Submitted:
24 July 2024
Posted:
25 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Application of Environmental Remote Sensing Technology in Urban Planning
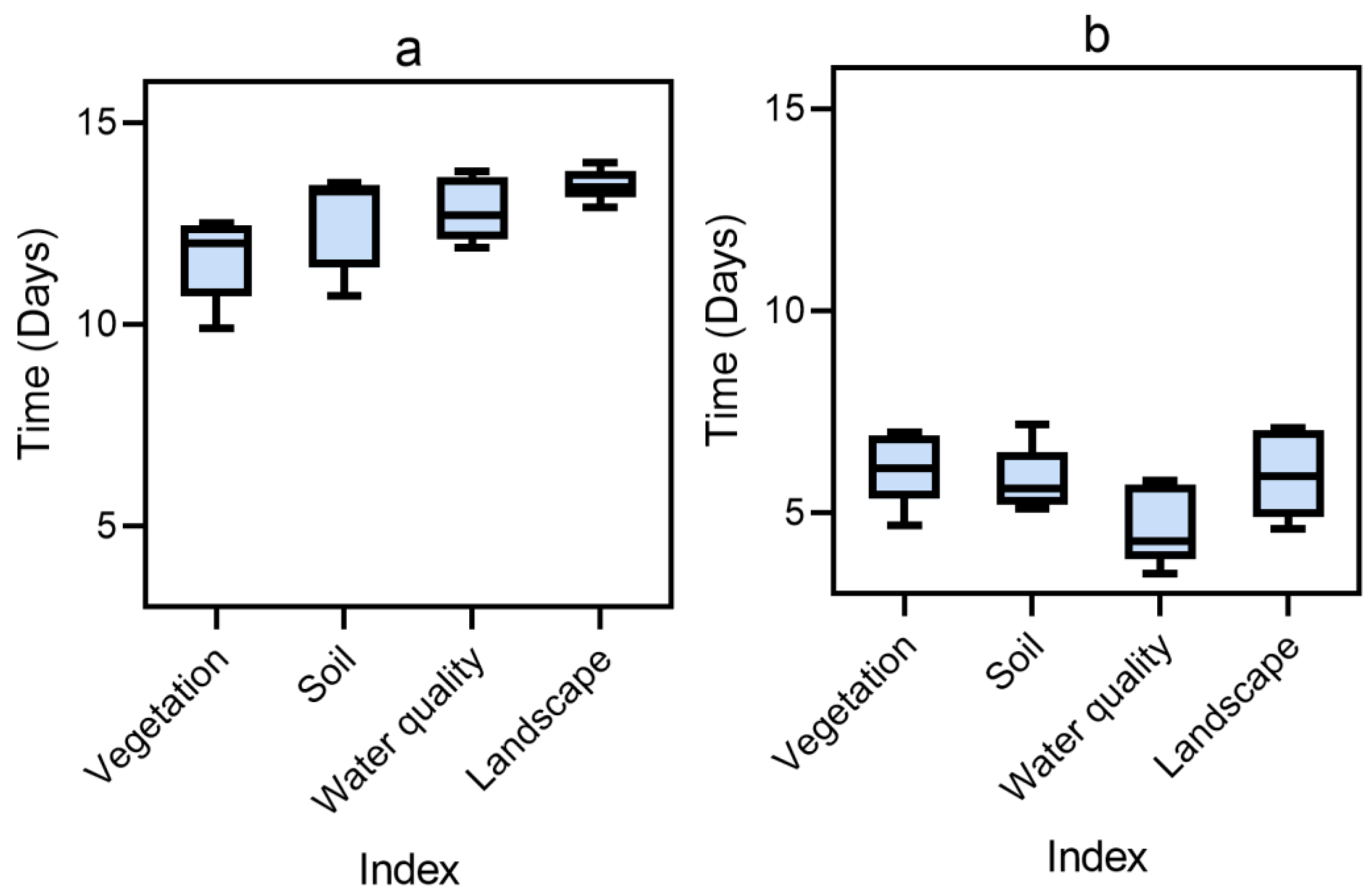
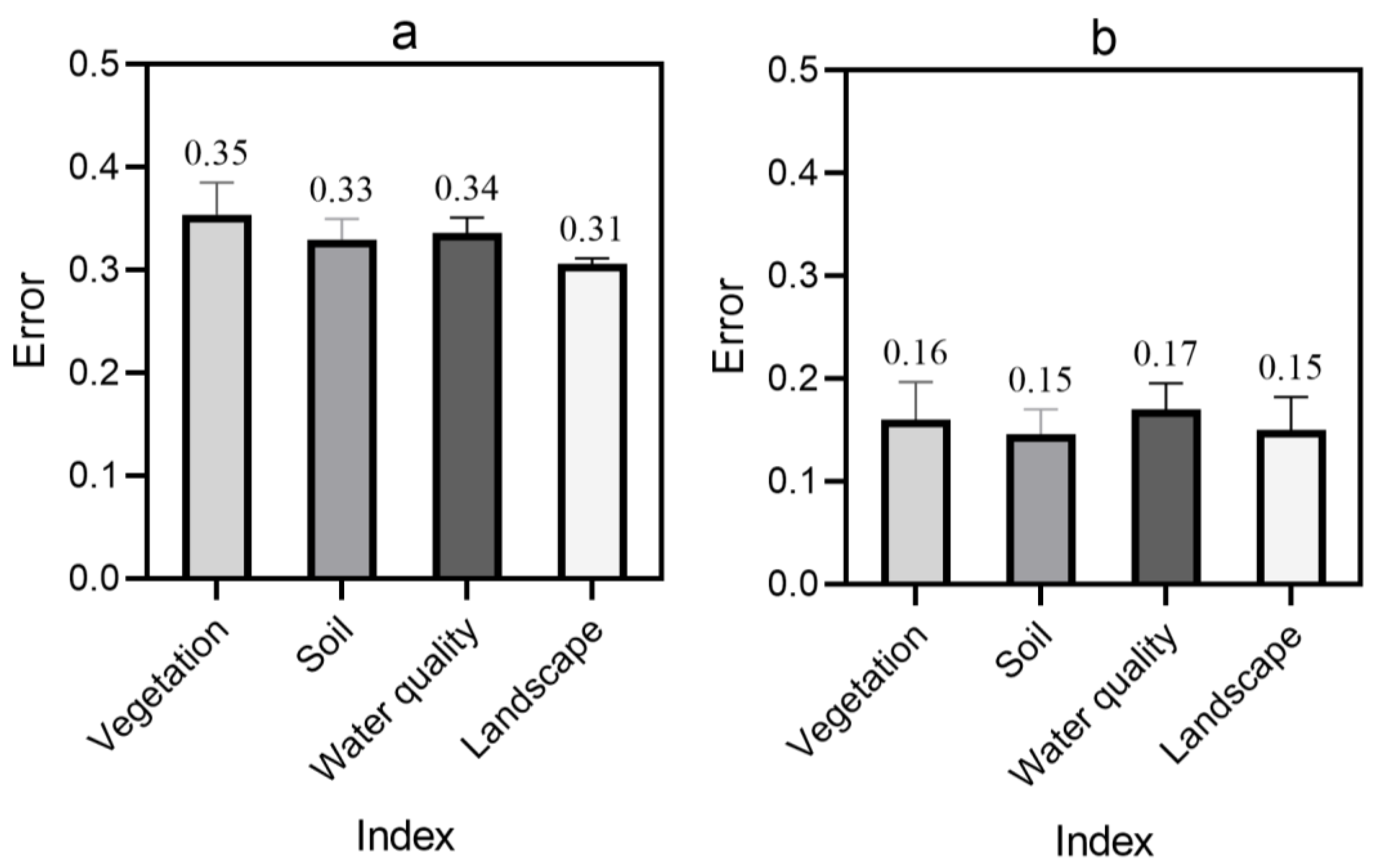
2.1. Monitoring of Environmental Remote Sensing Technology
2.2. Monitoring Data
2.3. Environmental Quality Assessment
3. Problems in Langfang
3.1. Low Level of Land Use
3.2. Low Utilization Rate of Ecological Landscape Resources
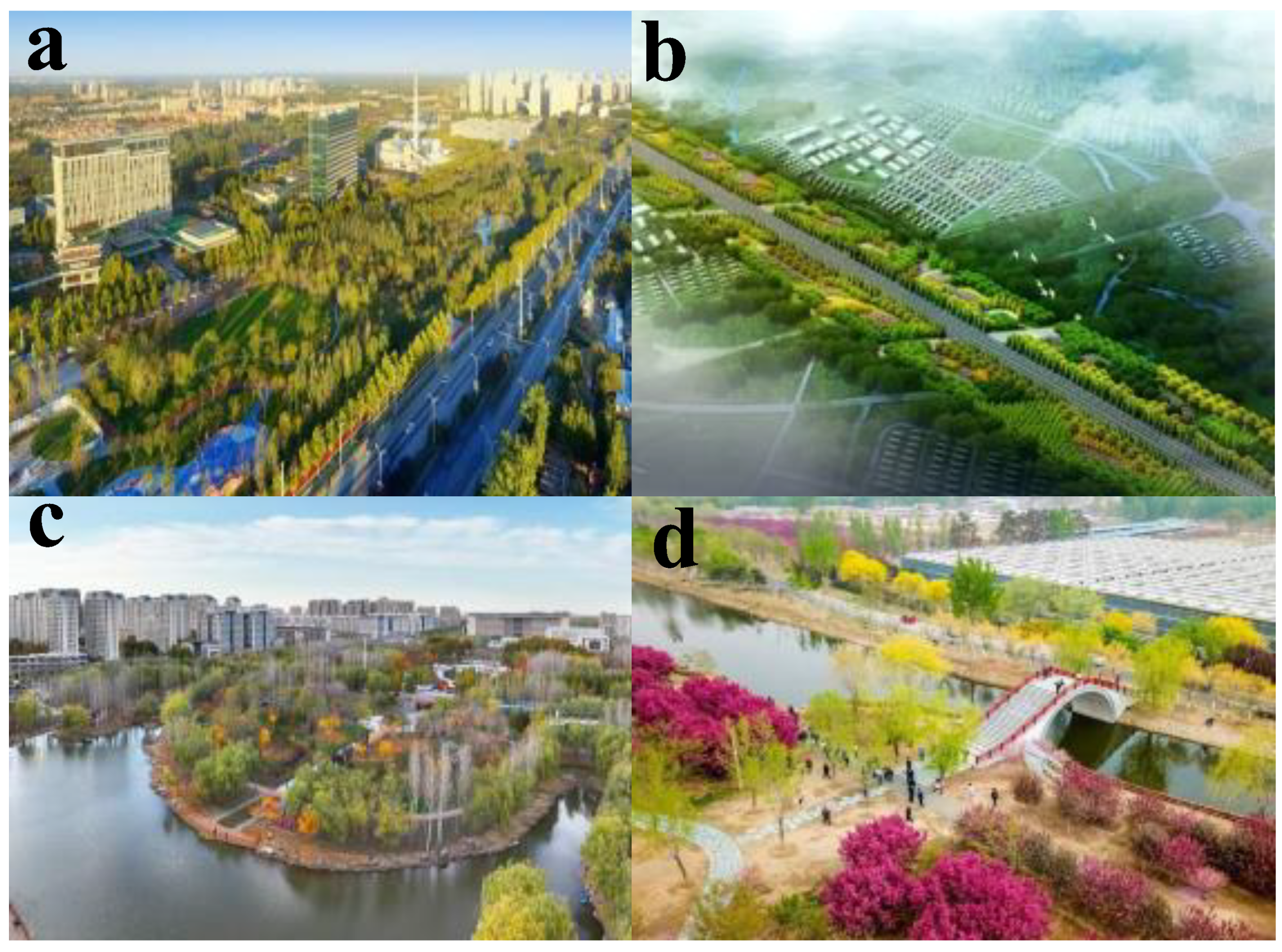
4. Ecological City Planning and Design
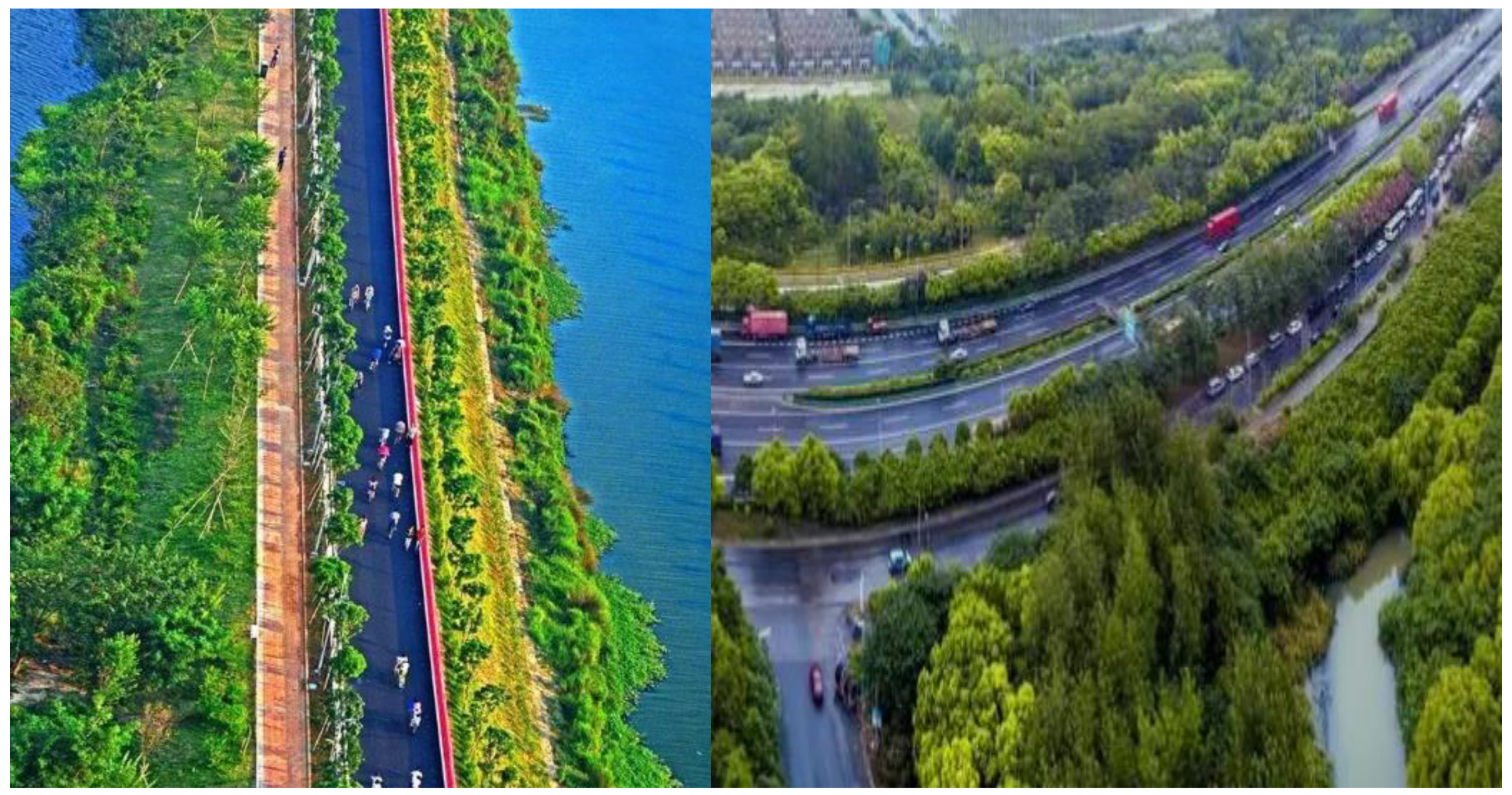
4.1. Planning of Urban Green Space
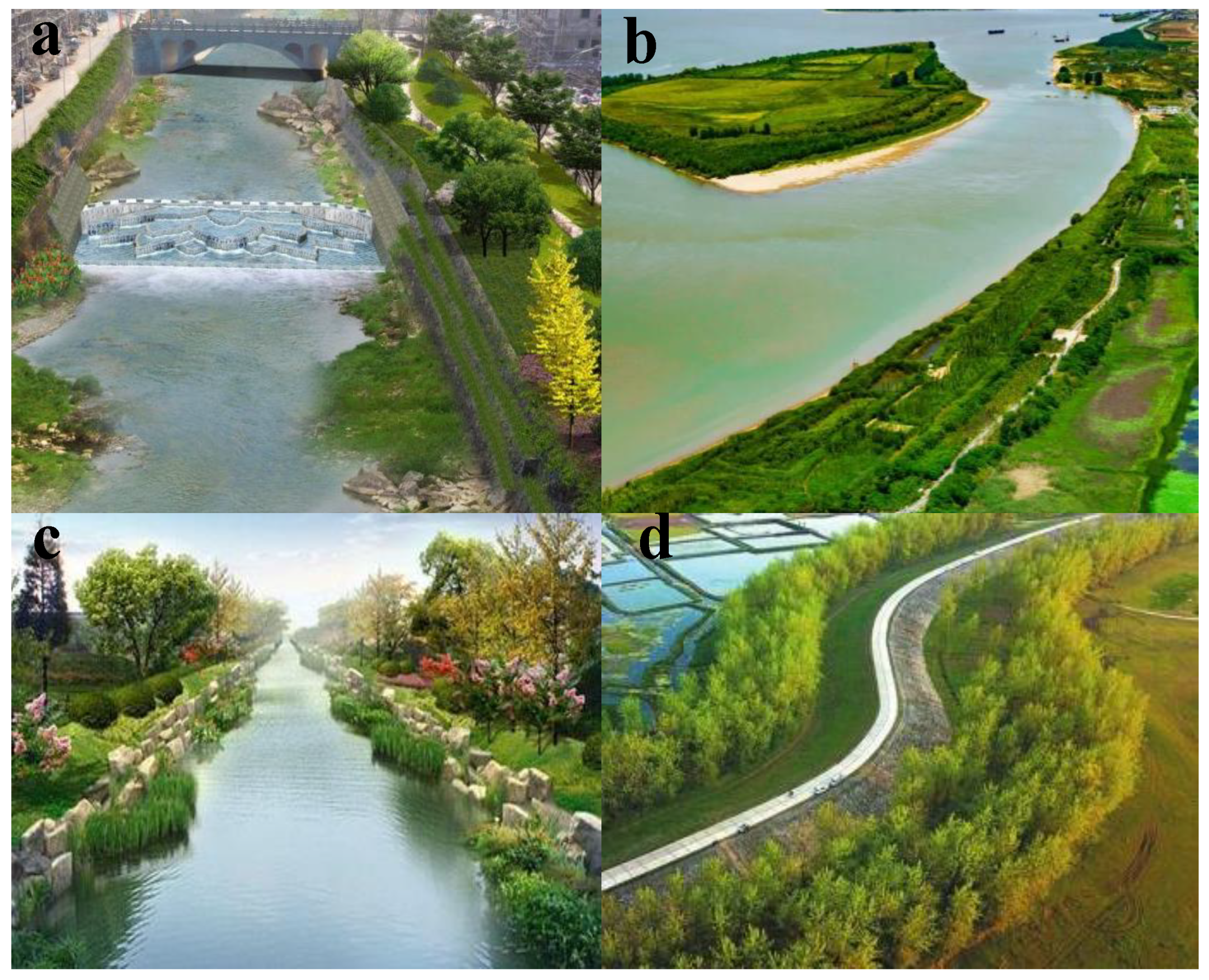
4.2. Urban Ecological Landscape Planning
5. Eco-City Planning and Design Effects
5.1. Effects of remote Sensing Technology
5.2. Improvement of Land Use Degree
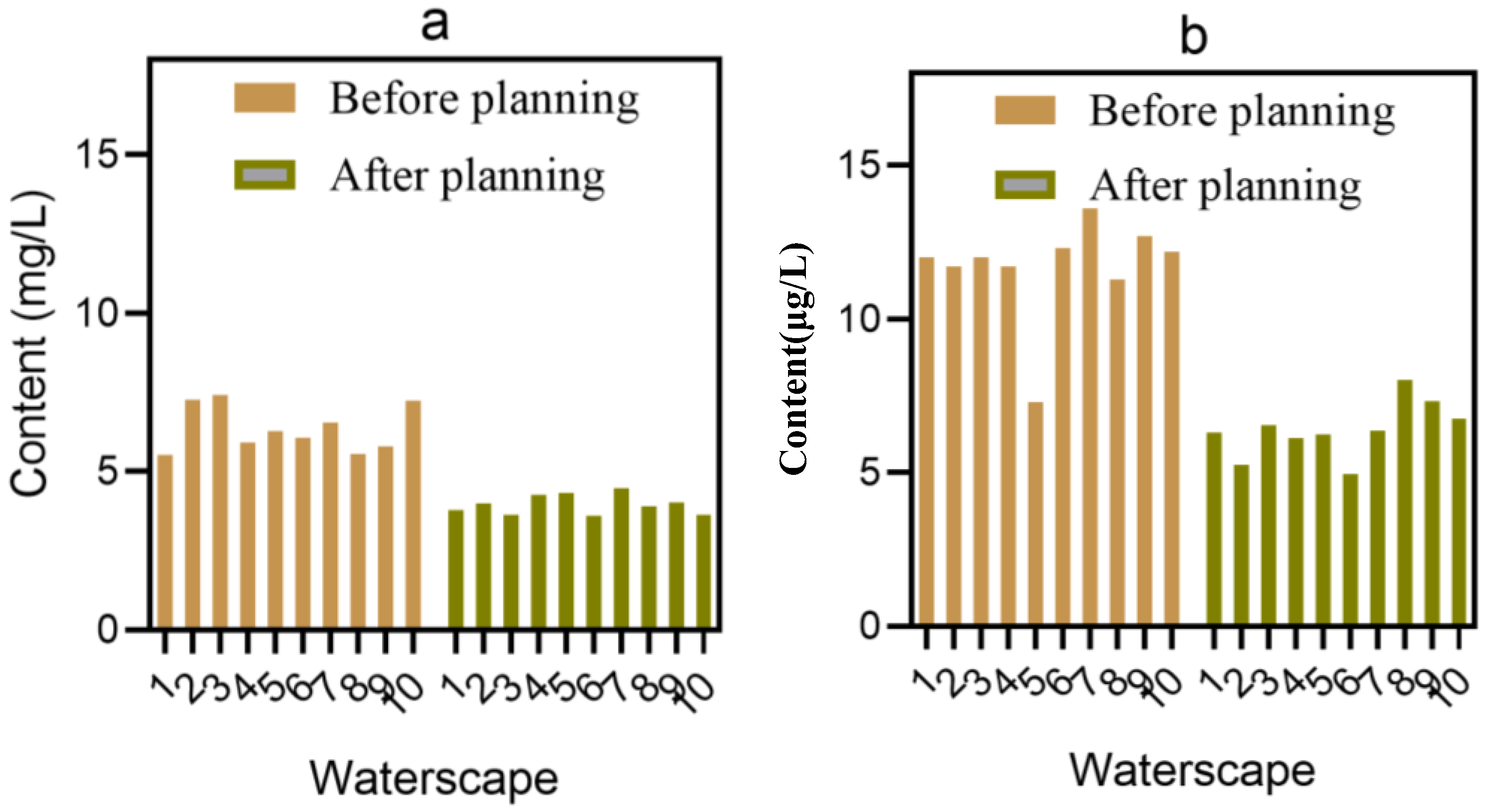
5.3. Ecological Environment Improvement
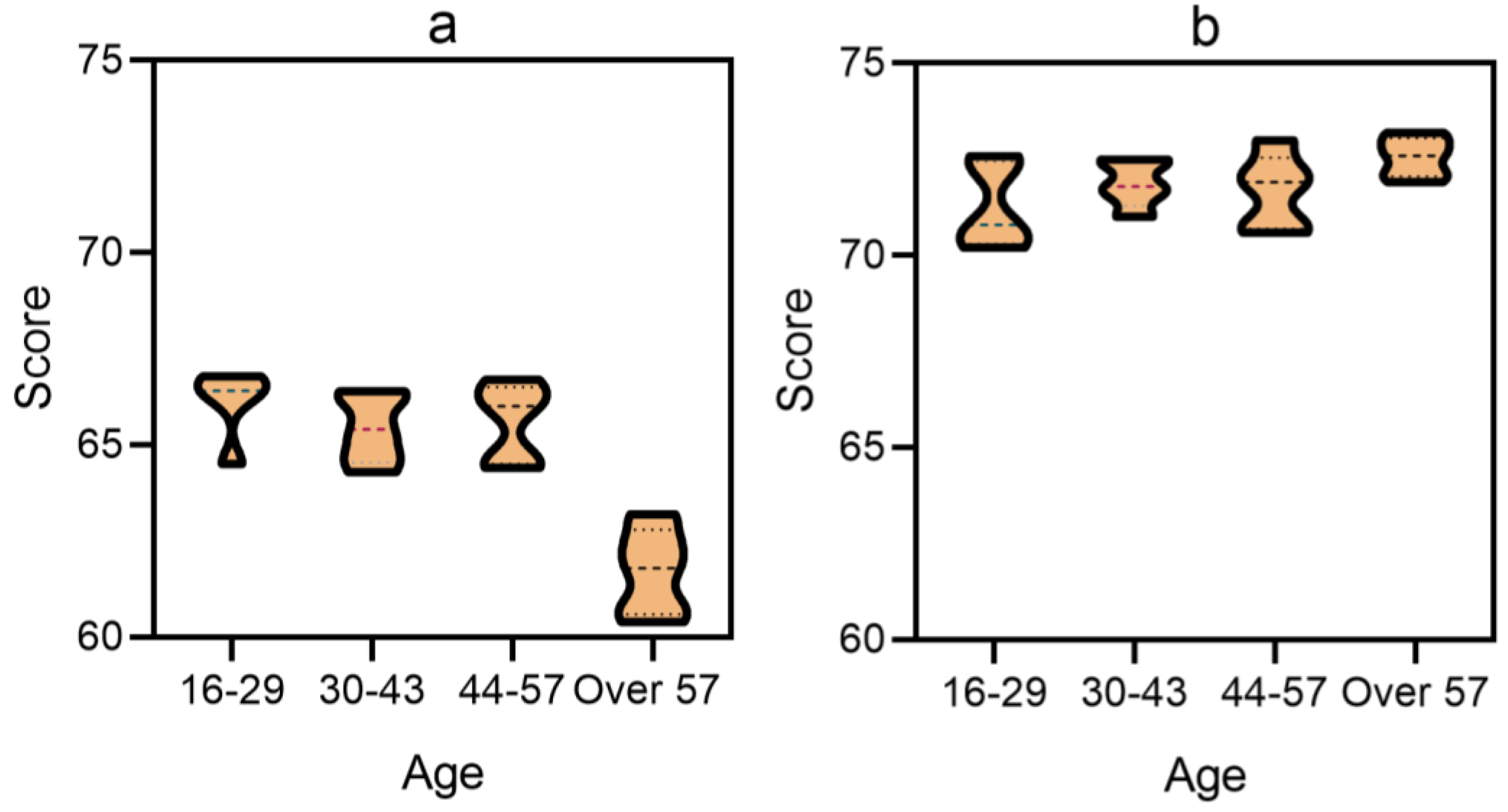
5.4. Public Satisfaction
6. Conclusions
Fund Projects
Academic Achievements
References
- Liu Junying, Sui Pheng Low, and Lin Fei Wang. "Critical success factors for eco-city development in China." International Journal of Construction Management 18.6 (2018): 497-506. [CrossRef]
- Shanwen Zheng, Zhu Chaoyang, and Wang Jianqiang. "A Practice-Oriented Ecological Urban Planning Path: Review of A Practical Guide to Eco-City." China City Planning Review 32.1 (2023): 84-86.
- Li Lingyue, Shi Xian, and Zhixin Qi. "Planning for Eco-City in China: Policy Mobility in Path Creation of Eco-Zhuhai." Sustainable Development Research 4.2 (2022): p27-p27. [CrossRef]
- Di Suchuang,Zhao-Liang Li, Ronglin Tang,Xingyao Pan,Honglu Liu,Yong Niu. "Urban green space classification and water consumption analysis with remote-sensing technology: a case study in Beijing, China." International Journal of Remote Sensing 40.5-6 (2019): 1909-1929. [CrossRef]
- Zhifeng Cheng, and He Qisheng. "Remote sensing evaluation of the ecological environment of Su-Xi-Chang city group based on remote sensing ecological Index (RSEI)." Remote Sensing Technology and Application 34.3 (2019): 531-539. [CrossRef]
- Feng Chengyu, Yixin Lu, and Jianqiang Zhang. "The quantitative assessment of the ecological assets in the center region of Chengdu City based on remote sensing and GIS technology." Ekoloji 28.107 (2019): 1325-1335.
- Xie, Linjun, Ali Cheshmehzangi,May TanMullins,Andrew Flynn,Tim Heath,Richard E. Hanley. "Urban entrepreneurialism and sustainable development: A comparative analysis of Chinese eco-developments." Journal of Urban technology 27.1 (2020): 3-26. [CrossRef]
- Grochulska-Salak, Magdalena. "Re-urbanization in a model of sustainable development of an eco-city." Acta Scientiarum Polonorum Architectura 20.1 (2021): 3-12. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Kun. "Impact of water–tourism–ecosystem nexus on the sustainable development of eco-city." Water Supply 23.5 (2023): 2233-2247. [CrossRef]
- Pow, Choon-Piew. "Building a harmonious society through greening: Ecological civilization and aesthetic governmentality in China." Annals of the American Association of Geographers 108.3 (2018): 864-883. [CrossRef]
- Tao, Xu, Y Xu,D Xiang,Y Sun. "Construction of a Low Carbon Eco-City Index System Based on CAS Theory: A Case of Hexi Newtown in Nanjing, China." International Journal of Urban and Civil Engineering 12.6 (2018): 645-650. [CrossRef]
- Aboneama, Wael A. "Applying sustainable development in architecture, planning and infra-structure of Abha to be the first eco-city in the Middle East." European Journal of Sustainable Development 7.4 (2018): 289-289. [CrossRef]
- Zebin, Huang, Wang Jianwei, and Fu Xin. "Design and Implementation of Eco-city Commuting Analysis System Based on Spatio-temporal Big Data." Ekoloji 28.107 (2019): 3305-3313.
- Bibri, Simon Elias. "Data-driven smart eco-cities and sustainable integrated districts: A best-evidence synthesis approach to an extensive literature review." European Journal of Futures Research 9.1 (2021): 1-43. [CrossRef]
- Sonn, Jung Won, and Joon Park. "Smart city, eco city, world city, creative city, et cetera et cetera: a Marxian interpretation of urban discourses’ short lifecycles." Cambridge Journal of Economics 47.2 (2023): 393-407. [CrossRef]
- Azamat, Berdikulov, and Shoboeva Rukhshona. "Eco-city is a product of urbanization." Academicia Globe: Inderscience Research 2.04 (2021): 156-160.
- Saidi, Mehdi, Mozhgan Ansari, and Faezeh Torabinejad. "Investigating the Realization Rate of the Eco-City Indicators and the Conceptual Framework for its Development Based on Residents’ Satisfaction (Case study: Ozgol neighborhood of Tehran)." Journal of Iranian Architecture & Urbanism (JIAU) 12.2 (2021): 5-23. [CrossRef]
- Williams, Austin. "Eco-City Comparison: West versus East." Sustainability: The Journal of Record 11.5 (2018): 229-236. [CrossRef]


| Index | Vegetation coverage (%) | Available water resources (billion cubic meters) | Proportion of plain (%) | Per capita green park area (square meters) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual data | 47.25% | 7.74 | 98% | 13.93 |
| Monitoring data | 47.24% | 7.74 | 97.98% | 13.92 |
| Error | 0.01% | 0 | 0.02% | 0.01 |
| District | Road density (km/km²) | Building coverage (%) | Utilization rate of land resources (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.1 | 42.1 | 0.256 |
| 2 | 7.1 | 40.9 | 0.349 |
| 3 | 6.3 | 41.1 | 0.286 |
| 4 | 6.4 | 41.4 | 0.327 |
| 5 | 6.1 | 43.0 | 0.421 |
| District | Utilization rate of public green space (%) | Forest utilization rate (%) | Utilization rate of wetland (%) | Water utilization rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.7 | 15.6 | 13.1 | 15.5 |
| 2 | 15.5 | 15.1 | 11.9 | 16.4 |
| 3 | 13.8 | 16.1 | 13.7 | 15.1 |
| 4 | 14.4 | 15.4 | 10.7 | 14.3 |
| 5 | 15.2 | 14.4 | 11.2 | 16.6 |
| District | Road density (km/km²) | Building coverage (%) | Utilization rate of land resources (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.3 | 43.6 | 0.352 |
| 2 | 8.2 | 42.7 | 0.388 |
| 3 | 8.2 | 42.9 | 0.301 |
| 4 | 8.0 | 41.8 | 0.354 |
| 5 | 8.1 | 44.5 | 0.479 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





