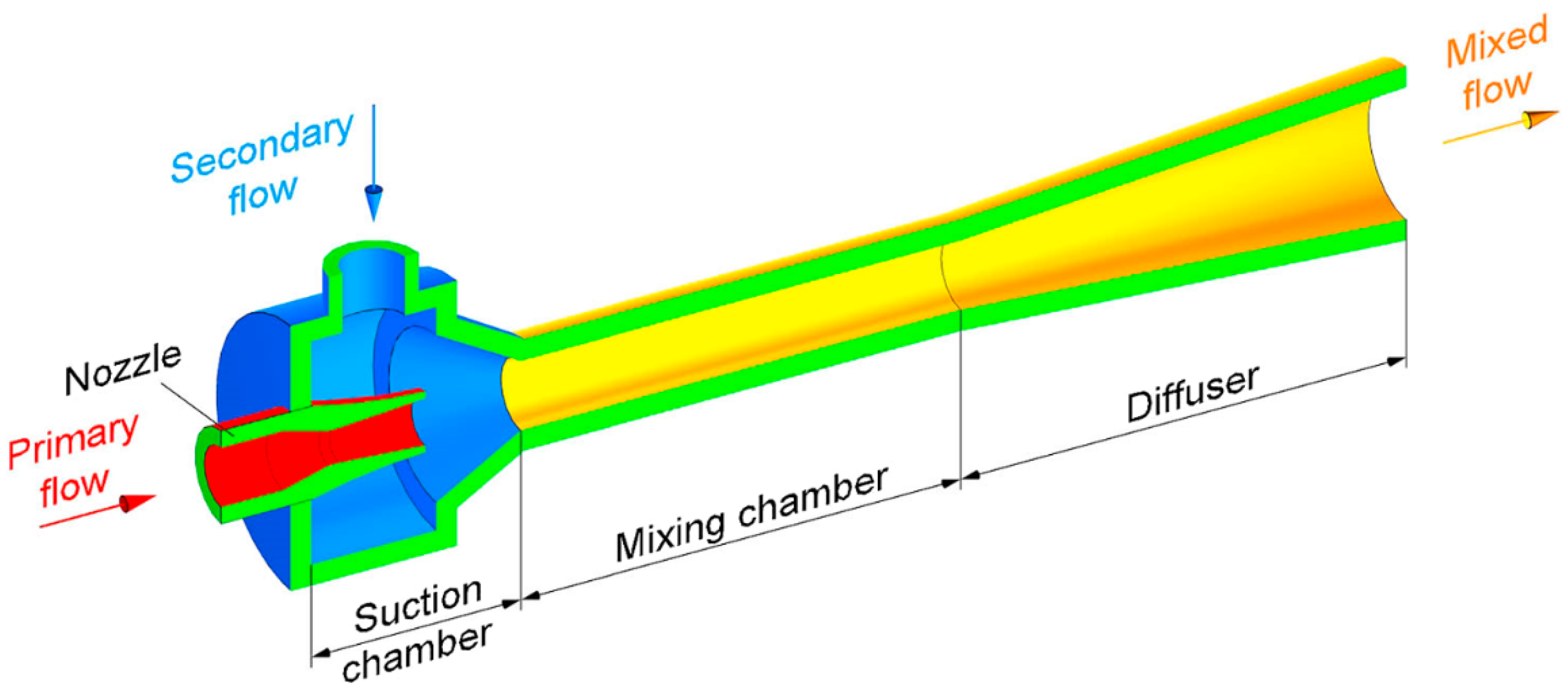
2. Fundamental of Ejectors
- The primary fluid’s pressure energy is converted into kinetic energy within the nozzle
- The low-velocity secondary fluid is entrained and mixed with the high-velocity primary fluid in the mixing throat, driven by viscous friction and the suction created by the pressure drop at the nozzle exit
- The combined fluid’s kinetic energy is transformed back into pressure energy within the diffuser.
2.1. Entrainment Ratio
2.2. Pressure Ratio
2.3. Efficiency of Ejector
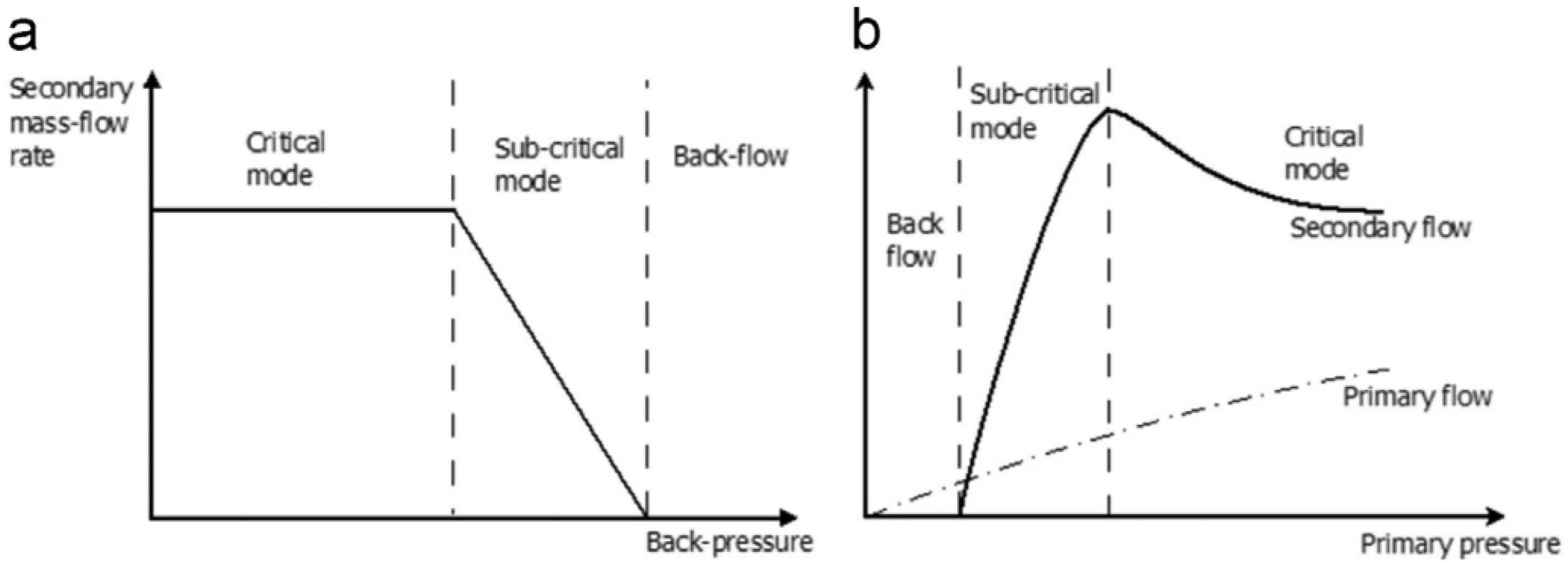
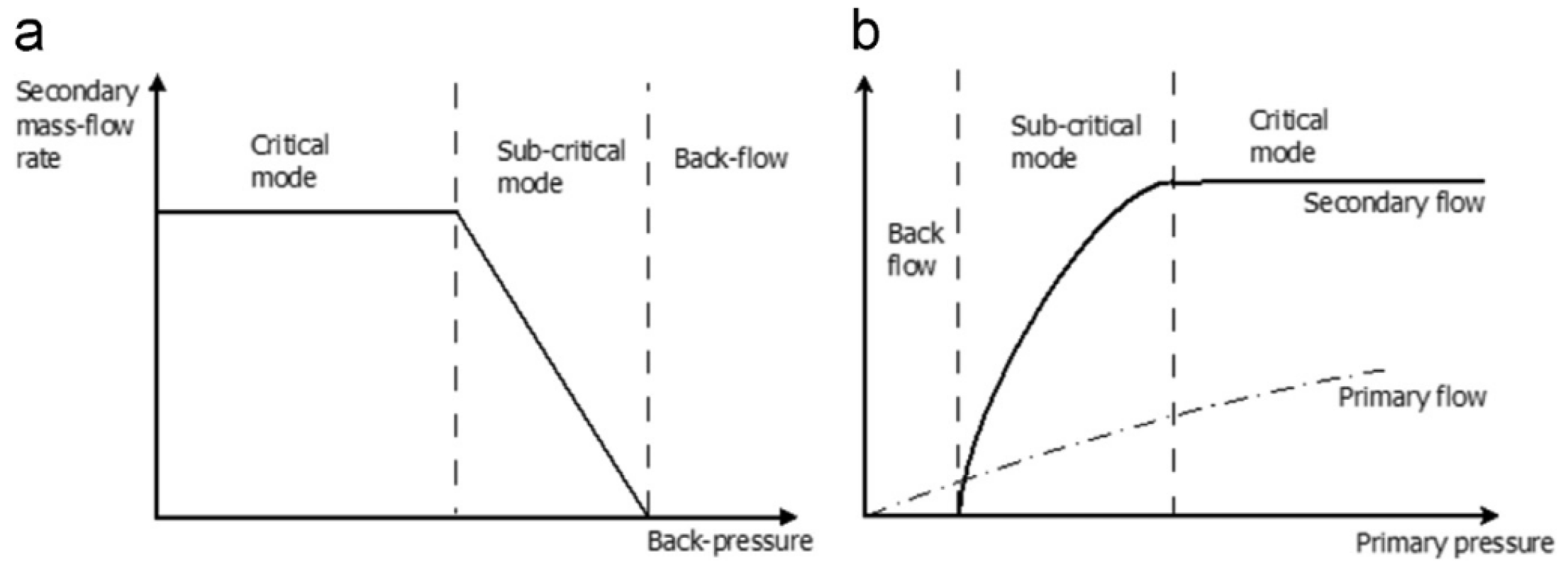
2.4. Subsonic Ejectors
2.5. Supersonic Ejectors
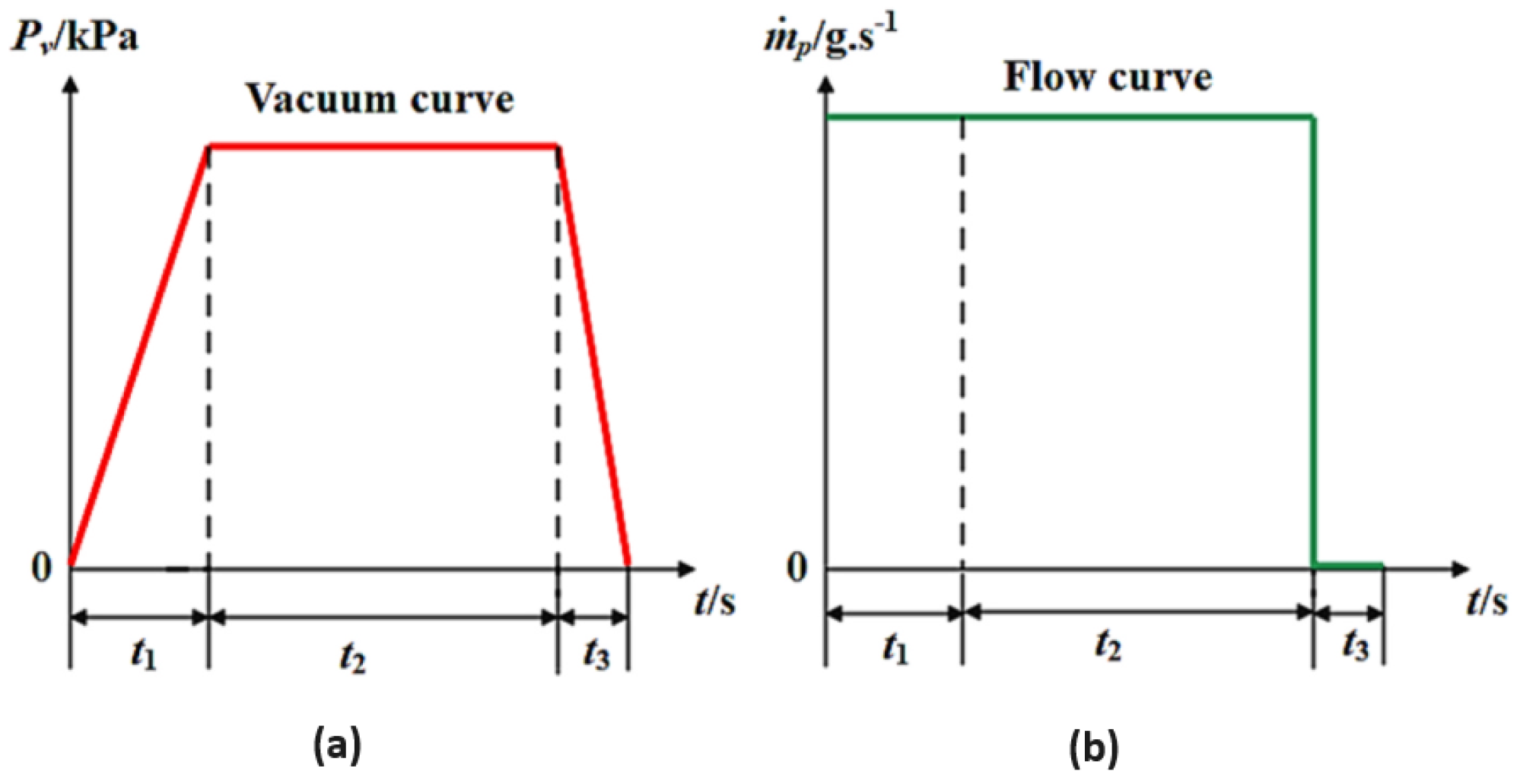
2.6. Vacuum Ejectors
- The response time of the vacuum system is important - if it is too long, it can reduce work efficiency and increase air consumption.
- The vacuum maintenance time or workpiece suction time is a significant portion of the overall work cycle, 50-80%. During this time, high-pressure air is continuously supplied to maintain the vacuum level.
- In practice, the priority should be minimizing the response time, even if it means using a lower supply pressure to reduce energy consumption.
- Improving the entrainment capacity of the vacuum ejector or reducing air consumption during the vacuum holding stage could lead to more energy-efficient and effective vacuum system applications.
2.7. Applications
2.7.1. Single-Phase and Two-Phase Ejectors
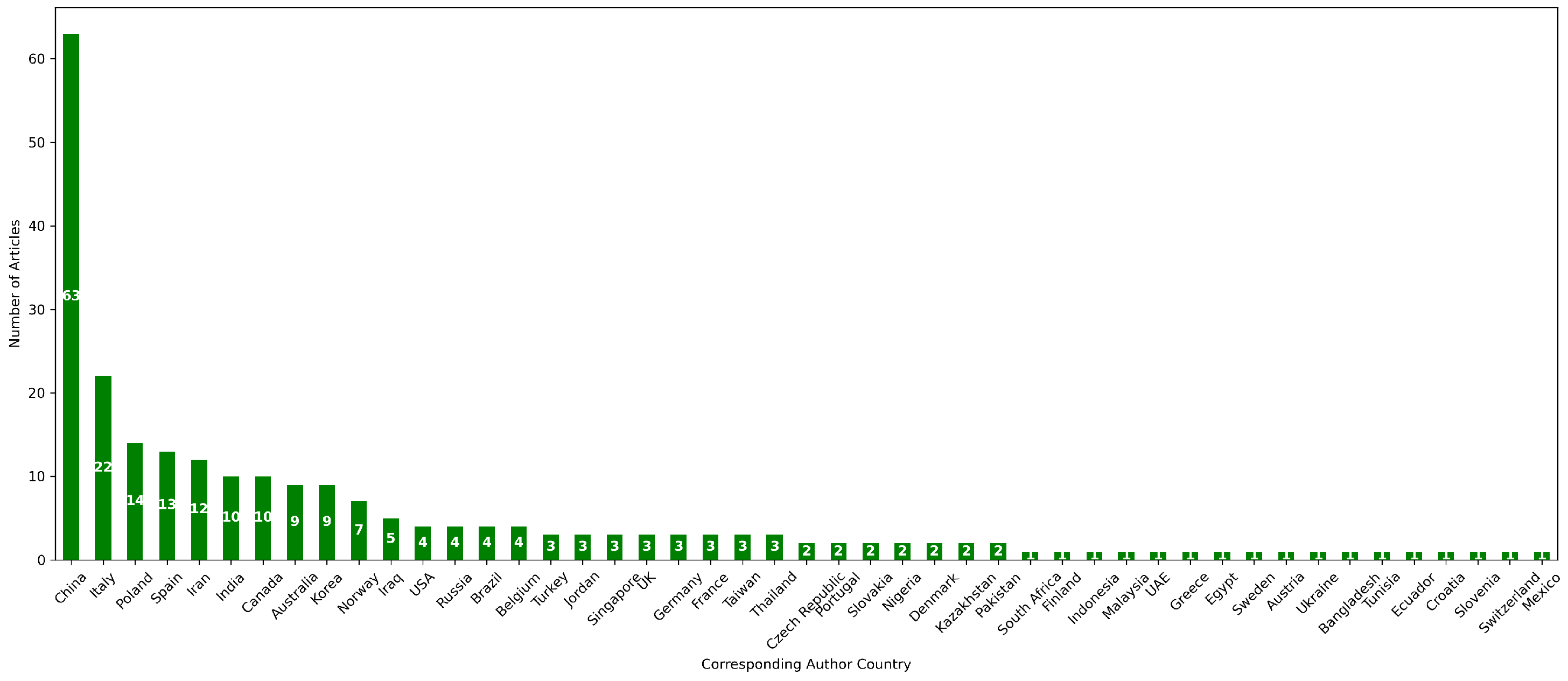
2.7.2. Geography of Ejectors Research
3. Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Ejectors
3.1. Single-Phase Ejector CFD Simulation
3.2. Two-Phase Ejectors CFD Simulation
3.3. Numerical Methods
- Volume of Fluid (VOF): Suitable for simulating fluids with a sharp interface, such as liquid-gas flows.
- Mixture model: often used for simulating homogeneous multiphase flows or when the interface is not of primary interest.
3.4. Geometry and Mesh
3.5. Boundary Conditions
3.6. Solvers and Software
3.7. Turbulence Modeling
3.8. Validation and Verification
3.9. Parametric Study
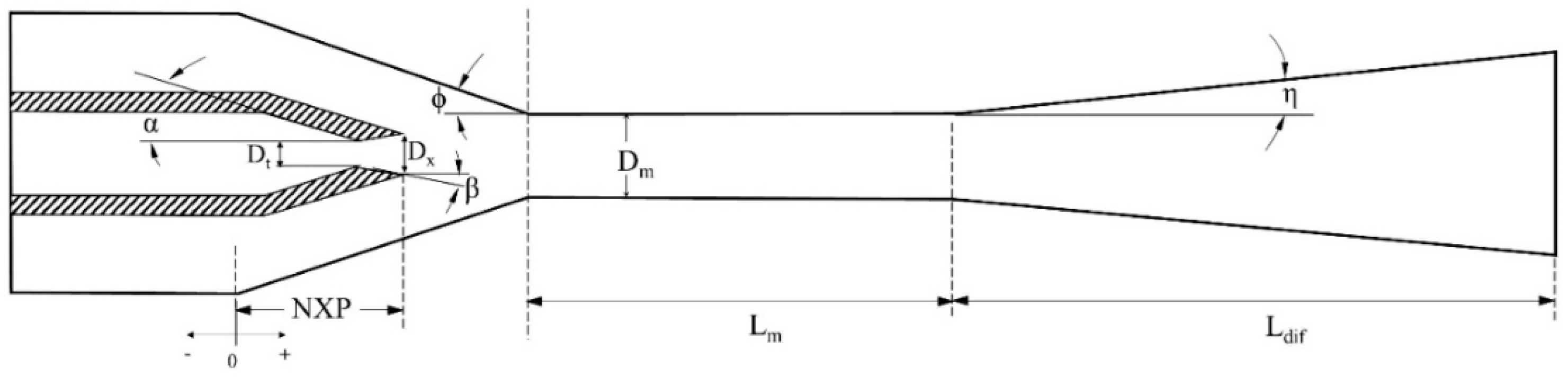
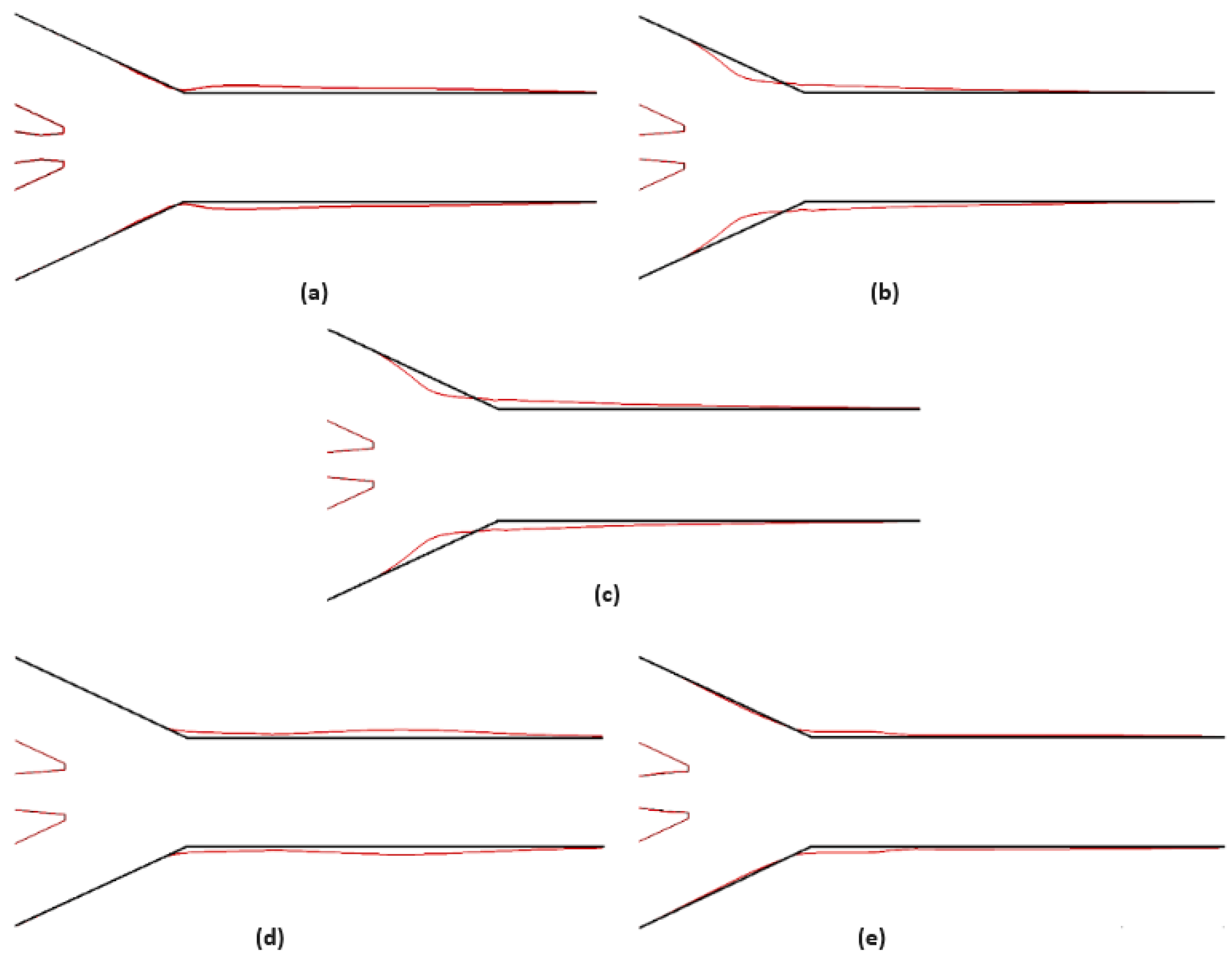
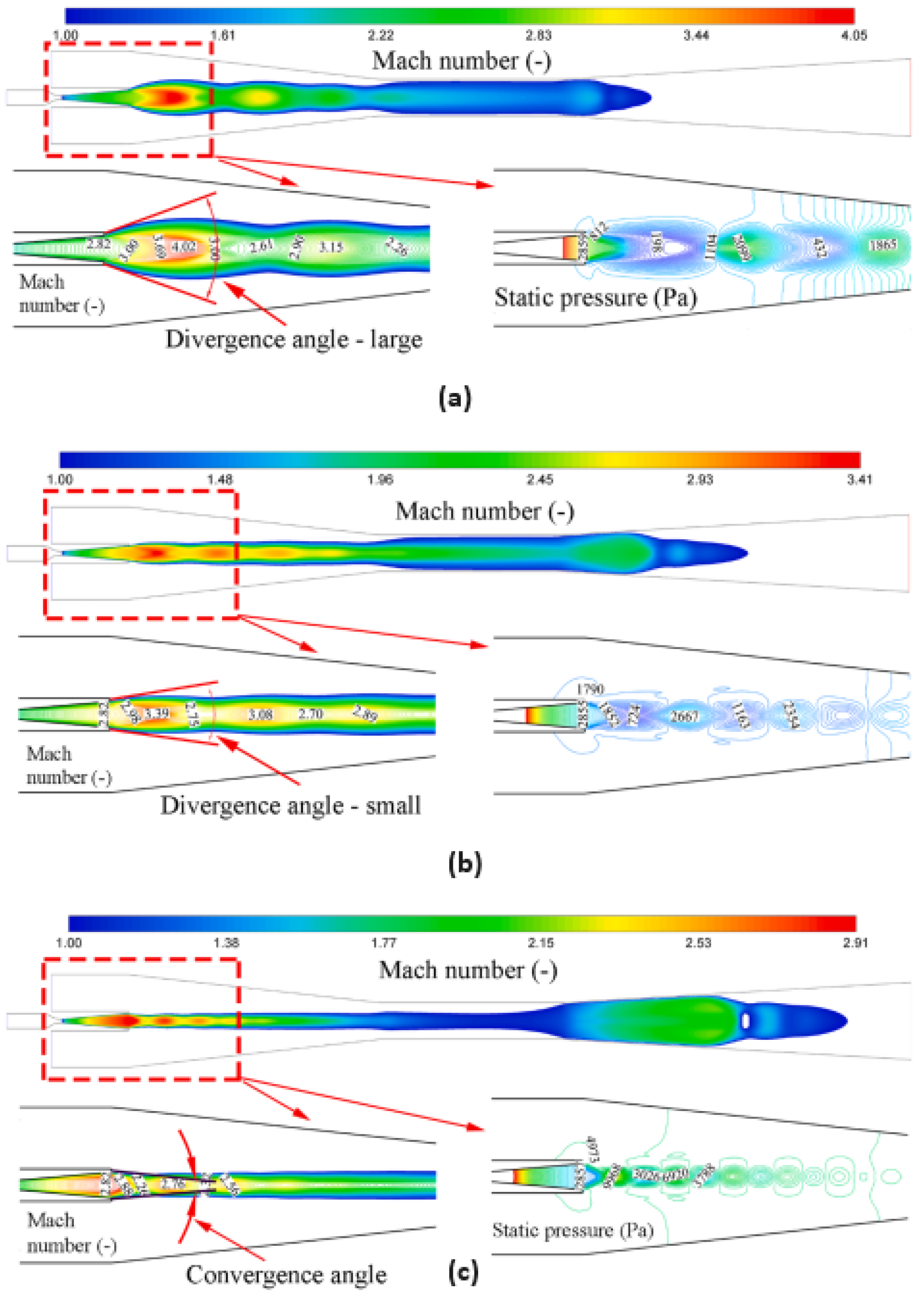
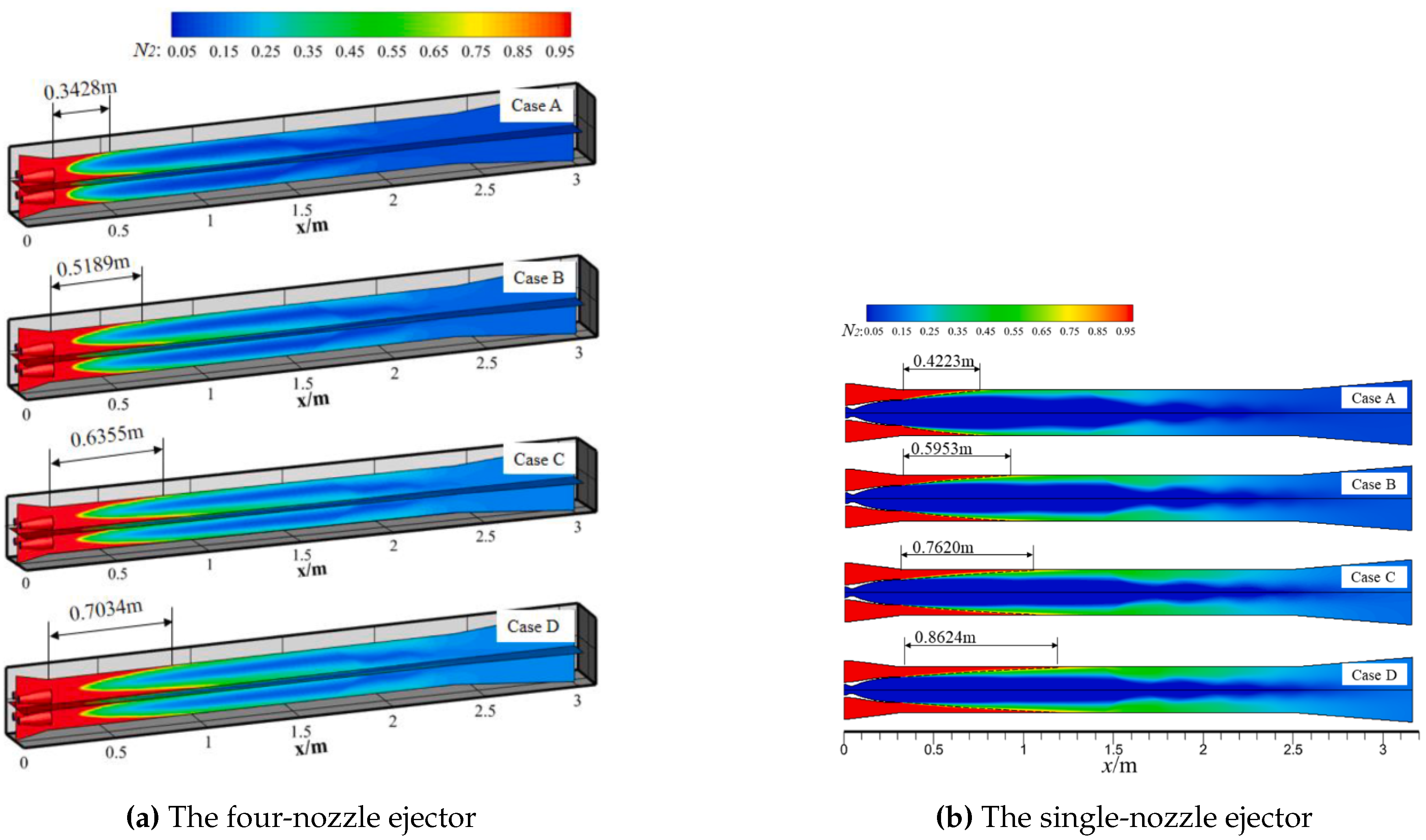
3.9.1. Nozzle exit position
3.9.2. Nozzle Area Ratio
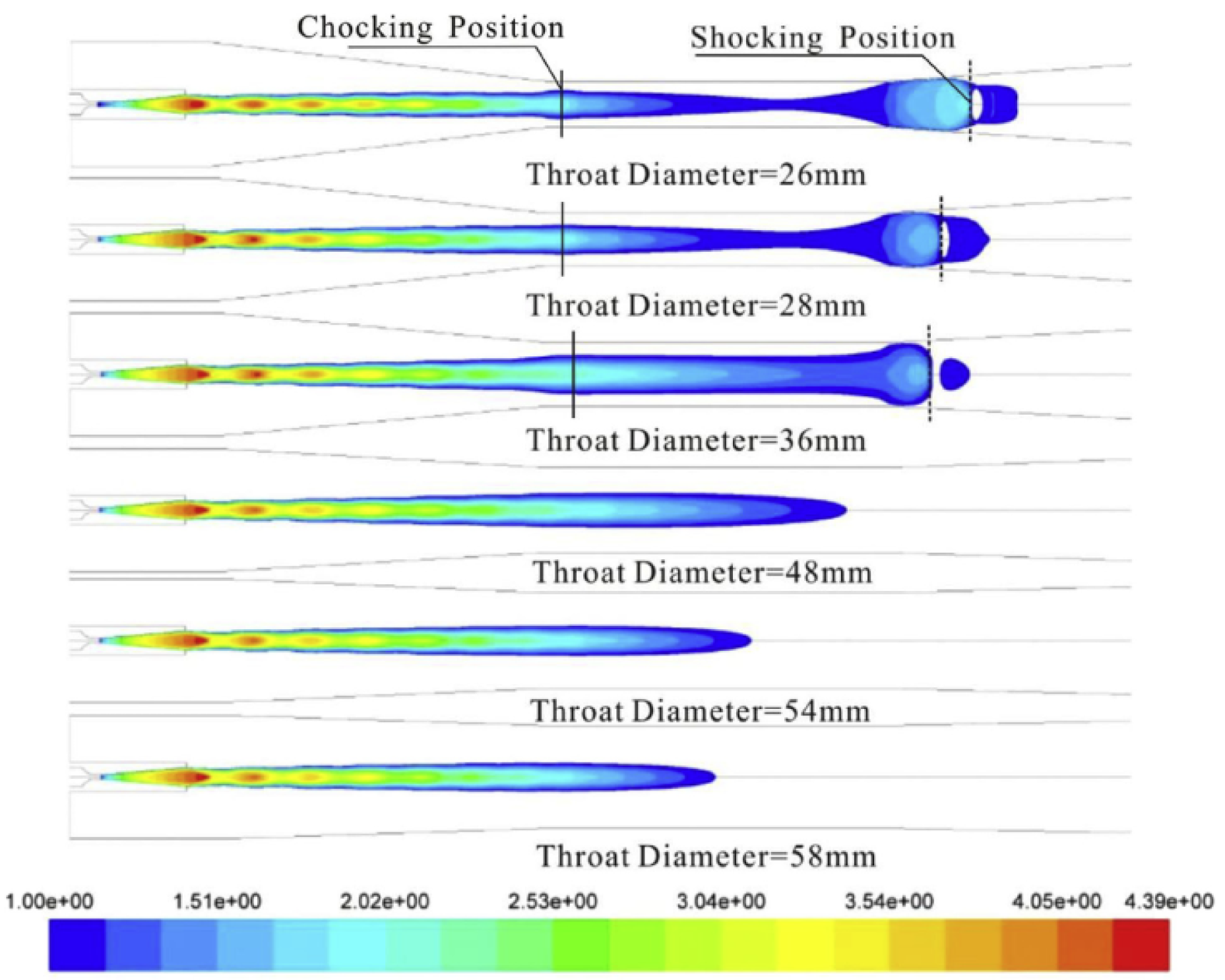
3.9.3. Mixing Throat Diameter
3.9.4. Other Geometric Aspects
3.9.5. Operating Conditions
3.10. Optimization
3.11. Entropy Loss
- Entropy generation through viscous dissipation caused by average velocity gradients.
- Entropy Generation through heat conduction resulting from average temperature gradients.
- Entropy generation through viscous dissipation caused by fluctuating velocity gradients (turbulent dissipation).
- Entropy generation through heat conduction due to fluctuating temperature gradients (turbulent heat transfer).
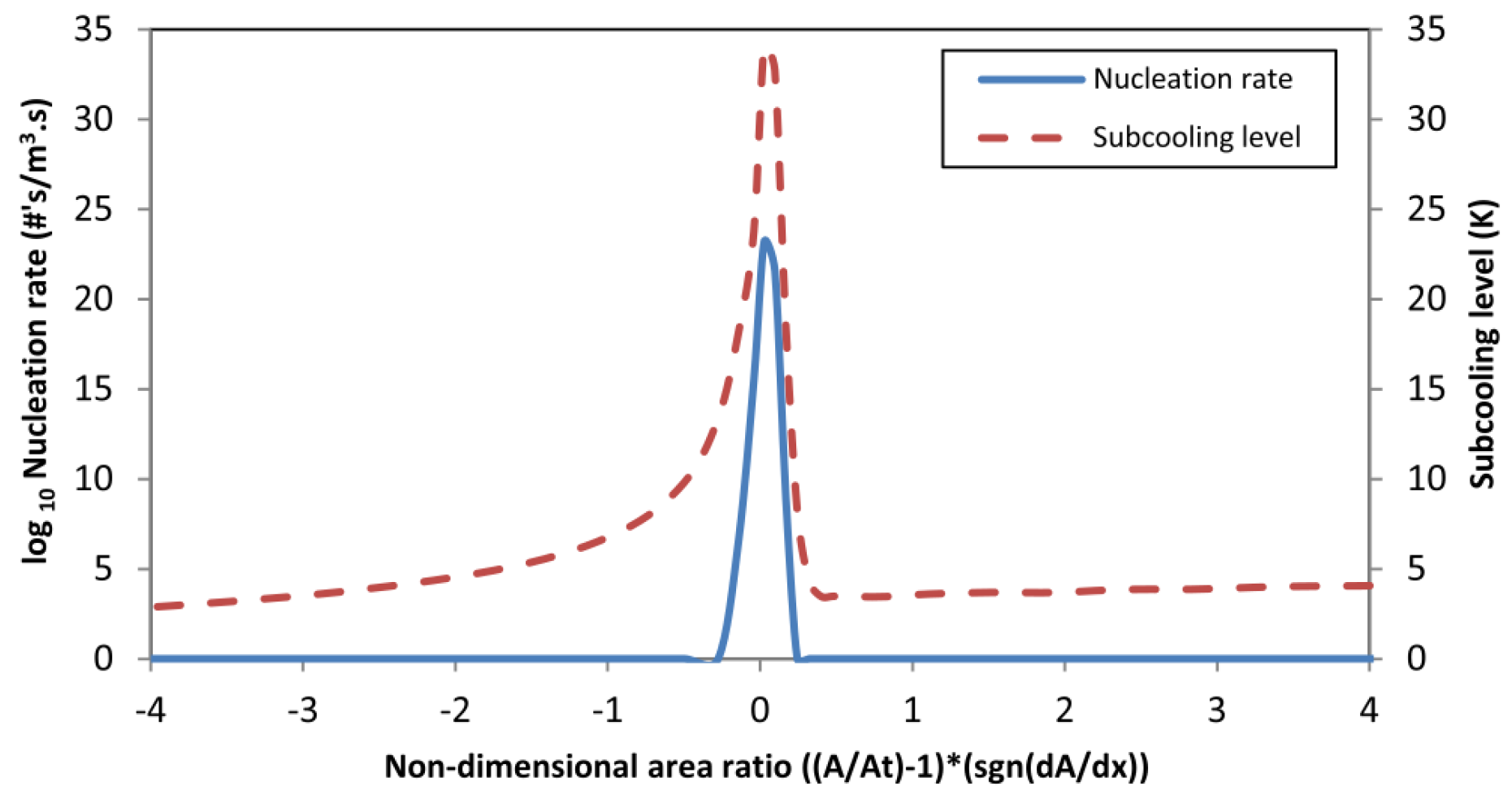
3.12. Entrainment Ratio Behavior
- implementing advanced turbulence models
- optimizing geometry; involving nozzle design, mixing chamber shape, diffuser design
- adjusting operating conditions
-
utilizing adjoint optimization.Additional factors can also be added to this list such as:
- incorporation of real gas effects
- boundary layer control involving wall treatments.
| Paper | Primary-secondary flow | Fluid flow | Geometry | Elements no. |
| Chai et al. 2024 [38] | Saturated steam-water two-phase | supersonic | 3D | 294480 |
| Li et al. 2024 [43] | Nitrogen-air single phase | Supersonic | 2D for single nozzle and 3D for 4-nozzles | 374000 for single nozzle 16 million for 4-nozzles |
| Talebiyan et al. 2024 [33] | Gas-gas (both ideal gas) single phase | supersonic | 2D with rectangular cross-section | 430000 |
| Singer et al. 2024 [44] | Pure hydrogen-mixed single phase | supersonic | 2D axis-symmetric | 330000 |
| Feng et al. 2024 [50] | Steam-water two-phase | supersonic | 2D axis-symetric | 140,000 |
| Kus and Madejski [45]2024 | water- two-phase | subsonic | 2D axis-symetric | 28299 |
| Tavakoli et al. 2023 [34] | Air-air (both ideal gas) single phase | subsonic | 2D without and with fluidic oscillator | 50000 |
| Hou et al. 2022[36] | Steam-steam (both ideal saturated steam) single phase | supersonic | 3D | 982,362 |
| Dadpour et al. 2022 [46] | Wet steam- wet steam two phase | supersonic | 2D | 40000 |
| Koirala et al. 2022 [39] | Sub-cooled water- vapor two-phase | subsonic | 3D | 1.8 million |
| Wen et al. 2020 [40] | Vapour-liquid two phase | supersonic | 2D | 73000 |
| Macia et al. 2019 [35] | Air-air(both ideal gas) single phase | supersonic | 2D axisymmetric | 20300 |
| Han et al. 2019 [47] | Steam-steam(both ideal gas) single phase | supersonic | 2D axisymmetric | 46352 |
| Banu and Mani 2019 [37] | Steam-steam (both ideal gas) single phase | - | 3D | 700000 |
| Giacomelli et al. 2016 [41] | wet steam-wet steam two phase | supersonic | 2D axis-symmetric | 45000 |
| Ariafar et al. 2014 [48] | wet steam nozzle (of an ejector) two phase | supersonic | 2D axis-symmetric with rectangular cross section | 6510 |
| Paper | Boundary conditions | Solver and Software | Turbulence modeling and wall function | Validation and verification |
| Chai et al. 2024 [38] | Inlet: mass flow rate for primary and secondary, , Outlet: | Pressure based Ansys Fluent | k-,Scalable wall function | - |
| Li et al. 2024 [43] | ,, , , , | coupled implicit density-based, FLUENT 19 | k- SST | Experimental |
| Talebiyan et al. 2024 [33] | Inlet: , , , , Outlet: , | Pressure based Ansys Fluent 2022 R2 | k- SST | Karthick et al. 2016(exp), Samsam-Khayani et al. 2022(Num) |
| Singer et al. 2024 [44] | Inlet: , Outlet: with variation of pure hydrogen and mixed volume percentage | pressure-based using pressure-velocity coupling, Ansys Fluent 2023 R1 | Spallart allmaras, Standard k- wall function:Enhanced Wall Treatment, RNG k-, Realizable k-, k-, SST k-, Generalized k- (GEKO), RSM stress-BSL | Experimental |
| Feng et al. 2024 [50] | Inlet: , , , Outlet: , | density-based implicit, FLUENT 19.2 | k- SST | Experimental and CFD by Sriveerakul [74] |
| Kus and Madejski [45]2024 | Inlet: , , , , , Outlet: | Segregated flow model, Siemens StarCCM+ 2022.1.1 | Realizable k- | - |
| Tavakoli et al. 2023 [34] | Inlet: , , Outlet: | URANS equations (unsteady) Ansys Fluent 2022 R2 | k- and k- SST | - |
| Hou et al. 2022[36] | Inlet: , , , Outlet: : an independent variable, : saturated steam temperature corresponding to the | Pressure-based (steady state) Fluent | Realizable k-,standard wall function | Numerical |
| Dadpour et al. 2022 [46] | B-Moore nozzle:, , , , Ejector: , , , Outlet: , | using Gauss-Seidel method coupled with implicit scheme, Open FOAM | k- model | B-Moore nozzle |
| Koirala et al. 2022 [39] | Inlet: , , , Outlet: | Pressure based (steady and unsteady) Ansys Fluent 2019 R2 | k- model | Zhang et al. 2012 |
| Wen et al. 2020 [40] | total pressure and total temperature for the entrances and exit | URANS equations (unsteady) Ansys Fluent 19 | k- SST | Sharifi and Boroomand 2013(exp) Laval nozzle Moses and Stein 1978 (exp) Starzman et al. 2018 |
| Macia et al. 2019 [35] | Inlet: , Neumann condition for velocity, , Outlet: | Density-based explicit (rhoCentralFoam) implicit (HiSA) solvers OpenFOAM | k- SST | Experimental |
| Han et al. 2019 [47] | Inlet: , , Outlet: | ANSYS Fluent 17 | Standard k-, RNG k-, realizable k-, with Standard Wall Function and Enhanced Wall Function, and k- SST | Experimental |
| Banu and Mani 2019 [37] | Inlet: | Density-based (steady) Ansys Fluent | k- SST | Experimental Banu et al. 2014 PIV study |
| Giacomelli et al. 2016 [41] | Inlet: , ;primary and secondary pressures are the saturation pressures corresponding to | Ansys Fluent | - | WS model in Fluent |
| Ariafar et al. 2014 [48] | , , Outlet: | Coupled implicit solver Ansys Fluent 14.5 | Realizable k- | two experimental cases by Moor et al 1980 and Bakhtar et al. 1981 |
| Paper | Two-phase model | Best turbulence model reported | Entrainment ratio remarks | Heat and mass transfer model and parameters |
| Chai et al. 2024 [38] | inhomogeneous multiphase model | - | - | Non-equilibrium condensation model |
| Li et al. 2024 [43] | - | - | Reported versus compression ratio, non-mixing length | - |
| Talebiyan et al. 2024 [33] | - | k- SST | The adjoint optimization method notably improved entrainment ratio by around 20.8%, 15.3%, and 16.5% for different operating modes | - |
| Singer et al. 2024 [44] | - | RSM with adjusted GEKO parameters | Reported versus the percentage of the fuel cell stack’s maximum load point/Generalized k- turbulence model decreases overprediction of entrainment ratio by 25% | - |
| Feng et al. 2024 [50] | Eulerian-eulerian | - | Reported versus liquid mass fraction, droplet number/increase of droplet mass fraction led to a 9.15% decrease in M | classical homogeneous nucleation theory |
| Tavakoli et al. 2023 [34] | - | k- SST k- | reported versus pressure ratio/Ejector with oscillator improved entrainment ratio by 38.3% | |
| Kus and Madejski [45]2024 | * | - | - | Direct contact condensation and Mixture multiphase mode(MMP) |
| Hou et al. 2022 [36] | - | - | Reported versus oultlet back pressure | - |
| Dadpour et al. 2022 [46] | Eulerian-eulerian | - | Reported versus back pressure/injection leads to a decrease in M by approximately 22.93% | - |
| Koirala et al. 2022 [39] | Eulerian multiphase model | - | Back pressure ratio on entrainment ratio Primary flow temperature on entrainment ratio Entrainment pressure on entrainment ratio Time on entrainment ratio Condensation on entrainment ratio/ | Direct contact condensation resistance models for heat transfer interaction Ranz-marshall to zero-resistance |
| Wen et al. 2020 [40] | * | k- SST | Reported versus inlet pressure of suction chamber on entrainment ratio/ M grows as the pressure in the suction chamber increases | Non-equilibrium condensation model |
| Macia et al. 2019 | - | - | - | - |
| Han et al. 2019 [47] | - | realizable k- | Reported versus primary fluid temperature, Back pressure, Throat diameter, NXP/ | |
| Banu and Mani 2019 [37] | - | - | Reported versus pressure drive ratio and for different sweep angles of cavity type swirl generator/ | - |
| Giacomelli et al. 2016 [41] | Eulerian multiphase model | - | Reported versus outlet pressure/HEM predicts a lower value of M | Non-equilibrium condensation model Homogeneous Non-equilibrium model |
| Ariafar et al. 2014 [42] | Eulerian-Eulerian approach | - | described without curves | * |
3.13. Internal Flow Visualization
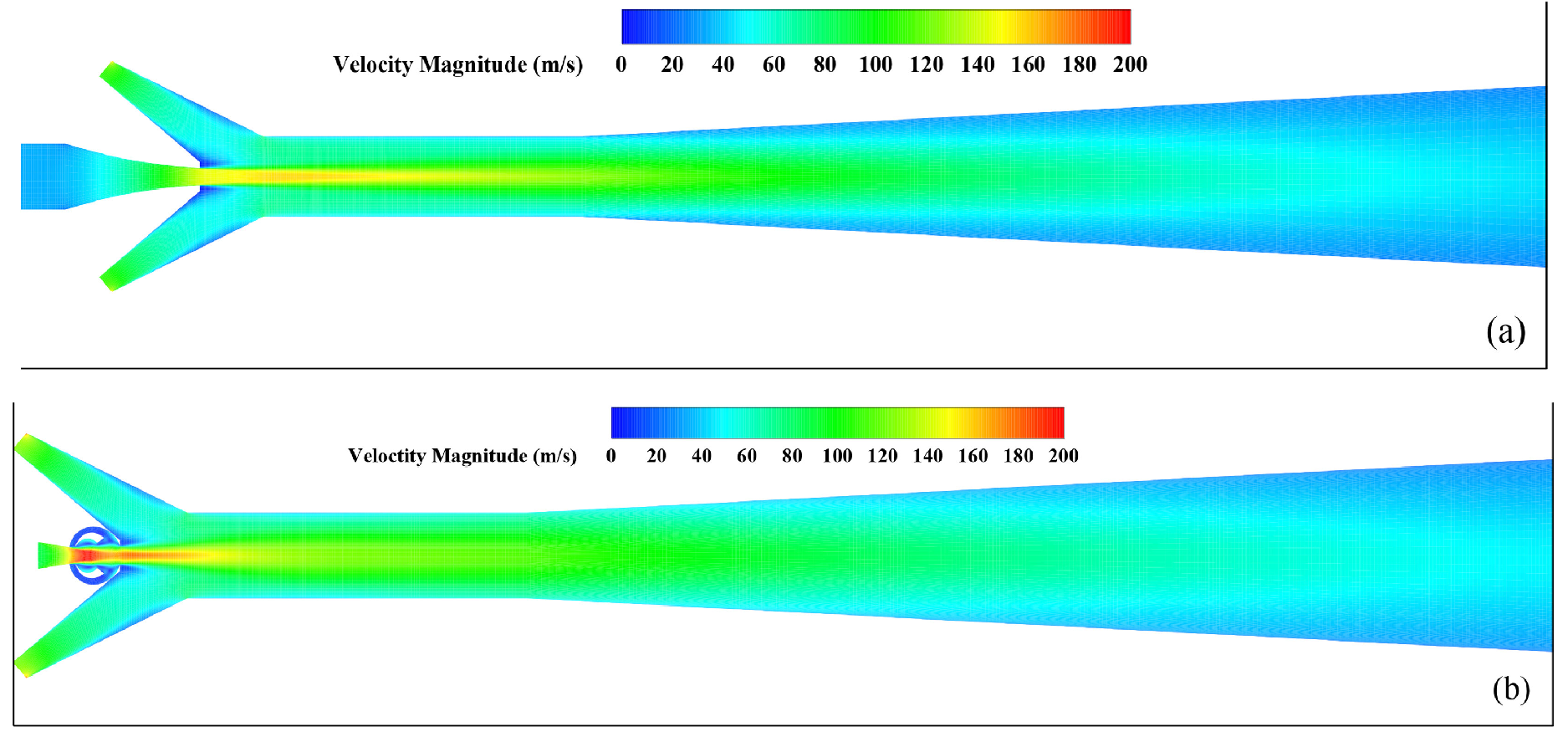
3.13.1. Mixing Characteristics
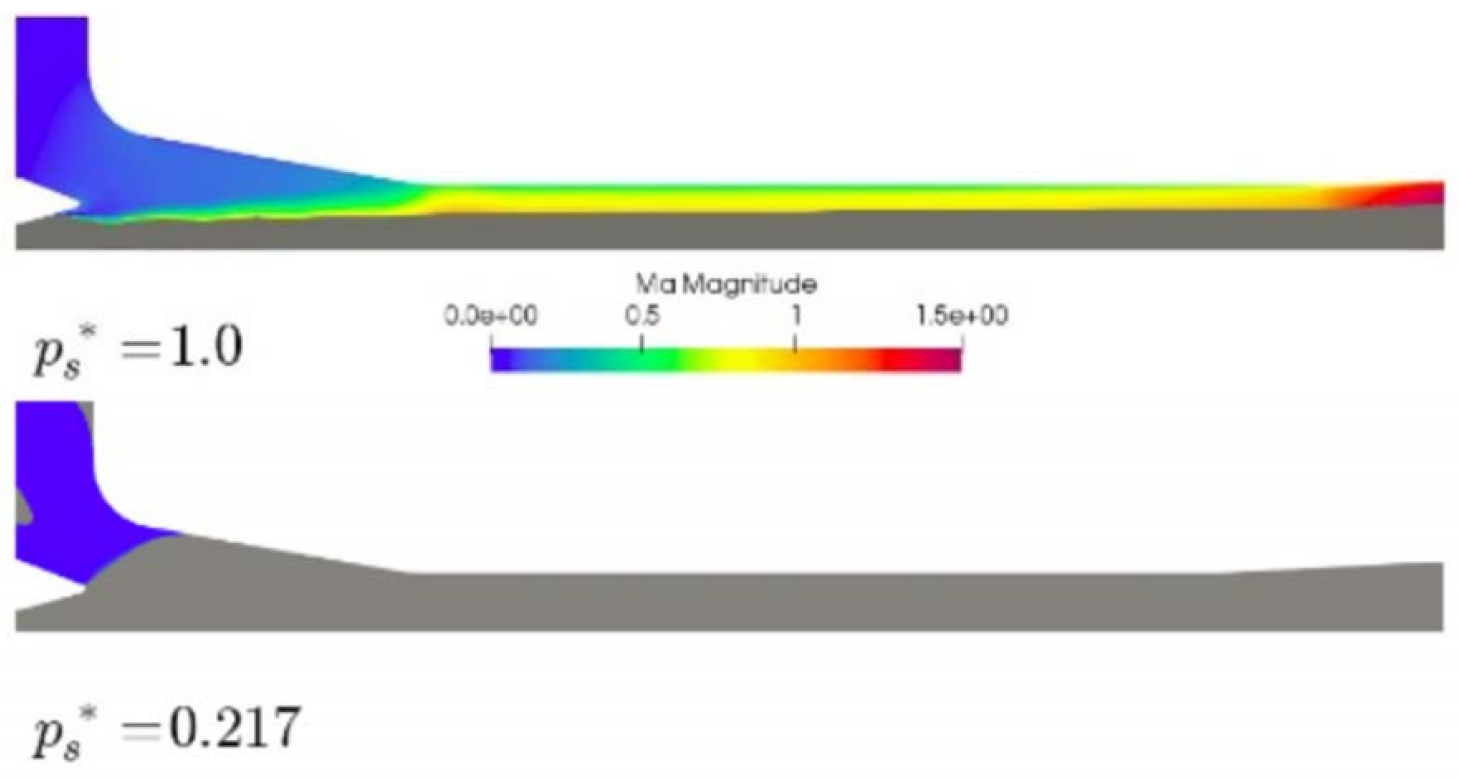
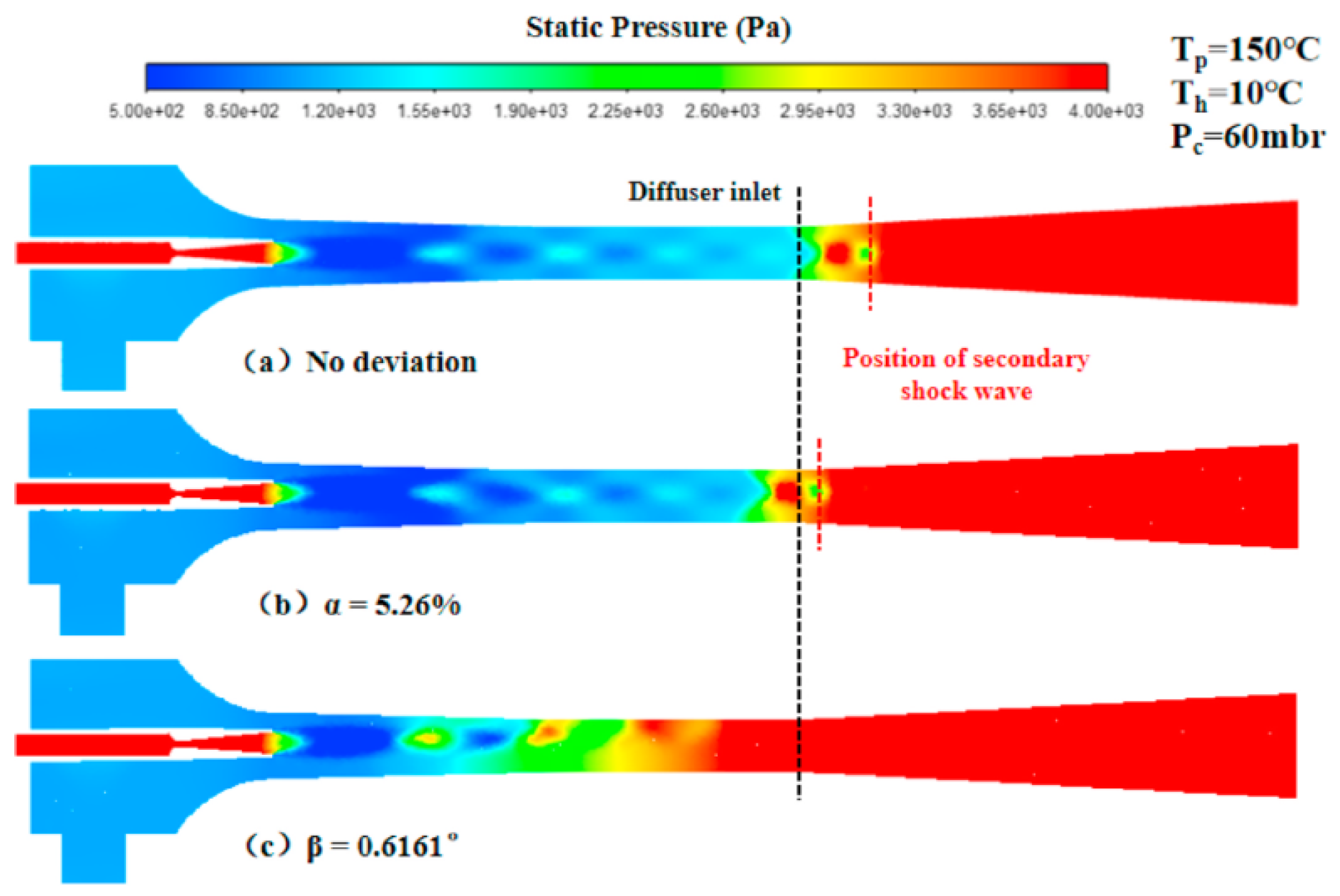
3.13.2. Shock Structure
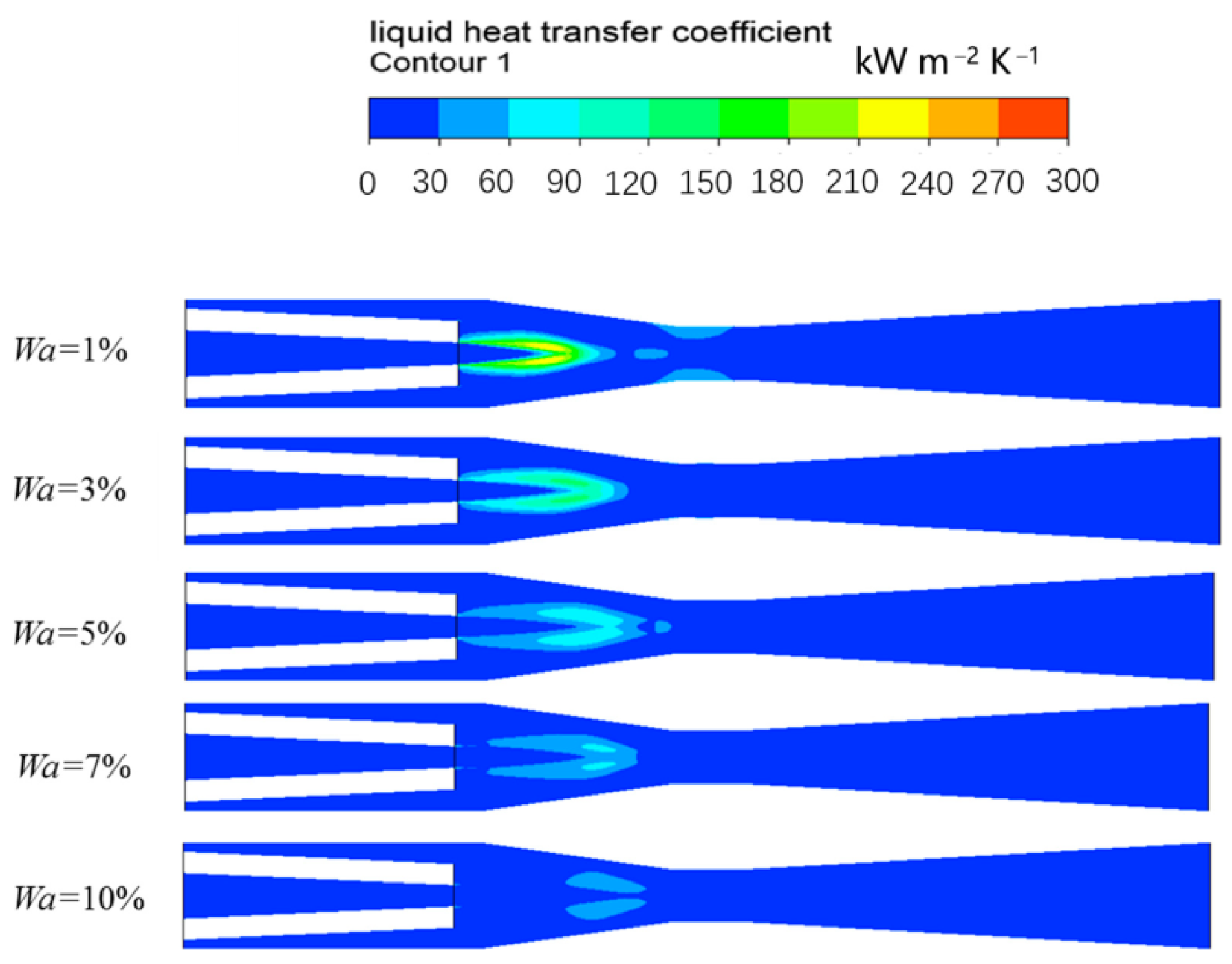
3.14. Investigation into the Properties of Heat and Mass Transfer
3.14.1. Condensation Effect
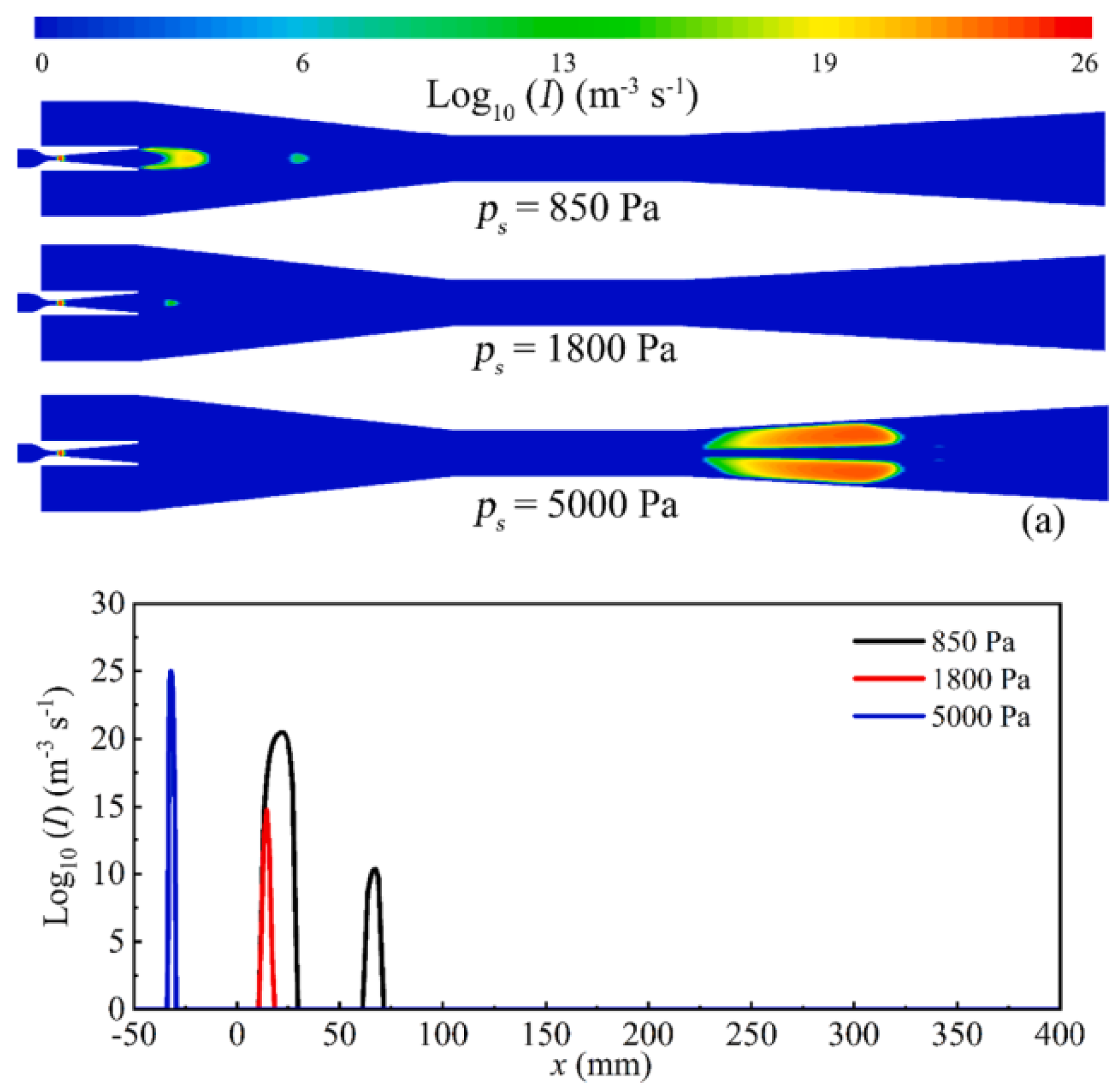
3.14.2. Nucleation
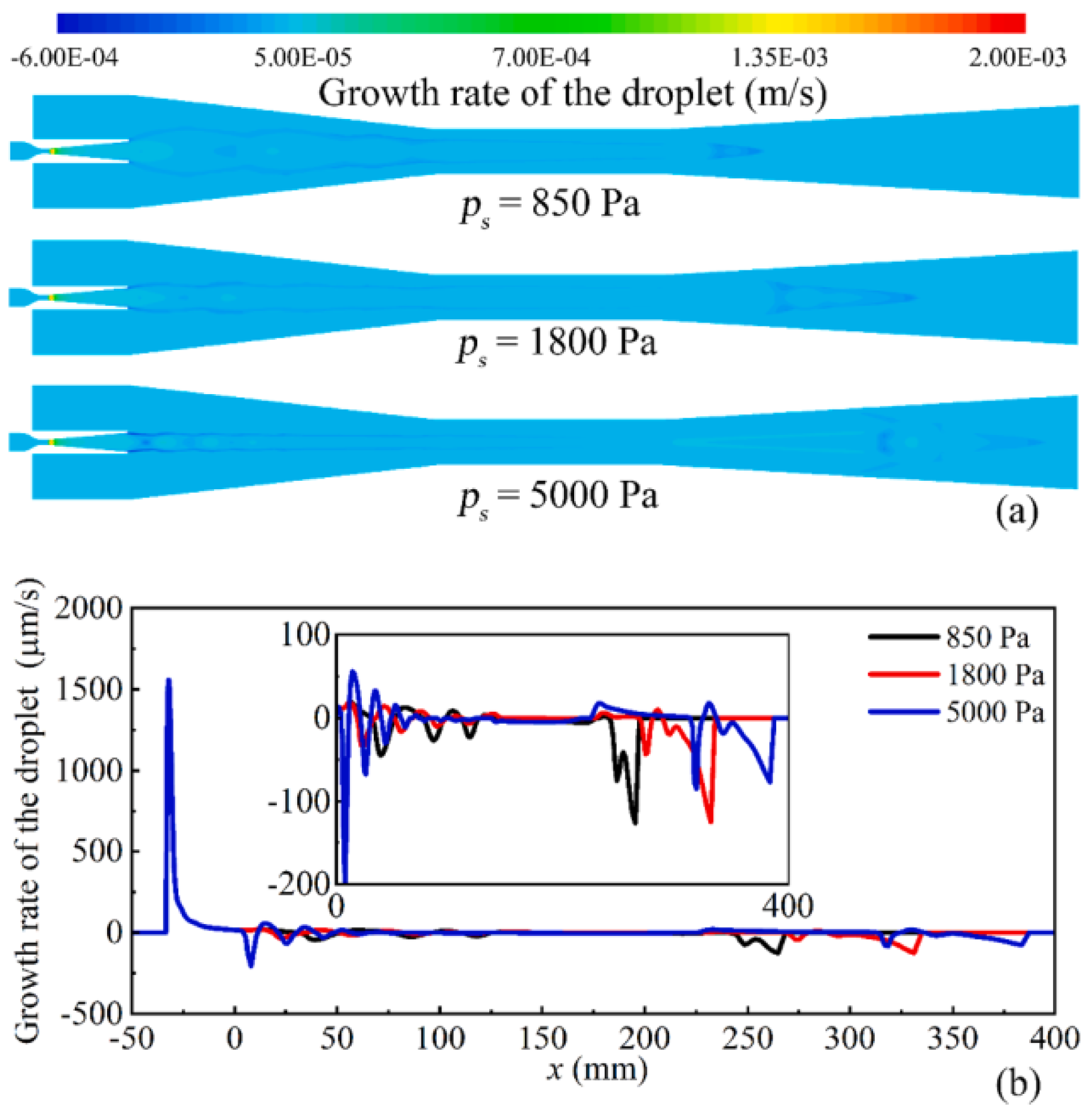
3.14.3. Droplet Growth
3.14.4. Condensing Nozzle
4. Conclusions
References
- Tashtoush, B.M.; Al-Nimr, M.A.; Khasawneh, M.A. A comprehensive review of ejector design, performance, and applications, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jarall, S.; Havtun, H.; Palm, B. A review on versatile ejector applications in refrigeration systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2015, 49, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbel, S.; Lawrence, N. Review of recent developments in advanced ejector technology, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Besagni, G.; Mereu, R.; Inzoli, F. Ejector refrigeration: A comprehensive review, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Little, A.; Garimella, S. A critical review linking ejector flow phenomena with component- and system-level performance. International Journal of Refrigeration 2016, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidoun, Z.; Ameur, K.; Falsafioon, M.; Badache, M. Current advances in ejector modeling, experimentation and applications for refrigeration and heat pumps. Part 2: Two-phase ejectors. Inventions 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidoun, Z.; Ameur, K.; Falsafioon, M.; Badache, M. Current advances in ejector modeling, experimentation and applications for refrigeration and heat pumps. Part 2: Two-phase ejectors. Inventions 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, R.; Ve, Q.L.; Zhu, B.; Inthavong, K.; Date, A. A review on process and practices in operation and design modification of ejectors, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Besagni, G.; Cristiani, N.; Croci, L.; Guédon, G.R.; Inzoli, F. Computational fluid-dynamics modelling of supersonic ejectors: Screening of modelling approaches, comprehensive validation and assessment of ejector component efficiencies. Applied Thermal Engineering 2021, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G.Cunningham, R., JetPumpTheory-1.pdf.
- Kwidziński, R. Control-volume-based model of the steam-water injector flow. Archives of Thermodynamics 2010, 31, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazzini, G.; Milazzo, A.; Piazzini, S. Prediction of condensation in steam ejector for a refrigeration system. International Journal of Refrigeration 2011, 34, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzelli, F.; Giacomelli, F.; Milazzo, A. CFD modeling of condensing steam ejectors: Comparison with an experimental test-case. International Journal of Thermal Sciences 2018, 127, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, E.; Al-Mutairi, K.; Hussain, B.; El-Gizawy, A.S. DEVELOPMENT OF ANALYTICAL MODEL FOR PREDICTING DUAL-PHASE EJECTOR PERFORMANCE, 2016.
- Winoto, S.H.; Li, H.; Shah, D.A. EFFICIENCY OF JET PUMPS, 2000.
- Karassik, I.J. Pump handbook; McGraw-Hill, 2001.
- Niu, L.; Zhang, X. Comparison of the performance enhancement of vacuum ejector by means of structure optimization and bypass methods. Energy 2024, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couper, J.R. Chemical process equipment: selection and design; Gulf professional publishing, 2005.
- Megdouli, K.; Tashtoush, B.M.; Nahdi, E.; Elakhdar, M.; Mhimid, A.; Kairouani, L. Analyse de performance d’un cycle à compression de vapeur combiné et d’un cycle à éjecteur pour la cogénération de froid. International Journal of Refrigeration 2017, 74, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Yu, J. 4E assessment of ejector-enhanced R290 heat pump cycle with a sub-cooler for cold region applications. Energy 2024, 131369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, F.; Belusko, M.; Halawa, E. CO2 refrigeration and heat pump systems—a comprehensive review. Energies 2019, 12, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Aghaie, H.R.; Saghafian, M. Design and analysis of a suction mechanism for the vacuum degassing process. Ironmaking & Steelmaking 2021, 48, 457–465. [Google Scholar]
- Peris Pérez, B.; Ávila Gutiérrez, M.; Expósito Carrillo, J.A.; Salmerón Lissén, J.M. Performance of Solar-driven Ejector Refrigeration System (SERS) as pre-cooling system for air handling units in warm climates. Energy 2022, 238, 121647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braimakis, K. Solar ejector cooling systems: A review. Renewable Energy 2021, 164, 566–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Dhahad, H.A.; Hussen, H.M.; Parikhani, T. Proposal and evaluation of two innovative combined gas turbine and ejector refrigeration cycles fueled by biogas: Thermodynamic and optimization analysis. Renewable Energy 2022, 181, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, P.; Hafner, A.; Banasiak, K.; Minetto, S.; Kriezi, E.E. Multi-Ejector Concept: A Comprehensive Review on its Latest Technological Developments. Energies 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tu, Z.; Chan, S.H. Applications of ejectors in proton exchange membrane fuel cells: A review, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, M.; Emadi, M.; Akbarpoor, A.M.; Mollaei, M. Energy and exergy investigation of a combined cooling, heating, power generation, and seawater desalination system. Applied Thermal Engineering 2018, 140, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, M.; Kouhikamali, R. Investigation of two phase liquid jet ejector with simultaneous air and water suction in fresh water distillation system. Energy 2024, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milow, B.; Zarza, E. Advanced MED solar desalination plants. Configurations, costs, future — seven years of experience at the Plataforma Solar de Almeria (Spain). Desalination 1997, 108, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Mañas, J.; Requena, I.; Ruiz-Aguirre, A.; Zaragoza, G. Performance modelling and optimization of three vacuum-enhanced membrane distillation modules for upscaled solar seawater desalination. Separation and Purification Technology 2022, 287, 120396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferziger, J.H.; Perić, M.; Street, R.L. Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics.
- Talebiyan, M.A.; Nili-Ahmadabadi, M.; Ha, M.Y. Adjoint optimization of a supersonic ejector for under-expanded, isentropic, and over-expanded primary flow modes. Chemical Engineering Science 2024, 292, 119979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Nili-Ahmadabadi, M.; Joulaei, A.; Ha, M.Y. Enhancing subsonic ejector performance by incorporating a fluidic oscillator as the primary nozzle: a numerical investigation. International Journal of Thermofluids 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macia, L.; Castilla, R.; Gámez, P.J. Simulation of ejector for vacuum generation. Institute of Physics Publishing, 2019, Vol. 659. [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; Zheng, J.; Chong, D.; Yan, J. Numerical simulation study on the influence of primary nozzle deviation on the steam ejector performance. International Journal of Thermal Sciences 2022, 179, 107633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, J.P.; Mani, A. Numerical studies on ejector with swirl generator. International Journal of Thermal Sciences 2019, 137, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, C.; Ke, H.; Li, B. Numerical Simulation on Two-Phase Ejector with Non-Condensable Gas. Energies 2024, 17, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, R.; Inthavong, K.; Date, A. Numerical study of flow and direct contact condensation of entrained vapor in water jet eductor. Experimental and Computational Multiphase Flow 2022, 4, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Gong, L.; Ding, H.; Yang, Y. Steam ejector performance considering phase transition for multi-effect distillation with thermal vapour compression (MED-TVC) desalination system. Applied Energy 2020, 279, 115831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, F.; Biferi, G.; Mazzelli, F.; Milazzo, A. CFD Modeling of the Supersonic Condensation Inside a Steam Ejector. Elsevier Ltd, 2016, Vol. 101, pp. 1224–1231. [CrossRef]
- Ariafar, K.; Buttsworth, D.; Al-Doori, G.; Malpress, R. Effect of mixing on the performance of wet steam ejectors. Energy 2015, 93, 2030–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Liang, T.; Ye, W.; Zhang, Z. Experimental and numerical studies on the performance of supersonic multi-nozzle ejector. Applied Thermal Engineering 2024, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, G.; Pinsker, R.; Stelzer, M.; Aggarwal, M.; Pertl, P.; Trattner, A. Ejector validation in proton exchange membrane fuel cells: A comparison of turbulence models in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) with experiment. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2024, 61, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuś, T.; Madejski, P. Numerical Investigation of a Two-Phase Ejector Operation Taking into Account Steam Condensation with the Presence of CO2. Energies 2024, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadpour, D.; Lakzian, E.; Gholizadeh, M.; Ding, H.; Han, X. Numerical modeling of droplets injection in the secondary flow of the wet steam ejector in the refrigeration cycle. International Journal of Refrigeration 2022, 136, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, G.; Guo, L.; Tu, J. CFD simulation on the boundary layer separation in the steam ejector and its influence on the pumping performance. Energy 2019, 167, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariafar, K.; Buttsworth, D.; Sharifi, N.; Malpress, R. Ejector primary nozzle steam condensation: Area ratio effects and mixing layer development. Applied Thermal Engineering 2014, 71, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Sen, S.; Poncet, S.; Bartosiewicz, Y.; Nesreddine, H.; Monney, D. Advanced modelling of a transcritical CO2 ejector. 2020, Vol. 2020-December. [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Yao, A.; Han, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jia, L.; Sun, W. Effect of droplets in the primary flow on ejector performance of MED-TVC systems. Energy 2024, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianthong, K.; Seehanam, W.; Behnia, M.; Sriveerakul, T.; Aphornratana, S. Investigation and improvement of ejector refrigeration system using computational fluid dynamics technique. Energy Conversion and Management 2007, 48, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launder, B.; Spalding, D. The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 1974, 3, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.; Rusche, H.; Schroeder, A.; Koehler, J. Numerical investigation of a two-phase CO2 ejector. International Journal of Refrigeration 2014, 43, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, W.R.I.; Scalon, V.L. Numerical Simulation of an Ejector Using the OpenFOAM® Solvers. Associacao Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciencias Mecanicas - ABCM, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Klyuyev, A.S.; Chernyshev, Y.I.; Ivanov, E.A.; Borshchev, I.O. Comparison of jet pump numerical calculation results in ansys and openfoam cfd packages. EDP Sciences, 2021, Vol. 320. [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, Q.; Masud, J. Visualization of flow field of a liquid ejector pump using embedded LES methodology. Journal of Visualization 2017, 20, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croquer, S.; Lamberts, O.; Poncet, S.; Moreau, S.; Bartosiewicz, Y. Large Eddy Simulation of a supersonic air ejector. Applied Thermal Engineering 2022, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roache, P. Verification and Validation in Computational Science and Engineering; Hermosa Publishers, 1998.
- Moore, M. Predicting the fog-drop size in wet-steam turbines. Wet steam 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Moses, C.A.; Stein, G.D. On the Growth of Steam Droplets Formed in a Laval Nozzle Using Both Static Pressure and Light Scattering Measurements. Journal of Fluids Engineering 1978, 100, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtar, F.; Mohammadi Tochai, M. An investigation of two-dimensional flows of nucleating and wet steam by the time-marching method. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow 1980, 2, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwidzinski, R. Experimental and theoretical investigations of two-phase flow in low pressure steam–water injector. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 2019, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwidzinski, R. Condensation heat and mass transfer in steam–water injectors. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 2021, 164, 120582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthick, S.; Rao, S.M.; Jagadeesh, G.; Reddy, K. Experiments in Supersonic Gaseous Ejector Using 2D-PIV Technique. 31st International Symposium on Shock Waves 2: Applications 31. Springer, 2019, pp. 785–793.
- Karthick, S.; Rao, S.; Jagadeesh, G.; Reddy, K. Parametric experimental studies on mixing characteristics within a low area ratio rectangular supersonic gaseous ejector. Physics of Fluids 2016, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rbaihat, R.; Saleh, K.; Malpress, R.; Buttsworth, D. Experimental investigation of a novel variable geometry radial ejector. Applied Thermal Engineering 2023, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Chen, W. Investigation of steam ejector parameters under three optimization algorithm using ANN. Applied Thermal Engineering 2023, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Pu, L.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Z.; Li, G. Multi-objective optimization of CO2 ejector by combined significant variables recognition, ANN surrogate model and multi-objective genetic algorithm. Energy 2024, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, L.; Jia, L.; Cai, W.; Gao, R. Optimization design of steam ejector primary nozzle for MED-TVC desalination system. Desalination 2019, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbel, A.; Shklyar, A.; Hershgal, D.; Barak, M.; Sokolov, M. Ejector irreversibility characteristics. J. Fluids Eng. 2003, 125, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Pallares, J.; García del Valle, J.; García Carrascal, P.; Castro Ruiz, F. A computational study about the types of entropy generation in three different R134a ejector mixing chambers. International Journal of Refrigeration 2016, 63, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvar, A.; Ghazikhani, M.; Razavi, S.M.R.M. Entropy analysis of a solar-driven variable geometry ejector using computational fluid dynamics. Energy conversion and management 2016, 119, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanis, N.; Sorin, M. Ejector design and performance prediction. International Journal of Thermal Sciences 2016, 104, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriveerakul, T.; Aphornratana, S.; Chunnanond, K. Performance prediction of steam ejector using computational fluid dynamics: Part 1. Validation of the CFD results. International Journal of Thermal Sciences 2007, 46, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.M.V.; Jagadeesh, G. Observations on the non-mixed length and unsteady shock motion in a two dimensional supersonic ejector. Physics of Fluids 2014, 26, 036103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, R. Progress of mathematical modeling on ejectors. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2009, 13, 1760–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmierciew, K.; Gagan, J.; Butrymowicz, D. Application of numerical modelling for design and improvement of performance of gas ejector. Applied Thermal Engineering 2019, 149, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodys, J.; Smolka, J.; Palacz, M.; Haida, M.; Banasiak, K. Non-equilibrium approach for the simulation of CO2 expansion in two-phase ejector driven by subcritical motive pressure. International Journal of Refrigeration 2020, 114, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolka, J.; Bulinski, Z.; Fic, A.; Nowak, A.J.; Banasiak, K.; Hafner, A. A computational model of a transcritical R744 ejector based on a homogeneous real fluid approach. Applied Mathematical Modelling 2013, 37, 1208–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacz, M.; Smolka, J.; Fic, A.; Bulinski, Z.; Nowak, A.J.; Banasiak, K.; Hafner, A. Application range of the HEM approach for CO2 expansion inside two-phase ejectors for supermarket refrigeration systems. International Journal of Refrigeration 2015, 59, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarnejad, S.; Ziabasharhagh, M. A study of the application of wet steam modeling for thermocompressor simulation in TVC desalination. Desalination and Water Treatment 2024, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Manea, A.; Saleh, K. Supersonic Steam Ejectors: Comparison of Dry and Wet, 2022.
- Foroozesh, F.; Khoshnevis, A.B.; Lakzian, E. Improvement of the wet steam ejector performance in a refrigeration cycle via changing the ejector geometry by a novel EEC (Entropy generation, Entrainment ratio, and Coefficient of performance) method. International Journal of Refrigeration 2020, 110, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marynowski, T.; Desevaux, P.; Mercadier, Y. Experimental and numerical visualizations of condensation process in a supersonic ejector. Journal of visualization 2009, 12, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Fatouh, M.; Elgendy, E. Ejector design and theoretical study of R134a ejector refrigeration cycle. International Journal of refrigeration 2011, 34, 1684–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, V.P.; Oyumi, S.M.; Ahmed, S. Post-nucleation growth of water microdroplets in supersaturated gas mixtures: a molecular simulation study, 1997.
- Banasiak, K.; Hafner, A. 1D Computational model of a two-phase R744 ejector for expansion work recovery. International Journal of Thermal Sciences 2011, 50, 2235–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazzini, G.; Milazzo, A.; Mazzelli, F.; Grazzini, G.; Milazzo, A.; Mazzelli, F. Physics of the Ejectors. Ejectors for Efficient Refrigeration: Design, Applications and Computational Fluid Dynamics 2018, 21–69. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.K.; Pandey, K.M.; Gupta, R. Recent advances on principles of working of ejectors: A review. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021, 45, 6298–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, P.; Mack, L. Condensation in Supersonic and Hypersonic Wind Tunnels; Elsevier, 1958; Vol. 5, Advances in Applied Mechanics, pp. 307–447. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H.; Du, Z.; Ding, Z. Effects of superheated steam on non-equilibrium condensation in ejector primary nozzle. International Journal of Refrigeration 2016, 67, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzmann, J.; Hughes, F.R.; Schuster, S.; White, A.J.; Halama, J.; Hric, V.; Kolovratník, M.; Lee, H.; Sova, L.; Št’astný, M.; Grübel, M.; Schatz, M.; Vogt, D.M.; Patel, Y.; Patel, G.; Turunen-Saaresti, T.; Gribin, V.; Tishchenko, V.; Gavrilov, I.; Kim, C.; Baek, J.; Wu, X.; Yang, J.; Dykas, S.; Wróblewski, W.; Yamamoto, S.; Feng, Z.; Li, L. Results of the International Wet Steam Modeling Project. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy 2018, 232, 550–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, P.G. Condensation of water vapour during supersonic expansion in nozzles. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 1966, 25, 593–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Gué, A. Simulation model and droplet ejection performance of a thermal-bubble microejector. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2010, 145, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Walther, J.H.; Yan, Y.; Wen, C. CFD modeling of condensation process of water vapor in supersonic flows. Applied Thermal Engineering 2017, 115, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High Pressure Subsonic Nucleation in 1D Nozzles — An Experimental Study, Vol. Volume 1B: Marine; Microturbines, Turbochargers and Small Turbomachines; Steam Turbines, Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, 2014, [https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/GT/proceedings-pdf/GT2014/45585/V01BT27A051/2422848/ v01bt27a051-gt2014-27241.pdf]. [CrossRef]
- Starzmann, J.; Hughes, F.R.; Schuster, S.; White, A.J.; Halama, J.; Hric, V.; Kolovratník, M.; Lee, H.; Sova, L.; Št’astný, M.; Grübel, M.; Schatz, M.; Vogt, D.M.; Patel, Y.; Patel, G.; Turunen-Saaresti, T.; Gribin, V.; Tishchenko, V.; Gavrilov, I.; Kim, C.; Baek, J.; Wu, X.; Yang, J.; Dykas, S.; Wróblewski, W.; Yamamoto, S.; Feng, Z.; Li, L. Results of the International Wet Steam Modeling Project. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy 2018, 232, 550–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





