1. Introduction
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the top ten public health threats facing humanity, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). This AMR is promoted by the indiscriminate and improper use of antimicrobials, leading to the emergence of multirug-resistant (MDR) or pan-resistant bacteria (superbugs), which cause common infections that cannot be treated with conventional antibiotics [
1].
The incidence of MDR microorganisms is increasing in both community and hospital settings. Additionally, the appearance of MDR bacteria in areas with high antibiotic consumption per person, such as Intensive Care Units (ICUs), makes the population more susceptible to nosocomial infections caused by these microorganisms, posing a danger to general well-being [
2]. It is known that infection by MDR bacteria is associated with therapeutic failure, prolonged hospital stays, increased hospital costs, and increased mortality, especially in critically ill patients [
3]. The social costs caused by antibiotic resistance have been estimated at 1.5 billion euros. Furthermore, antibiotic resistance has been associated with 25000 deaths per year in the European Union [
4].
Prevention, early diagnosis, and adequate treatment of nosocomial infections are among the main challenges in hospitalized patient care [
5,
6,
7,
8]. According to the ENVIN-HELICS report (National Surveillance Study of Nosocomial Infection in the ICU), it is advisable to work on reducing the number of days that patients spend on antibiotic therapy for hospital infections, as the data provided reflect a prolonged duration of antibiotic treatment [
9].
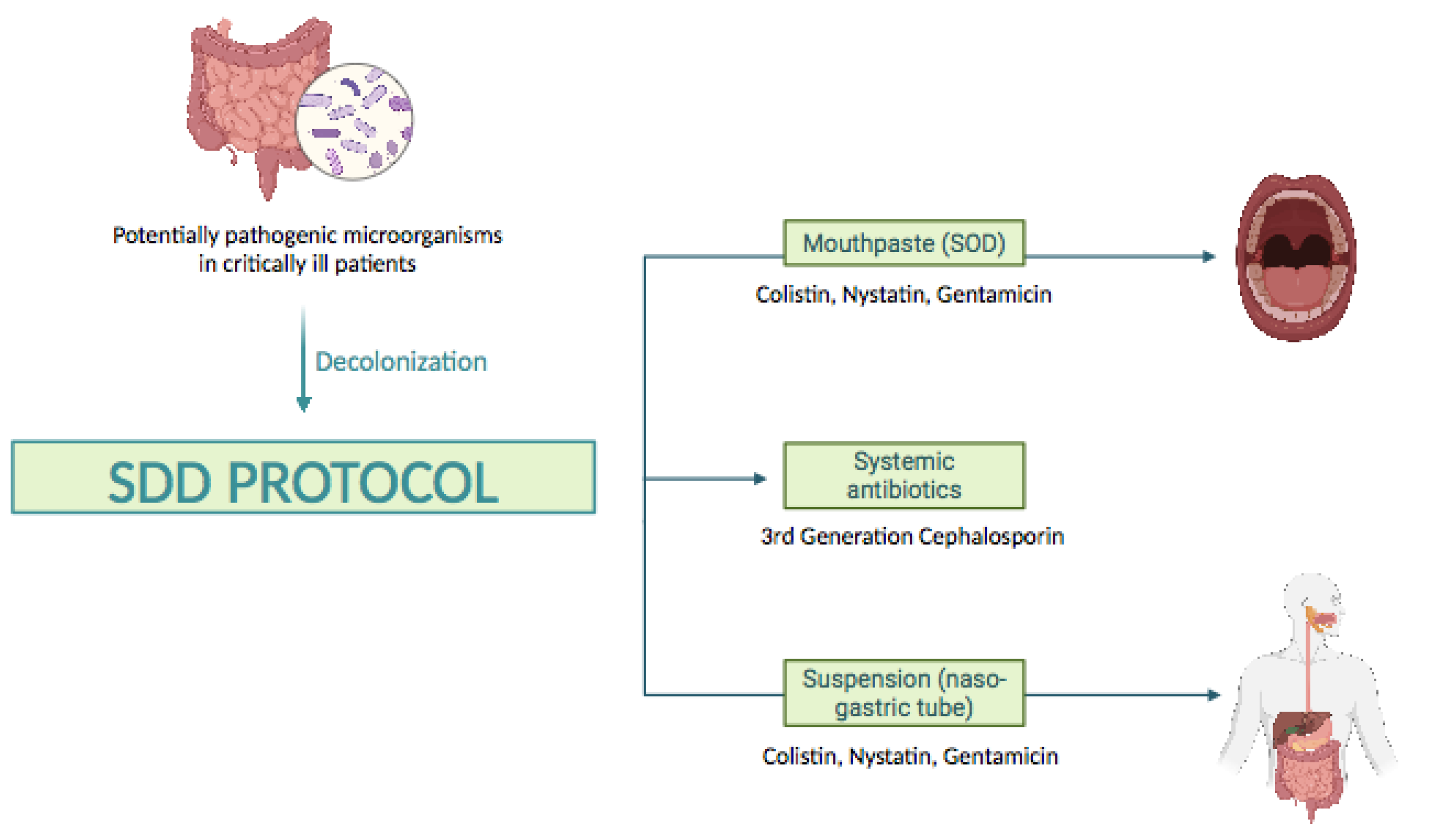
In this context, Selective Digestive Decontamination (SDD) (
Figure 1), proposed more than 30 years ago, is a measure to prevent infections in patients admitted to the ICU [
10]. It consists of the application of an oropharyngeal paste (Selective Oropharyngeal Decontamination, SOD) and a suspension for Selective Decontamination of the Digestive Tract containing non-absorbable topical antibiotics (gentamicin/tobramycin and colistin) and an antifungal (nystatin), as well as a broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotic, usually a third-generation cephalosporin, administered during the first 3-4 days of ICU admission [
11]. The aim of SDD is to prevent or minimize endogenous and exogenous infections caused by potentially pathogenic microorganisms, such as aerobic gram-negative bacilli, methicillin-sensitive
Staphylococcus aureus,
Pseudomonas, and yeasts present in the oropharynx or intestine, without harming the anaerobic microbiota, to reduce mortality in critically ill patients [
12]. SDD is indicated for patients with an expected ICU stay of at least two to three days requiring mechanical ventilation [
13].
SDD has been extensively studied for almost 40 years in more than 70 clinical trials and has been shown to be effective in preventing infections and reducing mortality. It is even presented as a procedure for reducing antibiotic consumption in ICUs [
14,
15,
16,
17]. Although SDD is already routinely employed in ICUs throughout Europe, its use has not become widespread in clinical practice [
18], despite the available evidence on its efficacy and safety. The most important concern about introducing SDD into clinical practice is the long-term ecological impact of this measure. However, Buitinck et al., 2029 have shown in a 21-year longitudinal study in an ICU that the administration of SDD does not increase the incidence rates of resistant microorganisms [
19]. Therefore, analyzing antibiotic consumption in patients admitted to ICUs is key.
The main objective of this study is to compare the pattern of antibiotic consumption in the ICU of our hospital before and after the implementation of the SDD protocol.
2. Results
A total of 3266 (100%) patients were consecutively admitted during the study period. Of these, 1532 (46.91%) were admitted between June 2021 and June 2022, forming the pre-intervention control group. Subsequently, a total of 1734 (53.09%) patients were admitted between June 2022 and June 2023, forming the intervention group. The clinical characteristics of the patients are shown in
Table 1.
2.1. Antibiotic Consumption
There was a significant decrease in overall antibiotic consumption in the post-SDD period compared to pre-SDD period, with total 76.6 DDD per 100 Stays in ICU in the pre SDD group, and 53.7 in the post-SDD group (
Table 2) (mean differences= 1.04; 95%CI= 0.13- 1.95; p= 0.028).
Based on therapeutic groups, a decrease in DDD/100 stays in the post-SDD period was observed for carbapenems (Δ=-4.1), 4th generation cephalosporins (Δ=-1.8), tetracyclines (Δ=-1.6), sulfonamides (Δ=-2.5), aminoglycosides (Δ=-0.6), monobactams (Δ=-0.4), and quinolones (Δ=-5.8). This translates into a reduction in the consumption of these antibiotics by 27.7%, 62.1%, 72.7%, 54.3%, 28.6%, 50.0%, and 49.3%, respectively. Individually, it is relevant to mention that the consumption of daptomycin decreased by 56.7% after the implementation of the SDD protocol in the ICU (
Table 2).
Although there was a significant decrease in the consumption of most antibiotics, it is important to highlight that there were therapeutic groups that consumed more grams (g) of antibiotics in the post-SDD period than in the pre-SDD period, increasing their consumption by 14.0% for 3rd generation cephalosporins, 5.5% for macrolides, and 4.0% for β-lactams (
Table 2).
2.2. Microbiological Findings
There was a decrease in the Incidence Density (ID) of colonizations understood as number of colonizations per 100 days of ICU stay in the occurrence of colonized patients in the post-DDS period. The ID in the pre-DDS period was 3.26, while in the post-DDS period it was 2.36 so the difference tended to be significant (IDR=0.724; 95% CI= 0.467-1.117; p=0.127.
The number of nosocomial infections in the pre-DDS period was 38 (mechanical ventilation-associated pneumonia: 6; primary or secondary bacteremia: 17; catheter-associated urinary tract infection: 15) in 1531 patients admitted to ICU, however, in the post-DDS period there were 31 infections (mechanical ventilation-associated pneumonia: 8; primary or secondary bacteremia: 6; catheter-associated urinary tract infection: 17) in 1734 patients. The ID of ENVIN infections in the pre-DDS period was 9.21, while in the post-DDS period it was 6.54 (IDR= 0.711; 95% CI= 0.428 - 1.172; p= 0.16) (
Table 3).
On the other hand, we observed a decrease in the occurrence of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) in the post-SDD period compared to pre-SDD period. The detection of CPE bacteria decreased from 33 to only 7, resulting in a significant decrease (mean differences= 2.31; CI 95%= 0.66-3.95; p= 0.0099). The isolated bacteria are shown in
Table 4.
3. Discussion
The inappropriate use of antibiotics and the challenge of developing new therapeutic strategies have made MDR bacteria a major threat to global health [
20]. Several meta-analyses have shown that the routine use of SDD does not increase the risk of developing MDR bacteria in patients with nosocomial infections. Furthermore, SDD has been demonstrated to be cost-effective, to prevent severe infections, and to reduce the risk of mortality in critically ill patients [
4].
In this regard, the ICU warrants special attention due to its high antimicrobial consumption. The elevated use of antibiotics in this setting may be attributed to the need for prompt and appropriate empirical treatment, which is crucial for managing critically ill patients. However, initial treatments are not always targeted due to a lack of diagnosis of the underlying infection and inadequate therapeutic de-escalation. Consequently, the indiscriminate use of antibiotics in the ICU, coupled with a lack of monitoring of potentially pathogenic colonizing microorganisms, promotes the spread of antibiotic resistance within these hospital areas.
On the other hand, DDD per 100 stays, defined as the duration from a patient’s admission to the hospital until discharge, whether through returning home, transfer to another care center, or death, has proven to be a simple and effective method for monitoring antibiotic consumption following the implementation of measures to optimize antibiotic use, as corroborated by Collado et al., 2015 [
21]. Additionally, DDD per 100 stays can be used to evaluate the exposure of a given medical service to antimicrobials over a defined period, yielding promising results.
In our study, we detected that antibiotic consumption was reduced in the post-SDD period, with a significant decrease in carbapenems and quinolones. Additionally, a significant reduction in carbapenemase-producing bacteria (MDR bacteria) was observed during this period. It is known that the indiscriminate use of carbapenems has led to the emergence of bacteria with resistance mechanisms to these antibiotics, which is a global concern since carbapenems are often the last resort for treating MDR gram-negative bacilli, specifically those producing AmpC and extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. The WHO has classified Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) as pathogens of critical priority in the search for new therapeutic alternatives, as they pose a significant challenge to universal health care [
22]. Based on this, SDD appears to be an encouraging measure for preventing the emergence of MDR bacteria and colonizations, aligning with the results obtained by Sánchez-Ramirez et al., 2018 [
23], which showed a significant reduction (P<0.001) in infections caused by MDR bacteria (Relative Risk = 0.31; 95% CI, 0.23-0.41) after applying the SDD protocol, and was associated with low rates of colistin- and tobramycin-resistant colonizing microorganisms [
24].
In parallel with the implementation of DDS, a decrease in the use of daptomycin has also been observed, which seems to support the guidelines of the experts from the European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (EUCAST). These guidelines restrict this high-impact antibiotic to skin and soft tissue infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes, as well as to right-sided endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus [
25].
Regarding the use of quinolones, the decrease in the post-SDD period has been influenced by health alerts from the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) related to the safety of these antibiotics. The FDA has reported severe hypoglycemia and significant psychological disturbances in patients treated with quinolones [
26], while the EMA has associated fluoroquinolones with prolonged (lasting months or years), severe, disabling, and potentially irreversible adverse reactions affecting multiple systems, organ classes, and senses [
27]. For all these reasons, the use of quinolones is increasingly restricted.
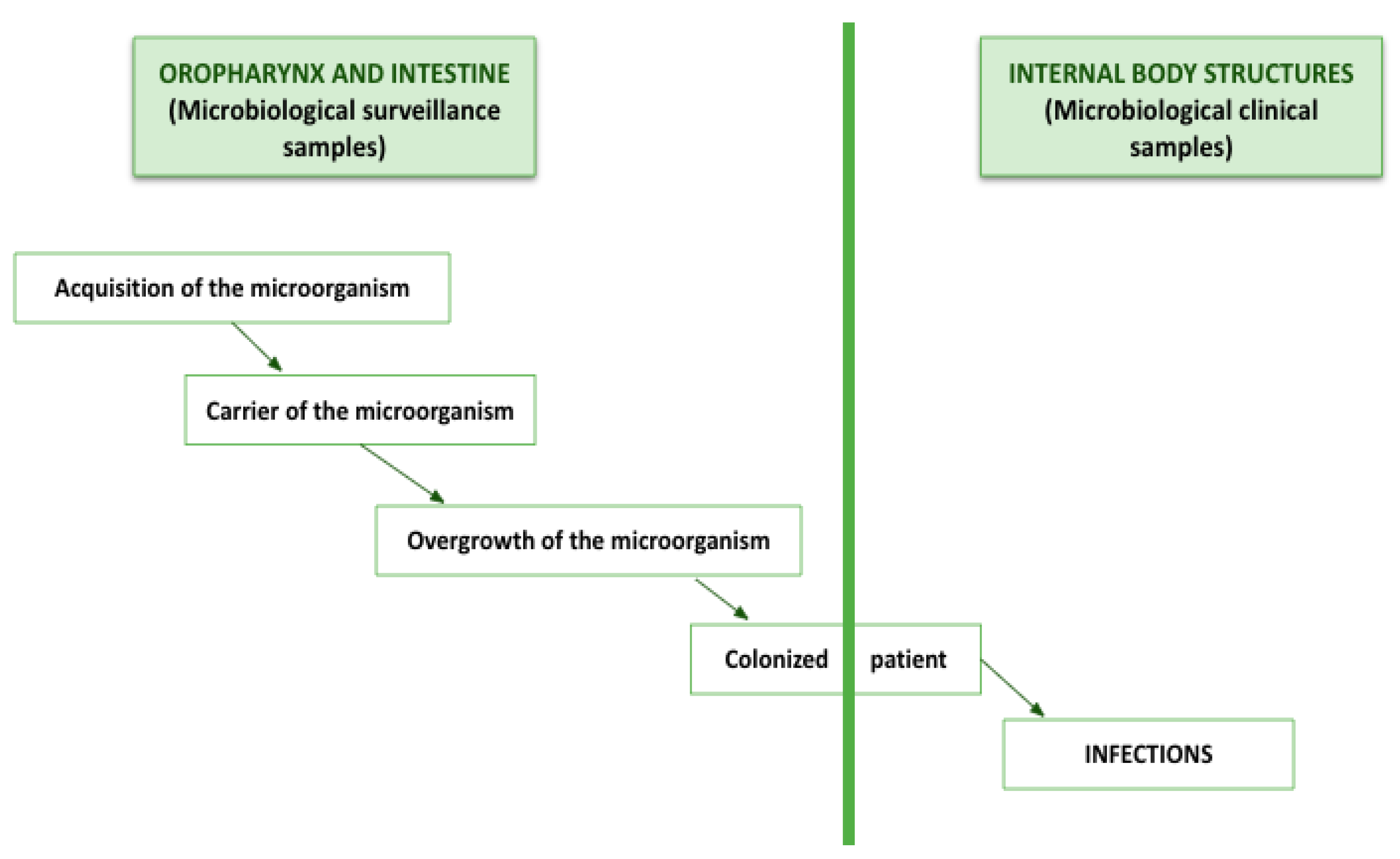
It is common for the overgrowth of microorganisms in the intestine and oropharynx to precede most infections in the ICU, as they migrate to other body structures and cause damage. Therefore, our results seem potentially beneficial for critically ill patients. The SDD protocol not only reduces the number of nosocomial infections but also decreases the number of colonizing microorganisms (
Figure 2).
Finally, SDD is not associated with an increase in antimicrobial resistance; rather, the opposite. Sanchez-Ramirez et al., 2018 demonstrated fewer infections caused by MDR bacteria, with low rates of resistance to tobramycin and colistin [
23]. Despite its use for more than 20 years, no evidence has been found that SDD has a clinically relevant impact on the emergence and spread of resistance. Furthermore, SDD intuitively conflicts with initiatives to reduce antimicrobial use in hospitalized patients. This is consistent with our results, which show a clear trend towards a decrease in the occurrence of carbapenemase-producing gram-negative bacilli in microbiological surveillance samples from our ICU in the post-SDD period (
Table 4). The use of SDD should by no means be considered a strategy for the indiscriminate use of antimicrobials. However, given the current body of evidence on its beneficial effects on mortality and other important patient outcomes, it should no longer be ignored and should be implemented in all ICUs [
28,
29,
30].
3.1. Limitations
Our study has several limitations that we must acknowledge. First, we did not design our protocol to assess the impact of individual interventions on outcomes. Our approach was epidemiological with the objective of studying the impact of DDD on annual antibiotic consumption.
Second, the study had a retrospective, nonrandomized design. Given the before/after design of the study, the results could be biased due to residual confounding factors that were not accounted for. However, the study was designed to address a clinical need and represents real-life data following the implementation of a clinical practice measure.
Third, our study was conducted in a single center, and the clinical results may not be directly translatable to other centers. Finally, other outcomes such as the duration or adequacy of antimicrobial treatment were not recorded. The aim of our study was to evaluate antibiotic consumption, specifically to compare the pattern of antibiotic consumption in our hospital’s ICU before and after the implementation of the SDD protocol.
For all these reasons, it would be interesting and necessary to conduct more studies comparing various groups to obtain more conclusive results.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Population
This is a pre-post quasi-experimental study of an intervention. The intervention involved the implementation of the DDS protocol in the ICU of a second-level university hospital equipped with 22 beds. Two one-year periods were compared: the pre-SDD period in the ICU (June 2021 - June 2022) and the post-SDD period in the ICU (June 2022 - June 2023). The demographic variables collected from the patients included: sex, age, diagnosis on admission, patient origin (community or other hospital unit), patient exitus during ICU stay, length of ICU stay, and severity status measured with the APACHE-II (Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II) scale.
The SDD protocol was applied to patients who met the following criteria: positive growth in any clinical or surveillance sample of any MDR microorganism; patients who underwent tracheal intubation lasting more than 72 hours; non-intubated patients who presented any risk factor (necrotizing pancreatitis, transplant and/or neutropenia, burns, low level of consciousness with a Glasgow Coma Score ≤ 11/15 or a Glasgow Coma Score ≤ 8T/11).
Both the suspension (nasogastric tube) and the mouthpaste (SOD) were prepared by the Hospital Pharmacy Service following the standards for correct preparation and quality control of master formulas. Both had the same composition, so that for each 125 mg (mouthpaste) or 125 ml (suspension), there were: 2.5 grams of colistin sulfate, 4 grams of gentamicin sulfate, and 2.5 grams of nystatin. The protocol was applied to the selected patients after adequate oral hygiene using a 0.1% chlorhexidine aqueous solution while aspirating secretions. It consisted of: 1) topical application to the buccal mucosa and oropharynx of 0.5 grams of mouthpaste every six hours; 2) application of 20 milliliters of suspension every six hours via nasogastric tube or orally if the patient did not have a nasogastric tube ; 3) administration of a third-generation cephalosporin during the first four days of admission to the ICU unless the patient had already been treated with specific antibiotics active against Gram-negative bacteria, in which case no additional antibiotics were administered.
4.2. Antimicrobial Consumption Data
All antibiotics routinely used in the ICU were selected for the study: doxycycline (IV), ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate (IV), piperacillin-tazobactam (IV), cefotaxime (IV), ceftazidime (IV), ceftriaxone (IV), cefepime (IV), aztreonam (IV), imipenem-cilastatin (IV), meropenem (IV), ertapenem (IV), sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (IV), azithromycin (IV), amikacin (IV), ciprofloxacin (IV), levofloxacin (IV), moxifloxacin (IV), vancomycin (IV), metronidazole (IV), fosfomycin (IV), linezolid (IV), and daptomycin (IV). The list of antibiotic consumption was obtained through the ATHOS Pharmacy economic management module. For data extraction, an Excel database was designed to record the characteristics of antimicrobial consumption: type of antimicrobial and amount consumed in grams. Next, DDD per 100 stays was analyzed for each selected antibiotic using the following formula: DDD per 100 stays = (grams of selected antibiotic consumed / DDD in grams) x 100 / number of stays in the chosen period, according to the ATC/DDD methodology based on the 2014 version of the WHO ATC/DDD classification [
24].
4.3. Nosocomial Infection Prevention Measures
Nosocomial infection prevention measures were applied throughout the study (both periods) according to the established national protocols (Pneumonia Zero®, Bacteremia Zero®, and Resistance Zero®) in ENVIN-HELICS (vhebron.net) (accessed May 20, 2024). As part of the clinical routine of the unit and following the recommendations of the Resistance Zero® program, microbiological surveillance was performed to detect the colonization status of the patients. For this purpose, samples of the pharyngeal microbiota and perianal exudate were taken on admission of all patients meeting the DSS criteria and then weekly throughout their stay in the unit. Perianal samples were seeded in ESBL and CARB/OXA media (Biomérieux) and incubated at 37ºC for 48 hours. Multidrug-resistant isolates from the pre-decontamination and post-decontamination periods were compared. The types of infections defined according to the ENVIN registry were recorded.
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Differences between pre- and post-intervention cohorts for continuous variables were assessed using a 2-sample t-test or Wilcoxon rank-sum test, depending on the distribution. Differences between categorical variables were assessed using the χ² test or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate. To evaluate the change in the incidence density of infectious complications and colonizations, we used rate ratios (RR), also known as incidence density ratios (IDR). A p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Finally, a comparative analysis was conducted on the data obtained from both periods to measure the efficacy in reducing antibiotic consumption with the implementation of SSD protocol in the ICU. The results were expressed descriptively as means, medians, and proportions according to the type of variable studied. The Epidat program was used.
4.5. Ethical Statement
The protocol of this study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Granada (CEIC) (Approval ID 0600-N-23). All patients provided their consent before being included in the study.
5. Conclusions
Based on our results, we conclude that implementing a SDD protocol in the ICU is essential for controlling antimicrobial consumption in this setting. By doing so, we not only reduce the use of drugs at risk of depletion, such as antibiotics, but also prevent the spread of bacterial resistance mechanisms. Additionally, it is important to note that the mortality rate of critically ill patients decreases by reducing the occurrence of nosocomial infections or those derived from the patients’ own colonization.
Author Contributions
M.M.-P and R.F.-F: conceptualization, methodology, visualization, formal analysis, writing—original draft; E.F.-V, M.C and X.D-V.: methodology, data curation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing; A. A., and M.C.: software, investigation, resources; M.T.N-S. and M.E.Y.: validation, data curation, writing—review and editing. M.C.: supervision, project administration; R.M.: conceptualization, methodology, visualization, formal analysis, writing—original draft.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Granada (protocol code 0600-N-23 and date of approval: 13 March 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to containing clinical and personal information.
Acknowledgments
We want to kindly thank patients participating in the study and sanitary personnel of the Hospital Universitario San Cecilio collaborating in the recruitment of patients.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- World Health Organization: WHO. Resistencia a los antimicrobianos. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Alós, J.-I. Resistencia bacteriana a los antibióticos: una crisis global. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2015, 33, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, P.; Moreno, L.; Yagüe, G.; Andreu, E.; Jara, R.; Segovia, M. Colonización por microorganismos multirresistentes en pacientes de UCI durante la pandemia de la COVID-19. Med. Intensiva 2021, 45, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The bacterial challenge: time to react. A call to narrow the gap between multidrug-resistant bacteria in the EU and the development of new antibacterial agents. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, 2009. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/media/en/publications/Publications/0909_TER_The_Bacterial_Challenge_Time_to_React.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Vincent, J.L.; Sakr, Y.; Singer, M.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Machado, F.R.; Marshall, J.C.; EPIC III Investigators. Prevalence and outcomes of infection among patients in intensive care units in 2017. JAMA 2020, 323, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melsen, W.G.; Rovers, M.M.; Groenwold, R.H.; Bergmans, D.C.; Camus, C.; Bauer, T.; et al. Attributable mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomized prevention studies. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrie, C.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Ibn Essaied, W.; Schwebel, C.; Darmon, M.; Mourvillier, B.; et al. Attributable mortality of ICU-acquired bloodstream infections: Impact of the source, causative microorganism, resistance profile and antimicrobial therapy. J. Infect. 2017, 74, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejerina-Álvarez, E.E.; de la Cal López, M.A. Selective decontamination of the digestive tract: concept and application. Med. Intensiva (Engl. Ed.) 2023, 47, 2173–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estudio Nacional de Vigilancia de Infección Nosocomial en servicios de medicina intensiva. ENVIN-HELICS. Informe 2022. Sociedad Española de Medicina Intensiva Crítica y Unidades Coronarias (SEMICYUC). Grupo de trabajo de enfermedades infecciosas y sepsis. Available online: https://hws.vhebron.net/envin-helics/Help/Informe%20ENVIN-UCI%202022.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Wittekamp, B.H.J.; Oostdijk, E.A.N.; Cuthbertson, B.H.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Bonten, M.J.M. Selective decontamination of the digestive tract (SDD) in critically ill patients: a narrative review. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ramírez, C.; Hípola-Escalada, S.; Cabrera-Santana, M.; Hernández-Viera, M.A.; Caipe-Balcázar, L.; Saavedra, P.; Artiles-Campelo, F.; Sangil-Monroy, N.; Lübbe-Vázquez, C.F.; Ruiz-Santana, S. Long-term use of selective digestive decontamination in an ICU highly endemic for bacterial resistance. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hout, D.; Plantinga, N.L.; Bruijning-Verhagen, P.C.; Oostdijk, E.A.N.; de Smet, A.M.G.A.; de Wit, G.A.; Bonten, M.J.M.; van Werkhoven, C.H. Cost-effectiveness of selective digestive decontamination (SDD) versus selective oropharyngeal decontamination (SOD) in intensive care units with low levels of antimicrobial resistance: an individual patient data meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittekamp, B.H.; Plantinga, N.L.; Cooper, B.S.; et al. Decontamination strategies and bloodstream infections with antibiotic-resistant microorganisms in ventilated patients: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2018, 320, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrucchio, G.; D’Amico, R. Topical antibiotic prophylaxis to reduce respiratory tract infections and mortality in adults receiving mechanical ventilation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 1, CD000022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waele, J.J.; Leroux-Roels, I.; Depuydt, P. Selective digestive decontamination - Pro. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 979–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plantinga, N.L.; de Smet, A.M.G.A.; Oostdijk, E.A.N.; de Jonge, E.; Camus, C.; Krueger, W.A.; Bergmans, D.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bonten, M.J.M. Selective digestive and oropharyngeal decontamination in medical and surgical ICU patients: individual patient data meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, N.E.; Myburgh, J.; Seppelt, I.; Garside, T.; Vlok, R.; Mahendran, S.; Adigbli, D.; Finfer, S.; Gao, Y.; Goodman, F.; Guyatt, G.; Santos, J.A.; Venkatesh, B.; Yao, L.; Di Tanna, G.L.; Delaney, A. Association between selective decontamination of the digestive tract and in-hospital mortality in intensive care unit patients receiving mechanical ventilation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2022, 328, 1922–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, D.R.; Citerio, G.; Perner, A.; Dimopoulos, G.; Torres, A.; Hoes, A.; Beale, R.; de Smet, A.M.; Kesecioglu, J. Use of selective digestive tract decontamination in European intensive cares: the ifs and whys. Minerva Anestesiol. 2015, 81, 734–742. [Google Scholar]
- Buitinck, S.; Jansen, R.; Rijkenberg, S.; Wester, J.P.J.; Bosman, R.J.; van der Meer, N.J.M.; van der Voort, P.H.J. The ecological effects of selective decontamination of the digestive tract (SDD) on antimicrobial resistance: a 21-year longitudinal single-centre study. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Paño-Pardo, J.R.; Alvarez-Rocha, L.; Asensio, A.; Calbo, E.; Cercenado, E.; Cisneros, J.M.; Cobo, J.; Delgado, O.; Garnacho-Montero, J.; Grau, S.; Horcajada, J.P.; Hornero, A.; Murillas-Angoiti, J.; Oliver, A.; Padilla, B.; Pasquau, J.; Pujol, M.; Ruiz-Garbajosa, P.; San Juan, R.; Sierra, R. ; Grupo de Estudio de la Infección Hospitalaria-Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica; Sociedad Española de Farmacia Hospitalaria; Sociedad Española de Medicina Preventiva, Salud Pública e Higiene. Programas de optimización de uso de antimicrobianos (PROA) en hospitales españoles: documento de consenso GEIH-SEIMC, SEFH y SEMPSPH. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2012, 30, 22.e1–22e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, L.; De la Rosa, M.; Álvaro, EA.; Toro, P.; Moreno, L.; Pérez, M. Evaluación del consumo de antimicrobianos mediante DDD/100 estancias versus DDD/100 altas en la implantación de un Programa de Optimización del Uso de Antimicrobianos. Rev Esp Quimioter 2015, 28, 284–292. [Google Scholar]
- WHO publishes list of bacteria for which new antibiotics are urgently needed. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news/item/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Sánchez-Ramírez, C.; Hípola-Escalada, S.; Cabrera-Santana, M.; Hernández-Viera, M.A.; Caipe-Balcázar, L.; Saavedra, P.; Artiles-Campelo, F.; Sangil-Monroy, N.; Lübbe-Vázquez, C.F.; Ruiz-Santana, S. Long-term use of selective digestive decontamination in an ICU highly endemic for bacterial resistance. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Available online: https://www.whocc.no/ddd/definition_and_general_considera/ (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Daptomycin Rationale Document 2.0. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Rationale_documents/Daptomycin_Rationale_Document_2.0_20210512.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- FDA reinforces safety information about serious low blood sugar levels and mental health side effects. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-reinforces-safety-information-about-serious-low-blood-sugar-levels-and-mental-health-side (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Disabling and potentially permanent side effects lead to suspension or restrictions of quinolone and fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/disabling-potentially-permanent-side-effects-lead-suspension-or-restrictions-quinolone-fluoroquinolone-antibiotics (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Roquilly, A.; Marret, E.; Abraham, E.; Asehnoune, K. Pneumonia prevention to decrease mortality in intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Sakr, Y.; Singer, M.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Machado, F.R.; Marshall, J.C.; Finfer, S.; Pelosi, P.; Brazzi, L.; Aditianingsih, D.; Timsit, J.F.; Du, B.; Wittebole, X.; Máca, J.; Kannan, S.; Gorordo-Delsol, L.A.; De Waele, J.J.; Mehta, Y.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Khanna, A.K.; Kollef, M.; Human, M.; Angus, D.C. ; EPIC III Investigators. Prevalence and Outcomes of Infection Among Patients in Intensive Care Units in 2017. JAMA 2020, 323, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Waele, J.J.; Leroux-Roels, I.; Depuydt, P. Selective digestive decontamination - Pro. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 979–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).