Submitted:
25 July 2024
Posted:
25 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Study Participants
2.2. Sample Preparation for Metabolite Profiling
2.3. NMR Metabolomic Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Pathway Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Study Participants
3.2. Anthropometric, Clinical and Dietary Intake Changes Following 6-Month Intervention
3.3. Multivariate Analysis
3.4. Identification and Relative Quantification of Metabolites
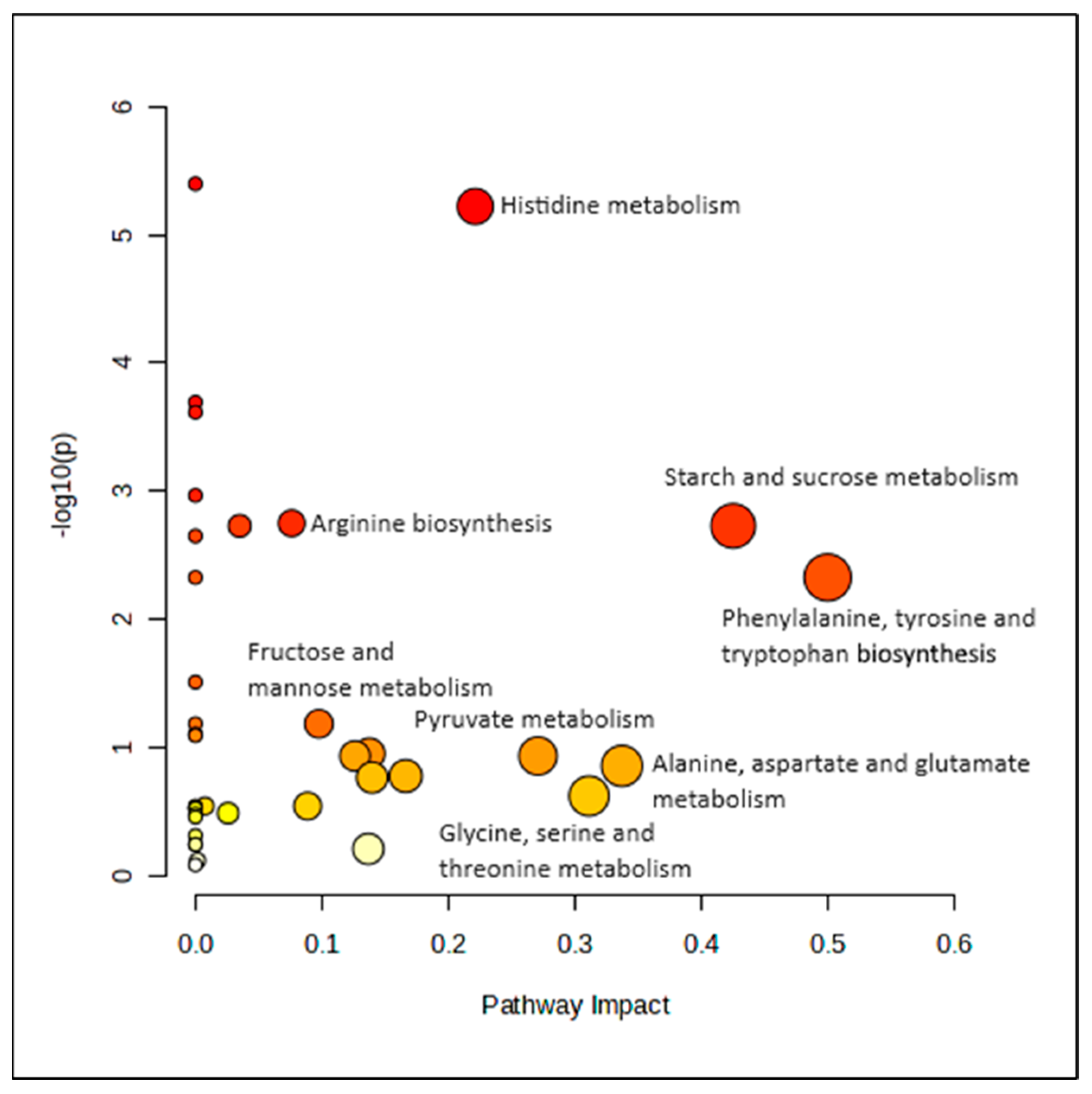
3.5. Pathway Analysis
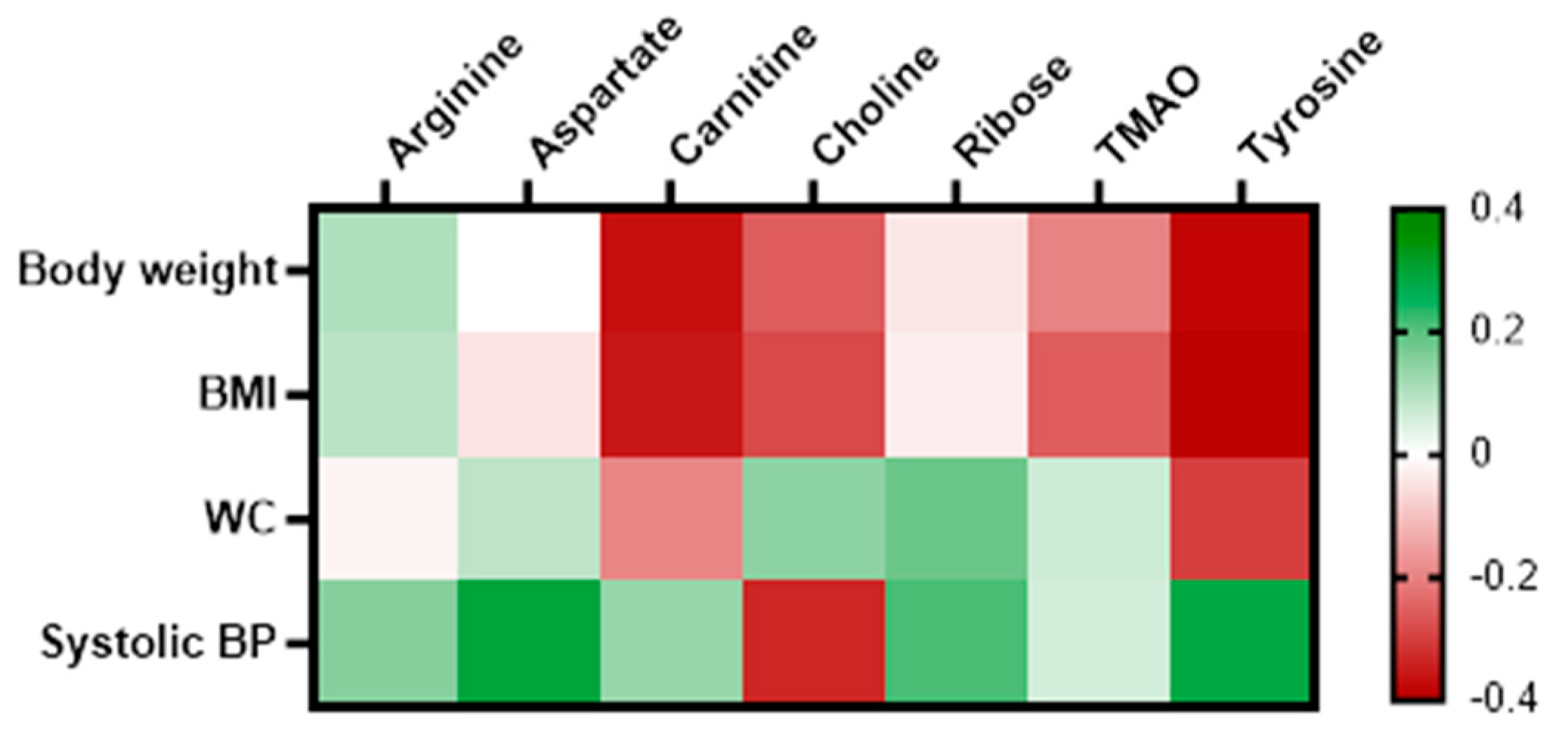
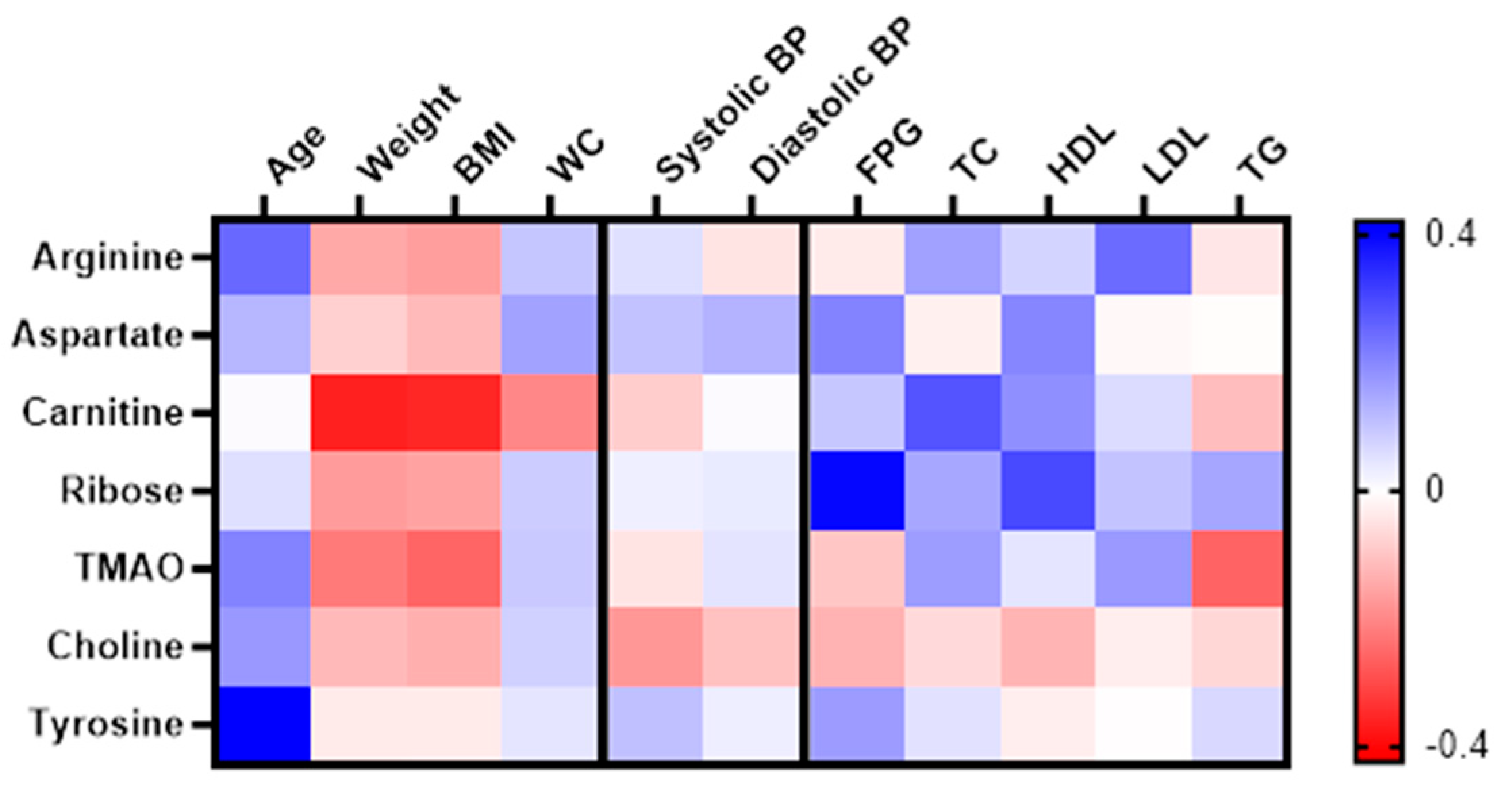
3.6. Correlation between the Significantly Changed Metabolites with Anthropometry and Clinical Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight Fact Sheets. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
- IPH. National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS) 2023 Fact Sheet. Available online: https://iku.gov.my/nhms-2023.
- Hu, F.B. Globalization of diabetes: the role of diet, lifestyle, and genes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, P.; Giles, T.D.; Bray, G.A.; Hong, Y.; Stern, J.S.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Eckel, R.H. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: Pathophysiology, Evaluation, and Effect of Weight Loss. Circulation 2006, 113, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palau-Rodriguez, M.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Minarro, A.; Bernal-Lopez, M.R.; Brunius, C.; Gomez-Huelgas, R.; Landberg, R.; Tinahones, F.J.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Effects of a long-term lifestyle intervention on metabolically healthy women with obesity: Metabolite profiles according to weight loss response. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksandrova, K.; Egea Rodrigues, C.; Floegel, A.; Ahrens, W. Omics Biomarkers in Obesity: Novel Etiological Insights and Targets for Precision Prevention. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochfort, S. Metabolomics Reviewed: A New “Omics” Platform Technology for Systems Biology and Implications for Natural Products Research. Journal of Natural Products 2005, 68, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Aziz, N.S.; Shahar, S.; Ambak, R.; Mohamad Nor, N.S.; Jamil, A.T.; Aris, T. Influence of co-morbidity on body composition changes after weight loss intervention among overweight housewives: a follow-up study of the MyBFF@home. BMC Womens Health 2018, 18, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liyana, A.Z.; Appannah, G.; Sham, S.Y.Z.; Fazliana, M.; Nor, N.S.M.; Ambak, R.; Samad, A.A.; Dahlan, N.Y.; Aris, T. Effectiveness of a community-based intervention for weight loss on cardiometabolic risk factors among overweight and obese women in a low socio-economic urban community: findings of the MyBFF@home. BMC Womens Health 2018, 18, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, F.; Mohamad Nor, N.S.; Appannah, G.; Zaki, N.A.M.; Ambak, R.; Omar, A.; Fazliana, M.; Salleh, R.; Yusof, B.N.M.; Muksan, N.; et al. Prediction of body fat loss in relation to change in nutrient intake among housewives participating in the MyBFF@home study. BMC Womens Health 2018, 18, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yoo, H.J.; Ko, J.; Lee, J.H. Metabolically unhealthy overweight individuals have high lysophosphatide levels, phospholipase activity, and oxidative stress. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulidiani; Abas, F.; Khatib, A.; Perumal, V.; Suppaiah, V.; Ismail, A.; Hamid, M.; Shaari, K.; Lajis, N.H. Metabolic alteration in obese diabetes rats upon treatment with Centella asiatica extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 180, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Hui, F.; Xu, L.; Viau, C.; Spigelman, A.F.; MacDonald, P.E.; Wishart, D.S.; Li, S.; et al. MetaboAnalyst 6.0: towards a unified platform for metabolomics data processing, analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W398–W406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, N.D.; Stevens, R.D.; Antinozzi, P.A.; Anderson, A.; Bergman, R.N.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Newgard, C.B.; Bowden, D.W. Metabolomic profile associated with insulin resistance and conversion to diabetes in the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh, H.; Emamgholipour, S.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Arjmand, B.; Rezaei, N.; Dilmaghani-Marand, A.; Ghasemi, E.; Panahi, N.; Dehghanbanadaki, H.; Ghodssi-Ghassemabadi, R.; et al. The association between acylcarnitine and amino acids profile and metabolic syndrome and its components in Iranian adults: Data from STEPs 2016. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1058952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.J.; Kwak, S.Y.; Jo, G.; Song, T.J.; Shin, M.J. Serum metabolite profile associated with incident type 2 diabetes in Koreans: findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, C.; Oh, S.F.; Wada, S.; Rowe, G.C.; Liu, L.; Chan, M.C.; Rhee, J.; Hoshino, A.; Kim, B.; Ibrahim, A.; et al. A branched-chain amino acid metabolite drives vascular fatty acid transport and causes insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanweert, F.; Schrauwen, P.; Phielix, E. Role of branched-chain amino acid metabolism in the pathogenesis of obesity and type 2 diabetes-related metabolic disturbances BCAA metabolism in type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2022, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottosson, F.; Smith, E.; Ericson, U.; Brunkwall, L.; Orho-Melander, M.; Di Somma, S.; Antonini, P.; Nilsson, P.M.; Fernandez, C.; Melander, O. Metabolome-Defined Obesity and the Risk of Future Type 2 Diabetes and Mortality. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, T.; Rohrmann, S.; Sookthai, D.; Johnson, T.; Katzke, V.; Kaaks, R.; von Eckardstein, A.; Muller, D. Intra-individual variation of plasma trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), betaine and choline over 1 year. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, R.; Merz, B.; Rist, M.J.; Ferrario, P.G.; Bub, A.; Kulling, S.E.; Watzl, B. Associations of current diet with plasma and urine TMAO in the KarMeN study: direct and indirect contributions. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgitta Venho, S.V., Veli-Pekka Valkonen, Jyrki Virtanen, Timo A Lakka, Tiina H Rissanen, Marja-Leena Ovaskainen, Matti Laitinen, and Jukka T Salonen. Arginine intake, blood pressure, and the incidence of acute coronary events in men: the Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 359 - 364.
- Zell, J.A.; Taylor, T.H.; Albers, C.G.; Carmichael, J.C.; McLaren, C.E.; Wenzel, L.; Stamos, M.J. Phase IIa Clinical Biomarker Trial of Dietary Arginine Restriction and Aspirin in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, Y.F.; Sun, X.Y.; Han, L.; Li, S.N.; Gu, W.Q.; Song, M.; Jiang, C.T.; Yang, X.; Fang, Z.Z. Plasma tyrosine and its interaction with low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Akter, S.; Kuwahara, K.; Matsushita, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Konishi, M.; Honda, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Hayashi, T.; Noda, M.; et al. Serum amino acid profiles and risk of type 2 diabetes among Japanese adults in the Hitachi Health Study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darst, B.F.; Koscik, R.L.; Hogan, K.J.; Johnson, S.C.; Engelman, C.D. Longitudinal plasma metabolomics of aging and sex. Aging 2019, 11, 1262–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talenezhad, N.; Mohammadi, M.; Ramezani-Jolfaie, N.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H.; Salehi-Abargouei, A. Effects of l-carnitine supplementation on weight loss and body composition: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 37 randomized controlled clinical trials with dose-response analysis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 37, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeva-Andany, M.M.; Calvo-Castro, I.; Fernandez-Fernandez, C.; Donapetry-Garcia, C.; Pedre-Pineiro, A.M. Significance of l-carnitine for human health. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 578–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schooneman, M.G.; Napolitano, A.; Houten, S.M.; Ambler, G.K.; Murgatroyd, P.R.; Miller, S.R.; Hollak, C.E.; Tan, C.Y.; Virtue, S.; Vidal-Puig, A.; et al. Assessment of plasma acylcarnitines before and after weight loss in obese subjects. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 606, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ceglarek, U.; Huang, T.; Li, L.; Rood, J.; Ryan, D.H.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Schwarzfuchs, D.; Thiery, J.; et al. Weight-loss diets and 2-y changes in circulating amino acids in 2 randomized intervention trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tochikubo, O.; Nakamura, H.; Jinzu, H.; Nagao, K.; Yoshida, H.; Kageyama, N.; Miyano, H. Weight loss is associated with plasma free amino acid alterations in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Nutr. Diabetes 2016, 6, e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, P.K.; Pekkala, S.; Autio, R.; Munukka, E.; Xu, L.; Saltevo, J.; Cheng, S.; Kujala, U.M.; Alen, M.; Cheng, S. Serum metabolic profiles in overweight and obese women with and without metabolic syndrome. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Tseng, Y.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Tsai, Y.S.; Chang, C.S.; Kuo, T.C.; Yao, W.J.; Shieh, C.C.; Wu, C.H.; Kuo, P.H. The metabolome profiling and pathway analysis in metabolic healthy and abnormal obesity. Int J Obes (Lond) 2015, 39, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libert, D.M.; Nowacki, A.S.; Natowicz, M.R. Metabolomic analysis of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes: amino acid and acylcarnitine levels change along a spectrum of metabolic wellness. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randrianarisoa, E.; Lehn-Stefan, A.; Wang, X.; Hoene, M.; Peter, A.; Heinzmann, S.S.; Zhao, X.; Konigsrainer, I.; Konigsrainer, A.; Balletshofer, B.; et al. Relationship of Serum Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) Levels with early Atherosclerosis in Humans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Zhou, J.; Fu, Q.; Xu, X.; Wei, S.; Yang, S.; Chen, B. The associations between TMAO-related metabolites and blood lipids and the potential impact of rosuvastatin therapy. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Bonder, M.J.; Cenit, M.C.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Maatman, A.; Dekens, J.A.; Brandsma, E.; Marczynska, J.; Imhann, F.; Weersma, R.K.; et al. The Gut Microbiome Contributes to a Substantial Proportion of the Variation in Blood Lipids. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaumont, M.; Portune, K.J.; Steuer, N.; Lan, A.; Cerrudo, V.; Audebert, M.; Dumont, F.; Mancano, G.; Khodorova, N.; Andriamihaja, M.; et al. Quantity and source of dietary protein influence metabolite production by gut microbiota and rectal mucosa gene expression: a randomized, parallel, double-blind trial in overweight humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bel Lassen, P.; Belda, E.; Prifti, E.; Dao, M.C.; Specque, F.; Henegar, C.; Rinaldi, L.; Wang, X.; Kennedy, S.P.; Zucker, J.D.; et al. Protein supplementation during an energy-restricted diet induces visceral fat loss and gut microbiota amino acid metabolism activation: a randomized trial. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrier, M.; Shih, D.M.; Burrows, A.C.; Ferguson, D.; Gromovsky, A.D.; Brown, A.L.; Marshall, S.; McDaniel, A.; Schugar, R.C.; Wang, Z.; et al. The TMAO-Generating Enzyme Flavin Monooxygenase 3 Is a Central Regulator of Cholesterol Balance. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canyelles, M.; Tondo, M.; Cedo, L.; Farras, M.; Escola-Gil, J.C.; Blanco-Vaca, F. Trimethylamine N-Oxide: A Link among Diet, Gut Microbiota, Gene Regulation of Liver and Intestine Cholesterol Homeostasis and HDL Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepandi, M.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Qobady, S.; Taghdir, M. Effect of L-Arginine supplementation on lipid profiles and inflammatory markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cӑtoi, A.F.; Parvu, A.E.; Andreicut, A.D.; Mironiuc, A.; Crӑciun, A.; Cӑtoi, C.; Pop, I.D. Metabolically Healthy versus Unhealthy Morbidly Obese: Chronic Inflammation, Nitro-Oxidative Stress, and Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Bhatta, A.; Xu, Z.; Chen, J.; Toque, H.A.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Bagi, Z.; Lucas, R.; Huo, Y.; et al. Obesity-induced vascular inflammation involves elevated arginase activity. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 313, R560–R571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovamees, O.; Shemyakin, A.; Eriksson, M.; Angelin, B.; Pernow, J. Arginase inhibition improves endothelial function in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia irrespective of their cholesterol levels. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 279, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui-Li Yang, Y.-H.S., Gang Hao, Wu Li, Guo-Wei Le. Increasing Oxidative Stress with Progressive Hyperlipidemia in Human: Relation between Malondialdehyde and Atherogenic Index. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2008, 154 - 158.
- Bian, F.; Cui, J.; Zheng, T.; Jin, S. Reactive oxygen species mediate angiotensin II-induced transcytosis of low-density lipoprotein across endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbaghi, O.; Kashkooli, S.; Amini, M.R.; Shahinfar, H.; Djafarian, K.; Clark, C.C.T.; Shab-Bidar, S. The effects of L-carnitine supplementation on lipid concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Res. 2020, 12, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musazadeh, V.; Alinejad, H.; Esfahani, N.K.; Kavyani, Z.; Keramati, M.; Roshanravan, N.; Mosharkesh, E.; Dehghan, P. The effect of L-carnitine supplementation on lipid profile in adults: an umbrella meta-analysis on interventional meta-analyses. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1214734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xu, Y.; He, T.; He, R. d-Ribose contributes to the glycation of serum protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 2285–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.M.; Rawat, D.; Weinstein, L.S.; Gupte, S.A.; Richards, W.O. Effects of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase activity in obese type 2 diabetics. Surgical Endoscopy 2011, 26, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.J.; Choe, S.S.; Sohn, J.H.; Kim, J.B. The role of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Adipocyte 2017, 6, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, M.; Choe, S.S.; Shin, K.C.; Choi, G.; Kim, J.-W.; Noh, J.-R.; Kim, Y.-H.; Ryu, J.-w.; Yoon, K.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; et al. Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency Improves Insulin Resistance with Reduced Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2624–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, E.S.; Lee, M.H.; Murphy, R.E.; Malloy, C.R. Pentose phosphate pathway activity parallels lipogenesis but not antioxidant processes in rat liver. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 314, E543–E551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Woloshynowych, M.; Britto, J.C.; Bilkevic, I.; Glassar, B.; Chapman, S.; Ford-Adams, M.E.; Desai, A.; Bain, M.; Tewfik, I.; et al. Obesity, oxidative DNA damage and vitamin D as predictors of genomic instability in children and adolescents. International Journal of Obesity 2021, 45, 2095–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, T.; Yang, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tong, X. The Role of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway in Diabetes and Cancer. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, B.; Shu, H.; Zhang, L.; Bao, M.; Yi, W.; Tan, Y.; Ji, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. Human serum metabolomic analysis reveals progression for high blood pressure in type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| MHO | MUO | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n=36 | n=34 | ||||
| Age (year), mean ± SD | 41.65 ± 8.46 | 50.01 ± 6.26 | <0.001* | ||
| Age group (year), n, % | |||||
| 18 - 39 | 12 | 33.3 | 3 | 8.8 | 0.004* |
| 40 -49 | 18 | 50 | 14 | 41.2 | |
| ≥ 50 | 6 | 16.7 | 17 | 50 | |
| Race, n, % | |||||
| Malay | 33 | 91.7 | 30 | 88.2 | 0.706 |
| Indian | 3 | 8.3 | 4 | 11.8 | |
| Level of education, n, % | |||||
| Primary school | 3 | 8.6 | 13 | 39.4 | |
| Secondary school/ tertiary education | 32 | 91.4 | 20 | 60.6 | 0.003* |
| Household income (RM), n, % | |||||
| ≤ 1500 | 12 | 33.3 | 23 | 67.6 | |
| 1501 - 2500 | 15 | 41.7 | 7 | 20.6 | 0.016* |
| ≥ 2501 | 9 | 25 | 4 | 11.8 | |
| Family history, n, % | |||||
| Diabetes | 11 | 31.4 | 15 | 44.1 | 0.326 |
| Hypertension | 16 | 44.4 | 20 | 60.6 | 0.230 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 3 | 8.3 | 6 | 18.2 | 0.294 |
| Body weight (kg) | 71.20 ± 11.39 | 75.32 ± 10.27 | 0.117 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.66 ± 4.05 | 31.64 ± 3.45 | 0.031* | ||
| Waist circumference (cm) | 91.07 ± 9.11 | 96.93 ± 7.94 | 0.006* | ||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 113.76 ± 11.67 | 133.06 ± 20.13 | <0.001* | ||
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 73.06 ± 10.11 | 84.02 ± 12.98 | <0.001* | ||
| FPG (mmol/L) | 5.19 ± 0.55 | 6.21 ± 1.63 | 0.001* | ||
| HbA1c (%) | 5.35 ± 0.55 | 6.05 ± 1.05 | 0.002* | ||
| TC (mmol/L) | 5.44 ± 1.18 | 5.30 ± 0.89 | 0.590 | ||
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.31 ± 0.30 | 1.32 ± 0.22 | 0.888 | ||
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 3.95 ± 1.46 | 3.98 ± 0.87 | 0.922 | ||
| Triglyceride (TG) (mmol/L) | 1.15 ± 0.56 | 1.35 ± 0.47 | 0.129 | ||
| Variables | Group | Estimated marginal means (95% CI) | Mean difference (%) |
Within group | Between group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 6th month | p | Wald Chi-Square | p | |||
| Body weight (kg) | MHO | 69.68 (65.41, 73.94) | 69.52 (65.24, 73.80) | -0.156 (-0.23) | 0.719 | 8.125 | 0 .043 |
| MUO | 72.64 (68.79, 76.50) | 71.72 (67.93, 75.51) | -0.926 (-1.30) | 0.015 | |||
| BMI | MHO | 30.78 (30.52, 31.03) | 30.74 (30.33, 31.16) | -0.034 (-0.11) | 0.853 | 5.464 | 0.141 |
| MUO | 30.79 (30.54, 31.04) | 30.43 (30.06, 30.79) | -0.362 (-1.17) | 0.023 | |||
| WC (cm) | MHO | 90.01 (85.67, 94.35) | 92.77 (88.74, 96.81) | 2.761 (3.05) | 0.483 | 12.306 | 0 .006 |
| MUO | 93.18 (91.64, 94.73) | 90.86 (89.06, 92.67) | -2.322 (-2.48) | <0.001 | |||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | MHO | 117.52 (111.38, 123.66) | 121.00 (111.45, 127.56) | 3.486 (2.91) | 0.105 | 7.321 | 0.062 |
| MUO | 123.95 (119.64, 128.27) | 114.65 (104.69, 124.61) | -9.309 (-7.36) | 0.049 | |||
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | MHO | 75.24 (69.39, 81.09) | 76.57 (69.81, 83.34) | 1.333 (1.76) | 0.523 | 4.629 | 0.201 |
| MUO | 80.43 (75.43, 85.43) | 76.68 (68.91, 84.45) | -3.750 (-4.63) | 0.226 | |||
| Glucose (mmol/L) | MHO | 6.44 (5.75, 7.54) | 6.51 (5.94, 7.08) | -0.139 (-2.16) | 0.679 | 0.268 | 0.966 |
| MUO | 6.53 (5.69, 7.37) | 6.43 (5.48, 7.37) | -0.101 (-1.61) | 0.847 | |||
| TC (mmol/L) | MHO | 5.91 (4.65, 7.16) | 6.02 (5.17, 6.88) | 0.113 (1.93) | 0.802 | 0.444 | 0.931 |
| MUO | 6.14 (5.26, 7.03) | 6.21 (5.34, 7.07) | 0.064 (1.05) | 0.676 | |||
| HDL (mmol/L) | MHO | 1.64 (1.16, 2.13) | 1.51 (1.30, 1.72) | -0.130 (-8.18) | 0.518 | 3.656 | 0.301 |
| MUO | 1.49 (1.21, 1.77) | 1.54 (1.26, 1.82) | 0.053 (3.71) | 0.089 | |||
| LDL (mmol/L) | MHO | 4.66 (3.53, 5.78) | 4.96 (4.03, 5.89) | 0.305 (6.56) | 0.378 | 1.515 | 0.679 |
| MUO | 4.79 (3.98, 5.61) | 4.93 (4.19, 5.67) | 0.134 (2.80) | 0.461 | |||
| TG (mmol/L) | MHO | 2.18 (1.59, 2.77) | 1.95 (1.57, 2.33) | -0.229 (-10.13) | 0.358 | 3.84 | 0.279 |
| MUO | 1.70 (1.32, 2.09) | 1.77 (1.31, 2.23) | 0.062 (3.46) | 0.539 | |||
| Calorie intake | MHO | 1559.99 (1308.06, 1811.93) | 1148.70 (915.12, 1382.28) | -411.29 (-26.36) | <0.001 | 17.287 | <0.001 |
| MUO | 1315.36 (1105.33, 1525.39) | 1082.19 (855.40, 1308.98) | -233.17 (-17.73) | 0.014 | |||
| Carbohydrate | MHO | 201.41 (167.84, 234.97) | 152.50 (118.03, 186.98) | -48.90 (-24.28) | 0.005 | 12.353 | 0.006 |
| MUO | 169.12 (140.16, 198.08) | 142.85 (109.04, 176.66) | -26.27 (-15.53) | 0.046 | |||
| Cholesterol | MHO | 224.64 (173.93, 275.34) | 139.40 (83.97, 194.84) | -85.23 (-37.94) | 0.007 | 11.117 | 0.011 |
| MUO | 168.70 (125.87, 211.53) | 139.96 (93.60, 186.32) | -28.74 (-17.04) | 0.066 | |||
| Dietary fiber | MHO | 8.13 (5.11, 11.15) | 5.39 (2.85, 7.92) | -2.74 (-33.70) | 0.011 | 11.429 | 0.01 |
| MUO | 6.95 (4.41, 9.48) | 4.82 (2.16, 7.48) | -2.13 (-30.65) | 0.036 | |||
| Potassium | MHO | 1057.04 (836.51, 1277.57) | 846.48 (619.61, 1073.35) | -210.56 (-19.92) | 0.023 | 11.097 | 0.011 |
| MUO | 969.53 (778.77, 1160.29) | 773.54 (564.77, 982.31) | -195.99 (-20.21) | 0.016 | |||
| Protein | MHO | 60.37 (49.24, 71.49) | 43.84 (32.56, 55.12) | -16.53 (-27.38) | 0.003 | 19.53 | <0.001 |
| MUO | 54.29 (44.73, 63.84) | 40.25 (30.23, 50.28) | -14.04 (-25.86) | 0.001 | |||
| Saturated fat | MHO | 15.32 (11.65, 19.00) | 11.75 (8.09, 15.40) | -3.58 (-23.37) | 0.024 | 15.063 | 0.002 |
| MUO | 11.93 (9.10, 14.75) | 8.57 (5.18, 11.96) | -3.36 (-28.16) | 0.009 | |||
| Sodium | MHO | 2188.44 (1748.27, 2628.61) | 1685.29 (1314.10, 2056.48) | -503.15 (-22.99) | 0.021 | 8.721 | 0.033 |
| MUO | 1441.14 (1044.33, 1837.95) | 1370.37 (907.81, 1832.93) | -70.77 (-4.91) | 0.643 | |||
| Total fat | MHO | 58.76 (46.94, 70.58) | 41.61 (30.99, 52.22) | -17.16 (-29.20) | <0.001 | 16.557 | <0.001 |
| MUO | 46.12 (36.83, 55.40) | 37.76 (28.56, 46.95) | -8.36 (-18.13) | 0.038 | |||
| Metabolites | MHO (n=36) | MUO (n=34) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | |||
| Glucose | 4.16 ± 0.06 | 4.25 ± 0.14 | 0.001 |
| Indole-3-acetate | 2.67 ± 0.16 | 2.75 ± 0.20 | 0.047 |
| τ-methylhistidine | 2.73 ± 0.15 | 2.82 ± 0.16 | 0.021 |
| 6th month | |||
| Acetate | 2.58 ± 0.26 | 2.71 ± 0.27 | 0.030 |
| Arginine | 2.57 ± 0.31 | 2.75 ± 0.27 | 0.014 |
| Aspartate | 3.00 ± 0.21 | 3.15 ± 0.11 | <0.001 |
| Betaine | 2.73 ± 0.12 | 2.85 ± 0.16 | 0.001 |
| Fructose | 3.49 ± 0.08 | 3.44 ± 0.08 | 0.044 |
| Glucose | 4.15 ± 0.08 | 4.23 ± 0.12 | 0.002 |
| Histidine | 2.77 ± 0.19 | 2.92 ± 0.12 | <0.001 |
| Isobutyrate | 2.69 ± 0.12 | 2.77 ± 0.17 | 0.025 |
| Isoleucine | 2.87 ± 0.19 | 2.98 ± 0.24 | 0.031 |
| Leucine | 2.67 ± 0.26 | 2.82 ± 0.35 | 0.049 |
| N-acetylcysteine | 2.63 ± 0.19 | 2.72 ± 0.18 | 0.030 |
| Phenylacetate | 2.82 ± 0.21 | 2.94 ± 0.25 | 0.024 |
| TMAO | 2.66 ± 0.12 | 2.77 ± 0.14 | 0.001 |
| Tyrosine | 3.12 ± 0.19 | 3.24 ± 0.18 | 0.014 |
| Valine | 2.93 ± 0.17 | 3.02 ± 0.18 | 0.037 |
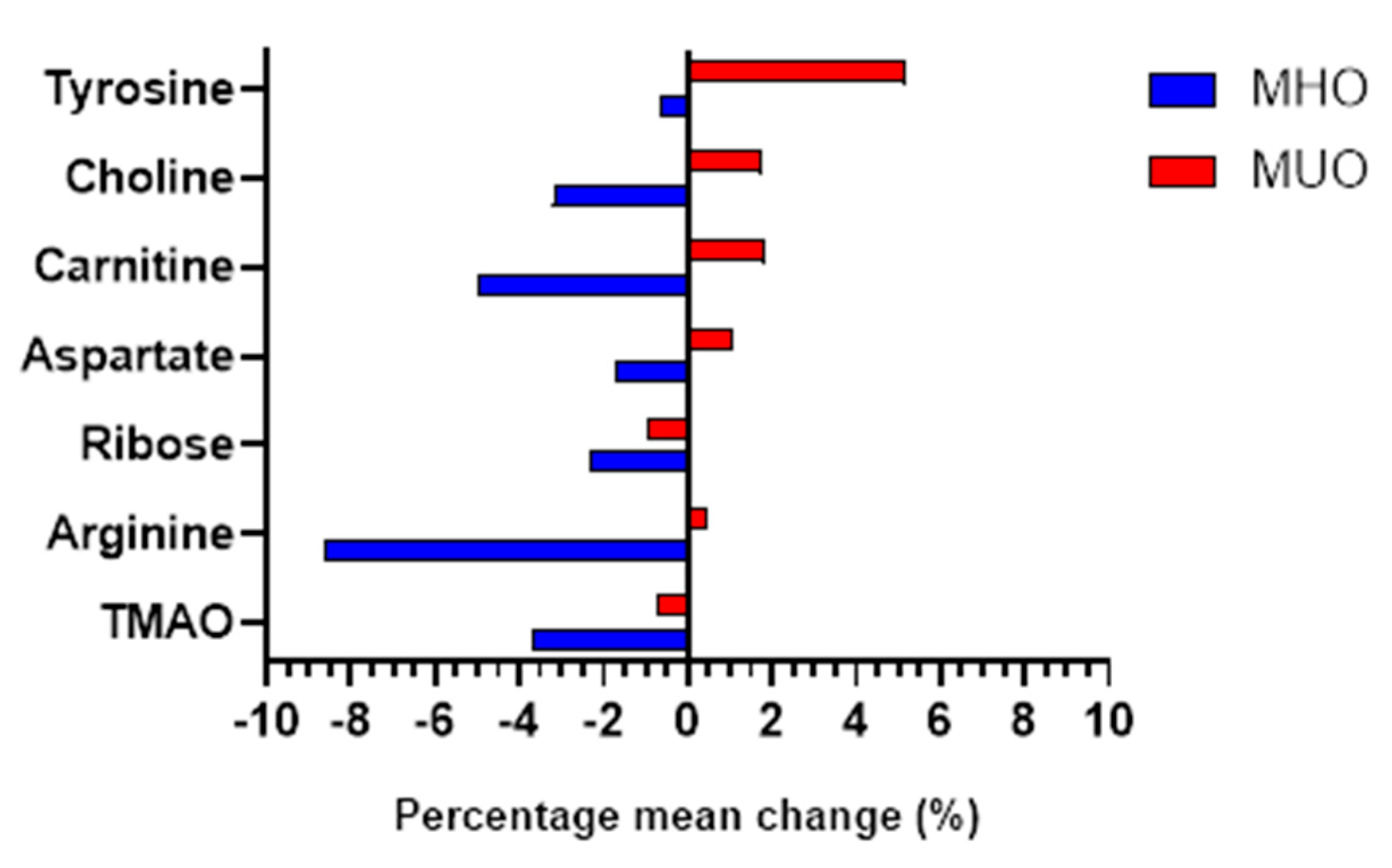
| Metabolites | Group | Baseline | 6th month | Mean difference (%) |
Within group | Between group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | p | |||||
| TMAO | MHO | 2.80 (2.72, 2.88) | 2.70 (2.62, 2.77) | -0.103 (-3.68) | <0.001 | < 0.001 |
| MUO | 2.79 (2.71, 2.87) | 2.77 (2.69, 2.85) | -0.021(-0.75) | 0.387 | ||
| Arginine | MHO | 2.89 (2.76, 3.02) | 2.64 (2.51, 2.77) | -0.249 (-8.62) | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| MUO | 2.80 (2.67, 2.94) | 2.81 (2.69, 2.94) | 0.012 (0.43) | 0.835 | ||
| Ribose | MHO | 3.64 (3.56, 3.71) | 3.55 (3.48, 3.62) | -0.084 (-2.31) | 0.008 | 0.002 |
| MUO | 3.67 (3.61, 3.72) | 3.63 (3.57, 3.70) | -0.034 (-0.93) | 0.079 | ||
| Aspartate | MHO | 3.09 (2.97, 3.21) | 3.04 (2.93, 3.15) | -0.054 (-1.75) | 0.152 | 0.005 |
| MUO | 3.20 (3.11, 3.28) | 3.23 (3.15, 3.31) | 0.034 (1.06) | 0.142 | ||
| Carnitine | MHO | 2.78 (2.68, 2.89) | 2.65 (2.53, 2.77) | -0.138 (-4.96) | 0.001 | 0.005 |
| MUO | 2.66 (2.54, 2.78) | 2.71 (2.60, 2.82) | 0.049 (1.84) | 0.301 | ||
| Choline | MHO | 2.75 (2.62, 2.88) | 2.67 (2.54, 2.79) | -0.088 (-3.20) | 0.066 | 0.006 |
| MUO | 2.55 (2.43, 2.67) | 2.60 (2.47, 2.73) | 0.045 (1.76) | 0.432 | ||
| Tyrosine | MHO | 2.93 (2.75, 3.10) | 2.91 (2.73, 3.09) | -0.019 (-0.65) | 0.821 | 0.008 |
| MUO | 3.08 (3.92, 3.25) | 3.24 (3.10, 3.38) | 0.159 (5.16) | 0.016 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





