Submitted:
21 July 2024
Posted:
25 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
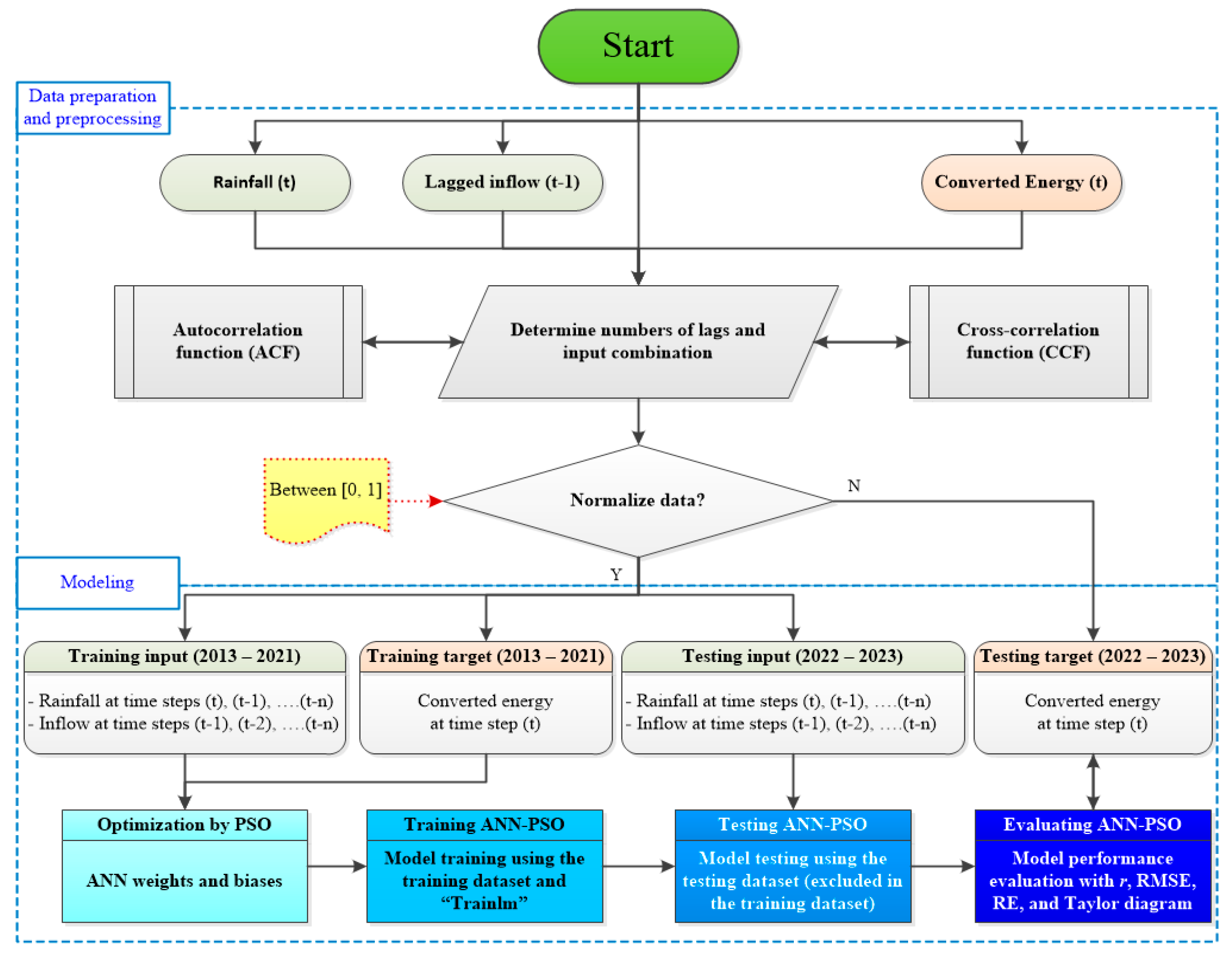
2. Methodology
2.1. Research Framework
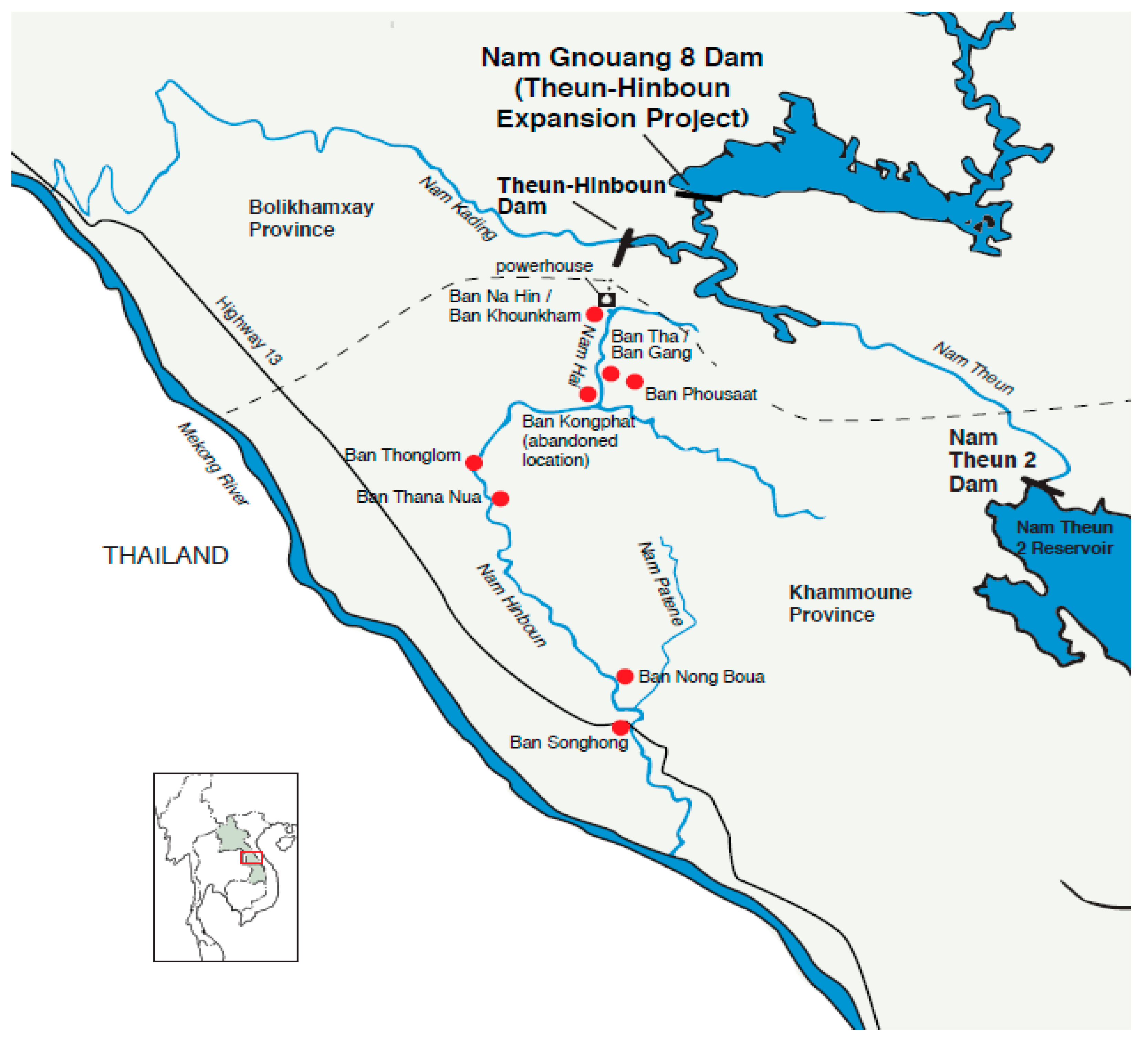
2.2. Study Area
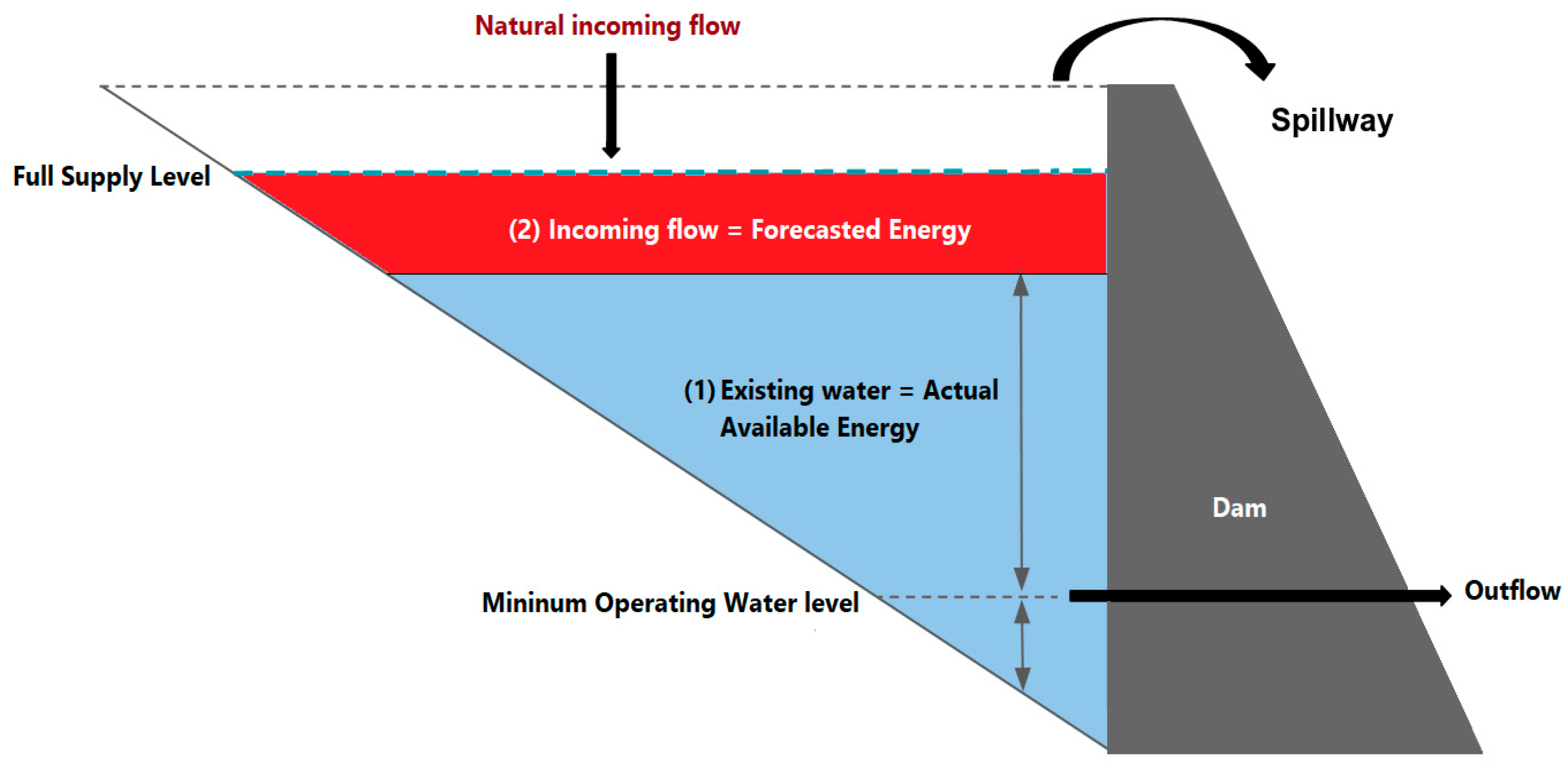
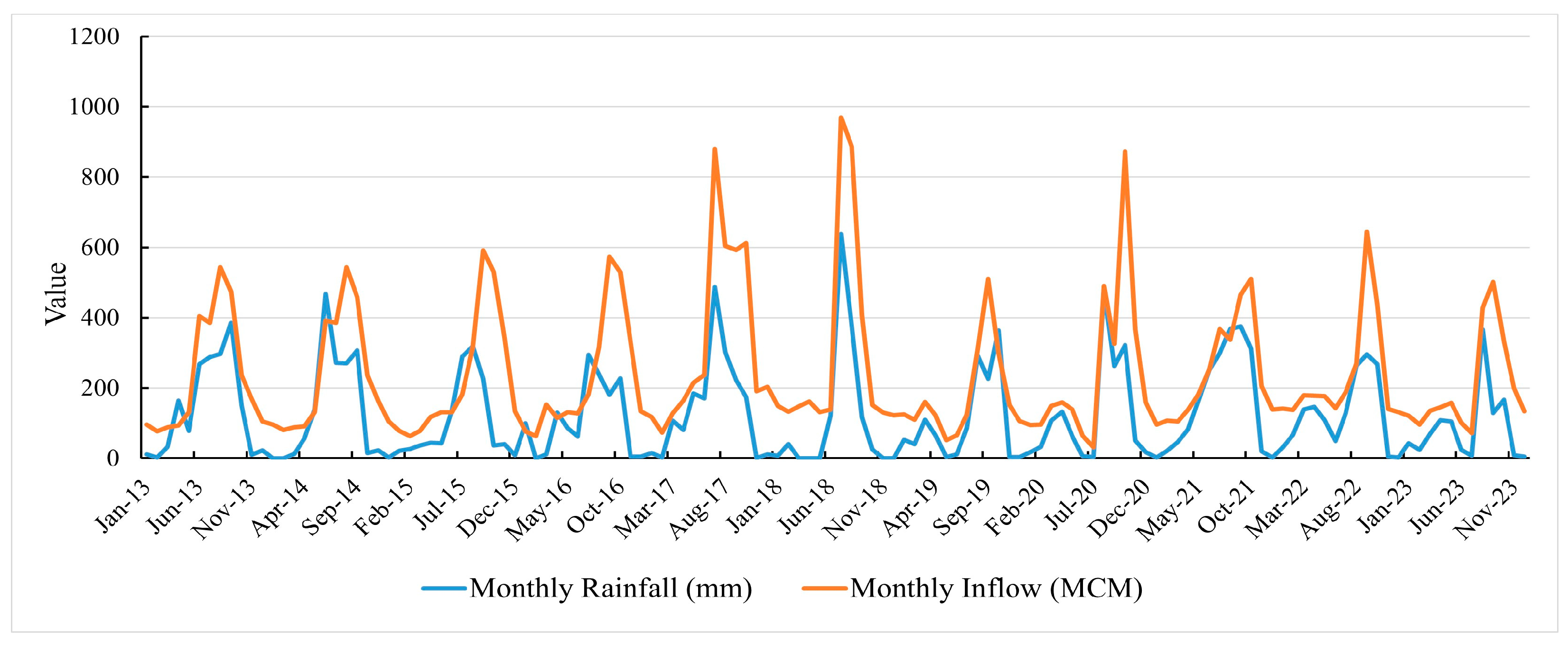
2.3. Data Preparation
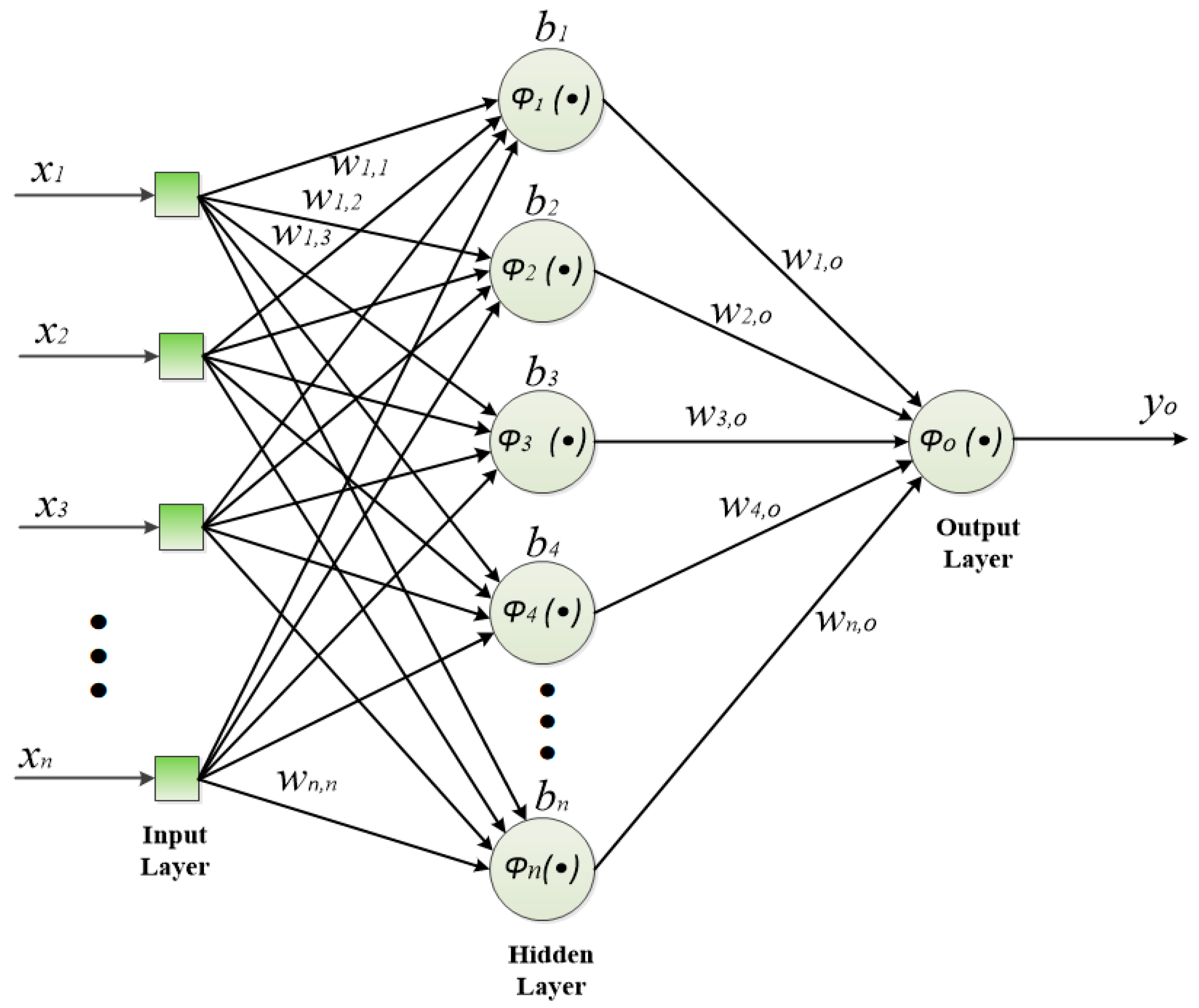
2.4. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
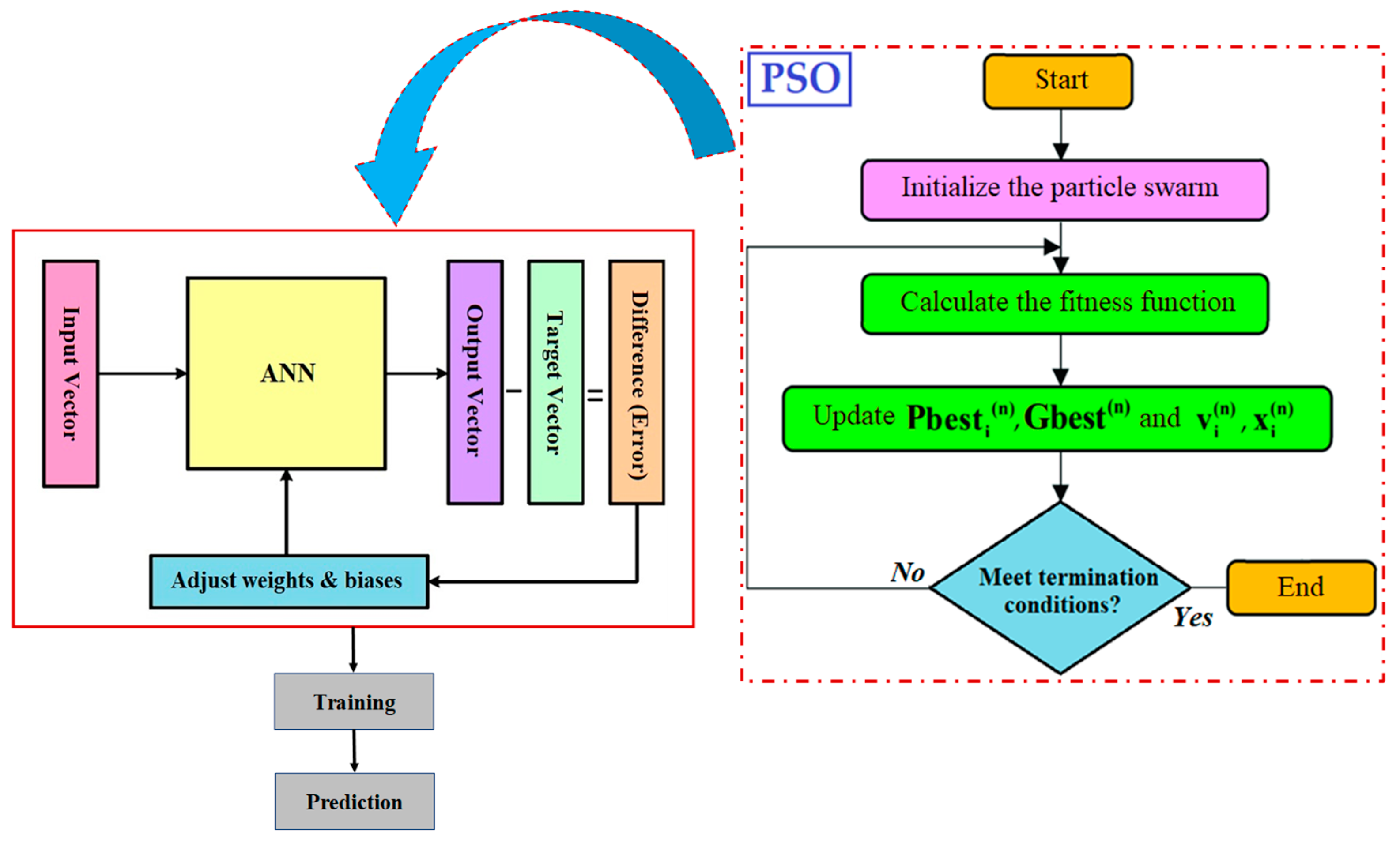
2.5. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
2.6. Proposed PSO-ANN Hybrid Models
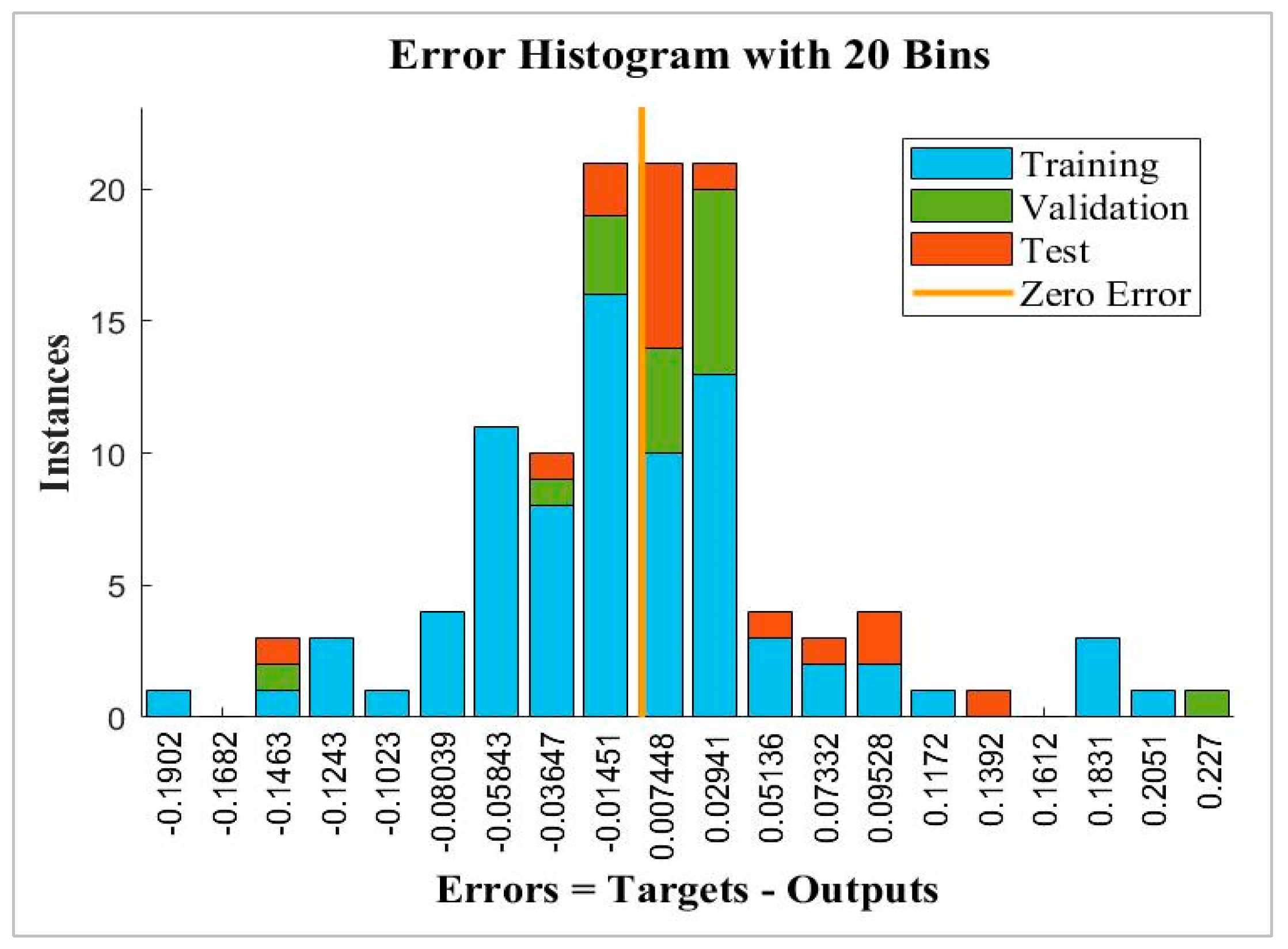
3. Prediction Error
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Hyperparameter Determination
4.2. Results of the Proposed Approach
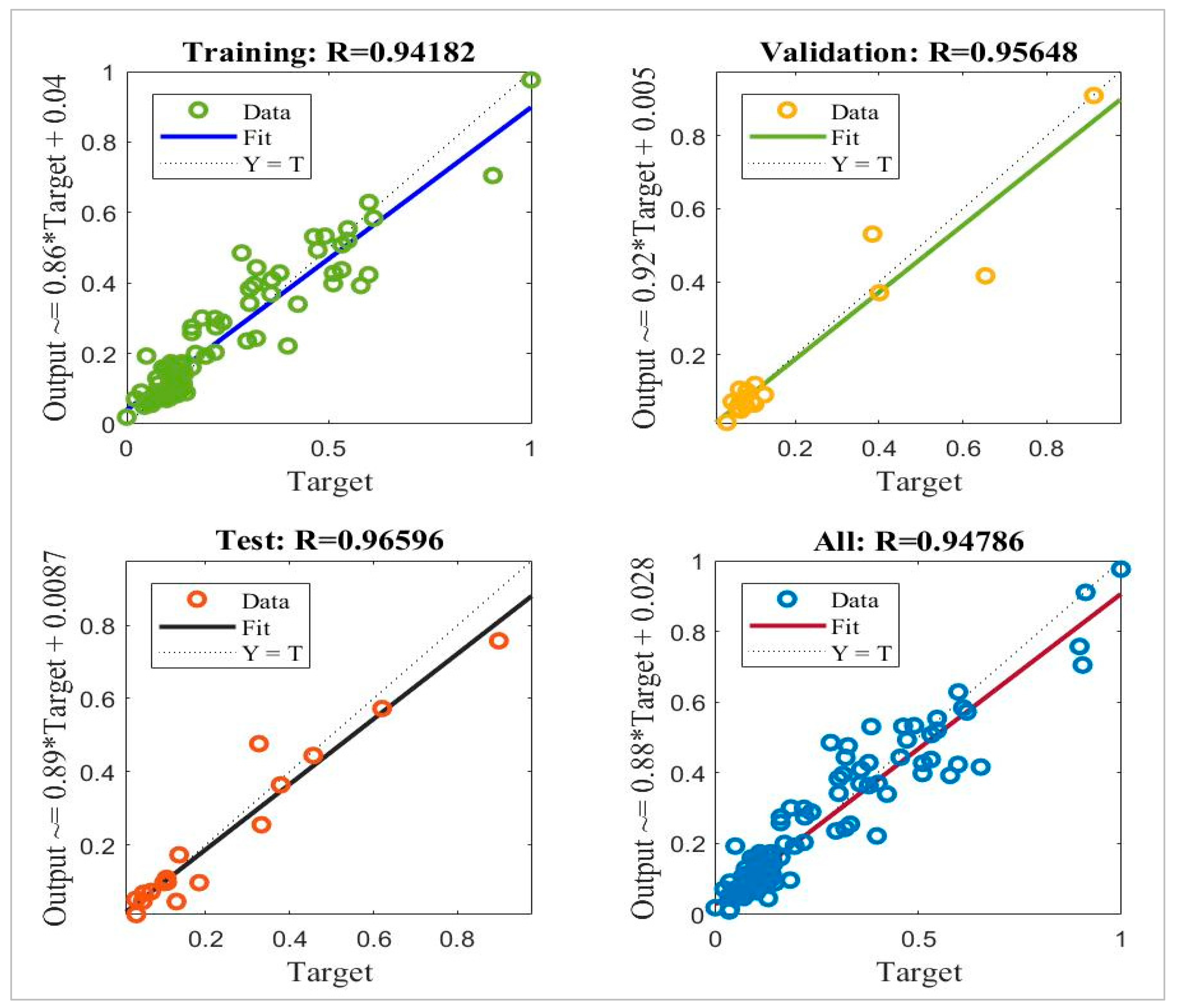
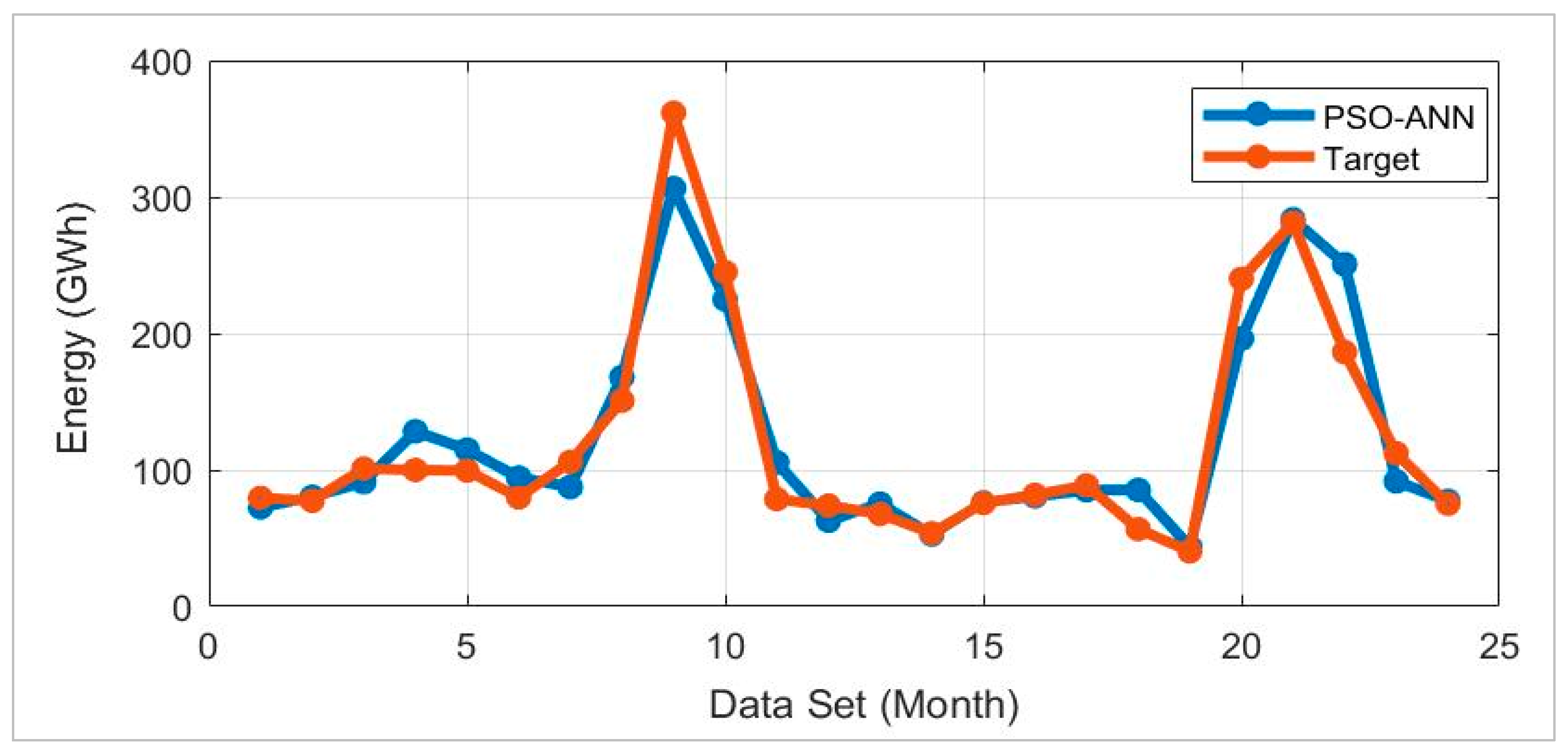
4.3. Training Results
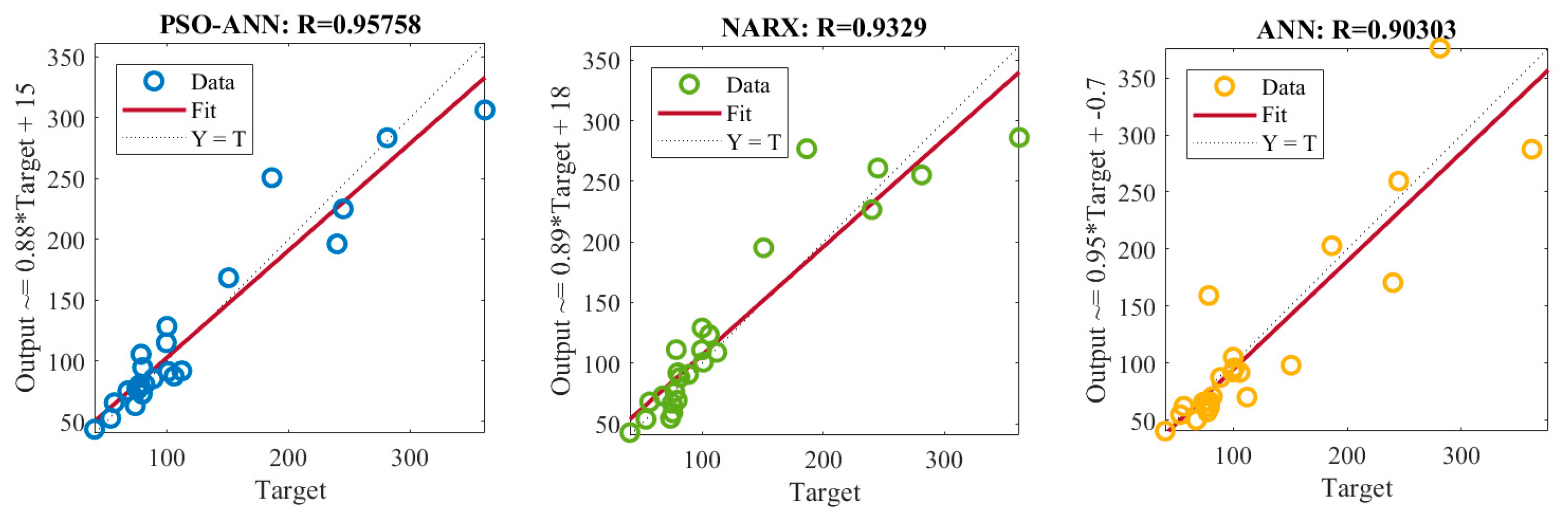
4.4. Comparison of PSO-ANN, ANN and NARX models
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, Y.; Ahmadianfar, I.; Samadi-Koucheksaraee, A.; Azarsa, R.; Scholz, M.; Yaseen, Z.M. An accelerated gradient-based optimization development for multi-reservoir hydropower systems optimization. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 7854–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, C.; Ling, S. Seasonal Inflow Forecasts Using Gridded Precipitation and Soil Moisture Information: Implications for Reservoir Operation. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 3743–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ma, G.; Chen, S.; Huang, W. An Ensemble Modeling Approach to Forecast Daily Reservoir Inflow Using Bidirectional Long- and Short-Term Memory (Bi-LSTM), Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD), and Energy Entropy Method. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 2941–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Anishka, S.; Viksit, P.S.; Arohi, S.; Rehana, S. Improving Short-range Reservoir Inflow Forecasts with Machine Learning Model Combination. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 37, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chang, W.-S.; Dong, Y. Building Energy Prediction Models and Related Uncertainties: A Review. Buildings 2022, 12, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorram, S.; Jehbez, N. A Hybrid CNN-LSTM Approach for Monthly Reservoir Inflow Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 4097–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, S.M.; Othman, F.; Tan, C.G.; Allawi, M.F.; Sherif, M.; El-Shafie, A. Utilizing deep learning machine for inflow forecasting in two different environment regions: a case study of a tropical and semi-arid region. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, S.D.; Ahmed, A.N. A review of deep learning and machine learning techniques for hydrological inflow forecasting. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 12189–12216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, J.A.; Bae, D.-H. Improving ANFIS Based Model for Long-term Dam Inflow Prediction by Incorporating Monthly Rainfall Forecasts. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F. J. , Lo, Y. C., Chen, P. A., Chang, L. C., & Shieh, M. C. Multi-step-ahead reservoir inflow forecasting by artificial intelligence techniques. Smart Innovation System and Technology 2015, 30, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiamsathit, C.; Adeloye, A.J.; Bankaru-Swamy, S. Inflow forecasting using Artificial Neural Networks for reservoir operation. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2019, 373, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Moeini, R.; Ehsanzadeh, E. Artificial Neural Network and Support Vector Machine Models for Inflow Prediction of Dam Reservoir (Case Study: Zayandehroud Dam Reservoir). Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 2203–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorbeh, P.; Noorbeh, P.; Roozbahani, A.; Roozbahani, A.; Moghaddam, H.K.; Moghaddam, H.K. Annual and Monthly Dam Inflow Prediction Using Bayesian Networks. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 2933–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadiyan, P.P.; Moeini, R.; Ehsanzadeh, E.; Karvanpour, M. Trend Analysis of Water Inflow Into the Dam Reservoirs Under Future Conditions Predicted By Dynamic NAR and NARX Models. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 2703–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoon, M.S.; Ahmed, A.N.; Razzaq, A.; Oudah, A.Y.; Alkhayyat, A.; Huang, Y.F.; Kumar, P.; El-Shafie, A. Prediction of hydropower generation via machine learning algorithms at three Gorges Dam, China. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, S.N.; Deo, R.C.; Shojafar, M.; Conti, M.; Shamshirband, S. Computational intelligence approaches for energy load forecasting in smart energy management grids: State of the art, future challenges, and research directions. Smart Grid 2018, 11, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeeni, H.; Bonakdari, H.; Ebtehaj, I. Monthly reservoir inflow forecasting using a new hybrid SARIMA genetic programming approach. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 126, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, L.; Quan, Y.; Miao, Q. A Decomposition-Ensemble Learning Model Based on LSTM Neural Network for Daily Reservoir Inflow Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 4123–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizi, H.; Apaydin, H.; Sattari, M.T.; Colak, M.S.; Sibtain, M. Improving reservoir inflow prediction via rolling window and deep learning-based multi-model approach: case study from Ermenek Dam, Turkey. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 3149–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, M.; Honar, T.; Nikoo, M.R. A fusion-based neural network methodology for monthly reservoir inflow prediction using MODIS products. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 63, 2076–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, N.; Park, J.-H. Particle Swarm Optimization Based Demand Response Using Artificial Neural Network Based Load Prediction. 2023 North American Power Symposium (NAPS).
- Panyadee, P.; Champrasert, P.; Aryupong, C. Water level prediction using artificial neural network with particle swarm optimization model. Natural Disaster Management 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.S.; Ibrahim, R.; Ismail, I. Neural network model with particle swarm optimization for prediction in gas metering systems. Intelligent and Advanced System 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Hassan, M. Artificial Neural Networks and Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithms for Preference Prediction in Multi-Criteria Recommender Systems. Informatics 2018, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlallah, S.O.; Anderson, T.N.; Nates, R.J. Artificial Neural Network–Particle Swarm Optimization (ANN-PSO) Approach for Behaviour Prediction and Structural Optimization of Lightweight Sandwich Composite Heliostats. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 12721–12742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguini, M.; Boutchicha, D.; Nedjar, D. Crack prediction in pipeline using ANN-PSO based on numerical and experimental modal analysis. Smart Structures and System 2021, 27, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wu, J.; Ruan, Y.; Qian, F.; Meng, H.; Gao, Y.; Xu, T. A multi-source transfer learning model based on LSTM and domain adaptation for building energy prediction. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 149, 109024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayed, F.A.; Shell, R.L. Application of Artificial Neural Network Models in Occupational Safety and Health Utilizing Ordinal Variables. Ann. Work. Expo. Heal. 2021, 55, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, F.-Y.; Ma, K.-L. Opening the black box | data driven visualization of neural networks. Computer Science 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Neural Networks in Materials Science. ISIJ Int. 1999, 39, 966–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shami, T.M.; El-Saleh, A.A.; Alswaitti, M.; Al-Tashi, Q.; Summakieh, M.A.; Mirjalili, S. Particle Swarm Optimization: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 10031–10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hao, K.; Chen, L.; Wang, T.; Jiang, C. A novel hybrid particle swarm optimization using adaptive strategy. Inf. Sci. 2021, 579, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semero, Y.K.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, J. A PSO-ANFIS based Hybrid Approach for Short Term PV Power Prediction in Microgrids. Electr. Power Components Syst. 2018, 46, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J. The behavior of particles. In Proceedings of the Transactions on Petri Nets and Other Models of Concurrency XV; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 579–589. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.K.; Hota, H.S.; Brown, K.; Handa, R. Integration of genetic algorithm with artificial neural network for stock market forecasting. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2021, 13, 828–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |



| Design Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Original Weir Dam (run-of-river type): | |
| Concrete Gravity Free Overflow Weir: Spillway radial gates Head Pond Full Supply Level Two concrete-lined headrace tunnels length Installed capacity NG Dam (storage type): Concrete Gravity Dam Reservoir Full Supply Level Max Actual Storage Volume Spillway radial gates Installed capacity |
268 x 27 m (L x H) 2 400 m asl 5,289 m and 5,496 m 2 x 110 MW (+ 220 MW) 480 x 65 m (L x H) 455 m asl 2,430 MCM 5 2 x 30 MW |
| Model Scenario | Input combinations | Output |
|---|---|---|
| SC1 | R(t), I(t-1) | |
| SC2 SC3 SC4 SC5 |
R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) |
E(t) |
| Model Scenarios | Model Input combinations |
Model Output | Different Models |
Model Structures | r | RMSE | RE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA1 PA2 PA3 PA4 PA5 |
R(t), I(t-1) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) |
E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) |
PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN |
(2,30,1) (4,30,1) (5,30,1) (5,30,1) (6,30,1) |
0.951 0.968 0.973 0.942 0.930 |
38.168 33.261 22.994 32.924 34.354 |
8.261 18.459 1.038 7.847 3.662 |
| Model Scenarios | Model Input combinations |
Model Output | Different Models |
Model Structures | r | RMSE | RE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA1 PA2 PA3 PA4 PA5 |
R(t), I(t-1) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) |
E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) |
PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN |
(2,30,1) (4,30,1) (5,30,1) (5,30,1) (6,30,1) |
0.905 0.965 0.966 0.930 0.956 |
44.925 30.668 24.846 36.757 27.934 |
15.059 5.832 2.853 7.928 3.001 |
| Model Scenarios | Model Input combinations |
Model Output | Different Models |
Model Structures | r | RMSE | RE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA1 PA2 PA3 PA4 PA5 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 N1 N2 N3 N4 N5 |
R(t), I(t-1) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), I(t-1) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), I(t-1) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) |
E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) |
PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN ANN ANN ANN ANN ANN NARX NARX NARX NARX NARX |
(2,30,1) (4,30,1) (5,30,1) (5,30,1) (6,30,1) (2,30,1) (4,30,1) (5,30,1) (5,30,1) (6,30,1) (2,30,1) (4,30,1) (5,30,1) (5,30,1) (6,30,1) |
0.951 0.968 0.973 0.942 0.930 0.894 0.900 0.905 0.821 0.775 0.894 0.832 0.939 0.796 0.844 |
38.168 33.261 22.994 32.924 34.354 43.444 55.512 36.851 76.032 55.106 40.182 55.317 30.315 51.605 45.577 |
8.261 18.459 1.038 7.847 3.662 18.178 41.521 7.872 27.723 10.051 3.030 16.462 3.491 7.338 4.250 |
| Model Scenarios | Model Input combinations |
Model Output | Different Models |
Model Structures | r | RMSE | RE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA1 PA2 PA3 PA4 PA5 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 N1 N2 N3 N4 N5 |
R(t), I(t-1) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), I(t-1) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), I(t-1) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2) R(t), R(t-1), R(t-2), I(t-1), I(t-2),I(t-3) |
E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) E(t) |
PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN PSO-ANN ANN ANN ANN ANN ANN NARX NARX NARX NARX NARX |
(2,30,1) (4,30,1) (5,30,1) (5,30,1) (6,30,1) (2,30,1) (4,30,1) (5,30,1) (5,30,1) (6,30,1) (2,30,1) (4,30,1) (5,30,1) (5,30,1) (6,30,1) |
0.905 0.965 0.966 0.930 0.956 0.909 0.873 0.942 0.910 0.821 0.905 0.922 0.960 0.943 0.911 |
44.925 30.668 24.846 36.757 27.934 44.268 51.048 37.238 55.710 57.602 43.566 39.719 28.320 34.179 39.604 |
15.059 5.832 2.853 7.928 3.001 24.058 28.574 3.619 25.550 11.466 14.521 5.724 3.548 6.101 7.106 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





