Submitted:
22 July 2024
Posted:
24 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
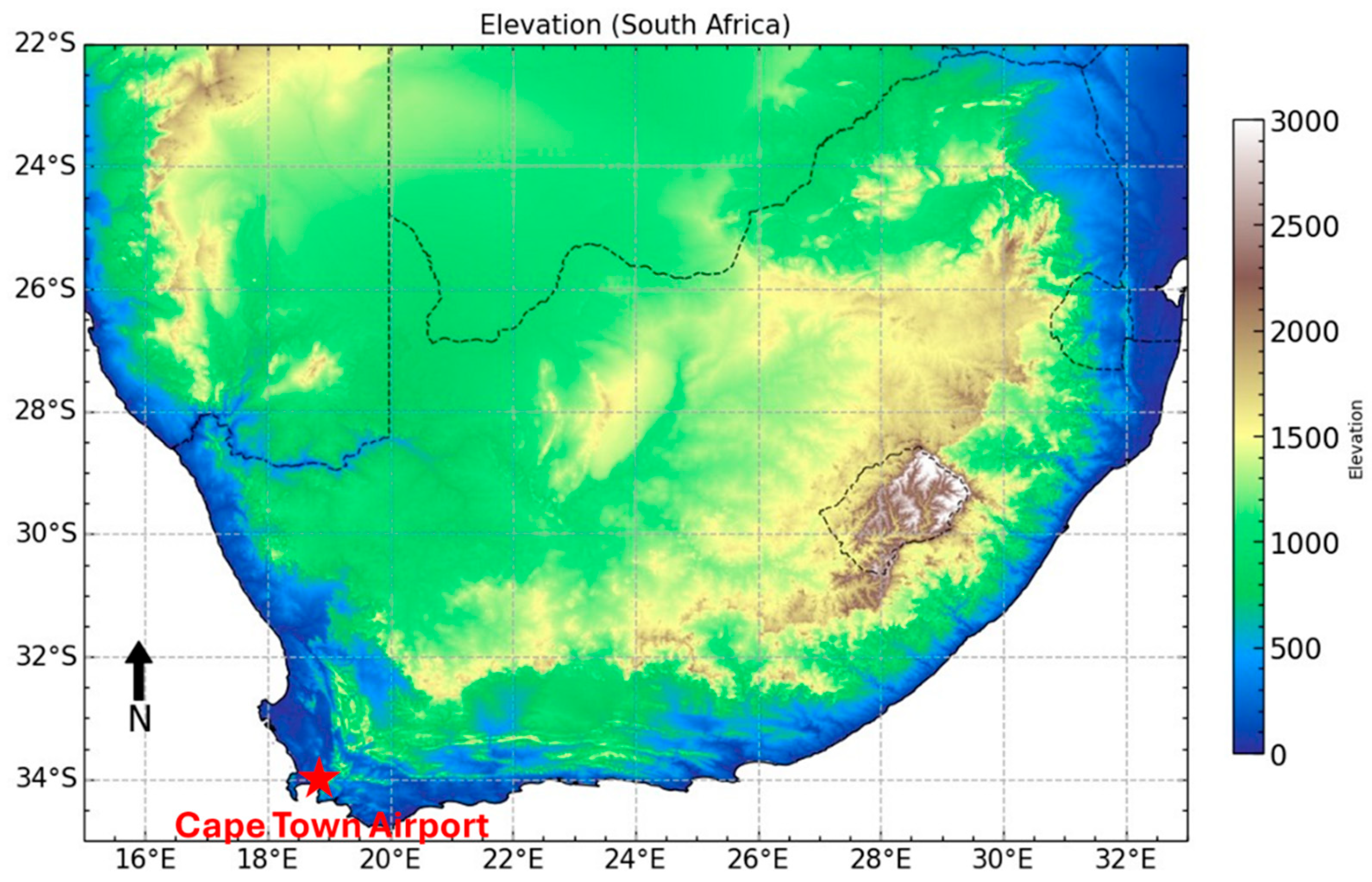
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Mann-Kendall Test Statistics
2.2. Innovative Trend Analysis
2.3. Standardized Precipitation Index Calculation
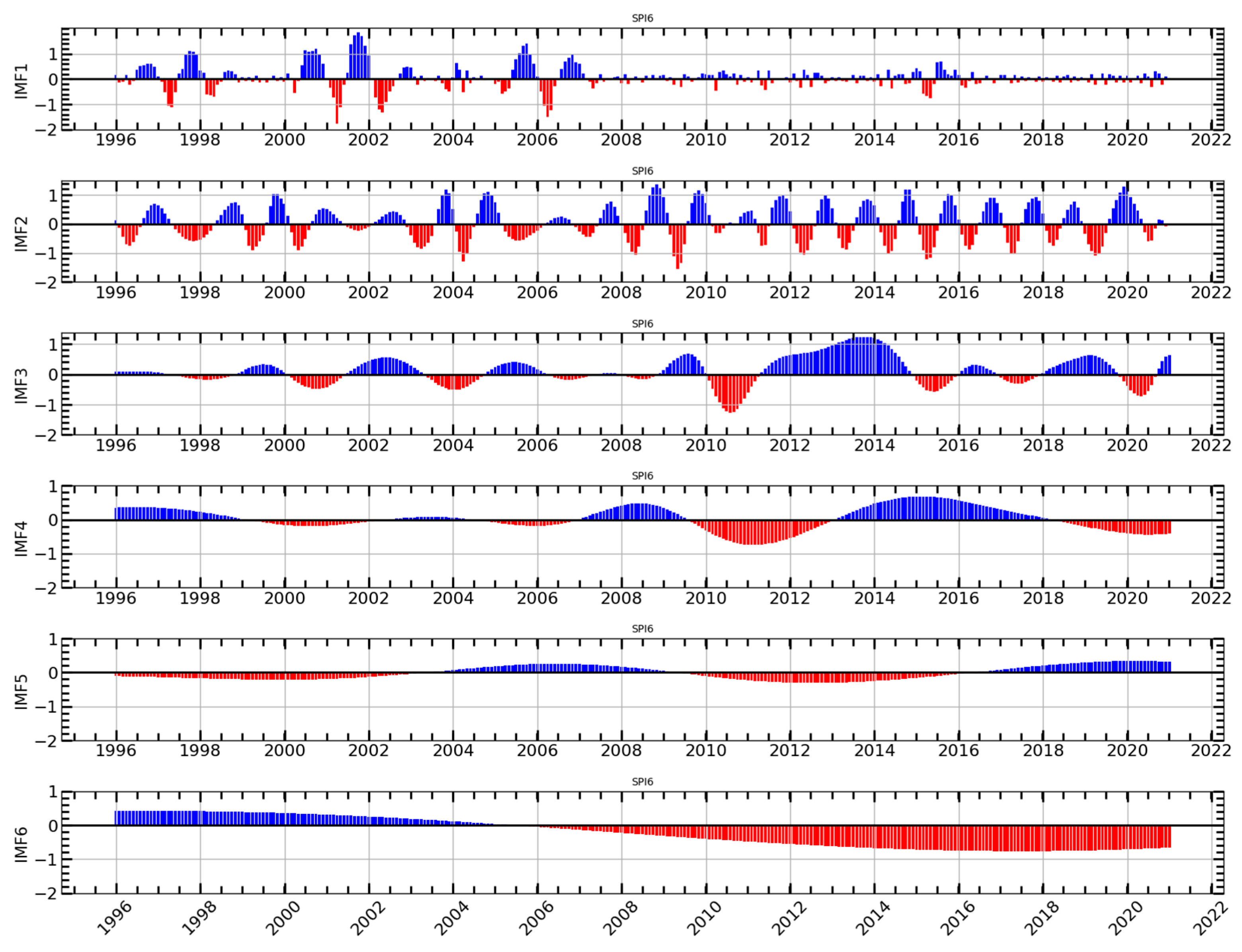
2.2.2. The Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode with Adaptive Noise (CEEMDAN)
- The EMD decomposition is performed for to obtain N new sequences and calculate the mean worth to be the first model component IMF1. The first remaining component will be calculated
- 2.
- Adding specific noise to the new signal, EMD decomposition is continued to obtain the second IMF2 of the original signal and corresponding residual
- 3.
- In the following stage, for , the k-th mode component and the corresponding residual signal can be computed in the following equation.
- 4.
- Repeat step 3 until the residual satisfies the stoppage criterion.
- 5.
- Finally, the decomposition consequence of the original signal can be described as
2.4. Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average
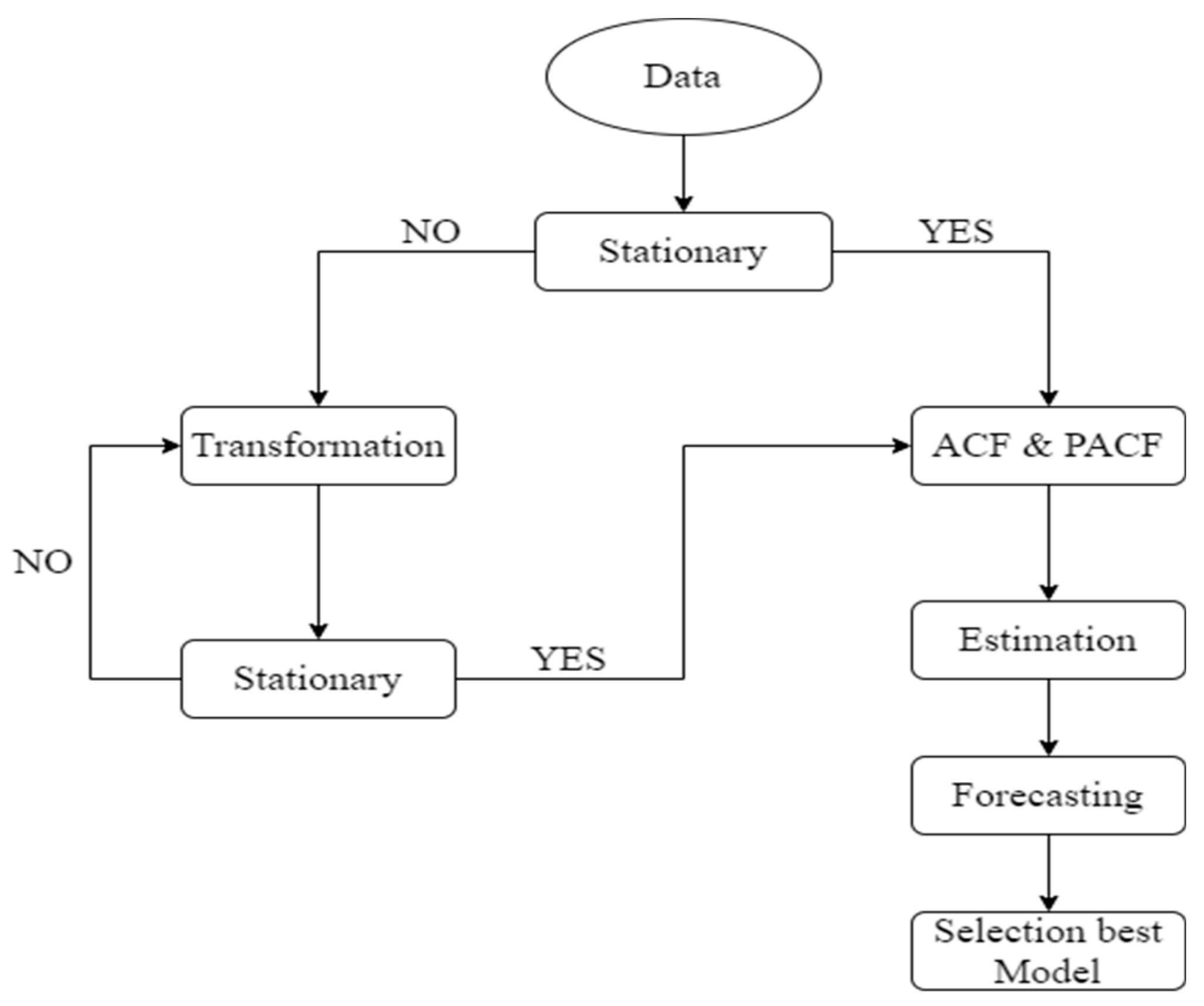
- Stationarity test: The augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) test is employed to determine whether a time series is stationary or nonstationary. If the time series is nonstationary, it should be subjected to differential operation.
- Order identification: The orders of the ARIMA model are determined by examining the autocorrelation coefficient function (ACF) and partial autocorrelation coefficient function (PACF) of the time series. Another approach Python package is the auto_arima function that conducts a systematic search across potential ARIMA hyperparameters in a stepwise manner.
- Model fitting: The Kalman filter and the maximum likelihood function are used to estimate and fit the model's unknown parameters. Furthermore, the model is examined to see if the residual sequence contains white noise. Otherwise, the orders must be inappropriate and must be re-identified.
- Application: The ARIMA model is utilized to forecast the SPI index, and the data is added to the training sample. Before the next forecast, the model should be updated. Figure 3 depicts the forecasting process using the best ARIMA model.
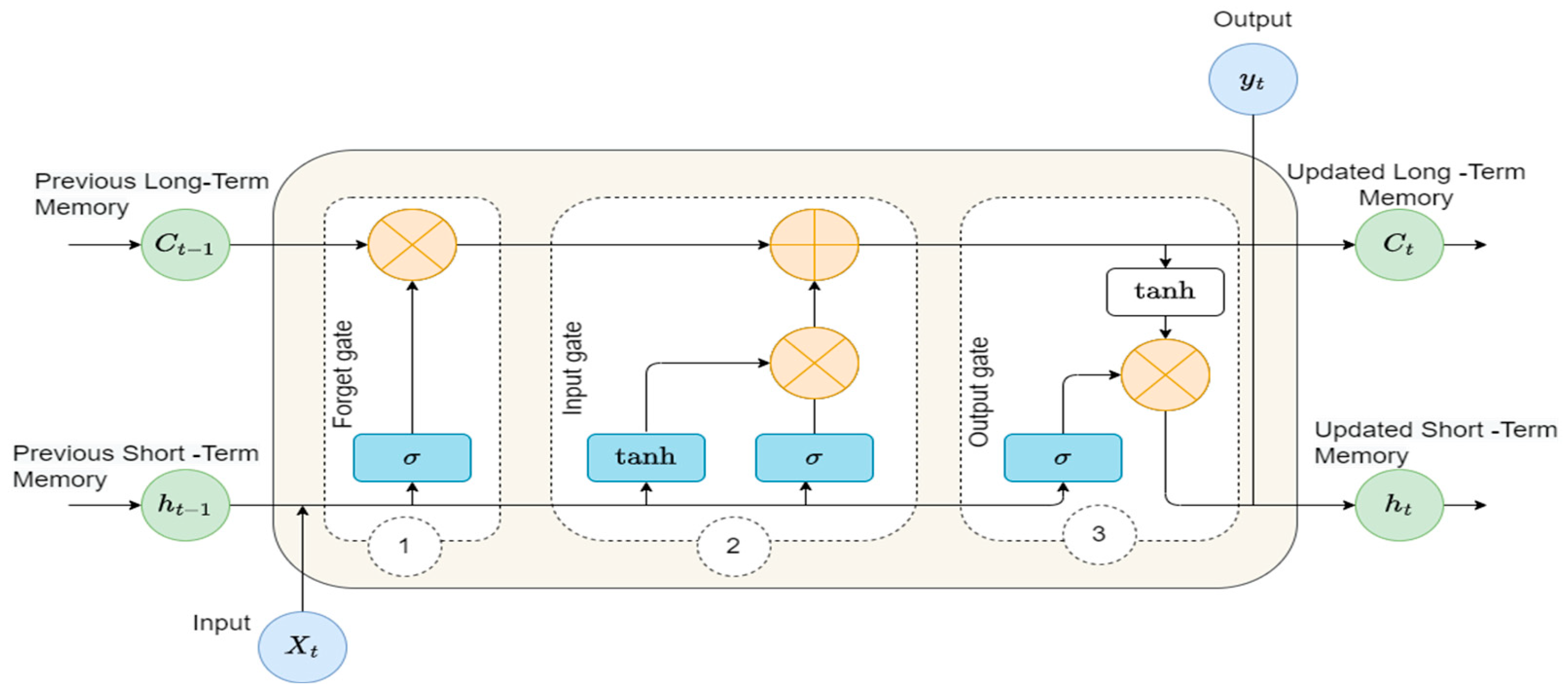
2.5. Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network
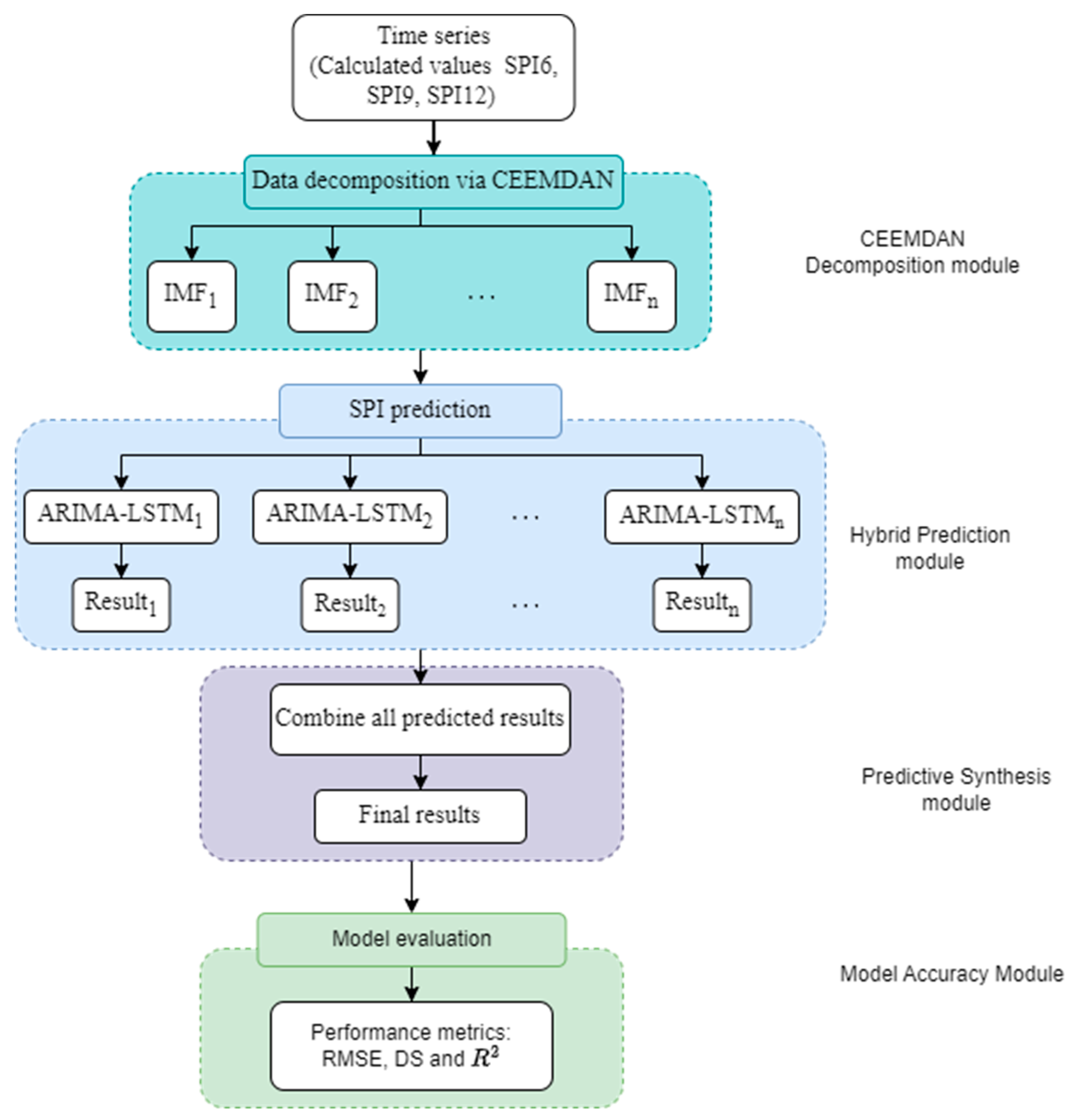
2.6. The Development of the Hybrid CEEMDAN-ARIMA-LSTM Model
- Decompose the original data into Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs) and a residual component using the CEEMDAN technique. CEEMDAN decomposes the time series into numerous oscillatory mode components with varying frequencies, capturing both high-frequency and low-frequency components, thereby making it easier for subsequent models to capture distinct patterns.
- The ARIMA models are used to capture temporal dependencies and trends, as well as to analyse individually each of the retrieved IMFs and the residual component derived from CEEMDAN. Develop separate ARIMA models for the IMF and residual. The residual is then combined with the forecasts from the ARIMA models of each IMF to reconstruct the predicted series.
- From the ARIMA fitted results, the calculated residuals serve as inputs of the LSTM model. Train the LSTM model using the training set to generate 1-step ahead forecasts.
- The prediction result is derived by adding the predicted values of the high-frequency components using LSTM and the predicted value of the low-frequency components using ARIMA.
- Repeat steps (1) to (4) for yields the final prediction.
2.7. Model Performance Criteria
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rainfall Data Series and Trend Analysis
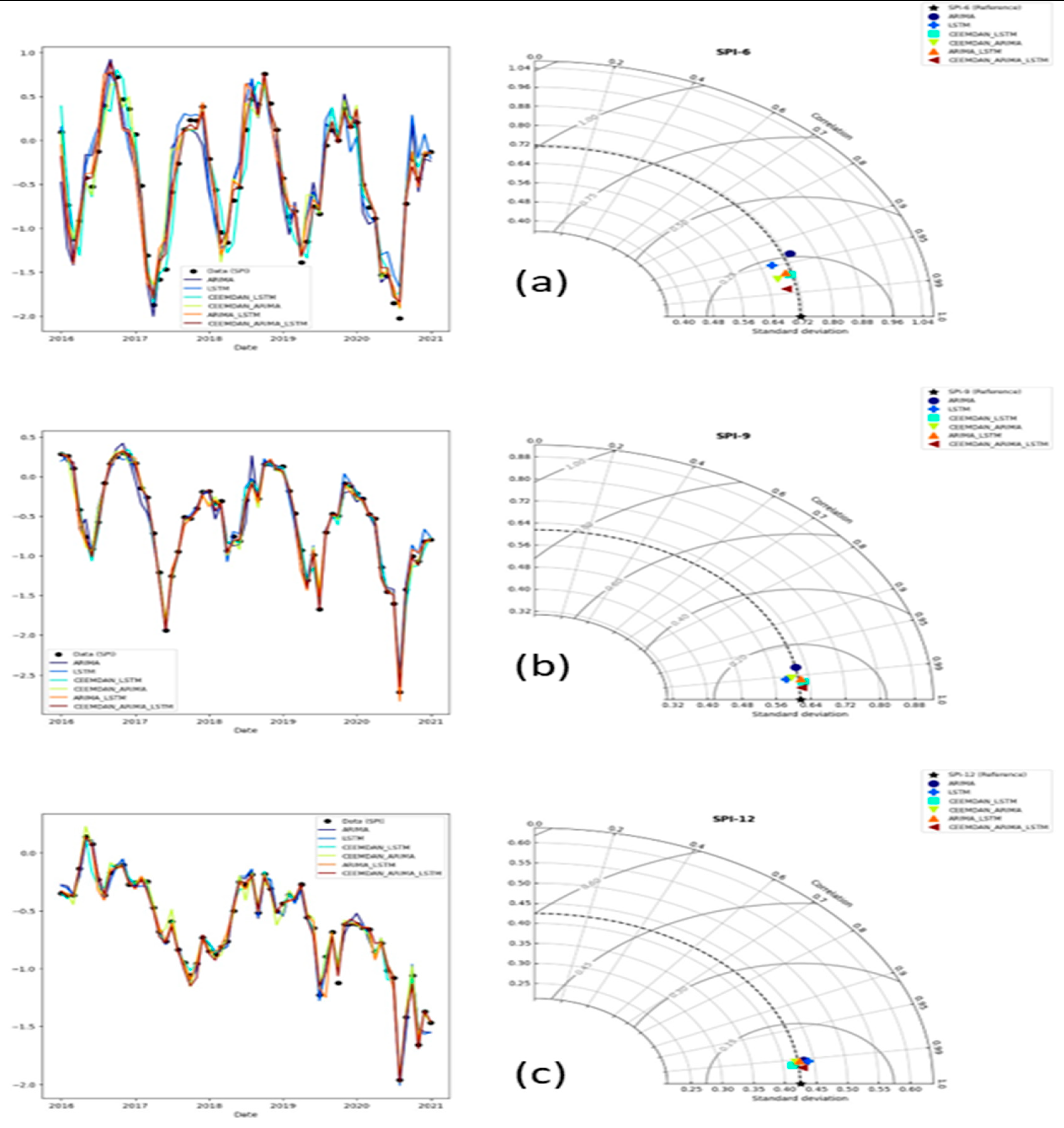
3.2. SPI Time Series and Forecusting Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, Ouya, Qi-Bin Zhang, Yann Vitasse, Roman Zweifel, and Paolo Cherubini. "The frequency and severity of past droughts shape the drought sensitivity of juniper trees on the Tibetan plateau." Forest Ecology and Management 486 (2021): 118968. [CrossRef]
- Murgatroyd, Anna, Helen Gavin, Olivia Becher, Gemma Coxon, Doug Hunt, Emily Fallon, Jonny Wilson, Gokhan Cuceloglu, and Jim W. Hall. "Strategic analysis of the drought resilience of water supply systems." Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A 380, no. 2238 (2022): 20210292.
- Garrick, Dustin, Lucia De Stefano, Winston Yu, Isabel Jorgensen, Erin O’Donnell, Laura Turley, Ismael Aguilar-Barajas et al. "Rural water for thirsty cities: A systematic review of water reallocation from rural to urban regions." Environmental Research Letters 14, no. 4 (2019): 043003.
- Vorosmarty, Charles J., Pamela Green, Joseph Salisbury, and Richard B. Lammers. "Global water resources: vulnerability from climate change and population growth." science 289, no. 5477 (2000): 284-288.
- Hall, Jim W., David Grey, Dustin Garrick, Fai Fung, Casey Brown, Simon J. Dadson, and Claudia W. Sadoff. "Coping with the curse of freshwater variability." Science 346, no. 6208 (2014): 429-430.
- Murgatroyd, A., and J. W. Hall. "Regulation of freshwater use to restore ecosystems resilience." Climate Risk Management 32 (2021): 100303.
- Jin, Li, Paul G. Whitehead, Gianbattista Bussi, Feyera Hirpa, Meron Teferi Taye, Yosef Abebe, and Katrina Charles. "Natural and anthropogenic sources of salinity in the Awash River and Lake Beseka (Ethiopia): modelling impacts of climate change and lake-river interactions." Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies 36 (2021): 100865. [CrossRef]
- Hall, Jim W., Edoardo Borgomeo, Alexa Bruce, Manuela Di Mauro, and Mohammad Mortazavi-Naeini. "Resilience of water resource systems: lessons from England." Water Security 8 (2019): 100052.
- Khan, Md Munir Hayet, Nur Shazwani Muhammad, and Ahmed El-Shafie. "Wavelet based hybrid ANN-ARIMA models for meteorological drought forecasting." Journal of Hydrology 590 (2020): 125380.
- Han, Ping, Pengxin Wang, Miao Tian, Shuyu Zhang, Junming Liu, and Dehai Zhu. "Application of the ARIMA models in drought forecasting using the standardized precipitation index." In Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture VI: 6th IFIP WG 5.14 International Conference, CCTA 2012, Zhangjiajie, China, October 19-21, 2012, Revised Selected Papers, Part I 6, pp. 352-358. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2013.
- Ding, Yan, Guoqiang Yu, Ran Tian, and Yizhong Sun. "Application of a hybrid CEEMD-LSTM model based on the standardized precipitation index for Drought forecasting: the case of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China." Atmosphere 13, no. 9 (2022): 1504.
- Liu, Ming-De, Lin Ding, and Yu-Long Bai. "Application of hybrid model based on empirical mode decomposition, novel recurrent neural networks and the ARIMA to wind speed prediction." Energy Conversion and Management 233 (2021): 113917.
- Poornima, S., and M. Pushpalatha. "Drought prediction based on SPI and SPEI with varying timescales using LSTM recurrent neural network." Soft Computing 23 (2019): 8399-8412.
- Dikshit, Abhirup, Biswajeet Pradhan, and Abdullah M. Alamri. "Long lead time drought forecasting using lagged climate variables and a stacked long short-term memory model." Science of The Total Environment 755 (2021): 142638.
- Balti, Hanen, Ali Ben Abbes, Nedra Mellouli, Yanfang Sang, Imed Riadh Farah, Myriam Lamolle, and Yanxin Zhu. "Big data based architecture for drought forecasting using LSTM, ARIMA, and Prophet: Case study of the Jiangsu Province, China." In 2021 International Congress of Advanced Technology and Engineering (ICOTEN), pp. 1-8. IEEE, 2021.
- Wang, Zhi-Yu, Jun Qiu, and Fang-Fang Li. "Hybrid models combining EMD/EEMD and ARIMA for Long-term streamflow forecasting." Water 10, no. 7 (2018): 853.
- Mathivha, Fhumulani, Caston Sigauke, Hector Chikoore, and John Odiyo. "Short-term and medium-term drought forecasting using generalized additive models." Sustainability 12, no. 10 (2020): 4006. [CrossRef]
- Guoyang, Zhao, Tu Xinjun, Wang Tian, X. I. E. Yuting, and M. O. Xiaomei. "Drought Prediction Based on Artificial Neural Network and Support Vector Machine." Pearl River 42, no. 4 (2021): 1.
- Wu, Guodong, Jun Zhang, and Heru Xue. "Long-Term Prediction of Hydrometeorological Time Series Using a PSO-Based Combined Model Composed of EEMD and LSTM." Sustainability 15, no. 17 (2023): 13209.
- Xu, Dehe, Yan Ding, Hui Liu, Qi Zhang, and De Zhang. "Applicability of a CEEMD–ARIMA Combined Model for Drought Forecasting: A Case Study in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region." Atmosphere 13, no. 7 (2022): 1109.
- Mann, H. B. (1945). Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica: Journal of the econometric society, 245-259.
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: London, UK, 1975.
- Seenu, PZ, & Jayakumar KV. (2021). Comparative study of innovative trend analysis technique with Mann-Kendall tests for extreme rainfall. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14, 1-15.
- Körük, A. E., Kankal, M., Yıldız, M. B., Akçay, F., Şan, M., & Nacar, S. (2023). Trend analysis of precipitation using innovative approaches in northwestern Turkey. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 131, 103416.
- Mbatha, N., & Xulu, S. (2018). Time series analysis of MODIS-Derived NDVI for the Hluhluwe-Imfolozi Park, South Africa: Impact of recent intense drought. Climate, 6(4), 95.
- Onoz, B., & Bayazit, M. (2003). The power of statistical tests for trend detection. Turkish journal of engineering and environmental sciences, 27(4), 247-251.
- Othman, M. A., Zakaria, N. A., Ghani, A. A., Chang, C. K., & Chan, N. W. (2016). Analysis of trends of extreme rainfall events using Mann Kendall test: a case study in Pahang and Kelantan river basins. Jurnal Teknologi, 78(9-4).
- Hamed, K. H., & Rao, A. R. (1998). A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. Journal of hydrology, 204(1-4), 182-196.
- Kumar, S., Machiwal, D., & Dayal, D. (2017). Spatial modelling of rainfall trends using satellite datasets and geographic information system. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 62(10), 1636-1653.
- Singh, R. N., Sah, S., Das, B., Potekar, S., Chaudhary, A., & Pathak, H. (2021). Innovative trend analysis of spatio-temporal variations of rainfall in India during 1901–2019. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 145(1), 821-838.
- Sneyers, R. (1991) On the Statistical Analysis of Series of Observations; Technical Note No. 143, WMO No. 415; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, p. 192.
- Bisai, D., Chatterjee, S., & Khan, A. (2014). Detection of recognizing events in lower atmospheric temperature time series (1941-2010) of Midnapore Weather Observatory, West Bengal, India. J Environ Earth Sci, 4(3), 61-66.
- Şen, Z. (2012). Innovative trend analysis methodology. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 17(9), 1042-1046.
- McKee, Thomas B., Nolan J. Doesken, and John Kleist. "The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales." In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, vol. 17, no. 22, pp. 179-183. 1993.
- Belayneh, A., and J. Adamowski. "Standard precipitation index drought forecasting using neural networks, wavelet neural networks, and support vector regression." Applied computational intelligence and soft computing 2012 (2012): 6-6.
- Elbeltagi, Ahmed, Chaitanya B. Pande, Manish Kumar, Abebe Debele Tolche, Sudhir Kumar Singh, Akshay Kumar, and Dinesh Kumar Vishwakarma. "Prediction of meteorological drought and standardized precipitation index based on the random forest (RF), random tree (RT), and Gaussian process regression (GPR) models." Environmental Science and Pollution Research 30, no. 15 (2023): 43183-43202. [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Hughes, Benjamin, and Mark A. Saunders. "A drought climatology for Europe." International Journal of climatology: a journal of the royal meteorological society 22, no. 13 (2002): 1571-1592.
- Torres, María E., Marcelo A. Colominas, Gaston Schlotthauer, and Patrick Flandrin. "A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise." In 2011 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp. 4144-4147. IEEE, 2011.
- Box, George EP, Gwilym M. Jenkins, and WISCONSIN UNIV MADISON DEPT OF STATISTICS. "Time Series Analysis Forecasting and Control." (1970).
- Sharma, Rishi Raj, Mohit Kumar, Shishir Maheshwari, and Kamla Prasan Ray. "EVDHM-ARIMA-based time series forecasting model and its application for COVID-19 cases." IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 70 (2020): 1-10.
- Hochreiter, Sepp, and Jürgen Schmidhuber. "Long short-term memory." Neural computation 9, no. 8 (1997): 1735-1780.
- Alexander, David LJ, Alexander Tropsha, and David A. Winkler. "Beware of R 2: simple, unambiguous assessment of the prediction accuracy of QSAR and QSPR models." Journal of chemical information and modeling 55, no. 7 (2015): 1316-1322. [CrossRef]
- Calverley, C. M., & Walther, S. C. (2022). Drought, water management, and social equity: Analyzing Cape Town, South Africa's water crisis. Frontiers in Water, 4, 910149.
- Sun, Y., & Liu, J. (2022). Aqi prediction based on ceemdan-arma-lstm. Sustainability, 14(19), 12182.
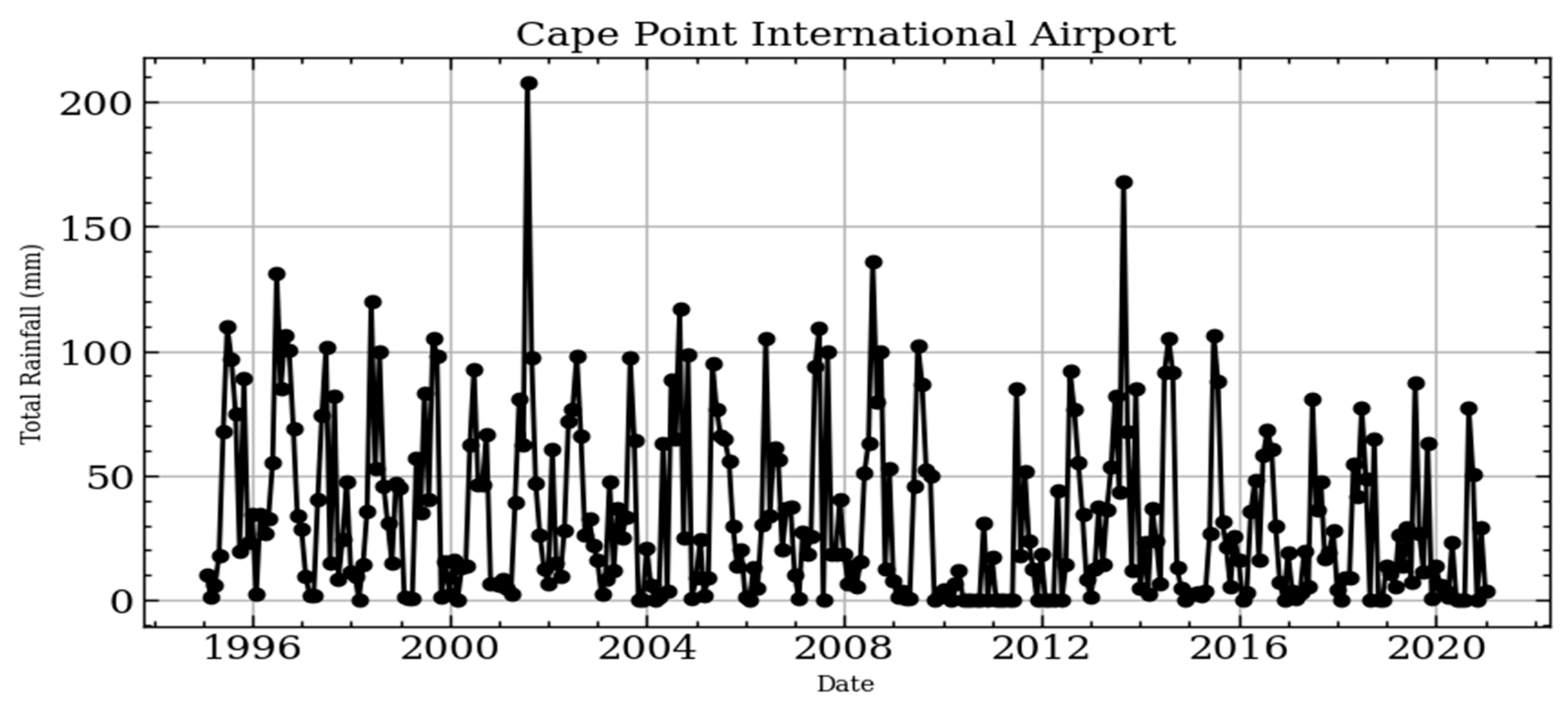
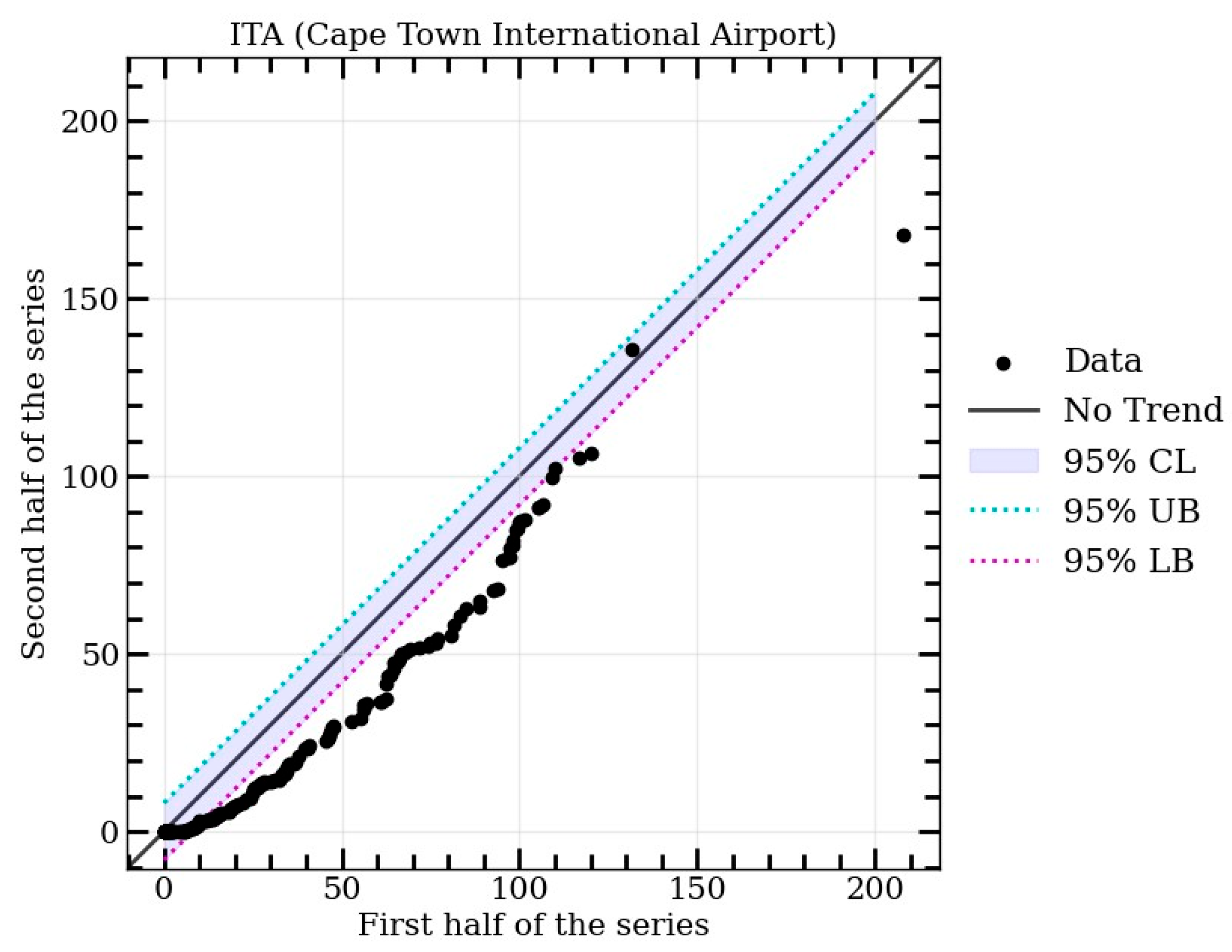
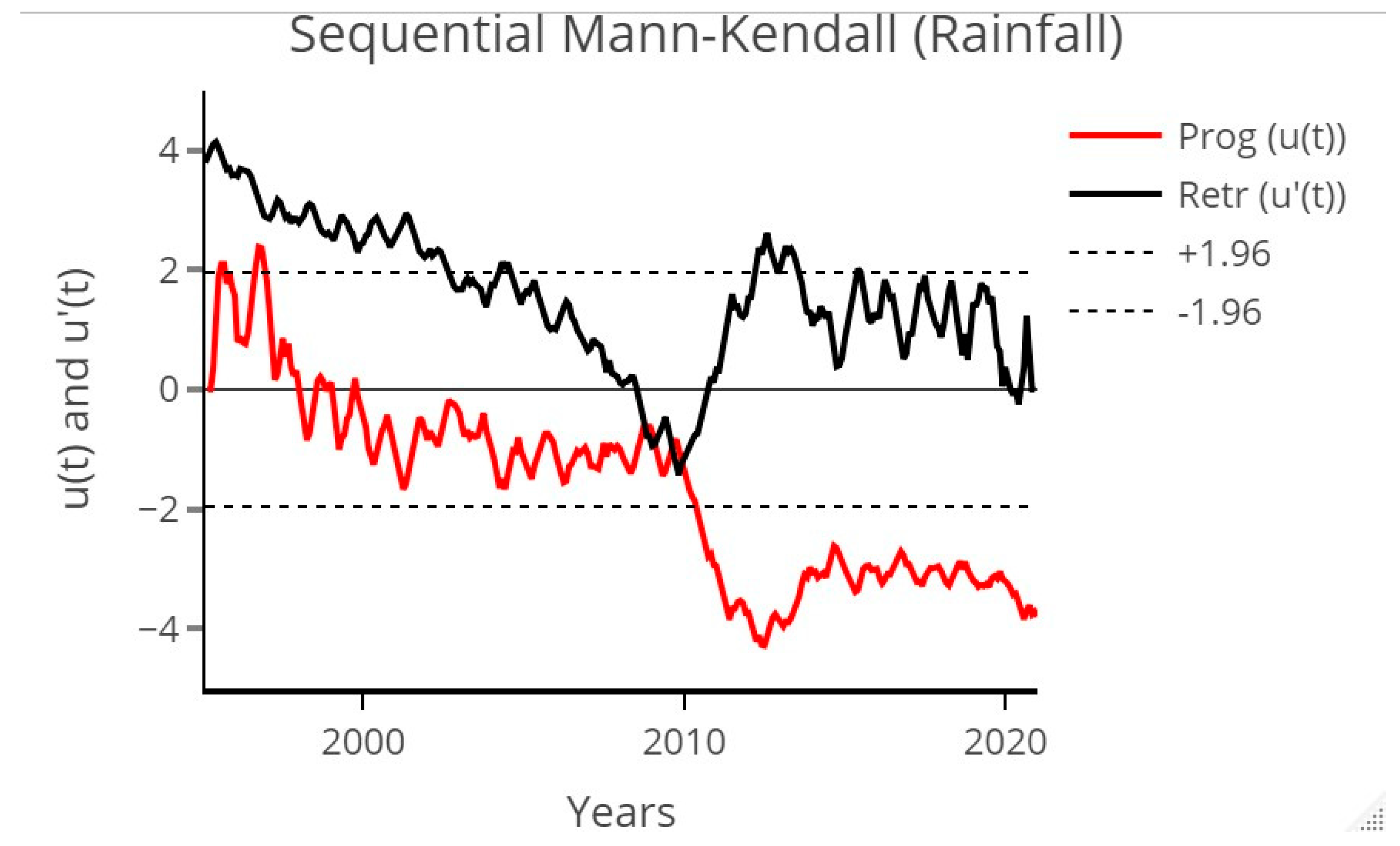
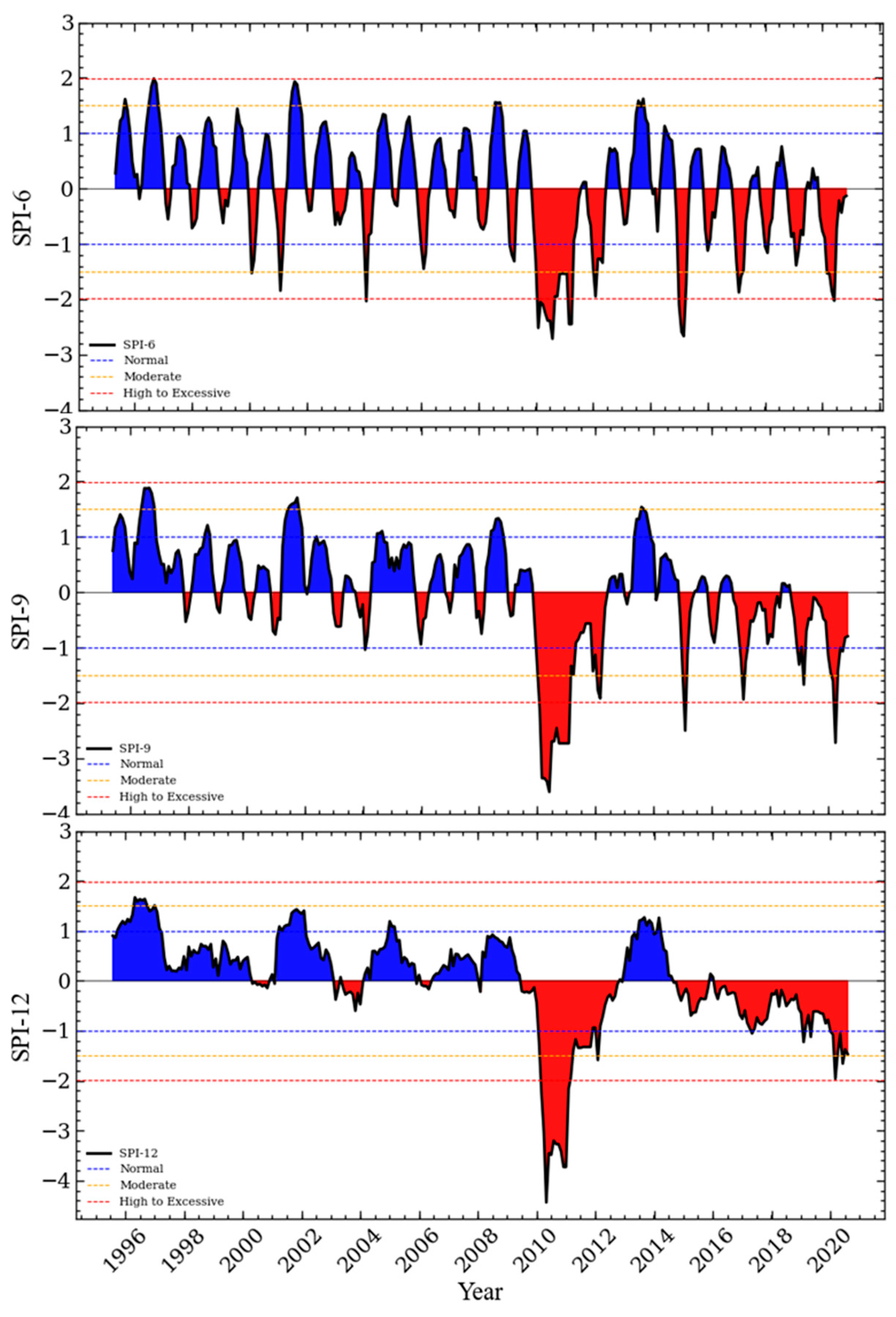
| SPI Value | Class | Probability (%) |
|---|---|---|
| SPI ≥ 2.00 | Extremely wet | 2.3 |
| 1.5 ≤ SPI < 2.00 | Severely wet | 4.4 |
| SPI < 1.50 | Moderately wet | 9.2 |
| SPI < 1.00 | Mildly wet | 34.1 |
| −1.00 ≤ SPI < 0.00 | Mild drought | 34.1 |
| −1.50 ≤ SPI < −1.00 | Moderate drought | 9.2 |
| −2.00 ≤ SPI < −1.50 | Severe drought | 4.4 |
| SPI < −2.00 | Extreme drought | 2.3 |
| ITA Variables | Values |
|---|---|
| Trend slope | -0.083083 |
| Trend indicator | -3.214672 |
| Correlation | 0.985378 |
| Slope standard deviation | 0.002202 |
| Confidence Limit () | 0.003415 |
| Variables | Mann-Kendall | Modified Mann-Kendall |
|---|---|---|
| slope | ||
| S | ||
| Var(s) | ||
| z-value | ||
| p-value | ||
| Decision (Trend) | Decreasing | Decreasing |
| Model | SPI-6 | SPI-9 | SPI-12 | ||||||
| RMSE | DS | RMSE | DS | RMSE | DS | ||||
| ARIMA | 0.262 | 0.872 | 0.867 | 0.118 | 0.964 | 0.850 | 0.059 | 0.981 | 0.867 |
| LSTM | 0.234 | 0.897 | 0.883 | 0.081 | 0.984 | 0.883 | 0.058 | 0.984 | 0.883 |
| ARIMA-LSTM | 0.186 | 0.931 | 0.883 | 0.077 | 0.983 | 0.867 | 0.057 | 0.985 | 0.900 |
| CEEMDAN-ARIMA | 0.169 | 0.945 | 0.850 | 0.083 | 0.983 | 0.833 | 0.054 | 0.984 | 0.933 |
| CEEMDAN- LSTM | 0.178 | 0.938 | 0.800 | 0.066 | 0.987 | 0.917 | 0.047 | 0.989 | 0.950 |
| CEEMDAN-ARIMA-LSTM | 0.121 | 0.972 | 0.950 | 0.044 | 0.991 | 0.917 | 0.042 | 0.995 | 0.950 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





