Submitted:
25 July 2024
Posted:
26 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
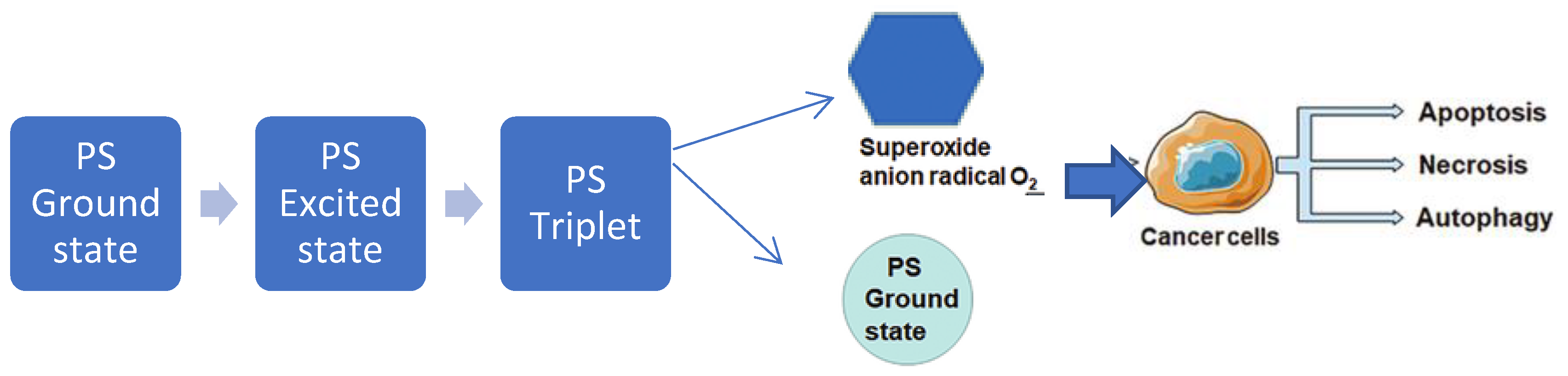
2. Investigating the Mechanism of Action for Enhanced Efficacy.
3. Chlorella sp. and Subcellular Localization
Chlorophyll a (C₅₅H₇₂O₅N₄Mg) (1) and Chlorophyll b (C₅₅H₇₀O₆N₄Mg) (2):
Carotenoids (β-carotene, C₄₀H₅₆) (3) :
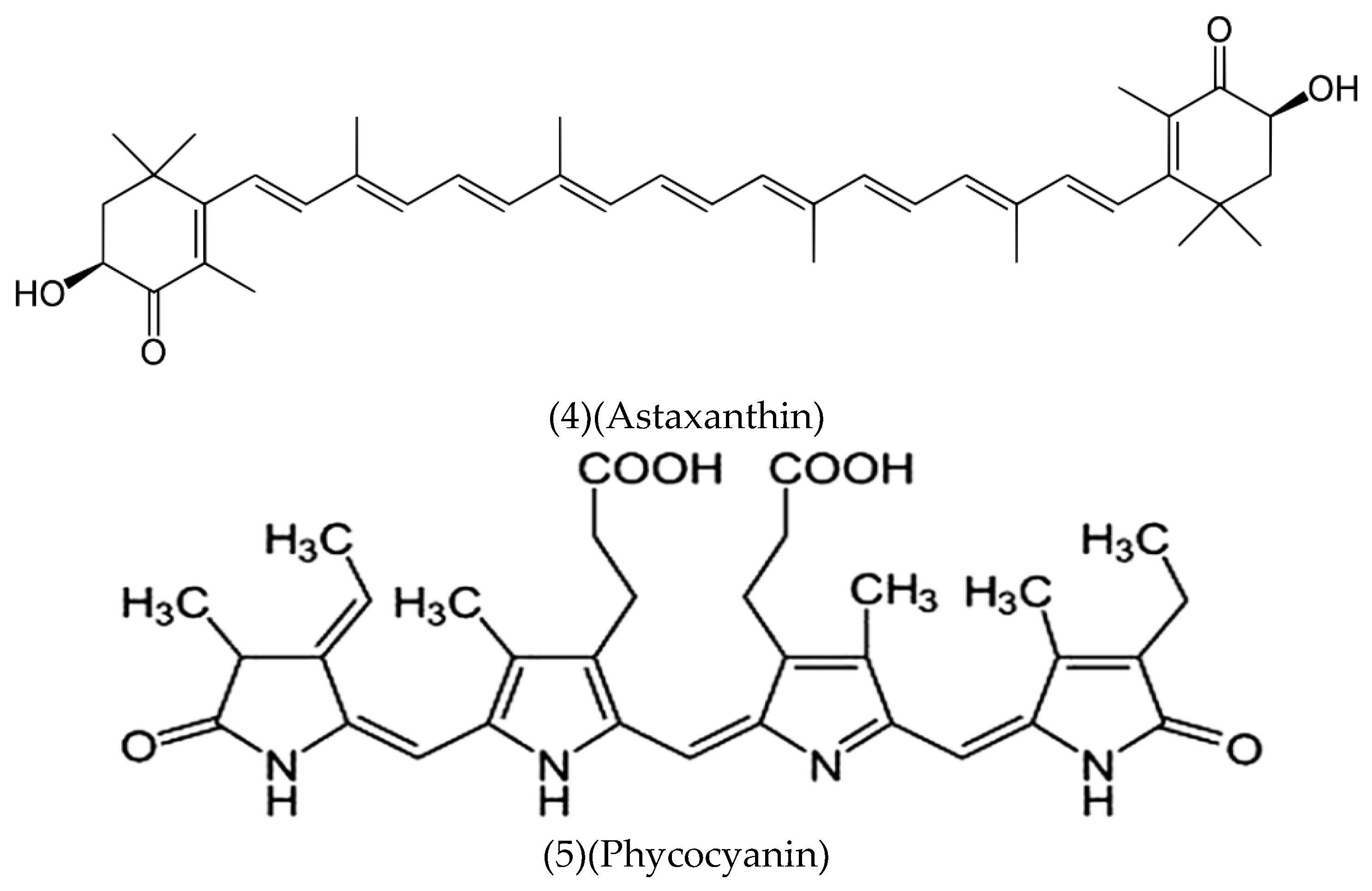
Astaxanthin (C₄₀H₅₂O₄) (4):
Phycocyanin (C₃₇H₆₄N₈O₁₆S₄) (5):
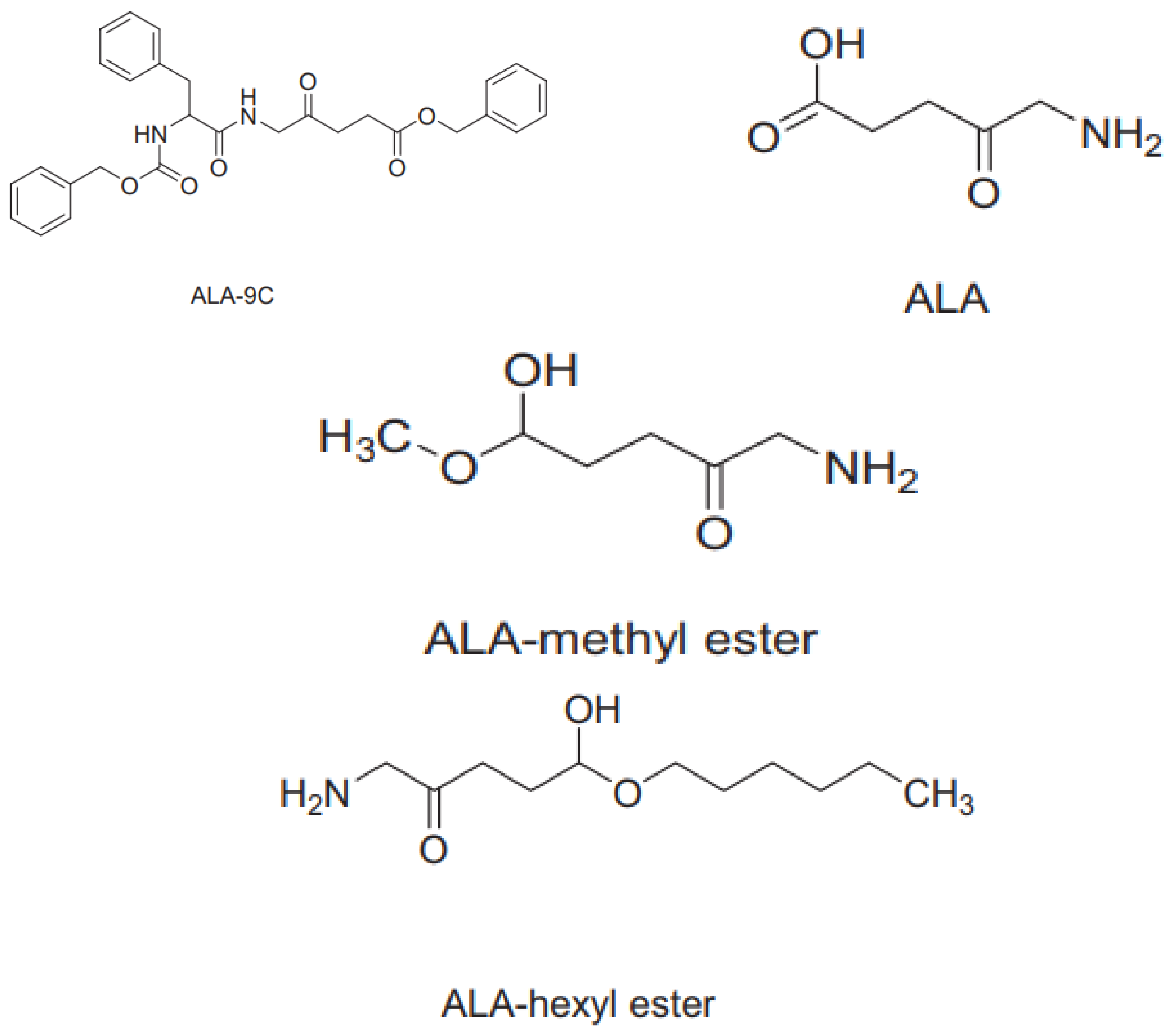
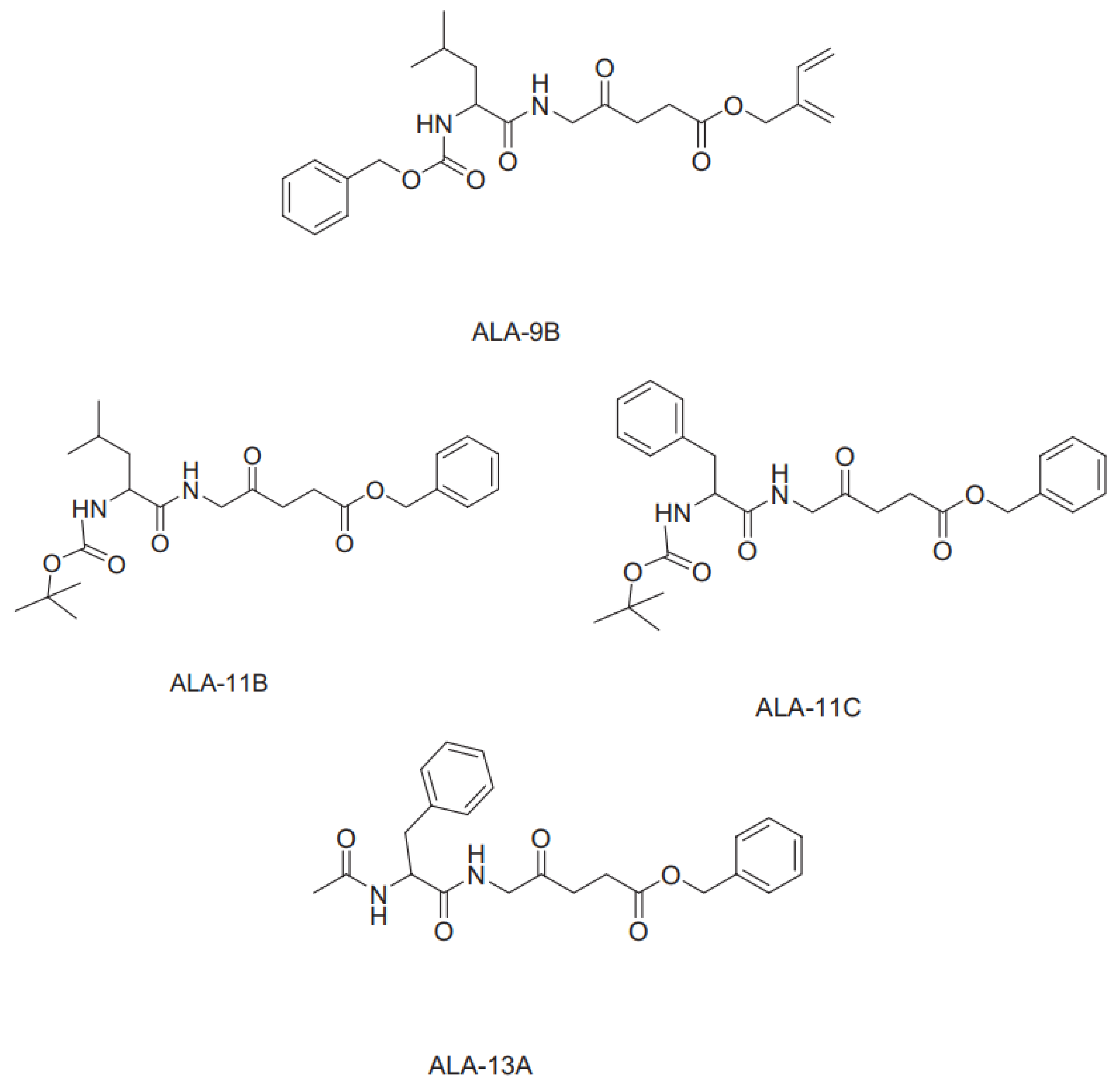
4. Isolation of Sensitizing Substances from Microalgae Using Column Chromatography.
5. Conclusion
Funding
List of Abbreviations
| PDT | photodynamic therapy |
| eg | exampleli gratia |
| 2-EP | 2-ethylpyridine |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical. |
| 5-ALA | (5-aminolevulinic acid) |
| PS | photosensitizers |
| g | gramm |
| kg | kilogramm |
| etc | et cetera |
| ml | milliliter |
| i.e., | id est |
| ALA | alanine |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| UV | ultraviolet |
| UV-Vis | ultraviolet-visible |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffered Saline |
| TLC | Thin Layer Chromatography |
| HPLC | High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| DCFDA | Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate |
References
- Jabeen et al., “Effect of the Photodynamic Therapy Applications with Potent Microalgae Constituents on Several Types of Tumor”.
- W. Pang et al., “Nucleolus-Targeted Photodynamic Anticancer Therapy Using Renal-Clearable Carbon Dots”.
- J. A. Miller et al., “Photodynamic therapy with the phthalocyanine photosensitizer Pc 4: The case experience with preclinical mechanistic and early clinical–translational studies”.
- Yoon, J. Li and Y. K. Shim, “Advance in Photosensitizers and Light Delivery for Photodynamic Therapy”.
- Saide, C. Lauritano and A. Ianora, “Pheophorbide a: State of the Art”.
- K. C. D. Andrade, C. Lauritano, G. Romano and A. Ianora, “Marine Microalgae with Anti-Cancer Properties”.
- “Photodynamic Therapy to Treat Cancer - NCI”.
- Y. Tian, L. L. Wang and W. Wang, “Progress in photodynamic therapy on tumors”.
- 9. T J Dougherty, C J Gomer, B W Henderson, G Jori, D Kessel, M Korbelik, J Moan, Q Peng Photodynamic therapy.
- Paul Harrod-Kim, “Tumor ablation with photodynamic therapy: introduction to mechanism and clinical applications.”.
- Conte, F. Ungaro, A. Mazzaglia and F. Quaglia, “Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer: Principles, Clinical Applications, and Nanotechnological Approaches”.
- Y. Qiao et al., “Engineered algae: A novel oxygen-generating system for effective treatment of hypoxic cancer”.
- T. J. Dougherty et al., “Photodynamic Therapy”.
- S. Cogno, P. Gilardi, L. R. Comini, S. C. Núñez-Montoya, J. L. Cabrera and V. Rivarola, “Natural photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy: In vitro activity against monolayers and spheroids of human colorectal adenocarcinoma SW480 cells”.
- K. L. M. Santos et al., “Prospective application of phthalocyanines in the photodynamic therapy against microorganisms and tumor cells: a mini-review.”.
- Y. Karakaş, H. T. Şahin, B. İnan, D. Özçimen and Y. Erginer, “In vitro cytotoxic activity of microalgal extracts loaded nano–micro particles produced via electrospraying and microemulsion methods”.
- S. Braune, A. Krüger-Genge, S. Kammerer, F. Jung and J. Küpper, “Phycocyanin from Arthrospira platensis as Potential Anti-Cancer Drug: Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies”.
- S. S. Kulthe, Y. Choudhari, N. Inamdar and V. Mourya, “Polymeric micelles: authoritative aspects for drug delivery”.
- R. R. Allison and K. Moghissi, “Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): PDT Mechanisms”.
- Mazzaglia, “Photodynamic Tumor Therapy with Cyclodextrin Nanoassemblies”.
- M. Olszowy, M. Nowak-Perlak and M. Woźniak, “Current Strategies in Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) and Photodynamic Diagnostics (PDD) and the Future Potential of Nanotechnology in Cancer Treatment”.
- L. E. Ibarra et al., “Selective Photo-Assisted Eradication of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells through Aptamer Decoration of Doped Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles”.
- Lima and L. V. Reis, “Photodynamic Therapy: From the Basics to the Current Progress of N-Heterocyclic-Bearing Dyes as Effective Photosensitizers”.
- P. Agostinis et al., “Photodynamic therapy of cancer: An update”.
- X. Wang, D. Luo and J. P. Basilion, “Photodynamic Therapy: Targeting Cancer Biomarkers for the Treatment of Cancers”.
- T. A. Mishchenko, I. V. Balalaeva, A. A. Gorokhova, M. V. Vedunova and D. V. Krysko, “Which cell death modality wins the contest for photodynamic therapy of cancer?”.
- V. Straten, V. Mashayekhi, H. S. D. Bruijn, S. Oliveira and D. J. Robinson, “Oncologic Photodynamic Therapy: Basic Principles, Current Clinical Status and Future Directions”.
- T. Nelius, W. D. Riese and S. Filleur, “Photodynamic therapy: a promising alternative in oncology”.
- U. Chilakamarthi and L. Giribabu, “Photodynamic Therapy: Past, Present and Future”.
- C. Serra et al., “A look at clinical applications and developments of photodynamic therapy”.
- T. Tran et al., “Identification of Small Molecule Modulators of Gene Transcription with Anticancer Activity”.
- Paul Harrod-Kim “Tumor ablation with photodynamic therapy”.
- Thomas J. Dougherty, Charles J. Gomer, Barbara W. Henderson, Giulio Jori, David Kessel, Mladen Korbelik, Johan Moan, and Qian Peng* “Photodynamic Therapy.
- Chun-Yan Wang “Photosensitization of phycocyanin extracted from Microcystis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells: implication of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis.”.
- D C Shackley, “Photodynamic therapy”.
- C. J. Gomer, A. Ferrario, M. Luna, N. Rucker and S. Wong, “Photodynamic therapy: Combined modality approaches targeting the tumor microenvironment”.
- S. Kwiatkowski et al., “Photodynamic therapy – mechanisms, photosensitizers and combinations”.
- H. Barr, C. Kendall, J. Reyes-Goddard and N. Stone, “Clinical Aspects of Photodynamic Therapy”.
- J. Zhang, C. Jiang, J. P. F. Longo, R. B. Azevedo, H. Zhang and L. A. Muehlmann, “An updated overview on the development of new photosensitizers for anticancer photodynamic therapy”.
- Qian Peng, Johan Moan, Jahn M Nesland, Peng n.d. “Correlation of subcellular and intratumoral photosensitizer localization with ultrastructural features after photodynamic therapy.”.
- Magdalena Cañete, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Cantoblanco, “Preclinical photodynamic therapy research in Spain. 3. Localization of photosensitizers and mechanisms of cell death in vitro”.
- D. Chen, C. A. Dougherty, K. Zhu and H. Hong, “Theranostic applications of carbon nanomaterials in cancer: Focus on imaging and cargo delivery”.
- T. Schluep et al., “Pharmacokinetics and tumor dynamics of the nanoparticle IT-101 from PET imaging and tumor histological measurements”.
- W. Park et al., “Advanced smart-photosensitizers for more effective cancer treatment”.
- D. Kessel, “Correlation between subcellular localization and photodynamic efficacy”.
- P. Mróz, A. Yaroslavsky, G. B. Kharkwal and M. R. Hamblin, “Cell Death Pathways in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer”.
- Xiao Yan He, “Effectiveness of photosensitive dye during uptake and redistribution”.
- L. Yang et al., “Boosting the photodynamic therapy efficiency with a mitochondria-targeted nanophotosensitizer”.
- S. Sansaloni-Pastor, J. Bouilloux and N. Lange, “The Dark Side: Photosensitizer Prodrugs”.
- C. Constantin and M. Neagu, “Photosensitizers Imprinting Intracellular Signaling Pathways in Dermato-Oncology Therapy”.
- T. M. Busch, “Local physiological changes during photodynamic therapy”.
- “Photodynamic Therapy to Treat Cancer”.
- S. Kumari, A. K. Badana, M. M. G, G. Shailender and R. Malla, “Reactive Oxygen Species: A Key Constituent in Cancer Survival”.
- P. Jia, C. Dai, P. Cao, D. I. Sun, R. Ouyang and Y. Miao, “The role of reactive oxygen species in tumor treatment”.
- W. H. Ahsan, “Reactive oxygen species: role in the development of cancer and various chronic conditions”.
- Yu, J. Yan, Z. Li, L. Yang, F. Ju and Y. Sun, “Recent trends in emerging strategies for ferroptosis-based cancer therapy”.
- J. P. Fruehauf and F. L. Meyskens, “Reactive Oxygen Species: A Breath of Life or Death?”.
- T. Hu, Z. Wang, W. Shen, R. Liang, D. Yan and M. Wei, “Recent advances in innovative strategies for enhanced cancer photodynamic therapy”.
- S. Mallidi, S. Anbil, A. Bulin, G. Obaid, M. Ichikawa and T. Hasan, “Beyond the Barriers of Light Penetration: Strategies, Perspectives and Possibilities for Photodynamic Therapy”.
- Shannon M Gallagher-colombo, Amanda L Maas, “Photodynamic therapy-induced angiogenic signaling: consequences and solutions to improve therapeutic response.”.
- R. L. Yanovsky, D. W. Bartenstein, G. S. Rogers, S. J. Isakoff and S. T. Chen, “Photodynamic therapy for solid tumors: A review of the literature”.
- C P Lowdell, “Photodynamic therapy: an update.”.
- N. Shah et al., “Deep-Tissue Activation of Photonanomedicines: An Update and Clinical Perspectives”.
- “Advances in Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer Bentham Science”.
- D. L. Sai, J. Lee, D. L. Nguyen and Y. Kim, “Tailoring photosensitive ROS for advanced photodynamic therapy”.
- R. K. Pandey et al., “Nature: A rich source for developing multifunctional agents. tumor-imaging and photodynamic therapy”.
- Agnieszka Szurko “Spectroscopic and biological studies of a novel synthetic chlorin derivative with prospects for use in PDT.”.
- Z. Zhuo, Z. Song, Z. Ma, Y. Zhang, G. Xu and G. Chen, “Chlorophylline6-mediated photodynamic therapy inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells”.
- 69. Shaikh Abdur Razzak Comprehensive overview of microalgae-derived carotenoids and their applications in diverse industries.
- 70. Po-Fung Ip, Feng Chen Production of astaxanthin by the green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis in the dark.
- Mafalda Trovão, Lucas Cardoso, Lisa Schüler, Adriana Machado, Gonçalo Espírito Santo, Humberto Pedroso, Ana Reis, Ana Barros, Nádia Correia, Monya Costa, Sara Ferreira, Helena Cardoso, Marília Mateus, Joanam Silva, Hugo Pereira, Filomena Freitas, João Varela. Oxyfluorfen: a novel metabolic inhibitor to select microalgal chlorophyll-deficient mutant strains for nutritional applications.
- T. Lafarga Effect of microalgal biomass incorporation into foods: nutritional and sensorial attributes of the end products.
- Andrêssa S. Fernandes, Patrícia A. Caetano, Eduardo Jacob-Lopes, Leila Queiroz Zepka, Veridiana Vera de Rosso. Alternative green solvents associated with ultrasound-assisted extraction: A green chemistry approach for the extraction of carotenoids and chlorophylls from microalgae.
- Arti Sharma, Meenu Chhabra, Shashi Kumar. Performance evaluation of genetically modified microalgae in photosynthetic microbial fuel cells for carotenoids and power generation.
- Yamini Sumathi, Prashant Kumar, Reeta Rani Singhania, Chiu-Wen Chen, Baskar Gurunathan, Cheng-Di Dong, Anil Kumar Patel. Harnessing Fe3O4 nanoparticles for sustainable harvesting of astaxanthin-producing microalgae: Advancing industrial-scale biorefinery.
- Yanlong Gu, Michelle Yee Mun Teo, Lionel Lian Aun In, Kazuya Shimizu, Kyu-Jung Chae, Tran Thi Ngoc Thu, Kuan Shiong Khoo. Genetic engineering of Haematococcus pluvialis microalgae for the enhancement of astaxanthin production.
- Zengyu Yu, Weiyang Zhao, Han Sun, Haijin Mou, Jin Liu, Hui Yu, Lei Dai, Qing Kong, Shufang Yang. Phycocyanin from microalgae: A comprehensive review covering microalgal culture, phycocyanin sources and stability.
- Shuyu Liu, Zitong Wu, Xin Min, Hong Liu, Nijuan Nian, Pei Zhang, Xiaoyu Li. Synergism Variation between intracellular Glutathione, phycocyanin and SOD in microalgae by carbon quantum dot fluorescence.
- 79. Israel Emiezi Agarry, Desheng Ding, Yunchang Li, Zihan Jin, Huiling Deng, Jiang Hu, Tian Cai, Jianquan Kan, Kewei Chen In vitro bioaccessibility evaluation of chlorophyll pigments in single and binary carriers.
- Eric Biehler, Anouk Kaulmann, Lucien Hoffmann, Elmar Krause, Torsten Bohn. Dietary and host-related factors influencing carotenoid bioaccessibility from spinach (Spinacia oleracea).
- Kewei Chen, María Roca. In vitro digestion of chlorophyll pigments from edible seaweeds.
- Zhuo Chen, Jiu-Qiang Xiong. Recovery mechanism of a microalgal species, Chlorella sp. from toxicity of doxylamine: Physiological and biochemical changes, and transcriptomics.
- Nathanan Preechaphonkul, Sukrit Sirikwanpong, Cherdsak Maneeruttanarungroj. Freshwater green alga Chlorella sp. KLSc59 produced all forms of omega-3 oil: ALA, EPA, and DHA.
- Gökhun Çağatay Erbil, Mahmut Elp, Yaşar Durmaz. Myo-inositol as a carbon source in Chlorella sp. production.
- Vaibhav Sunil Tambat, Anil Kumar Patel, Reeta Rani Singhania, Akash Pralhad Vadrale, Archana Tiwari, Chiu-Wen Chen, Cheng-Di Dong. Sustainable mixotrophic microalgae refinery of astaxanthin and lipid from Chlorella zofingiensis.
- Yamini Sumathi, Prashant Kumar, Reeta Rani Singhania, Chiu-Wen Chen, Baskar Gurunathan, Cheng-Di Dong, Anil Kumar Patel. Harnessing Fe3O4 nanoparticles for sustainable harvesting of astaxanthin-producing microalgae: Advancing industrial-scale biorefinery.
- Dong-Yeon Kim, Durairaj Vijayan, Ramasamy Praveenkumar, Jong-In Han, Kyubock Lee, Ji-Yeon Park, Won-Seok Chang, Jin-Suk Lee, You-Kwan Oh. Cell-wall disruption and lipid/astaxanthin extraction from microalgae: Chlorella and Haematococcus.
- Birgitta Narindri Rara Winayu, Kuan-Ya Chiu, Hsin-Ta Hsueh, Hsin Chu. Thermosynechococcus sp. CL-1 (TCL-1) as an efficient cyanobacterium in CO2 fixation, C-phycocyanin production, and removal of Cd and Pb.
- Birgitta Narindri Rara Winayu, Yu-Ting Lin, Hsin-Ta Hsueh, Hsin Chu. Importance of lighting color and period for CO2 fixation and C-phycocyanin production during Thermosynechococcus sp. CL-1 growth.
- Birgitta Narindri Rara Winayu, Hsin-Ta Hsueh, Hsin Chu. CO2 fixation and cultivation of Thermosynechococcus sp. CL-1 for the production of phycocyanin.
- F. D. Santos et al., “Distinct photo-oxidation-induced cell death pathways lead to selective killing of human breast cancer cells”.
- Moserová and J. Králová, “Role of ER Stress Response in Photodynamic Therapy: ROS Generated in Different Subcellular Compartments Trigger Diverse Cell Death Pathways”.
- Y. Adar et al., “Imidazoacridinone-dependent lysosomal photodestruction: a pharmacological Trojan horse approach to eradicate multidrug-resistant cancers”.
- W. Jiang, M. Liang, Q. Lei, G. Li and S. Wu, “The Current Status of Photodynamic Therapy in Cancer Treatment”.
- S. Sharma, P. Mróz, T. Dai, Y. Huang, T. G. S. Denis and M. R. Hamblin, “Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer and for Infections: What Is the Difference?”.
- M. Zahra, A. Chota, H. Abrahamse and B. P. George, “Efficacy of Green Synthesized Nanoparticles in Photodynamic Therapy: A Therapeutic Approach”.
- J. Nyst, I. B. Tan, F. Stewart and A. J. M. Balm, “Is photodynamic therapy a good alternative to surgery and radiotherapy in the treatment of head and neck cancer?”.
- L. Onofrejová et al., “Bioactive phenols in algae: The application of pressurized-liquid and solid-phase extraction techniques”.
- M. Plaza, M. Herrero, A. Cifuentes and E. Ibáñez, “Innovative natural functional ingredients from microalgae.”.
- Jesus, M. Correia-da-Silva, C. Afonso, M. Pinto and H. Cidade, “Isolation and Potential Biological Applications of Haloaryl Secondary Metabolites from Macroalgae”.
- Saide, K. A. Martínez, A. Ianora and C. Lauritano, “Unlocking the Health Potential of Microalgae as Sustainable Sources of Bioactive Compounds”.
- P. Abreu, R. Martins and J. Nunes, “Emerging Applications of Chlorella sp. and Spirulina (Arthrospira) sp.”.
- G. A. Colusse, J. Carneiro, M. E. R. Duarte, J. C. D. Carvalho and M. D. Noseda, “Advances in microalgal cell wall polysaccharides: a review focused on structure, production, and biological application”.
- M. Cañete, J. C. Stockert and A. Villanueva, “Preclinical photodynamic therapy research in Spain. 3. Localization of photosensitizers and mechanisms of cell death in vitro”.
- R. Wang, X. Li and J. Yoon, “Organelle-Targeted Photosensitizers for Precision Photodynamic Therapy”.
- S. P. M. Ventura et al., “Extraction of value-added compounds from microalgae”.
- G. Perin, E. Cimetta, F. Monetti, T. Morosinotto and F. Bezzo, “Novel micro-photobioreactor design and monitoring method for assessing microalgae response to light intensity”.
- Pulz and P. Kretschmer, “Perspectives of phototrophic microorganisms in environment protection and ecology”.
- R. Calori, B. Hong and A. C. Tedesco, “Expanding the Limits of Photodynamic Therapy: The Design of Organelles and Hypoxia-Targeting Nanomaterials for Enhanced Photokilling of Cancer”.
- “Chromatography Adsorbents - Silica Gel and Aluminium Oxide”.
- Saitoh, I. Awaka and N. Suzuki, “Determination of chlorophylls by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with isocratic elution and the column-switching technique”.
- H. Inoue, K. Furuya, K. Watanabe, K. Tanaka, T. Shirai and E. Miyoshi, “Separation and Determination of Copper(II) Chlorophylls by Reversed-Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography”.
- W. Zheng, N. Thorne and J. C. McKew, “Phenotypic screens as a renewed approach for drug discovery”.
- S. Kraljević, P. J. Stambrook and K. Pavelić, “Accelerating drug discovery”.
- “Discovery and Development”.
- N. Suvorov, V. Pogorilyy, E. Diachkova, Y. Vasil’ev, А. Ф. Мирoнoв and M. A. Grin, “Derivatives of Natural Chlorophylls as Agents for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy”.
- A. H. A. Akhras, “Introducing the Effect of Chinese Chlorella as a Photosensitizing Drug at Different Temperatures”.
- G. Fasya, N. Millati, L. M. Rahmawati, R. Iyani, A. Hanapi, R. Ningsih, D. Yuliani и D. S. Megawati Isolation and bioactivity of steroids isolates from petroleum ether fraction of Chlorella sp.
- N. Meyer, N. R. Ferrigni, J. E. Putnarn, L. B. Jacobsen, D. E. Nichols, and J. L. McLaughlin, Planta Medica 45 (5), 31–34 (1982).
- G. Fasya, A. R. Dinasti, S. M. Syofiyah, L. M. Rahmawati, N. Millati, D. A. Safitri, S. Handoko, A. Hanapi, and R. Ningsih, ALCHEMY: Journal of Chemistry 5 (1), 5–9 (2016).
- F. Aprelia and Suyatno, UNESA Journal of Chemistry 2 (3), 94–99 (2013).
- D. Astuti, A. Maulana, and E. M. Kuntowati, Prosiding Seminar Nasional Kimia Universitas Negeri Surabaya, (Universitas Negeri Surabaya, 2014).
- Yousef Y. Sultan 1 , Diaa A. Marrez Isolation and Purification of Antifungal Compounds from the Green Microalga Chlorella vulgaris.
- Marrez DA, Naguib MM, Sultan YY, Daw ZY, Zaher SS, Higazy AM. Phytoplankton profile and toxicity assessment of dominant algal species from different Egyptian aquatic ecosystems. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci. 2016;7(2):1453-61.
- Yang J, Guo J, Yuan J. In vitro antioxidant properties of rutin. LWT Food Sci Technol. 2008;41(6):1060-6. [CrossRef]
- Prabhadevi V, Sahaya SS, Johnson M, Venkatramani B, Janakiraman N. Phytochemical studies on Allamanda cathartica L. using GC–MS. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012;2(2):S550-4. [CrossRef]
- Mujeeb F, Bajpai P, Pathak N. Phytochemical evaluation, antimicrobial activity, and determination of bioactive components from leaves of Aegle marmelos. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:497606. [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar P, Sambath R, Vasantharaj S. Antimicrobial potential and screening of antimicrobial compounds of Ruellia tuberose using GC-MS. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2013;20(1):184-9.
- Marrez DA, Sultan YY. Antifungal activity of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa against mycotoxigenic fungi. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2016;6(11):191- 8. [CrossRef]
- Sultan YY, Ali MA, Darwesh OM, Embaby MA, Marrez DA. Influence of nitrogen source in culture media on antimicrobial activity of Microcoleus lacustris and Oscillatoria rubescens. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci. 2016;7(2):1444-52.
- Marrez, DA, Sultan YY, Embaby MA. Biological activity of the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria brevis extracts as a source of nutraceutical and bio-preservative agents. Int J Pharmacol. 2017;13(8):1010-19. [CrossRef]
- Marrez DA, Naguib MM, Sultan YY, Higazy AM. Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of Scenedesmus obliquus metabolites. Heliyon. 2019;5(3):e01404. doi:10 .1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01404.
- Marrez DA, Sultan YY, Naguib MM, Higazy AM. Antimicrobial Activity, Cytotoxicity and Chemical Constituents of the Freshwater Microalga Oscillatoria princeps. Biointerface Res Appl Chem. 2022, 12(1):961- 77. [CrossRef]
- Ordog V, Stirk WA, Lenobel R, Bancířová M, Strnad M, Van Staden J, et al. Screening microalgae for some potentially useful agricultural and pharmaceutical secondary metabolites. J Appl Phycol. 2004;16(4):309- 14. [CrossRef]
- Khosravi K. The potential Health Benefits of Atgae and Micro Algae in Medicine: A Review on Spirulina Platensis. Curr Nutr Food Sci. 2011;7(4):279-85. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini S, Shahbazizadeh S, Khosravi-Darani K, Mozafari M. Spirulina paltensis: Food and Function. Curr Nutr Food Sci. 2013;9(3):189-93. [CrossRef]
- Shinya Shibata, Chiyoko Ishihara, Keisuke Matsumoto. Improved separation method for highly purified lutein from Chlorella powder using jet mill and flash column chromatography on silica gel.
- Matsuno, T. Structure and characterization of carotenoids from various habitats and natural sources. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 213, 22-31.
- Goodwin, T. W.; Britton, G. Distribution and analysis of carotenoids. In Plant Pigments; Goodwin, T. W., Ed.; Academic Press: London, 1988; pp 61-127.
- Ichioka, M.; Endo, H. Effect of light on cellular carotenoids formation of Chlorella regularis S-50 grown on glucose (in Japanese). Annu. Rep. Yakult Central Inst. Microbiol. Res. 1974, 5, 91-99.
- Yen-Ju Lee, Ying-Chen Yi, Yu-Chieh Lin, Chao-Chung Chen, Jia-Horung Hung, Jia-Yi Lin,I-Son Ng. Purification and biofabrication of 5-aminolevulinic acid for photodynamic therapy against pathogens and cancer cells.
- Armbruster CE, Mobley HL. Merging mythology and morphology: the multifaceted lifestyle of Proteus mirabilis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012;10:743–754. [CrossRef]
- Bunke A, Zerbe O, Schmid H, Burmeister G, Merkle HP, Gander B. Degradation mechanism and stability of 5-aminolevulinic acid. J Pharm Sci. 2000;89:1335–1341. [CrossRef]
- Cai J, Zheng Q, Huang H, Li B. 5-aminolevulinic acid mediated photodynamic therapy inhibits survival activity and promotes apoptosis of A375 and A431 cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2018;21:257–262. [CrossRef]
- Chen H, Jiang JG. Toxic effects of chemical pesticides (trichlorfon and dimehypo) on Dunaliella salina. Chemosphere. 2011;84:664–670. [CrossRef]
- Di Venosa G, Fukuda H, Perotti C, Batlle A, Casas A. A method for separating ALA from ALA derivatives using ionic exchange extraction. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2004;75:7–163. [CrossRef]
- Din, Lim SJ, Maskat MY, Abd Mutalib S, Zaini NAM. Lactic acid separation and recovery from fermentation broth by ion-exchange resin: a review. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2021;8:1–23. [CrossRef]
- Feng Lianga, Xueying Anc, Ruoxi Wang, Wenshu Wu, Lin Yang , Yixin Zheng, Qing Jiang, Xingquan Xu, Danni Zhong, Min Zhou. Microalgae-based drug delivery system for tumor microenvironment photo-modulating and synergistic chemo-photodynamic therapy of osteosarcoma.
- Bing-Chung Liau, Chun-Ting Shen, Fong-Ping Liang, Siang-En Hong, Shih-Lan Hsu, Ting-Ting Jong, Chieh-Ming J. Chang. Supercritical fluids extraction and anti-solvent purification of carotenoids from microalgae and associated bioactivity.
- M.M. Rebolloso-Fuentes, A. Navarro-Perez, F. Garcia-Camacho, J.J. RamosMiras, J.L. Guil-Guerrero, Biomass nutrient profiles of the microalga Nannochloropsis, J. Agricultural Food Chemistry 49 (2001) 2966–2972.
- T.L. Walker, S. Purton, D.K. Becker, C. Collet, Microalgae as bioreactors, Plant Cell Reports 24 (2005) 629–641.
- P.Z. Margalith, Production of ketocarotenoids by microalgae, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 51 (1999) 431–438.
- Herrero, A. Cifuentes, E. Ibanez, Sub- and supercritical fluid extraction ˜ of functional ingredients from different natural sources: plants, foodby-products, algae and microalgae: a review, Food Chem. 98 (2006) 136–148.
- L. Rodolfi, G. Chini Zittelli, N. Bassi, G. Padovani, N. Biondi, G. Bonini,M.R. Tredici, Microalgae for oil: strain selection, induction of lipid synthesis and outdoor mass cultivation in a low-cost photobioreactor, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 102 (2009) 100–112.
- Bhosale, Environmental and cultural stimulants in the production of carotenoids from microorganisms, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 63 (2004) 351–361.
- M.D. Macias-Sanchez, C. Mantell Serrano, M. Rodriguez Rodriguez, E. Martinez de la Ossa, L.M. Lubian, O. Montero, Extraction of carotenoids and chlorophyll from microalgae with supercritical carbon dioxide and ethanol as cosolvent, J. Sep. Sci. 31 (2008) 1352–1362.
- C.J. Chang, A.D. Randolph, Precipitation of microsize organic particles from supercritical fluids, AIChE J. 35 (1989) 1876–1882.
- 158. Victor Abrahamsson, Irene Rodriguez-Meizoso, Charlotta Turner Determination of carotenoids in microalgae using supercritical fluid extraction and chromatography.
- A.V. Rao, L.G. Rao, Pharmacological Research 55 (2007) 207.
- B.D. Ribeiro, D.W. Barreto, M.A.Z. Coelho, Food and Bioprocess Technology 4 (2011) 693.
- Rodríguez-Bernaldo de Quirós, H.S. Costa, Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 19 (2006) 97.
- L.C. Sander, K.E. Sharpless, M. Pursch, Journal of Chromatography A 880 (2000) 189.
- Su, K.G. Rowley, N.D.H. Balazs, Journal of Chromatography B: Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences 781 (2002) 393.
- J. Oliver, A. Palou, Journal of Chromatography A 881 (2000) 543.
- C.J. Welch, N. Wu, M. Biba, R. Hartman, T. Brkovic, X. Gong, R. Helmy, W. Schafer, J. Cuff, Z. Pirzada, L. Zhou, TrAC - Trends in Analytical Chemistry 29 (2010) 667.
- M.D. Macías-Sánchez, C. Mantell, M. Rodríguez, E. Martínez de la Ossa, L.M. Lubián, O. Montero, Journal of Supercritical Fluids 39 (2007) 323.
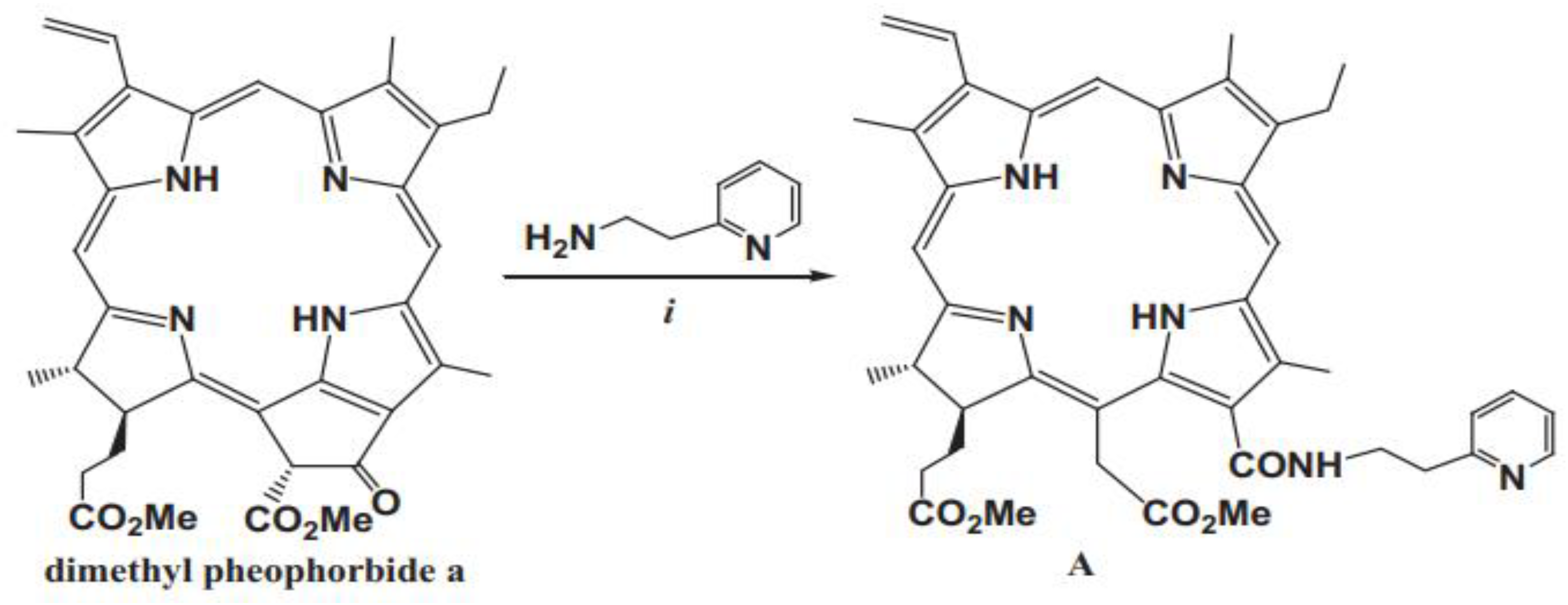
- Sonja Srdanovic , Ying-Hua Gao, Dan-Ye Chen, Yi-Jia Yan, Davor Margetic, Zhi-Long Chen. The photodynamic activity of 13-[2-(2-pyridyl)ethylamine] Сhlorin e6 photosensitizer in human esophageal cancer.
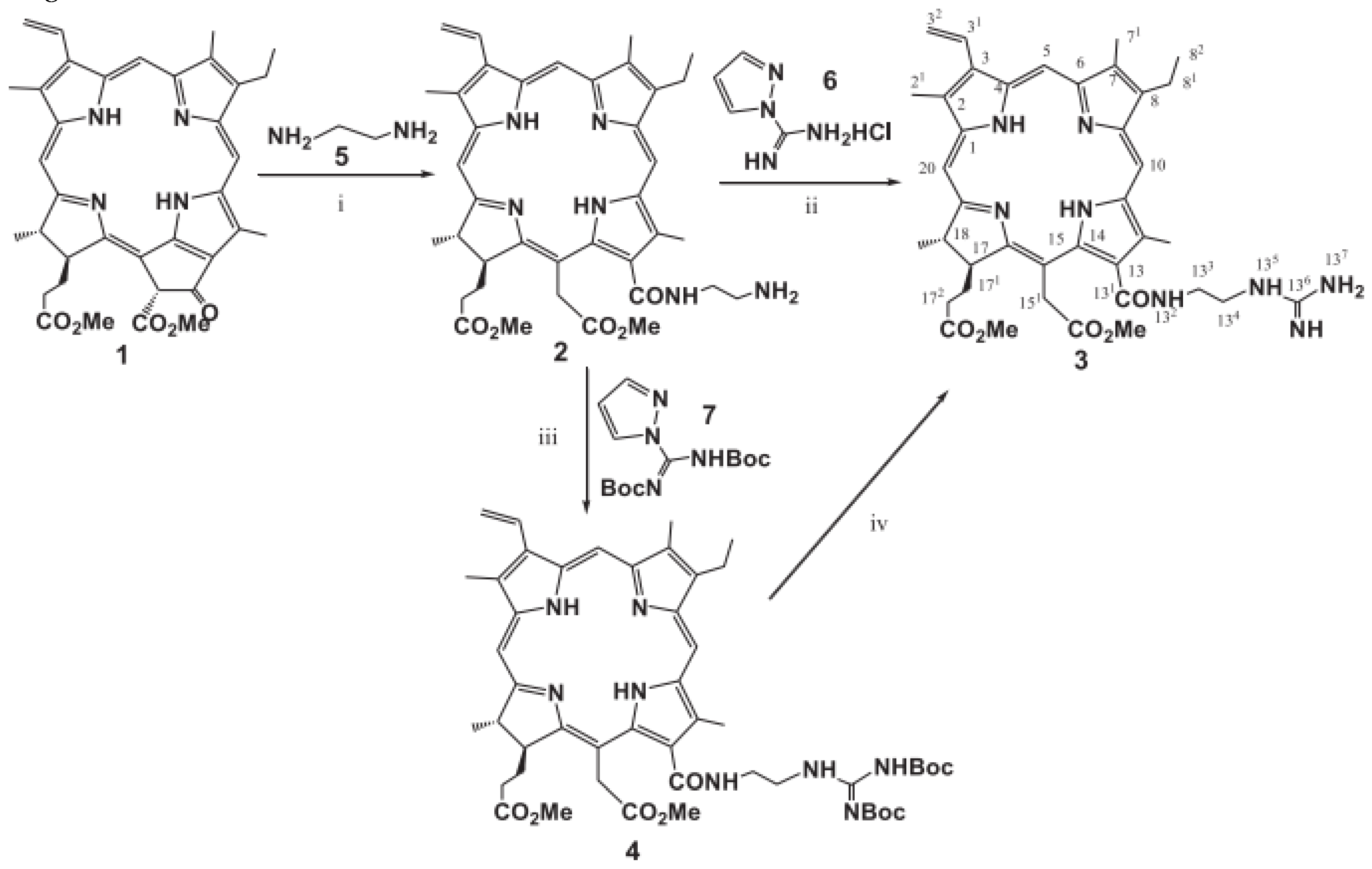
- Briš A, Marinic. Zˇ , Chen ZL, Margetic. D. Synthesis of chlorins by Diels-Alder cycloadditions of pheophorbide a and its derivatives. Synlett. 2015;26:991–994.
- Belykh DV, Kopylov EA, Gruzdev IV, Kuchin AV. Opening of the extra ring in pheophorbide a methyl ester by the action of amines as a one-step method for introduction of additional fragments at the periphery of chlorin macroring. Russ J Org Chem. 2010;46:577–585.
- Ying-Hua Gao, Vanda Lovrekovic, Akmaral Kussayeva, Dan-Ye Chen, Davor Margetic, Zhi-Long Chen. The photodynamic activities of dimethyl 13-[2-(guanidinyl)ethylamino] Сhlorin e6 photosensitizers in A549 tumor.
- R.G.W. Jinadasa, X. Hu, M.G.H. Vicente, K.M. Smith, Synthesis and cellular investigations of 173-, 152- and 131- amino acid derivatives of Chlorin e6, J. Med. Chem. 54 (2011) 7464-7476.
- M. Dud, Z. Glasovac, D. Margetic. The utilization of ball-milling in synthesis of aryl guanidines through guanidinylation and N-Boc-deprotection sequence, Tetrahedron 75 (2019) 109-115.
- 173. Ying-Hua Gao, Vanda Lovrekovi, Akmaral Kussayeva, Dan-Ye Chen, Davor Margetic, Zhi-Long Chen, The photodynamic activities of dimethyl 131 -[2-(guanidinyl) ethylamino] chlorin e6 photosensitizers in A549 tumor.
- 174. Автoры Faiza Sajjad, Ning-Ning Sun, Ting Chen, Yi-Jia Yan, Davor Margetić, Zhi-Long Chen «Evaluation of antimicrobial photodynamic activities of 5-aminolevulinic acid derivatives».

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




