Submitted:
26 July 2024
Posted:
29 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
A Priori Research Hypothesis
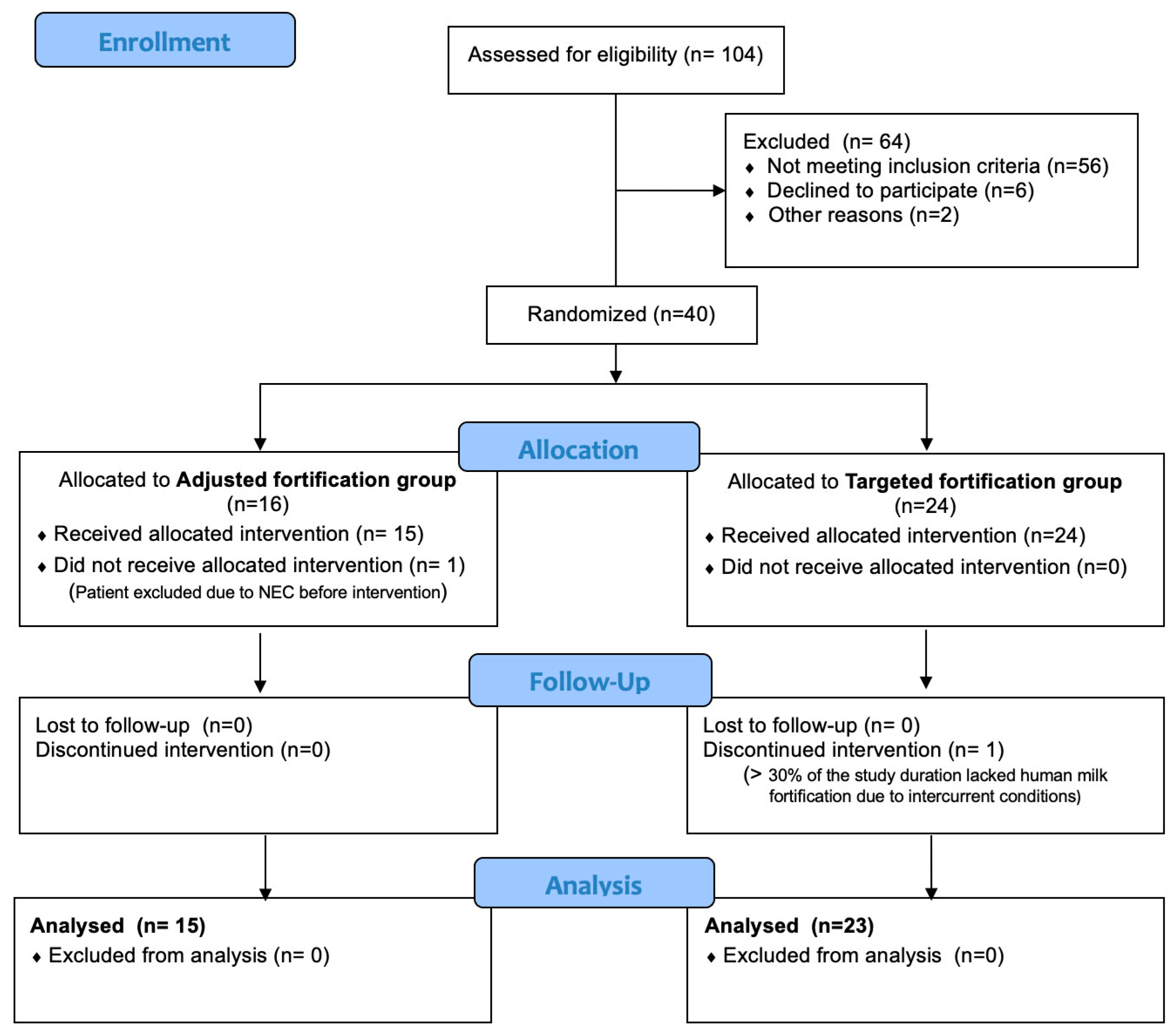
2.2. Participants
Randomization
2.3. Nutritional Intervention
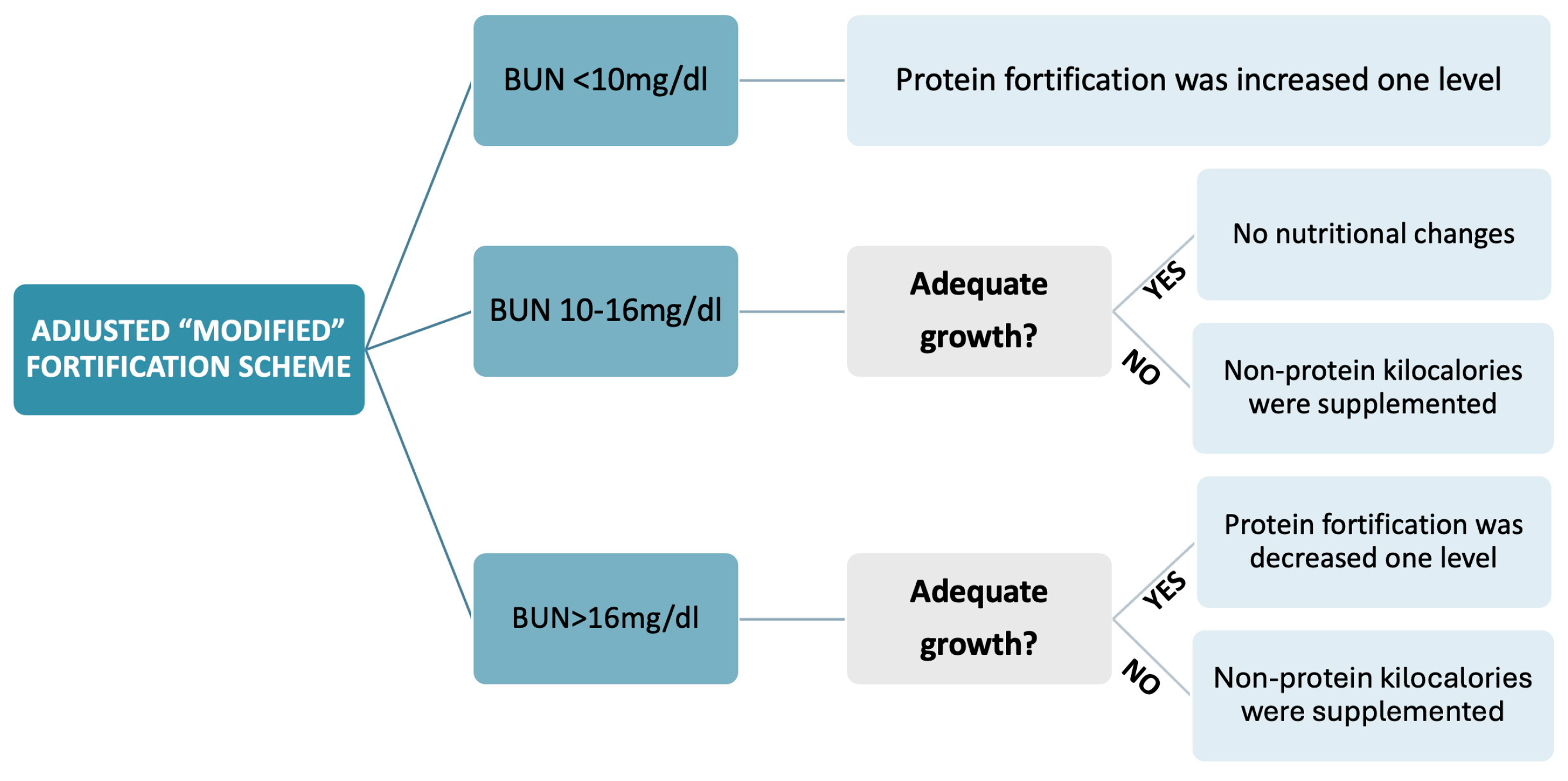
2.3.1. Adjusted “Modified” Fortification
- BUN < 10 mg/dl: protein fortification was increased one level by adding a protein fortification module [oligopeptides (Clinical Nutrition, SA, Barcelona, Spain) 0.5 g/100 ml, 1 g/100 ml or 1.5 g/100 ml].
- BUN > 16 mg/dl: fortification was decreased one level if growth was adequate. If BUN > 10 mg/dl but growth was inadequate defined as decrease in weight z-score on Fenton curves, an insufficient intake of other macronutrients was inferred, and non-protein kilocalories were supplemented with lipids in the form of medium-chain triglycerides [MCT 1-2 ml/kg (Nutricion Medica, Madrid, Spain)] and glucose polymer powder [0.97 g carbohydrates/g (Fantomalt, Nutricia, Netherlands) 2 g/100 ml].
2.3.2. Targeted Fortification
2.4. Analysis of Human Milk
2.5. Biochemical Analyses
2.6. Outcomes
- Length and head circumference (HC) growth. Cranial-heel length was measured on a length board in supine position (Añó sayol, Barcelona, Spain), and HC was measured with a non-stretching tape to the nearest 0.5 cm.
- Standard deviation score (SDS) differences, based on Fenton graphs [41], for weight, length and HC between the periods studied (SDS different time points − SDS birth). The research team performed all anthropometric measurements.
- Actual enteral macronutrient intake (g/kg/day and Kcal/kg/day).
- Nutritional achievements: initiation of enteral nutrition (hours), exclusive enteral nutrition (150 ml/kg/day) (days), parenteral nutrition cessation (days), start of HM fortification (days) and volume of enteral feeding at the beginning of fortification (ml/kg/day).
- Predominant HM type (>50% of intake during the study period): MOM or DHM.
- Perinatal characteristics and neonatal morbidities: early-onset sepsis [44], intraventricular hemorrhage ≥ grade II [45], white matter injury [46], significant ductus arteriosus [47,48], necrotizing enterocolitis defined as Bell’s stage > 2 [49], retinopathy [50], moderate-severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia [51,52], cholestasis [53], late-onset sepsis [44] and death.
- Neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) and hospital stay (days).
2.7. Sample Size and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
| General characteristics of study population | Adjusted fortification (n = 15) | Targeted fortification (n = 23) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Gestational age (weeks) Mean (CI 95%) |
27 (26.27, 28.01) | 27 (25.88, 27.79) | 0.64 |
|
Birth weight (g) Mean (CI 95%) |
765 (669.79, 860.74) | 819 (767.77, 870.58) | 0.26 |
|
Birth weight z-score Mean (CI 95%) |
-0.8 (-1.42, -0.38) | -0.9 (-0.79, 0.18) | 0.09 |
|
Length birth (cm) Mean (CI 95%) |
32.5 (31.18, 33.82) | 33.5 (32.51, 34.51) | 0.19 |
|
Head circumference at birth (cm) Mean (CI 95%) |
23.3 (22.42, 24.17) | 23.6 (22.96, 24.16) | 0.58 |
| Male No (%) | 9/15 (60) | 11/23 (47.8) | 0.46 |
| Multiple gestation No (%) | 4/15 (26.7) | 11/23 (47.8) | 0.19 |
|
Umbilical cord pH Median (CI 95%) |
7.29 (7.17, 7.38) | 7.33 (7.23, 7.36) | 0.12 |
|
Initial weight loss (%) Mean (CI 95%) |
6.7 (4.30, 9.43) | 6.18 (4.23, 8.12) | 0.73 |
|
Birth weight regain (day) Median (CI 95%) |
6 (4.86, 7.81) | 7 (5.34, 7.96) | 0.47 |
|
Weight at hospital discharge (g) Mean (CI 95%) |
2691 (2364.26, 3017.07) | 2816 (2543.68, 3088.49) | 0.54 |
|
Length at hospital discharge (cm) Median (CI 95%) |
45 (43.57, 46.50) | 45 (43.96, 46.29) | 0.66 |
|
Head circumference at discharge (cm) Mean (CI 95%) |
33.7 (32.85, 34.45) | 33.2 (32.52, 33.96) | 0.43 |
3.1. Nutritional Strategy
| HM analyses | Adjusted fortification (n = 15) | Targeted fortification (n = 23) | p-value | Intake | Adjusted fortification (n = 15) | Targeted fortification (n = 23) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Protein HM (g/100 ml) Mean (CI 95%) |
1.34 (1.25, 1.45) | 1.27 (1.21, 1.35) | 0.20 |
Protein g/kg/day Mean (CI 95%) |
5.02 (4.73, 5.30) | 4.48 (4.41, 4.56) | 0.001 |
|
Lipid HM (g/100 ml) Median (CI 95%) |
7.32 (7.23, 7.77) | 7.61 (7.35, 7.79) | 0.10 |
Lipid g/kg/day Mean (CI 95%) |
7.15 (6.45, 7.85) | 6.56 (6.39, 6.74) | 0.10 |
|
Carbohydrates HM (g/100 ml) Median (CI 95%) |
3.30 (3.16, 3.90) | 3.20 (3.05, 3.34) | 0.80 |
Carbohydrates g/kg/day Mean (CI 95%) |
15.15 (14.09, 16.22) | 15.15 (14.54, 15.76) | 0.99 |
|
Energy HM (kcal/100 ml) Median (CI 95%) |
65.66 (63.67, 69.96) | 64.08 (62.78, 65.57) | 0.156 |
Energy kcal/kg/day Mean (CI 95%) |
144.72 (135.62, 153.83) | 137.63 (134.94, 140.32) | 0.13 |
3.2. Growth Outcomes
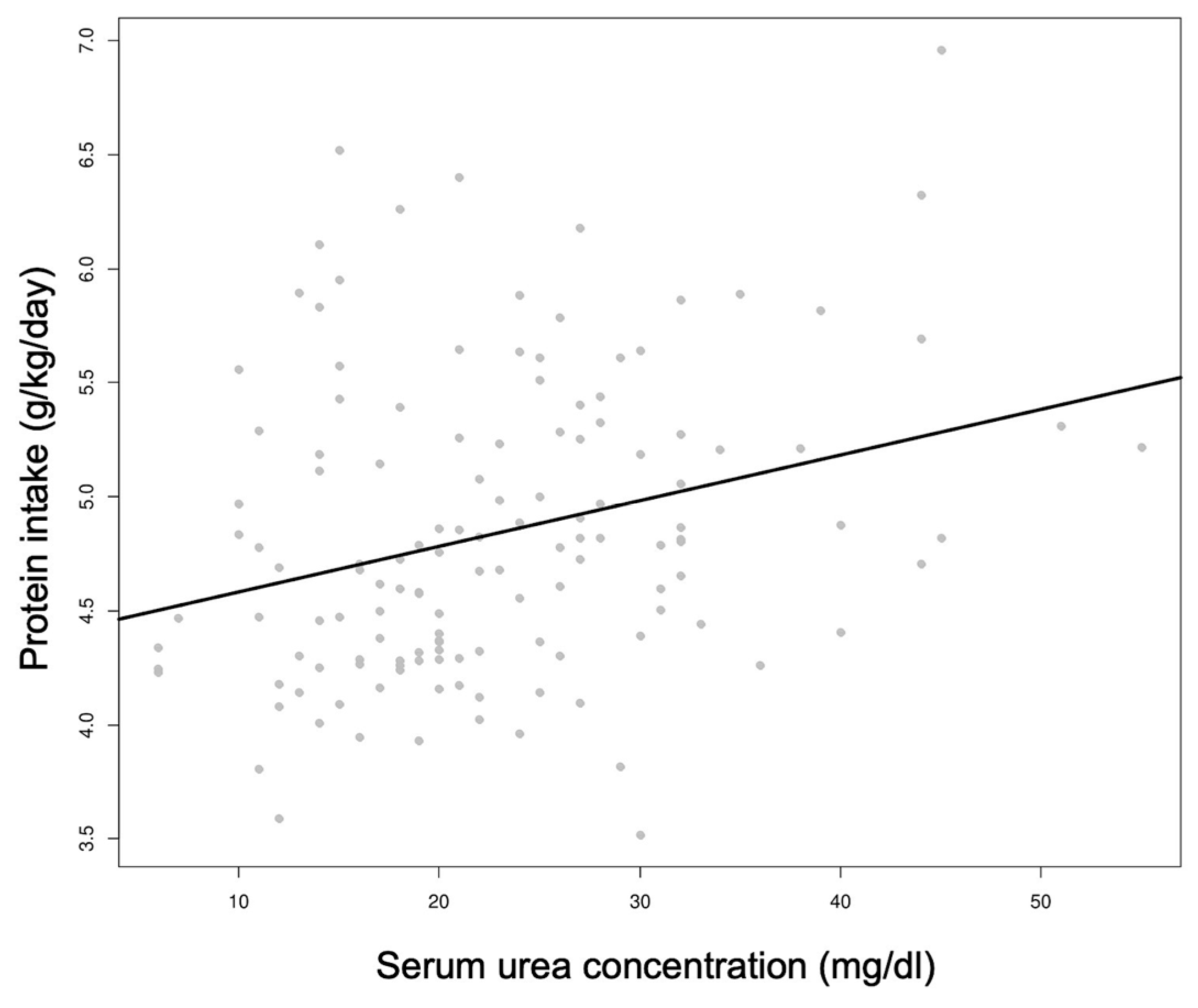
3.3. Biochemical Parameters
3.4. Neonatal Morbidity and Hospital Stay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arslanoglu, S.; Boquien, C.Y.; King, C.; Lamireau, D.; Tonetto, P.; Barnett, D.; Bertino, E.; Gaya, A.; Gebauer, C.; Grovslien, A.; Moro, G.E.; Weaver, G.; Wesolowska, A.M.; Picaud, J.C. Fortification of Human Milk for Preterm Infants: Update and Recommendations of the European Milk Bank Association (EMBA) Working Group on Human Milk Fortification. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetta, K.E.; Schulz, E.V.; Wagner, C.L. Outcomes improved with human milk intake in preterm and full-term infants. Semin. Perinatol. 2021, 45, 151384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisk, P.M.; Lovelady, C.A.; Gruber, K.J.; Dillard, R.G.; O'Shea, T.M. Human milk consumption and full enteral feeding among infants who weigh ≤1250 grams. Pediatrics 2008, 121, 2007–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanler, R.J. Evaluation of the evidence to support current recommendations to meet the needs of premature infants: the role of human milk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 625S–628S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohr, B.R.; Poindexter, B.B.; Dusick, A.M.; McKinley, L.T.; Higgins, R.D.; Langer, J.C.; Poole, W.K.; Wright, L.L.; Bauer, C.R.; Meinzen-Derr, J.; Parrott, R.H. Persistent beneficial effects of breast milk ingested in the neonatal intensive care unit on outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants at 30 months of age. Pediatrics 2007, 120, e953–e959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, S.; Schanler, R.J.; Kim, J.H.; Patel, A.L.; Trawöger, R.; Kiechl-Kohlendorfer, U.; Chan, G.M.; Blanco, C.L.; Abrams, S.; Cotton, C.M.; Laroia, N.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Dudell, G.; Cristofalo, E.A.; Meier, P.P.; Lee, M.L.; Rechtman, D.J.; Lucas, A. An exclusively human milk-based diet is associated with a lower rate of necrotizing enterocolitis than a diet of human milk and bovine milk-based products. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, 562–567.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinzen-Derr, J.; Poindexter, B.B.; Wrage, L.A.; Morrow, A.L.; Stoll, B.J.; Ehrenkranz, R.A. Role of human milk in extremely low birth weight infants' risk of necrotizing enterocolitis or death. J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslanoglu, S.; Ziegler, E.E.; Moro, G.E. Donor human milk for preterm infants: current evidence and research directions. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, M.; Embleton, N.D.; McGuire, W. Formula versus donor breast milk for feeding preterm or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 7, CD002971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergner, E.M.; Taylor, S.N.; Gollins, L.A.; Hair, A.B. Human Milk Fortification: A Practical Analysis of Current Evidence. Clin. Perinatol. 2022, 49, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, A.B.; Scottoline, B.; Good, M. Dilemmas in human milk fortification. J. Perinatol. 2023, 43, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcik, K.Y.; Rechtman, D.J.; Lee, M.L.; Montoya, A.; Medo, E.T. Macronutrient analysis of a nationwide sample of donor breast milk. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T.T.; Poindexter, B.B. Human Milk Fortification Strategies in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Clin. Perinatol. 2023, 50, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, G.E.; Benso, L.; Brovedani, P.; Cerbo, R.; Coscia, A.; Ferrero, I.; Finessi, M.; Migliore, S.; Nosetti, L.; Bertino, E. XII. Human Milk in Feeding Premature Infants: Consensus Statement. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61 (Suppl 1), S16–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanoglu, S.; Moro, G.E.; Ziegler, E.E.; The WAPM Working Group on Nutrition. Optimization of human milk fortification for preterm infants: new concepts and recommendations. J. Perinat. Med. 2010, 38, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radmacher, P.G.; Adamkin, D.H. Fortification of human milk for preterm infants. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 22, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, E.E. Human milk and human milk fortifiers. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 110, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, W.W.; Ziegler, E.E. Growth failure among preterm infants due to insufficient protein is not innocuous and must be prevented. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beggs, M.R.; Bando, N.; Unger, S.; O'Connor, D.L. State of the evidence from clinical trials on human milk fortification for preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2022, 111, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera Lafuente, M.; Manzanedo, R.; Estévez, M.; Segura, A. A prospective analysis of intake and composition of mother's own milk in preterm newborns less than 32 weeks' gestational age. J. Perinat. Med. 2018, 47, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Younes, N.; Lemons, J.A.; Fanaroff, A.A.; Donovan, E.F.; Wright, L.L.; Katsikiotis, V.; Tyson, J.E.; Oh, W.; Shankaran, S.; et al. Growth in the neonatal intensive care unit influences neurodevelopmental and growth outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrizio, V.; Turoli, D.; Da Frè, M.; Fanni, G.; Munno, A.; Stefanelli, A.; Zamprogna, S.; De Cunto, A. Individualized versus standard diet fortification for growth and development in preterm infants receiving human milk. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 11, CD013465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslanoglu, S.; Moro, G.E.; Ziegler, E.E. Preterm infants fed fortified human milk receive less protein than they need. J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.K.; Singhal, A.; Vaidya, U.; Banerjee, S.; Anwar, F.; Rao, S.; Modi, N.; Narang, A.; Sriram, K. Optimizing Nutrition in Preterm Low Birth Weight Infants-Consensus Summary. Front. Nutr. 2017, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embleton, N.D.; Berrington, J.E.; McGuire, W.; Stewart, C.J.; Cummings, S.P. Enteral Nutrition in Preterm Infants (2022): A Position Paper From the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition and Invited Experts. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 76, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanoglu, S.; Moro, G.E.; Ziegler, E.E. Adjustable fortification of human milk fed to preterm infants: does it make a difference? J. Perinatol. 2006, 26, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanoglu, S.; Corpeleijn, W.; Moro, G.E.; Braegger, C.; Campoy, C.; Colomb, V.; Decsi, T.; Domellöf, M.; Fewtrell, M.; Hojsak, I.; et al. Update of adjustable fortification regimen for preterm infants: a new protocol. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2012, 26 (Suppl. 3), 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Arslanoglu, S. IV. Individualized Fortification of Human Milk: Adjustable Fortification. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61 (Suppl 1), S4–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamkin, D.H. Use of human milk and fortification in the NICU. J. Perinatol. 2023, 43, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochow, N.; Fusch, G.; Choi, A.; Chessell, L.; Elliott, L.; McDonald, K.; Kuiper, E.; Purcha, M.; Turner, S.; Chan, E.; Fusch, C. Target fortification of breast milk with fat, protein, and carbohydrates for preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlino Barr, S.; Groh-Wargo, S. Targeted fortification with human milk analysis: An opportunity for innovation. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 27, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidrewicz, D.A.; Fenton, T.R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the nutrient content of preterm and term breast milk. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochow, N.; Fusch, G.; Choi, A.; Chessell, L.; Elliott, L.; McDonald, K.; Kuiper, E.; Purcha, M.; Turner, S.; Chan, E.; Fusch, C. Target fortification of breast milk: how often should milk analysis be done? Nutrients 2015, 7, 2297–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, C.; Fusch, G.; Bahonjic, A.; Rochow, N.; Fusch, C. Infrared analyzers for breast milk analysis: fat levels can influence the accuracy of protein measurements. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 1931–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parat, S.; Groh-Wargo, S.; Merlino, S.; Wijers, C.; Super, D.M. Validation of mid-infrared spectroscopy for macronutrient analysis of human milk. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusch, G.; Kwan, C.; Kotrri, G.; Fusch, C. "Bed Side" Human Milk Analysis in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review. Clin. Perinatol. 2017, 44, 209–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffin, R.; Pinon, P.; Winer, N.; Lizee, S.; Guillet, R.; Bouderlique, C.; Laffont, I.; Jourdes, E.; Darmaun, D.; Rozé, J.C. Assessment of human milk composition using mid-infrared analyzers requires calibration adjustment. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramey, S.R.; Merlino Barr, S.; Moore, K.A.; Groh-Wargo, S. Exploring Innovations in Human Milk Analysis in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: A Survey of the United States. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 692600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, T.R. A new growth chart for preterm babies: Babson and Benda's chart updated with recent data and a new format. BMC Pediatr. 2003, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, T.R.; Anderson, D.; Groh-Wargo, S.; Hoyos, A.; Ehrenkranz, R.A. Accuracy of preterm infant weight gain velocity calculations vary depending on method used and infant age at time of measurement. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, C.; Buonocore, G.; Carnielli, V.P.; De Curtis, M.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.D.; Fusch, C.; Genzel-Boroviczeny, O.; et al. Enteral nutrient supply for preterm infants: commentary from the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, C. Best Practices for Handling and Administration of Expressed Human Milk and Donor Human Milk for Hospitalized Preterm Infants. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.L.; Engstrom, J.L.; Meier, P.P.; Kimura, R.E. Accuracy of methods for calculating postnatal growth velocity for extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2005, 116, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.H.; Hanna, M.; Canpolat, F.E.; Mohan, P. Diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: the past, present and future. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 91, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Govaert, P.; Horsch, S.; Bravo, M.C.; Ramenghi, L.A.; eurUS.brain group. Cranial ultrasound findings in preterm germinal matrix haemorrhage, sequelae and outcome. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 87 (Suppl 1), 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agut, T.; Gosselin, J.; Dong, W.; Fortin-Pellerin, E.; Saint-Martin, C.; Brochu, M.E. Preterm white matter injury: ultrasound diagnosis and classification. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 87 (Suppl 1), 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Laere, D.; van Overmeire, B.; Schepens, P.; Smits, M.; Devlieger, H. Application of NPE in the assessment of a patent ductus arteriosus. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84 (Suppl 1), 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boode, W.P.; Kluckow, M.; McNamara, P.J.; Gupta, S. Role of neonatologist-performed echocardiography in the assessment and management of patent ductus arteriosus physiology in the newborn. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 23, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.J.; Ternberg, J.L.; Feigin, R.D.; Keating, J.P.; Marshall, R.; Barton, L.; Brotherton, T. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann. Surg. 1978, 187, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.F.; Quinn, G.E.; Fielder, A.R.; Ostmo, S.R.; Paul Chan, R.V.; Berrocal, A.; Flynn, J.T.; Hammersmith, J.A.; Hubbard, G.B.; Kushner, B.J.; et al. International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity, Third Edition. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, e51–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobe, A.H.; Bancalari, E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancalari, E.; Jain, D. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Can We Agree on a Definition? Am. J. Perinatol. 2018, 35, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.R.; Rosenthal, P.; Escobar, G.J.; Newman, T.B. Interpreting conjugated bilirubin levels in newborns. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Halleux, V.; Close, A.; Stalport, S.; Studzinski, F.; Habibi, F.; Rigo, J. Intérêt de la supplémentation du lait maternel << à la carte>> [Advantages of individualized fortification of human milk for preterm infants]. Arch. Pediatr. 2007, 14 (Suppl 1), S5–S10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Halleux, V.; Rigo, J. Variability in human milk composition: benefit of individualized fortification in very-low-birth-weight infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 529S–535S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlacchi, L.; Mallardi, D.; Giannì, M.L.; Roggero, P.; Amato, O.; Piemontese, P.; Mosca, F. Is targeted fortification of human breast milk an optimal nutrition strategy for preterm infants? An interventional study. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadıoğlu Şimşek, G.; Tayman, C.; Aydemir, O.; Altun, H.; Bağcı, O. Comparison of the Effect of Three Different Fortification Methods on Growth of Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Breastfeed. Med. 2019, 14, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochow, N.; Fusch, G.; Ali, A.; Fusch, C. Individualized target fortification of breast milk with protein, carbohydrates, and fat for preterm infants: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulut, O.; Coban, A.; Uzunhan, O.; Ince, Z. Effects of Targeted Versus Adjustable Protein Fortification of Breast Milk on Early Growth in Very Low-Birth-Weight Preterm Infants: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020, 35, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, E.E.; Thureen, P.J.; Carlson, S.J. Aggressive nutrition of the very low birthweight infant. Clin. Perinatol. 2002, 29, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Makrides, M.; Gibson, R.A.; McPhee, A.J.; Stanford, T.E.; Morris, S.; Huang, R.C.; Ryan, P.; Collins, C.T. Effect of increasing protein content of human milk fortifier on growth in preterm infants born at <31 wk gestation: a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathes, M.; Briana, D.D.; Bergmann, R.; Schuller, A.; Göpel, W.; Herting, E.; Kattner, E.; Windhorst, A.; Klerk, J.P.D.; Maier, R.F. Effect of increased enteral protein intake on plasma and urinary urea concentrations in preterm infants born at < 32 weeks gestation and < 1500 g birth weight enrolled in a randomized controlled trial—A secondary analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochow, N.; Landau-Crangle, E.; Fusch, C. Challenges in breast milk fortification for preterm infants. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusch, S.; Rochow, N.; Choi, A.; Fusch, C. Individualized Target Fortification of Breast Milk: Optimizing Macronutrient Content Using Different Fortifiers and Approaches. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 652641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Weight gain g/kg/day | Adjusted fortification (n = 15) | Targeted fortification (n = 23) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
From birth to 28 days from the start of HM fortification Mean (CI 95%) |
14.06 (12.31, 15.81) | 13.24 (12.13, 14.36) | 0.38 |
|
From birth to 36 weeks PMA Median (CI 95%) |
15.31 (13.37, 16.42) | 14.02 (13.16, 16.41) | 0.53 |
|
From birth to discharge Median (CI 95%) |
14.53 (13.01, 15.46) | 14.04 (13.35, 15.12) | 0.68 |
|
During the intervention Mean (CI 95%) |
16.33 (15.26, 17.40) | 16.89 (15.44, 18.34) | 0.56 |
| Length growth cm/week | Adjusted fortification (n = 15) | Targeted fortification (n = 23) | p-value | Head circumference growth cm/week | Adjusted fortification (n = 15) | Targeted fortification (n = 23) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
From birth to 28 days from the start of HM fortification Mean (CI 95%) |
0.91 (0.78, 1.05) | 0.86 (0.74, 0.98) | 0.536 |
From birth to 28 days from the start of HM fortification Mean (CI 95%) |
0.78 (0.65, 0.93) | 0.73 (0.64, 0.83) | 0.44 |
|
From birth to 36 weeks PMA Median (CI 95%) |
0.95 (0.89, 1.08) | 0.88 (0.70, 1.49) | 0.38 |
From birth to 36 weeks PMA Median (CI 95%) |
0.85 (0.76, 0.94) | 0.86 (0.70, 1.18) | 0.86 |
|
From birth to discharge Median (CI 95%) |
0.91 (0.89, 1.07) | 0.94 (0.79, 1.33) | 0.47 |
From birth to discharge Median (CI 95%) |
0.83 (0.75, 0.91) | 0.79 (0.67, 1.09) | 0.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





