1. Introduction
The current understanding of sustainable forest management goes beyond the principle of sustainable harvesting and is shaped by a number of different societal needs [
1]. Many countries are seeing some re-evaluation of the existing functions performed by forests [
2,
3,
4]. Forests traditionally used as a source of timber are more often used as recreational areas. Recreational use of forests has increased dramatically as a result of increased leisure time and urban infrastructure development [
5]. Increased health consciousness in societies, changing lifestyles, and changing leisure activities and motivations have also contributed to increased interest in the forest as a recreational area. There is no indication that this trend will change over the next decades. Sys-tematically, the world’s human population is growing; according to UN forecasts, by 2060 the world’s po-pulation will exceed 10 billion people [
6], and although demographic trends for Europe are shaping the opposite of global trends, the extensive urbanization of space means that opportunities for outdoor, green recreation are diminishing.
The demand for recreation is reflected in the values of public forests and attitudes toward their management [
1]. Dudek [
7] showed that there is a relationship between selected forest management activities and the suitability of forests for recreational use. Today’s challenge for foresters, especially those administering public forests, is to understand that changes are needed in the approach to forest management, which must take even greater account of social and ecological benefits. Many studies [
8,
9,
10] confirm the clear increase in the importance of the environmental and cultural ecosystem services of the forest. Among the social benefits, protection of people’s health and improvement of their well-being come to the fore. Many people, when choosing a forest as a place for recreation, are guided consciously or subconsciously by the benefits the forest provides for their physical and mental health.
In recent years, there has been a growing amount of scientific evidence pointing to the beneficial effects of the forest on human health. Visits to nature contribute to renewal and preservation of mental health [
11,
12,
13], as well as stress reduction [
14,
15,
16]. Some researchers (e.g. [
17,
18]), believe that human well-being is related to the aesthetics of space, and they emphasize the importance of scenic qualities of the landscape for increasing visitor preference. People often have negative attitudes toward forest management activities, especially near urban areas, even if the effects of these activities were imperceptible or even beautiful [
19]. A study by Giergiczny et al. [
20] found that the level of intensity of forest management had the greatest negative impact on respondents’ recreational choices. Higher go-management intensity was associated with higher forest non-use. Shifley et al. [
21] pointed to forest management, particularly the intensity of forest use, as the main factor affecting the forest landscape. The general public, especially people with higher education, prefer forest management that results in a near-natural forest. Also, Pastorella et al.‘s [
22] findings show that most people prefer forests with a high level of naturalness, such as undeveloped forests or forests managed in a near-natural way. Thompson et al. [
23] found that people would like a compromise between a very wild forest and a forest park: partially managed areas, but also very natural, with no visible signs of human influence where possible. People are little aware that managing a forest for profit inevitably involves converting stands in ways that many may perceive as unattractive, such as generating clear cuts that leave behind both exposed stumps and logging residue [
24].
Second-growth forest and clear-cutting area the most obvious manifestations of ongoing forest management in forests. Indeed, can contact with a forest landscape perceived as visually unattractive lead to reduced relaxation benefits? And do features such as clear-cutting area and second-growth forest characteristic of a managed forest landscape lead to fewer health benefits than those provided by a mature forest? The purpose of our study was to compare the benefits derived from exposure to mature forest stand, second-growth forest and clear-cutting area. The study adopted the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1. All analyzed elements of the commercial forest landscape: second-growth forest, clear-cutting area and mature forest stand have a regenerative effect on people (an increase in perceived regenerative outcomes, subjective vitality and positive emotions, and a decrease in negative emotions).
Hypothesis 2. There are differences between the regenerative effects obtained from exposure to second-growth forest and clear-cutting area, as well as mature forest stands.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
Fifty-five students of the Warsaw University of Life Sciences—SGGW (WULS-SGGW) participated in the study. There were 36 women and 19 men in the group. Volunteer students who agreed to participate in the research were informed about the study goals as well as the procedure of its conduct prior to the beginning of the experiment. Participants in the research were young adults aged 21–25. Unhealthy adults with mental or physical diseases or metabolic syndromes were excluded from the study.
2.2. Study Sites
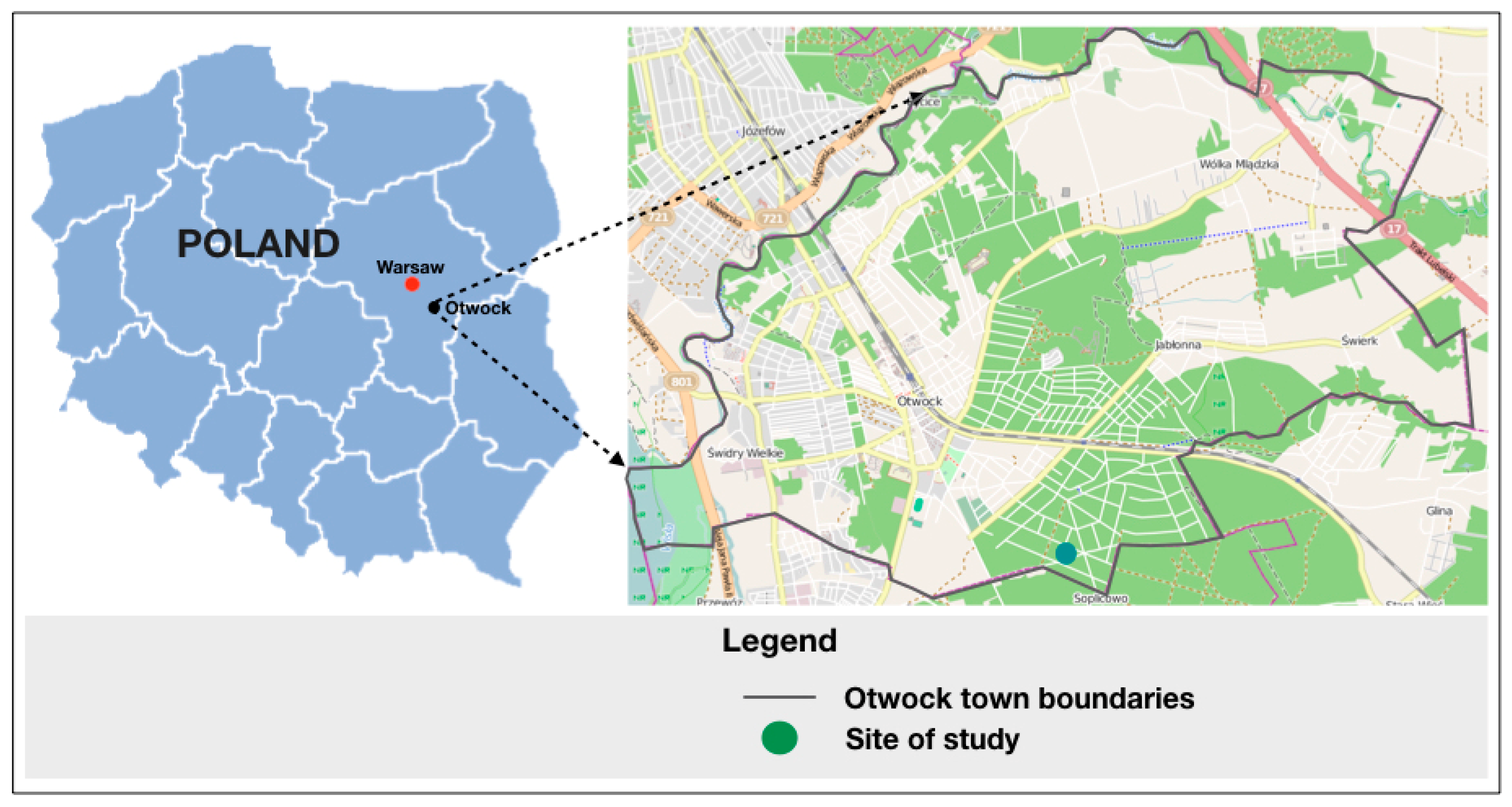
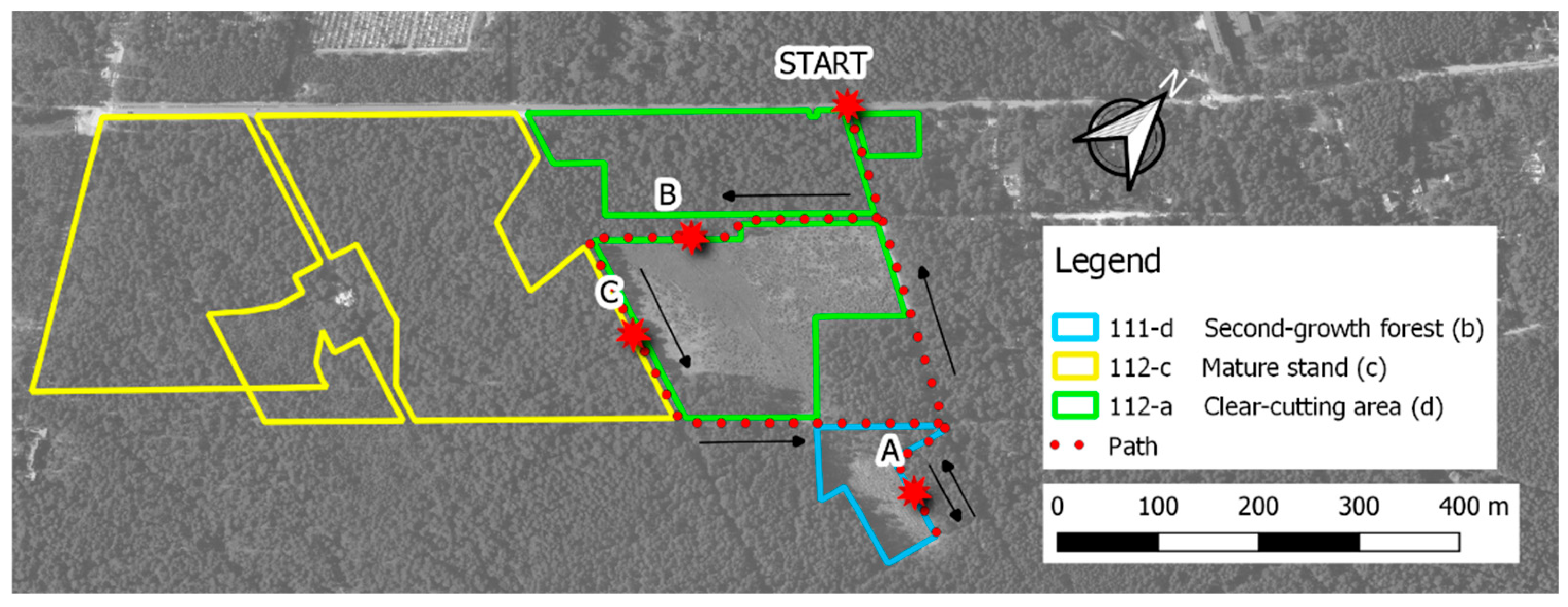
The survey was conducted in October 2023 (October 20, 2023) in a forest within the city of Otwock (southern part of the city), located at a distance of 32 km from Warsaw - the capital of Poland. This forest is managed by Celestynów Forest District, Otwock Forestry Division (Regional Directorate of State Forests in Warsaw), forest address 17-01-1-02-111 -d (second-growth forest), 17-01-1-02-112 -a (clear cutting area), 17-01-1-02-112 -c (mature forest stand). The second-growth forest area is 0.97 hectares, occurs on fresh mixed coniferous forest habitat. Tree species in the cultivation are Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) 60% share of the area at 2 years of age and beech (Fagus sil-vatica L.) - 40% share of the area at 2 years of age. The clear-cutting area accounts for 3.94 hectares, and occurs also on mixed fresh forest. The mature forest stand occurs on the forest habitat type - fresh forest. The stand is dominated (90%) by Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) aged 114 years, the remaining 10% of the area is occupied by Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) aged 79. In places, there are red oak (Quercus rubra L.) at the age of 39, Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) at the age of 144, Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) at the age of 39, and single oak (Quercus L.) at the age of 39. Juniper (Juniperus L.), oak (Quercus L.), red oak (Quercus rubra L.) and common buckthorn (Frangula alnus Mill.) appear in the undergrowth. Stand density is moderate. The meteorological data in effect at the time of the experiment were determined using data from the nearest meteorological station—the Meteo Station in Otwock located at an altitude of 94 m above sea level (location: 52°6’55.729´´N and 21°14´15.418´´E). The average daily temperature was 6.3 ◦C (7.9maximum ◦C, 5.3 minimum ◦C), the relative humidity was 95.52%-96.30%, the average cloudiness was 5.3 (on the octane scale), the atmospheric pressure was 1008 hPa, and the wind speed was up to 4.5 m/s. Noise and sunlight levels were controlled during the experiment. Sound and light levels were also measured with an iPhone 12 using the LUX Light Meter FREE and Sound Level Analyzer Lite applications. Similar applications have been used in other studies [
10,
25], and they meet standards comparable to professional laboratory equipment for sound analysis. Sound and light were measured at each exposure point before, 2 × during, and immediately after completing the psychological test questionnaire. The average sound level measured with the sound level meter amounted to 47.6 ÷ 56.5 dB. The mean light intensities in forest amounted to 829 ÷ 881 lx.
Figure 1.
Map with the location of the test sites.
Figure 1.
Map with the location of the test sites.
2.3. Procedure
The experiment began at 10 a.m. Each participant in the study arrived at the site alone. The collection site was located at the entrance to the forest, about 100 meters from the first study plot. Upon reaching the forest, each volunteer was asked to answer questions on the standardized psychological test questionnaires we used (see
Section 2.4 for a description of the tests) - Pre-test. The psychological questionnaires used in the study were anonymous, with the students adopting pseudonyms for the duration of the study. Each questionnaire form, upon completion, was checked by the study supervisors (2 people) for completeness. Subsequently, participants were randomly divided into three groups: A (20 participants) and B (22 participants) and C (22 participants). Each group, along with a researcher guide, went to the forest for the next stage of the experiment. Group A started with an exposition to a second-growth forest, group B- at the same time observed a clear cutting area, and group C- a mature forest stand -
Figure 2. All observations were made from the forest roads along which the aforementioned plots were located. The participants were at a distance of about 5 meters from each other. The time of exposure to the landscape was 15 minutes each time. After this time, each respondent again answered the questions included in the psychological tests (Post-test). Each group then rotated visiting the next study area. Group A would go to a road bordered by a clear-cutting area, group B to a road passing through a mature forest stand, and group C would arrive at a second-growth forest. In this way, at each site at the same time there were max. 22 survey participants and each participant viewed both the second-growth forest, clear cutting area and the mature forest stand. All three locations were very close to each other at a distance of about 300 m -
Figure 3. All actions taken during the research were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Polish Committee for Ethics in Science and the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki, as amended.
2.4. Measurements
Four psychological questionnaires were used to measure the effects of viewing of forest environment on psychological responses on the participants:
The Polish version of D. Watson’s and L.A. Clark’s Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS) elaborated by Brzozowski [
26] was used to evaluate the feelings of participants. It is composed of 20 questions of which the same number refers to positive and to negative feelings. Each question was evaluated with a five-point Likert type scale (1—strongly disagree, 5—strongly agree). The credibility and validity of the PANAS questionnaire are high [
27].
Restorative Outcome Scale (ROS)—test contains six items, each of which is evaluated by the participants by a seven-point Likert type scale (1—very unlikely, 7—very likely). In the research, we used the scale modified for forest-related experience [
28,
29]. The modified scale was adapted to the Polish language [
30]. According to Korpela et al. [
31,
32], it is a credible tool to evaluate the level of restorative outcome. The Subjective Vitality Scale (SVS), a test for the evaluation of vitality, which reflects feelings of energy, vitality, and well-being, was used; namely, the version with four items (e.g., “I feel alive and vital” or “I look forward to each new day”), adjusted for research in forest areas [
28,
29]. Four items were evaluated by the participants with the use of a seven-point Likert type scale (1—very unlikely, 7—very likely).
The 65-position version of the Profile of Mood States questionnaire (POMS). The Polish adaptation of the questionnaire (originally compiled by D.M. McNair, M. Lorr, L.F. Droppelman) was performed by Dudek and Koniarek [
33]. POMS is a credible and contemporary measure of mood state, used previously for the evaluation of the forest environment’s effect on individuals’ moods [
16,
28,
30,
34,
35,
36,
37]. It is a tool that measures six subscales of mood state: confusion or bewilderment, fatigue, anger or hostility, tension or anxiety, depression or dejection, and vigor. For each question, a five-point Likert type scale was used to estimate the mood state of the participants from 0 (strongly disagree) to 4 (strongly agree). The PANAS, ROS, SVS, and POMS questionnaires allow various time frames to be used, but, in this study, as in earlier studies [
16,
30,
38,
39], the used time frame was “at this particular moment”.
3.2. Data Analysis
All raw data were stored in Excel (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA), and mean values and standard deviation (SD) values were calculated using this program. Further analysis was performed using STATISTICA version 13.3 (TIBCO Software Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA). To compare the measurements of the PRE-Test and POST-Test, a paired T-test was used. The distribution of data was similar to the normal distribution. A parametric, one-factor repeated measure ANOVA was conducted to analyze the effects of different expositions on the PANAS, ROS, SVS and POMS scores. The psychological effects and benefits were compared before entering the forest and inside the forest (A—second growth forest, B—clear cutting area, C—mature stand forest). After ANOVA, post hoc comparisons using Tukey’s HSD test were conducted. The analyses considered the results for which “p > 0.05” was statistically significant in both the ANOVA and post hoc tests.
3. Results
3.1. Positive and Negative Effect Schedule
Cronbach’s alpha reliability analysis for the PANAS scale established on the basis of the data obtained was: 0.851 (PANAS Positive) and 0.844 (PANAS Nagative). Significant interactions were observed for positive and negative PANAS indices (
Table 1). The positive PANAS index was highest in the case of exposure to a mature forest stand, and reached its lowest value in the case of exposure to clear cutting area. Statistically significant differences occurred only between the mean values from the post-exposure test for second-growth forest and clear cutting area and also mature forest stand and clear cutting (
Table 1). In the case of PANAS Negative, a significant difference was observed between the mean value determined at the Pre- test stage and exposure to clear cutting area. As a result of exposure to a mature forest stand, its value significantly decreased, representing the lowest average value. The strength of the effect of exposure to clear cutting area compared to the control sample and the other two exposures - to the second-growth forest and to the mature forest stand - is also very pronounced for negative feelings. Exposure to a mature forest stand significantly reduces negative feelings, while exposure to logging raises them very significantly.
3.2. Restorative Outcome Scale and Subjective Vitality Scale
Cronbach’s alpha reliability analysis for the ROS and SVS scale established on the basis of the data obtained was: 0.915 (ROS) and 0.826 (SVS). The ROS and SVS ratios increased significantly after exposure to the second-growth forest and mature forest stand (pre-test vs. post-test,
Table 2). With regard to ROS, among the three analyzed plots, the ratio had the lowest value for exposure to the second-growth forest, while it had the highest value for exposure to the mature forest stand. At the same time, statistically significant differences occurred only between the mean values from the Pre-test and mature forest stand exposure, and after exposure to second-growth forest and clear cutting area and also: mature forest stand and clear cutting area (
Table 2). The SVS index, on the other hand, had the highest mean value for mature forest stand exposure. Statistically significant differences occurred only between the mean values from Pre-test and exposure to mature forest stand and following exposure to second-growth forest and mature forest stand.
3.3. Profile of Mood States
Cronbach’s alpha reliability analysis for the POMS scale established on the basis of the data obtained was: 0.677 (Tension), 0.882 (Depresion), 0.827 (Anger), 0.867 (Fatigue), 0.613 (Confusion), 0.879 (Vigour). The results of the post hoc analysis following ANOVA indicated that there were statistically significant differences in the regenerative effects of the analyzed variants of the forest landscape in all POMS subscales except the Fatigue scale (
Table 3). A statistically significant difference was found for the Total Mood Disorder (TMD) score of the Profile of Mood States (POMS). The highest value of this index was obtained from exposure to clear-cutting area. The mean values for exposure to second- growth forest and mature forest stand were similar to each other but significantly lower than for the control sample. Statistically significant differences for TMD averages were found as a result of exposure to second-growth forest and clear-cutting area, and also to mature forest stand and clear-cutting area.
Differences between groups were also found for other subscales (
Table 3). For example, for the ‘Tension’ subscale, it was found that exposure to clear cutting area, compared to the control sample (Pre-test), definitely contributes to elevated levels of ‘Tension’. In the case of the ‘Depression’ scale, the highest mean value was found for exposure to clear cutting area, while lower mean values were found for exposure to second-growth forest and mature forest stands. But there were statistically significant differences in the results of Pre-test and exposure to clear cutting area, exposure to second-growth forest and clear cutting area as well as exposure to mature forest stand and clear cutting area. ‘Anger’ levels were significantly lower (statistically significant difference) following exposure to second-growth forest and mature forest stand compared to Pre-test. There was also a statistically significant difference in Post-Test scores after exposure to the second-growth forest and mature forest stand compared to scores determined as a result of contact with the clear cutting area. The level of mean disorientation before the forest visit was higher than that determined after the experiment, regardless of the environmental variant. However, a statistically significant difference was observed only for the mean value determined in the Post-test after exposure to the second-growth forest compared to the Pre-test value. In the case of the ‘Vigor’ subscale, it was found that each time the mean value measuring this mood state was higher and statistically significantly different from the mean value found in the clear cutting area exposure results.
4. Discussion
4.1. Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS)
Our findings show that not every forest offers high health benefits. An outdoor recreation space must have certain attributes in order to have a restorative effect and lead to health benefits, including improved mood and well-being. Contact with nature, with nature, is not enough for this purpose, as many natural areas have been damaged by natural forces (post-hurricane areas, after fires, destroyed by insects, etc.) or by human activities (littering, warfare, etc.). Milligan and Bingley [
40] believe that the notion that “the natural environment is therapeutic” cannot be accepted without some criticism. Such tupu spaces, still natural after all, do not guarantee high quality recreation and do not have the expected restorative effects. Many authors draw attention to the need to modify the principles of forest management in forests with increased social function. As a rule, the basis for such a claim are the results of studies of recreational preferences, landscape preferences. The results of Zeidenitz et al. [
41] show that people highly value experiencing nature and beautiful landscapes during outdoor activities. The visual appearance of a forest is important because people experience the environment visually, and aesthetics is the most fundamental dimension of human-landscape interaction [
42]. People tend to prefer forest scenery that has a large number of large trees of different ages and species, and the understory consists of low, sparse ground vegetation [
43]. Traces of forest management such as clearcuts, stumps, logging waste, and forest crops are considered to be depreciating factors in the forest landscape [
44,
45,
46,
47,
48]. The view after forest clearing is the least preferred environment [
49,
50]. Logging reduces the aesthetics of the forest space. The highest landscape values are observed when trees are harvested in small areas, and the lowest when clear cuts are used [
51]. However, studies of landscape aesthetics have been accused of a certain amount of subjectivity. Kroll et al. [
52] points out that standardized approaches for the assessment and monitoring of landscape aes-thetics are still missing. In contrast to ecological or economic aspects, the assessment of aesthetics cannot easily be based on quantitative information [
53]. Hence-it is so important to seek answers to the question of the restorativeness of space features using tools other than indicators of aesthetics or landscape attractiveness.
In recent years, psychological tests such as PANS, which has already been applied in many studies [
30,
54,
55,
56], ROS - this tool has been used previously concerning relaxing features of the forest environment [
16,
28,
30,
56], POMS [
16,
38]. Our results show that of the three different wariants of space (second-growth forest, clear cutting area and mature forest stand), the least health benefits are offered by exposure to a clear cutting area. Exposure to a clear cutting area leads to a decrease in positive feelings and an increase in negative feelings. Only contact with a mature forest stand guaranteed a marked improvement in mood, an increase in positive feelings and a decrease in negative feelings, especially when compared with clear cutting area. This observation is significant because many previous works [
13,
16,
30,
56,
57,
58] have shown that recreation in the forest reduces negative emotions and improves well-being. It turns out that this is the case only when there is contact with a mature forest stand, not clear cutting area or second-growth forest, which are also treated as a forest in light of the definition of terms [definition of forest in the current Polish Forest Act [
59].
4.2. Restorative Outcome Scale (ROS) and Subjective Vitality Scale (SVS)
According to Simkin at al [
56], there is currently still little evidence based on field experiments comparing the effects of different forests on human well-being. Our study fills the knowledge gap on how different forest landscape elements differ in terms of regenerative effects. The results of our study based on ROS and SVS indices also demonstrate that forest contact has restorative properties, but only when it comes to exposure to mature forest stands. Here we observed statistically significant differences between the control sample (before entering the forest) and exposure to a mature forest stand. The restorative value of mature forets stands is significantly higher than that of clear cutting area or second-growth forest. We also found that the sense of vitality increases as a result of exposure to mature forest stands. In our study, we did not test different types of physical activity; participants in the experiment viewed the forest while sitting or standing. Viewing the landscape was one of the forms of recreation analyzed in the Park et al. [
60], Takayama et al. [
28], Janeczko et al. [
10] study. These studies also showed that viewing forest landscapes evoked feelings of subjective restoration (ROS). Studies conducted in forest environments have shown that recreation contributes to a sense of vitality [
30,
61]. Our previous work [
16] suggested that the level of vitality may be related to the type of physical activity and the level of exercise. However, it turns out that landscape quality may also be responsible for vitality levels. Exposure to a mature forest stand of trees guarantees a higher level of vitality than that which accompanied the participants in the experiment before entering the forest.
4.4. Profile of Mood States Questionnaire (POMS)
The results of our research in relation to the mood state of people visiting forests indicate that the features of the space project the quality of a person’s life, how their emotions are shaped, and thus their behavior. We prove that clear cutting area and the accompanying logging residues such as stumps are among the factors that depreciate the health benefits gained from contact with the forest. Thus, we concur with Daniel’s [
62] observation that people only accept or enjoy dramatic changes in forest ecosystems to a limited extent. Even a brief exposure to clear cutting arae leads to a complete mood disturbance. Clear cutting area performed much worse in this regard than second-growth forest and mature forest stands. The indices of four of the six POMS subscales (Tension, Anger, Depression and Vigor) were statistically significantly different in the non-exposure to logging. For ‘Tension’ and ‘Depression’, the mean values for logging exposure were the highest of all mean values (control sample, mature forest stand and second-growth forest). The ‘Tension’ index for post-felling exposure proved statistically different from that determined by the Pre-test. The ‘Depression’ index, on the other hand, was clearly statistically different from the values determined for the other locations. The sight of a clear cutting area evoked feelings of sadness, fearful thoughts. Some earlier work by Sreetheran and van den Bosch [
63] also linked dead wood to such feelings. The topic of the effects of dead wood on the human psyche has already been analyzed several times [
64,
65]. In our earlier work [
66], we found that exposure to a forest landscape with dead wood had no effect on the scale of ‘Depression’. However, we compared a commercial forest with signs of cutting, with a reserve forest and a forest infected by the bark beetle (lying and standing dead wood). Now we find that there is a clear activation of feelings related to the ‘Depression’ subscale in contact with clear-cutting area.
Our research indicates that people derive energy from landscapes that embody not only recreational functions, but also beneficial ecological functions. Exposure to a mature forest stand of trees compared to clear-cutting area brought significantly more benefits (decrease in ‘Depression’, ‘Anger’ and increase in ‘Vigor’). The greater environmental diversity provided by a fully-grown stand is conducive to improved mood, and has greater restorative properties. Previous studies [
30,
67] confirm that in a forest environment (a fully educated stand), the values of indices of ‘Tension’, ‘Depression’, ‘Anger’, ‘Confusion’ and ‘Fatigue’ decrease.
5. Limitation
Our study has several limitations. The experiment was conducted in a group of young adult Poles. This may mean that our results may have reference to just this group. The socio-cultural thread is important in participatory research. It has been proven repeatedly that landscape preference is determined by a number of factors, of which three socio-demographic characteristics such as age, gender and education are most often included in ba-days related to people’s landscape preferences (e.g. [
68]). Research by Gundersen and Frivold [
46] shows that young people find greater beauty in what is wild, unstructured, complex. In turn, for example, a higher level of environmental knowledge correlates with a preference for places with a more natural appearance [
69,
70]. Thus, we suggest that future studies should examine the health benefits of forest exposure in conjunction with demographic attributes. Another limitation is that we have only studied the effects of short exposures on the well-being of people observing the forest, and we do not know how both longer time in the forest and physical activity contribute to the psychological benefits of exposure to such landscape features. It would be worthwhile to determine in future studies whether longer exposure to the forest landscape produces the same benefits. Another limitation of the study is that we focused on the psychological effects immediately after the experiment, excluding potential long-term effects. This remains a topic for future research. In addition, the experiment involved a trip to the forest, and we had no way of eliminating the stress factor associated with traveling to a recreation site. The study was carried out in only one season - autumn, where days are short, access to sunlight is limited, and the weather is changeable, and which is not insignificant for human well-being. We can’t exclude that research conducted, for example, in winter (snow-covered logging area) would have yielded different results.
6. Conclusions
The visual forest landscape is an important source of information for the public in assessing the sustainability of forest resource management. Our research indicates that not all features of a commercial forest landscape have a regenerative effect on people, as measured by an increase in positive feelings, a decrease in negative feelings, an increase in subjective vitality and an improvement in mood. Contact with the forest, only in the case of a mature forest stand, provides the most benefits in terms of mood improvement. In contrast, exposure to clear-cutting area resulted in a decrease in positive feelings and an increase in negative feelings, leading to a complete disturbance of mood, an increase in ‘Tension’, ‘Depression’ and a decrease in feelings of ‘Vigor’. Clear-cutting area has significantly inferior restorative properties compared to mature forest stands and second-growth forest. This observation is important for managing forests within city limits and in the suburban zone of large cities. Results from these studies have been important for implementing recreational and scenic values in forestry policy, forest planning and forest management. Not only is clear cutting area not accepted by people visiting forests for recreational purposes, but it leads to a reduction in the health benefits provided by forests. Forest resource managers need to find ways to modify harvesting methods that will gain greater public acceptance, but also not lead to a dramatic decrease in the value of restoring forests.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, E.J. K.Cz. and M.W.; methodology, E.J. and M.W.; software, K.Cz., T.D and N.K.; validation, E.J., N.K. and J.F.; formal analysis, K.Cz. and T.D.; investigation, N.K. and J.F., M.W.; resources, M.W. and N.K.; data curation, K.Cz.; writing—original draft preparation, E.J.; writing—review and editing, M.W., J.F; visualization, K.Cz., E.J., N.K;
Funding
“This research received no external funding”
Conflicts of Interest
“The authors declare no conflicts of interest.”
References
- Ranacher, L., Sedmik, A. and Schwarzbauer, P. Public perceptions of forestry and the forest-based bioeconomy in the European Union. Knowledge to Action 03, 2020, European Forest Institute. [CrossRef]
- Konijnendijk, C.C. A decade of urban forestry in Europe. For. Policy Econ. 2003, 5, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.; Nordlund, A.M.; Olsson, O.; Westin, K. Recreation in Different Forest Settings: A Scene Preference Study. Forests 2012, 3, 923–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, K.-S.; Kim, S.; Song, M.K.; Kang, K.I.; Jeong, Y. The Effects of a Health Promotion Program Using Urban Forests and Nursing Student Mentors on the Perceived and Psychological Health of Elementary School Children in Vulnerable Populations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, O. Out of the Wild: Studies on the Forest as a Recreational Resource for Urban Residents. Ph.D. Thesis, Umeå Universitet, Umeå, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects 2022: Summary of Results. UN DESA/POP/2022/TR/NO. 3.
- Dudek, T. Effect of forest management on recreational usefulness of suburban forests. Sylwan 2017, 161, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-López, B.; Iniesta-Arandia, I.; García-Llorente, M.; Palomo, I.; Casado-Arzuaga, I.; Amo, D.G.D.; Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Oteros-Rozas, E.; Palacios-Agundez, I.; Willaarts, B.; et al. Uncovering ecosystem service bundles through social preferences. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38970. [Google Scholar]
- Nastran, M.; Pintar, M.; Železnikar, Š.; Cvejic ́, R. Stakeholders’ Perceptions on the Role of Urban Green Infrastructure in Providing Ecosystem Services for Human Well-Being. Land 2022, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeczko E., Banaś J., Woźnicka M., Zięba S., Banaś K.U., Janeczko K., Fialova, J. Sociocultural Profile as a Predictor of Perceived Importance of Forest Ecosystem Services: A Case Study from Poland. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14154. [CrossRef]
- Beil K., Hanes D. The influence of urban natural and built environments on physiological and psychological measures of stress—A pilot study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 1250–1267.
- White M., P. , Pahl S., Ashbullby K., Herbert S., Depledge M. H. Feelings of restoration from recent nature visits. J. Environ. Psychol. 2013, 35, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrväinen L., Ojala A., Korpela K., Lanki T., Tsunetsugu Y., Kagawa T. The influence of urban green environments on stress relief measures: A field experiment, Journal of Environmental Psychology, Volume 38, 2014: 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Hartig, T. , Staats H. The need for psychological restoration as a determinant of environmental preferences. J. Environ. Psychol. 2006, 26, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson S., U. , Grahn P. Stressed individuals’ preferences for activities and environmental characteristics in green spaces. Urban For. Urban Green. 2011, 10, 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Janeczko, E. , Bielinis E., Wójcik R., Woźnicka M., Kędziora W., Łukowski A., Elsadek M., Szyc K., Janeczko K. When Urban Environment is Restorative: The Effect of Walking in Suburbs and Forests on Psychological and Physiological Relaxation of Young Polish Adults. Forests 2020, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravenscroft, N. Tales from the tracks: Discourses of constraint in the use of mixed cycle and walking routes. Int. Rev. Sociol. Sport 2004, 39, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, K.D.; Wolch, J.; Byrne, J.; Chou, C.P.; Feng, G.; Weaver, S.; Jerrett, M. Trail characteristics as correlates of urban trail use. Am. J. Health Promot. 2007, 21, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahvanainen L., Tyrväinen L., Ihalainen M., Vuorela N., Kolehmainen O. 2001. Forest management and public perceptions — visual versus verbal information, Landscape and Urban Planning, Volume 53, Issues 1–4, 2001, Pages 53-70. [CrossRef]
- Giergiczny M., Czajkowski M., Żylicz T., Angelstam P. Choice experiment assessment of public preferences for forest structural attributes, Ecological Economics, Volume 119, 2015: 8-23. [CrossRef]
- Shifley S.R., Thompson F.R., Dijak W.D., Larson M.A., Millspaugh J.J.Simulated effects of forest management alternatives on landscape structure and habitat suitability in the Midwestern United States, Forest Ecology and Management,Volume 229, Issues 1–3, 2006: 361-377. [CrossRef]
- Pastorella, F., Avdagić, A., Čabaravdić, A., Mraković, A., Osmanović, M. and Paletto, A. Tourists’ perception of deadwood in mountain forests. Annals of Forest Research, 2016, 59(2), 311–326. [CrossRef]
- Thompson Coon, J.; Boddy, K.; Stein, K.; Whear, R.; Barton, J.; Depledge, M.H. Does Participating in Physical Activity in Outdoor Natural Environments Have a Greater Effect on Physical and Mental Wellbeing than Physical Activity Indoors? A Systematic Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen V., Stange E. E., Kaltenborn B. P., Vistad O. I. Public visual preferences for dead wood in natural boreal forests: The effects of added information. Landscape and Urban Planning 158. 2017. 12–24.
- Tsunetsugu, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, B.J.; Tyrväinen, L.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological and Psychological Effects of Viewing Urban Forest Landscapes Assessed by Multiple Measurements. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 113, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, P. Internal structure stability of positive and negative concepts. Pol. Psychol. Bull. 1991, 22, 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, J.R.; Henry, J.D. The Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS): Construct validity, measurement properties and normative data in a large non-clinical sample. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 2004, 43, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, N.; Fujiwara, A.; Saito, H.; Horiuchi, M. Management Effectiveness of a Secondary Coniferous Forest for Landscape Appreciation and Psychological Restoration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017a, 14, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, N.; Saito, H.; Fujiwara, A.; Horiuchi, M. The effect of slight thinning of managed coniferous forest on landscape appreciation and psychological restoration. Prog. Earth Planet Sci. 2017b, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielinis, E.; Takayama, N.; Boiko, S.; Omelan, A.; Bielinis, L. The effect of winter forest bathing on psychological relaxation of young Polish adults. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 29, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpela, K.; Ylén, M.; Tyrväinen, L.; Silvennoinen, H. Determinants of restorative experiences in everyday favourite places. Health Place 2008, 14, 636–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpela, K.; Ylén, M.; Tyrväinen, L.; Silvennoinen, H. Favorite green, waterside and urban environments, restorative experiences and perceived health in Finland. Health Promot. Int. 2010, 25, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, B.; Koniarek, J. The adaptation of Profile of Mood States (POMS) by D.M. McNair M. Lorr, L.F. Droppelman. Przegla ̨d Psychol. 1987, 30, 753–762. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-T.; Yu, C.-P.; Lee, H.-Y. The Effects of Forest Bathing on Stress Recovery: Evidence from Middle-Aged Females of Taiwan. Forests 2018, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-P.; Lin, C.-M.; Tsai, M.-J.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-Y. Effects of short forest bathing program on autonomic nervous system activity and mood states in middle-aged and elderly individuals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Park, B.J.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Ohira, T.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Effect of forest bathing on physiological and psychological responses in young Japanese male subjects. Public Health 2011, 125, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, R.A.; Irvine, K.N.; Devine-Wright, P.; Warren, P.H.; Gaston, K.J. Psychological benefits of green space increase with biodiversity. Biol. Lett. 2007, 3, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielinis, E.; Bielinis, L.; Krupińska-Szeluga, S.; Lukowski, A.; Takayama, N. The Effects of a Short Forest Recreation Program on Physiological and Psychological Relaxation in Young Polish Adults. Forests 2019, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korcz, N., Janeczko, E., Bielinis, E., Urban, D., Koba, J., Szabat, P., & Małecki, M. Influence of informal education in the forest stand redevelopment area on the psychological restoration of working adults. Forests, 2021, 12(8), 993.
- Milligan C., Bingley A. Restorative places or scary spaces? The impact of woodland on the mental well-being of young adults. Health & Place, 2007, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 799–811.
- Zeidenitz C., Mosler H. J., Hunziker1 M. Outdoor recreation: from analysing motivations to furthering ecologically responsible behaviour. For. Snow Landsc. Res. 2007, 81, 1/2: 175–190.
- Kaplan, R., & Kaplan, S. The experience of nature: A psychological perspective. Cambridge University Press, 1989.
- Herzog T.R.; Kutzli, G.E. Preference and perceived danger in field/forest settings. Environ. Behav. 2002. 34: 819–83.
- Silvennoinen, H. , Pukkala, T., & Tahvanainen, L. Effect of Cuttings on the Scenic Beauty of a Tree Stand. Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 2002, 17(3), 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radeloff, Volker, Hammer, Roger, Stewart, Susan,Fried, Jeremy, Holcomb, S.S., Mckeefry, And. The Wildland Urban Interface in the United States. Communications Ecological Applications, 2005, 15. 799-805. [CrossRef]
- Gundersen V. S., Frivold L. H. Public preferences for forest structures: A review of quantitative surveys from Finland, Norway and Sweden, Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, Volume 7, Issue 4, 2008: 241-258. [CrossRef]
- Edwards D., Jay M., Jensen F. S, Lucas B., Marzano M., Montagné C., Peace A., Weiss G. Public preferences for structural attributes of forests: Towards a pan-European perspective. Forest Policy and Economics, Volume 19, 2012: 12-19. [CrossRef]
- Stachová, J. Forests in the Czech public discourse. Journal of Landscape Ecology(Czech Republic), 2018, 11(3), 33–44. [CrossRef]
- Ribe R. G. In-stand scenic beauty of variable retention harvests and mature forests in the U.S. Pacific Northwest: The effects of basal area, density, retention pattern and down wood. Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 91, Issue 1, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Kearney A.R., Bradley G.A. The Effects of Viewer Attributes on Preference for Forest Scenes: Contributions of Attitudes, Knowledge, Demographic Factors, and Stakeholder Group Membership. Environ. Behav., 2011, 43, pp. 147-181. [CrossRef]
- Dudek, T. Effects of forest management in aesthetic quality of forest landscape. Acta Sci. Pol. Silv. Colendar. Ratio Ind. Lignar. 2017b, 16, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll F., Müller F., Haase D., Fohrer N. Rural–urban gradient analysis of ecosystem services supply and demand dynamic. Land Use Policy, Volume 29, Issue 3, 2012: 521-535. [CrossRef]
- Frank S., Fürst Ch., Koschke L., Witt A., Makeschin F. Assessment of landscape aesthetics—Validation of a landscape metrics-based assessment by visual estimation of the scenic beauty. Ecological Indicators, Volume 32, 2013: 222-231. [CrossRef]
- Takayama, N.; Korpela, K.; Lee, J.; Morikawa, T.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Park, B.-J.; Li, Q.; Tyrväinen, L.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kagawa, T. Emotional, restorative and vitalizing effects of forest and urban environments at four sites in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 7207–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamison, D.T.; Gelband, H.; Horton, S.E.; Jha, P.K.; Laxminarayan, R.; Mock, C.N.; Nugent, R. Disease control priorities: Improving health and reducing poverty (English). In Disease Control Priorities; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Simkin, J.; Ojala, A.; Tyrväinen, L. Restorative effects of mature and young commercial forests, pristine old-growth forest and urban recreation forest—A field experiment. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 48, 126567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.H.; Woo, J.M.; Ryu, J.S. Effect of a forest therapy program and the forest environment on female workers’ stress. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek T., Piegdoń A. The impact of forest recreation on health in the opinion of sanatorium patients. Sylwan 2021, 165, 841−852. [CrossRef]
- Ustawa o Lasach [Dz.U 1991 nr 101 poz.444 ze zm.].
- Park, B.-J.; Furuya, K.; Kasetani, T.; Takayama, N.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Relationship between Psychological Responses and Physical Environments in Forest Settings. Landscape and Urban Planning 2011, 102, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrväinen, L.; Pauleit, S.; Seeland, K.; De Vries, S. Benefits and Uses of Urban Forests and Trees. In Urban Forests and Trees; Konijnendijk, C., Nilsson, K., Randrup, T., Schipperijn, J., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005; pp. 81–114. ISBN 978-3-540-25126-2. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. Aesthetic preference and ecological sustainability. Forest and Landscapes. Linking ecology, sustainability and aesthetics. 2001, 15-29. [CrossRef]
- Sreetheran M., Konijnendijk van den Bosch C. C. A socio-ecological exploration of fear of crime in urban green spaces – A systematic review, Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2014, Volume 13, Issue 1: 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Martens D., Gutscher H., Bauer N. Walking in “wild” and “tended” urban forests: The impact on psychological well-being. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 2011, 31, 36-44. [CrossRef]
- Nielsen AB, Heyman E, Richnau G Liked, disliked and unseen forest attributes: relation to modes of viewing and cognitive con- structs. J Environ Manag, 2012, 113:456–466.
- Janeczko, E. , Bielinis, E., Tiarasari, U., Woźnicka, M., Kędziora, W., Przygodzki, S., & Janeczko, K. How Dead Wood in the Forest Decreases Relaxation? The Effects of Viewing of Dead Wood in the Forest Environment on Psychological Responses of Young Adults. Forests, 2021, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai H, Ikei H, Song C, Kobayashi M, Miura T, Kagawa T, Li Q, Kumeda S, Imai M, Miyazaki Y. Physiological and Psychological Effects of a Forest Therapy Program on Middle-Aged Females. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 1;12(12):15222-32. [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente De Val G., Mühlhauser S. H. Visual quality: An examination of a South American Mediterranean landscape, Andean foothills east of Santiago (Chile), Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, Volume 13, Issue 2, 2014: 261-271. [CrossRef]
- Ribe, R.G. The aesthetics of forestry: What has empirical forest research taught us? Environ. Manage. 1989, 13, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrväinen, L.; Silvennoinen, H.; Kolehmainen, O. Ecological and aesthetic values in urban forest management. Urban For. Urban Green. 2003, 1, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).