Submitted:
23 July 2024
Posted:
24 July 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Risk Factors for MS Development and Progression
Brain Plasticity
- Brain plasticity involves modifications in the strength and number of connections between neurons, known as synapses. This can occur through processes such as long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD), which are activity-dependent changes in synaptic transmission.
- Plasticity can also involve the creation of new synapses between neurons. This process, known as synaptogenesis, allows for the establishment of new connections and the rewiring of neural circuits.
- Plasticity can lead to alterations in the structure and function of individual neurons. This can include changes in dendritic branching, axonal sprouting, and the generation of new neurons through neurogenesis.
- Plasticity can be influenced by changes in the levels and activity of various neurotransmitters and neuromodulators. These substances can affect synaptic transmission and neuronal excitability, thereby influencing the plasticity of neural circuits.
Neurodegeneration in MS
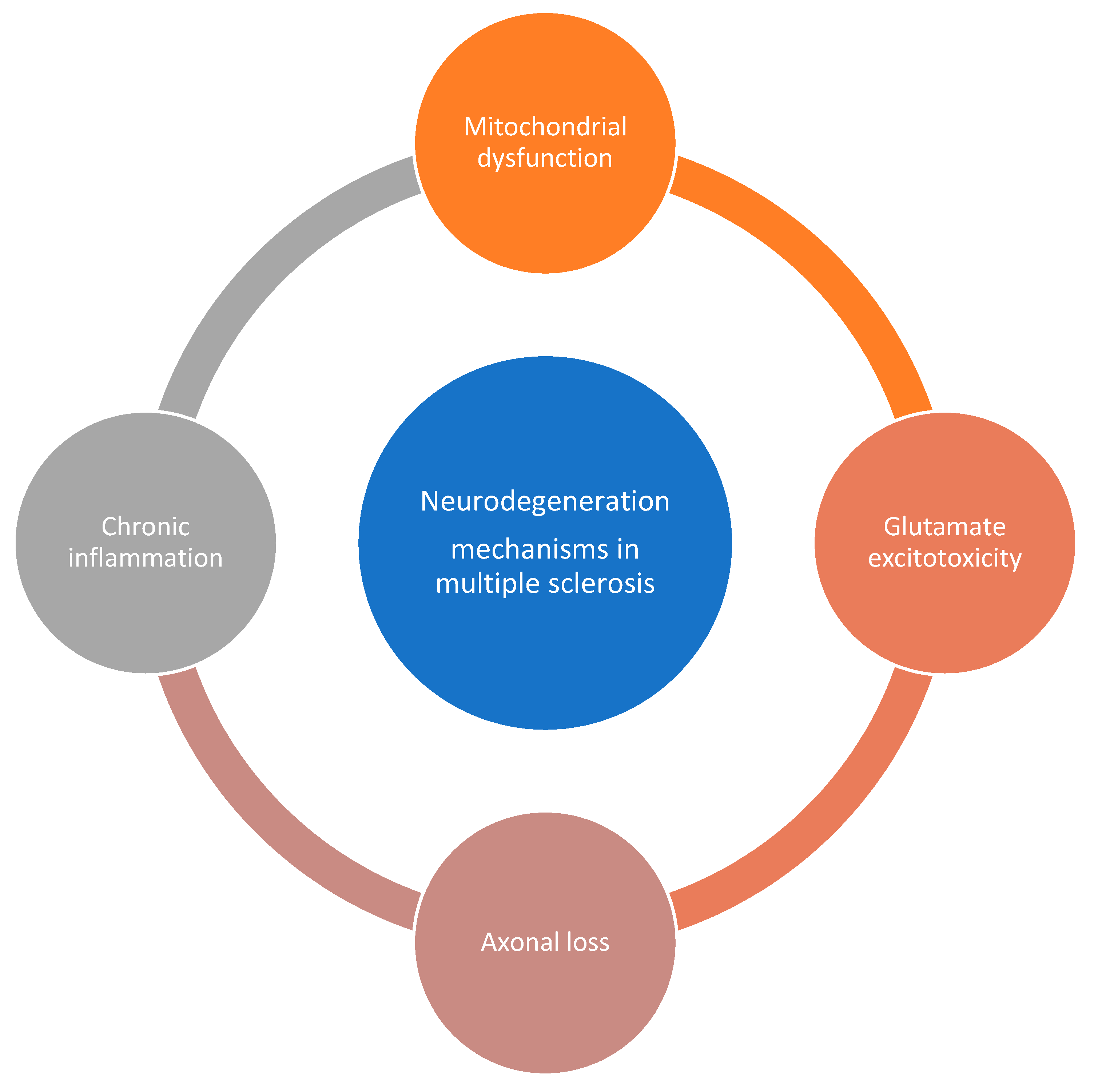
- Chronic inflammation in MS leads to the activation of microglia, which release inflammatory mediators and generate oxidative stress. This can result in damage to neurons and axons [43,44,45]. Neuroinflammation, characterized by the infiltration of immune cells into the central nervous system, can contribute to neurodegeneration in MS. Immune-mediated mechanisms, such as the release of inflammatory cytokines and autoantibodies, can cause neuronal damage [46].
- Glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter, can accumulate in the extracellular space during inflammation and demyelination in MS. Excessive glutamate can lead to excitotoxicity, causing damage to neurons and axons [45].
Nutraceuticals in MS
- Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) is an antioxidant that has shown promise in improving clinical and biological outcomes in MS, such as reducing fatigue and improving brain volume [59].
- Ginkgo biloba has been reported to improve clinical and biological outcomes in MS, including fatigue and antioxidant capacity [59].
- Biotin supplementation has shown potential in improving clinical outcomes in MS, such as reducing disability progression and improving walking ability [59].
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce inflammation in MS [58].
- Nutraceuticals such as polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), green tea flavonoids (epigallocatechin-3-gallate), curcumin, and scorpion toxins have been found to possess anti-inflammatory properties and can modulate the immune response in MS. They can inhibit pro-inflammatory signalling pathways, such as NF-κB or toll-like receptors and reduce the activity of auto-aggressive immune cells. These effects may help reduce inflammation and immune-mediated damage in MS [56].
- Oxidative stress is implicated in the pathogenesis of MS. Nutraceuticals like green tea, curcumin, and resveratrol have antioxidative properties and can scavenge free radicals, reducing oxidative damage. By reducing oxidative stress, these compounds may protect against neuronal damage and inflammation in MS [61].
- Nutraceuticals such as flavonoids, terpenoids, and polyphenols have shown potential in promoting neuroprotection and myelin repair in animal models of MS. They may support the survival and function of neurons, promote remyelination, and enhance endogenous repair processes [62].
- Epigenetic modifications play a role in MS. Some nutraceuticals, such as plant polyphenols, Ω-3 and Ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, and sulphur-containing compounds, can influence gene expression through epigenetic mechanisms. These compounds may regulate the production of pro-inflammatory proteins and modulate immune responses in MS [63].
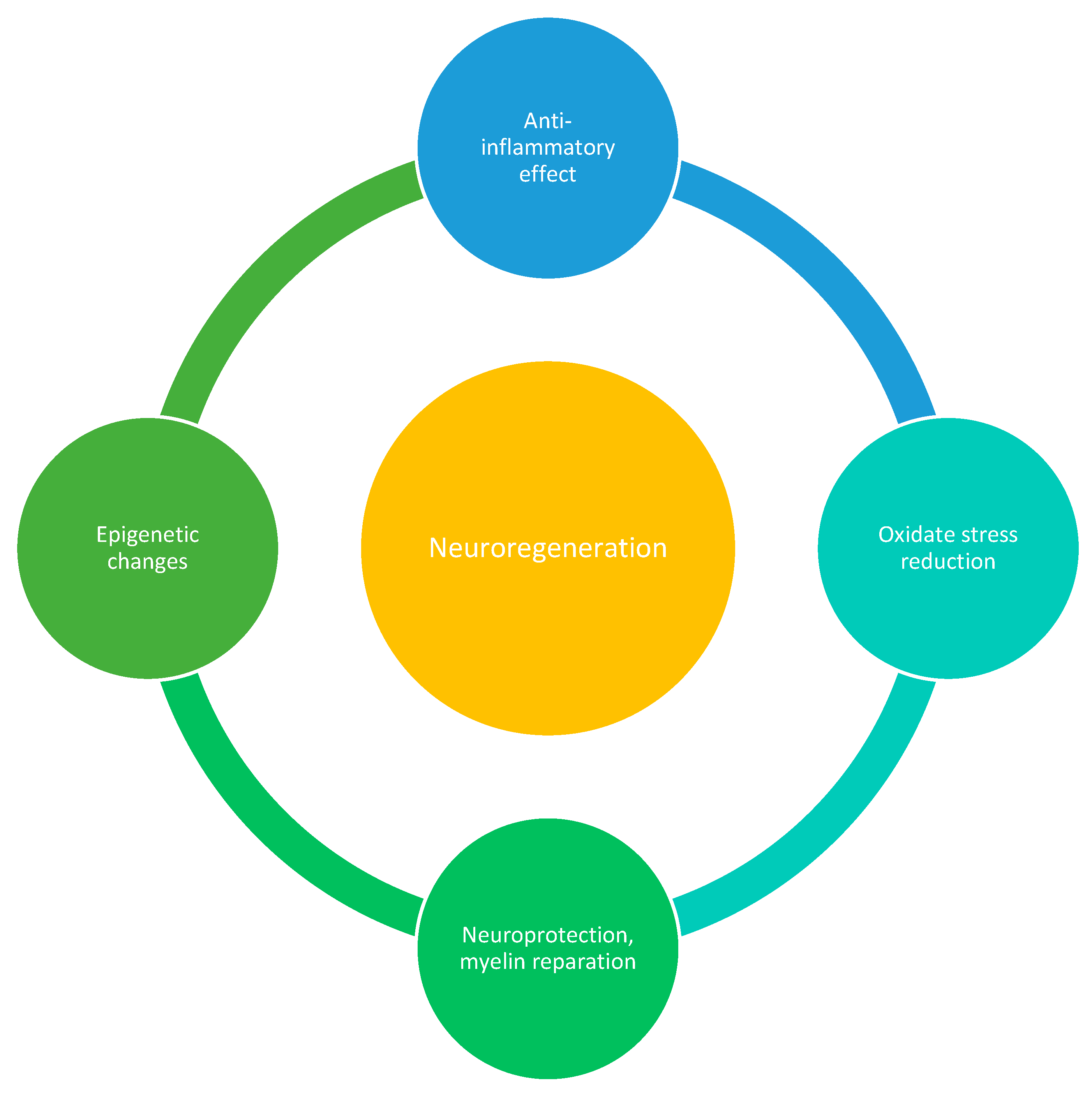
- Flavonoids have been found to exert neuroprotective effects by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key factors in MS [90,91]. They have also been shown to promote synaptogenesis and neurogenesis, which are important processes for brain plasticity [90]. Additionally, flavonoids have been found to modulate signaling pathways involved in neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity [92,93].
- In animal models of MS, flavonoids have demonstrated positive therapeutic effects. For example, the flavonoid luteolin has been shown to suppress clinical symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent relapse in rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an MS model [94]. A systematic review of studies on EAE and MS also reported positive outcomes for the therapeutic effect of flavonoids on these conditions [95].
- A study on mice with induced CNS demyelination found that an increased n-3 PUFA status promoted remyelination after toxic injury to CNS oligodendrocytes. This effect may be mediated by n-3 PUFA-derived lipid metabolites [104].
- Omega-3 PUFAs, such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), have been shown to modulate microglial responses to myelin pathology. They can inhibit inflammation while enhancing beneficial immune responses, such as microglial phagocytosis. In a mouse model of MS, n-3 PUFA supplementation reduced demyelination and shifted microglial polarization towards a beneficial phenotype [105].
- In vitro studies using oligodendroglia cells and primary oligodendrocytes have shown that supplementation with n-3 and n-6 PUFAs can promote oligodendrocyte differentiation. This was evidenced by increased expression of markers of oligodendroglia differentiation and enhanced myelin sheet formation [106].
- A study on healthy older adults found that omega-3 PUFAs were associated with individual differences in functional brain connectivity. Specifically, they were linked to connectivity within regions supporting executive function, memory, and emotion. These regions were also found to predict general, fluid, and crystallized intelligence [107].
- Polyphenols can scavenge and neutralize harmful free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and protecting cells from damage [136].
- Polyphenols have been investigated for their potential anti-carcinogenic effects. They may inhibit tumor growth, induce apoptosis in cancer cells, and have anti-mutagenic properties [140].
- Some polyphenols, such as resveratrol and epigallocatechin-3-gallate, have shown promise in protecting against neurodegenerative disorders by reducing mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress [141].
Obesity
- Obesity and high-calorie diets are associated with disturbances in gut microbiota. Emerging evidence suggests that gut dysbiosis may play a role in the development and progression of MS. Altered gut microbiota can influence immune responses and neuroinflammation, contributing to neurodegeneration in obese MS patients [161,173].
- Obesity is characterized by insulin and leptin resistance, which can impair neuroprotective signaling pathways. Insulin and leptin resistance may weaken the protective effects of these molecules in the CNS, leading to increased neurodegeneration in MS [174].
- Regular exercise is crucial for weight management and overall health. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends between 150-250 minutes per week of moderate-intensity physical activity for preventing weight gain and between 225-420 minutes per week for weight loss in people with MS [175].
- When designing exercise programs for individuals with MS, it is important to consider their specific needs and limitations. Exercise programs should exceed energy expenditure recommendations to effectively counteract weight gain [175].
- Intermittent fasting has shown beneficial effects on weight loss and lipid profile in people with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Although limited data is available for its effects on MS, intermittent fasting may be a safe and feasible intervention for individuals with MS [180].
- Tailored dietary change strategies, nutrition education, and counseling can play a significant role in managing metabolic comorbidities in MS. Addressing barriers and facilitators to dietary changes through behavior change techniques can help individuals achieve sustainable and tailored dietary behavior changes [181].
Conclusions
References
- Tafti D, Ehsan M, Xixis KL. Multiple Sclerosis. In Treasure Island (FL); 2024.
- Weiner HL. Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease. Arch Neurol. 2004 Oct;61(10):1613–5. [CrossRef]
- Dendrou CA, Fugger L, Friese MA. Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 Sep;15(9):545–58. [CrossRef]
- Cree BAC, Gourraud P-A, Oksenberg JR, Bevan C, Crabtree-Hartman E, Gelfand JM, et al. Long-term evolution of multiple sclerosis disability in the treatment era. Ann Neurol. 2016 Oct;80(4):499–510.
- Tarlinton RE, Martynova E, Rizvanov AA, Khaiboullina S, Verma S. Role of Viruses in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis. Viruses. 2020 Jun;12(6). [CrossRef]
- Ntranos A, Lublin F. Diagnostic Criteria, Classification and Treatment Goals in Multiple Sclerosis: The Chronicles of Time and Space. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016 Oct;16(10):90. [CrossRef]
- Noyes K, Weinstock-Guttman B. Impact of diagnosis and early treatment on the course of multiple sclerosis. Am J Manag Care. 2013 Nov;19(17 Suppl):s321-31.
- Marrie RA, Reider N, Cohen J, Stuve O, Sorensen PS, Cutter G, et al. A systematic review of the incidence and prevalence of autoimmune disease in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2015 Mar;21(3):282–93. [CrossRef]
- Nielsen NM, Westergaard T, Frisch M, Rostgaard K, Wohlfahrt J, Koch-Henriksen N, et al. Type 1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis: A Danish population-based cohort study. Arch Neurol. 2006 Jul;63(7):1001–4.
- Gupta G, Gelfand JM, Lewis JD. Increased risk for demyelinating diseases in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2005 Sep;129(3):819–26. [CrossRef]
- Goris A, Vandebergh M, McCauley JL, Saarela J, Cotsapas C. Genetics of multiple sclerosis: lessons from polygenicity. Lancet Neurol. 2022 Sep;21(9):830–42. [CrossRef]
- Barac IS, Iancu M, Văcăraș V, Cozma A, Negrean V, Sâmpelean D, et al. Potential Contribution of IL-27 and IL-23 Gene Polymorphisms to Multiple Sclerosis Susceptibility: An Association Analysis at Genotype and Haplotype Level. J Clin Med. 2021 Dec;11(1). [CrossRef]
- Vacaras V, Paraschiv A-C, Iluț S, Vacaras C, Nistor C, Marin G-E, et al. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Multiple Sclerosis Disability: A Prospective Study. Brain Sci. 2024 Feb;14(3). [CrossRef]
- Cusick MF, Libbey JE, Fujinami RS. Multiple sclerosis: Autoimmunity and viruses. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013;25(4):496–501.
- Taan M, Al Ahmad F, Ercksousi MK, Hamza G. Risk Factors Associated with Multiple Sclerosis: A Case-Control Study in Damascus, Syria. Mult Scler Int. 2021;2021:8147451. [CrossRef]
- Jacobs BM, Giovannoni G, Cuzick J, Dobson R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between Epstein-Barr virus, multiple sclerosis and other risk factors. Mult Scler. 2020 Oct;26(11):1281–97.
- Xu Y, Smith KA, Hiyoshi A, Piehl F, Olsson T, Montgomery S. Hospital-diagnosed infections before age 20 and risk of a subsequent multiple sclerosis diagnosis. Brain. 2021 Sep;144(8):2390–400. [CrossRef]
- Jacobs BM, Noyce AJ, Giovannoni G, Dobson R. BMI and low vitamin D are causal factors for multiple sclerosis: A Mendelian Randomization study. Neurol Neuroimmunol neuroinflammation. 2020 Mar;7(2).
- Manouchehrinia A, Tench CR, Maxted J, Bibani RH, Britton J, Constantinescu CS. Tobacco smoking and disability progression in multiple sclerosis: United Kingdom cohort study. Brain. 2013 Jul;136(Pt 7):2298–304. [CrossRef]
- Ramanujam R, Hedström A-K, Manouchehrinia A, Alfredsson L, Olsson T, Bottai M, et al. Effect of Smoking Cessation on Multiple Sclerosis Prognosis. JAMA Neurol. 2015 Oct;72(10):1117–23. [CrossRef]
- Sale A, Berardi N, Maffei L. Environment and brain plasticity: towards an endogenous pharmacotherapy. Physiol Rev. 2014 Jan;94(1):189–234. [CrossRef]
- Chandler LJ. Ethanol and brain plasticity: receptors and molecular networks of the postsynaptic density as targets of ethanol. Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Sep;99(3):311–26. [CrossRef]
- Kolb B, Whishaw IQ. Brain plasticity and behavior. Annu Rev Psychol. 1998;49:43–64. [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Leone A, Freitas C, Oberman L, Horvath JC, Halko M, Eldaief M, et al. Characterizing brain cortical plasticity and network dynamics across the age-span in health and disease with TMS-EEG and TMS-fMRI. Brain Topogr. 2011 Oct;24(3–4):302–15.
- Missitzi J, Gentner R, Geladas N, Politis P, Karandreas N, Classen J, et al. Plasticity in human motor cortex is in part genetically determined. J Physiol. 2011 Jan;589(Pt 2):297–306. [CrossRef]
- Tzounopoulos T, Kraus N. Learning to encode timing: mechanisms of plasticity in the auditory brainstem. Neuron. 2009 May;62(4):463–9. [CrossRef]
- Travaglia A, Bisaz R, Cruz E, Alberini CM. Developmental changes in plasticity, synaptic, glia and connectivity protein levels in rat dorsal hippocampus. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016 Nov;135:125–38. [CrossRef]
- Johnston M V. Plasticity in the developing brain: implications for rehabilitation. Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2009;15(2):94–101. [CrossRef]
- Strettoi E, Di Marco B, Orsini N, Napoli D. Retinal Plasticity. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan;23(3).
- Pearson-Fuhrhop KM, Kleim JA, Cramer SC. Brain plasticity and genetic factors. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2009;16(4):282–99. [CrossRef]
- Ding Q, Ying Z, Gómez-Pinilla F. Exercise influences hippocampal plasticity by modulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor processing. Neuroscience. 2011 Sep;192:773–80. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Zeev T, Shoenfeld Y, Hoffman JR. The Effect of Exercise on Neurogenesis in the Brain. Isr Med Assoc J. 2022 Aug;24(8):533–8.
- Smith AE, Goldsworthy MR, Garside T, Wood FM, Ridding MC. The influence of a single bout of aerobic exercise on short-interval intracortical excitability. Exp brain Res. 2014 Jun;232(6):1875–82. [CrossRef]
- Dishman RK, Berthoud H-R, Booth FW, Cotman CW, Edgerton VR, Fleshner MR, et al. Neurobiology of exercise. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006 Mar;14(3):345–56.
- Achiron A, Kalron A. [Physical activity: positive impact on brain plasticity]. Harefuah. 2008 Mar;147(3):252-255,276.
- Cirillo J, Lavender AP, Ridding MC, Semmler JG. Motor cortex plasticity induced by paired associative stimulation is enhanced in physically active individuals. J Physiol. 2009 Dec;587(Pt 24):5831–42. [CrossRef]
- Mori F, Kusayanagi H, Buttari F, Centini B, Monteleone F, Nicoletti CG, et al. Early treatment with high-dose interferon beta-1a reverses cognitive and cortical plasticity deficits in multiple sclerosis. Funct Neurol. 2012;27(3):163–8.
- Parry AMM, Scott RB, Palace J, Smith S, Matthews PM. Potentially adaptive functional changes in cognitive processing for patients with multiple sclerosis and their acute modulation by rivastigmine. Brain. 2003 Dec;126(Pt 12):2750–60. [CrossRef]
- Murphy T, Dias GP, Thuret S. Effects of diet on brain plasticity in animal and human studies: mind the gap. Neural Plast. 2014;2014:563160. [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Pinilla F, Ying Z. Differential effects of exercise and dietary docosahexaenoic acid on molecular systems associated with control of allostasis in the hypothalamus and hippocampus. Neuroscience. 2010 Jun;168(1):130–7. [CrossRef]
- Xu B-L, Wang R, Ma L-N, Dong W, Zhao Z-W, Zhang J-S, et al. Effects of Caloric Intake on Learning and Memory Function in Juvenile C57BL/6J Mice. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:759803. [CrossRef]
- Kalantarzadeh E, Radahmadi M, Reisi P. The impact of different dark chocolate dietary patterns on synaptic potency and plasticity in the hippocampal CA1 area of the rats under chronic isolation stress. Nutr Neurosci. 2023 Aug;26(8):756–65. [CrossRef]
- Libner CD, Salapa HE, Levin MC. The Potential Contribution of Dysfunctional RNA-Binding Proteins to the Pathogenesis of Neurodegeneration in Multiple Sclerosis and Relevant Models. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun;21(13). [CrossRef]
- Dong Y, D’Mello C, Pinsky W, Lozinski BM, Kaushik DK, Ghorbani S, et al. Oxidized phosphatidylcholines found in multiple sclerosis lesions mediate neurodegeneration and are neutralized by microglia. Nat Neurosci. 2021 Apr;24(4):489–503. [CrossRef]
- Gonsette RE. Neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis: the role of oxidative stress and excitotoxicity. J Neurol Sci. 2008 Nov;274(1–2):48–53. [CrossRef]
- Vyshkina T, Kalman B. Autoantibodies and neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Lab Invest. 2008 Aug;88(8):796–807. [CrossRef]
- Kalman B, Leist TP. A mitochondrial component of neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Neuromolecular Med. 2003;3(3):147–58. [CrossRef]
- Mahad DH, Trapp BD, Lassmann H. Pathological mechanisms in progressive multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2015 Feb;14(2):183–93. [CrossRef]
- Barnett MH, Mathey E, Kiernan MC, Pollard JD. Axonal damage in central and peripheral nervous system inflammatory demyelinating diseases: common and divergent pathways of tissue damage. Curr Opin Neurol. 2016 Jun;29(3):213–21.
- Zoupi L, Booker SA, Eigel D, Werner C, Kind PC, Spires-Jones TL, et al. Selective vulnerability of inhibitory networks in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2021 Mar;141(3):415–29. [CrossRef]
- Chapman C, Lucas RM, Ponsonby A-L, Taylor B. Predictors of progression from a first demyelinating event to clinically definite multiple sclerosis. Brain Commun. 2022;4(4):fcac181. [CrossRef]
- Alroughani RA, Akhtar S, Ahmed SF, Al-Hashel JY. Clinical predictors of disease progression in multiple sclerosis patients with relapsing onset in a nation-wide cohort. Int J Neurosci. 2015;125(11):831–7. [CrossRef]
- Simmons SB, Schippling S, Giovannoni G, Ontaneda D. Predicting disability worsening in relapsing and progressive multiple sclerosis. Curr Opin Neurol. 2021 Jun;34(3):312–21. [CrossRef]
- Motl RW, Dlugonski D, Pilutti L, Sandroff B, McAuley E. Premorbid physical activity predicts disability progression in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 2012 Dec;323(1–2):123–7. [CrossRef]
- Lin X, Zarghami A, Jelinek GA, Simpson-Yap S, Neate S, Nag N. Diet and omega-3 and vitamin D supplement use predict five-year fatigue and disability trajectories in people with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2024 Jun;86:105615. [CrossRef]
- Schmitz K, Barthelmes J, Stolz L, Beyer S, Diehl O, Tegeder I. “Disease modifying nutricals” for multiple sclerosis. Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Apr;148:85–113.
- O’Connor K, Weinstock-Guttman B, Carl E, Kilanowski C, Zivadinov R, Ramanathan M. Patterns of dietary and herbal supplement use by multiple sclerosis patients. J Neurol. 2012 Apr;259(4):637–44. [CrossRef]
- Bergien SO, Petersen CM, Lynning M, Kristiansen M, Skovgaard L. Use of natural medicine and dietary supplements concomitant with conventional medicine among people with Multiple Sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2020 Sep;44:102197. [CrossRef]
- Marx W, Hockey M, McGuinness AJ, Lane M, Christodoulou J, van der Mei I, et al. The effect of emerging nutraceutical interventions for clinical and biological outcomes in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2020 Jan;37:101486. [CrossRef]
- Spagnuolo P. Interactions Between Nutraceutical Supplements and Standard Acute Myeloid Leukemia Chemotherapeutics. J Pharm Pharm Sci a Publ Can Soc Pharm Sci Soc Can des Sci Pharm. 2015;18(4):339–43. [CrossRef]
- Szymaszkiewicz A, López-Gómez L, Zielińska M, Abalo R. Nutraceuticals and peripheral glial cells: a possible link? J Integr Neurosci. 2022 Jan;21(1):1.
- Yuan J, Tao Y, Wang M, Huang F, Wu X. Natural compounds as potential therapeutic candidates for multiple sclerosis: Emerging preclinical evidence. Phytomedicine. 2024 Jan;123:155248. [CrossRef]
- Rito Y, Torre-Villalvazo I, Flores J, Rivas V, Corona T. Epigenetics in Multiple Sclerosis: Molecular Mechanisms and Dietary Intervention. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2018 Jan;18(1):8–15. [CrossRef]
- Menéndez SG, Manucha W. Vitamin D as a Modulator of Neuroinflammation: Implications for Brain Health. Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(5):323–32. [CrossRef]
- Wergeland S, Torkildsen Ø, Myhr K-M, Aksnes L, Mørk SJ, Bø L. Dietary vitamin D3 supplements reduce demyelination in the cuprizone model. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26262. [CrossRef]
- Soleimani M, Jameie SB, Mehdizadeh M, Keradi M, Masoumipoor M, Mehrabi S. Vitamin D3 influence the Th1/Th2 ratio in C57BL/6 induced model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014 Oct;17(10):785–92.
- Dias da Silva W, Tambourgi D V. IgY: a promising antibody for use in immunodiagnostic and in immunotherapy. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010 Jun;135(3–4):173–80.
- Lee L, Samardzic K, Wallach M, Frumkin LR, Mochly-Rosen D. Immunoglobulin Y for Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications in Infectious Diseases. Front Immunol. 2021;12:696003. [CrossRef]
- Paraschiv AC, Vacaras V, Nistor C, Vacaras C, Nistor DT, Vesa SC, et al. Dysbiosis in Multiple Sclerosis: Can Immunoglobulin Y Supplements Help? J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2024 Mar;33(1):115–22.
- Shinto L, Calabrese C, Morris C, Sinsheimer S, Bourdette D. Complementary and alternative medicine in multiple sclerosis: survey of licensed naturopaths. J Altern Complement Med. 2004 Oct;10(5):891–7.
- Shinto L, Calabrese C, Morris C, Yadav V, Griffith D, Frank R, et al. A randomized pilot study of naturopathic medicine in multiple sclerosis. J Altern Complement Med. 2008 Jun;14(5):489–96. [CrossRef]
- Teixeira MZ. Immunomodulatory drugs (natalizumab), worsening of multiple sclerosis, rebound effect and similitude. Homeopathy. 2013 Jul;102(3):215–24. [CrossRef]
- Paraschiv A-C, Vacaras V, Nistor C, Vacaras C, Strilciuc S, Muresanu DF. The effect of multiple sclerosis therapy on gut microbiota dysbiosis: a longitudinal prospective study. Microb cell (Graz, Austria). 2024;11:106–15. [CrossRef]
- Tran Nguyen; Talal Alzahrani. Ginkgo Biloba [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2024 Jul 11]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541024/.
- Lovera JF, Kim E, Heriza E, Fitzpatrick M, Hunziker J, Turner AP, et al. Ginkgo biloba does not improve cognitive function in MS: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Neurology. 2012 Sep;79(12):1278–84.
- Lovera J, Bagert B, Smoot K, Morris CD, Frank R, Bogardus K, et al. Ginkgo biloba for the improvement of cognitive performance in multiple sclerosis: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Mult Scler. 2007 Apr;13(3):376–85.
- Yin J-J, He Y, An J, Miao Q, Sui R-X, Wang Q, et al. Dynamic Balance of Microglia and Astrocytes Involved in the Remyelinating Effect of Ginkgolide B. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:572. [CrossRef]
- Seifar F, Khalili M, Khaledyan H, Amiri Moghadam S, Izadi A, Azimi A, et al. α-Lipoic acid, functional fatty acid, as a novel therapeutic alternative for central nervous system diseases: A review. Nutr Neurosci. 2019 May;22(5):306–16. [CrossRef]
- Rocamonde B, Paradells S, Barcia JM, Barcia C, García Verdugo JM, Miranda M, et al. Neuroprotection of lipoic acid treatment promotes angiogenesis and reduces the glial scar formation after brain injury. Neuroscience. 2012 Nov;224:102–15. [CrossRef]
- Marracci GH, McKeon GP, Marquardt WE, Winter RW, Riscoe MK, Bourdette DN. Alpha lipoic acid inhibits human T-cell migration: implications for multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci Res. 2004 Nov;78(3):362–70.
- Espiritu AI, Remalante-Rayco PPM. High-dose biotin for multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2021 Oct;55:103159.
- Levy MJF, Garcia-Diaz B, Sedel F, Baron-Van Evercooren A, Mozafari S. High Dose Pharmaceutical Grade Biotin (MD1003) Accelerates Differentiation of Murine and Grafted Human Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells In Vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec;23(24). [CrossRef]
- Sedel F, Bernard D, Mock DM, Tourbah A. Targeting demyelination and virtual hypoxia with high-dose biotin as a treatment for progressive multiple sclerosis. Neuropharmacology. 2016 Nov;110(Pt B):644–53. [CrossRef]
- Cree BAC, Cutter G, Wolinsky JS, Freedman MS, Comi G, Giovannoni G, et al. Safety and efficacy of MD1003 (high-dose biotin) in patients with progressive multiple sclerosis (SPI2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2020 Dec;19(12):988–97. [CrossRef]
- Pietta PG. Flavonoids as antioxidants. J Nat Prod. 2000 Jul;63(7):1035–42.
- Ielpo MT, Basile A, Miranda R, Moscatiello V, Nappo C, Sorbo S, et al. Immunopharmacological properties of flavonoids. Fitoterapia. 2000 Aug;71 Suppl 1:S101-9. [CrossRef]
- Atucha NM, Romecín P, Vargas F, García-Estañ J. Effects of Flavonoids in Experimental Models of Arterial Hypertension. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(9):735–45. [CrossRef]
- Jaeger BN, Parylak SL, Gage FH. Mechanisms of dietary flavonoid action in neuronal function and neuroinflammation. Mol Aspects Med. 2018 Jun;61:50–62. [CrossRef]
- Williamson G, Kay CD, Crozier A. The Bioavailability, Transport, and Bioactivity of Dietary Flavonoids: A Review from a Historical Perspective. Compr Rev food Sci food Saf. 2018 Sep;17(5):1054–112. [CrossRef]
- Cichon N, Saluk-Bijak J, Gorniak L, Przyslo L, Bijak M. Flavonoids as a Natural Enhancer of Neuroplasticity-An Overview of the Mechanism of Neurorestorative Action. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). 2020 Oct;9(11). [CrossRef]
- Faysal M, Dehbia Z, Zehravi M, Sweilam SH, Haque MA, Kumar KP, et al. Flavonoids as Potential Therapeutics Against Neurodegenerative Disorders: Unlocking the Prospects. Neurochem Res. 2024 Aug;49(8):1926–44. [CrossRef]
- Vauzour D, Vafeiadou K, Rodriguez-Mateos A, Rendeiro C, Spencer JPE. The neuroprotective potential of flavonoids: a multiplicity of effects. Genes Nutr. 2008 Dec;3(3–4):115–26. [CrossRef]
- Bakoyiannis I, Daskalopoulou A, Pergialiotis V, Perrea D. Phytochemicals and cognitive health: Are flavonoids doing the trick? Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:1488–97.
- Hendriks JJA, Alblas J, van der Pol SMA, van Tol EAF, Dijkstra CD, de Vries HE. Flavonoids influence monocytic GTPase activity and are protective in experimental allergic encephalitis. J Exp Med. 2004 Dec;200(12):1667–72.
- Bayat P, Farshchi M, Yousefian M, Mahmoudi M, Yazdian-Robati R. Flavonoids, the compounds with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, as promising tools in multiple sclerosis (MS) therapy: A systematic review of preclinical evidence. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Jun;95:107562. [CrossRef]
- Marventano S, Kolacz P, Castellano S, Galvano F, Buscemi S, Mistretta A, et al. A review of recent evidence in human studies of n-3 and n-6 PUFA intake on cardiovascular disease, cancer, and depressive disorders: does the ratio really matter? Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2015;66(6):611–22. [CrossRef]
- Chénais B, Blanckaert V. The janus face of lipids in human breast cancer: how polyunsaturated Fatty acids affect tumor cell hallmarks. Int J Breast Cancer. 2012;2012:712536. [CrossRef]
- Davinelli S, Intrieri M, Corbi G, Scapagnini G. Metabolic indices of polyunsaturated fatty acids: current evidence, research controversies, and clinical utility. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(2):259–74. [CrossRef]
- Colussi G, Catena C, Baroselli S, Nadalini E, Lapenna R, Chiuch A, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids: from biochemistry to their clinical use in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2007 Jan;2(1):13–21. [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal S, Kelly L, Malik R, Prabhakaran D, Reddy S. Impact of omega-6 fatty acids on cardiovascular outcomes: A review. J Prev Cardiol. 2013 Feb;2(3):325–36.
- D’Archivio M, Scazzocchio B, Vari R, Santangelo C, Giovannini C, Masella R. Recent Evidence on the Role of Dietary PUFAs in Cancer Development and Prevention. Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(16):1818–36. [CrossRef]
- Mbarik M, Biam RS, Robichaud P-P, Surette ME. The impact of PUFA on cell responses: Caution should be exercised when selecting PUFA concentrations in cell culture. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2020 Apr;155:102083. [CrossRef]
- Benatti P, Peluso G, Nicolai R, Calvani M. Polyunsaturated fatty acids: biochemical, nutritional and epigenetic properties. J Am Coll Nutr. 2004 Aug;23(4):281–302. [CrossRef]
- Siegert E, Paul F, Rothe M, Weylandt KH. The effect of omega-3 fatty acids on central nervous system remyelination in fat-1 mice. BMC Neurosci. 2017 Jan;18(1):19. [CrossRef]
- Chen S, Zhang H, Pu H, Wang G, Li W, Leak RK, et al. n-3 PUFA supplementation benefits microglial responses to myelin pathology. Sci Rep. 2014 Dec;4:7458. [CrossRef]
- van Meeteren ME, Baron W, Beermann C, Dijkstra CD, van Tol EAF. Polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation stimulates differentiation of oligodendroglia cells. Dev Neurosci. 2006;28(3):196–208. [CrossRef]
- Talukdar T, Zamroziewicz MK, Zwilling CE, Barbey AK. Nutrient biomarkers shape individual differences in functional brain connectivity: Evidence from omega-3 PUFAs. Hum Brain Mapp. 2019 Apr;40(6):1887–97. [CrossRef]
- Lopresti AL. Potential Role of Curcumin for the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. CNS Drugs. 2022 Feb;36(2):123–41. [CrossRef]
- Xu X-Y, Meng X, Li S, Gan R-Y, Li Y, Li H-B. Bioactivity, Health Benefits, and Related Molecular Mechanisms of Curcumin: Current Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Nutrients. 2018 Oct;10(10). [CrossRef]
- Tossetta G, Fantone S, Giannubilo SR, Marzioni D. The Multifaced Actions of Curcumin in Pregnancy Outcome. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). 2021 Jan;10(1). [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H, Bahroudi Z, Hussen BM, Talebi SF, Taheri M, et al. Nrf2-Related Therapeutic Effects of Curcumin in Different Disorders. Biomolecules. 2022 Jan;12(1). [CrossRef]
- Liu S, Liu J, He L, Liu L, Cheng B, Zhou F, et al. A Comprehensive Review on the Benefits and Problems of Curcumin with Respect to Human Health. Molecules. 2022 Jul;27(14). [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi E, Momtazi AA, Johnston TP, Sahebkar A. Therapeutic effects of curcumin in inflammatory and immune-mediated diseases: A nature-made jack-of-all-trades? J Cell Physiol. 2018 Feb;233(2):830–48.
- Sadek MA, Rabie MA, El Sayed NS, Sayed HM, Kandil EA. Neuroprotective effect of curcumin against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis-induced cognitive and physical impairments in mice: an insight into the role of the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway. Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Apr;32(2):1499–518. [CrossRef]
- ELBini-Dhouib I, Manai M, Neili N-E, Marzouki S, Sahraoui G, Ben Achour W, et al. Dual Mechanism of Action of Curcumin in Experimental Models of Multiple Sclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug;23(15). [CrossRef]
- Salehi B, Calina D, Docea AO, Koirala N, Aryal S, Lombardo D, et al. Curcumin’s Nanomedicine Formulations for Therapeutic Application in Neurological Diseases. J Clin Med. 2020 Feb;9(2). [CrossRef]
- Kulashekar M, Stom SM, Peuler JD. Resveratrol’s Potential in the Adjunctive Management of Cardiovascular Disease, Obesity, Diabetes, Alzheimer Disease, and Cancer. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2018 Sep;118(9):596–605.
- Malhotra A, Bath S, Elbarbry F. An Organ System Approach to Explore the Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Cytoprotective Actions of Resveratrol. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:803971. [CrossRef]
- Jasiński M, Jasińska L, Ogrodowczyk M. Resveratrol in prostate diseases - a short review. Cent Eur J Urol. 2013;66(2):144–9. [CrossRef]
- Rocha-González HI, Ambriz-Tututi M, Granados-Soto V. Resveratrol: a natural compound with pharmacological potential in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008;14(3):234–47. [CrossRef]
- Springer M, Moco S. Resveratrol and Its Human Metabolites-Effects on Metabolic Health and Obesity. Nutrients. 2019 Jan;11(1). [CrossRef]
- Berman AY, Motechin RA, Wiesenfeld MY, Holz MK. The therapeutic potential of resveratrol: a review of clinical trials. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2017;1. [CrossRef]
- Vang O, Ahmad N, Baile CA, Baur JA, Brown K, Csiszar A, et al. What is new for an old molecule? Systematic review and recommendations on the use of resveratrol. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e19881. [CrossRef]
- Tomé-Carneiro J, Larrosa M, González-Sarrías A, Tomás-Barberán FA, García-Conesa MT, Espín JC. Resveratrol and clinical trials: the crossroad from in vitro studies to human evidence. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(34):6064–93. [CrossRef]
- Shamsher E, Khan RS, Davis BM, Dine K, Luong V, Somavarapu S, et al. Nanoparticles Enhance Solubility and Neuroprotective Effects of Resveratrol in Demyelinating Disease. Neurother J Am Soc Exp Neurother. 2023 Jul;20(4):1138–53. [CrossRef]
- Ghaiad HR, Nooh MM, El-Sawalhi MM, Shaheen AA. Resveratrol Promotes Remyelination in Cuprizone Model of Multiple Sclerosis: Biochemical and Histological Study. Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jul;54(5):3219–29. [CrossRef]
- Yao P, Liu Y. Terpenoids: Natural Compounds for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Therapy. Molecules. 2022 Dec;28(1). [CrossRef]
- Ahmad A, Tiwari RK, Ansari IA. Revisiting the Antiviral Efficacy of Terpenoids: Plausible Adjunct Therapeutics for Novel SARS-CoV-2? Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2021;21(12):2119–30.
- Paduch R, Kandefer-Szerszeń M, Trytek M, Fiedurek J. Terpenes: substances useful in human healthcare. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2007;55(5):315–27. [CrossRef]
- Shin M, Liu QF, Choi B, Shin C, Lee B, Yuan C, et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Limonene (+) against Aβ42-Induced Neurotoxicity in a Drosophila Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020 Mar;43(3):409–17. [CrossRef]
- Mony TJ, Elahi F, Choi JW, Park SJ. Neuropharmacological Effects of Terpenoids on Preclinical Animal Models of Psychiatric Disorders: A Review. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). 2022 Sep;11(9). [CrossRef]
- Yang H, Dou QP. Targeting apoptosis pathway with natural terpenoids: implications for treatment of breast and prostate cancer. Curr Drug Targets. 2010 Jun;11(6):733–44. [CrossRef]
- de las Heras B, Hortelano S. Molecular basis of the anti-inflammatory effects of terpenoids. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2009 Mar;8(1):28–39. [CrossRef]
- Carsanba E, Pintado M, Oliveira C. Fermentation Strategies for Production of Pharmaceutical Terpenoids in Engineered Yeast. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Mar;14(4). [CrossRef]
- Tomassini V, d’Ambrosio A, Petsas N, Wise RG, Sbardella E, Allen M, et al. The effect of inflammation and its reduction on brain plasticity in multiple sclerosis: MRI evidence. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016 Jul;37(7):2431–45. [CrossRef]
- Cicero AFG, Colletti A. Polyphenols Effect on Circulating Lipids and Lipoproteins: From Biochemistry to Clinical Evidence. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(2):178–90. [CrossRef]
- Giglio RV, Patti AM, Cicero AFG, Lippi G, Rizzo M, Toth PP, et al. Polyphenols: Potential Use in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(2):239–58. [CrossRef]
- Gorzynik-Debicka M, Przychodzen P, Cappello F, Kuban-Jankowska A, Marino Gammazza A, Knap N, et al. Potential Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Plant Polyphenols. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb;19(3). [CrossRef]
- Focaccetti C, Izzi V, Benvenuto M, Fazi S, Ciuffa S, Giganti MG, et al. Polyphenols as Immunomodulatory Compounds in the Tumor Microenvironment: Friends or Foes? Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr;20(7).
- Rodrigo R, Libuy M, Feliu F, Hasson D. Polyphenols in disease: from diet to supplements. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(4):304–17. [CrossRef]
- Vacca RA, Valenti D, Caccamese S, Daglia M, Braidy N, Nabavi SM. Plant polyphenols as natural drugs for the management of Down syndrome and related disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016 Dec;71:865–77. [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk M, El Ayed M, Démosthènes A, Aissouni Y, Aouani E, Daulhac-Terrail L, et al. Antioxidant effect of grape seed extract corrects experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis behavioral dysfunctions, demyelination, and glial activation. Front Immunol. 2022;13:960355. [CrossRef]
- Colovic MB, Vasic VM, Djuric DM, Krstic DZ. Sulphur-containing Amino Acids: Protective Role Against Free Radicals and Heavy Metals. Curr Med Chem. 2018 Jan;25(3):324–35. [CrossRef]
- Partti-Pellinen K, Marttila O, Vilkka V, Jaakkola JJ, Jäppinen P, Haahtela T. The South Karelia Air Pollution Study: effects of low-level exposure to malodorous sulfur compounds on symptoms. Arch Environ Health. 1996;51(4):315–20. [CrossRef]
- Jaakkola JJ, Partti-Pellinen K, Marttila O, Miettinen P, Vilkka V, Haahtela T. The South Karelia Air Pollution Study: changes in respiratory health in relation to emission reduction of malodorous sulfur compounds from pulp mills. Arch Environ Health. 1999;54(4):254–63. [CrossRef]
- Gurvitz M, Lui GK, Marelli A. Adult Congenital Heart Disease-Preparing for the Changing Work Force Demand. Cardiol Clin. 2020 Aug;38(3):283–94. [CrossRef]
- Caylak E, Aytekin M, Halifeoglu I. Antioxidant effects of methionine, alpha-lipoic acid, N-acetylcysteine and homocysteine on lead-induced oxidative stress to erythrocytes in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol Off J Gesellschaft fur Toxikologische Pathol. 2008 Aug;60(4–5):289–94. [CrossRef]
- Ghaiad HR, A Abd-Elmawla M, Gad ES, A Ahmed K, Abdelmonem M. Modulating miR-146a Expression by Hydrogen Sulfide Ameliorates Motor Dysfunction and Axonal Demyelination in Cuprizone-Induced Multiple Sclerosis. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023 Sep;14(17):3047–58.
- Yao G, Yun Y, Sang N. Differential effects between one week and four weeks exposure to same mass of SO2 on synaptic plasticity in rat hippocampus. Environ Toxicol. 2016 Jul;31(7):820–9. [CrossRef]
- Munger KL, Chitnis T, Ascherio A. Body size and risk of MS in two cohorts of US women. Neurology. 2009 Nov;73(19):1543–50. [CrossRef]
- Neto A, Fernandes A, Barateiro A. The complex relationship between obesity and neurodegenerative diseases: an updated review. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023;17:1294420. [CrossRef]
- Seidell JC. Obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes--a worldwide epidemic. Br J Nutr. 2000 Mar;83 Suppl 1:S5-8.
- Mokry LE, Ross S, Timpson NJ, Sawcer S, Davey Smith G, Richards JB. Obesity and Multiple Sclerosis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. PLoS Med. 2016 Jun;13(6):e1002053.
- Liu Z, Zhang T-T, Yu J, Liu Y-L, Qi S-F, Zhao J-J, et al. Excess Body Weight during Childhood and Adolescence Is Associated with the Risk of Multiple Sclerosis: A Meta-Analysis. Neuroepidemiology. 2016;47(2):103–8. [CrossRef]
- Hedström AK, Olsson T, Alfredsson L. Body mass index during adolescence, rather than childhood, is critical in determining MS risk. Mult Scler. 2016 Jun;22(7):878–83. [CrossRef]
- Hedström AK, Olsson T, Alfredsson L. High body mass index before age 20 is associated with increased risk for multiple sclerosis in both men and women. Mult Scler. 2012 Sep;18(9):1334–6. [CrossRef]
- Kavak KS, Teter BE, Hagemeier J, Zakalik K, Weinstock-Guttman B. Higher weight in adolescence and young adulthood is associated with an earlier age at multiple sclerosis onset. Mult Scler. 2015 Jun;21(7):858–65. [CrossRef]
- Kvistad SS, Myhr K-M, Holmøy T, Šaltytė Benth J, Wergeland S, Beiske AG, et al. Body mass index influence interferon-beta treatment response in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 2015 Nov;288:92–7. [CrossRef]
- Lutfullin I, Eveslage M, Bittner S, Antony G, Flaskamp M, Luessi F, et al. Association of obesity with disease outcome in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2023 Jan;94(1):57–61. [CrossRef]
- Harroud A, Manousaki D, Butler-Laporte G, Mitchell RE, Davey Smith G, Richards JB, et al. The relative contributions of obesity, vitamin D, leptin, and adiponectin to multiple sclerosis risk: A Mendelian randomization mediation analysis. Mult Scler. 2021 Nov;27(13):1994–2000. [CrossRef]
- Samara A, Cantoni C, Piccio L, Cross AH, Chahin S. Obesity, gut microbiota, and multiple sclerosis: Unraveling the connection. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023 Aug;76:104768. [CrossRef]
- Hedström AK, Lima Bomfim I, Barcellos L, Gianfrancesco M, Schaefer C, Kockum I, et al. Interaction between adolescent obesity and HLA risk genes in the etiology of multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2014 Mar;82(10):865–72. [CrossRef]
- Pakpoor J, Schmierer K, Cuzick J, Giovannoni G, Dobson R. Estimated and projected burden of multiple sclerosis attributable to smoking and childhood and adolescent high body-mass index: a comparative risk assessment. Int J Epidemiol. 2021 Jan;49(6):2051–7. [CrossRef]
- Daniele G, Lunghi C, Dardano A, Binda P, Ceccarini G, Santini F, et al. Bariatric surgery restores visual cortical plasticity in nondiabetic subjects with obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 2021 Aug;45(8):1821–9. [CrossRef]
- Lunghi C, Daniele G, Binda P, Dardano A, Ceccarini G, Santini F, et al. Altered Visual Plasticity in Morbidly Obese Subjects. iScience. 2019 Dec;22:206–13. [CrossRef]
- Sui SX, Ridding MC, Hordacre B. Obesity is Associated with Reduced Plasticity of the Human Motor Cortex. Brain Sci. 2020 Aug;10(9). [CrossRef]
- Hwang L-L, Wang C-H, Li T-L, Chang S-D, Lin L-C, Chen C-P, et al. Sex differences in high-fat diet-induced obesity, metabolic alterations and learning, and synaptic plasticity deficits in mice. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010 Mar;18(3):463–9.
- Al-Dalaeen A, Al-Domi H. Does obesity put your brain at risk? Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022 Mar;16(3):102444.
- Ji Z, Wu S, Xu Y, Qi J, Su X, Shen L. Obesity Promotes EAE Through IL-6 and CCL-2-Mediated T Cells Infiltration. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1881. [CrossRef]
- Stampanoni Bassi M, Iezzi E, Buttari F, Gilio L, Simonelli I, Carbone F, et al. Obesity worsens central inflammation and disability in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2020 Sep;26(10):1237–46. [CrossRef]
- Correale J, Marrodan M. Multiple sclerosis and obesity: The role of adipokines. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1038393. [CrossRef]
- Davanzo GG, Castro G, Monteiro L de B, Castelucci BG, Jaccomo VH, da Silva FC, et al. Obesity increases blood-brain barrier permeability and aggravates the mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023 Apr;72:104605. [CrossRef]
- Shahi SK, Ghimire S, Lehman P, Mangalam AK. Obesity induced gut dysbiosis contributes to disease severity in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:966417. [CrossRef]
- Spielman LJ, Little JP, Klegeris A. Inflammation and insulin/IGF-1 resistance as the possible link between obesity and neurodegeneration. J Neuroimmunol. 2014 Aug;273(1–2):8–21. [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarzade M, Agha-Alinejad H, Motl RW, Negaresh R, Baker JS, Zimmer P. Weight control and physical exercise in people with multiple sclerosis: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Complement Ther Med. 2019 Apr;43:240–6. [CrossRef]
- Bruce JM, Cozart JS, Shook RP, Ruppen S, Siengsukon C, Simon S, et al. Modifying Diet and Exercise in MS (MoDEMS): Study design and protocol for a telehealth weight loss intervention for adults with obesity & Multiple Sclerosis. Contemp Clin Trials. 2021 Aug;107:106495. [CrossRef]
- Bruce JM, Cozart JS, Shook RP, Befort C, Siengsukon CF, Simon S, et al. Modifying diet and exercise in multiple sclerosis (MoDEMS): A randomized controlled trial for behavioral weight loss in adults with multiple sclerosis and obesity. Mult Scler. 2023 Dec;29(14):1860–71. [CrossRef]
- Stenberg E, Forsberg L, Hedström A, Hillert J, Näslund E. Bariatric and metabolic surgery in patients with morbid obesity and multiple sclerosis - a nationwide, matched cohort study. Surg Obes Relat Dis Off J Am Soc Bariatr Surg. 2021 Jun;17(6):1108–14. [CrossRef]
- Bencsath K, Jammoul A, Aminian A, Shimizu H, Fisher CJ, Schauer PR, et al. Outcomes of Bariatric Surgery in Morbidly Obese Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. J Obes. 2017;2017:1935204. [CrossRef]
- Morales-Suarez-Varela M, Collado Sánchez E, Peraita-Costa I, Llopis-Morales A, Soriano JM. Intermittent Fasting and the Possible Benefits in Obesity, Diabetes, and Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients. 2021 Sep;13(9). [CrossRef]
- Allogmanny S, Probst Y. Dietary Modification Combined with Nutrition Education and Counseling for Metabolic Comorbidities in Multiple Sclerosis: Implications for Clinical Practice and Research. Curr Nutr Rep. 2024 Jun;13(2):106–12. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




