Submitted:
19 July 2024
Posted:
19 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Analysis of the Lipid Content
2.3. Assay of Actinorhodin Production
3. Results
3.1. Impact of the Deletion of Genes Encoding Proteins Playing a Role in Nitrogen Metabolism on the Lipid Content of Streptomyces Coelicolor M145
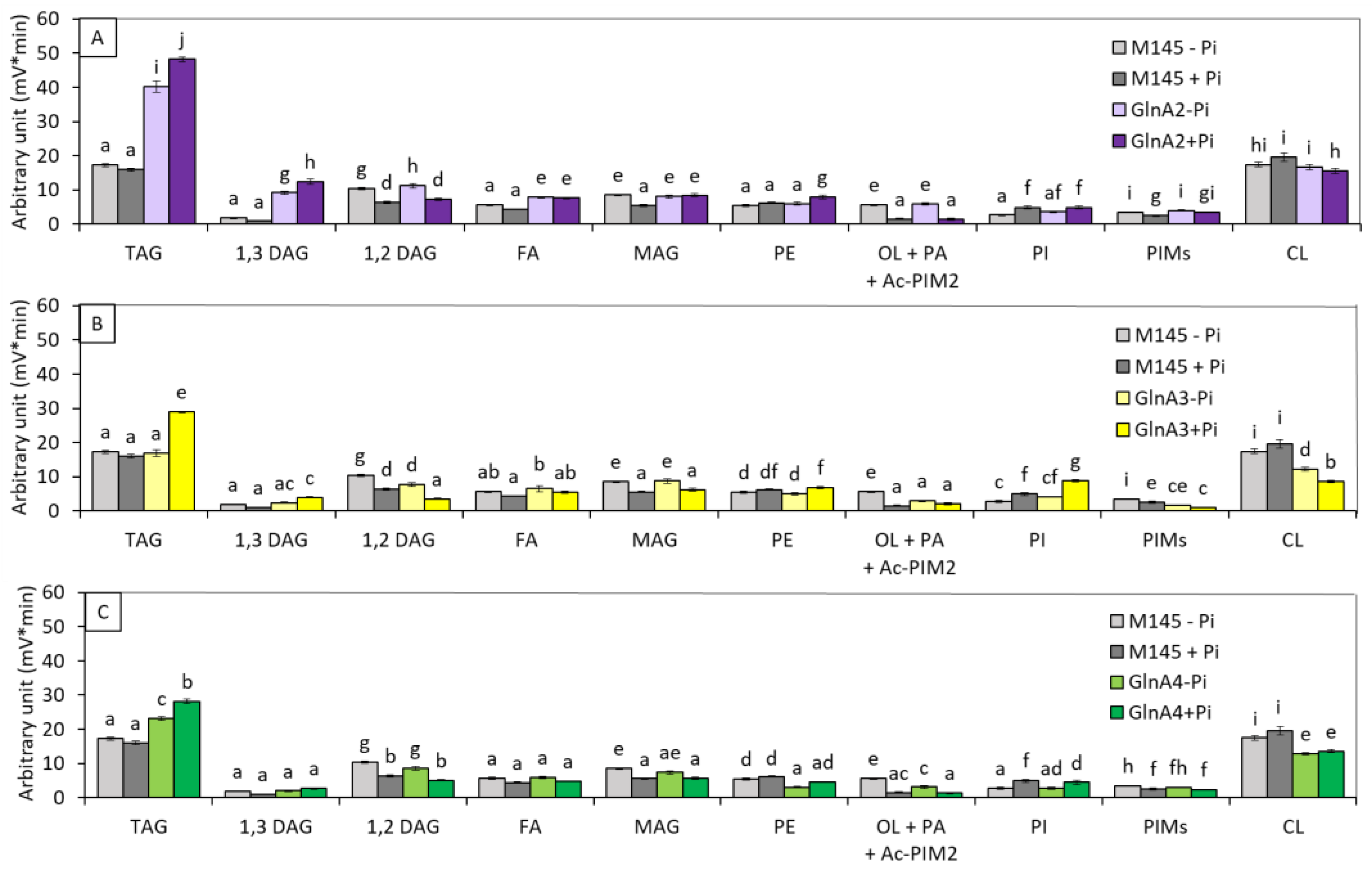
3.1.1. glnA2, glnA3 and glnA4 Deletion Mutants
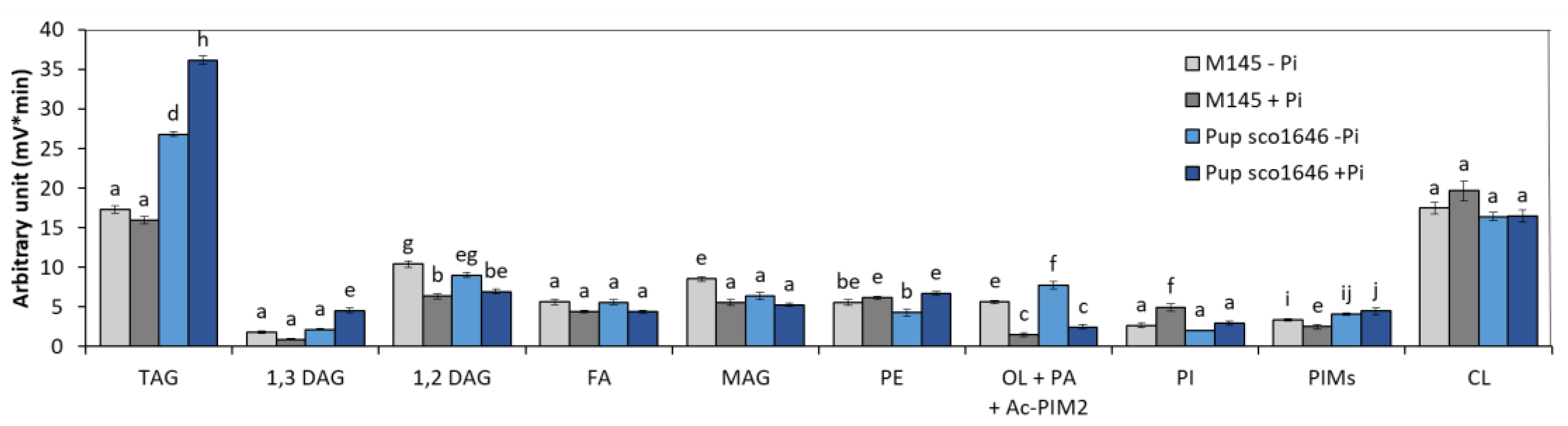
3.1.2. Pup Mutant
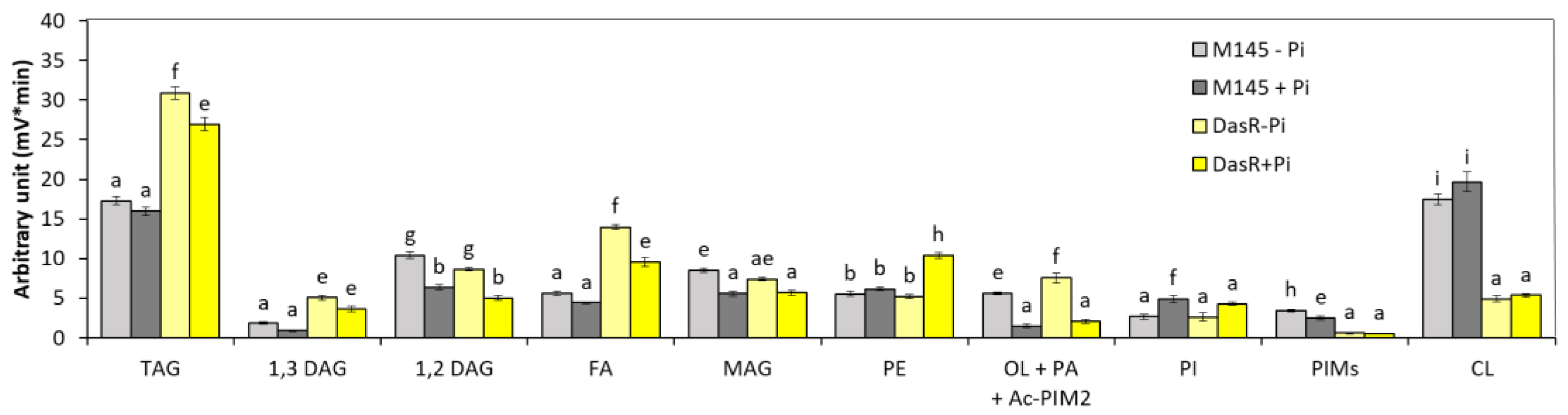
3.1.3. dasR Mutant
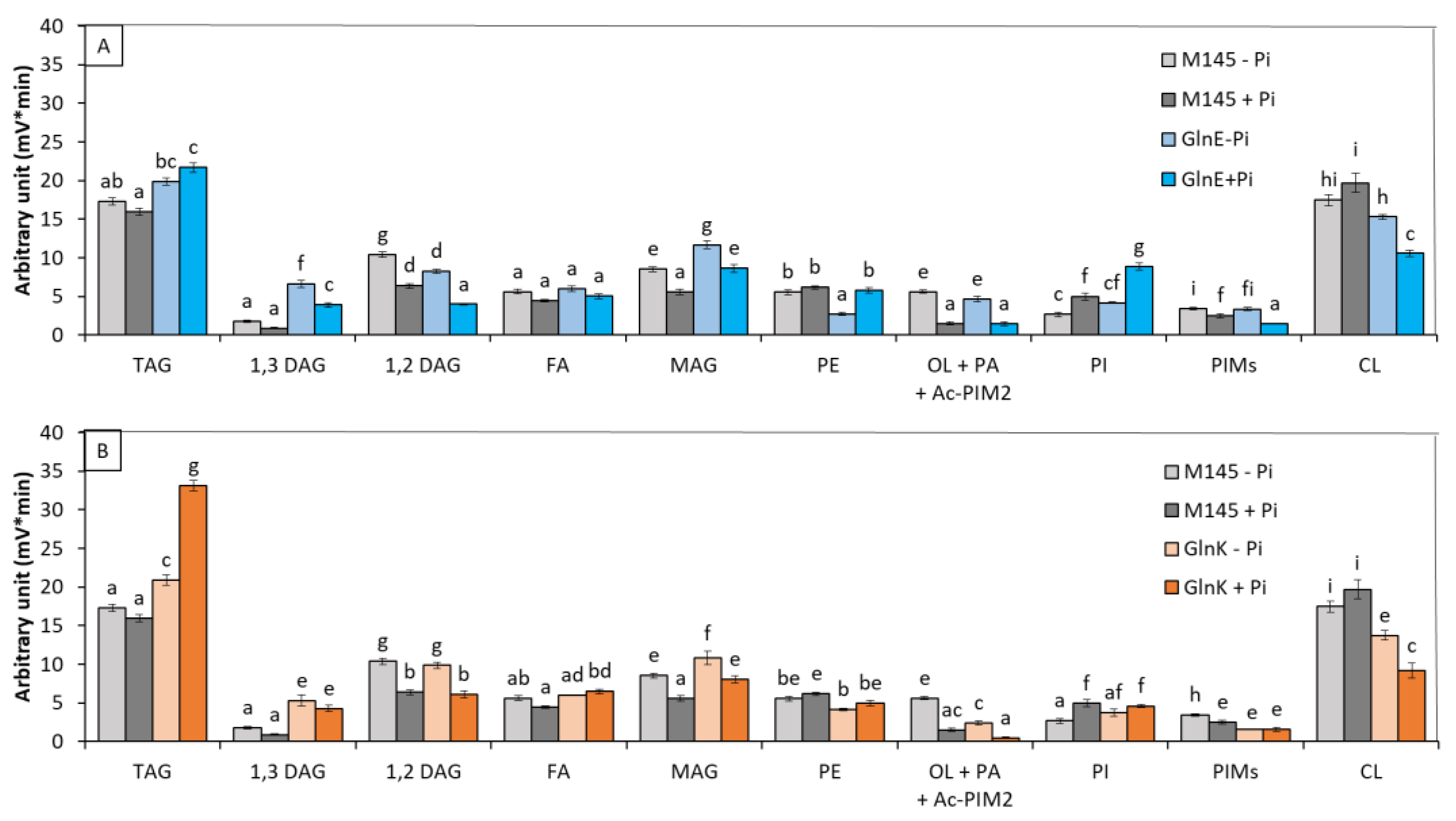
3.1.4. glnK and glnE Deletion Mutants
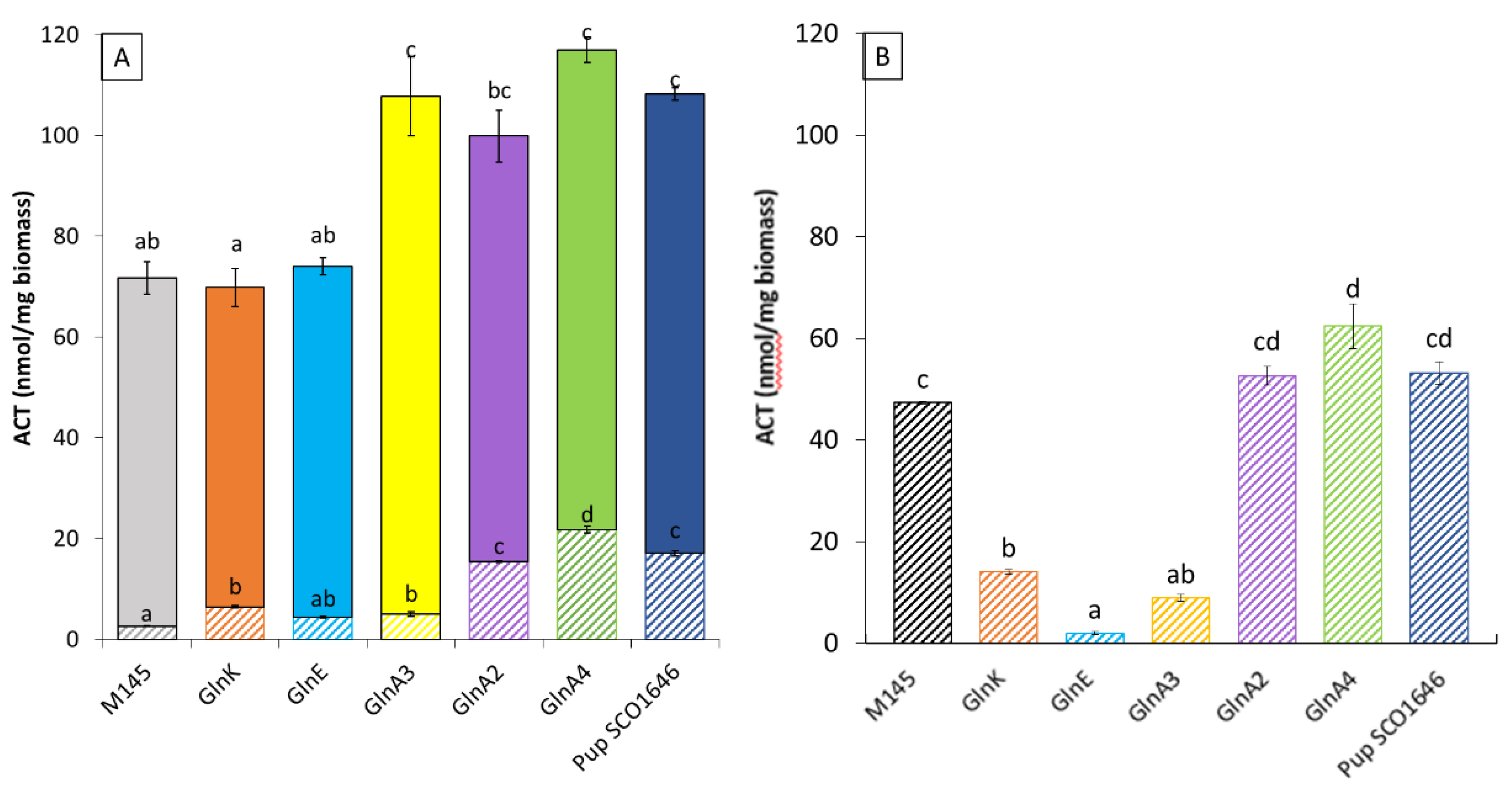
3.2. Impact of the Deletion of Genes Encoding Proteins Playing a Role in the Degradation of Nitrogen-Containing Biological Molecules on the Production of Actinorhodin in Streptomyces Coelicolor M145
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boubakri, H.; Seghezzi, N.; Duchateau, M.; Gominet, M.; Kofroňová, O.; Benada, O.; Mazodier, P.; Pernodet, J.-L. The Absence of Pupylation (Prokaryotic Ubiquitin-Like Protein Modification) Affects Morphological and Physiological Differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 3388–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compton, C.L.; Fernandopulle, M.S.; Nagari, R.T.; Sello, J.K. Genetic and Proteomic Analyses of Pupylation in Streptomyces coelicolor. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 2747–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysenko S, Okoniewski N, Nentwich M, Matthews A, Bauerle M, Zinser A, Busche T, Kulik A, Gursch S, Kemeny A, Bera A, Wohlleben W. 2022. A Second Gamma-Glutamylpolyamine Synthetase, GlnA2, Is Involved in Polyamine Catabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor. Int J Mol Sci 23.
- Krysenko, S.; Okoniewski, N.; Kulik, A.; Matthews, A.; Grimpo, J.; Wohlleben, W.; Bera, A. Gamma-Glutamylpolyamine Synthetase GlnA3 Is Involved in the First Step of Polyamine Degradation Pathway in Streptomyces coelicolor M145. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysenko, S.; Matthews, A.; Okoniewski, N.; Kulik, A.; Girbas, M.G.; Tsypik, O.; Meyners, C.S.; Hausch, F.; Wohlleben, W.; Bera, A. Initial Metabolic Step of a Novel Ethanolamine Utilization Pathway and Its Regulation in Streptomyces coelicolor M145. mBio 2019, 10, e00326–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevrekci, A. . The roles of polyamines in microorganisms. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 204–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysenko, S.; Wohlleben, W. Polyamine and Ethanolamine Metabolism in Bacteria as an Important Component of Nitrogen Assimilation for Survival and Pathogenicity. Med Sci. 2022, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigali, S.; Titgemeyer, F.; Barends, S.; Mulder, S.; Thomae, A.W.; A Hopwood, D.; van Wezel, G.P. Feast or famine: the global regulator DasR links nutrient stress to antibiotic production by Streptomyces. Embo Rep. 2008, 9, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigali S, Nothaft H, Noens EE, Schlicht M, Colson S, Muller M, Joris B, Koerten HK, Hopwood DA, Titgemeyer F, van Wezel GP. 2006. The sugar phosphotransferase system of Streptomyces coelicolor is regulated by the GntR-family regulator DasR and links N-acetylglucosamine metabolism to the control of development. Mol Microbiol 61:1237-1251.
- Nothaft H, Rigali S, Boomsma B, Swiatek M, McDowall KJ, van Wezel GP, Titgemeyer F. 2010. The permease gene nagE2 is the key to N-acetylglucosamine sensing and utilization in Streptomyces coelicolor and is subject to multi-level control. Mol Microbiol 75:1133-1144.
- Swiatek, M.A.; Tenconi, E.; Rigali, S.; van Wezel, G.P. Functional Analysis of the N-Acetylglucosamine Metabolic Genes of Streptomyces coelicolor and Role in Control of Development and Antibiotic Production. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santucci, P.; Johansen, M.D.; Point, V.; Poncin, I.; Viljoen, A.; Cavalier, J.-F.; Kremer, L.; Canaan, S. Nitrogen deprivation induces triacylglycerol accumulation, drug tolerance and hypervirulence in mycobacteria. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, N.R.; Page, M.D.; Liu, B.; Blaby, I.K.; Casero, D.; Kropat, J.; Cokus, S.J.; Hong-Hermesdorf, A.; Shaw, J.; Karpowicz, S.J.; et al. Three Acyltransferases and Nitrogen-responsive Regulator Are Implicated in Nitrogen Starvation-induced Triacylglycerol Accumulation in Chlamydomonas. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15811–15825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cen, K.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shang, Y.; Wang, C. Nitrogen-starvation triggers cellular accumulation of triacylglycerol in Metarhizium robertsii. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, M.A.; Lara, J.; Gago, G.; Gramajo, H.; Alvarez, H.M. The pleiotropic transcriptional regulator NlpR contributes to the modulation of nitrogen metabolism, lipogenesis and triacylglycerol accumulation in oleaginous rhodococci. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 103, 366–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banchio, C.; Gramajo, H. A Stationary-Phase Acyl-Coenzyme A Synthetase of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) Is Necessary for the Normal Onset of Antibiotic Production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4240–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craney, A.; Ozimok, C.; Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; Capretta, A.; Nodwell, J.R. Chemical Perturbation of Secondary Metabolism Demonstrates Important Links to Primary Metabolism. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Fan, K.; Tan, G.; Ai, G.; Lam, S.M.; Shui, G.; Yang, Z.; et al. Harnessing the intracellular triacylglycerols for titer improvement of polyketides in Streptomyces. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 38, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, M.; Lejeune, C.; Abreu, S.; Thibessard, A.; Leblond, P.; Chaminade, P.; Virolle, M.-J. Negative Correlation between Lipid Content and Antibiotic Activity in Streptomyces: General Rule and Exceptions. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulermo, T.; Lejeune, C.; Aybeke, E.; Abreu, S.; Bleton, J.; David, M.; Deniset-Besseau, A.; Chaminade, P.; Thibessard, A.; Leblond, P.; et al. Genome Analysis of a Variant of Streptomyces coelicolor M145 with High Lipid Content and Poor Ability to Synthetize Antibiotics. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millan-Oropeza, A.; Henry, C.; Lejeune, C.; David, M.; Virolle, M.-J. Expression of genes of the Pho regulon is altered in Streptomyces coelicolor. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virolle, M.-J. A Challenging View: Antibiotics Play a Role in the Regulation of the Energetic Metabolism of the Producing Bacteria. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, S.D.; Chater, K.F.; Cerdeño-Tárraga, A.-M.; Challis, G.L.; Thomson, N.R.; James, K.D.; Harris, D.E.; Quail, M.A.; Kieser, H.; Harper, D.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 2002, 417, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan-Oropeza, A.; Rebois, R.; David, M.; Moussa, F.; Dazzi, A.; Bleton, J.; Virolle, M.-J.; Deniset-Besseau, A. Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR FT-IR) for Rapid Determination of Microbial Cell Lipid Content: Correlation with Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 71, 2344–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, S.; Solgadi, A.; Chaminade, P. Optimization of normal phase chromatographic conditions for lipid analysis and comparison of associated detection techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1514, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejeune, C.; Abreu, S.; Chaminade, P.; Dulermo, T.; David, M.; Werten, S.; Virolle, M.-J. Impact of Phosphate Availability on Membrane Lipid Content of the Model Strains, Streptomyces lividans and Streptomyces coelicolor. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieser T, Bibb, M.J., Buttner, M. J., Chater, K. F. & Hopwood, D. A.. 2000. Practical Streptomyces Genetics.
- Sandoval-Calderón, M.; Guan, Z.; Sohlenkamp, C. Knowns and unknowns of membrane lipid synthesis in streptomycetes. Biochimie 2017, 141, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysenko, S.; Matthews, A.; Busche, T.; Bera, A.; Wohlleben, W. Poly- and Monoamine Metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor: The New Role of Glutamine Synthetase-Like Enzymes in the Survival under Environmental Stress. Microb. Physiol. 2021, 31, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaval, K.G.; Garsin, D.A. Ethanolamine Utilization in Bacteria. mBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Calderón, M.; Nguyen, D.D.; Kapono, C.A.; Herron, P.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Sohlenkamp, C. Plasticity of Streptomyces coelicolor Membrane Composition Under Different Growth Conditions and During Development. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohlenkamp, C.; Geiger, O. Bacterial membrane lipids: diversity in structures and pathways. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 133–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Zhang, B.-Q.; Ye, B.-C. GntR Family Regulator DasR Controls Acetate Assimilation by Directly Repressing the acsA Gene in Saccharopolyspora erythraea. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao CH, Yao LL, Ye BC. 2014. Three genes encoding citrate synthases in Saccharopolyspora erythraea are regulated by the global nutrient-sensing regulators GlnR, DasR, and CRP. Mol Microbiol.
- Sato R, Ara S, Yamazaki H, Ishiya K, Aburatani S, Takaku H. 2021. Citrate-Mediated Acyl-CoA Synthesis Is Required for the Promotion of Growth and Triacylglycerol Production in Oleaginous Yeast Lipomyces starkeyi. Microorganisms 9.
- Craig, M.; Lambert, S.; Jourdan, S.; Tenconi, E.; Colson, S.; Maciejewska, M.; Ongena, M.; Martin, J.F.; van Wezel, G.; Rigali, S. Unsuspected control of siderophore production by N-acetylglucosamine in streptomycetes. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2012, 4, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, F.J.; Martín, J.F. Iron-regulatory proteins DmdR1 and DmdR2 of Streptomyces coelicolor form two different DNA-protein complexes with iron boxes. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, F.J.; Barreiro, C.; Coque, J.J.R.; Martín, J.F. Functional analysis of two divalent metal-dependent regulatory genes dmdR1 and dmdR2 in Streptomyces coelicolor and proteome changes in deletion mutants. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunet, R.; Brock, A.; Rexer, H.-U.; Takano, E. Identification of genes involved in siderophore transport inStreptomyces coelicolorA3(2). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 262, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forchhammer, K.; Selim, K.A.; Huergo, L.F. New views on PII signaling: from nitrogen sensing to global metabolic control. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selim, K.A.; Alva, V. PII-like signaling proteins: a new paradigm in orchestrating cellular homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2024, 79, 102453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Ninfa, A.J. Escherichia coli PII Signal Transduction Protein Controlling Nitrogen Assimilation Acts As a Sensor of Adenylate Energy Charge in Vitro. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 12979–12996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosztolai, A.; Schumacher, J.; Behrends, V.; Bundy, J.G.; Heydenreich, F.; Bennett, M.H.; Buck, M.; Barahona, M. GlnK Facilitates the Dynamic Regulation of Bacterial Nitrogen Assimilation. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, D.; Falke, D.; Wohlleben, W.; Engels, A. Nitrogen metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): modification of glutamine synthetase I by an adenylyltransferase The EMBL accession number of the internal Streptomyces coelicolor glnE fragment is Y17736. Microbiology 1999, 145, 2313–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuther, J.; Wohlleben, W. Nitrogen Metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor: Transcriptional and Post-Translational Regulation. Microb. Physiol. 2007, 12, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesketh, A.; Fink, D.; Gust, B.; Rexer, H.; Scheel, B.; Chater, K.; Wohlleben, W.; Engels, A. The GlnD and GlnK homologues of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) are functionally dissimilar to their nitrogen regulatory system counterparts from enteric bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 46, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.E.; Sassaki, G.L.; Valdameri, G.; Pedrosa, F.O.; Souza, E.M.; Huergo, L.F. Fatty acid biosynthesis is enhanced in Escherichia coli strains with deletion in genes encoding the PII signaling proteins. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, E. CS, Kharwar S., Tiwari B., Shila Singh S. S. & Mishra A. K. 2021. Nitrogen starvation–induced oxidative stress relieves PII-mediated inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACCase) activity and signals enhanced lipid synthesis in Synechococcus PCC 7942. Journal of Applied Phycology 33:313–329.
- I AWJaC. 2020. Ammonium Transporters: A molecular dual carriageway. Elife 9:e61148.
- Barreiro, C.; Martínez-Castro, M. Regulation of the phosphate metabolism in Streptomyces genus: impact on the secondary metabolites. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, JF. 2004. Phosphate control of the biosynthesis of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites is mediated by the PhoR-PhoP system: an unfinished story. J Bacteriol 186:5197-5201.
- Urem, M.; Świątek-Połatyńska, M.A.; Rigali, S.; van Wezel, G.P. Intertwining nutrient-sensory networks and the control of antibiotic production inStreptomyces. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 102, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysenko, S. 2023. Impact of Nitrogen-Containing Compounds on Secondary Metabolism in Streptomyces spp.—A Source of Metabolic Engineering Strategies Syn Bio 1 (3) 205-205.
- Pai, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Su, J.; Lu, W. Effects of the pleiotropic regulator DasR on lincomycin production in Streptomyces lincolnensis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Li, X.-M.; Tang, Z.-K.; Qiao, J.; Zhao, G.-R. DasR positively controls monensin production at two-level regulation in Streptomyces cinnamonensis. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 43, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-H.; Xu, Y.; Rigali, S.; Ye, B.-C. DasR is a pleiotropic regulator required for antibiotic production, pigment biosynthesis, and morphological development in Saccharopolyspora erythraea. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10215–10224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świątek-Połatyńska, M.A.; Bucca, G.; Laing, E.; Gubbens, J.; Titgemeyer, F.; Smith, C.P.; Rigali, S.; van Wezel, G.P. Genome-Wide Analysis of In Vivo Binding of the Master Regulator DasR in Streptomyces coelicolor Identifies Novel Non-Canonical Targets. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0122479–e0122479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urzica, E.I.; Vieler, A.; Hong-Hermesdorf, A.; Page, M.D.; Casero, D.; Gallaher, S.D.; Kropat, J.; Pellegrini, M.; Benning, C.; Merchant, S.S. Remodeling of Membrane Lipids in Iron-starved Chlamydomonas. 2013, 288, 30246–30258. [CrossRef]
- Devadasu, E.; Subramanyam, R. Enhanced Lipid Production in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Caused by Severe Iron Deficiency. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Veen, H.W.; Abee, T.; Kortstee, G.J.J.; Konings, W.N.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Translocation of Metal phosphate via the Phosphate Inorganic Transport System of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.K.; Rajasekharan, R. Cardiolipin deficiency causes triacylglycerol accumulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 434, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, K.; Gohil, V.; Stuart, R.A.; Hunte, C.; Brandt, U.; Greenberg, M.L.; Schägger, H. Cardiolipin Stabilizes Respiratory Chain Supercomplexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52873–52880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, T.H.; A Dencher, N. Cardiolipin: a proton trap for oxidative phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 2002, 528, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, V.M.; Hayes, P.; Matsuyama, S.; Schägger, H.; Schlame, M.; Greenberg, M.L. Cardiolipin Biosynthesis and Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Function Are Interdependent. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 42612–42618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval-Calderón, M.; Geiger, O.; Guan, Z.; Barona-Gómez, F.; Sohlenkamp, C. A Eukaryote-like Cardiolipin Synthase Is Present in Streptomyces coelicolor and in Most Actinobacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 17383–17390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin JF, Demain AL. 1980. Control of antibiotic biosynthesis. Microbiol Rev 44:230-251.
- Esnault, C.; Dulermo, T.; Smirnov, A.; Askora, A.; David, M.; Deniset-Besseau, A.; Holland, I.-B.; Virolle, M.-J. Strong antibiotic production is correlated with highly active oxidative metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor M145. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, C.; Sago, L.; Cornu, D.; Redeker, V.; Virolle, M.-J. A Proteomic Analysis Indicates That Oxidative Stress Is the Common Feature Triggering Antibiotic Production in Streptomyces coelicolor and in the pptA Mutant of Streptomyces lividans. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 813993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan-Oropeza A, Henry C, Blein-Nicolas M, Aubert-Frambourg A, Moussa F, Bleton J, Virolle MJ. 2017. Quantitative Proteomics Analysis Confirmed Oxidative Metabolism Predominates in Streptomyces coelicolor versus Glycolytic Metabolism in Streptomyces lividans. J Proteome Res 16:2597-2613.
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Chen, H.; He, C.-L.; Wang, Q. Nitrogen Starvation Induced Oxidative Stress in an Oil-Producing Green Alga Chlorella sorokiniana C3. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e69225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilancioglu, K.; Cokol, M.; Pastirmaci, I.; Erman, B.; Cetiner, S. Oxidative Stress Is a Mediator for Increased Lipid Accumulation in a Newly Isolated Dunaliella salina Strain. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e91957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liufu, W.; Di, M.; Yingying, P.; Liqiu, S.; Wenzhi, W. Nitrogen limitation and hydrogen peroxide act synergistically to enhance lipids accumulation via ROS/Ca2+ dependent mechanism in Chlorella sorokiniana. Algal Res. 2023, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbourn, C.C. Toxicity of iron and hydrogen peroxide: the Fenton reaction. Toxicol. Lett. 1995, 82–83, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, M.K.; Tabor, C.W.; Tabor, H. Polyamines protect Escherichia coli cells from the toxic effect of oxygen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 2261–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rider, J.E.; Hacker, A.; Mackintosh, C.A.; Pegg, A.E.; Woster, P.M.; Casero, R.A., Jr. Spermine and spermidine mediate protection against oxidative damage caused by hydrogen peroxide. Amino Acids 2007, 33, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




