Submitted:
25 July 2024
Posted:
26 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
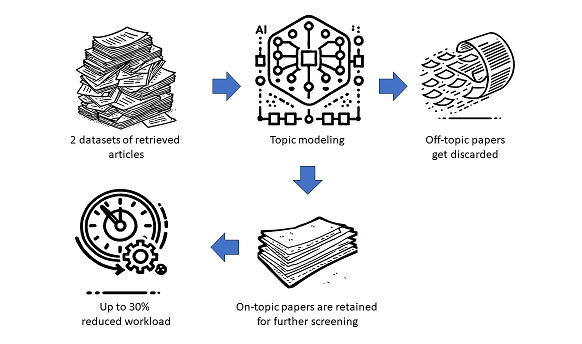
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Purpose of the Study
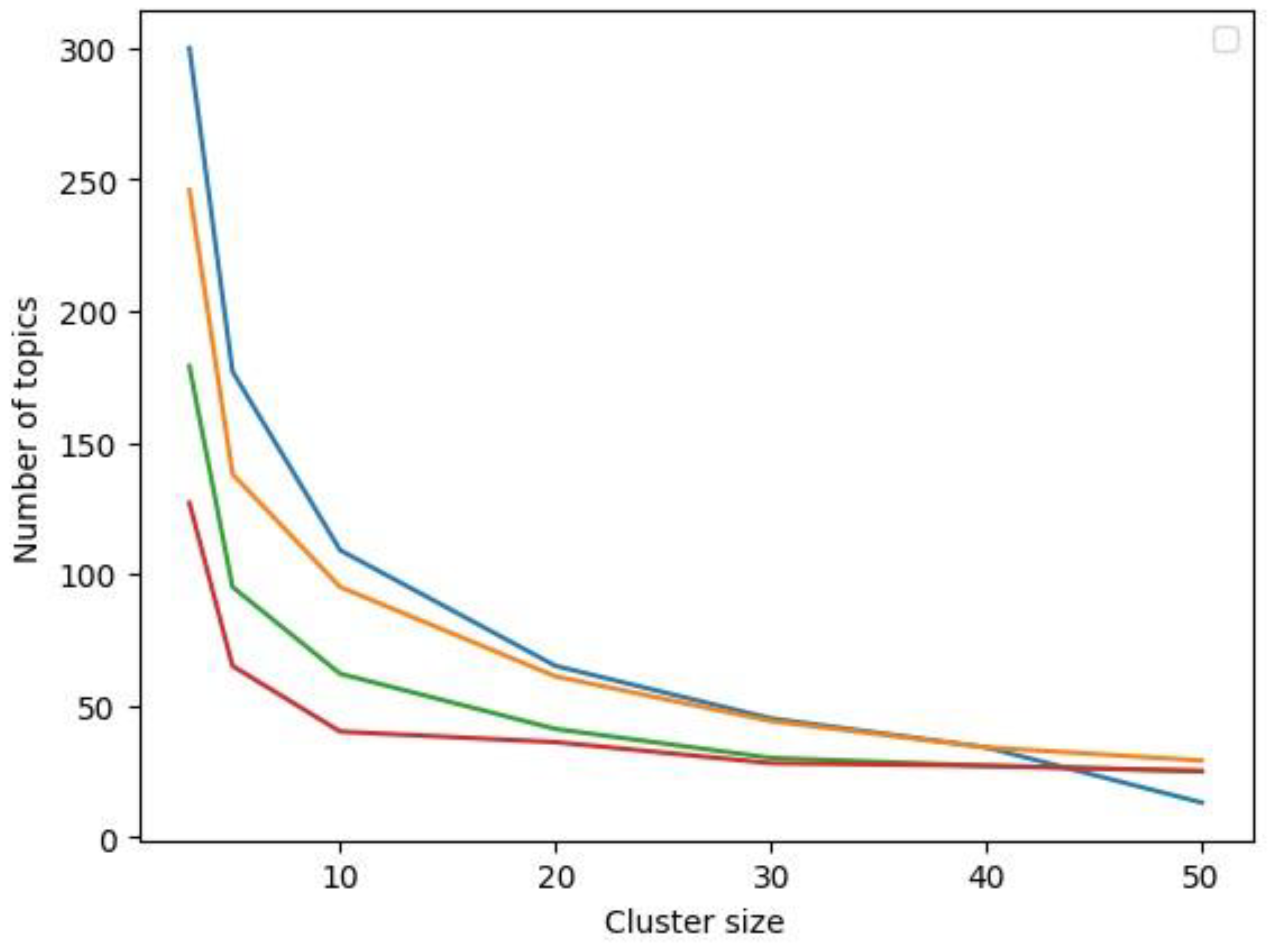
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
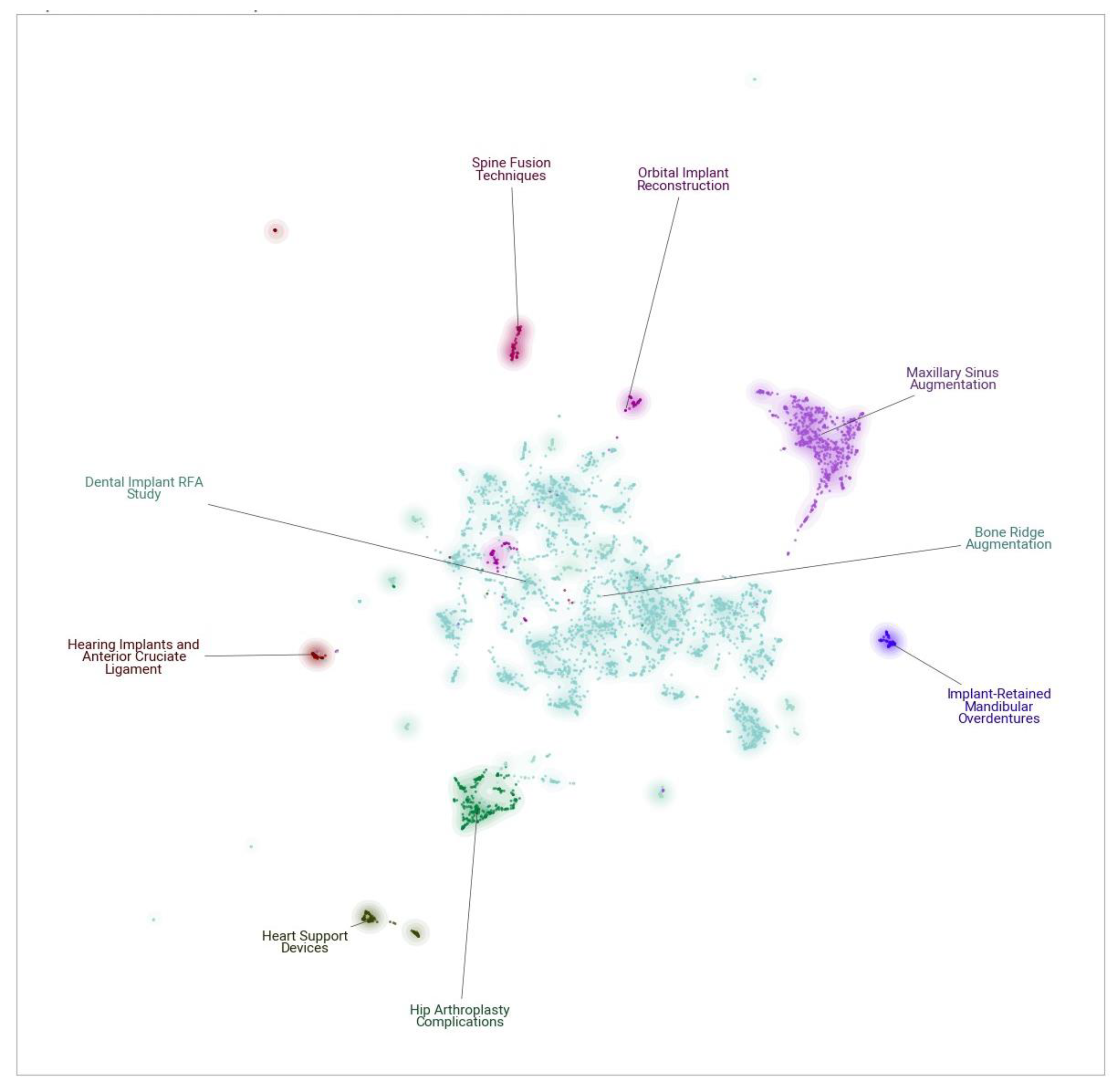
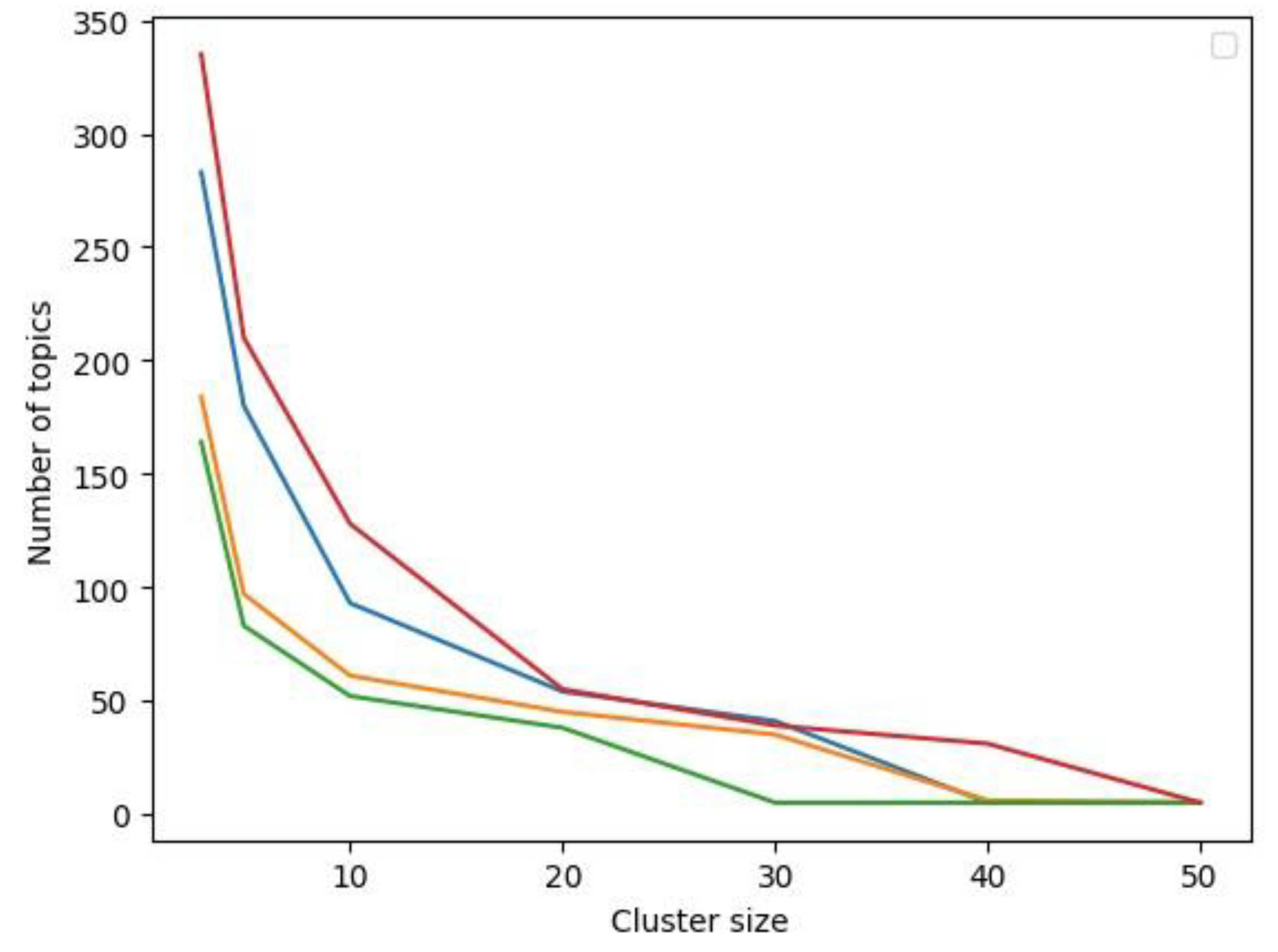
3.1. Peri-Implantitis Dataset Analysis
- “Long-term evaluation of the use of coralline hydroxyapatite in orthognathic surgery” [73]
- “Timing of cranial reconstruction after cranioplasty infections: are we ready for a re-thinking? A comparative analysis of delayed versus immediate cranioplasty after debridement in a series of 48 patients” [74]
- “HTR® polymer facial implants: A five-year clinical experience” [75]
- “Gore-Tex chin implants: a review of 324 cases” [76]
- “The application of alloplastic materials for augmentation in cosmetic facial surgery” [77]
- “Japanese National Questionnaire Survey in 2018 on Complications Related to Cranial Implants in Neurosurgery” [78]
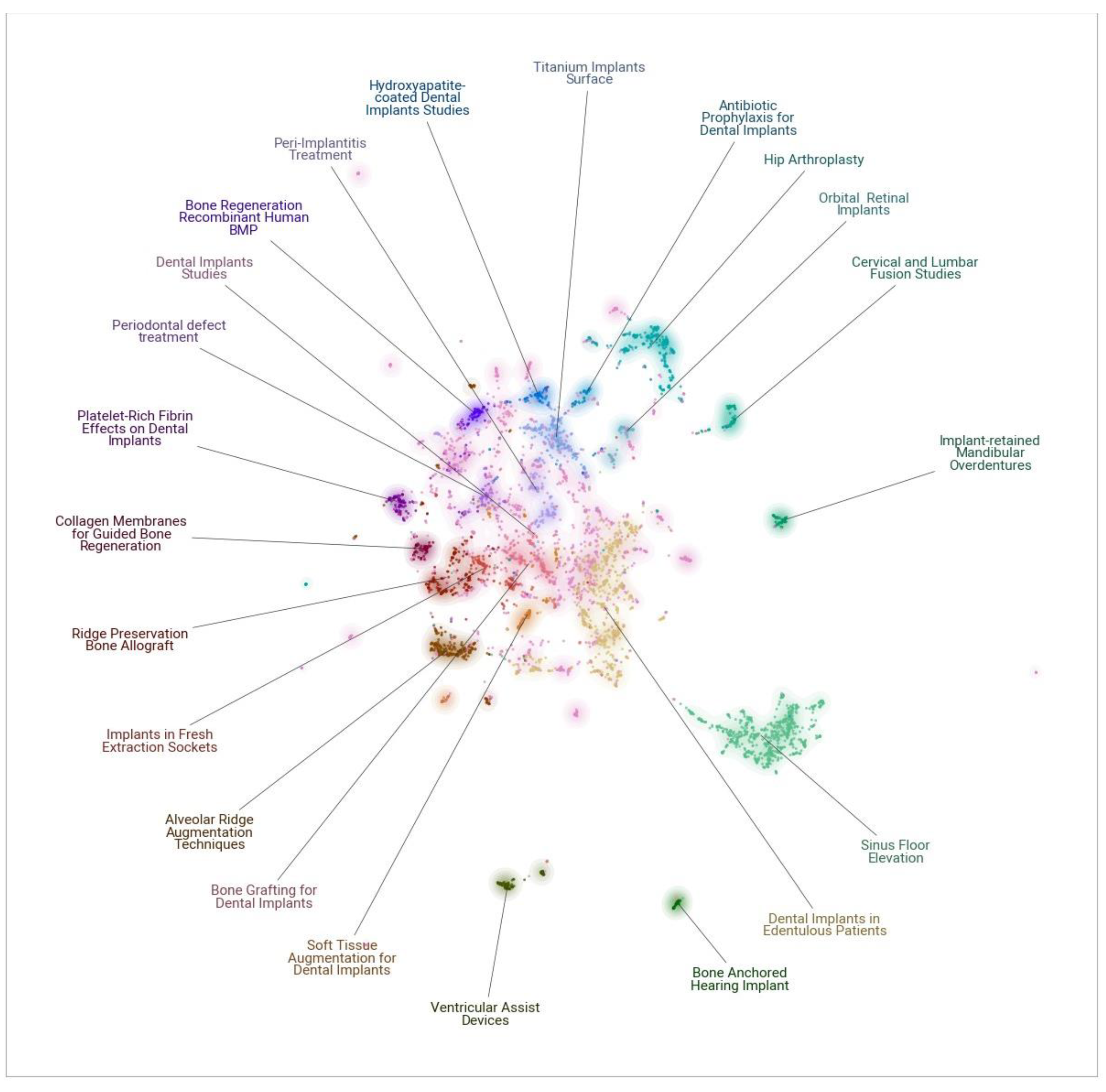
3.2. Bone Augmentation Dataset Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reips, U.-D.; Barak, A. How Internet-Mediated Research Changes Science; University Press, 2008; ISBN 0521694647.
- Hyland, K. Academic Publishing: Issues and Challenges in the Construction of Knowledge. 2016.
- Lee, I. Publish or Perish: The Myth and Reality of Academic Publishing. Language teaching 2014, 47, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landhuis, E. Scientific Literature: Information Overload. Nature 2016, 535, 457–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickersin, K.; Scherer, R.; Lefebvre, C. Systematic Reviews: Identifying Relevant Studies for Systematic Reviews. Bmj 1994, 309, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramer, W.M.; Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kleijnen, J.; Franco, O.H. Optimal Database Combinations for Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews: A Prospective Exploratory Study. Syst Rev 2017, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z. PubMed and beyond: A Survey of Web Tools for Searching Biomedical Literature. Database 2011, 2011, baq036–baq036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusenbauer, M.; Haddaway, N.R. Which Academic Search Systems Are Suitable for Systematic Reviews or Meta-analyses? Evaluating Retrieval Qualities of Google Scholar, PubMed, and 26 Other Resources. Res Synth Methods 2020, 11, 181–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivell, L. Mining the Bibliome: Searching for a Needle in a Haystack? EMBO Rep 2002, 3, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Leaman, R.; Lu, Z. PubMed and beyond: Biomedical Literature Search in the Age of Artificial Intelligence. EBioMedicine 2024, 100, 104988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Schoot, R.; de Bruin, J.; Schram, R.; Zahedi, P.; de Boer, J.; Weijdema, F.; Kramer, B.; Huijts, M.; Hoogerwerf, M.; Ferdinands, G. ASReview: Open Source Software for Efficient and Transparent Active Learning for Systematic Reviews. ArXiv, vol. abs/2006.12166.
- Khalil, H.; Ameen, D.; Zarnegar, A. Tools to Support the Automation of Systematic Reviews: A Scoping Review. J Clin Epidemiol 2022, 144, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nentidis, A.; Krithara, A.; Paliouras, G.; Gasco, L.; Krallinger, M. BioASQ at CLEF2022: The Tenth Edition of the Large-Scale Biomedical Semantic Indexing and Question Answering Challenge. In; 2022; pp. 429–435.
- Esteva, A.; Kale, A.; Paulus, R.; Hashimoto, K.; Yin, W.; Radev, D.; Socher, R. COVID-19 Information Retrieval with Deep-Learning Based Semantic Search, Question Answering, and Abstractive Summarization. NPJ Digit Med 2021, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, J.; Kavuluru, R. Improved Biomedical Word Embeddings in the Transformer Era. J Biomed Inform 2021, 120, 103867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likhareva, D.; Sankaran, H.; Thiyagarajan, S. Empowering Interdisciplinary Research with BERT-Based Models: An Approach Through SciBERT-CNN with Topic Modeling. arXiv preprint 2024, arXiv:2404.13078. [Google Scholar]
- Grootendorst, M. BERTopic: Neural Topic Modeling with a Class-Based TF-IDF Procedure. arXiv preprint 2022, arXiv:2203.05794. [Google Scholar]
- Calciolari, E.; Corbella, S.; Gkranias, N.; Viganó, M.; Sculean, A.; Donos, N. Efficacy of Biomaterials for Lateral Bone Augmentation Performed with Guided Bone Regeneration. A Network Meta-analysis. Periodontol 2000 2023, 93, 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donos, N.; Calciolari, E.; Ghuman, M.; Baccini, M.; Sousa, V.; Nibali, L. The Efficacy of Bone Reconstructive Therapies in the Management of Peri-Implantitis. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Clin Periodontol.
- Bassi, S. A Primer on Python for Life Science Researchers. PLoS Comput Biol 2007, 3, e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Maggioni, M.; Smith, J.; Scarpazza, D.P. Dissecting the NVidia Turing T4 GPU via Microbenchmarking. arXiv preprint 2019, arXiv:1903.07486. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, D.A.; Beckman, T.J.; Bordage, G. A Systematic Review of Titles and Abstracts of Experimental Studies in Medical Education: Many Informative Elements Missing. Med Educ 2007, 41, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, J. Planning That Title: Practices and Preferences for Titles with Colons in Academic Articles. Libr Inf Sci Res 2007, 29, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizzardi, S.; Colangelo, M.T.; Mirandola, P.; Galli, C. Modeling New Trends in Bone Regeneration, Using the BERTopic Approach. Regenerative Med 2023, 18, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, H.; Fernandez, M.; He, Y.; Alani, H. On Stopwords, Filtering and Data Sparsity for Sentiment Analysis of Twitter. 2014.
- Gutiérrez, L.; Keith, B. A Systematic Literature Review on Word Embeddings. In Proceedings of the Trends and Applications in Software Engineering: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Software Process Improvement (CIMPS 2018) 7; pp. 2019132–141.
- Wang, S.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, C. A Survey of Word Embeddings Based on Deep Learning. Computing 2020, 102, 717–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kusner, M.J.; Blunsom, P. A Survey on Contextual Embeddings. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2003.07278. [Google Scholar]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Melville, J. Umap: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction. arXiv preprint 2018, arXiv:1802.03426. [Google Scholar]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Astels, S. Hdbscan: Hierarchical Density Based Clustering. J. Open Source Softw. 2017, 2, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaiser, S.; Ali, R. Text Mining: Use of TF-IDF to Examine the Relevance of Words to Documents. Int J Comput Appl 2018, 181, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.D.; Wu, S.B. An Improved TFIDF Algorithm in Text Classification. Applied Mechanics and Materials 2014, 651, 2258–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschka, S.; Patterson, J.; Nolet, C. Machine Learning in Python: Main Developments and Technology Trends in Data Science, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence. Information 2020, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, B.; Jasser, M.B.; Chua, H.N.; Hamzah, M. A Comparative Study on Embedding Models for Keyword Extraction Using KeyBERT Method. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 13th International Conference on System Engineering and Technology (ICSET); IEEE; 2023; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Teknium Teknium/OpenHermes-2.5-Mistral-7B Available online:. Available online: https://huggingface.co/teknium/OpenHermes-2.5-Mistral-7B (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; Ting, D.S.J.; Elangovan, K.; Gutierrez, L.; Tan, T.F.; Ting, D.S.W. Large Language Models in Medicine. Nat Med 2023, 29, 1930–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddour, J.; Harris, J.; Mozes, M.; Bradley, H.; Raileanu, R.; McHardy, R. Challenges and Applications of Large Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.10169, 2023.
- Park, S.; Choi, J.; Lee, S.; Kang, U. A Comprehensive Survey of Compression Algorithms for Language Models. arXiv preprint 2024, arXiv:2401.15347. [Google Scholar]
- Meskó, B. Prompt Engineering as an Important Emerging Skill for Medical Professionals: Tutorial. J Med Internet Res 2023, 25, e50638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput Sci Eng 2007, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskom, M. Seaborn: Statistical Data Visualization. J Open Source Softw 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, L. DataMapPlot.
- Galli, C.; Donos, N.; Calciolari, E. Performance of 4 Pre-Trained Sentence Transformer Models in the Semantic Query of a Systematic Review Dataset on Peri-Implantitis. Information 2024, 15, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuRahma, A.F.; Robinson, P.A.; Jennings, T.G. Carotid-Subclavian Bypass Grafting with Polytetrafluoroethylene Grafts for Symptomatic Subclavian Artery Stenosis or Occlusion: A 20-Year Experience. J Vasc Surg 2000, 32, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R.; Horwitz, B.; Howes, J.; Novack, G.D.; Hart, K. Double-Masked, Placebo-Controlled Evaluation of Loteprednol Etabonate 0.5 for Postoperative Inflammation. J Cataract Refract Surg 1998, 24, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senova, S.; Hosomi, K.; Gurruchaga, J.-M.; Gouello, G.; Ouerchefani, N.; Beaugendre, Y.; Lepetit, H.; Lefaucheur, J.-P.; Badin, R.A.; Dauguet, J. Three-Dimensional SPACE Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery at 3 T to Improve Subthalamic Nucleus Lead Placement for Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease: From Preclinical to Clinical Studies. J Neurosurg 2016, 125, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almugathwi, M.; Wearden, A.; Green, K.; Hill-Feltham, P.; Powell, R. Online Support Group Users’ Perceptions and Experiences of Bone-Anchored Hearing Aids (BAHAs): A Qualitative Study. Int J Audiol 2020, 59, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, H.; Aass, A.M.; Wohlfahrt, J.C. Porous Titanium Granules in the Treatment of Peri-Implant Osseous Defects—a 7-Year Follow-up Study. Int J Implant Dent 2017, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, K.; Jepsen, S.; Laine, M.L.; Anssari Moin, D.; Pilloni, A.; Zeza, B.; Sanz, M.; Ortiz-Vigon, A.; Roos-Jansåker, A.M.; Renvert, S. Reconstruction of Peri-Implant Osseous Defects: A Multicenter Randomized Trial. J Dent Res 2016, 95, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfahrt, J.C.; Lyngstadaas, S.P.; Rønold, H.J.; Saxegaard, E.; Ellingsen, J.E.; Karlsson, S.; Aass, A.M. Porous Titanium Granules in the Surgical Treatment of Peri-Implant Osseous Defects: A Randomized Clinical Trial. International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 2012, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel, N.; Machtei, E.E.; Reichart, M.; Shapira, L. D-PLEX500: A Local Biodegradable Prolonged Release Doxycycline-Formulated Bone Graft for the Treatment for Peri-Implantitis. A Randomized Controlled Clinical Study. Quintessence Int (Berl) 2020, 51, 546–553. [Google Scholar]
- Renvert, S.; Giovannoli, J.; Roos-Jansåker, A.; Rinke, S. Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis with or without a Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral and a Native Bilayer Collagen Membrane: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Clin Periodontol 2021, 48, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isehed, C.; Holmlund, A.; Renvert, S.; Svenson, B.; Johansson, I.; Lundberg, P. Effectiveness of Enamel Matrix Derivative on the Clinical and Microbiological Outcomes Following Surgical Regenerative Treatment of Peri-implantitis. A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Clin Periodontol 2016, 43, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isehed, C.; Svenson, B.; Lundberg, P.; Holmlund, A. Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis Using Enamel Matrix Derivative, an RCT: 3-and 5-year Follow-up. J Clin Periodontol 2018, 45, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renvert, S.; Roos-Jansåker, A.; Persson, G.R. Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis Lesions with or without the Use of a Bone Substitute—a Randomized Clinical Trial. J Clin Periodontol 2018, 45, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nct Peri-Implantitis - Reconstructive Surgical Therapy Available online:. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03077061 2017 (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Froum, S.J.; Froum, S.H.; Rosen, P.S. A Regenerative Approach to the Successful Treatment of Peri-Implantitis: A Consecutive Series of 170 Implants in 100 Patients with 2-to 10-Year Follow-Up. International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2015, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez Regueiro, I.; Martinez Rodriguez, N.; Barona Dorado, C.; Sanz-Sánchez, I.; Montero, E.; Ata-Ali, J.; Duarte, F.; Martínez-González, J.M. Surgical Approach Combining Implantoplasty and Reconstructive Therapy with Locally Delivered Antibiotic in the Treatment of Peri-implantitis: A Prospective Clinical Case Series. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2021, 23, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isler, S.C.; Soysal, F.; Ceyhanlı, T.; Bakırarar, B.; Unsal, B. Regenerative Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis Using Either a Collagen Membrane or Concentrated Growth Factor: A 12-month Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2018, 20, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monaca, G.; Pranno, N.; Annibali, S.; Cristalli, M.P.; Polimeni, A. Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of a Surgical Reconstructive Approach in the Treatment of Peri-implantitis Lesions: A 5-year Prospective Case Series. Clin Oral Implants Res 2018, 29, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, F.; Hamlet, S.; Ivanovski, S. Regenerative Surgical Therapy for Peri-implantitis Using Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral with 10% Collagen, Enamel Matrix Derivative and Doxycycline—A Prospective 3-year Cohort Study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2018, 29, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymeri, A.; Anssari-Moin, D.; van der Horst, J.; Wismeijer, D.; Laine, M.L.; Loos, B.G. Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis Defects with Two Different Xenograft Granules: A Randomized Clinical Pilot Study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2020, 31, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccuzzo, M.; Gaudioso, L.; Lungo, M.; Dalmasso, P. Surgical Therapy of Single Peri-implantitis Intrabony Defects, by Means of Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral with 10% Collagen. J Clin Periodontol 2016, 43, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccuzzo, M.; Mirra, D.; Pittoni, D.; Ramieri, G.; Roccuzzo, A. Reconstructive Treatment of Peri-implantitis Infrabony Defects of Various Configurations: 5-year Survival and Success. Clin Oral Implants Res 2021, 32, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isrctn Reconstructive Surgical Therapy of Peri-Implantitis Bone Defects Available online:. Available online: https://trialsearch.who.int/Tri-al2.aspx?TrialID=ISRCTN67095066 2019 (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Aghazadeh, A.; Rutger Persson, G.; Renvert, S. A Single-centre Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial on the Adjunct Treatment of Intra-bony Defects with Autogenous Bone or a Xenograft: Results after 12 Months. J Clin Periodontol 2012, 39, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh, A.; Persson, R.G.; Renvert, S. Impact of Bone Defect Morphology on the Outcome of Reconstructive Treatment of Peri-Implantitis. Int J Implant Dent 2020, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nct Evaluation of Photodynamic Therapy in Treatment of Peri-Implantitis Available online:. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05187663 2022 (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Roos-Jansåker, A.; Renvert, H.; Lindahl, C.; Renvert, S. Submerged Healing Following Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis: A Case Series. J Clin Periodontol 2007, 34, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos-Jansåker, A.; Lindahl, C.; Persson, G.R.; Renvert, S. Long-term Stability of Surgical Bone Regenerative Procedures of Peri-implantitis Lesions in a Prospective Case–Control Study over 3 Years. J Clin Periodontol 2011, 38, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos-Jansåker, A.; Persson, G.R.; Lindahl, C.; Renvert, S. Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis Using a Bone Substitute with or without a Resorbable Membrane: A 5-year Follow-up. J Clin Periodontol 2014, 41, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, D.A.; Wolford, L.M. Long-Term Evaluation of the Use of Coralline Hydroxyapatite in Orthognathic Surgery. Journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery 1998, 56, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rienzo, A.; Colasanti, R.; Gladi, M.; Dobran, M.; Della Costanza, M.; Capece, M.; Veccia, S.; Iacoangeli, M. Timing of Cranial Reconstruction after Cranioplasty Infections: Are We Ready for a Re-Thinking? A Comparative Analysis of Delayed versus Immediate Cranioplasty after Debridement in a Series of 48 Patients. Neurosurg Rev 2021, 44, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eppley, B.L.; Sadove, A.M.; Holmstrom, H.; Kahnberg, K.-E. HTR® Polymer Facial Implants: A Five-Year Clinical Experience. Aesthetic Plast Surg 1995, 19, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godin, M.; Costa, L.; Romo, T.; Truswell, W.; Wang, T.; Williams, E. Gore-Tex Chin Implants: A Review of 324 Cases. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2003, 5, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansma, J.; Schepers, R.H.; Vissink, A. The Application of Alloplastic Materials for Augmentation in Cosmetic Facial Surgery. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd 2014, 121, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuhara, T.; Murai, S.; Mikuni, N.; Miyamoto, S.; Date, I. Japanese National Questionnaire Survey in 2018 on Complications Related to Cranial Implants in Neurosurgery. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2020, 60, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitridis, D.; Givissis, P.; Chalidis, B. Timing of Tibial Tubercle Osteotomy in Two-Stage Revision of Infected Total Knee Arthroplasty Does Not Affect Union and Reinfection Rate. A Systematic Review. Knee 2020, 27, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, S.S.; Han, S.J.; Lee, C.-K.; Chang, B.-S. A Long-Term Follow-up, Multicenter, Comparative Study of the Radiologic, and Clinical Results between a CaO-SiO2-P2O5-B2O3 Bioactive Glass Ceramics (BGS-7) Intervertebral Spacer and Titanium Cage in 1-Level Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Clin Spine Surg 2020, 33, E322–E329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaliyev, R.; Lesbekov, T.; Bekbossynov, S.; Nurmykhametova, Z.; Bekbossynova, M.; Novikova, S.; Medressova, A.; Smagulov, N.; Faizov, L.; Samalavicius, R. Heart Transplantation of Patients with Ventricular Assist Devices: Impact of Normothermic Ex-Vivo Preservation Using Organ Care System Compared with Cold Storage. J Cardiothorac Surg 2020, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naenni, N.; Stucki, L.; Hüsler, J.; Schneider, D.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Jung, R.E.; Thoma, D.S. Implants Sites with Concomitant Bone Regeneration Using a Resorbable or Non-resorbable Membrane Result in Stable Marginal Bone Levels and Similar Profilometric Outcomes over 5 Years. Clin Oral Implants Res 2021, 32, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basler, T.; Naenni, N.; Schneider, D.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Jung, R.E.; Thoma, D.S. Randomized Controlled Clinical Study Assessing Two Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration of Peri-implant Bone Defects: 3-year Results. Clin Oral Implants Res 2018, 29, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, J.L.; Grodin, E.; Lin, J.; Chen, M.C.; Ho, C.; Cochran, D. A Comparative, Randomized, Prospective, Two-center Clinical Study to Evaluate the Clinical and Esthetic Outcomes of Two Different Bone Grafting Techniques in Early Implant Placement. J Periodontol 2019, 90, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annen, B.M.; Ramel, C.F.; Hammerle, C.H.F.; Jung, R.E. Use of a New Cross-Linked Collagen Membrane for the Treatment of Peri-Implant Dehiscence Defects: A Randomised Controlled Double-Blinded Clinical Trial. Eur J Oral Implantol 2011, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Naenni, N.; Schneider, D.; Jung, R.E.; Hüsler, J.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Thoma, D.S. Randomized Clinical Study Assessing Two Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration of Peri-implant Bone Defects: Clinical and Histological Outcomes at 6 Months. Clin Oral Implants Res 2017, 28, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Baek, W.-S.; Lim, H.-C.; Cha, J.-K.; Choi, S.-H.; Jung, U.-W. Assessment of Dehydrothermally Cross-linked Collagen Membrane for Guided Bone Regeneration around Peri-Implant Dehiscence Defects: A Randomized Single-Blinded Clinical Trial. J Periodontal Implant Sci 2015, 45, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Jung, U.-W. Assessment of Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Guided Bone Regeneration with Dehydrothermally Cross-Linked Collagen Membrane around Peri-Implant Dehiscence Defects: Results from a 3-Year Randomized Clinical Trial. Oral Biology Research 2019, 43, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.; Al-Nawas, B.; Klein, M.O.; Schliephake, H.; Terheyden, H.; Schwarz, F. Use of a New Cross-linked Collagen Membrane for the Treatment of Dehiscence-type Defects at Titanium Implants: A Prospective, Randomized-controlled Double-blinded Clinical Multicenter Study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2009, 20, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Schmucker, A.; Becker, J. Long-term Outcomes of Simultaneous Guided Bone Regeneration Using Native and Cross-linked Collagen Membranes after 8 Years. Clin Oral Implants Res 2017, 28, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Hegewald, A.; Sahm, N.; Becker, J. Long-term Follow-up of Simultaneous Guided Bone Regeneration Using Native and Cross-linked Collagen Membranes over 6 Years. Clin Oral Implants Res 2014, 25, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Sahm, N.; Becker, J. Impact of the Outcome of Guided Bone Regeneration in Dehiscence-type Defects on the Long-term Stability of Peri-implant Health: Clinical Observations at 4 Years. Clin Oral Implants Res 2012, 23, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benic, G.I.; Eisner, B.M.; Jung, R.E.; Basler, T.; Schneider, D.; Hämmerle, C.H.F. Hard Tissue Changes after Guided Bone Regeneration of Peri-implant Defects Comparing Block versus Particulate Bone Substitutes: 6-month Results of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 2019, 30, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio, L.; Loza, J.; Lynch, S.; Genco, R. Guided Bone Regeneration around Endosseous Implants with Anorganic Bovine Bone Mineral. A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Bioabsorbable versus Non-resorbable Barriers. J Periodontol 2000, 71, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deesricharoenkiat, N.; Jansisyanont, P.; Chuenchompoonut, V.; Mattheos, N.; Thunyakitpisal, P. The Effect of Acemannan in Implant Placement with Simultaneous Guided Bone Regeneration in the Aesthetic Zone: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2022, 51, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, R.E.; Glauser, R.; Schärer, P.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Sailer, H.F.; Weber, F.E. Effect of RhBMP-2 on Guided Bone Regeneration in Humans: A Randomized, Controlled Clinical and Histomorphometric Study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2003, 14, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, R.E.; Windisch, S.I.; Eggenschwiler, A.M.; Thoma, D.S.; Weber, F.E.; Hämmerle, C.H.F. A Randomized-controlled Clinical Trial Evaluating Clinical and Radiological Outcomes after 3 and 5 Years of Dental Implants Placed in Bone Regenerated by Means of GBR Techniques with or without the Addition of BMP-2. Clin Oral Implants Res 2009, 20, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, R.E.; Kovacs, M.N.; Thoma, D.S.; Hämmerle, C.H.F. Informative Title: Guided Bone Regeneration with and without RhBMP-2: 17-year Results of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 2022, 33, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, R.E.; Hälg, G.A.; Thoma, D.S.; Hämmerle, C.H.F. A Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial to Evaluate a New Membrane for Guided Bone Regeneration around Dental Implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 2009, 20, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramel, C.F.; Wismeijer, D.A.; F Hämmerle, C.H.; Jung, R.E. A Randomized, Controlled Clinical Evaluation of a Synthetic Gel Membrane for Guided Bone Regeneration around Dental Implants: Clinical and Radiologic 1-and 3-Year Results. International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 2012, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, R.E.; Benic, G.I.; Scherrer, D.; Hämmerle, C.H.F. Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Regenerated Buccal Bone 5 Years after Simultaneous Implant Placement and Guided Bone Regeneration Procedures–a Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 2015, 26, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, R.E.; Mihatovic, I.; Cordaro, L.; Windisch, P.; Friedmann, A.; Blanco Carrion, J.; Sanz Sanchez, I.; Hallman, M.; Quirynen, M.; Hammerle, C.H.F. Comparison of a Polyethylene Glycol Membrane and a Collagen Membrane for the Treatment of Bone Dehiscence Defects at Bone Level Implants—A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, Multicenter Clinical Trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 2020, 31, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benic, G.I.; Bienz, S.P.; Song, Y.W.; Cha, J.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Jung, U.; Jung, R.E. Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Comparing Guided Bone Regeneration of Peri-implant Defects with Soft-type Block versus Particulate Bone Substitutes: Six-month Results of Hard-tissue Changes. J Clin Periodontol 2022, 49, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-W.; Kim, K.-T.; Joo, Y.-S.; Yoo, M.-K.; Yu, J.-A.; Ryu, J.-J. The Role of Two Different Collagen Membranes for Dehiscence Defect around Implants in Humans. Journal of Oral Implantology 2015, 41, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattout, P.; Nowzari, H.; Mattout, C. Clinical Evaluation of Guided Bone Regeneration at Exposed Parts of Brånemark Dental Implants with and without Bone Allograft. Clin Oral Implants Res 1995, 6, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merli, M.; Moscatelli, M.; Mariotti, G.; Pagliaro, U.; Raffaelli, E.; Nieri, M. Comparing Membranes and Bone Substitutes in a One-Stage Procedure for Horizontal Bone Augmentation. A Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur J Oral Implantol 2015, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Merli, M.; Moscatelli, M.; Mariotti, G.; Pagliaro, U.; Raffaelli, E.; Nieri, M. Comparing Membranes and Bone Substitutes in a One-Stage Procedure for Horizontal Bone Augmentation. Three-Year Post-Loading Results of a Double-Blind Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur J Oral Implantol 2018, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Lee, K.; Oh, T.; Misch, C.E.; Shotwell, J.; Wang, H. Effect of Absorbable Membranes on Sandwich Bone Augmentation. Clin Oral Implants Res 2008, 19, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.; Weber, F.E.; Grunder, U.; Andreoni, C.; Burkhardt, R.; Jung, R.E. A Randomized Controlled Clinical Multicenter Trial Comparing the Clinical and Histological Performance of a New, Modified Polylactide-co-glycolide Acid Membrane to an Expanded Polytetrafluorethylene Membrane in Guided Bone Regeneration Procedures. Clin Oral Implants Res 2014, 25, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, A.; Cortellini, S.; Van Dessel, J.; De Greef, A.; Jacobs, R.; Dhondt, R.; Teughels, W.; Quirynen, M. Bovine-derived Xenograft in Combination with Autogenous Bone Chips versus Xenograft Alone for the Augmentation of Bony Dehiscences around Oral Implants: A Randomized, Controlled, Split-mouth Clinical Trial. J Clin Periodontol 2020, 47, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simion, M.; Misitano, U.; Gionso, L.; Salvato, A. Treatment of Dehiscences and Fenestrations around Dental Implants Using Resorbable and Nonresorbable Membranes Associated with Bone Autografts: A Comparative Clinical Study. International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 1997, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Urban, I.A.; Wessing, B.; Alández, N.; Meloni, S.; González-Martin, O.; Polizzi, G.; Sanz-Sanchez, I.; Montero, E.; Zechner, W. A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial Using a Novel Collagen Membrane for Guided Bone Regeneration at Dehisced Single Implant Sites: Outcome at Prosthetic Delivery and at 1-year Follow-up. Clin Oral Implants Res 2019, 30, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessing, B.; Urban, I.; Montero, E.; Zechner, W.; Hof, M.; Alandez Chamorro, J.; Alandez Martin, N.; Polizzi, G.; Meloni, S.; Sanz, M. A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Using a New Resorbable Non-cross-linked Collagen Membrane for Guided Bone Regeneration at Dehisced Single Implant Sites: Interim Results of a Bone Augmentation Procedure. Clin Oral Implants Res 2017, 28, e218–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Assche, N.; Michels, S.; Naert, I.; Quirynen, M. Randomized Controlled Trial to Compare Two Bone Substitutes in the Treatment of Bony Dehiscences. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2013, 15, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veis, A.A.; Tsirlis, A.T.; Parisis, N.A. Effect of Autogenous Harvest Site Location on the Outcome of Ridge Augmentation for Implant Dehiscences. International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2004, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.-C.; Fu, J.-H.; Wang, H.-L. Effect of Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral at Implant Dehiscence Defects Grafted by the Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2018, 38, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.; Tsao, J.; Wang, C.; Grodin, E.; Lin, J.; Chen, C.; Ho, C.; Cochran, D.; Mau, J.L.P. Stability of Contour Augmentation of Implant-supported Single Crowns in the Esthetic Zone: One-year Cone-beam Computed Tomography Results of a Comparative, Randomized, Prospective, Two-center Clinical Study Using Two Different Bone Grafting Techniques in Early Implant Placement. J Periodontol 2022, 93, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Topic | Count | Name | KeyBERT | LLM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 357 | -1_treatment_hydroxyapatite_bone_implant | [‘peri implantitis’, ‘hydroxyapatite coated’, ‘coated implants’, ‘dental implant’, ‘dental implants’, ‘spinal implant’, ‘peri implant’, ‘hydroxyapatite’, ‘implantitis’, ‘implant’] | Treating Implant Infections |
| 0 | 3733 | 0_implant_implants_peri_bone | [‘peri implantitis’, ‘implant bone’, ‘dental implant’, ‘peri implant’, ‘dental implants’, ‘implant placement’, ‘implants placed’, ‘bone regeneration’, ‘implant’, ‘implantitis’] | Peri-Implant Bone Study |
| 1 | 587 | 1_valve_coronary_stent_patients | [‘coronary stent’, ‘stent implantation’, ‘eluting stents’, ‘eluting stent’, ‘stents’, ‘artery bypass’, ‘stent’, ‘coronary artery’, ‘patients coronary’, ‘stenting’] | Valves and Stents in Coronary Arteries |
| 2 | 232 | 2_cataract_intraocular_cataract surgery_lens | [‘inflammation cataract’, ‘lens implantation’, ‘incision cataract’, ‘intraocular lens’, ‘following cataract’, ‘extracapsular cataract’, ‘intraocular lenses’, ‘postoperative inflammation’, ‘cataract extraction’, ‘cataract surgery’] | Intraocular Lens Inflammation |
| 3 | 192 | 3_breast_breast reconstruction_reconstruction_breast implants | [‘breast reconstruction’, ‘reconstruction breast’, ‘mammary implants’, ‘breast implant’, ‘implant breast’, ‘breast augmentation’, ‘prosthetic breast’, ‘breast prostheses’, ‘breast implants’, ‘breast surgery’] | Breast Reconstruction & Implants |
| 4 | 174 | 4_stimulation_parkinson_parkinson disease_brain | [‘stimulation parkinson’, ‘subthalamic stimulation’, ‘nucleus stimulation’, ‘nucleus parkinson’, ‘brain stimulation’, ‘implants parkinson’, ‘nerve stimulation’, ‘stimulation subthalamic’, ‘neuromodulation’, ‘parkinson disease’] | Parkinson’s Disease and Deep Brain Stimulation |
| 5 | 144 | 5_sinus_floor_sinus floor_elevation | [‘sinus floor’, ‘sinus elevation’, ‘osteotome sinus’, ‘sinus augmentation’, ‘sinus surgery’, ‘maxillary sinus’, ‘sinus implants’, ‘sinus lift’, ‘transcrestal sinus’, ‘eluting sinus’] | Sinus Floor Elevation |
| 6 | 137 | 6_laser_therapy_photodynamic_photodynamic therapy | [‘implantitis laser’, ‘peri implantitis’, ‘implantitis randomized’, ‘peri implant’, ‘laser therapy’, ‘implantitis’, ‘laser treatment’, ‘implant diseases’, ‘laser peri’, ‘photodynamic therapy’] | Photodynamic Therapy for Peri-implantitis Treatment |
| 7 | 132 | 7_overdentures_mandibular_mandibular overdentures_retained | [‘implant overdentures’, ‘mandibular overdentures’, ‘mandibular overdenture’, ‘implants mandibular’, ‘mandibular implant’, ‘maxillary overdentures’, ‘retained overdentures’, ‘overdentures retained’, ‘supported mandibular’, ‘overdentures supported’] | Implant-retained Mandibular Overdentures |
| 8 | 127 | 8_orbital_porous_polyethylene_porous polyethylene | [‘implants orbital’, ‘orbital implant’, ‘orbital implants’, ‘hydroxyapatite orbital’, ‘polyethylene implants’, ‘polyethylene implant’, ‘implant repair’, ‘treatment orbital’, ‘implant enucleation’, ‘orbital fractures’] | Orbital Reconstruction Implants |
| 9 | 96 | 9_cochlear_cochlear implantation_hearing_implantation | [‘cochlear implantation’, ‘cochlear implants’, ‘cochlear implant’, ‘implants cochlear’, ‘undergoing cochlear’, ‘unilateral cochlear’, ‘pediatric cochlear’, ‘following cochlear’, ‘hearing implants’, ‘outcomes cochlear’] | Cochlear Implantation |
| 10 | 89 | 10_fusion_cervical_lumbar_disc | [‘cervical disc’, ‘cervical discectomy’, ‘disc arthroplasty’, ‘discectomy fusion’, ‘lumbar fusion’, ‘cervical spine’, ‘spinal fusion’, ‘disc disease’, ‘anterior cervical’, ‘degenerative lumbar’] | Cervical Fusion and Disc Disease |
| 11 | 76 | 11_endometriosis_endometrial_borderline_endometrium | [‘tumors ovary’, ‘ovarian serous’, ‘ovary clinicopathologic’, ‘borderline ovarian’, ‘serous tumors’, ‘endometriosis’, ‘borderline tumors’, ‘human endometrium’, ‘ovarian’, ‘endometrium’] | Serous Borderline Ovary Tumors. |
| 12 | 61 | 12_zirconia_abutments_clinical_single | [‘zirconia implants’, ‘zirconia dental’, ‘veneered zirconia’, ‘zirconia abutments’, ‘tooth implant’, ‘implant reconstructions’, ‘dental implants’, ‘zirconia oral’, ‘oral implants’, ‘implant abutments’] | Zirconia Implants and Abutments |
| Authors | Title | Topic | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Andersen, Heidi, Aass, Anne Merete and Wohlfahrt, Johan Caspar | Porous titanium granules in the treatment of peri-implant osseous defects-a 7-year follow-up study | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [49] |
| Jepsen, K., Jepsen, S., Laine, M. L., Anssari Moin, D., Pilloni, A., Zeza, B., Sanz, M., Ortiz-Vigon, A., Roos-Jansaker, A. M. and Renvert, S. | Reconstruction of Peri-implant Osseous Defects: A Multicenter Randomized Trial | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [50] |
| Wohlfahrt, Johan Caspar, Lyngstadaas, Stale Petter, Ronold, Hans Jacob, Saxegaard, Erik, Ellingsen, Jan Eirik, Karlsson, Stig and Aass, Anne Merete | Porous titanium granules in the surgical treatment of peri-implant osseous defects: a randomized clinical trial | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [51] |
| Emanuel, Noam, Machtei, Eli E., Reichart, Malka and Shapira, Lior | D-PLEX500: a local biodegradable prolonged release doxycycline-formulated bone graft for the treatment for peri-implantitis. A randomized controlled clinical study | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [52] |
| Renvert, Stefan, Giovannoli, Jean-Louis, Roos-Jansaker, Ann-Marie and Rinke, Sven | Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis with or without a deproteinized bovine bone mineral and a native bilayer collagen membrane: A randomized clinical trial | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [53] |
| Isehed, C., Holmlund, A., Renvert, S., Svenson, B., Johansson, I. and Lundberg, P. | Effectiveness of enamel matrix derivative on the clinical and microbiological outcomes following surgical regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis. A randomized controlled trial | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [54] |
| Isehed, C., Svenson, B., Lundberg, P. and Holmlund, A. | Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis using enamel matrix derivative, an RCT: 3- and 5-year follow-up | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [55] |
| Renvert, Stefan, Roos-Jansaker, Ann-Marie and Persson, Gosta Rutger | Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis lesions with or without the use of a bone substitute-a randomized clinical trial | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [56] |
| Nct | Peri-implantitis - Reconstructive Surgical Therapy | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [57] |
| Froum, Stuart J., Froum, Scott H. and Rosen, Paul S. | A Regenerative Approach to the Successful Treatment of Peri-implantitis: A Consecutive Series of 170 Implants in 100 Patients with 2- to 10-Year Follow-up | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [58] |
| Gonzalez Regueiro, Iria, Martinez Rodriguez, Natalia, Barona Dorado, Cristina, Sanz-Sanchez, Ignacio, Montero, Eduardo, Ata-Ali, Javier, Duarte, Fernando and Martinez-Gonzalez, Jose Maria | Surgical approach combining implantoplasty and reconstructive therapy with locally delivered antibiotic in the treatment of peri-implantitis: A prospective clinical case series | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [59] |
| Isler, S.C., Soysal, F., Ceyhanli, T., Bakirarar, B. and Unsal, B. | Regenerative surgical treatment of peri-implantitis using either a collagen membrane or concentrated growth factor: A 12-month randomized clinical trial | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [60] |
| La Monaca, Gerardo, Pranno, Nicola, Annibali, Susanna, Cristalli, Maria Paola and Polimeni, Antonella | Clinical and radiographic outcomes of a surgical reconstructive approach in the treatment of peri-implantitis lesions: A 5-year prospective case series | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [61] |
| Mercado, Faustino, Hamlet, Stephen and Ivanovski, Saso | Regenerative surgical therapy for peri-implantitis using deproteinized bovine bone mineral with 10% collagen, enamel matrix derivative and Doxycycline-A prospective 3-year cohort study | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [62] |
| Polymeri, Angeliki, Anssari-Moin, David, van der Horst, Joyce, Wismeijer, Daniel, Laine, Marja L. and Loos, Bruno G. | Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis defects with two different xenograft granules: A randomized clinical pilot study | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [63] |
| Roccuzzo, Mario, Gaudioso, Luigi, Lungo, Marco and Dalmasso, Paola | Surgical therapy of single peri-implantitis intrabony defects, by means of deproteinized bovine bone mineral with 10% collagen | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [64] |
| Roccuzzo, Mario, Mirra, Davide, Pittoni, Dario, Ramieri, Guglielmo and Roccuzzo, Andrea | Reconstructive treatment of peri-implantitis infrabony defects of various configurations: 5-year survival and success | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [65] |
| Isrctn | Reconstructive surgical therapy of peri-implantitis bone defects | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [66] |
| Aghazadeh, A., Rutger Persson, G. and Renvert, S. | A single-centre randomized controlled clinical trial on the adjunct treatment of intra-bony defects with autogenous bone or a xenograft: results after 12 months | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [67] |
| Aghazadeh, A., Persson, R.G. and Renvert, S. | Impact of bone defect morphology on the outcome of reconstructive treatment of peri-implantitis | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [68] |
| Nct | Evaluation of Photodynamic Therapy in Treatment of Peri-implantitis | #6 Photodynamic Therapy for Peri-implantitis Treatment | [69] |
| Roos-Jansaker, Ann-Marie, Renvert, Helena, Lindahl, Christel and Renvert, Stefan | Submerged healing following surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: a case series | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [70] |
| Roos-Jansaker, Ann-Marie, Lindahl, Christel, Persson, G. Rutger and Renvert, Stefan | Long-term stability of surgical bone regenerative procedures of peri-implantitis lesions in a prospective case-control study over 3 years | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [71] |
| Roos-Jansaker, Ann-Marie, Persson, Gosta Rutger, Lindahl, Christel and Renvert, Stefan | Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis using a bone substitute with or without a resorbable membrane: a 5-year follow-up | #0 Peri-Implant Bone Study | [72] |
| Topic | Count | Name | KeyBERT | LLM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 1515 | -1_bone_implant_implants_dental | [‘bone augmentation’, ‘implant placement’, ‘implants placed’, ‘dental implant’, ‘bone regeneration’, ‘dental implants’, ‘implant’, ‘peri implant’, ‘implants’, ‘osseointegration’] | Dental Implants Studies |
| 0 | 727 | 0_implants_implant_immediate_year | [‘dental implant’, ‘dental implants’, ‘single implants’, ‘implant placement’, ‘implants placed’, ‘edentulous maxilla’, ‘implant stability’, ‘edentulous patients’, ‘implants year’, ‘posterior mandible’] | Dental Implants in Edentulous Patients |
| 1 | 692 | 1_sinus_maxillary sinus_sinus floor_floor | [‘sinus grafting’, ‘sinus augmentation’, ‘sinus floor’, ‘osteotome sinus’, ‘maxillary sinus’, ‘sinus elevation’, ‘sinus lift’, ‘sinus membrane’, ‘bone graft’, ‘lateral sinus’] | Sinus Floor Elevation |
| 2 | 296 | 2_hip_arthroplasty_total_femoral | [‘hip arthroplasty’, ‘hip replacement’, ‘revision hip’, ‘total hip’, ‘femoral stem’, ‘femoral stems’, ‘acetabular revision’, ‘arthroplasty using’, ‘knee arthroplasty’, ‘bone grafting’] | Hip Arthroplasty |
| 3 | 265 | 3_alveolar_alveolar ridge_ridge_preservation | [‘alveolar ridge’, ‘alveolar ridges’, ‘alveolar bone’, ‘placement alveolar’, ‘study alveolar’, ‘trial alveolar’, ‘vertical alveolar’, ‘following alveolar’, ‘alveolar distraction’, ‘alveolar cleft’] | Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Techniques |
| 4 | 225 | 4_titanium_titanium implants_surface_implants | [‘titanium dental’, ‘titanium implant’, ‘titanium implants’, ‘osseointegration titanium’, ‘implant surfaces’, ‘etched titanium’, ‘titanium surfaces’, ‘titanium surface’, ‘dental implants’, ‘porous titanium’] | Titanium Implants Surface Acid-Etching Osse |
| 5 | 167 | 5_ridge_ridge augmentation_ridge preservation_preservation | [‘bone allograft’, ‘tooth extraction’, ‘ridge preservation’, ‘autogenous bone’, ‘dried bone’, ‘ridge augmentation’, ‘bone mineral’, ‘molar extraction’, ‘tooth’, ‘bovine bone’] | Ridge Preservation Bone Allograft |
| 6 | 147 | 6_bone_guided_regeneration_guided bone | [‘implants regenerated’, ‘bone regeneration’, ‘bone grafting’, ‘dental implants’, ‘dental implant’, ‘bone grafts’, ‘implants using’, ‘bone augmentation’, ‘bone graft’, ‘immediate implant’] | Bone Grafting for Dental Implants |
| 7 | 146 | 7_buccal_tissue_soft_soft tissue | [‘mucosa implants’, ‘implant mucosa’, ‘tissue augmentation’, ‘dental implants’, ‘implant soft’, ‘buccal dehiscence’, ‘buccal soft’, ‘immediate implant’, ‘implant placement’, ‘dermal graft’] | Soft Tissue Augmentation for Dental Implants |
| 8 | 140 | 8_peri_peri implantitis_implantitis_peri implant | [‘peri implantitis’, ‘peri implant’, ‘implantitis randomized’, ‘implantitis prospective’, ‘implantitis using’, ‘implantitis systematic’, ‘implantitis defects’, ‘implantitis lesions’, ‘implantitis impact’, ‘implant health’] | Peri-Implantitis Treatment |
| 9 | 138 | 9_sockets_extraction_socket_extraction sockets | [‘socket implant’, ‘grafted sockets’, ‘extraction socket’, ‘sockets clinical’, ‘socket augmentation’, ‘healing extraction’, ‘implant placement’, ‘socket preservation’, ‘extraction sockets’, ‘implants placed’] | Implants in Fresh Extraction Sockets |
| 10 | 117 | 10_assist_ventricular_heart_ventricular assist | [‘ventricular assist’, ‘biventricular assist’, ‘circulatory support’, ‘heart transplantation’, ‘cardiogenic shock’, ‘life support’, ‘heart transplant’, ‘bridge heart’, ‘left ventricular’, ‘extracorporeal’] | Ventricular Assist Devices |
| 11 | 102 | 11_platelet_platelet rich_rich_rich fibrin | [‘implants platelet’, ‘fibrin socket’, ‘implant stability’, ‘using platelet’, ‘platelet gel’, ‘fibrin membrane’, ‘use platelet’, ‘effects platelet’, ‘influence platelet’, ‘bone healing’] | Platelet-Rich Fibrin Effects on Dental Implants |
| 12 | 93 | 12_fusion_lumbar_cervical_interbody | [‘cervical fusion’, ‘cervical discectomy’, ‘cervical disc’, ‘lumbar fusion’, ‘disc arthroplasty’, ‘discectomy fusion’, ‘fusion lumbar’, ‘spine fusion’, ‘spine surgery’, ‘cervical spine’] | Cervical and Lumbar Fusion Studies |
| 13 | 89 | 13_bone morphogenetic_morphogenetic_protein_morphogenetic protein | [‘bone morphogenetic’, ‘recombinant bone’, ‘bone regeneration’, ‘osteogenesis’, ‘bone formation’, ‘osteoconductive bulking’, ‘morphogenetic protein’, ‘protein bone’, ‘morphogenetic proteins’, ‘osseointegration dental’] | Bone Regeneration Recombinant Human BMP |
| 14 | 81 | 14_hydroxyapatite_hydroxyapatite coated_coated_implants | [‘hydroxyapatite implants’, ‘hydroxyapatite implant’, ‘hydroxyapatite coated’, ‘hydroxyapatite coating’, ‘treated hydroxyapatite’, ‘nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite’, ‘nano hydroxyapatite’, ‘ceramic hydroxyapatite’, ‘threaded hydroxyapatite’, ‘supported hydroxyapatite’] | Hydroxyapatite-coated Dental Implants Studies |
| 15 | 73 | 15_periodontal_defects_intrabony_treatment | [‘periodontal intrabony’, ‘intrabony periodontal’, ‘periodontal therapy’, ‘treatment periodontal’, ‘periodontal defects’, ‘periodontal infrabony’, ‘human periodontal’, ‘periodontal’, ‘enamel matrix’, ‘intrabony defects’] | Periodontal defect treatment |
| 16 | 71 | 16_membranes_guided bone_guided_membrane | [‘bone regeneration’, ‘linked collagen’, ‘membrane collagen’, ‘regeneration dental’, ‘collagen membrane’, ‘collagen membranes’, ‘guided tissue’, ‘guided bone’, ‘collagen’, ‘resorbable membranes’] | Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration |
| 17 | 64 | 17_overdentures_retained_mandibular_mandibular overdentures | [‘implant overdentures’, ‘mandibular overdentures’, ‘mandibular overdenture’, ‘implants mandibular’, ‘mandibular implant’, ‘retained overdentures’, ‘maxillary overdentures’, ‘overdentures retained’, ‘retained mandibular’, ‘retained overdenture’] | Implant-retained Mandibular Overdentures |
| 18 | 57 | 18_antibiotic_antibiotics_implant_infection | [‘implant infections’, ‘antibiotic prophylaxis’, ‘prophylactic antibiotic’, ‘infection dental’, ‘antibiotics clinical’, ‘antibiotic regimens’, ‘antimicrobial’, ‘preoperative antibiotics’, ‘dental implant’, ‘dental implants’] | Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Dental Implants |
| 19 | 54 | 19_hearing_anchored hearing_bone anchored_anchored | [‘cochlear implants’, ‘cochlear implantation’, ‘cochlear implant’, ‘hearing implant’, ‘hearing implants’, ‘implant bone’, ‘anchored hearing’, ‘auditory osseointegrated’, ‘hearing aids’, ‘pediatric cochlear’] | Bone Anchored Hearing Implant |
| 20 | 50 | 20_orbital_retinal_lens_intraocular | [‘orbital implant’, ‘orbital implants’, ‘retinal prosthesis’, ‘infancy orbital’, ‘retinal detachment’, ‘inferior orbital’, ‘acrylic intraocular’, ‘study retinal’, ‘intravitreal’, ‘intraocular lens’] | Orbital & Retinal Implants |
| Authors | Title | Topic | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
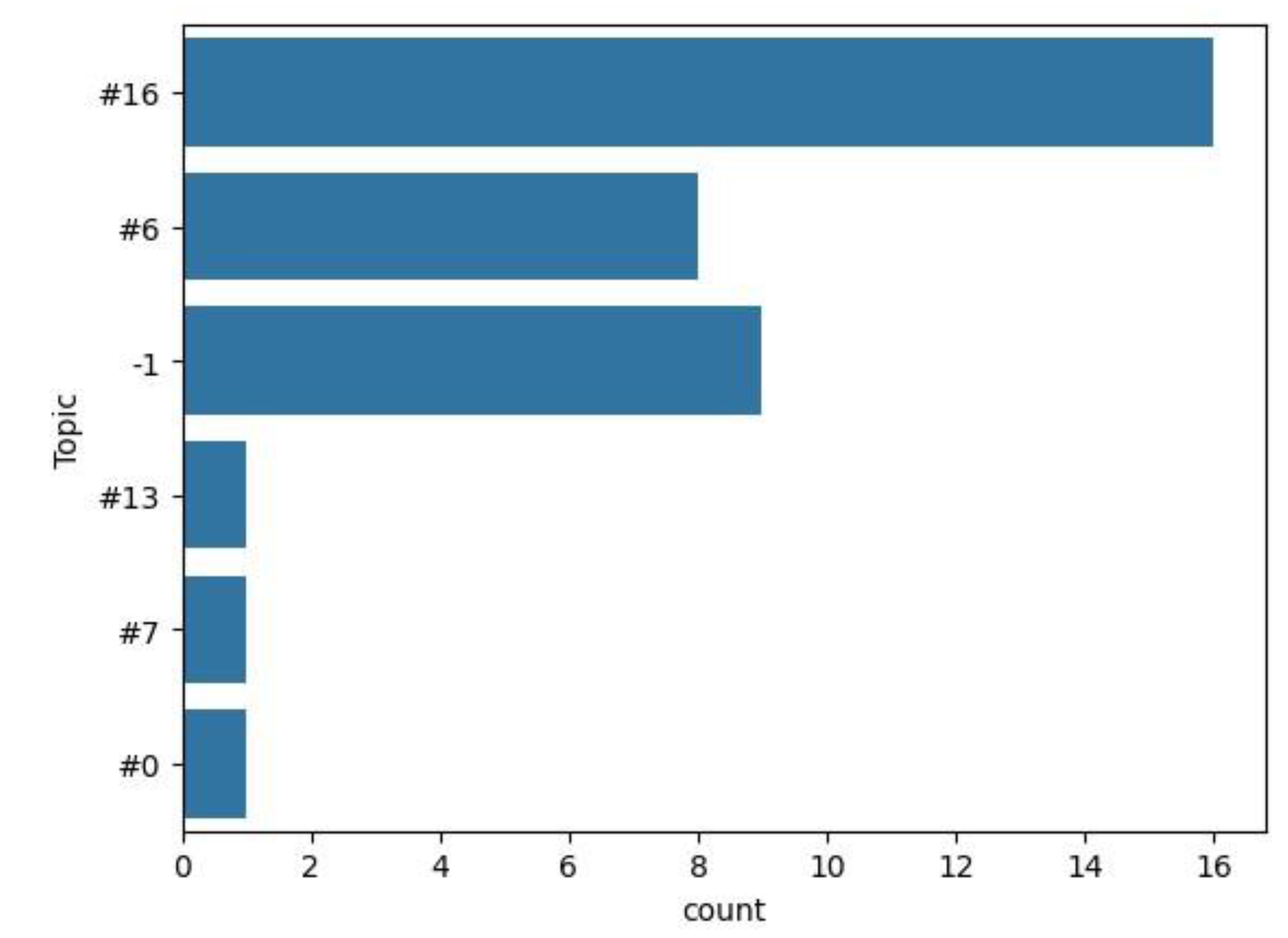
| Naenni, N., Stucki, L., Hüsler, J., Schneider, D., Hämmerle, C.H., Jung, R.E. and Thoma, D.S., | Implants sites with concomitant bone regeneration using a resorbable or non-resorbable membrane result in stable marginal bone levels and similar profilometric outcomes over 5 years. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [82] |
| Basler, T., Naenni, N., Schneider, D., Hämmerle, C.H., Jung, R.E. and Thoma, D.S | Randomized controlled clinical study assessing two membranes for guided bone regeneration of peri-implant bone defects: 3-year results. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [83] |
| Mau, J.L., Grodin, E., Lin, J.J., Chen, M.C.J., Ho, C.H. and Cochran, D., | A comparative, randomized, prospective, two-center clinical study to evaluate the clinical and esthetic outcomes of two different bone grafting techniques in early implant placement. | #6 ‘Bone Grafting for Dental Implants | [84] |
| Annen, B.M., Ramel, C.F., Hammerle, C.H.F. and Jung, R.E., | Use of a new cross-linked collagen membrane for the treatment of peri-implant dehiscence defects: a randomised controlled double-blinded clinical trial. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [85] |
| Naenni, N., Schneider, D., Jung, R.E., Hüsler, J., Hämmerle, C.H. and Thoma, D.S., | Randomized clinical study assessing two membranes for guided bone regeneration of peri-implant bone defects: clinical and histological outcomes at 6 months. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [86] |
| Lee, J.H., Lee, J.S., Baek, W.S., Lim, H.C., Cha, J.K., Choi, S.H. and Jung, U.W. | Assessment of dehydrothermally cross-linked collagen membrane for guided bone regeneration around peri-implant dehiscence defects: a randomized single-blinded clinical trial. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [87] |
| Lee, J.H., Park, S.H., Kim, D.H. and Jung, U.W. | Assessment of clinical and radiographic outcomes of guided bone regeneration with dehydrothermally cross-linked collagen membrane around peri-implant dehiscence defects: Results from a 3-year randomized clinical trial. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [88] |
| Becker, J., Al-Nawas, B., Klein, M.O., Schliephake, H., Terheyden, H. and Schwarz, F., | Use of a new cross-linked collagen membrane for the treatment of dehiscence-type defects at titanium implants: a prospective, randomized-controlled double-blinded clinical multicenter study. | -1 Dental Implants Studies | [89] |
| Schwarz, F., Schmucker, A. and Becker, | Long-term outcomes of simultaneous guided bone regeneration using native and cross-linked collagen membranes after 8 years. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [90] |
| Schwarz, F., Hegewald, A., Sahm, N. and Becker, J. | Long-term follow-up of simultaneous guided bone regeneration using native and cross-linked collagen membranes over 6 years. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [91] |
| Schwarz, F., Sahm, N. and Becker, J. | Impact of the outcome of guided bone regeneration in dehiscence-type defects on the long-term stability of peri-implant health: clinical observations at 4 years. | #6 Bone Grafting for Dental Implants | [92] |
| Benic, G.I., Eisner, B.M., Jung, R.E., Basler, T., Schneider, D. and Hämmerle, C.H., | Hard tissue changes after guided bone regeneration of peri-implant defects comparing block versus particulate bone substitutes: 6-month results of a randomized controlled clinical trial. | #6 Bone Grafting for Dental Implants | [93] |
| Carpio, L., Loza, J., Lynch, S. and Genco, R. | Guided bone regeneration around endosseous implants with anorganic bovine bone mineral. A randomized controlled trial comparing bioabsorbable versus non-resorbable barriers. | #6 Bone Grafting for Dental Implants | [94] |
| Deesricharoenkiat, N., Jasilynn, P., Chuenchompoonut, V., Mattheos, N. and Thunyakitpisal, P. | The effect of acemannan in implant placement with simultaneous guided bone regeneration in the aesthetic zone: A randomized controlled trial. | #6 Bone Grafting for Dental Implants | [95] |
| Jung, R.E., Glauser, R., Schärer, P., Hämmerle, C.H., Sailer, H.F. and Weber, F.E., | Effect of rhBMP-2 on guided bone regeneration in humans: A randomized, controlled clinical and histomorphometric study. | -1 Dental Implants Studies | [96] |
| Jung, R.E., Windisch, S.I., Eggenschwiler, A.M., Thoma, D.S., Weber, F.E. and Hämmerle, C.H. | A randomized-controlled clinical trial evaluating clinical and radiological outcomes after 3 and 5 years of dental implants placed in bone regenerated by means of GBR techniques with or without the addition of BMP-2. | #6 Bone Grafting for Dental Implants | [97] |
| Jung, R.E., Kovacs, M.N., Thoma, D.S. and Hämmerle, C.H. | Informative title: guided bone regeneration with and without rhBMP-2: 17-year results of a randomized controlled clinical trial. | #13 Bone Regeneration Recombinant Human BMP | [98] |
| Jung, R.E., Hälg, G.A., Thoma, D.S. and Hämmerle, C.H. | A randomized, controlled clinical trial to evaluate a new membrane for guided bone regeneration around dental implants. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [99] |
| Ramel, C.F., Wismeijer, D.A., F Hämmerle, C.H. and Jung, R.E. | A randomized, controlled clinical evaluation of a synthetic gel membrane for guided bone regeneration around dental implants: clinical and radiologic 1-and 3-year results. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [100] |
| Jung, R.E., Benic, G.I., Scherrer, D. and Hämmerle, C.H. | Cone beam computed tomography evaluation of regenerated buccal bone 5 years after simultaneous implant placement and guided bone regeneration procedures–a randomized, controlled clinical trial. | #7 Soft Tissue Augmentation for Dental Implants. | [101] |
| Jung, R.E., Mihatovic, I., Cordaro, L., Windisch, P., Friedmann, A., Blanco Carrion, J., Sanz Sanchez, I., Hallman, M., Quirynen, M. and Hammerle, C.H. | Comparison of a polyethylene glycol membrane and a collagen membrane for the treatment of bone dehiscence defects at bone level implants—A prospective, randomized, controlled, multicenter clinical trial. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [102] |
| Benic, G.I., Bienz, S.P., Song, Y.W., Cha, J.K., Hämmerle, C.H., Jung, U.W. and Jung, R.E. | Randomized controlled clinical trial comparing guided bone regeneration of peri-implant defects with soft-type block versus particulate bone substitutes: six-month results of hard-tissue changes. | -1 Dental Implant Studies | [103] |
| Lee, D.W., Kim, K.T., Joo, Y.S., Yoo, M.K., Yu, J.A. and Ryu, J.J. | The role of two different collagen membranes for dehiscence defect around implants in humans. | -1 Dental Implant Studies | [104] |
| Mattout, P., Nowzari, H. and Mattout, C., | Clinical evaluation of guided bone regeneration at exposed parts of Brånemark dental implants with and without bone allograft. | #6 Bone Grafting for Dental Implants | [105] |
| Merli, M., Moscatelli, M., Mariotti, G., Pagliaro, U., Raffaelli, E. and Nieri, M. | Comparing membranes and bone substitutes in a one-stageprocedurefor horizontal bone augmentation. A double-blindrandomisedcontrolled trial | -1 Dental Implant Studies | [106] |
| Merli, M., Moscatelli, M., Mariotti, G., Pagliaro, U., Raffaelli, E. and Nieri, M. | Comparing membranes and bone substitutes in a one-stage procedure for horizontal bone augmentation. Three-year post-loading results of a double-blind randomised controlled trial. | -1 Dental Implant Studies | [107] |
| Park, S.H., Lee, K.W., Oh, T.J., Misch, C.E., Shotwell, J. and Wang, H.L. | Effect of absorbable membranes on sandwich bone augmentation. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [108] |
| Schneider, D., Weber, F.E., Grunder, U., Andreoni, C., Burkhardt, R. and Jung, R.E. | A randomized controlled clinical multicenter trial comparing the clinical and histological performance of a new, modified polylactide-co-glycolide acid membrane to an expanded polytetrafluorethylene membrane in guided bone regeneration procedures. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [109] |
| Temmerman, A., Cortellini, S., Van Dessel, J., De Greef, A., Jacobs, R., Dhondt, R., Teughels, W. and Quirynen, M. | Bovine-derived xenograft in combination with autogenous bone chips versus xenograft alone for the augmentation of bony dehiscences around oral implants: A randomized, controlled, split-mouth clinical trial. | -1 Dental Implant Studies | [110] |
| Simion, M., Misitano, U., Gionso, L. and Salvato, A. | Treatment of dehiscences and fenestrations around dental implants using resorbable and nonresorbable membranes associated with bone autografts: a comparative clinical study. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [111] |
| Urban, I.A., Wessing, B., Alández, N., Meloni, S., González-Martin, O., Polizzi, G., Sanz-Sanchez, I., Montero, E. and Zechner, W. | A multicenter randomized controlled trial using a novel collagen membrane for guided bone regeneration at dehisced single implant sites: Outcome at prosthetic delivery and at 1-year follow?up. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [112] |
| Wessing, B., Urban, I., Montero, E., Zechner, W., Hof, M., Alandez Chamorro, J., Alandez Martin, N., Polizzi, G., Meloni, S. and Sanz, M. | A multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial using a new resorbable non-cross-linked collagen membrane for guided bone regeneration at dehisced single implant sites: interim results of a bone augmentation procedure. | #16 Collagen Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration | [113] |
| Van Assche, N., Michels, S., Naert, I. and Quirynen, M. | Randomized controlled trial to compare two bone substitutes in the treatment of bony dehiscences. | #6 Bone Grafting for Dental Implants | [114] |
| Veis, A.A., Tsirlis, A.T. and Parisis, N.A. | Effect of autogenous harvest site location on the outcome of ridge augmentation for implant dehiscences. | -1 Dental Implant Studies | [115] |
| Wen, S.C., Fu, J.H. and Wang, H.L. | Effect of Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral at Implant Dehiscence Defects Grafted by the Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique. | -1 Dental Implant Studies | [116] |
| Tsai, Y.L., Tsao, J.P., Wang, C.L., Grodin, E., Lin, J.J., Chen, C.J., Ho, C.H., Cochran, D. and Mau, J.L.P. | Stability of contour augmentation of implant-supported single crowns in the esthetic zone: One-year cone-beam computed tomography results of a comparative, randomized, prospective, two-center clinical study using two different bone grafting techniques in early implant placement. | #0 Dental Implants in Edentulous Patients | [117] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





