Submitted:
29 July 2024
Posted:
30 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.3. Specific Absorption Rate Analysis
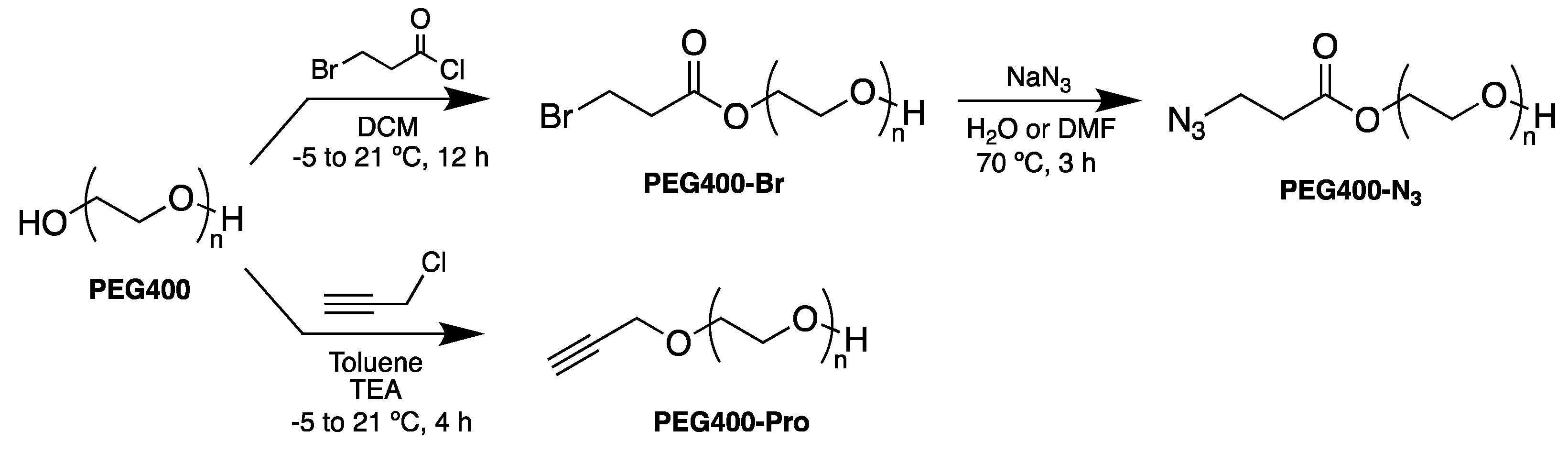
2.4. Synthesis of PEG Derivatives: PEG400-N3 and PEG400-Pro (Scheme 1)
2.5. Synthesis of MNPs
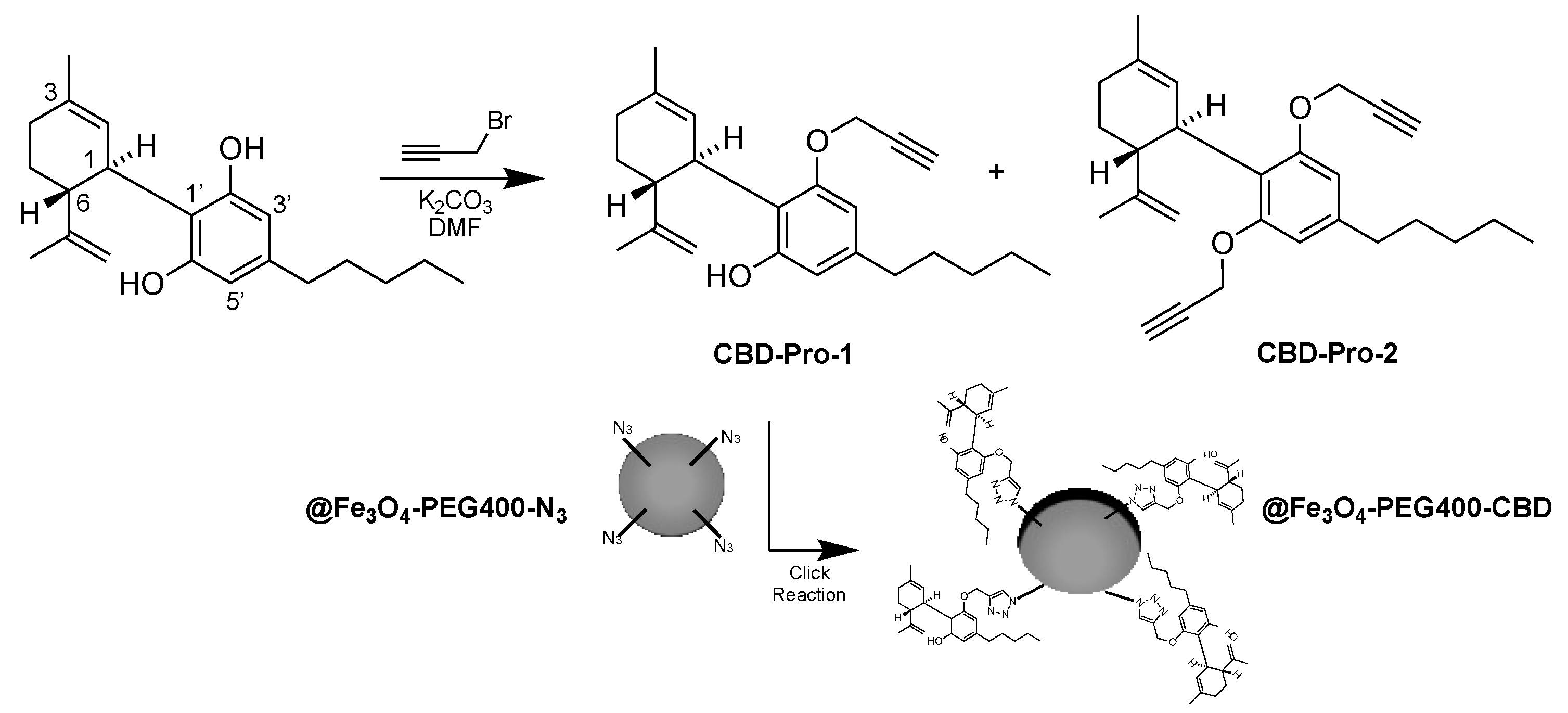
2.6. Synthesis of CBD-Pro Derivatives and @Fe3O4-PEG400-N3 Covalent Surface Functionalization with CBD to Obtain @Fe3O4-PEG400-CBD (Scheme 2)
2.7. In Vitro Proliferation Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of PEG Derivatives
3.2. Preparation of MNPs Systems
3.3. Preparation of @Fe3O4-PEG400-CBD
3.4. Magnetic Measurements
3.3. Hyperthermia and In Vitro Proliferation Analyses
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Ehrmann, A.; Nguyen, T.A.; Ahmadi, M.; Farmani, A.; Nguyen-Tri, P. Magnetic nanoparticle-based hybrid materials, fundamentals, and applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier Ltd. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmati, S.; David, A.E. A review of design criteria for cancer-targeted, nanoparticle-based MRI contrast agents. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, B.; Yari, P.; Sanders, S.M.; Wang, H.; Chugh, V.K.; Liang, S.; Mostufa, S.; Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Gómez-Pastora, J.; et al. Magnetic Nanoparticles: A Review on Synthesis, Characterization, Functionalization, and Biomedical Applications. Small 2023, 20, e2304848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwed, M.; Marczak, A. Application of Nanoparticles for Magnetic Hyperthermia for Cancer Treatment—The Current State of Knowledge. Cancers 2024, 16, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena-Serrano, C.; Lucena-Serrano, A.; Díaz, A.; Valpuesta, M.; Villaverde, G.; López-Romero, J.M.; Sarabia, F.; Laurenti, M.; Rubio-Retama, J.; Contreras-Cáceres, R. SPION nanoparticles for delivery of dopaminergic isoquinoline and benzazepine derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2022, 69, 116910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Surface Functionalization Strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Khan, F.; Alshehri, S.; Khan, A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Wu, H.-F.; Taha, E.I.; Elbagory, I. Unique Properties of Surface-Functionalized Nanoparticles for Bio-Application: Functionalization Mechanisms and Importance in Application. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unni, M.; Uhl, A.M.; Savliwala, S.; Savitzky, B.H.; Dhavalikar, R.; Garraud, N.; Arnold, D.P.; Kourkoutis, L.F.; Andrew, J.S.; Rinaldi, C. Thermal Decomposition Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Diminished Magnetic Dead Layer by Controlled Addition of Oxygen. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathe, L.S.; Mohamed, M.A.; Yunus, R.M.; Berhanuddin, D.D. Magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles in biomedical application: from synthesis to surface functionalization. Magnetochem 2020, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, L.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Pazos-Perez, N. Surface Modifications of Nanoparticles for Stability in Biological Fluids. Materials 2018, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pinel, B.; Ortega-Rodríguez, A.; Porras-Alcalá, C.; Cabeza, L.; Contreras-Cáceres, R.; Ortiz, R.; Díaz, A.; Moscoso, A.; Sarabia, F.; Prados, J.; et al. Magnetically active pNIPAM nanosystems as temperature-sensitive biocompatible structures for controlled drug delivery. Artif. Cells, Nanomedicine, Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, I.; Aghazadeh, M.; Doroudi, T.; Ganjali, M.R.; Kolivand, P.H. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles Coated with PEG/PEI for Biomedical Applications: A Facile and Scalable Preparation Route Based on the Cathodic Electrochemical Deposition Method. Adv. Phys. Chem. 2017, 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Khanduri, H.; Pathak, S.; Singh, A.; Basheed, G.A.; Pant, R.P. Temperature selectivity for single phase hydrothermal synthesis of PEG-400 coated magnetite nanoparticles. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 8672–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Li, X.; Peng, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Monodisperse Magnetic Single-Crystal Ferrite Microspheres. Angew. Chem. 2005, 44, 2782–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, F.; He, H.; Dramou, P. Study of the solvothermal method time variation effects on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) features. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ali, Z.; Tian, K.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Hou, Y. Monodisperse Fe3O4 spheres: Large-scale controlled synthesis in the absence of surfactants and chemical kinetic process. Sci. China Mater. 2019, 62, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; He, C.; Shih, K. Facile synthesis of morphology and size-controlled α -Fe 2 O 3 and Fe 3 O 4 nano-and microstructures by hydrothermal/solvothermal process: The roles of reaction medium and urea dose. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 14793–14804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zou, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, X.; Xiong, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Zhao, D. Highly Water-Dispersible Biocompatible Magnetite Particles with Low Cytotoxicity Stabilized by Citrate Groups. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5875–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, F.; Cai, W.; Zhang, X. Trisodium citrate-assisted synthesis of highly water-dispersible and superparamagnetic mesoporous Fe3O4 hollow microspheres via solvothermal process. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 636, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xu, F.; Gu, H. Facile synthesis and morphology evolution of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in different polyol processes. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotoulas, A.; Dendrinou-Samara, C.; Angelakeris, M.; Kalogirou, O. The Effect of Polyol Composition on the Structural and Magnetic Properties of Magnetite Nanoparticles for Magnetic Particle Hyperthermia. Materials 2019, 12, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, R.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, C. Solvothermal synthesis in ethylene glycol and adsorption property of magnetic Fe3O4 microspheres. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 55, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidiyan, M.; Shirani, A.; Alahyarizadeh, G. Solvothermal synthesis and characterization of magnetic Fe3O4nanoparticle by different sodium salt sources. Mater. Sci. 2017, 35, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.S.; Chen, D.-H. Magnetic Nanoparticles Grafted with Cyclodextrin for Hydrophobic Drug Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 6345–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badruddoza, A.; Tay, A.; Tan, P.; Hidajat, K.; Uddin, M. Carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin conjugated magnetic nanoparticles as nano-adsorbents for removal of copper ions: Synthesis and adsorption studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 185, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; He, J.; Du, X.; Lu, R.; Huang, L.; Ge, X. A facile and flexible process of β-cyclodextrin grafted on Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and host–guest inclusion studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 9056–9062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinniah, S.; Mohamad, S.; Manan, N.S. Magnetite nanoparticles coated with β-cyclodextrin functionalized-ionic liquid: Synthesis and its preliminary investigation as a new sensing material. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sharaf, M.G.; Rowe, E.M.; Serrano, K.; Devine, D.V.; Unsworth, L.D. Hemocompatibility of β-Cyclodextrin-Modified (Methacryloyloxy)ethyl Phosphorylcholine Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Majeed, A.; Singh, R.; George, N.; Singh, G.; Gupta, S.; Singh, H.; Kaur, G.; Singh, J. CuAAC ensembled 1,2,3-triazole linked nanogels for targeted drug delivery: a review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 2912–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Romero, J.M.; Moya-Utrera, F.; Carrasco, A.R.; Sarabia, F. Cannabinoid synthesis starting out from olivetol and terpene in dichloromethane with FeCl3 as catalyst, WO2024028516A1, 2024.
- Garcés, V.; González, A.; Gálvez, N.; Delgado-López, J.M.; Calvino, J.J.; Trasobares, S.; Fernández-Afonso, Y.; Gutiérrez, L.; Dominguez-Vera, J.M. Magneto-optical hyperthermia agents based on probiotic bacteria loaded with magnetic and gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 5716–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, C.-T.; Xie, Y.-R.; Niu, Y.; Liu, Z.-H.; Yang, L.; Xi, Y.-K.; Li, Z.-J.; Zhang, F.-M.; Xiang, Z.-M.; Sheng, J. New cannabidiol (CBD) derivatives: Synthesis, anti-inflammatory activity, and molecular docking. Phytochem. Lett. 2022, 51, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz R, R.; Cabeza, L.; Arias, J.L. Poly(butylcyanoacrylate) and Poly(ε-caprolactone) Nanoparticles Loaded with 5-Fluorouracil Increase the Cytotoxic Effect of the Drug in Experimental Colon Cancer. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelmann, U.; Buhl, E.M.; Baumann, M.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Slabu, I. Agglomeration of magnetic nanoparticles and its effects on magnetic hyperthermia. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 3, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, S.C.; Saha, A.; Devi, P.S. PEGylated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for pH Responsive Drug Delivery Application. Mater. Today: Proc. 2018, 5, 9715–9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvear-Jiménez, A.; Gutierrez, I.Z.; Shen, Y.; Villaverde, G.; Lozano-Chamizo, L.; Guardia, P.; Tinoco, M.; Garcia-Pinel, B.; Prados, J.; Melguizo, C.; et al. Electrospraying as a Technique for the Controlled Synthesis of Biocompatible PLGA@Ag2S and PLGA@Ag2S@SPION Nanocarriers with Drug Release Capability. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, J.; Kumar, R.; Harilal, S.; Mathew, G.E.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Prabhu, A.; Uddin, S.; Aleya, L.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia in cancer treatment: an emerging tool. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 19214–19225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.; Fernandez, T.; Metze, S.; Balakrishnan, P.B.; Mai, B.T.; Conteh, J.; De Mei, C.; Turdo, A.; Di Franco, S.; Stassi, G.; et al. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Hyperthermia Mediates Drug Delivery and Impairs the Tumorigenic Capacity of Quiescent Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 15959–15972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.-H.; Al Faruque, H.; Kee, H.; Kim, E.; Park, S. Exosome-based hybrid nanostructures for enhanced tumor targeting and hyperthermia therapy. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2021, 205, 111915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswamy, V.; Al-Omari, I.A.; Kamzin, A.S.; Issa, B.; Tekin, H.O.; Khourshid, H.; Kumar, H.; Mallya, A.; Sambasivam, S.; Obaidat, I.M. Specific Absorption Rate Dependency on the Co2+ Distribution and Magnetic Properties in CoxMn1-xFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2011, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
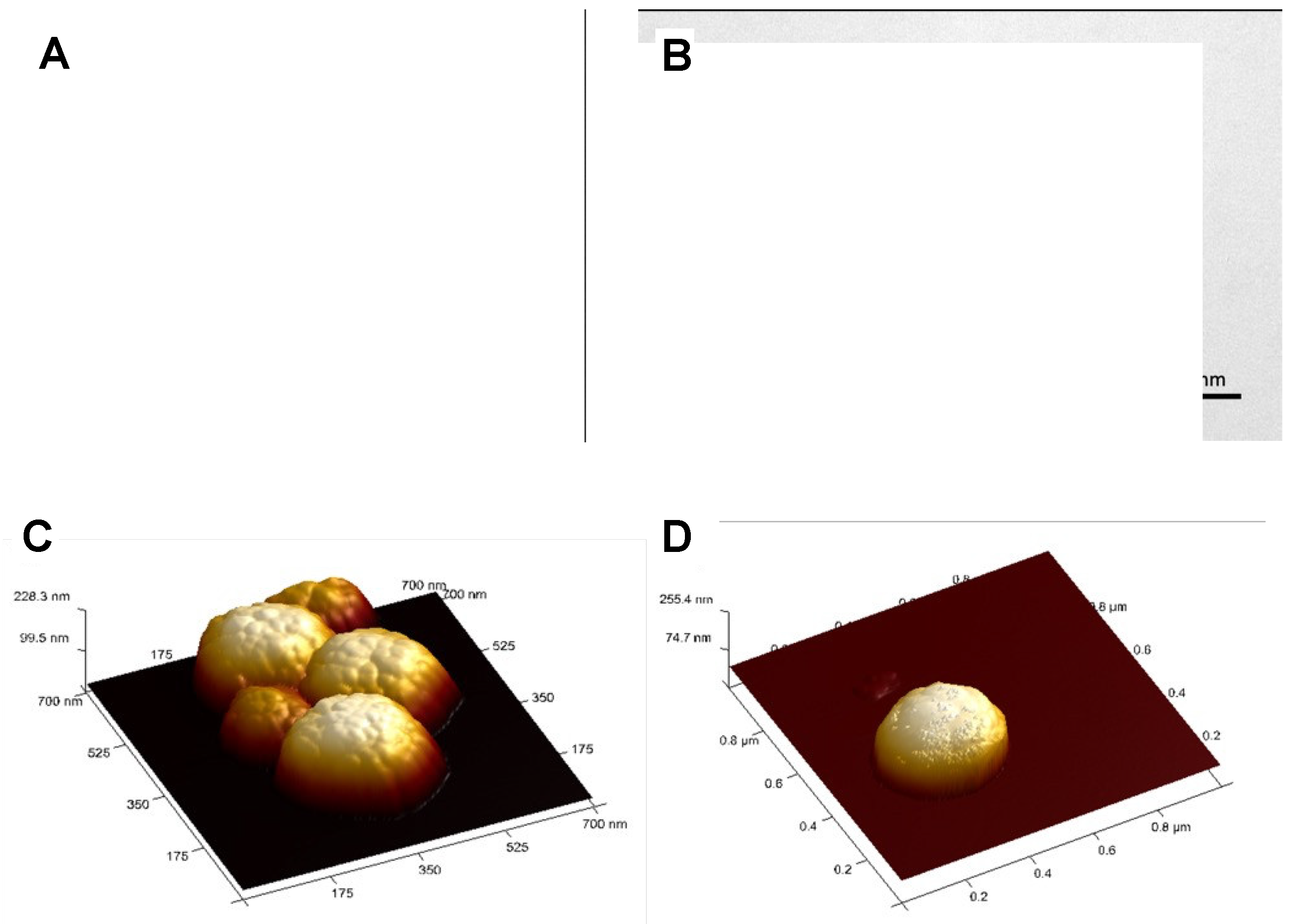
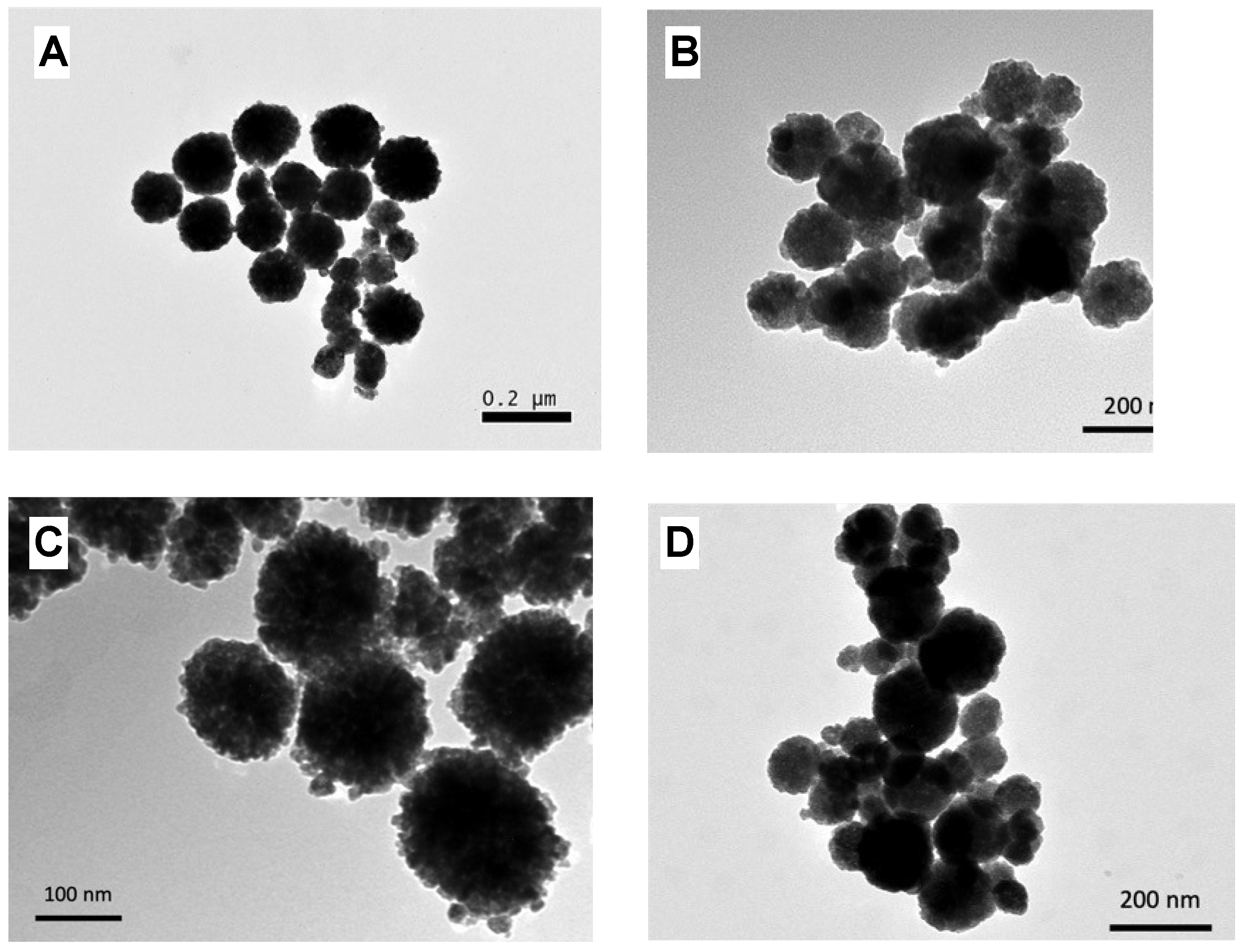
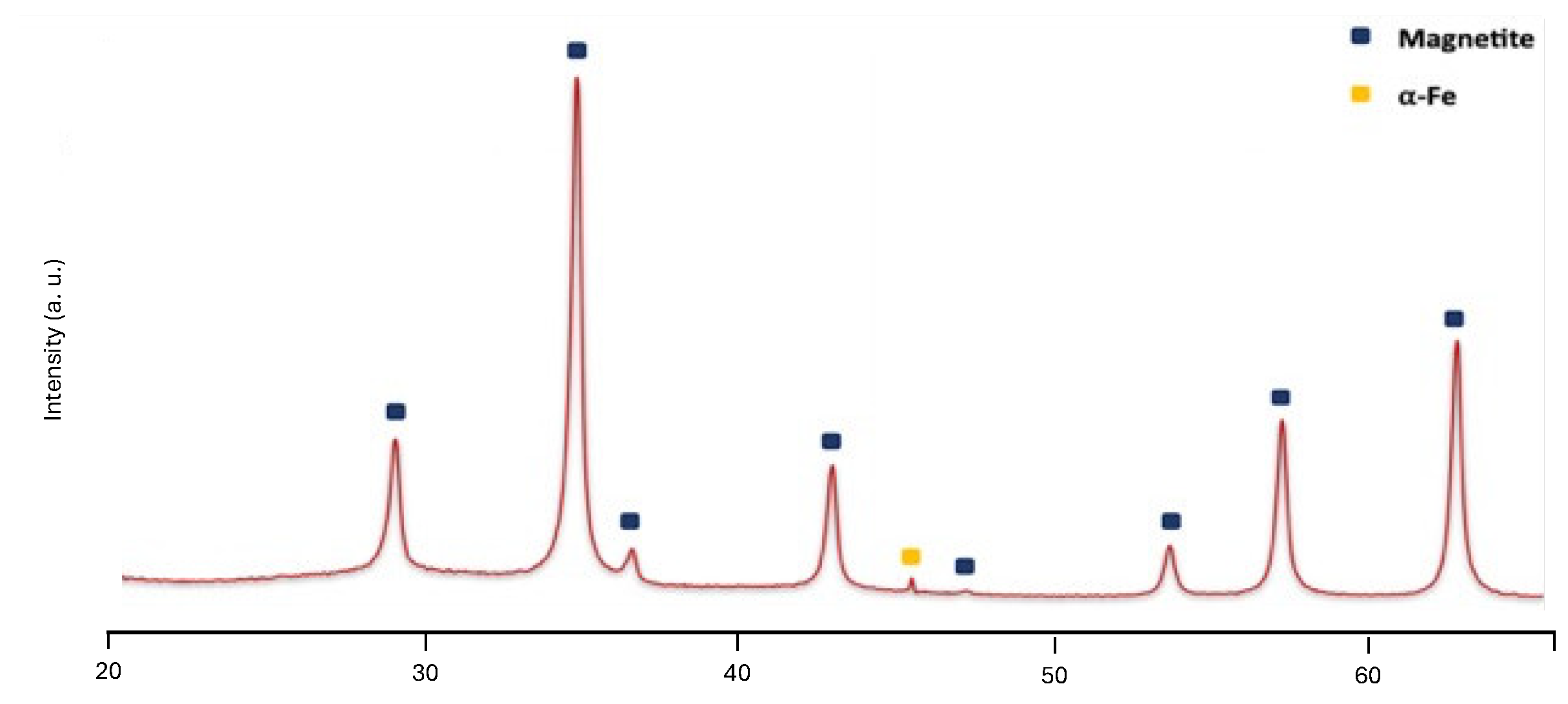
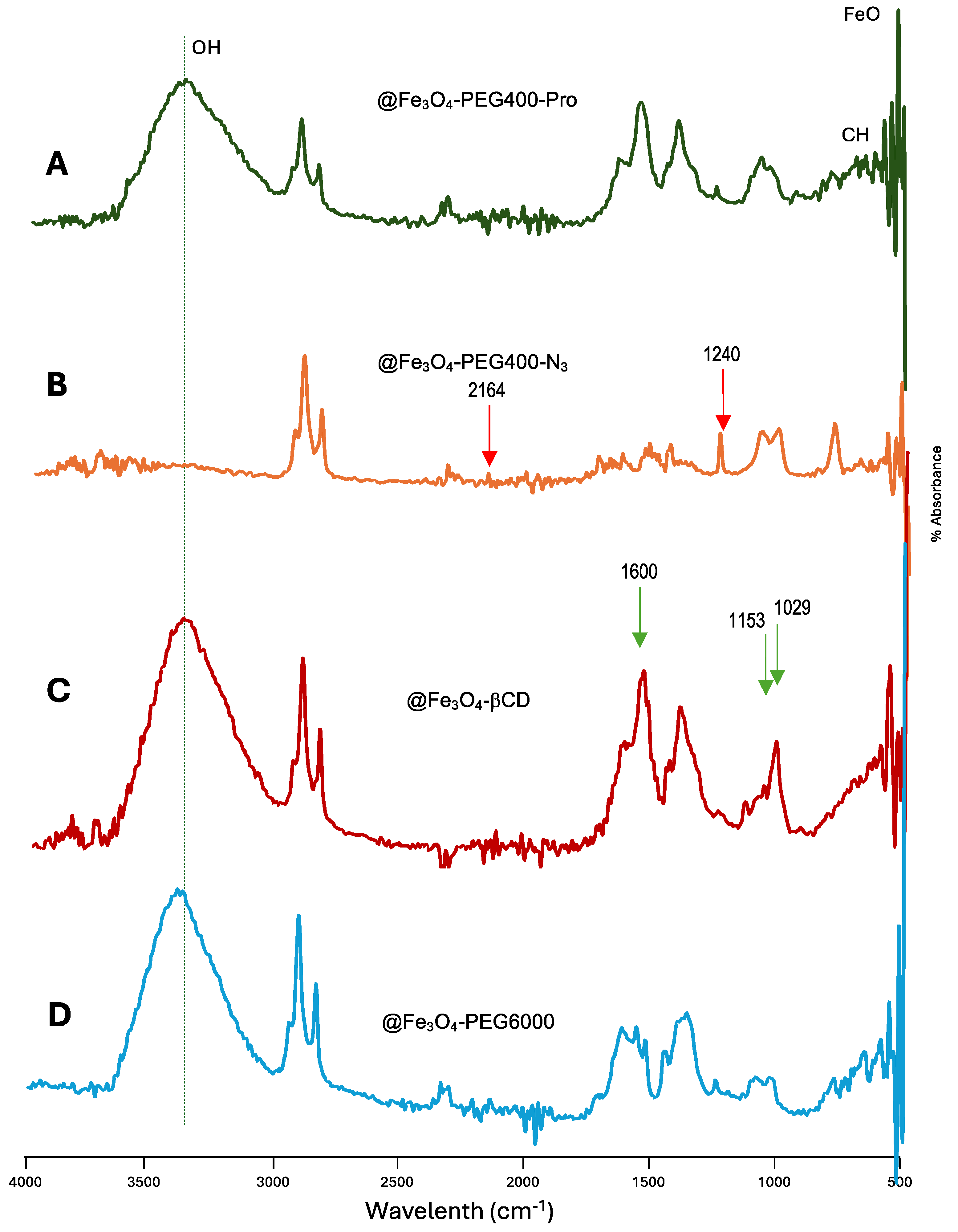
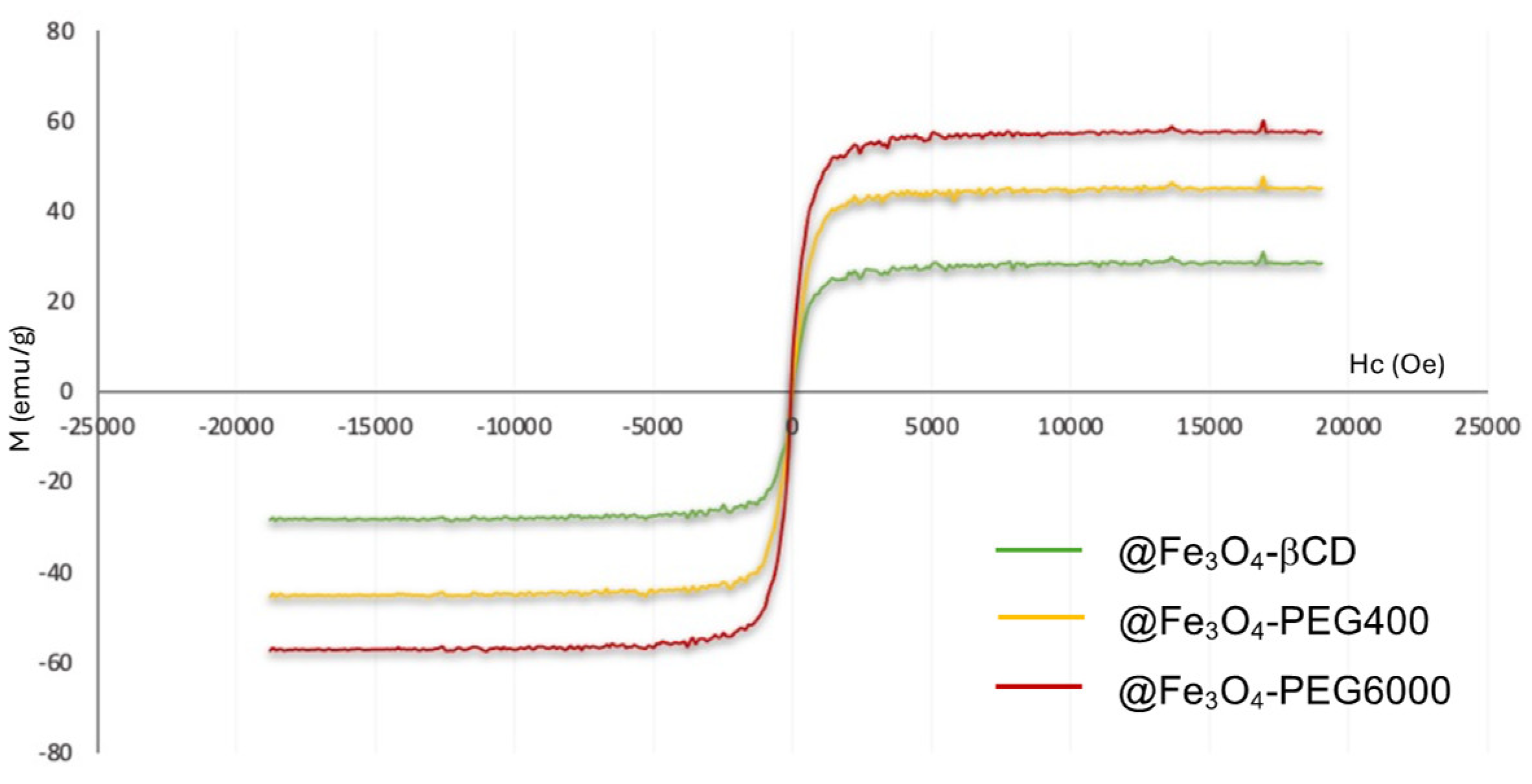
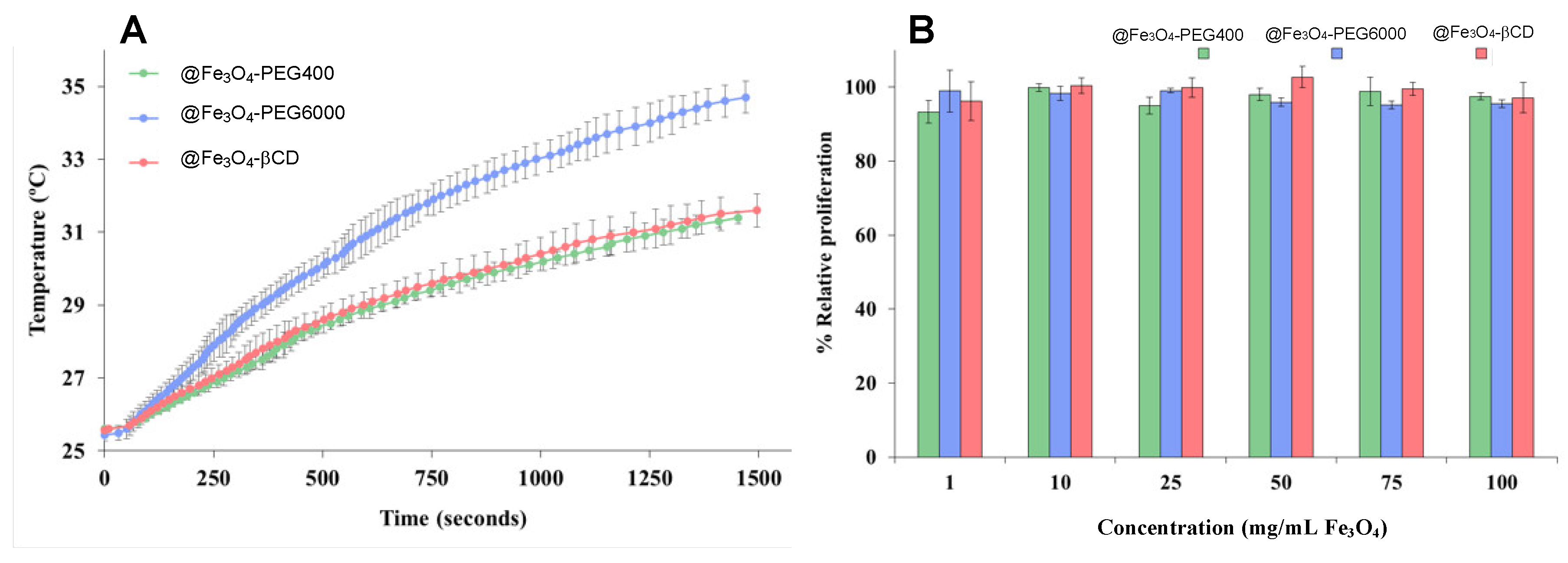
| MNP | Size (nm) | Concentration (mg/mL) |
| @Fe3O4-PEG400 | 250 | 6.3 |
| @Fe3O4-PEG6000 | 150 | 7.5 |
| @Fe3O4-PEG400-N3 | 90 | 6.7 |
| @Fe3O4-PEG400-Pro | 200 | 6.9 |
| @Fe3O4-βCD | 155 | 7.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





