Submitted:
30 July 2024
Posted:
30 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
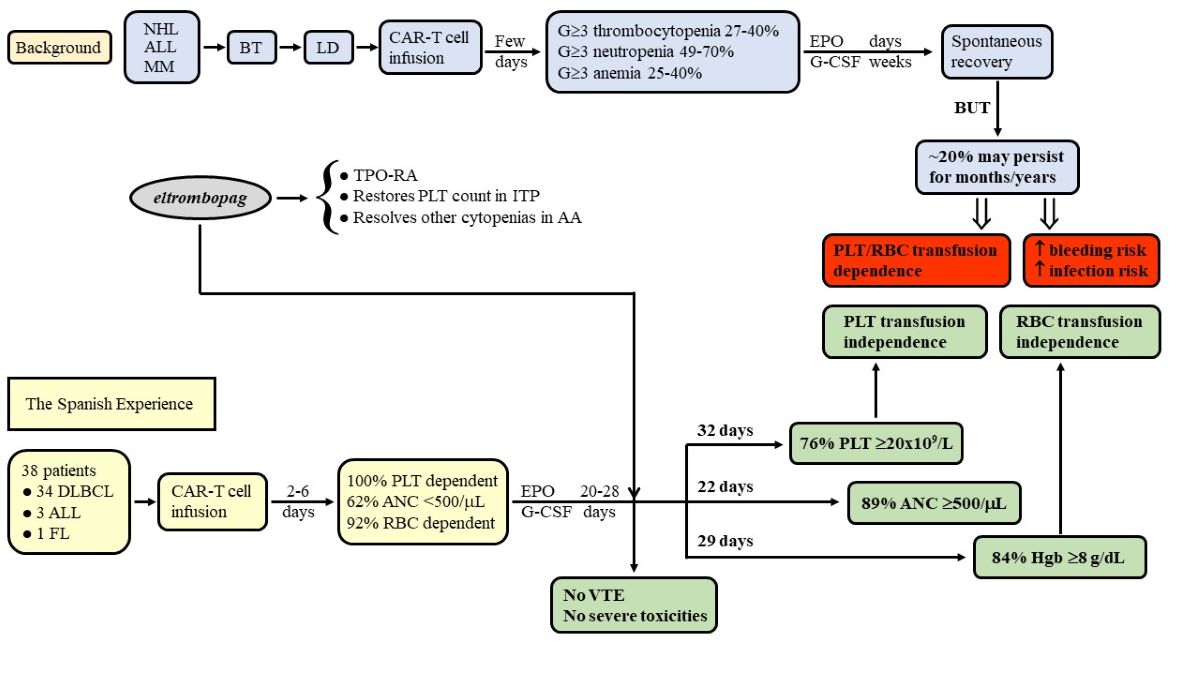
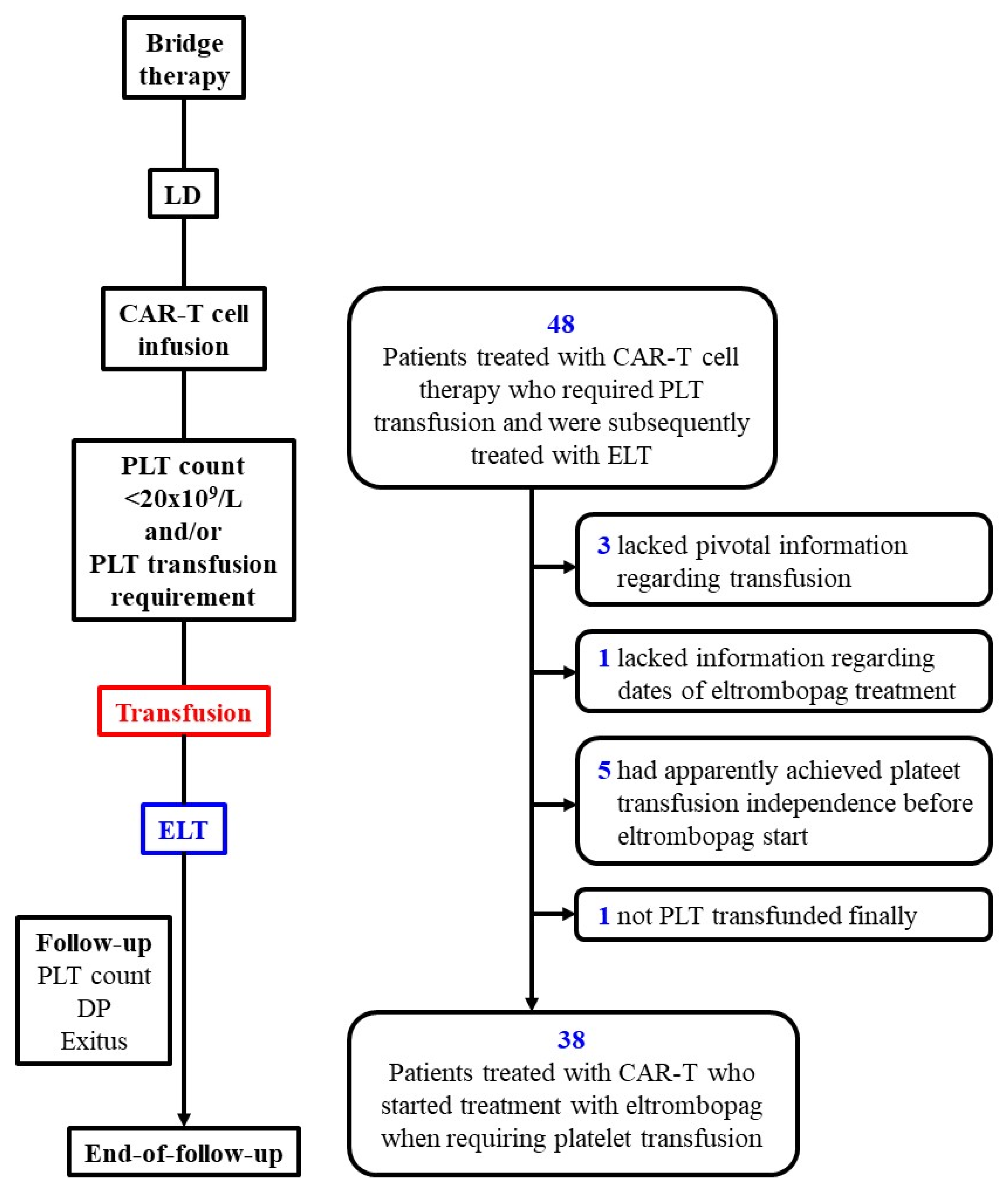
2.1. Patients and Study Design
2.2. CAR-T Cell Products
2.3. Determinations and Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
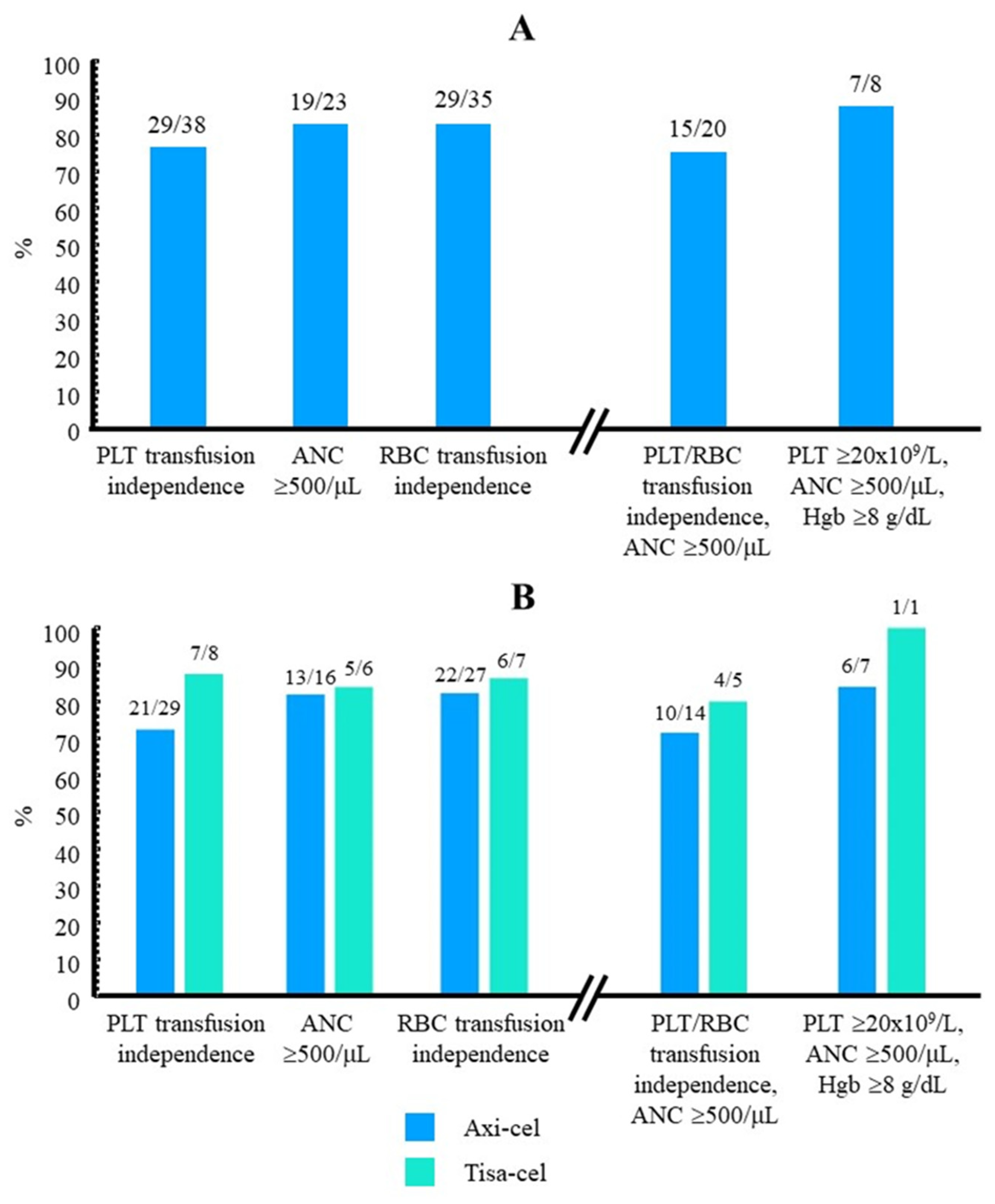
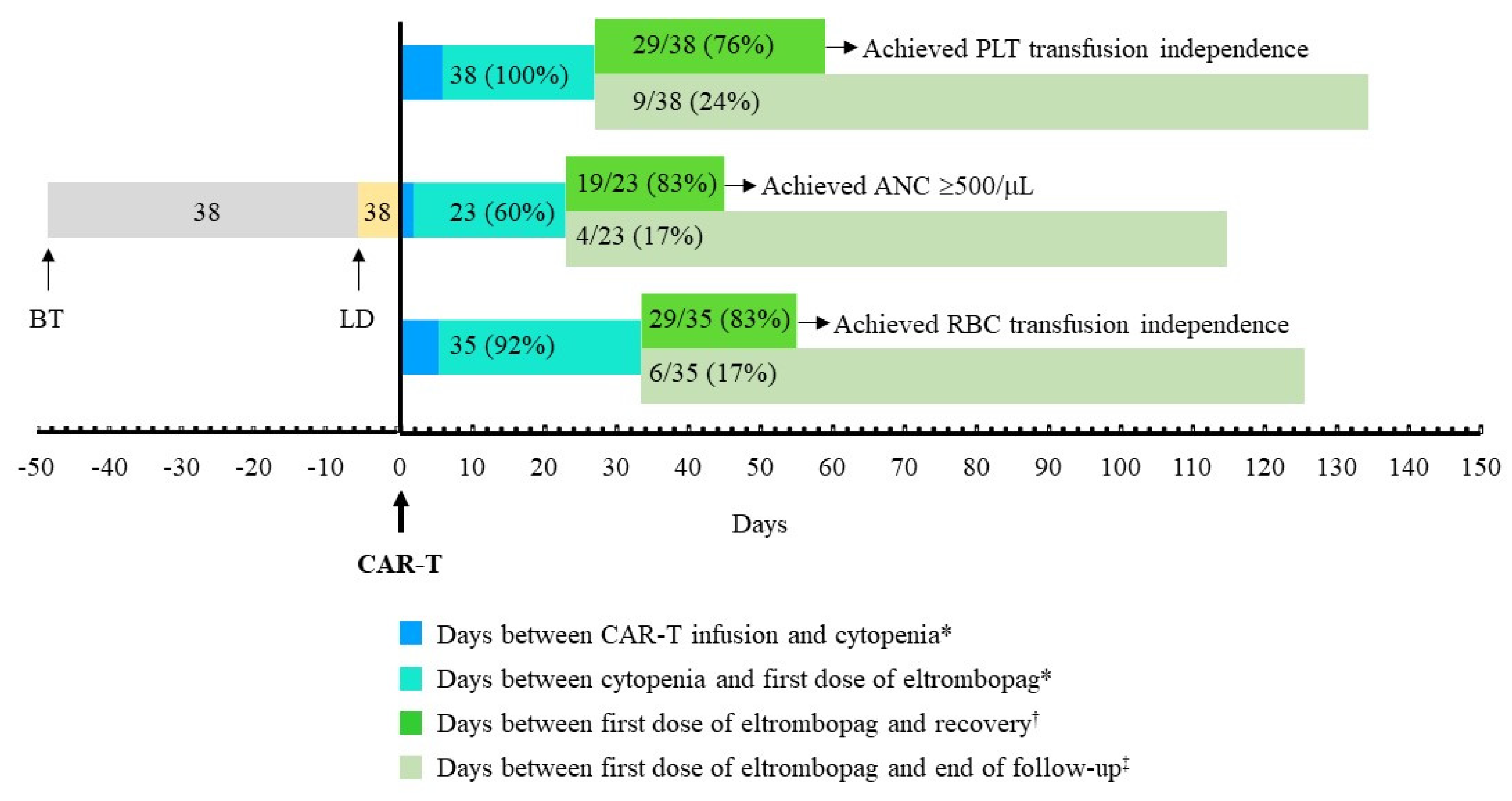
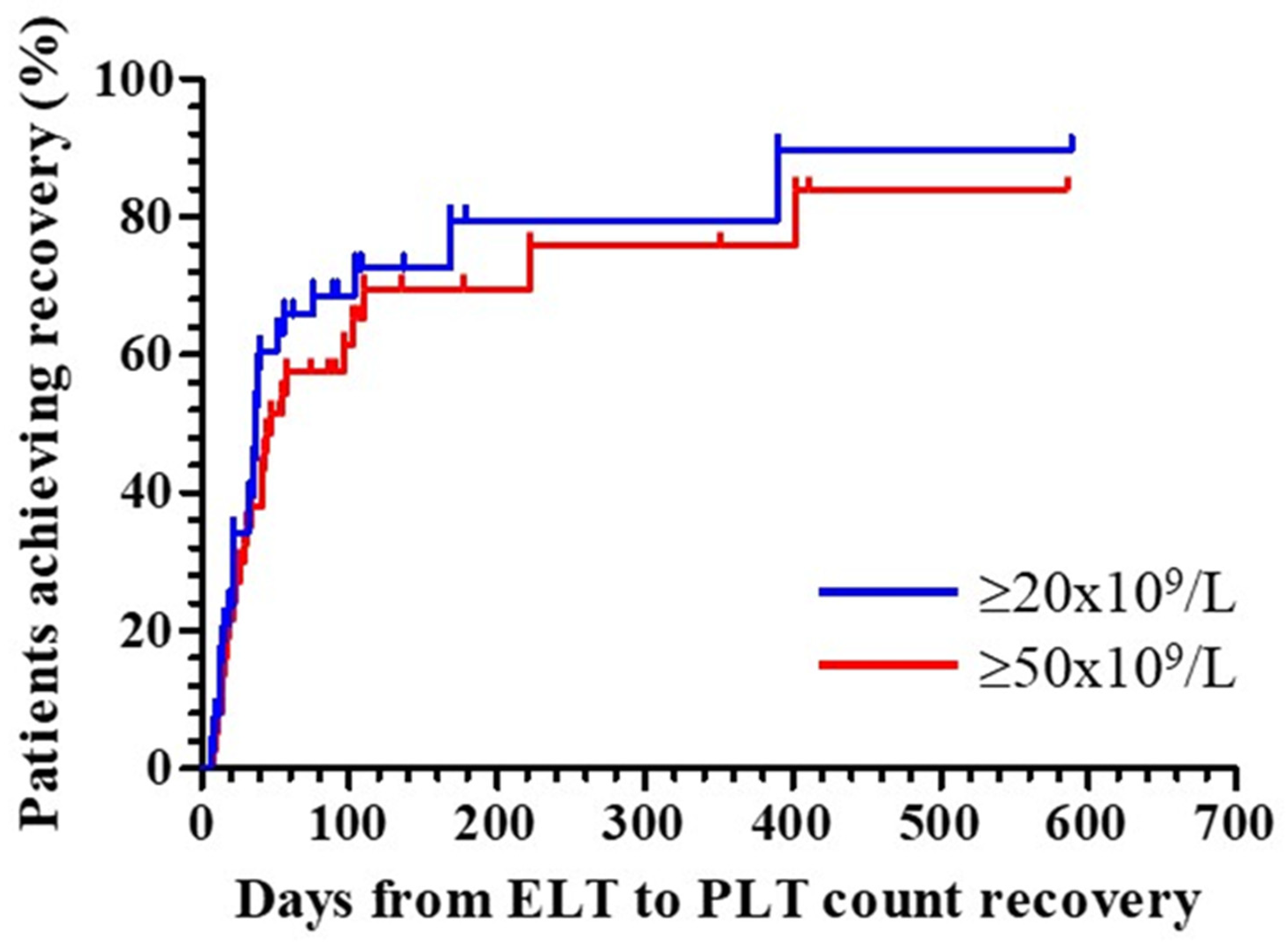
3.1. Recovery from Thrombocytopenia after Initiating Treatment with Eltrombopag
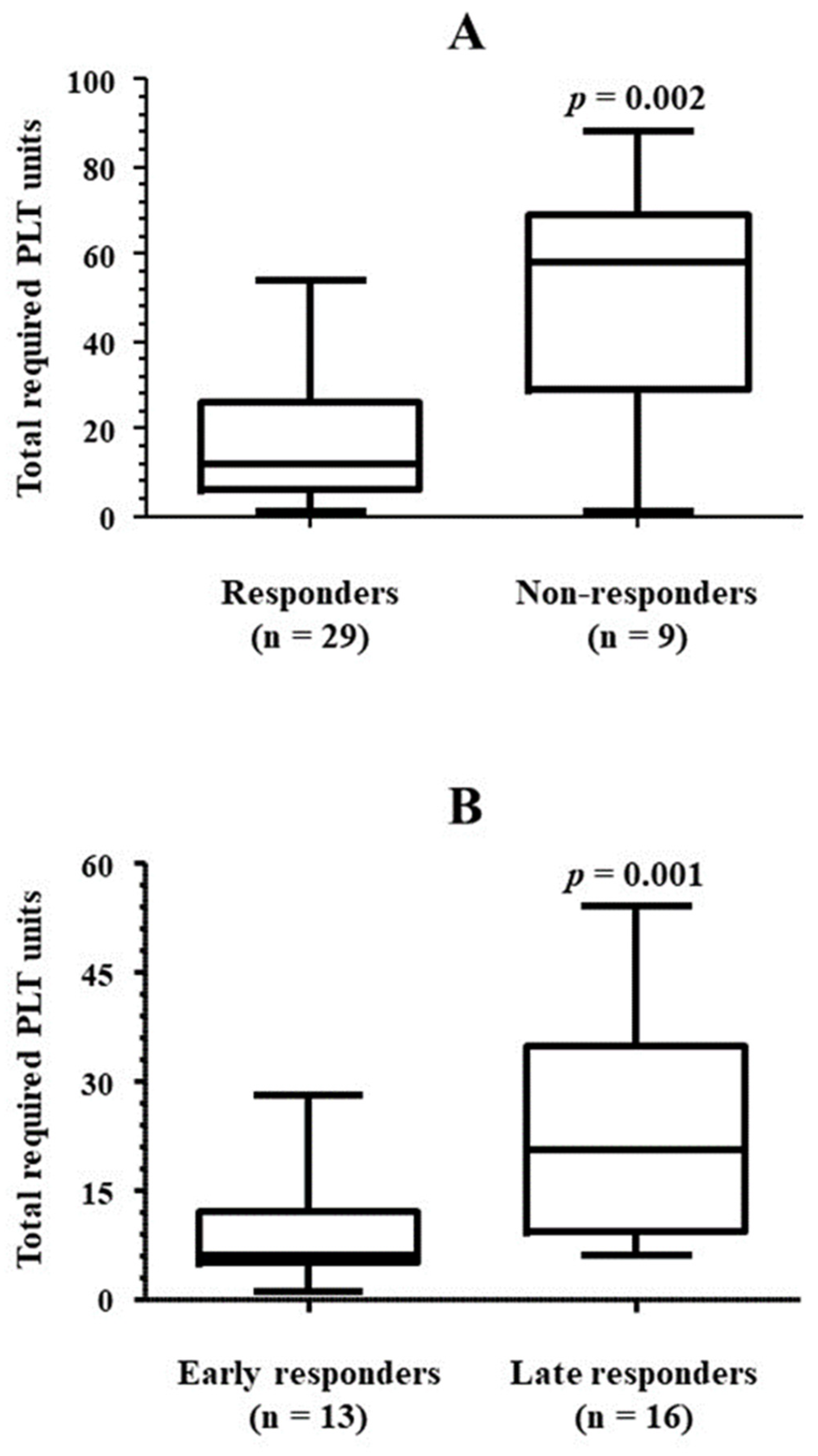
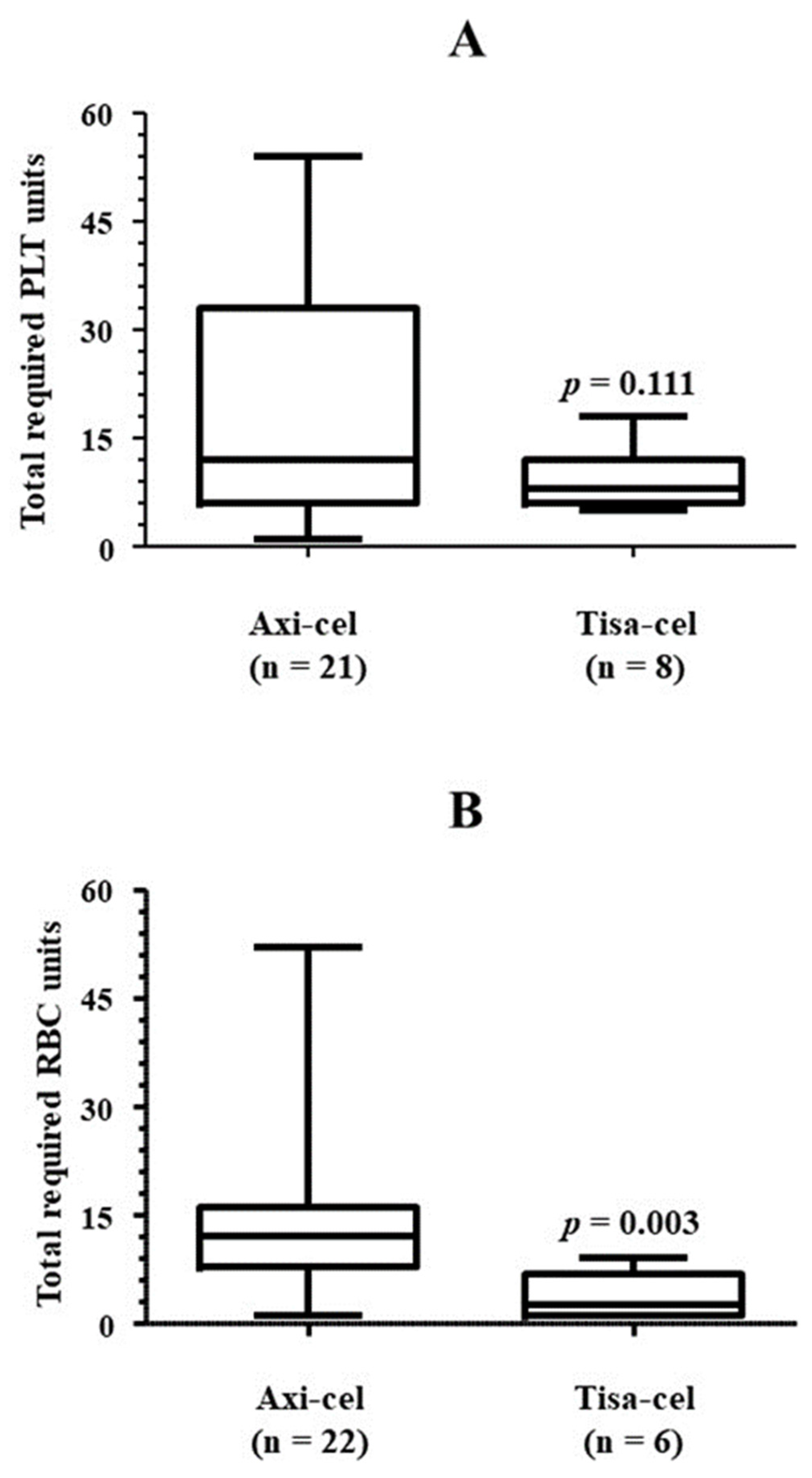
3.2. Platelet Transfusion Requirement
3.3. Bleeding Events during the Study
3.4. Other Cytopenias and Concomitant Therapy
3.5. Recovery When Platelet/RBC Transfusion Dependence and Severe Neutropenia Presented Simultaneously
3.6. Safety
3.6.1. Adverse Events Associated with CAR-T Cell Therapy
3.6.2. Adverse Events Associated with Eltrombopag
3.7. Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Recovery from Thrombocytopenia
4.2. Platelet Transfusion Requirement
4.3. Recovery from Other Cytopenias
4.4. Efficacy of Eltrombopag in Patients with Aplasia
4.5. Safety
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbaum, L. Tragedy, Perseverance, and Chance - The Story of CAR-T Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1313-1315.
- Johnson, P.C.; Abramson, J.S. Engineered T Cells: CAR T Cell Therapy and Beyond. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 23–31. [CrossRef]
- Manier, S.; Ingegnere, T.; Escure, G.; Prodhomme, C.; Nudel, M.; Mitra, S.; Facon, T. Current state and next-generation CAR-T cells in multiple myeloma. Blood Rev. 2022, 54, 100929. [CrossRef]
- Karsten, H.; Matrisch, L.; Cichutek, S.; Fiedler, W.; Alsdorf, W.; Block, A. Broadening the horizon: potential applications of CAR-T cells beyond current indications. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1285406. [CrossRef]
- Daamen, A.R.; E Lipsky, P. Potential and pitfalls of repurposing the CAR-T cell regimen for the treatment of autoimmune disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 696–699. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Santomasso, B.D.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Turtle, C.J.; Brudno, J.N.; Maus, M.V.; Park, J.H.; Mead, E.; Pavletic, S.; et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 625–638.
- Rejeski, K.; Subklewe, M.; Aljurf, M.; Bachy, E.; Balduzzi, A.C.; Barba, P.; Bruno, B.; Benjamin, R.; Carrabba, M.G.; Chabannon, C.; et al. Immune effector cell–associated hematotoxicity: EHA/EBMT consensus grading and best practice recommendations. Blood 2023, 142, 865–877. [CrossRef]
- Rejeski, K.; Perez, A.P.; Sesques, P.; Hoster, E.; Berger, C.S.; Jentzsch, L.; Mougiakakos, D.; Frölich, L.; Ackermann, J.; Buecklein, V.; et al. CAR-HEMATOTOX: a model for CAR T-cell–related hematologic toxicity in relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2021, 138, 2499–2513. [CrossRef]
- Jain, T.; Knezevic, A.; Pennisi, M.; Chen, Y.; Ruiz, J.D.; Purdon, T.J.; Devlin, S.M.; Smith, M.; Shah, G.L.; Halton, E.; et al. Hematopoietic recovery in patients receiving chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for hematologic malignancies. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 3776–3787. [CrossRef]
- Logue, J.M.; Peres, L.C.; Hashmi, H.; Colin-Leitzinger, C.M.; Shrewsbury, A.M.; Hosoya, H.; Gonzalez, R.M.; Copponex, C.; Kottra, K.H.; Hovanky, V.; et al. Early cytopenias and infections after standard of care idecabtagene vicleucelin relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 6109-6119. [CrossRef]
- Logue, J.M.; Zucchetti, E.; Bachmeier, C.A.; Krivenko, G.S.; Larson, V.; Ninh, D.; Grillo, G.; Cao, B.; Kim, J.; Chavez, J.C.; et al. Immune reconstitution and associated infections following axicabtagene ciloleucel in relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2020, 106, 978–986. [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Du, M.; Kou, H.; Lu, C.; Mei, H.; Hu, Y. Adverse effects in hematologic malignancies treated with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Jain, T.; Olson, T.S.; Locke, F.L. How I Treat Cytopenias after CAR T-cell Therapy. Blood 2023, 141, 2460–2469. [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Li, D.; Huang, L.; Zhu, X. Inflammatory abrasion of hematopoietic stem cells: a candidate clue for the post-CAR-T hematotoxicity?. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1141779. [CrossRef]
- Bussel, J.B.; Pinheiro, M.P. Eltrombopag. Cancer Treat. Res. 2011, 157, 289-303. [CrossRef]
- Mingot-Castellano, M.E.; Hirnyk, M.C.; Sánchez-González, B.; Álvarez-Román, M.T.; Bárez-García, A.; Bernardo-Gutiérrez, Á.; Bernat-Pablo, S.; Bolaños-Calderón, E.; Butta-Coll, N.; Caballero-Navarro, G.; et al. Recommendations for the Clinical Approach to Immune Thrombocytopenia: Spanish ITP Working Group (GEPTI). J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6422. [CrossRef]
- Fattizzo, B.; Levati, G.; Cassin, R.; Barcellini, W. Eltrombopag in Immune Thrombocytopenia, Aplastic Anemia, and Myelodysplastic Syndrome: From Megakaryopoiesis to Immunomodulation. Drugs 2019, 79, 1305–1319. [CrossRef]
- Townsley, D.M.; Scheinberg, P.; Winkler, T.; Desmond, R.; Dumitriu, B.; Rios, O.; Weinstein, B.; Valdez, J.; Lotter, J.; Feng, X.; et al. Eltrombopag Added to Standard Immunosuppression for Aplastic Anemia. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1540–1550. [CrossRef]
- Drexler, B.; Passweg, J. Current evidence and the emerging role of eltrombopag in severe aplastic anemia. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2021, 12, 2040620721998126. [CrossRef]
- Bento, L.; Bastida, J.M.; García-Cadenas, I.; García-Torres, E.; Rivera, D.; Bosch-Vilaseca, A.; De Miguel, C.; Martínez-Muñoz, M.E.; Fernández-Avilés, F.; Roldán, E.; et al. Thrombopoietin Receptor Agonists for Severe Thrombocytopenia after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: Experience of the Spanish Group of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 1825–1831. [CrossRef]
- Drillet, G.; Lhomme, F.; De Guibert, S.; Manson, G.; Houot, R. Prolonged thrombocytopenia after CAR T-cell therapy: the role of thrombopoietin receptor agonists. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 537–540. [CrossRef]
- Wesson, W.; Ahmed, N.; Rashid, A.; Tabak, C.; Logan, E.; Marchena-Burgos, J.; Nelson, M.; Davis, J.A.; McGann, M.; Shune, L.; et al. Safety and efficacy of eltrombopag in patients with post-CAR T cytopenias. Eur. J. Haematol. 2023, 112, 538–546. [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, R.M.; Djulbegovic, B.; Gernsheimer, T.; Kleinman, S.; Tinmouth, A.T.; Capocelli, K.E.; Cipolle, M.D.; Cohn, C.S.; Fung, M.K.; Grossman, B.J.; et al. Platelet Transfusion: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the AABB. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 205–213. [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [CrossRef]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Rives, S.; Boyer, M.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Stefanski, H.E.; Myers, G.D.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [CrossRef]
- Castella, M.; Boronat, A.; Martín-Ibáñez, R.; Rodríguez, V.; Suñé, G.; Caballero, M.; Marzal, B.; Pérez-Amill, L.; Martín-Antonio, B.; Castaño, J.; et al. Development of a Novel Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor: A Paradigm for an Affordable CAR T Cell Production at Academic Institutions. Mol. Ther. - Methods Clin. Dev. 2018, 12, 134–144. [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D.; Horning, S.J.; Coiffier, B.; Shipp, M.A.; Fisher, R.I.; Connors, J.M.; Lister, T.A.; Vose, J.; Grillo-López, A.; Hagenbeek, A.; et al. Report of an International Workshop to Standardize Response Criteria for Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 1244–1244. [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.A.; Shah, B.; Fathi, A.; Wieduwilt, M.; Advani, A.; Aoun, P.; Barta, S.K.; Boyer, M.W.; Bryan, T.; Burke, P.W.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Version 1.2017. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2017, 15, 1091–1102. [CrossRef]
- Al-Samkari, H. Optimal management of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia with thrombopoietin receptor agonists. Blood Rev. 2024, 63, 101139. [CrossRef]
- Stafylidis, C.; Vlachopoulou, D.; Syriopoulou, S.; Chatzidavid, S.; Viniou, N.-A. Novel Perspectives on Thrombopoietin Receptor Agonists Applications. Hamostaseologie 2024. [CrossRef]
- Corman, S.L.; A Mohammad, R. Eltrombopag: A Novel Oral Thrombopoietin Receptor Agonist. Ann. Pharmacother. 2010, 44, 1072–1079. [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Dou, Y.; Liu, R.; Xu, T.; Yang, F.; Xue, F.; Zheng, P.; Feng, S.; Guo, Y.; Shi, H.; et al. P1206: Gastrointestinal bleeding significantly reduced the efficacy and survival of CD19 CAR-T cell therapy in patients with gastrointestinal tract involvement of refractory/relapsed B-cell lymphoma. HemaSphere 2022, 6, 1092–1093. [CrossRef]
- Johnsrud, A.J.; Craig, J.; Baird, J.H.; Spiegel, J.Y.; Muffly, L.; Zehnder, J.L.; Tamaresis, J.S.; Negrin, R.S.; Johnston, L.; Arai, S.; et al. Incidence and risk factors associated with bleeding and thrombosis following chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 4465–4475. [CrossRef]
- Beyar-Katz, O.; Perry, C.; Bar On, Y.; Amit, O.; Gutwein, O.; Wolach, O.; Kedar, R.; Pikovsky, O.; Avivi, I.; Gold, R.; et al. Thrombopoietin receptor agonist for treating bone marrow aplasia following anti-CD19 CAR-T cells—single-center experience. Ann. Hematol. 2022, 101, 1769–1776. [CrossRef]
- Baur, R.; Jitschin, R.; Kharboutli, S.; Stoll, A.; Völkl, S.; Büttner-Herold, M.; Schmidt, D.; Rösler, W.; Mackensen, A.; Mougiakakos, D. Thrombopoietin receptor agonists for acquired thrombocytopenia following anti-CD19 CAR-T-cell therapy: a case report. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002721. [CrossRef]
- Gagelmann, N.; Bishop, M.; Ayuk, F.; Bethge, W.; Glass, B.; Sureda, A.; Pasquini, M.C.; Kröger, N. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel versus Tisagenlecleucel for Relapsed or Refractory Large B Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2024, 30, 584.e1–584.e13. [CrossRef]
- Bachy, E.; Le Gouill, S.; Di Blasi, R.; Sesques, P.; Manson, G.; Cartron, G.; Beauvais, D.; Roulin, L.; Gros, F.X.; Rubio, M.T.; et al. A real-world comparison of tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T cells in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2145–2154. [CrossRef]
- Freyer, C.W.; Porter, D.L. Cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity following CAR T-cell therapy for hematologic malignancies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 940–948. [CrossRef]
- Fried, S.; Avigdor, A.; Bielorai, B.; Meir, A.; Besser, M.J.; Schachter, J.; Shimoni, A.; Nagler, A.; Toren, A.; Jacoby, E. Early and late hematologic toxicity following CD19 CAR-T cells. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 54, 1643–1650. [CrossRef]
- Qualls, D.; Jacobson, C. A road map for navigating CAR T hematotoxicity. Blood 2023, 142, 859–861. [CrossRef]
- Kampouri, E.; Little, J.S.; Rejeski, K.; Manuel, O.; Hammond, S.P.; Hill, J.A. Infections after chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T-cell therapy for hematologic malignancies. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2023, 25 Suppl 1, e14157. [CrossRef]
- Peffault de Latour, R.; Kulasekararaj, A.; Iacobelli, S.; Terwel, S. R.; Cook, R.; Griffin, M.; Halkes, C. J. M.; Recher, C.; Barraco, F.; Forcade, E.; et al. Severe Aplastic Anemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Eltrombopag Added to Immunosuppression in Severe Aplastic Anemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 11-23. [CrossRef]
- Drexler, B.; Passweg, J. Current evidence and the emerging role of eltrombopag in severe aplastic anemia. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2021, 12, 2040620721998126. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Feng, X.; Wu, Z.; Winkler, T.; Desmond, R.; Olnes, M.; Dumitriu, B.; Townsley, D.M.; Dunbar, C.E.; Young, N.S. Persistent elevation of plasma thrombopoietin levels after treatment in severe aplastic anemia. Exp. Hematol. 2017, 58, 39–43. [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, L.J.; Huntsman, H.D.; Cheng, H.; Townsley, D.M.; Winkler, T.; Feng, X.; Dunbar, C.E.; Young, N.S.; Larochelle, A. Eltrombopag maintains human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells under inflammatory conditions mediated by IFN-γ. Blood 2019, 133, 2043–2055. [CrossRef]
- Sanfilippo, K.; Wang, T.; Gage, B.; Luo, S.; Riedell, P.; Carson, K. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Thromb. Res. 2016, 143, 86–90. [CrossRef]
- Ku, G.H.; White, R.H.; Chew, H.K.; Harvey, D.J.; Zhou, H.; Wun, T. Venous thromboembolism in patients with acute leukemia: incidence, risk factors, and effect on survival. Blood 2009, 113, 3911–3917. [CrossRef]
- Schorr, C.; Forindez, J.; Espinoza-Gutarra, M.; Mehta, R.; Grover, N.; Perna, F. Thrombotic Events Are Unusual Toxicities of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8349. [CrossRef]
- Chitkara, A.; Sreenivsan, S.; Rai, M.; Sadashiv, S. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) in Post-CAR-T Patients - a Meta-Analysis of Phase 2 & 3 Clinical Trials. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl.1), 6929–6929. [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.N.; Bussel, J.B.; Cheng, G.; Meyer, O.; Bailey, C.K.; Arning, M.; Brainsky, A.; EXTEND Study Group. Safety and efficacy of eltrombopag for treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenia: results of the long-term, open-label EXTEND study. Blood 2013, 121, 537–545. [CrossRef]
- Rodeghiero, F.; Stasi, R.; Giagounidis, A.; Viallard, J.; Godeau, B.; Pabinger, I.; Cines, D.; Liebman, H.; Wang, X.; Woodard, P. Long-term safety and tolerability of romiplostim in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia: a pooled analysis of 13 clinical trials. Eur. J. Haematol. 2013, 91, 423–436. [CrossRef]

| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR) | 59.0 (50.1, 64.3) |
| Sex (female) | 17/38 (44.7) |
| Disorder | |
| DLBCL | 34/38 (89.5) |
| ALL | 3/38 (7.9) |
| FL | 1/38 (2.6) |
| Bridge therapy | 30/38 (78.9) |
| Type | |
| R-GEMOX | 12/30 (40.0) |
| R-GDP | 6/30 (20.0) |
| BR | 3*/30 (10.0) |
| R-ICE | 1/30 (3.3) |
| Polatuzumab and BR | 1/30 (3.3) |
| R-ESHAP | 1/30 (3.3) |
| Inotuzumab | 1/30 (3.3) |
| R-MINE | 1/30 (3.3) |
| Radiotherapy | 1/30 (3.3) |
| R-MTX | 1/30 (3.3) |
| Burkimab | 1/30 (3.3) |
| Several strategies | 1/30 (3.3) |
| FluCy lymphodepletion | 38/38 (100) |
| CAR-T type | |
| AXI-CEL | 29/38 (76.3) |
| TISA-CEL | 8/38 (21.0) |
| Other | 1/38 (2.6) |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Time from CAR-T infusion to PLT transfusion requirement, days | 6.0 (2.0, 21.5) |
| Platelet count when the first dose of eltrombopag was administered, x109/L | 12.5 (9.0, 18.1) |
| Time from first platelet transfusion to start of eltrombopag, days | 21.0 (7.5, 55.0) |
| Eltrombopag dose, mg/d | |
| Initial | 50 (50, 50) |
| Maximum | 150 (50, 150) |
| Time on eltrombopag treatment, days | 68 (48, 154) |
| Follow-up since the start of eltrombopag, days | 122 (66, 398) |
| Patients who recovered counts at follow-up end, and time required | |
| Achieved platelet count ≥20x109/L, n/N (%) | 29/38 (76.3) |
| Time from start of eltrombopag to platelet count ≥20x109/L, days | 32 (14, 38) |
| Achieved platelet count ≥50x109/L, n/N (%) | 26/38 (68.4) |
| Time from start of eltrombopag to platelet count ≥50x109/L, days | 33 (19, 57) |
| Patients who did not reach counts ≥20x109/L at follow-up end | |
| Time on treatment with eltrombopag, days | 108 (63, 154) |
| Follow-up since the start of eltrombopag, days | 108 (82, 158) |
| Variable | Responders (n = 29) |
Non-responders (n = 9) |
p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 59.8 (48.0, 64.5) | 58.4 (53.8, 67.3) | 0.810 |
| Sex (female), n/N (%) | 15/29 (51.7) | 2/9 (22.2) | 0.148 |
| Diagnosis (DLBCL), n/N (%) | 27/29 (93.1) | 7/9 (77.8) | 0.233 |
| PLT count at ELT start (x109/L) | 12 (9, 15) | 15 (9, 23) | 0.633 |
| Time between PLT transfusion start and ELT start, days | 15 (6, 46) | 36 (22, 68) | 0.196 |
| DP before the end of the study, n/N (%) | 9/29 (31.0) | 3/9 (33.3) | 1.000 |
| Exitus before the end of the study, n/N (%) | 13/29 (44.8) | 7/9 (77.8) | 0.130 |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Patients requiring PLT transfusion at the start of eltrombopag*, n/N (%) | 38/38 (100) |
| Time from platelet count <20x109/L to start of eltrombopag, days | 21 (7, 55) |
| Time between first and last PLT transfusion, days | 55 (28, 129) |
| Total transfused PLT units | 14 (6, 34) |
| Patients who achieved PLT transfusion independence at follow-up end, n/N (%) | 29/38 (76.3) |
| Bleeding while on Eltrombopag Treatment | Value |
| Patients, n/N (%) | 3/38* (7.9) |
| WHO grade | 3.0 (3.0, 4.0) |
| Fatal, n/N (%) | 0/3 (0) |
| Location, n/N (%) | |
| Several† | 1/3 (33.3) |
| Subdural | 1/3 (33.3) |
| Nasopharynx | 1/3 (33.3) |
| Features of patients who had a bleeding episode | |
| Platelet count before start of eltrombopag | 18.5 (20.0, 27.0) |
| Time from platelet count <20x109/L to start of eltrombopag, days | 32 (18, 75) |
| Time on eltrombopag treatment when bleeding occurred, days | 16 (15, 70) |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Severe neutropenia* at start of eltrombopag, n/N (%) | 23/37† (62.2) |
| ANC at start of eltrombopag, cells /μL | 10 (0, 840) |
| Use of G-CSF, n/N (%) | 37/37† (100) |
| Time on treatment, months | 1.50 (1.00, 2.75) |
| Patients who recovered ANC by follow-up end, and time required | |
| From <500/μL to ≥500/μL, n/N (%) | 19/23 (82.86) |
| Time from start of eltrombopag to ANC ≥500/μL, days | 22 (11, 31) |
| From <500/μL to ≥1,000/μL, n/N (%) | 19/23 (82.86) |
| Time from start of eltrombopag to ANC ≥1,000/μL, days | 28 (18, 35) |
| Severe anemia‡ at start of eltrombopag, n/N (%) | 13/33§ (39.4) |
| Hemoglobin at start of eltrombopag, g/dL | 8.2 (7.6, 9.3) |
| Use of EPO | 19/38 (50.0) |
| Time on treatment, months | 2.00 (2.00, 3.00) |
| Patients requiring RBC transfusion, n/N (%) | 35/38 (92.1) |
| Total transfused RBC units | |
| Overall | 12.0 (4.0, 27.0) |
| In patients with hemoglobin <8 g/dL | 12.0 (6.5, 17.5) |
| Patients who achieved RBC transfusion independence, n/N (%) | 29/35 (82.9) |
| Time from start of eltrombopag to RBC transfusion independence, days | 29 (17, 44) |
| Patients who achieved hemoglobin ≥8 g/dL by follow-up end, n/N (%) | 11/13 (84.6) |
| Patients with severe pancytopenia¶ at start of eltrombopag, n/N (%) | 8/38 (21.0) |
| Patients who recovered all lineages by follow-up end, n/N (%) | 7/8 (87.5) |
| Adverse Events before and/or during Eltrombopag Treatment | |
|---|---|
| CRS | |
| Patients, n/N (%) | 32/38 (84.2) |
| Time from CAR-T cell infusion to onset, days | 2 (1, 4) |
| Grade | 2 (1, 2) |
| Time from onset to resolution, days | 5 (4, 9) |
| ICANS | |
| Patients, n/N (%) | 21/38 (55.3) |
| Time from CAR-T cell infusion to onset, days | 6 (5, 8) |
| Grade | 2 (2, 3) |
| Time from onset to resolution, days | 4 (2, 7) |
| Infection, n/N (%) | 19/38 (50.0) |
| Fatal, n/N (%) | 6/19 (26.3) |
| Toxicities during eltrombopag treatment | |
| Patients with toxicities requiring eltrombopag suspension, n/N (%) | 1/38 (2.6) |
| Type of toxicity | |
| Cholestasis, transaminitis*, n/N (%) | 1/1 (100) |
| Patients with other toxicities not requiring hospitalization or suspension, n/N (%) | 1/38 (2.6) |
| Type of toxicity | |
| Hyperbilirubinemia†, n/N (%) | 1/1 (100) |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Follow-up from CAR-T cell infusion to end of study, days, median (IQR) | 175 (99, 489) |
| DP by follow-up end | 12/38 (31.6) |
| Time from CAR-T infusion to DP, days, median (IQR) | 98 (89, 131) |
| Exitus by follow-up end | 20/38 (52.6) |
| Cause | |
| Disease progression | 12/20 (60.0) |
| Infection | 6/20 (30.0) |
| Late ICANS | 1/20 (5.0) |
| Unspecified | 1/20 (5.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





