1. Introduction
Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC) is an aggressive cancer representing approximately 3% to 5% of all head and neck squamous cell cancers [
1]. The standard treatment for hypopharyngeal cancer is surgery and/or radiotherapy (RT) [
2,
3,
4]. The choice of treatment modality may vary depending on tumor localization, stage, operability and clinical experience of the physician [
5,
6]. Surgery or RT alone can be used in early-stage tumors without regional lymph node involvement whereas concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CRT) seems the best option when the anatomic location and spread of the tumor restrict surgical resection [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Hypopharyngeal cancers are diagnosed mostly in advanced stages. Surgical management leads to disruption of speech, organ dysfunction, difficulties in closing the defect after surgery, and concerns about patients’ quality of life. Therefore, non-surgical treatments have gained importance in recent years [
10,
11,
12]. In a study published by the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) in 1996 and an update of this study published in 2012, the larynx could be preserved in 59.5% of patients who survived for 5 years with definitive RT after induction chemotherapy [
13,
14]. This trial is the only randomized evidence focused specifically on hypopharynx cancer and demonstrated that an organ-preserving approach of induction, followed by radiotherapy leads to similar outcomes than surgery [
14]. In another study, treatment with radiotherapy alone is reported to have a worse prognosis compared to combined treatment with surgery and radiotherapy, particularly in stage IV disease. The addition of chemotherapy to primary radiotherapy protocols results in outcomes comparable to surgery and postoperative radiotherapy with the advantage of larynx preservation in a large number of cases [
6,
10]. There is however still some level of equipoise in the optimal management of locally advanced hypopharynx cancer, and the assumed equivalence of organ preserving and surgery is contested in T4 disease. Many centers have accepted organ-preserving concomitant CRT protocols with or without induction chemotherapy and salvage surgery as the standard of care for the treatment of hypopharyngeal cancers. During the past decade developments in RT technology have brought notable advances. Based on computed tomography (CT) three-dimensional conformal RT (3DCRT/IMRT) and volumetric arc therapy (VMAT) had much superiority to conventionally RT (2DRT) in delivering high doses accurately to the target and sparing normal tissues. These modern systems have enabled radiation oncologists to significantly reduce side effects. In this study, we retrospectively compared the long-term treatment results of patients with hypopharyngeal cancer who underwent definitive RT with conventional 2D (Group I) and 3DCRT/IMRT and VMAT (Group II) RT technique in accordance with our treatment protocol.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients
In this study, 81 patients with histologically confirmed squamous cell carcinoma of the hypopharynx treated with curative RT or CRT between January 1992 and December 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. Pre-treatment evaluation consisted of full medical history, clinical examination, blood sample, imaging of the primary site and neck by CT or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), chest x-ray (thorax CT was performed in case of advanced-stage disease or if a suspicious lesion is detected in chest x-ray). In the case of clinical suspicion, bone scintigraphy and liver ultrasonography were performed before 2010. After the year 2010, all patients with locally advanced disease were evaluated with BT and/or MRI, whole-body positron emission tomography (PET-CT) especially in patients with T3-4 and neck positive disease. Histopathological diagnosis is achieved after primary tumor biopsy by direct laryngopharyngoscopy under general anesthesia. AJCC TNM 2010 was used for staging [
15] Before the year 2010, TNM stage of each patient was determined by evaluating the recorded data of T and N stage of patients file and were adapted to TNM 2010. According to the radiotherapy technique patients were divided into two groups: Group I (2D Conventional Radiotherapy (2DRT) patients treated before 2004, Group II (3DCRT/IMRT and VMAT technique) patients treated after the year 2004. The number of patients in Group 2DRT, Group 3DCRT/IMRT and Group VMAT are 31 patients, 36 patients and 14 patients respectively. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the study and the data was anonymized and maintained with confidentiality. All study methods were carried out based on the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Treatment
According to our protocol, the treatment policy for early-stage comprises surgery ± RT ± chemotherapy or definitive RT (for organ sparing) ± chemotherapy; for locally advanced disease, surgery ± RT ± chemotherapy or definitive RT ± chemotherapy if the patient is not eligible for surgery; T1-T3 patients with neck positive disease were evaluated for organ preservation therapy. Patients who underwent surgery and treated with adjuvant RT+/- chemotherapy were not included in this study. Concomitant chemotherapy was given as 75-100 mg/m² cisplatin on days 1, 22, 43 depending on the patient’s comorbid condition. Cisplatin-based induction chemotherapy was applied in patients with bulky disease and good performance status.
In Group I the patients were immobilized in the supine position with a thermoplastic mask. According to tumor location radiotherapy was planned to hypopharynx and involved lymph nodes by using parallel–opposed fields for the upper part of the neck and an anterior supraclavicular field for the lower part or 2 oblique wedged fields were determined at the time of conventional simulation. The non-involved lymph node levels dose was 45-50 Gy and the primary tumor received at least 66 Gy to 70 Gy in 1.8 - 2 Gy per fraction in 33-35 fractions. In our standard practice the image for each patient obtained with CT from the isocenter was used to create 2DRT plan isodoses. Portal graphic was performed for patient set-up before treatment delivery. After the year 2004 patients were immobilized supine in a thermoplastic mask and CT simulation with 3-mm slice thickness was performed. Gross tumor volume (GTV) was the visible extent of disease on clinical examination, planning CT, and diagnostic imaging, such as MRI or positron emission tomography-CT, when available. In Group 3DCRT patients, based on extension of the gross tumor hypopharynx, nearby anatomical structures and regional neck lymphatics were contoured as clinical tumor volume (CTV). The high-risk clinical tumor volume (CTV1) encompassed the primary tumor and involved lenf nodes with a 1 cm margin. The intermediate risk CTV (CTV2) included adjacent areas of involved nodes and primary tumors. Low risk CTV (CTV3) included ipsilateral level 2-4, additionally, level V and contralateral neck levels II–IV if ipsilateral neck nodes were involved. The planning target volume (PTV1, PTV2 and PTV3)) was created by addition of 5 mm margin to each CTV. Treatment planning was performed with 5 to 7 non-coplanar beams (two opposed, an anterior or posterior cord sparing field, right and left posterior oblique fields excluding the spinal cord in the neck) in the Oncentra Masterplan V.1.4 treatment planning system. Irradiation was performed 1.8 - 2 Gy per fraction, once daily with Siemens- Primus® model linear accelerator. PTV3 was irradiated until 50 Gy as well as PTV2 60 Gy. Finally sequential boost was applied to gross tumor and involved lymph nodes (PTV1) at least 66 - 70 Gy. Non-coplanar beams were shaped with multileaf collimators (MLCs). Beam angles including multiple segments conformed the coverage of the target while minimizing the normal tissue exposure. Depending on the target volumes, additional segments have been added. The treatment planning is based on a careful design of each segment and optimization of the associated beam weights. This technique used in 3DCRT group is a kind of forward IMRT. After the year 2014, patients were planned with VMAT technique (Varian Eclipse TPS, Accuros XB dose calculation). The planning target volumes are derived from the identical contoured CTV as 3DCRT by adding a margin for systematic and random setup errors and internal motion of 3 mm. The dose prescription was for the simultaneous integrated boost radiation therapy for PTV1, PTV2 and PTV3, in total doses (TD) of 69, 60 and 54 Gy respectively, in 33 fractions. The final plans were normalized to insure that 95% of the PTV received the prescribed dose respecting the prescription guidelines of the International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) report 83. Since 2004 image guidance technique EPİD was used in 3DCRT and kV/CBCT was performed in VMAT patients.
2.3. Follow-Up
Follow-up time was calculated to all patients who stayed alive until the last follow-up. The acute and late side effects were evaluated and graded according to Radiotherapy and Oncology Group (RTOG) / European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) criteria. Patients were examined weekly during treatment in terms of acute effect and tumor response. Late side effects were evaluated at each control in patients who lived longer than 6 months after treatment. Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) were used to quantify the efficacy of RT treatment according to the degree of tumor regression [
16]. Upon treatment completion, patients were followed up every 3 to 4 months to evaluate late side effects and tumor response together in the first 2 years, then every 6 months until 5 years and annually thereafter. Treatment response was evaluated clinically and radiological 3-4 months after the completion of radiotherapy. Routine clinical follow-up included physical examination, a complete airway evaluation including flexible endoscopy and if necessary, direct endoscopy with anesthesia. CT/MRI scan or PET-CT was performed, if clinically indicated. Patients with recurrence were evaluated for individual salvage treatments, considering primary treatments.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Survival rates were estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method. Overall survival (OS) was calculated from the dates of diagnosis to the date of death. Disease-specific survival (DSS) and local regional relapse-free survival (LRRFS) was calculated from the dates of diagnosis to death caused by HSCC for DSS and the date of first locoregional recurrence for LRRFS.
For univariate and multivariate analyses Log-rank and Cox regression tests were used. The follow-up time was calculated from the last day of RT. The SPSS statistical program (version 18.0, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for statistical analysis. P-values less than 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
The median age of the patients was 58 (13-83) and 56 (67.5%) of them were male and the median follow up time was 26 (6-290) months. Nine patients (29.3%) in Group I and 36 (%72.0) patients in Group II were treated with concomitant chemotherapy. Additionally, 3 (9.7%) patients in Group I and 2 patients (4.0%) in Group II were treated with concurrent chemotherapy after cisplatin-based induction therapy. All (%100) patients had Karnofsky performance score (KPS) >70, 24 (29%) had a comorbid disease and 40 (48%) patients had a weight loss of 5% or more in the last 6 months. A prophylactic percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tube was placed in 5 (16.1%) patients in Group I and 11 (22.0%) patients in Group II. While 7 (22.6%) patients in Group I and 3 (6.0%) patients in Group II needed parenteral nutrition during treatment, nasogastric feeding was administered to one patient in each group (
Table 1).
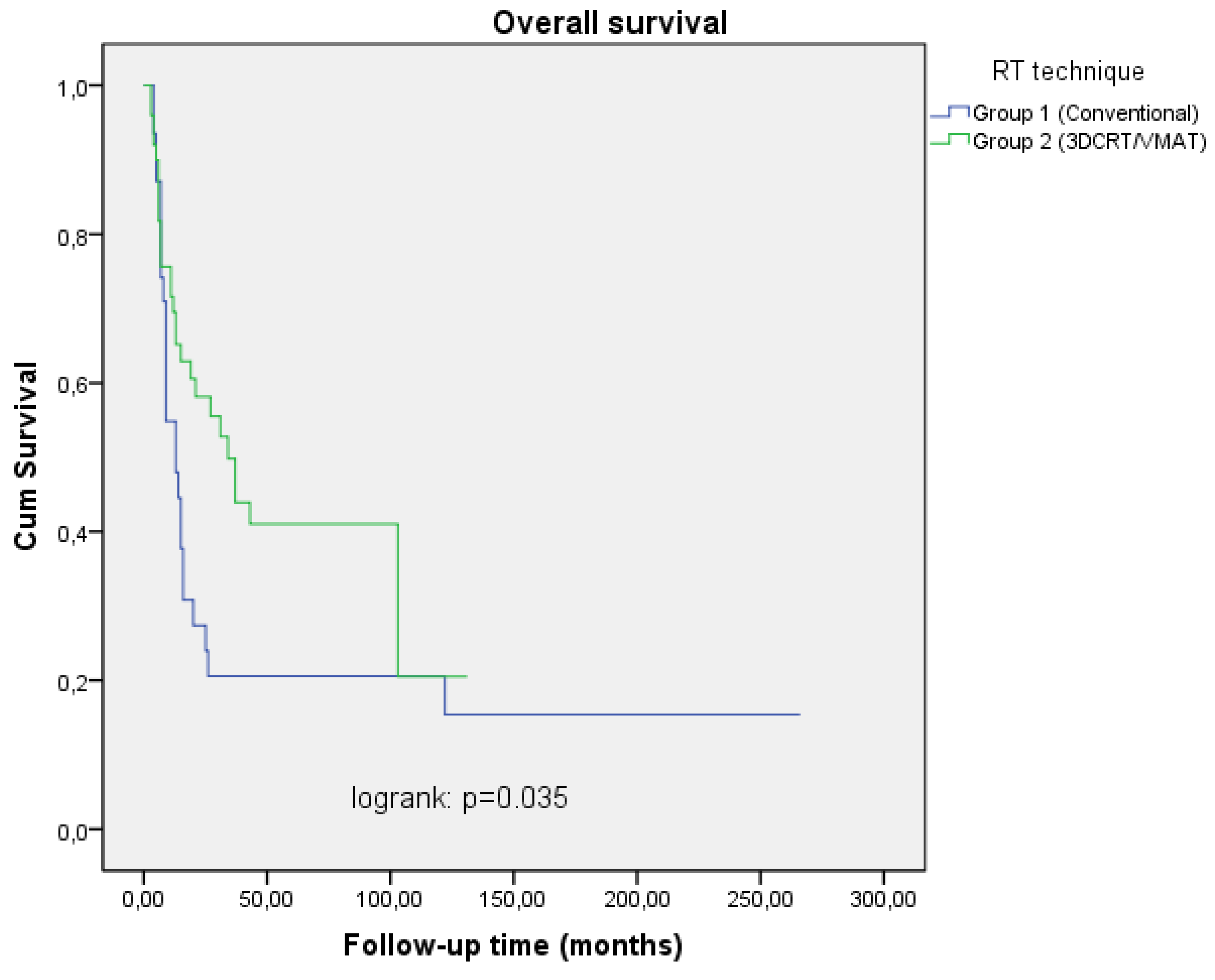
The median RT dose was 70 (60-70) Gy for patients treated before the year 2014 and 69 (66-70) Gy for treatment after the year 2014. The median follow-up time was 22 (6-266) months. Two and 5 year OS rates were 27.4%, 20.6% in Group I and 58.3%, 42.1% in Group II patients respectively (
Table 2,
Figure 1). This difference in survival rates between the two groups was significant in univariate and multivariate analysis (p=0.035 RR=2.45 95% CI 1.11-4.68), p=0.049 RR=2.32 95% CI 1.12-3.89) ,
Table 2 and
Table 3). Age, N stage, T stage, and KPS were found statistical significance prognostic factors affecting OS in univariate and multivariate analyses (
Table 2 and
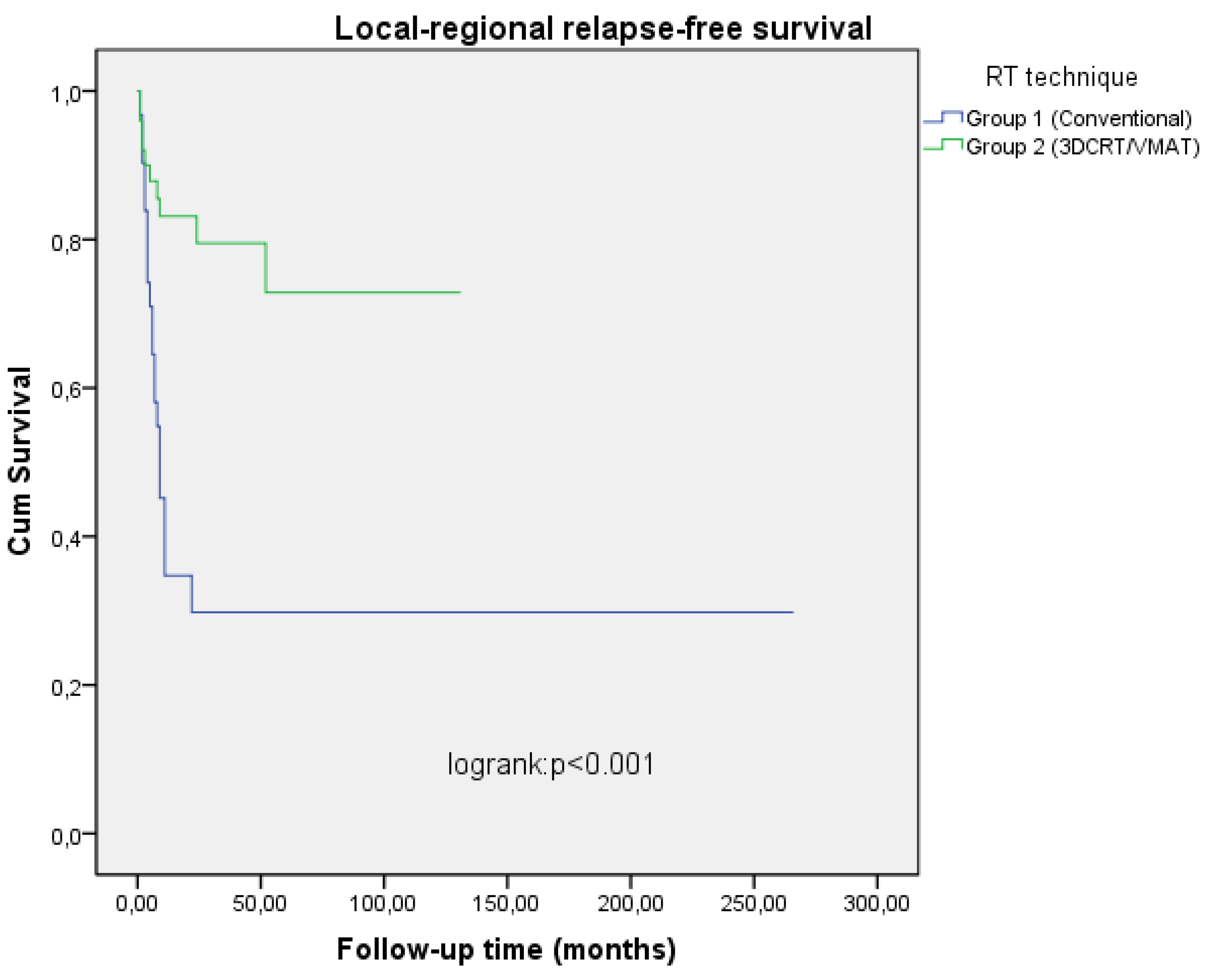
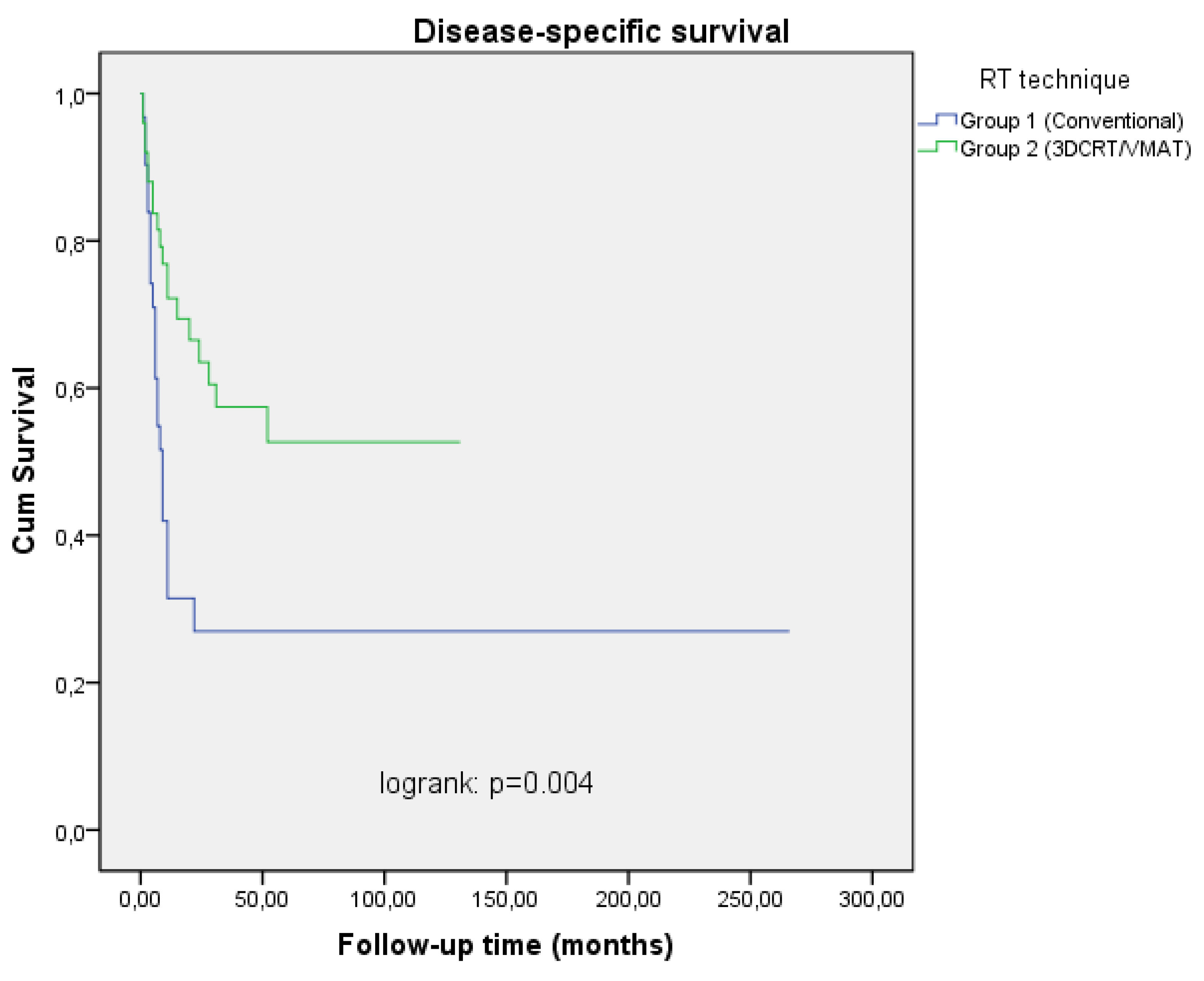
Table 3). Two and 5 years local-regional relapse-free survival (LRRFS) rates were 34.7%, 29.8% in Group I, 79.5%, 72.9% in Group II patients, DSS rates were 31.5%, 27% in Group I and 63.5%, 52.7% in Group II patients respectively (
Table 2,
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). In the univariate analysis, a statistically significant difference was found between the two groups in terms of both LRRFS and DSS (p<0.001 RR=4.13 95% CI 1.41-7.80), p=0.004 RR=2.90 95% 1.69-5.34), but in multivariate analysis, only LRRFS was statistically significant (p=0.025 RR=4.08 95% CI 2.62-10.46) and p=0.106 RR=1.45 95% CI 0.29-4.57). Chemotherapy was found to be a significant prognostic factor for LRRFS and DSS in univariate analysis, but no impact on OS (p=0.005 RR=4.10 95% CI 1.21-10.20), p=0.005 RR=2.56 95% CI 0.78-4.22), p=0.129 RR= 1.766 95% CI 0.44-7.90). Excluding stage 3 patients, and analyzing only stage 4A and 4B patients on both arms revealed a similar result in terms of T and N stages (p=0.034 RR= 3.56 95 CI 0.56-18.22), p=0.044 RR=2.22 95% CI 0.344-11.900) and p=0.05 RR= 6.62 95% CI 0.41-32.01, p=0.045 RR= 3.22 95% CI 1.43-11.26). No statistically significant difference was found between the groups with and without chemotherapy in terms of side effects (p=0.402 RR=0.88 95% CI 0.23-4.76). Most of the patients had skin, mucosal and salivary gland RTOG/EORTC grade 1-2 side effects during treatment but grade 3-4 early side effects were higher in Group I (25.8%) than in Group II patients (4.0%) (p=0.046 RR=1.88 95% CI 0.64-6.12) (Table 4). In long-term follow-up, the side effects were less common in Group II treated with VMAT technique (p=0.038 RR=2.10 95% CI 0.78-4.26).
4. Discussion
Advanced radiation therapy (RT) techniques and planning systems (e.g., IMRT, VMAT, etc.) provide significantly better results in terms of target coverage and dose constraints. In our study, cases were treated with 2DRT before 2004 and 3DCRT/IMRT or VMAT techniques since 2004. The clinical T2/T3 disease was found to be 28.9% in Group II and 3.6% in Group I. The distribution of patients in terms of T4 disease was higher in Group I. Node-negative disease was mostly observed in Group II, whereas the distributions of N2/N3 cases were similar. Furthermore, early-stage (Stage 3) disease was detected at a higher rate in Group II, and almost all cases in Group I were Stage 4 disease. A statistically significant difference was found between the two groups in terms of stage (p = 0.013). The reason for this difference can be explained by the fact that RT applications for organ preservation before 2005 were rare, and surgery was preferred in the early stages of hypopharyngeal carcinoma. However, in the current treatment modality, surgery has been replaced by RT or CRT in early-stage disease, especially T1-3 disease [
17,
18,
19].
Many studies have emphasized the prognostic significance of clinical T and N stages in patients with hypopharyngeal cancer [
19,
20,
21]. In our study, T and N stages were found to be prognostic factors affecting both overall survival (OS) (p = 0.001, RR = 2.50, 95% CI 1.86-8.05; p = 0.035, RR = 4.79, 95% CI 2.68-12.91) and locoregional recurrence-free survival (LRRFS) (p = 0.02, RR = 3.79, 95% CI 1.56-9.12; p = 0.026, RR = 3.98, 95% CI 2.11-20.01) in multivariate analysis (
Table 3).”
Advanced age was found to be another prognostic factor affecting OS (p = 0.027, RR = 2.24, 95% CI 0.87-3.50). Concurrent chemotherapy application was significantly higher in Group II (p < 0.01). In the literature, an increase in concurrent chemotherapy applications has been reported after the year 2000 [
22,
23,
24,
25]. Two meta-analyses of randomized trials have demonstrated the efficacy of concomitant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced head and neck cancers [
8,
26]. However, there is still some level of equipoise in the optimal management of locally advanced hypopharyngeal cancer, and the assumed equivalence of organ preservation and surgery is contested in T4 disease [
27]. In our study, 45 (54.2%) patients underwent concurrent chemotherapy. Local-regional control and disease-specific survival were better in patients who underwent concurrent chemotherapy (p = 0.005, RR = 4.10, 95% CI 1.21-10.20; p = 0.005, RR = 2.56, 95% CI 0.78-4.22). Among the patients treated with 2DRT/3DRT/IMRT/VMAT, 55.6% received neoadjuvant and concurrent or concurrent chemotherapy. We believe that this benefit is due to the combination of radiotherapy technique and chemotherapy. Side effects are more common in patients receiving chemotherapy according to the literature [
10,
12]. Although side effects were observed more frequently in patients receiving chemotherapy, a statistically significant difference could not be seen in our study.
In Group I patients, the two and 5-year LRRFS rates were worse than those reported in the literature; however, in Group II patients, locoregional relapse rates were similar compared with recent literature [
5,
6,
8,
26]. In terms of radiotherapy technique, one of the largest series of studies in the literature, Gupta et al., evaluated 501 hypopharyngeal cancer patients treated with conventional methods [
28]. At a median follow-up of 12 months, the 3-year local-regional control rate was 50% for T1-2 tumors and 43.1% for T3-4 tumors. In our study, the 2 and 5-year locoregional control rates were 34.7% and 29.8% in Group I, respectively. Additionally, Blanchard et al. reported 5-year local and regional control rates as 68% and 69%, respectively, in 249 piriform sinus cases who underwent radical radiotherapy [
11]. Huang et al. evaluated 33 patients with hypopharyngeal cancer and reported a 3-year locoregional control rate of 68.2% at a median follow-up of 18.8 months treated definitively with IMRT technique [
29]. In a study conducted by Reis et al., the 2 and 5-year overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival rates (DFS) in 25 hypopharyngeal cancer patients treated with 3DCRT, IMRT, or VMAT technique were reported as 47.5%, 29.2% and 39.1%, 24.1%, respectively [
30]. In a study published in 2015 by Mok et al., IMRT and 3DCRT techniques were compared in the treatment of patients with hypopharyngeal cancer, and a higher local control rate was detected in patients treated with IMRT than in 3DCRT (75% vs. 58%; p: 0.003). There was no difference in terms of OS and DFS [
31]. In a similar single-center study conducted by Katsoulakis et al. in 2015, comparing 3DCRT and IMRT techniques in hypopharyngeal cancer patients, no difference was found between the two groups in terms of local control and OS [
32]. Bertelsen et al. showed that doses of organs at risk can be reduced if patients with hypopharyngeal carcinoma are treated with VMAT compared to IMRT technique [
33]. Suat et al. evaluated the data of 3928 hypopharyngeal cancer patients in 2018, and in terms of RT technique, overall survival advantage was found in IMRT Group (p=0.013) [
34]. In our study, the 2 and 5-year OS and locoregional control rates for 3DCRT/IMRT and VMAT groups were 58.3%, 42.1% and 79.5%, 72.9%, respectively. The difference between groups in terms of local control and OS was statistically significant (p < 0.001, RR: 4.13, 95% CI 1.41-7.80; p = 0.049, RR = 2.32, 95% CI 1.12-3.89). The current study, which had a larger cohort and longer follow-up period, found that patients treated with VMAT had significantly higher 5-year OS, DSS, and LRFS rates compared to other series. The advantages of VMAT or IMRT could have improved conformity with the target dose and facilitated dose escalation. Additionally, patients treated with VMAT or IMRT experienced fewer incidents of treatment-related toxicity.
The evolution of diagnostic imaging technology has played an important role in the improvement of survival outcomes by increasing the accuracy of tumor target planning. MRI over CT on discriminating soft tissue invasion, and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/CT demonstrated good accuracy in N and M staging of patients with newly diagnosed Head and Neck cancer [
35,
36]. In our study, CT was the main imaging technique from 1992 to 2004. In the latter decades, MRI gradually replaced CT and the use of PET/CT increased after 2010. These changes increased the accuracy of nearby organs and cervical nodes assessment, resulting in improved tumor target design and locoregional survival rates. Additionally, few studies have shown that treatment with image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) increases the local-regional control rate in patients with head and neck cancer [
37,
38]. In our clinic, since 2005 patients have been treated with EPİD image guidance, and after 2014, the VMAT technique has been used with daily image guidance (kV/CBCT). This new technology treatment modality has led to a reduction in side effects and an increase in local control rates. Additionally, multivariate analysis revealed a better LRRFS rate in Group II receiving RT with new technology (p = 0.025, RR: 4.10, 95% CI 2.62-10.46). This difference was attributed not only to modern treatment methods but also to differences in diagnostic imaging and the number of patients between the groups. However, in multivariate analyses, the significant effect of RT technique suggests the positive impact of modern technology.
In a study published by Fu-Min Fang et al. in 2006, patients treated with conventional and 3DCRT were evaluated for side effects, and quality of life scores were found statistically significant in favor of patients treated with 3DCRT (p = 0.02) [
39]. Two separate prospective studies have reported that long-term side effects are less frequent in patients treated with modern RT systems compared to conventional methods since the pharyngeal constrictor muscles involved in swallowing function receive lower doses [
40,
41]. Lee et al. reported that patients with hypopharyngeal cancer may require a feeding tube because of stricture after CRT [
42]. Mok et al., in a study comparing IMRT and 3DCRT treatment techniques, found no difference between the two groups in terms of feeding tube use [
26]. Al-Mamgani et al. detected less permanent dependence on PEG in patients planned with IMRT than the conventional method [
10]. In the present study, 16 patients underwent PEG during treatment, and 3 of these had persistent PEG due to limitation of oral intake and pharyngeal stricture after treatment, and this difference was statistically significant between the two groups compared to Group I (p = 0.035, RR: 3.44, 95% CI 1.64-8.86). Grade 3-4 early side effects were significantly more frequent in Group I patients than in Group II patients (p = 0.046, RR = 1.88, 95% CI 0.64-6.12). The higher incidence of side effects in Group I patients can be attributed to the fact that the dose distribution outside the planning target volume could not be maintained at the intended level in patients planned by conventional methods. Moreover, in Group II, the dose could be applied to the target volume with a more homogeneous distribution and close safety margins while preserving healthy tissues with the 3DCRT/VMAT technique. With the advantage of the new technology, late side effects were also less frequent in Group II (p = 0.038, RR: 2.12, 95% CI 0.898-19.44).
The most significant limitations of this non-randomized study were the differences in stage distribution and chemotherapy use between the groups. The use of PET-CT in the staging method is an important advancement that could certainly confound the findings of this study, and the improved staging could influence the differences in cancer control outcomes. However, it is important to achieve similar results obtained in prospective studies with selected patient groups in routine practice.