1. Introduction
Renal cancer is among the most common malignant tumors worldwide [
1], While mortality rates have been steadily declining, the incidence of renal cancer has been increasing since the early 1970s, with an estimated 431,288 new cases globally in 2020 [
2].Due to its insidious and asymptomatic nature, renal cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced or metastatic stage, with a five-year survival rate of less than 20% for these patients (accounting for 30% of cases) [
3]. Unlike early localized kidney cancer, which can be treated surgically, advanced and metastatic renal cancer is primarily managed with immunotherapy, targeted drugs, and chemotherapy [
4].Despite the effectiveness of current treatments to some extent, therapeutic options remain limited, making it crucial to research and develop new antitumor strategies. Interestingly, recent studies have found that renal cancer is sensitive to ferroptosis [
5].
Ferroptosis is a novel form of cell death distinct from traditional apoptosis, driven by the accumulation of lipid peroxidation products and lethal reactive oxygen species (ROS) resulting from iron metabolism [
6]. Over the past decade, research has revealed that ferroptosis involves complex biological processes triggered by iron metabolism, lipid peroxidation accumulation, and antioxidant imbalance. With advancements in understanding the mechanisms of tumor ferroptosis regulation, substantial evidence suggests that inducing ferroptosis in tumor cells holds promise as a new therapeutic approach for cancer treatment [
7,
8,
9,
10]. This paper reviews the induction of ferroptosis in renal cancer cells from the perspectives of traditional Chinese medicine, natural compounds, resistance mechanisms, combination therapies, and nanomaterials, providing new strategies for ferroptosis-based therapy.
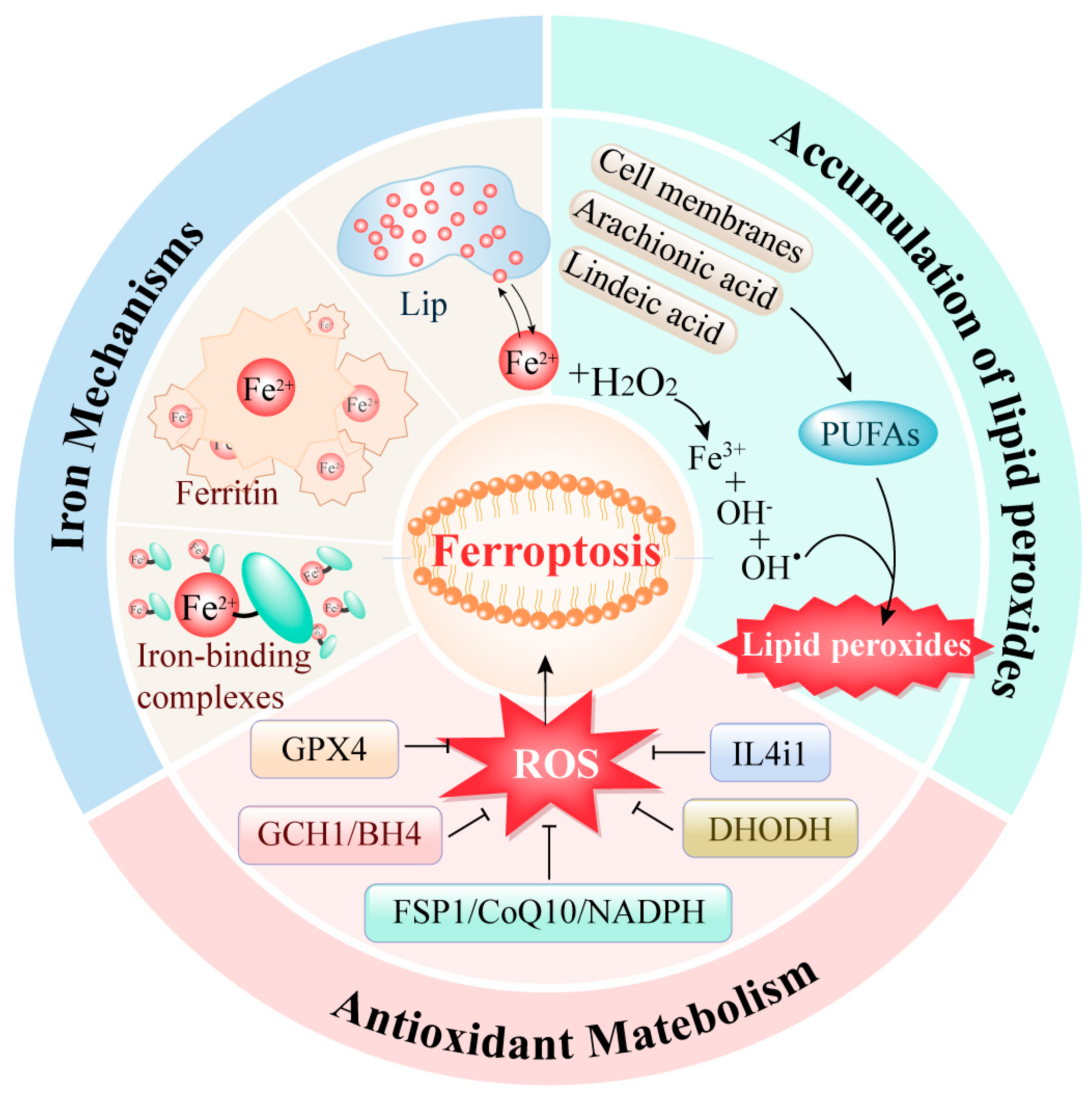
2. Mechanisms of Ferroptosis Regulation (Figure 1)
2.1. Iron Metabolism Abnormalities
Iron metabolism is a crucial cellular process in the occurrence of ferroptosis. Research indicates that an overload of intracellular iron can lead to ferroptosis in tumor cells [
11]. In the human body, iron typically exists in two forms: ferric ion (Fe³⁺) and ferrous ion (Fe²⁺). Ferric ions bind with transferrin and interact with transferrin receptor 1 (TFR1) to enter the cell [
12]. Once inside, ferric ions are reduced to ferrous ions by the ferric reductase STEAP3. These ferrous ions preferentially form various iron-binding complexes involved in numerous physiological and biochemical reactions. When these complexes approach saturation, excess ferrous ions accumulate within the cell, forming a labile iron pool. Additionally, excess iron can be stored as ferritin. Ferritin heavy chain possesses ferroxidase activity, converting ferrous ions back to ferric ions, safely encapsulating them within the ferritin shell to reduce the levels of free iron.
Thus, intracellular iron is primarily stored in two states: as ferritin or as free ferrous ions in the labile iron pool. Under normal circumstances, the intracellular iron concentration remains dynamically stable. However, during ferroptosis, the excess ferrous ions in the labile iron pool participate excessively in the Fenton reaction, generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as hydroxyl radicals. The accumulation of ROS leads to lipid peroxidation of the cell membrane, resulting in cellular dysfunction and death.
2.2. Abnormal Accumulation of Lipid Peroxides
The excessive accumulation of lipid peroxides is a critical trigger for ferroptosis. The regulation of lipid peroxidation within cells is a highly sophisticated system. Currently, two primary processes for intracellular lipid peroxidation are known. One process involves the enzyme-catalyzed peroxidation of lipids: polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are converted into highly reactive lipid peroxides through the catalytic action of various enzymes. Studies have shown that the main sources of these PUFAs include not only the cell membrane system but also arachidonic acid (AA) and linoleic acid, which are widely present within cells [
13].
The other process of lipid peroxidation within cells is mediated by free iron ions through the Fenton reaction. During ferroptosis, the excessive free ferrous ions undergo the Fenton reaction, producing ROS that reacts with the PUFAs in the lipid membrane to generate lipid peroxides. Subsequently, these lipid peroxides interact with ferrous ions to produce peroxyl radicals, which can extract hydrogen from adjacent acyl groups in the lipid membrane environment, thereby propagating the lipid peroxidation process [
14].
2.3. Antioxidant Metabolism
Iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation within cells are the two central biochemical tightly controlled by the cellular antioxidant defense system. Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) is a crucial antioxidant enzyme first identified in the ferroptosis process. Its mechanism involves eliminating hydroperoxides in the lipid bilayer and preventing the accumulation of lethal lipid ROS [
15].In addition to the GPX4 pathway, three other mechanisms have been discovered to be involved in ferroptosis regulation: the FSP1/CoQ10/NADPH pathway [
16], the DHODH pathway [
17] and the GCH1/BH4 pathway [
18]. These pathways primarily regulate intracellular reducing agents like GSH and CoQ10, thereby reducing ROS levels to control lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis.
Moreover, a recently reported amino acid oxidase, interleukin-4-induced-1 (IL4i1), has also been found to clear free radicals and regulate genes associated with ferroptosis inhibition, thereby suppressing ferroptosis [
19]. This represents an emerging potential approach for ferroptosis regulation.
3. Ferroptosis and Renal Cancer
Renal cancer has become a prominent threat to human life. Histologically, the majority (90%) of renal cancer cases are renal cell carcinoma (RCC), which mainly includes clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC; 70%), papillary renal cell carcinoma (pRCC; 10-15%), and chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (ChRCC; 5%) [
1]. To explore the deep connection between ferroptosis and tumors, studies have used erastin—a classical ferroptosis inducer—on 60 tumor cell lines from eight tissues, revealing that RCC cells are more susceptible to erastin-induced ferroptosis. Further investigation showed that this induction is accompanied by ROS accumulation and decreased GPX4 expression, and these effects can be reversed by antioxidants [
20]. This suggests that erastin-induced cell death in RCC is closely related to ferroptosis.
Additionally, based on data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) database, the expression of key ferroptosis regulators such as GPX4, SLC7A11, and FSP1 was found to be significantly upregulated, while ACSL4 expression was notably downregulated in the three major types of RCC [
21]. In studies of the most common type, ccRCC, silencing GPX4 was found to reduce GSH synthesis, induce lipid peroxidation, and significantly decrease ccRCC cell number [
20]. Furthermore, ferroptosis inducers like erastin, BSO, sulfasalazine, and sorafenib can directly or indirectly promote GSH depletion, inducing ferroptosis and thereby inhibiting RCC progression. SLC7A11 also plays an important role in RCC development; both p53 and BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1) can inhibit SLC7A11 expression, thus promoting ferroptosis to suppress RCC development [
22,
23,
24].
ChRCC cells contain high levels of glutathione and GSSG and exhibit higher sensitivity to ferroptosis inducers [
25]. In hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer (HLRCC), inactivation of fumarate hydratase (FH) leads to significant accumulation of fumarate [
26], resulting in extensive protein acidification, reduced GPX4 activity, and increased susceptibility to ferroptosis. Researchers have also found that the density of RCC cells affects their sensitivity to ferroptosis via the transcription regulator taz-mediated epithelial membrane protein 1 (EMP1)-NOX4 pathway [
27].
Therapeutically, sorafenib has been approved by the FDA for second-line treatment of metastatic and advanced RCC. It is not only a tyrosine kinase inhibitor but also an inducer of ferroptosis in certain cancer cells. In addition to sorafenib, other ferroptosis inducers, such as artesunate and salinomycin, have been identified and developed for renal cancer treatment.
Moving beyond the exclusive use of ferroptosis inducer, further research also suggested the great potential of combining ferroptosis induction treatment and chemotherapy as a strategy to overcome drug resistance. Moreover, key ferroptosis factors GPX4 and ACSL4 are closely associated with multiple tumor-related signaling pathways, including tumor proliferation, EMT, angiogenesis, and tumor inflammation pathways. The expression of various ferroptosis-related genes can accurately predict the prognosis and survival outcomes of patients, serving as potential prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets [
28].
These findings collectively indicate that ferroptosis is involved in the initiation, progression, and metastasis of renal cancer. Compared to normal renal cells, cancer cells exhibit higher sensitivity to ferroptosis. Targeting ferroptosis can reduce damage to normal cells during treatment and alleviate drug resistance in cancer cells. Thus, we believe that ferroptosis-targeted therapies for renal cancer can better guide personalized and precise treatment. Future research should continue to explore more ferroptosis-targeted therapeutic methods and drugs for RCC.
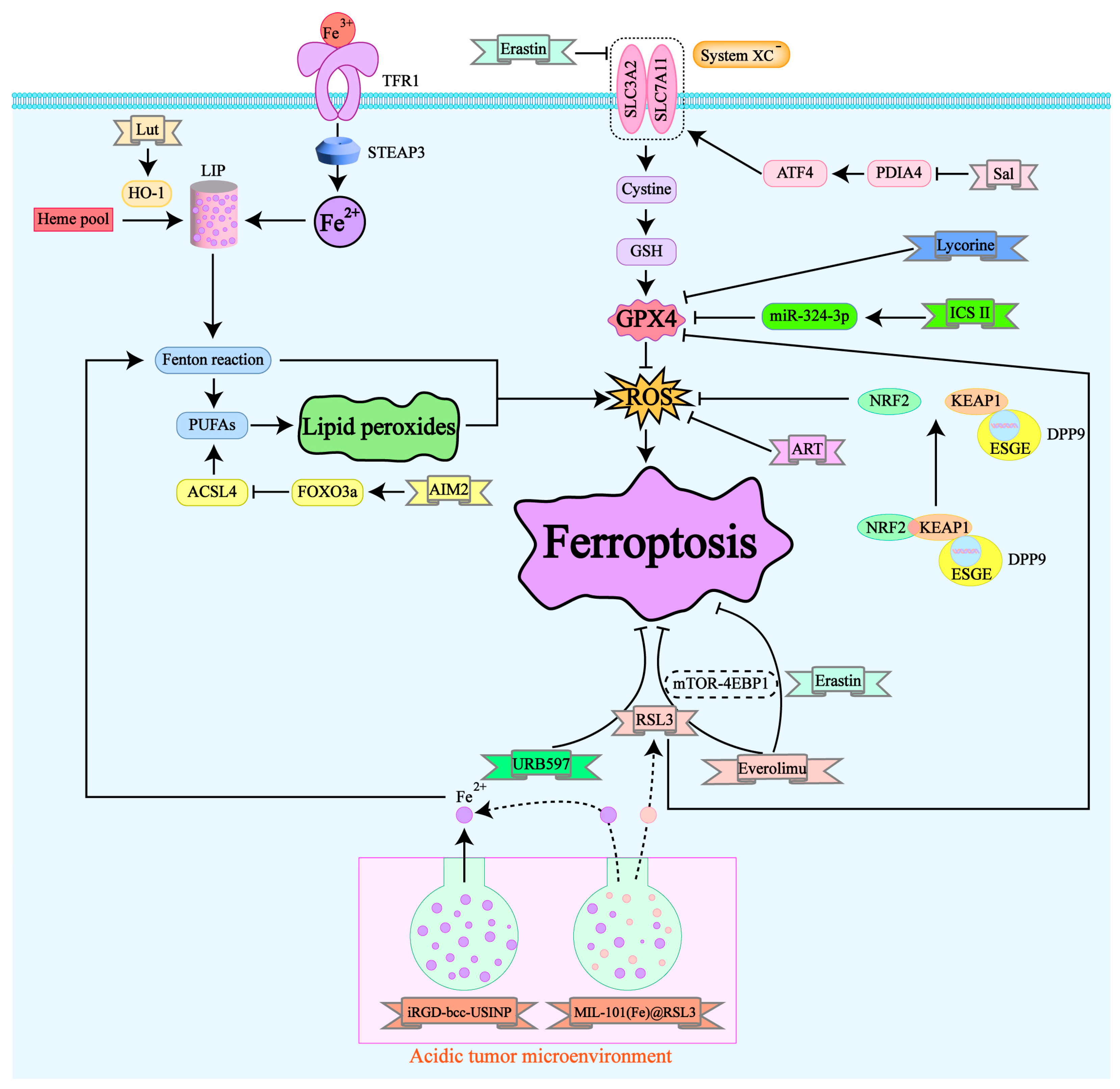
4. Current Status of Drug Research Targeting Ferroptosis in Renal Cancer (Figure 2)
4.1. Traditional Chinese Medicine and Natural Compounds in Treating Renal Cancer
4.1.1. Icariin II
Icariin II (ICS II) is a flavonoid compound with antitumor activity isolated from the traditional Chinese medicine Epimedium koreanum. A study in 2022 found that ICS II can inhibit the proliferation, migration, and invasion of RCC cells. This inhibition is believed to be closely related to ferroptosis, as it is accompanied by the accumulation of ferrous ions, lipid peroxidation, ROS, and a reduction in GSH levels. In both in vitro and in vivo experiments, ICS II demonstrated antitumor effects specifically targeting RCC cells without affecting the viability of normal renal cells. Mechanistically, ICS II downregulates GPX4 in a p53-independent manner, thereby triggering ferroptosis in RCC cells. Additionally, ICS II treatment leads to the upregulation of miR-324-3p, which negatively regulates GPX4 expression [
29].
These findings suggest that ICS II may be a promising therapeutic agent for RCC. However, current research has limitations, such as validation in only two cell lines and animal models. As a promising candidate for RCC treatment, further exploration of ICS II is necessary to fully understand its potential and efficacy.
4.1.2. Artesunate
Artesunate (ART) is a derivative extracted from artemisinin, a traditional Chinese medicine. It has demonstrated antitumor effects in various non-urinary system cancers [
30,
31,
32,
33]. Due to the development of drug resistance in renal cancer, traditional drugs like sunitinib have limitations. Researchers studied the effect of ART on sunitinib-resistant renal cancer cell lines Caki-1, 78-O, KTCTL-26, and A-498 [
34], finding that ART inhibits the growth of three of these cell lines through mechanisms involving cell cycle arrest and regulation of cell cycle proteins. Notably, in the KTCTL-26 cell line, ART's effect was unique, involving ROS generation and ferroptosis-related metabolic changes. Additionally, p53 expression, closely related to ferroptosis, was altered only in the KTCTL-26 cell line [
35]. These results suggest that ferroptosis plays a role in ART's inhibitory effect on KTCTL-26 cell growth, and p53 may serve as a targeted predictive marker for ART efficacy. Overall, ART may offer a promising supplementary treatment option for patients with advanced or drug-resistant renal cancer.
4.1.3. Lycorine
Lycorine, a compound isolated from plants of the Amaryllidaceae family, is commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine. It exhibits various biological activities, including antiviral, antimalarial, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor effects with relatively low side effects [
36]. Despite the unclear potential targets and mechanisms of lycorine, the significant antitumor activity makes lycorine a candidate anticancer drug [
37,
38]. Research suggests that lycorine's antitumor effect in renal cancer may be associated with the induction of ferroptosis [
39]:treatment with lycorine significantly reduced GPX4 expression and increased ACSL4 expression in renal cancer cells, effects that could be reversed by the ferroptosis inhibitor Ferrostatin-1. However, this hypothesis has limitations as it has only been validated in cell lines, lacking animal and clinical studies.
4.1.4. Luteolin
Luteolin (Lut) [
40] is a natural flavonoid widely found in fruits and vegetables and has been shown to have potent anticancer activity [
41]. Studies have revealed that Lut significantly inhibits the survival of renal cancer cells both in vivo and in vitro, a phenomenon accompanied by excessive intracellular ferrous ion accumulation and abnormal depletion of GSH. Additionally, Lut induces mitochondrial membrane potential imbalance, classic mitochondrial ferroptosis morphological changes, ROS production, and iron-dependent lipid peroxidation in renal cancer cells. These changes induced by Lut can be partially reversed by the ferroptosis inhibitors DFO and Ferrostatin-1, indicating that Lut-treated renal cancer cells undergo ferroptosis. Mechanistically, Lut exerts its anticancer effects by excessively upregulating HO-1 expression and activating the labile iron pool (LIP), triggering ferroptosis during the treatment process. This makes Lut a promising candidate for renal cancer treatment. However, further validation across various renal cancer cell lines is needed, and whether Lut can be used as a clinical anticancer drug remains unclear, requiring extensive and large-scale clinical trials and follow-up studies.
4.1.5. Salinomycin
Recent studies have shown that natural compounds and their derivatives possess antitumor effects, especially when combined with established therapies, achieving unexpected therapeutic outcomes [
42,
43,
44]. Salinomycin (Sal) is one such natural compound, a monocarboxylic polyether ionophore antibiotic that gained attention in cancer research in 2009. A high-throughput screening of 16,000 compounds revealed its robust antitumor properties [
45]. Subsequent studies confirmed Sal's specific targeting of cancer stem cells (CSCs) and its ability to sensitize treatment-resistant cells [
46]. Recent research indicates that Sal exerts anticancer effects in renal cancer by conferring sensitivity to ferroptosis. Firstly, studies found that PDIA4, the largest protein member of the PDI family, mainly functions as a molecular chaperone binding to unfolded protein substances. PDIA4 catalyzes the formation of disulfide bonds between cysteine residues, facilitating protein folding and increasing in response to intensified endoplasmic reticulum stress [
47,
48]. PDIA4 is upregulated in RCC, and Sal treatment downregulation of PDIA4 suppressed activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) and its downstream protein SLC7A11, thereby inactivating GPX4 and promoting ferroptosis. Furthermore, research shows that high PDIA4 levels are associated with poorer prognosis in RCC patients, suggesting that PDIA4 could be a potential prognostic marker for RCC. Sal, meanwhile, emerges as a promising therapeutic agent for RCC.
4.2. Drug Resistance and Ferroptosis in Classic Therapies
4.2.1. Sorafenib Resistance
Sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor, was the first targeted drug approved by the FDA for the treatment of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) [
49]. Initially, researchers believed it could act as an effective inducer of ferroptosis by inhibiting SLC7A11 activity [
50]. Unfortunately, the high incidence of sorafenib resistance has emerged as a significant obstacle in its therapeutic application. Recent studies have identified the overexpression of dipeptidyl peptidase 9 (DPP9) as a contributor to sorafenib resistance [
51]. DPP9 is a member of the dipeptidyl peptidase family that can cleave dipeptides at the N-terminal proline site. Its expression is elevated in various cancers and is associated with poor clinical prognosis and chemotherapy resistance [
52].
By analyzing publicly available TCGA datasets, researchers found that DPP9 mRNA expression is significantly upregulated in ccRCC tissues compared to normal renal tissues. Affinity purification and mass spectrometry confirmed the presence of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) in the DPP9 protein complex, indicating a protein-level interaction between DPP9 and KEAP1. KEAP1 interacts with the conserved KEAP1 binding motif ESGE in the DPP9 protein sequence, and DPP9 competitively binds to KEAP1, blocking KEAP1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (NRF2) [
53]. This interaction promotes NRF2-mediated oxidative stress pathways, reducing intracellular ROS levels.
Further experiments revealed that the overexpression of DPP9 blocks NRF2 ubiquitination and degradation, leading to upregulated SLC7A11 protein levels, which in turn causes resistance to ferroptosis in tumor cells. This mechanism is in direct contrast to the previously mentioned mechanism where sorafenib induces ferroptosis by inhibiting SLC7A11 activity, thus providing new theoretical insights into sorafenib resistance. Subsequent in vivo animal experiments and organoid models validated that knocking out DPP9 can partially reverse sorafenib resistance.
Therefore, for patients with DPP9-overexpressing resistant ccRCC, it might be possible to attempt reversing targeted therapy resistance by using small molecule compounds to block the interaction between DPP9 and KEAP1, thereby inhibiting the excessive activation of NRF2 signaling.
4.2.2. Sunitinib Resistance
In recent years, tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and immune checkpoint inhibitors have become the preferred treatments for inoperable renal cancer. However, these treatments still face significant limitations. While molecular targeted therapies have improved outcomes for some patients, most eventually develop resistance, and sunitinib is no exception. For patients resistant to sunitinib, clinical treatment options are quite limited, presenting a significant challenge in the clinical management of renal cancer [
54].
Recent studies have identified the Absent in Melanoma 2 (AIM2) inflammasome as a novel biomarker for renal cancer, promoting cancer progression and contributing to sunitinib resistance [
55]. Further research has shown that AIM2 is involved in iron ion homeostasis and response, a critical component of ferroptosis. AIM2 is closely related to the ferroptosis-associated gene ACSL4, which promotes the formation of phospholipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), thereby inducing ferroptosis [
56].
Mechanistic exploration has revealed that the AIM2 inflammasome promotes the phosphorylation and proteasomal degradation of Forkhead Box O3a (FOXO3a), thereby reducing its transcriptional effect on ACSL4 and inhibiting ferroptosis. This mechanism has been observed in both resistant and normal renal cancer cell lines, indicating that AIM2 contributes to sunitinib resistance by this pathway. These findings suggest that targeting ferroptosis and the FOXO3a-ACSL4 axis might offer a new approach to overcoming sunitinib resistance in renal cancer treatment.
4.3. Combination Therapy with Ferroptosis Inducers
4.3.1. Everolimus Combined with Ferroptosis Inducers Can Overcome Sorafenib and Sunitinib Resistance
Everolimus, approved by the FDA as a mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor, is used as a second-line treatment for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) resistant to sorafenib or sunitinib. However, the efficacy of Everolimus has also been hampered by resistance. Erastin and RSL3 are classic ferroptosis inducers that induce ferroptosis by inhibiting the cystine/glutamate antiporter system Xc⁻ and GPX4, respectively [
20]. Recent studies have shown that combining Everolimus with RSL3/Erastin can inhibit renal cancer cell activity and induce ferroptosis by suppressing the mTOR-4EBP1 axis [
57]. This combination presents a promising therapeutic option for patients with resistant renal cancer and helps overcome the clinical limitations of Everolimus.
4.3.2. URB597
Studies have reported that the ferroptosis inducer RSL3, in combination with URB597, can significantly inhibit the growth and metastasis of renal cancer cells [
58]. URB597 is an effective, orally active, selective fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitor. FAAH, a member of the serine hydrolase family, was initially identified as a major catabolic enzyme that regulates various metabolic pathways and pathophysiological processes, including cancer cell proliferation. FAAH expression is upregulated in multiple tumor tissues, and its inhibitors have demonstrated anti-invasive and anti-metastatic effects on various cancer cells. Some FAAH inhibitors have shown synergistic effects with chemotherapeutic drugs [
59,
60], which has become a research hotspot in cancer treatment, especially since clinical trials have shown that FAAH inhibitors have good tolerability and minimal toxicity [
61].
In renal tumor tissues, GPX4 expression is positively correlated with FAAH. To explore the relationship between these two, researchers used unbiased drug combination screening to identify potential synergistic therapies targeting both FAAH and ferroptosis in renal cancer cells. They found that the FAAH inhibitor URB597 and RSL3 combination reduced RCC cell viability by inducing ferroptosis and causing G1 cell cycle arrest. This combination exhibited strong inhibition rates and high specificity. The effects of the URB597 and RSL3 combination on ferroptosis-related gene expression, cell proliferation, cell cycle, and cell migration and invasion were more significant than those of single-agent treatments [
58]. Combining ferroptosis drugs for the treatment of renal cancer is a feasible strategy, and future research may introduce more combinational therapies for renal cancer treatment.
4.4. Novel Synthetic Materials
4.4.1. MIL-101(Fe)@RSL3
MIL-101(Fe) nanoparticles loaded with RSL3 form a new ferroptosis activator, MIL-101(Fe)@RSL3. By utilizing iron-rich MIL-101(Fe) nanoparticles for targeted delivery and responsive release of the ferroptosis inducer RSL3, MIL-101(Fe)@RSL3 exhibits high encapsulation efficiency and tumor-targeted delivery of RSL3. This combination triggers a cascade of ferroptosis treatment in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) [
62]. In the acidic tumor microenvironment, the gradually degrading MIL-101(Fe)@RSL3 releases iron ions and RSL3, which promotes hydroxyl radical (·OH) production through the Fenton reaction. These radicals attack polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), leading to the abnormal accumulation of lipid peroxides (L-OOH). Ferrous ions further catalyze the irreversible transformation of L-OOH into highly active lipid alkoxy radicals (L-O·), initiating a cascade of ferroptosis. Additionally, RSL3 directly inhibits GPX4's detoxification of L-OOH. Unlike the limited antitumor effects of free RSL3, MIL-101(Fe)@RSL3 has a high encapsulation rate (88.7%), resulting in significantly enhanced antitumor effects and abnormal PUFA metabolism in renal cancer. Notably, experiments have confirmed that this novel synthetic nanomaterial does not exhibit noticeable cytotoxicity to normal cells even at high concentrations, making it a promising drug for renal cancer treatment.
4.4.2. iRGDbcc-USINP
Iron nanoparticles, such as MIL-101(Fe), as well as widely used iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) and iron-organic frameworks for cancer diagnosis and therapy [
63,
64],induce ferroptosis through catalyzing the Fenton reaction and accelerating reactive oxygen species (ROS) production for cancer-specific treatment. [
65], They can also activate immune responses by releasing damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) during ferroptosis, contributing to cancer immunotherapy. Most iron nanomaterials rely on the release of ferrous ions to trigger the Fenton reaction [
66]. However, due to the low ROS conversion efficiency of ferrous ions in the tumor microenvironment (pH 5.5-6.5), these nanoparticles often require synergistic action with other components or combined therapies. For example, FDA-approved Ferumoxytol shows certain antitumor immunotherapy effects via the Fenton reaction but requires a high dosage [
67].
Recent studies have synthesized ultra-small single-crystal Fe nanoparticles (bcc-USINPs) composed of a 2.3±0.2 nm bcc zero-valent iron core and a 0.7±0.1 nm crystalline Fe3O4 shell [
68],Under normal physiological conditions, the ultra-thin iron oxide shell protects Fe(0) from oxidation, masking its activity. In the acidic tumor environment, the iron oxide shell corrodes and breaks, exposing Fe(0), which effectively induces ferroptosis in tumor cells through the Fenton reaction. After modification with iRGD peptides, these nanoparticles exhibit high tumor accumulation and retention. Moreover, iRGD-bcc-USINP treatment effectively induces immunogenic cell death (ICD), promotes dendritic cell (DC) maturation, and triggers adaptive T cell responses, combining with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) immune checkpoint blockade for immunotherapy. iRGD-bcc-USINP-mediated ferroptosis therapy significantly enhances immune response rates and establishes strong immune memory. Compared to other iron-based therapeutic systems that typically require high-dose injections or combination with other ferroptosis inducers to effectively treat cancer, bcc-USINPs can induce tumor cell ferroptosis and ICD at extremely low concentrations. Their ultra-small size enables rapid renal clearance, providing a simple, safe, effective, and tumor-responsive Fe(0) delivery system for ferroptosis-based immunotherapy.
5. Conclusions
Ferroptosis is closely associated with disruptions in iron, lipid metabolism, and antioxidant systems. Renal cancer cells are prone to iron accumulation and exhibit abnormal amino acid and lipid metabolism. Traditional Chinese medicine and natural compounds as ferroptosis activators offer new potential drugs for developing renal cancer treatment strategies. Ferroptosis inducers have been found to counteract drug resistance when used in combination with classic renal cancer treatments. Notably, the discovery of novel nanomaterials that target excessive iron accumulation in tumor cells to induce ferroptosis presents many new directions for renal cancer therapy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Lingyan Yu.; validation, Lingyan Yu.,and Yuyueyang Qiu.; formal analysis, Lingyan Yu.; investigation, Lingyan Yu.; resources, Lingyan Yu.; writing—original draft preparation, Lingyan Yu.; writing—review and editing, Yuyueyang Qiu.; visualization, Lingyan Yu.; supervision, Xiangmin Tong; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- BRAY FREDDIE, LAVERSANNE MATHIEU, SUNG HYUNA, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 2024, 74(3): 229-263. [CrossRef]
- BUKAVINA LAURA, BENSALAH KARIM, BRAY FREDDIE, et al. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma: 2022 Update[J]. European Urology, 2022, 82(5): 529-542. [CrossRef]
- Survival Rates for Kidney Cancer[EB/OL]. [2023-08-28].https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/kidney-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-rates.html.
- CHEN, HERNANDEZ-MEZA, AGRAWAL, et al. Time on Therapy for at Least Three Months Correlates with Overall Survival in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma[J]. Cancers, 2019, 11(7): 1000. [CrossRef]
- FENG QI, YANG YANG, REN KAIDI, et al. Broadening horizons: the multifaceted functions of ferroptosis in kidney diseases[J]. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 2023, 19(12): 3726-3743. [CrossRef]
- CHEN XIN, LI JINGBO, KANG RUI, 等. Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation[J]. Autophagy, 17(9): 2054-2081. [CrossRef]
- ZHANG YUAN YUAN, NI ZHI JING, ELAM ELNUR, et al. Juglone, a novel activator of ferroptosis, induces cell death in endometrial carcinoma Ishikawa cells[J]. Food & Function, 2021, 12(11): 4947-4959.
- BASULI DEBARGHA, TESFAY LIA, DENG ZHIYONG, et al. Iron addiction: A novel therapeutic target in ovarian cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36(29): 4089-4099. [CrossRef]
- ELING NILS, REUTER LUKAS, HAZIN JOHN, et al. Identification of artesunate as a specific activator of ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Oncoscience, 2015, 2(5): 517-532. [CrossRef]
- GREENSHIELDS ANNA L, SHEPHERD TREVOR G, HOSKIN DAVID W. Contribution of reactive oxygen species to ovarian cancer cell growth arrest and killing by the anti-malarial drug artesunate: IMPACT OF ARTESUNATE ON OVARIAN CANCER[J]. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 2017, 56(1): 75-93. [CrossRef]
- LEI GUANG, ZHUANG LI, GAN BOYI. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2022, 22(7): 381-396. [CrossRef]
- FENG HUIZHONG, SCHORPP KENJI, JIN JENNY, et al. Transferrin Receptor Is a Specific Ferroptosis Marker[J]. Cell Reports, 2020, 30(10): 3411-3423.e7. [CrossRef]
- LIANG DEGUANG, MINIKES ALEXANDER M, JIANG XUEJUN. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling[J]. Molecular Cell, 2022, 82(12): 2215-2227. [CrossRef]
- LE POPE, SJ DIXON. Regulation of ferroptosis by lipid metabolism[J]. Trends in cell biology, 2023, 33(12): 1077-1087. [CrossRef]
- LIU YI, WAN YICONG, JIANG YI, et al. GPX4: The hub of lipid oxidation, ferroptosis, disease and treatment[J]. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta. Reviews on Cancer, 2023, 1878(3): 188890. [CrossRef]
- DOLL SEBASTIAN, FREITAS FLORENCIO PORTO, SHAH RON, et al. FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor[J]. Nature, 2019, 575(7784): 693-698.
- MAO CHAO, LIU XIAOGUANG, ZHANG YILEI, et al. DHODH-mediated ferroptosis defence is a targetable vulnerability in cancer[J]. Nature, 2021, 593(7860): 586-590. [CrossRef]
- KRAFT VANESSA AN, BEZJIAN CARLA T, PFEIFFER SUSANNE, et al. GTP Cyclohydrolase 1/Tetrahydrobiopterin Counteract Ferroptosis through Lipid Remodeling[J]. ACS central science, 2020, 6(1): 41-53.
- ZEITLER LEONIE, FIORE ALESSANDRA, MEYER CLAUDIA, et al. Anti-ferroptotic mechanism of IL4i1-mediated amino acid metabolism[J]. eLife, 2021, 10: e64806. [CrossRef]
- YANG WAN SEOK, SRIRAMARATNAM ROHITHA, WELSCH MATTHEW E, 等. Regulation of Ferroptotic Cancer Cell Death by GPX4[J]. Cell, 2014, 156(1): 317-331.
- LI JINGHAN, ZHENG SUJUAN, FAN YUMEI, et al. Emerging significance and therapeutic targets of ferroptosis: a potential avenue for human kidney diseases[J]. Cell Death & Disease, 2023, 14(9): 628. [CrossRef]
- ZHANG YILEI, SHI JIEJUN, LIU XIAOGUANG, et al. BAP1 links metabolic regulation of ferroptosis to tumour suppression[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2018, 20(10): 1181-1192.
- AFFAR EL BACHIR, CARBONE MICHELE. BAP1 regulates different mechanisms of cell death[J]. Cell Death & Disease, 2018, 9(12): 1151.
- JIANG LE, KON NING, LI TONGYUAN, et al. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression[J]. Nature, 2015, 520(7545): 57-62.
- ZHANG LONG, HOBEIKA CHARBEL S, KHABIBULLIN DAMIR, et al. Hypersensitivity to ferroptosis in chromophobe RCC is mediated by a glutathione metabolic dependency and cystine import via solute carrier family 7 member 11[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2022, 119(28): e2122840119. [CrossRef]
- KERINS MICHAEL J, MILLIGAN JOHN, WOHLSCHLEGEL JAMES A, et al. Fumarate hydratase inactivation in hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer is synthetic lethal with ferroptosis induction[J]. Cancer Science, 2018, 109(9): 2757-2766.
- YANG WEN HSUAN, DING CHIEN KUANG CORNELIA, SUN TIANAI, et al. The Hippo Pathway Effector TAZ Regulates Ferroptosis in Renal Cell Carcinoma[J]. Cell Reports, 2019, 28(10): 2501-2508.e4.
- LAI YONGCHANG, ZENG TAO, LIANG XIONGFA, et al. Cell death-related molecules and biomarkers for renal cell carcinoma targeted therapy[J]. Cancer Cell International, 2019, 19: 221.
- YU RUI, ZHOU YOUFENG, SHI SHUFENG, et al. Icariside II induces ferroptosis in renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating the miR-324-3p/GPX4 axis[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 102: 154182. [CrossRef]
- Z HUANG, S GAN, X ZHUANG, et al. Artesunate Inhibits the Cell Growth in Colorectal Cancer by Promoting ROS-Dependent Cell Senescence and Autophagy[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(16): 2472.
- MA ZHAOCHEN, CHEN WENJIA, LIU YUDONG, et al. Artesunate Sensitizes human hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib via exacerbating AFAP1L2-SRC-FUNDC1 axis-dependent mitophagy[J]. Autophagy, 2024, 20(3): 541-556. [CrossRef]
- EFFERTH THOMAS. From ancient herb to modern drug: Artemisia annua and artemisinin for cancer therapy[J]. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 2017, 46: 65-83.
- LEE HYE MIN, MOON AREE. Amygdalin Regulates Apoptosis and Adhesion in Hs578T Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells[J]. Biomolecules & Therapeutics, 2016, 24(1): 62-66. [CrossRef]
- MARKOWITSCH SASCHA D, SCHUPP PATRICIA, LAUCKNER JULIA, et al. Artesunate Inhibits Growth of Sunitinib-Resistant Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells through Cell Cycle Arrest and Induction of Ferroptosis[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(11): 3150.
- KANG RUI, KROEMER GUIDO, TANG DAOLIN. The tumor suppressor protein p53 and the ferroptosis network[J]. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 2019, 133: 162-168.
- XIAO HAOXIANG, XU XUEZENG, DU LUYANG, et al. Lycorine and organ protection: Review of its potential effects and molecular mechanisms[J]. Phytomedicine: International Journal of Phytotherapy and Phytopharmacology, 2022, 104: 154266. [CrossRef]
- J QI, M MENG, J LIU, et al. Lycorine inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth and neovascularization by inducing Notch1 degradation and downregulating key vasculogenic genes[J]. Biochemical pharmacology, 2023, 217:115833.
- Z LI, Q ZHOU, X LIU, et al. Lycorine upregulates the expression of RMB10, promotes apoptosis and inhibits the proliferation and migration of cervical cancer cells[J]. International journal of molecular medicine, 2022, 50(6): 145.
- DU YANG, ZHAO HONG CHAO, ZHU HENG CHENG, et al. Ferroptosis is involved in the anti-tumor effect of lycorine in renal cell carcinoma cells[J]. Oncology Letters, 2021, 22(5): 781. [CrossRef]
- HAN SHANGTING, LIN FANGYOU, QI YUCHENG, et al. HO-1 Contributes to Luteolin-Triggered Ferroptosis in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma via Increasing the Labile Iron Pool and Promoting Lipid Peroxidation[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2022, 2022: 1-26.
- CHEN YA HUI, WU JYUN XUE, YANG SHUN FA, et al. Synergistic Combination of Luteolin and Asiatic Acid on Cervical Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15(2): 548.
- E JUENGEL, A THOMAS, J RUTZ, et al. Amygdalin inhibits the growth of renal cell carcinoma cells in vitro[J]. International journal of molecular medicine, 2016, 37(2): 526-532.
- HM LEE, A MOON. Amygdalin Regulates Apoptosis and Adhesion in Hs578T Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells[J]. Biomolecules & therapeutics, 2016, 24(1): 62-66. [CrossRef]
- J RUTZ, S MAXEINER, E JUENGEL, et al. Growth and Proliferation of Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells Is Blocked by Low Curcumin Concentrations Combined with Visible Light Irradiation[J]. International journal of molecular sciences, 2019, 20(6): 1464.
- PB GUPTA, TT ONDER, G JIANG, et al. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening[J]. Cell, 2009, 138(4):645–659.
- J ZHOU, S LIU, Y WANG, et al. Salinomycin effectively eliminates cancer stem-like cells and obviates hepatic metastasis in uveal melanoma[J]. Molecular cancer, 2019, 18(1): 159. [CrossRef]
- WANG ZEYU, ZHANG HAO, CHENG QUAN. PDIA4: The basic characteristics, functions and its potential connection with cancer[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2020, 122: 109688.
- ZOU YILONG, PALTE MICHAEL J, DEIK AMY A, et al. A GPX4-dependent cancer cell state underlies the clear-cell morphology and confers sensitivity to ferroptosis[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1617.
- B ESCUDIER, T EISEN, WM STADLER, et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma[J]. The New England journal of medicine, 2007, 356(2): 125-134. [CrossRef]
- SJ DIXON, DN PATEL, M WELSCH, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of cystine-glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis[J]. eLife, 2014, 3(e02523).
- K CHANG, Y CHEN, X ZHANG, et al. DPP9 Stabilizes NRF2 to Suppress Ferroptosis and Induce Sorafenib Resistance in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma[J]. Cancer research, 2023, 83(23): 3940-3955.
- Z TANG, J LI, Q SHEN, et al. Contribution of upregulated dipeptidyl peptidase 9 (DPP9) in promoting tumoregenicity, metastasis and the prediction of poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[J]. International journal of cancer, 2017, 140(7): 1620-1632. [CrossRef]
- GAO RUIZE, KALATHUR RAVI KR, COTO-LLERENA MAIRENE, et al. YAP/TAZ and ATF4 drive resistance to Sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma by preventing ferroptosis[J]. EMBO Molecular Medicine, 2021, 13(12): e14351.
- PARK JEE SOO, KOO KYO CHUL, CHUNG DOO YONG, et al. Visceral Adiposity as a Significant Predictor of Sunitinib-Induced Dose-Limiting Toxicities and Survival in Patients with Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(12): 3602.
- Q WANG, S GAO, Y SHOU, et al. AIM2 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression and sunitinib resistance through FOXO3a-ACSL4 axis-regulated ferroptosis[J]. International journal of biological sciences, 2023, 19(4): 1266-1283. [CrossRef]
- B GAN. ACSL4, PUFA, and ferroptosis: new arsenal in anti-tumor immunity[J]. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, 2022, 7(1):128.
- YANGYUN WANG, GUOWEI SHI, SHUFEN SHI, et al. Everolimus accelerates Erastin and RSL3-induced ferroptosis in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Gene, 2022, 809: 145992.
- HAO JUNFENG, CHEN QIGUANG, FENG YONGMIN, et al. Combination treatment with FAAH inhibitors/URB597 and ferroptosis inducers significantly decreases the growth and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma cells via the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway[J]. Cell Death & Disease, 2023, 14(4): 247. [CrossRef]
- S JAISWAL, SR AYYANNAN. Anticancer Potential of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase and Monoacylglycerol Lipase[J]. ChemMedChem, 2021, 16(14): 1-17.
- D FIORE, MC PROTO, S PISANTI, et al. Antitumor effect of pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine-15 and its synergistic effect with Oxaliplatin and 5-FU in colorectal cancer cells[J]. Cancer biology & therapy, 2016, 17(8): 849-858.
- N VAN EGMOND, VM STRAUB, M VAN DER STELT. Targeting Endocannabinoid Signaling: FAAH and MAG Lipase Inhibitors[J]. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 2021, 6: 1-23.
- NI WENJUN, LI YONGXIANG, LIANG LINGXIA, et al. Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive Nanodrug for Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Therapy via Triggering Waterfall-Like Cascade Ferroptosis[J]. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, 2022, 18(2): 327-342.
- LI FANGYUAN, LU JINGXIONG, KONG XUEQIAN, et al. Dynamic Nanoparticle Assemblies for Biomedical Applications[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(14): 1605897. [CrossRef]
- LIU BEI, HU FENG, ZHANG JINGFANG, et al. A Biomimetic Coordination Nanoplatform for Controlled Encapsulation and Delivery of Drug-Gene Combinations[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 2019, 58(26): 8804-8808.
- LIU JINGJING, WU MIN, PAN YUTONG, et al. Biodegradable Nanoscale Coordination Polymers for Targeted Tumor Combination Therapy with Oxidative Stress Amplification[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(13): 1908865. [CrossRef]
- Z LIU, T LI, F HAN, et al. A cascade-reaction enabled synergistic cancer starvation/ROS-mediated/chemo-therapy with an enzyme modified Fe-based MOF[J]. Biomaterials science, 2019, 7(9): 1-10.
- Y HUANG, JC HSU, H KOO, et al. Repurposing ferumoxytol: Diagnostic and therapeutic applications of an FDA-approved nanoparticle[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(2): 796-816.
- H LIANG, X WU, G ZHAO, et al. Renal Clearable Ultrasmall Single-Crystal Fe Nanoparticles for Highly Selective and Effective Ferroptosis Therapy and Immunotherapy[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(38): 15812−15823. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).