1. Introduction
The growing competitiveness that can be seen in all economic sectors, and where cost control is increasingly evident, makes performance management in this area more distinct and complex.
Thus, the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) emerged as the ideal tool for improving the performance of organizations. The BSC is a management tool with the potential to clarify companies’ strategic objectives and to assist in the selection of the most appropriate performance indicators. For its success, alignment between the organization’s strategy and the service strategy is important, as well as the involvement of management.
This work aimed to evaluate the impact of implementing the BSC in several organizations. From the research carried out, 694 articles related to BSC, from Web of Science, were selected for the literature review. From the analysis of these articles, it was possible to conclude that the implementation of this tool can represent added value for the success of organizations in general.
Empirical evidence suggests that, through the implementation of the BSC, organizations will be able to increase their level of quality, customer and professional satisfaction, as well as contributing to their efficiency and effectiveness. However, despite its benefits, the implementation of the BSC is still not a linear process, with several limitations and/or difficulties being identified in the process of designing and implementing this tool.
Literature reviews play a decisive role in the process of synthesizing scientific information and describing the state of the art(Hoffmann, 2020). The Bibliometric approach presents a systematic and objective process that is transparent, reliable, and easy to replicate.(Aria & Cuccurullo, 2017), and based on statistical techniques(Sergio, 2019). This approach is useful for network visualization and data exploration to analyze the social, intellectual and conceptual structure of knowledge(Aria & Cuccurullo, 2017).
2. Theoretical Frameworks: The Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
Since the early 1990s, Balanced Scorecards (BSC’s) have expanded traditional approaches to measuring organizational and/or strategic performance by emphasizing the utility of a multi-domain framework, as opposed to one that is finance-centric.(Bohm et al., 2021).
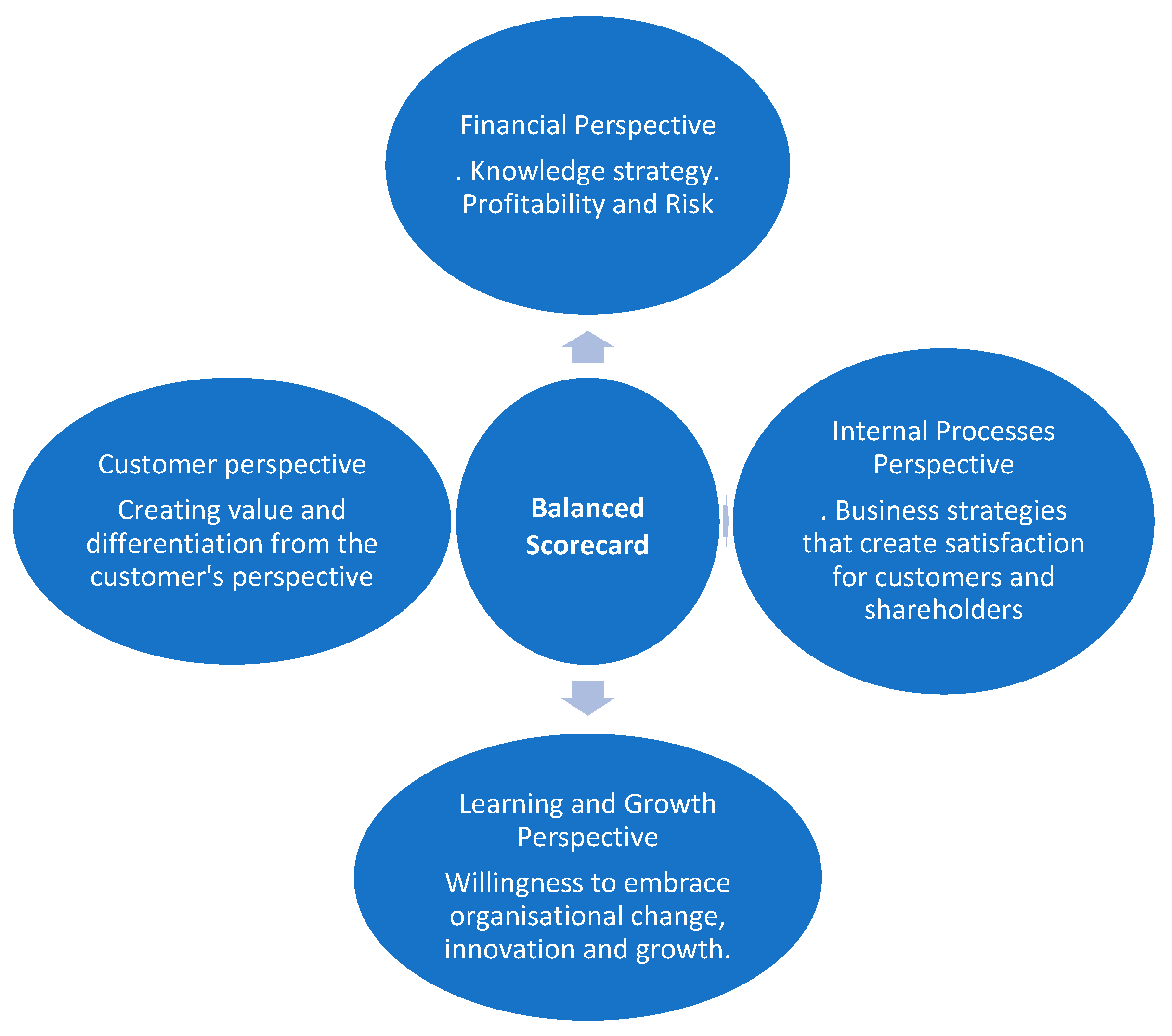
The BSC developed in the early 1990s by Kaplan and Norton aims to be a set of financial and non-financial measures that gives top executives a quick and comprehensive view of their business. It is presented as a means of evaluating the company’s performance(Bhagwat & Sharma, 2007)by incorporating 4 important perspectives(Kaplan & Norton, 1992):
Figure 1.
To the four perspectives of the BSC. Source: Source: Adapted from Kaplan and Norton (1992, p. 65).
Figure 1.
To the four perspectives of the BSC. Source: Source: Adapted from Kaplan and Norton (1992, p. 65).
In the specific case of this analysis, in the health sector, authors such as(Maria & Oliveira, 2020)state that although the BSC was initially developed for business organizations in the private sector, its use quickly spread to the public sector, including healthcare facilities. Also(Tricco et al., 2018) emphasize that BSC’s have been developed and implemented in the health sector since the mid-1990s, shortly after the tool’s first publication. The tool has been applied to address a variety of challenges ranging from the imperative to improve the quality and safety of care, to guide the administration of public or private healthcare services, and to support the profitability or competitiveness of healthcare corporations in market systems.
The BSC concept has evolved a lot since the publication of(Kaplan & Norton, 1992). The tool began as a new approach to organizational performance and ultimately evolved to become an innovative strategic management system(Voeler Katheleen E.; Jonathon S; G. Richard French., 2001) . It has since been adopted by a wide variety of sectors, including those involved in the provision of healthcare services, both public and private.(Zelman; WN; Pink GH; Matthias CB, 2003).
The BSC adds multidimensionality to an organization’s performance measurement framework by allocating measures across four perspectives (sometimes called domains): financial, customer, internal business process, and learning and growth.(Kaplan & Norton, 1992).
The financial perspective evaluates financial performance and is fundamental to the BSC, as all other objectives and measures must be linked to it through cause and effect. The customer perspective provides information about how the organization is perceived by its customers; the internal business process perspective reflects the organization’s performance in activities most closely related to meeting financial and customer objectives; and the learning and growth perspective reflects how an organization is enabling itself to achieve objectives in the other three perspectives, for example, through employee development or process innovation(Bohm et al., 2021). Like this,(Malagueno et al., 2018)showed that the use of the Balanced Scorecard comes with several benefits for organizations in terms of control capacity in order to achieve greater financial performance and exploratory innovation results.
Another development brought us the study of(Lueg, 2015), which indicated an evolution in BSC methods through the use of strategic maps, as the study demonstrates that these maps function as a way of obtaining support from employees in order to achieve the strategic objectives of the unit, in addition to the information that these provide, and that work to improve coordination between responsibility centers, rather than just supporting managers’ assessment.
According to(Santos, 2014), strategy communication and integration and recognition of performance are essential for the articulation and alignment of organizational objectives with individual ones. Research has shown a strong link between employees, users and organizational performance. Therefore, the focus on stakeholder involvement is a key factor in meeting users’ needs, unless it is included in the BSC(Thompson KR, 2013).
(Gao et al., 2018)developed a system of performance evaluation indicators in hospitals based on the Balanced Scorecard theory. Some methods overemphasize objective indicators or, conversely, only use subjective research and therefore lack an objective/direct perspective. The performance evaluation indicator system established using the BSC is practical and scientific. Analysis of results based on this system identified several factors that affect hospital performance, such as efficiency in the use of resources, price of medical service, staffing structure and doctor-patient relationship.
The BSC provides a strategic map “with the verification of cause-effect relationships between perspectives, objectives, goals and indicators”(Kaplan, R. & Norton, 2004, p. 6);(Azevedo, 2014). Cause-effect relationships act as a test to assess whether the BSC is effectively reflecting the organization’s strategy(Gomes, 2018).
However, despite the obvious virtues of applying the Balanced Scorecard, we must take into account that authors such as(Oliveira et al., 2019)found that the BSC incorporates bureaucratic concepts when seeking to provide accurate and relevant financial and non-financial measures to facilitate decision-making in organizations.
The BSC is a system that moves organizations from financially biased measurement to a more balanced approach. The development, competitiveness and growth of organizations effectively illustrate the implementation of organizational strategies(Graeme Cocks, 2010; Hsieh & Lin, 2010).The literature illustrates the popularity and widespread implementation of the BSC in many different types of organizations in the United States and across Europe(Rigby, 2011). Second(Kaplan, R., & Norton, 2000), successful BSC implementation happens when an organization’s strategy translates into action and obtains benefits.
However, many organizations that have adopted the BSC have not been successful in translating their organization’s strategy into action and have not derived any benefits from the BSC. According to(Atkinson, 2006), about 70% of BSC implementations fail.
Although there is a lot of literature on the BSC framework, there is a dearth of research on how the framework should be properly implemented(Mesut Kumru, 2010), and it is clear how this structure should be implemented in non-profit organizations. Furthermore, there is a lack of research on the strategies leaders use to guide their employees in the right direction after implementing the BSC.(Lueg, 2015).
Effective implementation of a performance measurement system like the BSC often leads to more successful execution of business strategies(Otheitis & Kunc, 2015).
Despite numerous organizations having identified and implemented the BSC as their chosen performance measurement system, up to 90% of companies still fail to execute their business strategy(Cândido & Santos, 2015).
The general problem, which our study focuses on, is to assess whether some private, public and non-profit organizations are negatively affected by BSC implementation problems, resulting in inefficient operations. The specific problem is that some leaders lack the necessary knowledge to implement a BSC effectively.
3. Methodological Approaches
To carry out this work, we chose to carry out a systematic review of the literature, as it seemed to be the most appropriate methodology for achieving the objective of this bibliometric analysis and, at the same time, providing answers to the questions listed. Furthermore, this methodology allows us to collect data on the topic under study, through research, selection and synthesis of literature, that is, it will allow us to search for articles that focus on the application of the BSC, draw conclusions about the state of the art and identify aspects that require special attention.
3.1. Main Steps of the Systematic Literature Review on the Application of the BSC
To better understand the application of the BSC in institutions, as already mentioned, a systematic review of the literature was used. With this methodology, the aim is to identify and systematize relevant information on this topic. After having previously explained what a systematic literature review is, we will now describe each of the stages of our investigation.
3.1.1. General Objective and Research Questions
The general objective of this investigation is to diagnose the state of the art regarding the implementation of the BSC in different organizations. To achieve this objective, the following research questions were developed: What are the characteristics of publications that report the application of the BSC?; What is the motivation for using the BSC?; What are the characteristics of the organizations where the BSC was implemented?; Who are the actors in the BSC design and implementation process?; What are the perspectives and performance indicators most frequently used when applying the BSC? ; What are the facilitating factors in design and implementation?; What are the results obtained with the implementation of the BSC?; What are the difficulties and/or limitations to implementing the BSC?; To answer these questions, we carried out a systematic review of the literature.
3.1. Descriptors
The search for publications in the databases was carried out according to the following descriptors: (“Balanced Scorecard” OR “BSC”). The use of the Boolean operator “OR” allowed us to combine the different descriptors (“Balanced Scorecard” and “BSC”). In turn, the Boolean operator “AND” allowed us to find articles that bring together two or more ideas, that is, in which both terms (i.e. Balanced Scorecard or BSC) appear simultaneously in the document.
3.2.1. Search Sources
In this bibliometric analysis, our focus was on works published in specialized journals. Using the keywords mentioned above, the “Web of Science” database was used, and the survey was carried out in May 2022. In this survey, a total of 694 publications of potential interest were identified in the “Web of Science”.
The research covered the years from 1956 to 2021, 65 years. We export all available results to text files, including citation information, bibliographic information, abstracts and keywords. To eliminate duplicate publications and organize all data, we use Mendeley software.
Table 1.
Operationalization of the investigation.
Table 1.
Operationalization of the investigation.
| Data base |
Web of Science (WOS) |
| Keywords used |
Balanced Scorecard and BSC |
Filters |
Last 65 years: 1956-2021
(articles = 694 articles) |
Subsequently, the information available in the title and summary of each of the aforementioned articles was read and analysed, identifying a set of characteristics/variables capable of outlining an outline on the topic: the general characterization of the works (number of articles published per year, number of authors per article, number of publications per journal, number of citations per article, number of publications per country), methodological procedures (research technique and data collection methods), areas of knowledge or more relevant themes studied and sector of activity covered.
The data collected was processed using descriptive statistics, in a quantitative manner, which we will present below.
4. Analysis and Discussion of Results
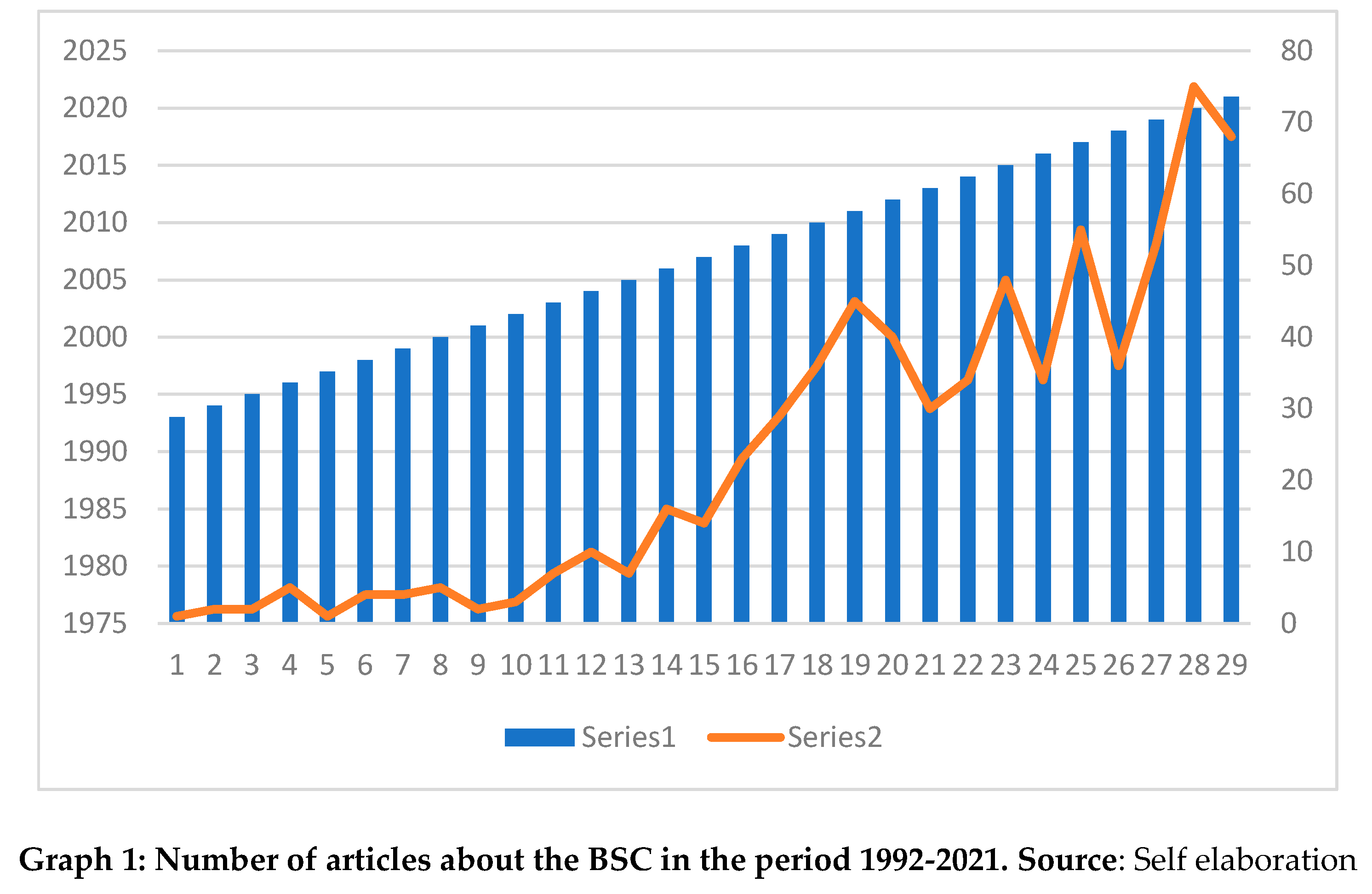
Published articles that addressed the BSC over the sixty-five years presented showed us that the first article was published by(Wilson, 1969)In 1969, and later only in 1976, two articles were published again that talked about BSC, but not as a strategic management tool. In 1981 and 1988, one publication in each year. As can be seen in
Table 2
It was only after 1992 that people began to talk about BSC, as a Strategic Management Tool (BSC), with Kaplan. The largest number of publications occurred in 2020, with 75 of the totals, presenting the year 2021 with a number of 68 compared to previous years.
In a total of 85 countries, where we found more than 20 articles/country were, in the period under analysis, it was done in England with (130) articles, followed by the USA, with (81) articles, followed by Taiwain, with (71), Iran with (46), Austria (36), China (43), Spain (42), Brazil, Canada and the Netherlands (23), Germany (27), Italy (29) All other countries shown in the following graph, with a number of inferior publications.
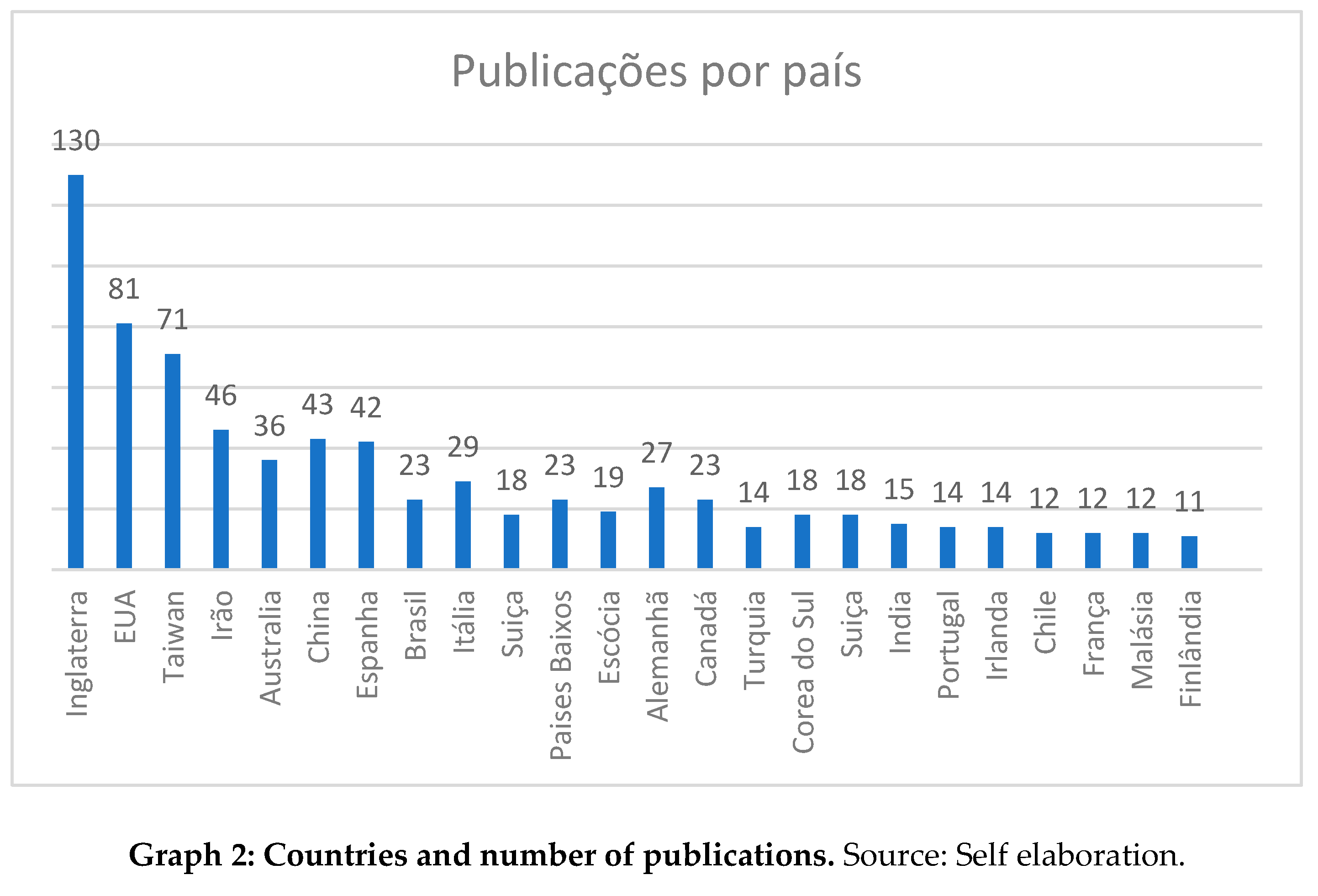
From the analysis carried out, we were able to verify that the BSC theme as a new paradigm for strategic management arouses the interest of the international scientific community.
The number of citations and the most cited articles are the most relevant indicators for evaluating the impact of documents in a given area. The analysis of these indicators allows us to draw conclusions about the existence of links between different researchers(Herrera Damas & Christofoletti, 2006). The connections between researchers and the number of citations are presented in this work as a significant scientific contribution among authors who seek to understand the dynamics of BSC implementation. (
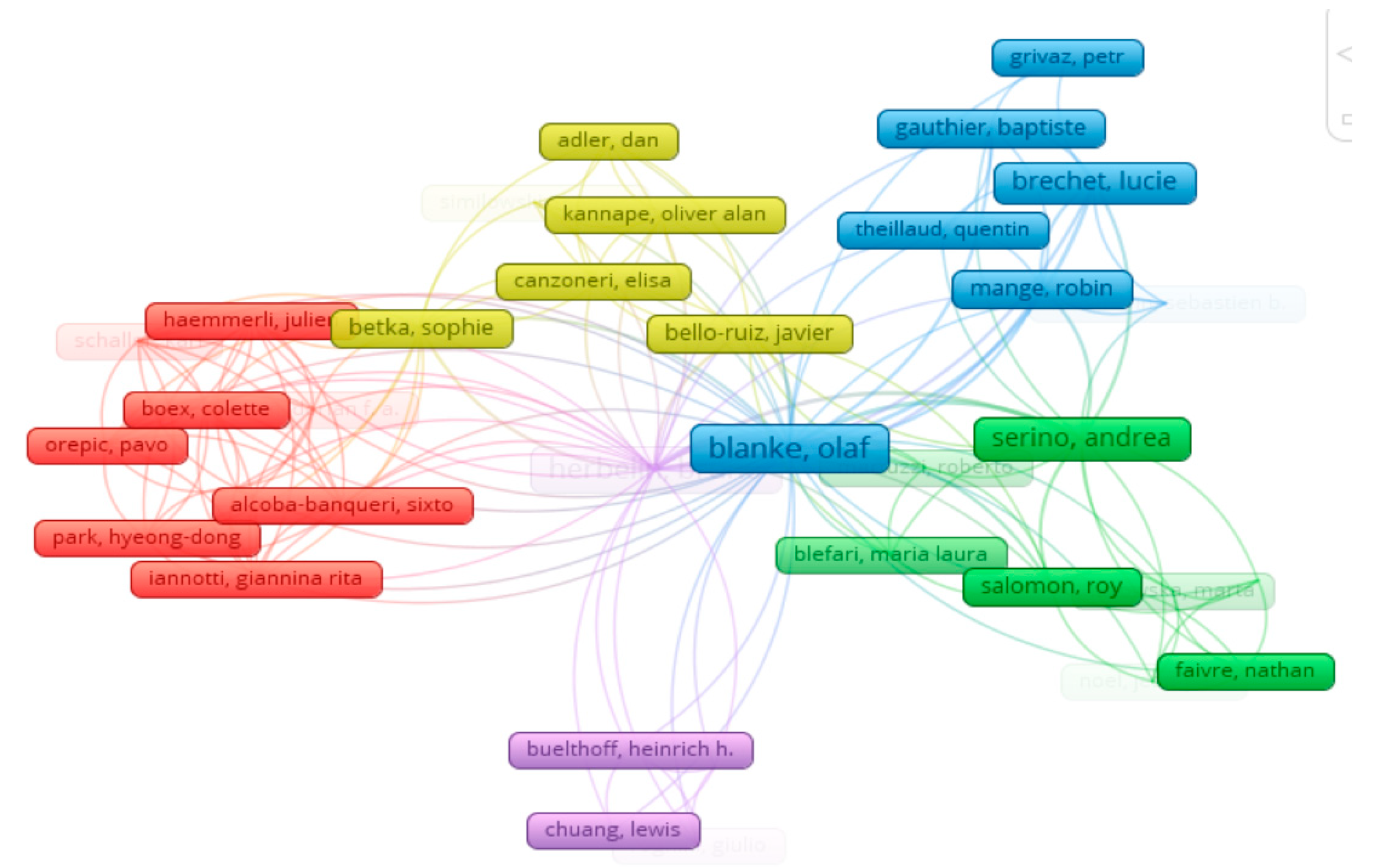
Figure 1) From this analysis, we were able to identify the Bibliometric maps in articles about the BSC by different authors in 5 clusters, namely red, yellow, green, blue and purple, which are shown in the following Figure.
Figure 2.
Authors cited in at least two academic works under the theme ‘Balanced Scorecard and BSC. Period: 1956-2021. Source: self-elaboration; software: Vosviewer.
Figure 2.
Authors cited in at least two academic works under the theme ‘Balanced Scorecard and BSC. Period: 1956-2021. Source: self-elaboration; software: Vosviewer.
Regarding the number of articles cited, 9877 were identified, with an average of articles per author of12,641. Articles without self-citation 9576. The average number of citations per article was9.34286. A total of 694 articles.
This type of bibliometric study allows us to assess the relevance of a given topic and uses the analysis of the most frequent keywords in publications (
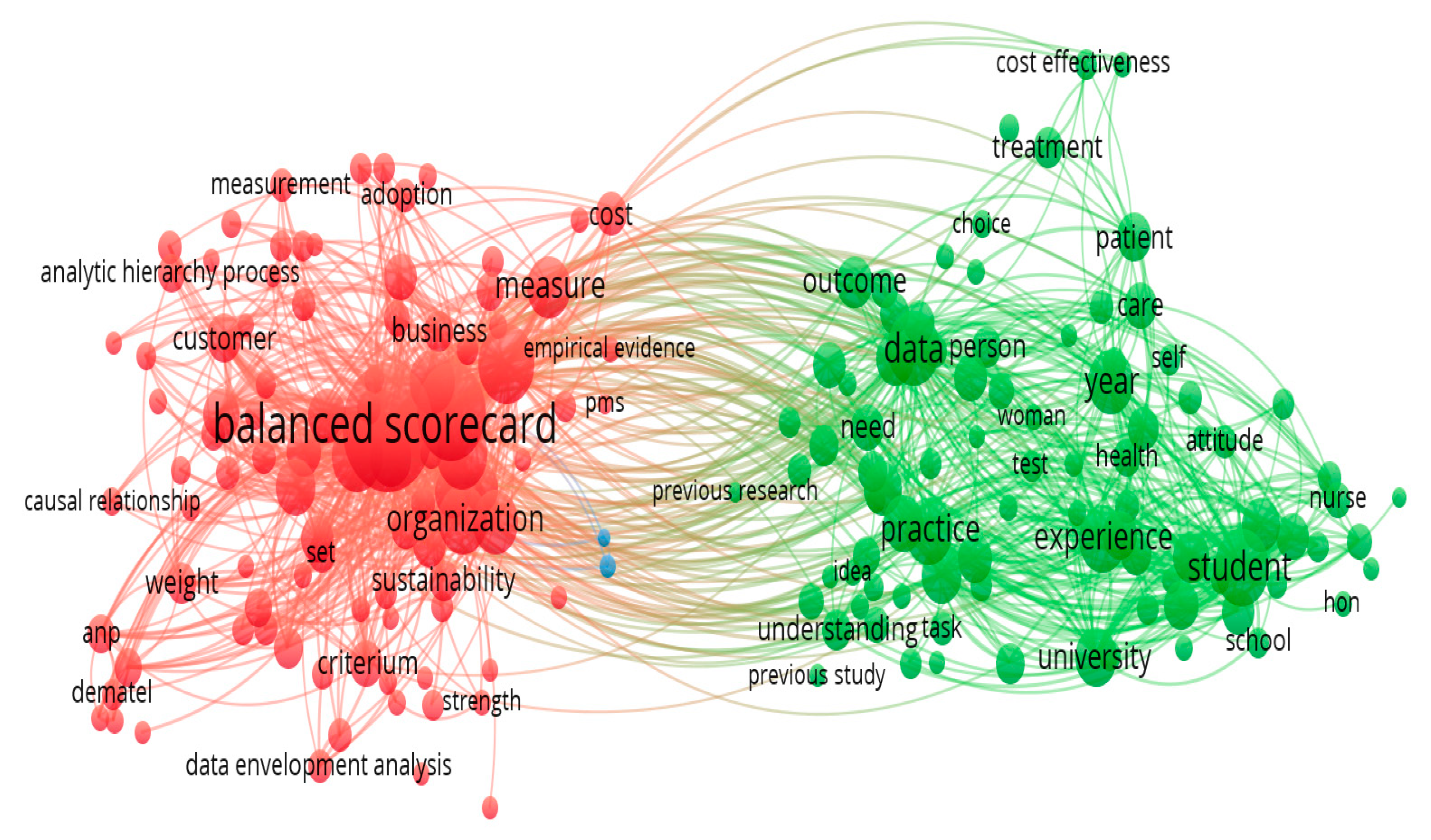
Figure 3), thus allowing us to identify which topics are most recurrent and where there are possible lacks of studies, It is essential to encourage future studies.
The 694 articles were indexed by Vosviewer with 188 items, divided into 3 clusters. With 9855 links and a link strength of 33 128. Terms prove to be more valuable than keywords per author for bibliometric analysis, but are less deductive in content analysis. These are the ones that can be seen in
Figure 2.
In
Figure 3 we have 3 groups of keywords, identified by different colours, and each one represents a specific topic. These clusters mean that keywords co-occur in the indexing of articles. We use this structure to learn about the topics covered and identify the most important and recent field of research. With the Vosviewer technique of keywords and authors (
Figure 3) they showed in cluster 1 - red that keywords such as Balanced Scorecard, BSC, organization, sustainability, in cluster 2 - green, words such as, experience, program, idea, in cluster 3 – blue, we find words such as design methodology approach and originality value.
Figure 3.
Network Total Keywords. Source: self-elaboration; software: Vosviewer.
Figure 3.
Network Total Keywords. Source: self-elaboration; software: Vosviewer.
Analyzing the most used words in the abstracts and titles of the 694 articles, we were able to observe in the previous figure that the authors indexed the articles with 188 keywords by Web of Science. The bibliometric analysis carried out based on the literature of (by Web of Science) has become an increasingly popular method for visualizing the structure of scientific fields.(Zhang et al., 2016).
Keywords are more effective for bibliometric analysis purposes when investigating the structure of different scientific areas, but are less comprehensive in representing the content of an article(Tan et al., 2017)(Zhang et al., 2016).
For the Balanced Scorecard theme, areas of interest were identified. The first, red, is related to organization, sustainability. The two other main focuses related to the most used keywords in academic studies on new strategic management proposals in which there is greater involvement of civil society are experience, program, idea. The definition and implementation of BSC can be understood as beneficial, but difficult for users to adapt.
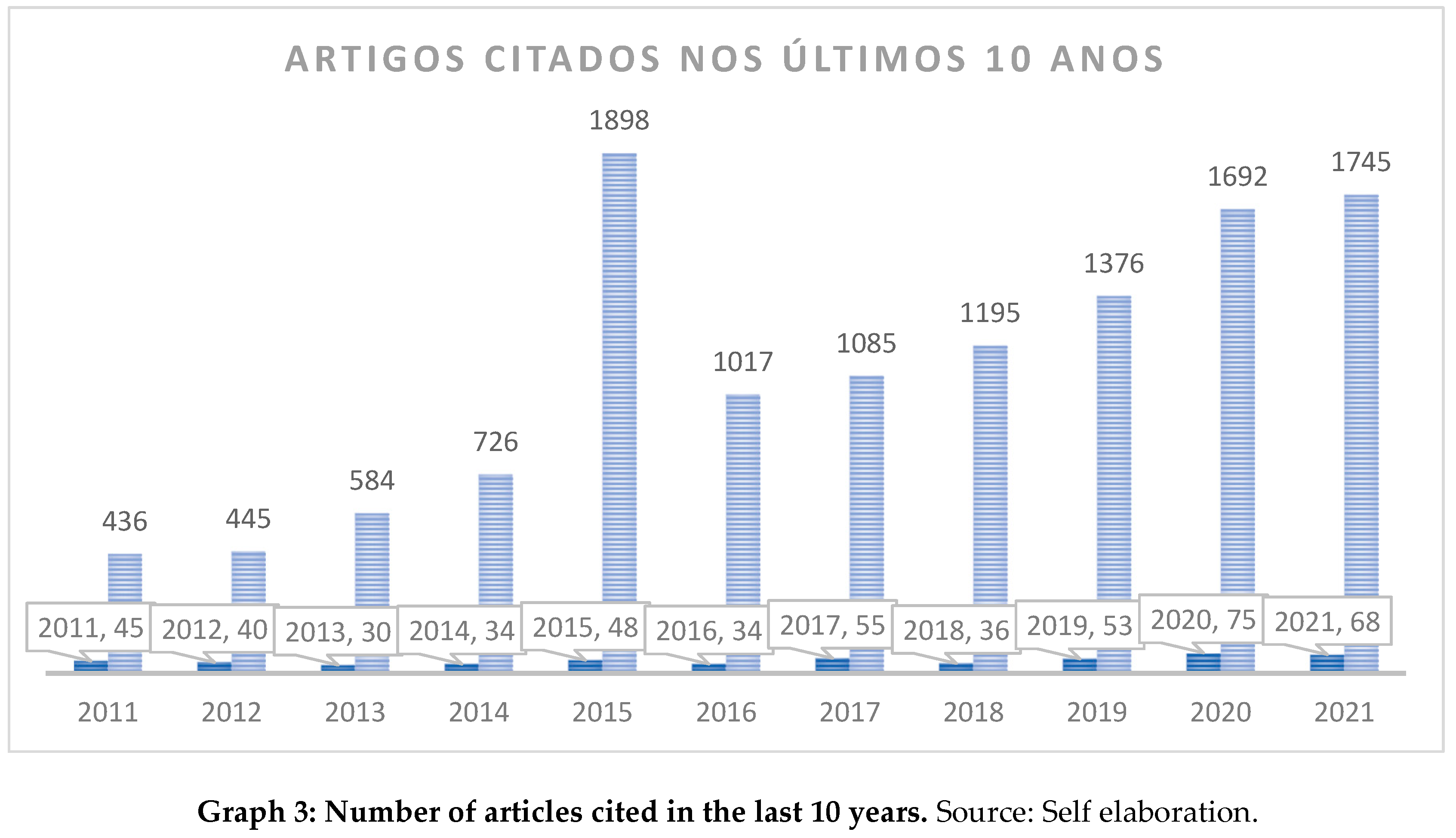
Graph 3 shows the evolution in the number of citations about BSC, where it can be seen that, from 2011 onwards, there was a significant increase in the number of citations under the theme evaluated. Thus, demonstrating great interest from the international academic community in presenting strategic management proposals that are closer to society’s desires.
Analyzing the publication of(Lumba-Brown et al., 2018)article with the most citations, conducted a systematic review and identified key gaps in diagnosis, prognosis and management. Significant relationships between social responsiveness and profitability,(Khiew et al., 2017)refers to the use of the BSC, brings a improving performance management for any company and not a threat. Therefore, all companies must utilize their limited resources and prioritize their performance factors in terms of a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) approach when designing their sustainability development. With the aim of selecting important elements from the sustainability indicators suggested in the literature and launching performance factors. the solutions show that supporting BSC integration decisions must involve recruitment, the articulation of financial motivations and the recognition of external pressures in the use of the BSC(Khalid et al.).
Another article, third most cited, that shows the importance of implementing the BSC to the banking sector is that of(Hasan et al., 2021), shows that there is a useful connection between the estimates of the BSC, and the performance of Islamic banks. Secondly, a high improvement was observed in Malaysian Islamic banks, which used the BSC measures.
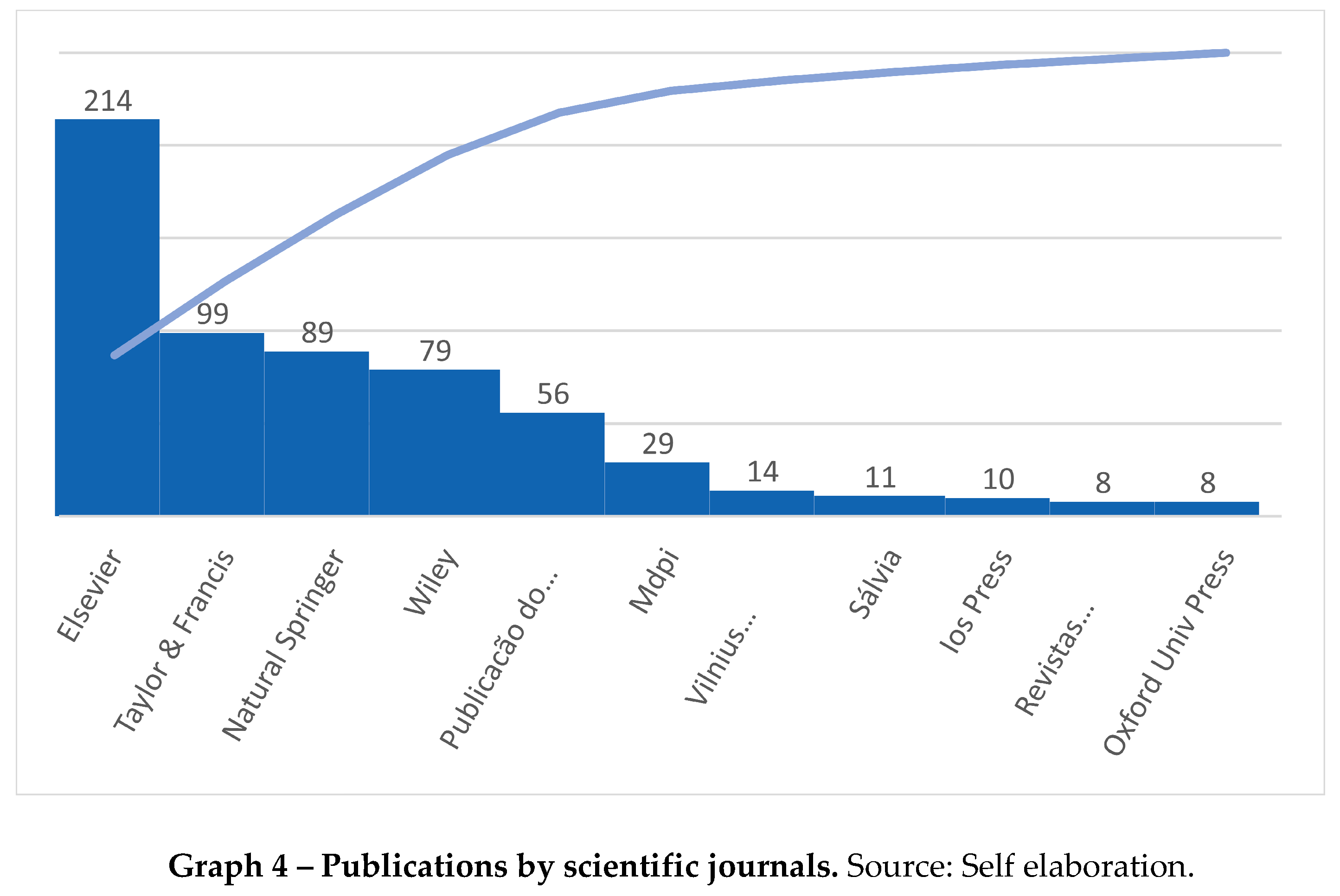
Regarding the magazines with the largest number of publications on the BSC, in the period analysed it was possible to observe that there were several magazines where they were published. The dispersion of articles across different magazines reveals the fact that the BSC is a transversal theme.
Table 4 presents the results for the journals where three or more articles were published on the topic under analysis. It is possible to observe a greater number of Elsevier publications on BSC.
It is important to highlight the fact that we filtered only articles with the expression “Balanced Scorecard” or “BSC” in the topic, limiting the number of articles per journal, that is, if the search were broader, the number of articles would considerably increase.
Table 4.
Number of articles by Editors.
Table 4.
Number of articles by Editors.
| Magazine |
Number of articles |
| Elsevier |
214 |
| Natural Springer |
89 |
| Emerald Group Publication |
56 |
| Taylor & Francis |
99 |
| mdpi |
29 |
| Wiley |
79 |
| Vilnius GediminasTechUniv |
14 |
| iOS Press |
10 |
| Sage |
11 |
| Academic Journals |
8 |
| Oxford Univ Press |
8 |
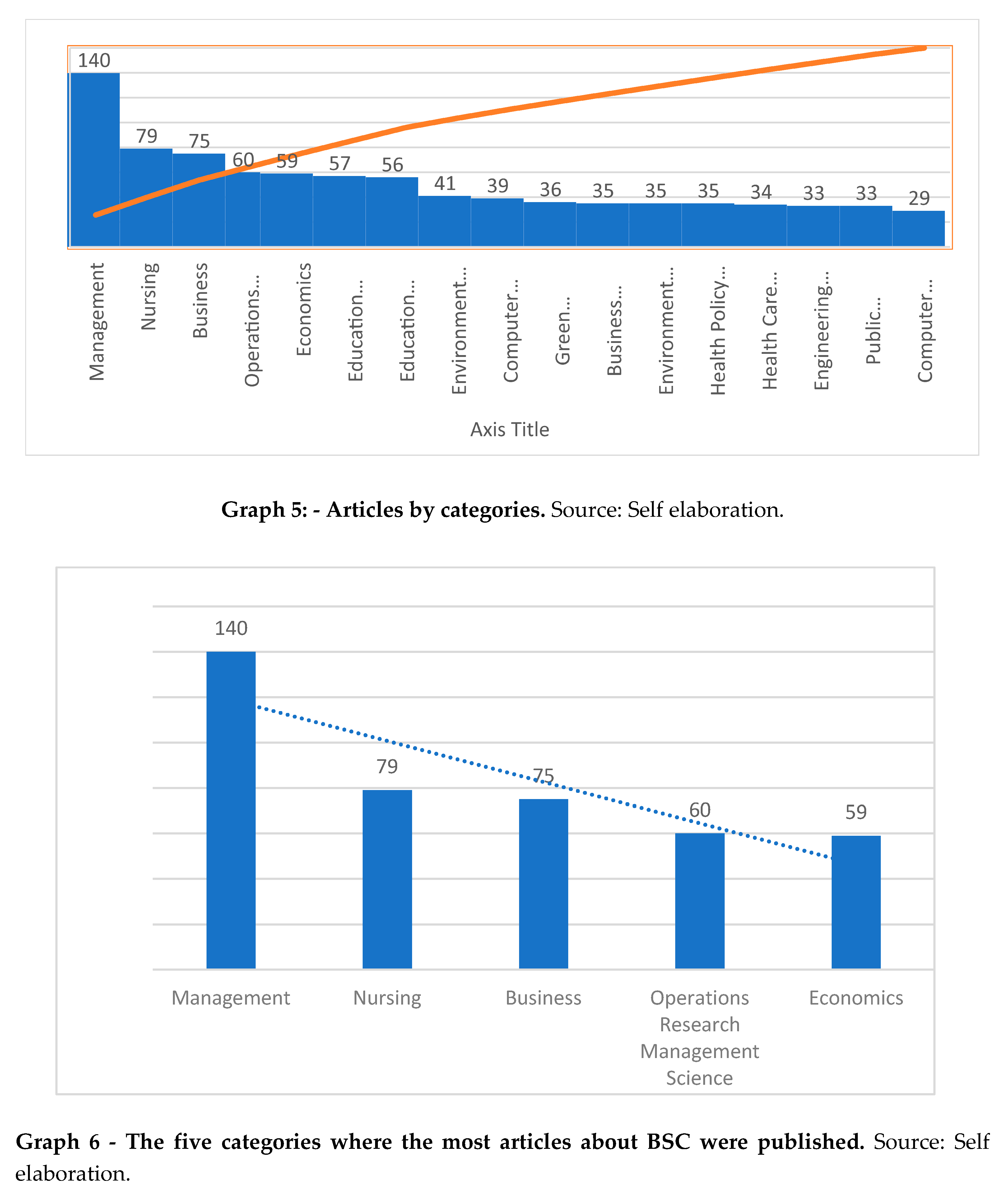
The documents fall into different categories, which we now present in graph 5, the respective distribution of articles where more about BSC has been published.
The relationships between concepts and keywords, most used in various publications to check what science is studying in the different themes developed in research(Aria et al., 2020);(Tijssen & Van Raan, 1989). Each scientific field or topic has been identified keywords from the database, Web of Science more(Eugene Garfield, 1993). According to(Aria et al., 2020), this technique is an extension of correspondence analysis, which analyses various relationships of categorical dependent variables. Analyze a set of observations described by a set of nominal variables.
5. Conclusions and Implications
The present work analysed the scientific production on the BSC in articles published in international scientific journals between the years 1956 and 2021, organizing a set of article characteristics and carrying out a systematic review of the literature of other Bibliometric studies and literature reviews already carried out. on the topic under study. These types of studies allow the researcher to quickly identify the journals, the authors, the subtopics investigated, the main research methods used, in all economic areas.
The theoretical contribution of this literature review aims to identify existing investigations and articles on the Balanced Scorecard/BSC. These studies are useful for the scientific community, editors of scientific articles, directors and administrators of different organizations. They thus allow you to be aware of current scientific developments, recognize influential articles and identify the most influential journals in this field, as well as find national and international collaborators.
We must emphasize that this study must be read in light of some limitations, particularly with regard to the chosen methodology: to obtain bibliographic data, the only database used was the Web of Science database. The use of other databases, such as Scopus, could have generated other publications and expanded the sample to be analysed. In addition, articles in were included as systematic literature reviews. The geographical dispersion of the articles was done without taking into account the populations of the countries. Another limitation was not dissecting the different areas of knowledge (last sixty-five years), to overcome the limitation found, for(Rodrigues, 2019), in a similar study with this type of limitation. Extend the study from 1992 onwards (the year in which the BSC was created). We can state that the studies found in years prior to 1992 have nothing to do with the BSC strategic management tool. The data was analysed without any manual editing. The majority of existing studies focus on BSC implementations, and no study reports events of failure in the use of this strategic tool, which was of particular interest, as such there is an urgent need to study and publish these cases of success and failure for the entire scientific community.
References
- Aria, M., & Cuccurullo, C. (2017). bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 11(4), 959–975. [CrossRef]
- Aria, M., Misuraca, M., & Spano, M. (2020). Mapping the Evolution of Social Research and Data Science on 30 Years of Social Indicators Research. Social Indicators Research 2020 149:3, 149(3), 803–831. [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, H. (2006). Strategy implementation: a role for the Balanced Scorecard? MANAGEMENT DECISION.
- Azevedo, E. E. G. C. (2014). O Balanced Scorecard e a Administração Local – Aplicação à Divisão Financeira do Município de Vila Franca de Xira. (Dissertação de Mestrado). Instituto Politécnico de Santarém.
- Bhagwat, R., & Sharma, M. K. (2007). Performance measurement of supply chain management: A balanced scorecard approach. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 53(1), 43–62. [CrossRef]
- Bohm, V., Lacaille, D., Spencer, N., & Barber, C. E. H. H. (2021). Scoping review of balanced scorecards for use in healthcare settings: Development and implementation. BMJ Open Quality, 10(3), 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Cândido & Santos. (2015). Strategy implementation: What is the failure rate? Journal of Management & Organization, 21. 10.1017/jmo.2014.77.
- Eugene Garfield, I. H. S. (1993). KeyWords PlusTM - indexação de derivativos algorítmicos - Garfield - 1993 - Journal of the American Society for Information Science - Wiley Online Library. [CrossRef]
- Gao, H., Chen, H., Feng, J., Qin, X., Wang, X., Liang, S., Zhao, J., & Feng, Q. (2018). Balanced scorecard-based performance evaluation of Chinese county hospitals in underdeveloped areas. Journal of International Medical Research, 46(5), 1947–1962. [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M. S. (2018). Impacto da Utilização da Ferramenta Balanced Scorecard – Estudo de Caso.
- Graeme Cocks. (2010). Emerging concepts for implementing strategy. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M., Iqbal, A., Ul Islam, M. R., Rahman, A. J. M. I., & Bosu, A. (2021). Using a balanced scorecard to identify opportunities to improve code review effectiveness: an industrial experience report. EMPIRICAL SOFTWARE ENGINEERING, 26(6). [CrossRef]
- Herrera Damas, S., & Christofoletti, R. (2006). Fiscalizar e alfabetizar: dois papéis dos observatórios de meios latino-americanos. Em Questão, 12(1), 131–148.
- Hoffmann, W. (2020). Congresso Brasileiro de Gestão do Conhecimento.
- Hsieh, L. F., & Lin, L. H. (2010). A performance evaluation model for international tourist hotels in Taiwan—An application of the relational network DEA. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 29(1), 14–24. [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R., & Norton, D. (2000). El Cuadro de Mando Integral (The Balanced Scorecard). Ediciones Gestión.
- Kaplan, R. & Norton, D. (2004). Strategy Maps: converting intangible assets into tangible outcomes. Boston, Massachusetts: Harvard Business School Press.
- Kaplan, R. S., & Norton, D. P. (1992). HarvardBusinessReview KaplanAndNorton(Bala - Onbekend. Harvard Bus., 70(1), 71–79.
- Khalid, S. K., Beattie, C., & Sands, J. S. (n.d.). Barriers and Motivations to Integrating Environmental Performance in the BSC: A case study in health care. SUSTAINABILITY ACCOUNTING MANAGEMENT AND POLICY JOURNAL. [CrossRef]
- Khiew, K.-F., Chen, M.-C., Shia, B.-C., & Pan, C.-H. (2017). Adapting the Balanced Scorecard into the HealthCare Industry: A Literature Review, New Insight and Future Directions. Open Journal of Business and Management, 05(04), 611–623. [CrossRef]
- Lueg, R. (2015). Strategy maps: The essential link between the balanced scorecard and action. Journal of Business Strategy, 36(2), 34–40. [CrossRef]
- Lumba-Brown, A., Yeates, K. O., Sarmiento, K., Breiding, M. J., Haegerich, T. M., Gioia, G. A., Turner, M., Benzel, E. C., Suskauer, S. J., Giza, C. C., Joseph, M., Broomand, C., Weissman, B., Gordon, W., Wright, D. W., Moser, R. S., McAvoy, K., Ewing-Cobbs, L., Duhaime, A.-C., … Timmons, S. D. (2018). Diagnosis and Management of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Children A Systematic Review. JAMA PEDIATRICS, 172(11). [CrossRef]
- Malagueno, R., Lopez-Valeiras, E., & Gomez-Conde, J. (2018). Balanced scorecard in SMEs: effects on innovation and financial performance. SMALL BUSINESS ECONOMICS, 51(1), 221–244. [CrossRef]
- Maria, H., & Oliveira, C. (2020). The Balanced Scorecard and Bureaucracy in the Hospital Environment: A Portuguese Case Study.
- Mesut Kumru. (2010). View of The validity in performance measures used in hospital planning.pdf. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H. C., Lima-Rodrigues, L., & Craig, R. (2019). The Presence of Bureaucracy in the Balanced Scorecard. REVISTA DE CONTABILIDAD-SPANISH ACCOUNTING REVIEW, 22(2), 218–224. [CrossRef]
- Otheitis & Kunc. (2015). Performance measurement adoption and business performance: An exploratory study in the shipping industry. MANAGEMENT DECISION.
- Rigby, D. & B. (2011). No Title. B Management Tools & Trends.
- Rodrigues, Q. L. (2019). Resumo O objetivo deste estudo é analisar as publicações internacionais sobre o Balanced Scorecard (BSC) nos últimos anos, identificando tendências de evolução e oportunidades de 1. 34, 1–27.
- Santos, L. F. G. (2014). Balanced Scorecard - Contributos para a Implementação na Administração Local. (Dissertação de Mestrado). Instituto Superior de Educação e Ciências de Lisboa., 144.
- Sergio, P. (2019). Qual ferramenta bibliométrica escolher ? Um estudo comparativo entre softwares COMPARATIVO ENTRE SOFTWARES Paulo Sergio da Conceição Moreira Universidade Federal do Paraná André José Ribeiro Guimarães Universidade Federal do Paraná Denise Fukumi Tsunoda U. November 2020.
- Tan, Y., Zhang, Y., & Khodaverdi, R. (2017). Service performance evaluation using data envelopment analysis and balance scorecard approach: an application to automotive industry. ANNALS OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH, 248(1–2), 449–470. [CrossRef]
- Thompson K. R., M. N. J. (2013). It’s Time to Add the Employee Dimension to the Balanced Scorecard. Organizational Dynamics, 42(2), 135 e 144. [CrossRef]
- Tijssen, R. J. W., & Van Raan, A. F. J. (1989). Mapping co-word structures: A comparison of multidimensional scaling and leximappe. Scientometrics 1989 15:3, 15(3), 283–295. [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A. C., Lillie, E., Zarin, W., O’Brien, K. K., Colquhoun, H., Levac, D., Moher, D., Peters, M. D. J., Horsley, T., Weeks, L., Hempel, S., Akl, E. A., Chang, C., McGowan, J., Stewart, L., Hartling, L., Aldcroft, A., Wilson, M. G., Garritty, C., … Straus, S. E. (2018). PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Annals of Internal Medicine, 169(7), 467–473. [CrossRef]
- Voeler Katheleen E.; Jonathon S; G. Richard French. (2001). No TitleThe balanced scorecard in healthcare organizations: a performance measurement and strategic planning methodology. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T. D. (1969). BSC DEGREE IN INFORMATION SCIENCE AT NEWCASTLE UPON TYNE. ASLIB PROCEEDINGS, 21(1), 18-. [CrossRef]
- Zelman; WN; Pink GH; Matthias CB. (2003). Use of the balanced scorecard in health care. J Health Care Finance .
- Zhang, J., Yu, Q., Zheng, F., Long, C., Lu, Z., & Duan, Z. (2016). Comparing keywords plus of WOS and author keywords: A case study of patient adherence research. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 67(4), 967–972. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).