Introduction and Background
Obesity and overweight are significant chronic health issues defined by having a body mass index (BMI) of ≥ 30 kg/m² and ≥ 25 kg/m², respectively [
1,
2,
3,
4]. These conditions are not just prevalent but are also escalating at an alarming rate globally. In 2015 alone, high BMI was linked to an estimated 4 million deaths worldwide, with cardiovascular illnesses contributing to over two-thirds of these fatalities. Projections indicate that by the year 2035, more than half of the global population will be overweight or obese [
5,
6].
Obesity's impact extends beyond cardiovascular conditions, encompassing a broad spectrum of health issues. It is associated with hypertension, dyslipidemia, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, gallbladder disorders, osteoarthritis, obstructive sleep apnea, and certain cancers. Moreover, obesity is a significant independent risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) [
7,
8,
9].
The initial approach for managing overweight and obese individuals involves lifestyle modifications, including dietary adjustments and increased physical activity. However, long-term adherence to these behavioral therapies often proves challenging, necessitating the introduction of pharmacotherapy for effective weight management [
10,
11,
12]. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved several pharmacotherapies for obesity treatment, including orlistat, a pancreatic and gastric lipase inhibitor; phentermine, a sympathomimetic amine; and liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) [
13].
GLP-1 receptor agonists have garnered significant attention due to their potent incretin effect. These drugs function by mimicking the action of the natural GLP-1 hormone, stimulating insulin secretion, and inhibiting glucagon release in a glucose-dependent manner [
14]. Beyond glycemic control, GLP-1 RAs slow gastric emptying and reduces appetite by acting on GLP-1 receptors in both the gastrointestinal system and the brain [
15,
16].
The efficacy of GLP-1 RAs in weight management has been demonstrated in numerous studies. Zhang et al.'s 2015 systematic review of eight randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving liraglutide and exenatide found that treatment with GLP-1 RAs resulted in an average weight loss of -2.85 kg, significantly greater than that observed in the control groups [
17]. In a 2018 study by O'Neil et al., the safety and efficacy of semaglutide in overweight and obese patients were evaluated, revealing an average weight loss of -11.3% in the semaglutide group compared to -2.3% in the placebo group [
18].
Recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses further support the superior anti-obesity effects of semaglutide. Guo et al. conducted a comprehensive review including liraglutide, exenatide, and semaglutide, concluding that semaglutide had a more pronounced impact on weight loss, BMI reduction, and waist circumference (WC) compared to placebo or metformin. Additionally, semaglutide demonstrated fewer gastrointestinal side effects relative to liraglutide and exenatide [
19].
In a significant advancement, the FDA approved tirzepatide on May 13, 2022, for managing blood sugar levels in adults with type 2 diabetes, complementing diet and exercise [
20]. Tirzepatide, a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and GLP-1 receptor agonist, represents a novel class of medication for managing obesity, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and T2DM [
21]. Emerging evidence suggests that tirzepatide significantly contributes to weight loss in T2DM patients [
22,
23,
24].
Given the rising prevalence of obesity and its associated health risks, our systematic review aims to evaluate the current evidence on the anti-obesity effects, safety, and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factor benefits of GLP-1 RAs, including tirzepatide, in non-diabetic patients. This comprehensive analysis will provide insights into the effectiveness and safety profile of these medications, highlighting their potential in addressing the global obesity epidemic.
Methods
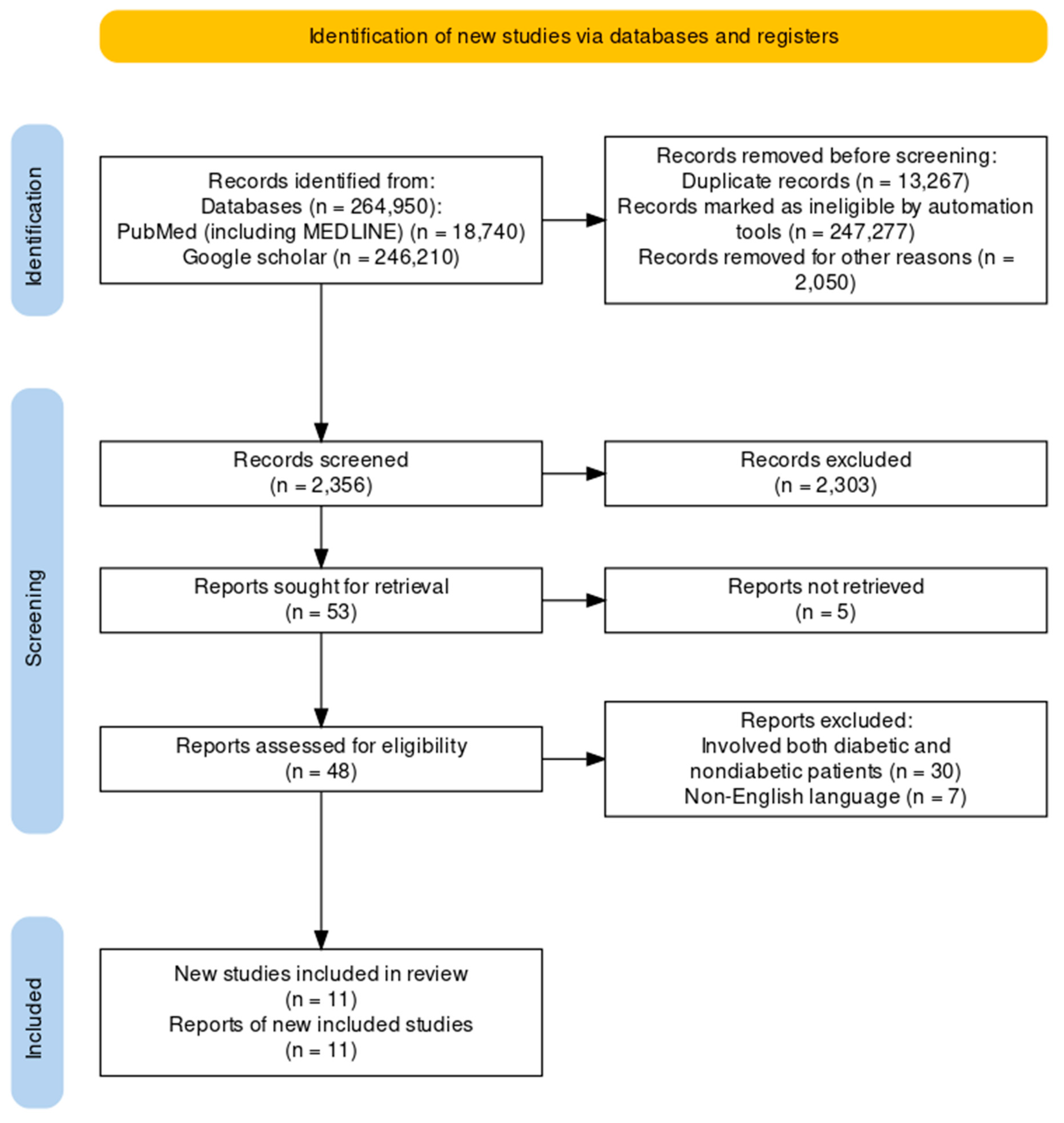
The clinical trials pertaining to the therapeutic intervention of obesity in people without diabetes using GLP-1RAs were the focus of this review. The review solely utilized data from published studies and adhered to the 2020 Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) standards, hence eliminating the need for ethical approval as shown in Figure 1.
Systematic Literature Search and Study Selection
We thoroughly searched the PubMed and Google Scholar databases for relevant publications, including MEDLINE (Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online). We had a list of abstracts that were independently examined for inclusion using predetermined criteria, in addition to research that were cited in editorials, comments, and review papers.
Criteria for Inclusion and Exclusion:
In order to accomplish our research objectives, we set precise standards for participant inclusion and exclusion. Table 1 provides a summary of our requirements. GLP-1 receptor agonist or tirzepatide usage and a well-defined clinical cohort—adult patients of 18 years of age and above without diabetes—were prerequisites for participation in the research. Publications that examined the safety and efficacy of GLP-1 RAs in individuals with type 1 or T2DM were also disregarded. Four reviewers conducted a dual review, and disagreements were resolved through discussion.
| |
Inclusion Criteria |
Exclusion Criteria |
| A |
English Text |
Non-English Text |
| B |
Human studies |
Animal studies |
| C |
Free papers |
Papers that needed to be purchased |
| D |
Age: =>18 years of age |
Age:<=18 years |
| E |
Gender: All |
Studies involving obesity in diabetic patients other than non-diabetic patients |
| F |
From 2013 to 2023 |
Papers outside the range of 2013 to 2023 |
Search Strategy
The search was conducted on PubMed (including MEDLINE) and Google Scholar databases, using relevant keywords, such as Efficacy and Safety, GLP-1 receptor agonists, weight loss, obesity, tirzepatide, semaglutide, liraglutide, exenatide and non-diabetic patients. The medical subject heading (MeSH) approach for PubMed (including MEDLINE) and Google Scholar, was employed to develop a comprehensive search strategy as detailed in Table 2.
| Database |
Search Strategy |
Results |
| PubMed (Including MEDLINE) |
(((((((((((((((((((Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists[Title/Abstract]) OR (GLP-1 receptor agonists[Title/Abstract])) OR (GLP-1 RAs[Title/Abstract])) OR (GIP[Title/Abstract])) OR (Semaglutide[Title/Abstract])) OR (Liraglutide[Title/Abstract])) OR (Tirzepatide[Title/Abstract])) OR (Exenatide[Title/Abstract])) OR (anti-obesity agents[MeSH Terms])) OR (Obesity management[MeSH Terms])) OR (agents, weight loss[MeSH Terms])) OR (weight loss[MeSH Terms])) OR (drugs, weight loss[MeSH Terms])) OR (weight reduction[MeSH Terms])) OR (Patients without diabetes[MeSH Terms])) OR (nondiabetic patients[MeSH Terms]))) OR (type 1 diabetes mellitus[MeSH Terms])) NOT (type 2 diabetes mellitus[MeSH Terms])) NOT (diabetes mellitus[MeSH Terms])
(((((((((glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists[Title/Abstract]) OR (glp 1[MeSH Terms])) OR (Obesity management[MeSH Terms])) OR (Diabetes and obesity[MeSH Terms])) OR (agents, weight loss[MeSH Terms])) OR (weight reduction[MeSH Terms])) OR (Non-diabetic[MeSH Terms])) OR (Non-diabetes[MeSH Terms])) OR (Non-diabetic patient[MeSH Terms])) AND (("2013/01/01"[Date - Publication] : "2023/10/27"[Date - Publication]))
((((((((((((((((((Glucagon like peptide 1 receptor agonists[Title/Abstract]) OR (Liraglutide[Title/Abstract])) OR (Semaglutide[Title/Abstract])) OR (glp 1[MeSH Terms])) OR (glucagon like peptide 1[MeSH Terms])) OR (anti obesity agents[MeSH Terms])) OR (anti obesity drugs[MeSH Terms])) OR (agents, anti obesity[MeSH Terms])) OR (Obesity management[MeSH Terms])) OR (agents, weight loss[MeSH Terms])) OR (weight reduction[MeSH Terms])) OR (overweight[MeSH Terms])) OR (Nondiabetes[MeSH Terms])) OR (Nondiabetic[MeSH Terms])) OR (Nondiabetic patient*[MeSH Terms])) OR (With no diabetes[Title/Abstract])) OR (Nondiabetic[Title/Abstract])) OR (Nondiabetic patients[Title/Abstract])) AND (("2013/01/01"[Date - Publication] : "2023/10/27"[Date - Publication]))
((((((((((((((((((Glucagon like peptide 1 receptor agonists) OR (Liraglutide[Title/Abstract])) OR (Semaglutide[Title/Abstract])) OR (Exenatide[Title/Abstract])) OR (Dulaglutide[Title/Abstract])) AND (Nondiabetic patients[MeSH Terms])) OR (Patients without diabetes ) NOT (Diabetes[MeSH Terms])) NOT (Diabetic patients[MeSH Terms])) AND (Obesity[MeSH Terms])) OR (Overweight[MeSH Terms])) OR (Weight reduction[MeSH Terms])) OR (antiobesity agents[MeSH Terms])) OR (antiobesity drugs[MeSH Terms])) AND (("2013/01/01"[Date - Publication] : "2023/11/19"[Date - Publication])) |
1535
22/11/2023
Filters applied:
Text AvailabilityArticle attributeArticle type
Clinical trial Meta-Analysis Randomized control trial Review Systematic review Publication dateSpeciesArticle language
Sex
Male Female Other Exclude preprints MEDLINE
3018
27/10/2023
Filters applied:
Text AvailabilityArticle attributeArticle type
Clinical trial Meta-Analysis Randomized control trial Review Systematic review Publication dateSpeciesArticle language
SexOther
Exclude preprints MEDLINE
6076
27/10/2023
Filters applied:
Text AvailabilityArticle attributeArticle type
Clinical trial Meta-Analysis Randomized control trial Review Systematic review Publication dateSpeciesArticle language
SexOther
Exclude preprints MEDLINE
8111
19/11/2023
Filters applied:
Text AvailabilityArticle attributeArticle type
Clinical trial Meta-Analysis Randomized control trial Review Systematic review Publication dateSpeciesArticle languageSexOther
Exclude preprints MEDLINE
|
| Google Scholar |
(((glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists* OR GLP-1 agonists OR Obesity) AND weight loss OR weight reduction OR Non-diabetic)
( "GLP-1 Agonists" OR "GLP-1 receptor agonists" OR "incretin mimetics" ) AND ( "obesity" OR "overweight" ) AND ( "non-diabetic" OR "non-diabetic patients" OR "normoglycemic" ) AND ( "efficacy" OR "effectiveness" OR "efficiency" ) AND ( "safety" OR "adverse
"Glucagon like peptide 1 receptor agonists" OR "Liraglutide" OR "Semaglutide" OR "glp 1" OR "glucagon like peptide 1" OR "anti obesity agents" OR "anti obesity drugs" OR "agents, anti obesity" OR "Obesity management" OR "agents, weight loss" OR "weight reduction" OR "overweight" OR "Nondiabetes" OR "Nondiabetic" OR "Nondiabetic patient*" OR "With no diabetes" OR "Nondiabetic patients" AND "2013/01/01"[Date - Publication] : "2023/11/19"[Date - Publication] |
27/10/2023
18800
Filter applied:
2013 -2023
27/10/2023
3410
Filter applied:
2013 -2023
19/11/2023
224000
Filter applied:
2013 -2023 |
Quality Evaluation
To make sure that the papers we chose were reliable, we employed a range of quality evaluation instruments. We employed the Cochrane bias tool evaluation, Newcastle-Ottawa tool and AMSTAR-2 checklist for RCTs, non-RCTs/observational studies and Systematic reviews respectively. as shown in Table 3.
| |
Quality Appraisal Tools Used |
Types of Studies |
| A |
Cochrane Bias Tool Assessment |
Randomized Control Trials |
| B |
Newcastle-Ottawa Tool |
Non-RCT and Observational Studies |
| C |
AMSTAR-2 |
Systematic Reviews |
| |
Selection |
Comparability |
Outcome |
Total Star |
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
1a |
1b |
1 |
2 |
3 |
| Chou et al. 2022 |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
9 |
| Launtenbach et al. 2022 |
* |
|
* |
* |
* |
|
* |
* |
* |
7 |
Newcastle Ottawa Checklist
Selection
1.Representativeness of the exposed cohort
2.Selection of the non-exposed cohort
3. Ascertainment of exposure
4. Demonstration that outcome of interest was not present at start of study
Comparability
1a. Comparability of cohorts on the basis of the design or analysis controlled for confounders
Outcomes
1.Assessment of outcome
2. Was follow-up long enough for outcomes to occur
3. Adequacy of follow-up of cohorts
| Author |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
TY |
TN |
TPY |
| Liu et al. 2023 |
Y |
N |
N |
PY |
N |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
N |
Y |
N |
N |
Y |
Y |
Y |
9 |
6 |
1 |
| Guo et al. 2022 |
Y |
N |
N |
PY |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
N |
Y |
N |
N |
Y |
N |
Y |
9 |
6 |
1 |
| Zhang et al. 2019 |
Y |
N |
N |
PY |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
N |
Y |
N |
N |
Y |
Y |
Y |
10 |
5 |
1 |
| Gao et al. 2022 |
Y |
N |
N |
PY |
N |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
N |
Y |
N |
N |
N |
Y |
Y |
8 |
7 |
1 |
AMSTAR-2 Checklist
1.Did the research questions and inclusion criteria for the review include the components of PICO?
2. Did the report of the review contain an explicit statement that the review methods were established prior to the conduct of the review and did the report justify any significant deviations from the protocol?
3. Did the review authors explain their selection of the study designs for inclusion in the review?
4. Did the review authors use a comprehensive literature search strategy?
5. Did the review authors perform study selection in duplicate?
6. Did the review authors perform data extraction in duplicate?
7. Did the review authors provide a list of excluded studies and justify the exclusions?
8. Did the review authors describe the included studies in adequate detail?
9. Did the review authors use a satisfactory technique for assessing the risk of bias (RoB) in individual studies that were included in the review?
10. Did the review authors report on the sources of funding for the studies included in the review?
11. If meta-analysis was performed did the review authors use appropriate methods for statistical combination of results?
12. If meta-analysis was performed, did the review authors assess the potential impact of RoB in individual studies on the results of the meta-analysis or other evidence synthesis?
13. Did the review authors account for RoB in individual studies when interpreting/ discussing the results of the review?
14. Did the review authors provide a satisfactory explanation for, and discussion of, any heterogeneity observed in the results of the review?
15. If they performed quantitative synthesis did the review authors carry out an adequate investigation of publication bias (small study bias) and discuss its likely impact on the results of the review?
16. Did the review authors report any potential sources of conflict of interest, including any funding they received for conducting the review?
Y- Yes, N- No, PY- Partial Yes, TY- Total number of Yes, TY- Total number of No, TPY- Total number of No
Results
From the PubMed, MEDLINE, and Google Scholar databases, we retrieved 264950 articles. After every paper was carefully reviewed using predetermined standards and filters, 247277 articles were excluded. Out of the 17673 papers that were still available, we removed 15317 papers due to duplication or insufficient abstracts and titles. After detailed evaluation of the 2356 remaining articles, we excluded an additional 2303 papers because their content did not meet our inclusion criteria. The remaining 53 articles were sought for retrieval with 48 being retrieved and 5 not retrieved. The 48 retrieved articles were accessed for eligibility and 11 articles selected for review. The next step was a rigorous quality review of the 11 papers that remained, and all met our standards. Our last systematic review included these 11 papers. Table 4 gives a thorough explanation of each.
| Article Title and Journal |
Author Names/ Year |
Country |
Study Design |
Database used |
Conclusion |
| Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity: N Engl J Med |
Jastreboff et al.,/2022 [25]. |
119 sites in nine countries |
Randomized Clinical Trial |
PubMed including MEDLINE |
All three of the once weekly tirzepatide doses showed a significant and long-lasting reduction in weight in adults with obesity during the clinical trial. |
| Evaluation of the efficacy of low dose liraglutide in weight control among Taiwanese non-diabetes patients; J of Diabetes Invest |
Chou et al/2020 [26]. |
Taiwan |
Retrospective study |
PubMed including MEDLINE |
Liraglutide at low dosages is comparatively effective in controlling weight in Taiwanese people, particularly in younger age groups. |
| Efficacy and safety of semaglutide on weight loss in obese or overweight patients without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials; Front. Pharmacol. |
Gao et al./2022 [27] |
NR |
Systematic review and Meta-Analysis of randomized controlled trial |
PubMed, CochraneLibrary, EMBASE, and ClinicalTrials.gov |
Semaglutide significantly lowered weight and BMI of obese or overweight patients without diabetes. |
| Effect of Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Daily Liraglutide on Body Weight in Adults with Overweight or Obesity Without Diabetes: The STEP 8 Randomized Clinical Trial; JAMA |
Rubino et al./2022 [28]. |
19 US sites |
Randomized Clinical Trial |
PubMed including MEDLINE |
Once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide plus diet and exercise counseling led to significantly greater weight loss at 68 weeks in overweight and obese individuals without diabetes than once-daily subcutaneous liraglutide. |
| Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity; N Engl J Med |
Wilding et al./2021 [29]. |
16 countries in Asia, Europe, North America, and South America |
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-
controlled trial
|
PubMed including MEDLINE |
This trial showed that among adults with overweight or obesity (without diabetes), once weekly subcutaneous semaglutide plus lifestyle intervention was associated with substantial, sustained, clinically relevant mean weight loss of 14.9%, with 86% of participants attaining at least 5% weight loss. |
| The Antiobesity Effect and Safety of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist in Overweight/Obese Patients Without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis; Horm Metab Res |
Guo et al./2022 [19] |
NR |
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis |
Medline Embase, The Cochrane Library, Web of science, and Scopus databases |
When compared to placebo/metformin, this study demonstrates that GLP-1RAs, such as liraglutide, exenatide, and semaglutide, had a more pronounced antiobesity benefit in terms of weight loss, BMI reduction, and WC. Research findings indicate that semaglutide, as opposed to liraglutide and exenatide, may have a more pronounced antiobesity impact and fewer gastrointestinal side effects. |
| The efficacy and safety of liraglutide in the obese, non-diabetic individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis; Afr H. Sci. |
Zhang et al./2019 [30]. |
NR |
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis |
Medline,
Embase and Cochrane Controlled Trials Register databases |
According to this meta-analysis, liraglutide is a safe and effective medication for people who are obese but do not have diabetes. |
| The Potential of Semaglutide Once-Weekly in Patients Without Type 2 Diabetes with Weight Regain or Insufficient Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery—a Retrospective Analysis: OBES SURG |
Lautenbach et al./2022 [31]. |
NR |
a Retrospective Analysis
|
|
Semaglutide medication resulted in a total weight reduction of − 6.0 ± 4.3% (mean ± SD, p < 0.001) after 3 months (3.2, IQR 3.0–3.5, n = 38) and − 10.3 ± 5.5% (mean ± SD, p < 0.001) after 6 months (5.8, IQR 5.8–6.4, n = 20). Following adjuvant semaglutide therapy for six months, 85% of patients lost more than five pounds, 45% more than ten pounds, and 5% more than fifteen pounds (Fig. 2). Within 14 days of the start of the treatment, gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea and a feeling of fullness were reported; they were typically moderate and did not result in stopping the treatment. |
| The Weight-loss Effect of GLP-1RAs Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Non-diabetic Individuals with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials; The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition |
Liu et al./2023 [32]. |
NR |
A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials |
PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Central Register of
Controlled Trials |
The study offered strong to moderate evidence that GLP-1RAs significantly reduced body weight in obese or overweight individuals without diabetes. Additionally, the TSA results provided solid proof of this weight-loss impact. Moreover, a nonlinear dose-response impact on weight loss was seen with GLP-1RAs. Interestingly, semaglutide may be the most efficient weight-loss medication. |
| Two-year effects of semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: the STEP 5 trial; Nat Med |
Garvey et al./2022 [33]. |
conducted at 41 sites across five countries (Canada, Italy, Hungary,
Spain and the United States) |
Randomized Clinical Trial |
PubMed including MEDLINE |
In adults with obesity (without diabetes) or overweight (with at least one weight-related comorbidity), treatment with once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide combined with behavioral intervention was linked to improvements in weight-related cardiometabolic risk factors and a clinically significant and long-lasting weight loss of 15.2% at week 104. |
| Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes: N Engl J Med |
Lincoff et al.,/2023 [34] |
801 clinical sites in 41 countries |
Randomized Clinical Trial |
PubMed including MEDLINE |
Semaglutide improved cardiovascular outcomes in this trial, whereas lifestyle and pharmacologic interventions for overweight or obesity tested in previous trials have uniformly failed to do so. |
Discussion
Although numerous studies on lifestyle modification, medications, and bariatric surgery have demonstrated that weight loss reduces morbidity, achieving and maintaining weight loss has consistently been a challenge. Before the recognition of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists as agents that could induce significant weight loss in patients with diabetes, medications such as phentermine, orlistat, lorcaserin, and the combination of phentermine-topiramate were approved for weight loss in the United States [
35].
The goal of our systematic review was to evaluate the anti-obesity effects, safety, and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factor benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists, including tirzepatide, in non-diabetic individuals with varying baseline characteristics. We aimed to determine the effectiveness and safety profile of each GLP-1 receptor agonist, highlighting their benefits and drawbacks across different scenarios and demographics within the non-diabetic obese population.
BMI, WC, and Weight Loss Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists:
In assessing the effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on BMI, waist circumference (WC), and weight loss, significant positive trends were observed. For instance, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial on once-weekly 2.4 mg semaglutide over 68 weeks in adults with overweight or obesity without diabetes showed an estimated mean weight change of −14.9% with semaglutide compared to −2.4% with placebo (estimated treatment difference, −12.4 percentage points; 95% CI, -13.4 to −11.5; P<0.001). Additionally, semaglutide was associated with greater reductions in WC (-13.54 cm with semaglutide vs. –4.13 cm with placebo; estimated treatment difference, -9.42 cm; 95% CI, –10.30 to –8.53) and BMI (–5.54 with semaglutide vs. –0.92 with placebo; estimated treatment difference, –4.61; 95% CI, –4.96 to –4.27) [
29]. Similar findings were reported by Garvey et al., where the semaglutide group (n=152) had a mean weight change of -15.2% from baseline to week 104, compared to -2.6% in the placebo group, resulting in an estimated treatment difference of -12.6 percentage points (95% CI, -15.3 to -9.8; P<0.0001) and WC reductions of -14.4 cm with semaglutide versus -5.2 cm with placebo [
33].
Significant reductions in BMI, WC, and body weight with semaglutide were also observed by Gao et al., [
27] Guo et al., [
19] Liu et al., [
32] and Lincoff et al. [
34] In the SURMOUNT-1 clinical trial, tirzepatide demonstrated its anti-obesity effect with weekly doses of 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg. At week 72, the average weight change was −15.0% (95% CI, −15.9 to −14.2) for a 5-mg dose, −19.5% (95% CI, −20.4 to −18.5) for a 10-mg dose, −20.9% (95% CI, −21.8 to −19.9) for a 15-mg dose, and −3.1% (95% CI, −4.3 to −1.9) for placebo. WC decreased by −14.0 cm with a 5-mg dose, −17.7 cm with a 10-mg dose, and −18.5 cm with a 15-mg dose [
25].
Exenatide-treated non-diabetic patients showed overall weight reduction of –3.23 kg (95% CI, –3.71 to –2.75), overall BMI reduction of –1.08 kg/m^2 (95% CI, –1.92 to –0.23), and overall, WC decline of –2.63 cm (95% CI, –4.39 to –0.87) according to a sub-group analysis by Guo et al. [
19]. Similarly, Zhang et al.'s systematic review and meta-analysis, which included 4754 participants (2996 in the liraglutide group and 1758 in the placebo group), showed that liraglutide 3.0 mg daily outperforms placebo in terms of weight loss, with a pooled estimate of MD of -5.52 (95% CI, -5.93 to -5.51; p<0.00001) [
30].
As these studies demonstrate, GLP-1 receptor agonists, including tirzepatide, appear to induce more pronounced decreases in body weight, BMI, and WC. These effects are linked to the activation of GLP-1 receptors at the level of central and peripheral enteric neurons, which slow intestinal transit, delay gastric emptying, and suppress appetite at the hypothalamic level—a mechanism known as the "ileal brake [
36]." Tirzepatide, distinct from previous peptide therapies, acts as an agonist at both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, adding to its weight loss efficacy [
37,
38].
In a comparative analysis, Guo et al. found that patients taking semaglutide experienced overall weight loss of -8.12 kg (95% CI, -12.44 to -3.80), those on liraglutide -5.45 kg (95% CI, -5.88 to -5.02), and those on exenatide –3.23 kg (95% CI, -3.71 to -2.75). BMI reductions were -4.18 kg/m^2 for semaglutide (95% CI, -4.97 to -3.38), -1.99 kg/m^2 for liraglutide (95% CI, -3.07 to -0.92), and -1.08 kg/m^2 for exenatide (95% CI, -1.92 to -0.23). WC reductions were -8.76 cm for semaglutide (95% CI, -10.48 to -7.05), -4.48 cm for liraglutide (95% CI, -4.92 to -4.04), and –2.63 cm for exenatide (95% CI, -4.39 to -0.87) [
19]. Rubino et al. in the STEP 8 randomized clinical trial observed a -15.8% mean change in body weight with semaglutide and -6.4% with liraglutide [
28].
These results suggest that semaglutide may have a greater effect on BMI, WC, and weight loss in non-diabetic obese individuals compared to liraglutide and exenatide, but tirzepatide appears to be superior. This is consistent with findings from the SURMOUNT-2 clinical trials of tirzepatide, which demonstrated greater weight loss than any other medication to date [
40];. Tirzepatide is likely to become the leading GLP-1 marketed therapy in the next decade, according to a meta-analysis presented at the 59th Annual European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2023 meeting [
39].
Benefits on CVD Risk Factors:
Weight loss, regardless of how it is achieved—medically, surgically, or through lifestyle modification—reduces comorbidities, improves quality of life, and lowers overall mortality. Lincoff et al. [
34] in a randomized placebo-controlled trial reported that the use of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide at a dose of 2.4 mg for a mean of 33 months decreased the risk of a composite of death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke by 20% among 17,604 patients with a BMI of 27 or higher and preexisting cardiovascular disease but without diabetes (hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.72 to 0.90). Semaglutide was also associated with improvements in cardiovascular risk biomarkers such as blood pressure, WC, glycemic control, nephropathy, C-reactive protein, and lipid levels. Wilding et al. [
29] reported benefits in fasting plasma glucose, C-reactive protein, glycated hemoglobin, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and fasting lipid levels with semaglutide.
Apart from semaglutide, a retrospective analysis by Chou and Chuang found that Taiwanese non-diabetic patients responded well to low-dose liraglutide, with statistically significant improvements in HbA1c, fasting glucose, serum insulin level, HOMA-IR, insulin and glucose ratio, serum cholesterol profiles, uric acid, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (HsCRP), and alanine aminotransferase [
26].
For tirzepatide, clinical trials indicated greater improvements in all measured cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors compared to placebo [
25]. This suggests that overweight or obese individuals without diabetes may benefit from the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists, including tirzepatide. Given the common comorbidities of obesity such as hypertension and diabetes, GLP-1 receptor agonists are important in managing obesity. Their mechanism may involve the direct stimulation of GLP-1 receptors in arteries and the renal system, enhancing endothelial function and exerting a vasodilator and natriuretic effect through the inhibition of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) [
41].
Safety and Tolerability:
Gastrointestinal adverse events, such as constipation, vomiting, diarrhea, and nausea, were reported in almost all studies analyzed. These events were typically transient, mild to moderate in severity, and subsided over time. However, gallbladder-related disorders, mostly cholecystitis, were reported in five studies, although the incidence was low among both GLP-1 receptor agonist and placebo groups [
25,
28,
29,
33,
34]. The GLP-1 receptor agonist groups also reported higher treatment discontinuations due to gastrointestinal disorders, especially during dose-escalation periods [
28,
29,
33]. This may be due to the tendency of GLP-1 receptor agonists to bind to receptors in the gastrointestinal tract, delaying gastric emptying and inhibiting intestinal peristalsis [
42].
Garvey et al. [
33], reported cases of malignant neoplasm, with two (1.3%) in the semaglutide group and four (2.6%) in the placebo group. Rubino et al. [
28], also reported malignant neoplasms in semaglutide, liraglutide, and placebo groups, but no solid evidence links GLP-1 receptor agonists to malignant neoplasm. Further research may be needed for conclusive evaluations. The liraglutide group reported more psychiatric disorders and one case of subclinical pancreatitis that did not require treatment, which may be related to previous findings of liraglutide slightly increasing the rate of insomnia and suicidal ideation [
43].
GLP-1 receptor agonists frequently cause gastrointestinal side effects, particularly during initiation and titration [
44,
45,
46]. Wharton et al. proposed the "three E's" approach for managing these side effects: Education and explanation to help patients understand potential side effects and mitigation strategies; Escalation to an appropriate dose using a gradual, individualized approach; and Effective management of gastrointestinal side effects using a stepwise severity-based approach [
47]. Overall, GLP-1 receptor agonists such as exenatide, liraglutide, semaglutide, and tirzepatide are generally well-tolerated.
Future Questions for Researchers and Gaps in Research:
The heterogeneity of study designs, which can introduce variations in techniques, patient demographics, and outcomes, may have an impact on the generalizability of results. While some studies have up to three-year follow-up periods, the long-term effects of GLP-1RAs have not been completely investigated beyond this time frame. The term ‘nondiabetic patients” may have been defined differently in different studies, which could lead to inconsistent reporting. It has also been noted that women and White participants predominate in several studies. Therefore, to address these shortcomings, future research should use well-designed trials with diverse populations, uniform definitions, and longer follow-up times.
Limitations:
Several limitations of this review warrant discussion. First, our analysis was confined to articles published within the last 10 years. This temporal limitation may have excluded earlier studies that could provide valuable insights or context for the current understanding of GLP-1RAs, including tirzepatide, in the management of obesity in nondiabetic patients.
Second, we focused exclusively on studies involving individuals aged 18 years and older. Consequently, the findings of this review cannot be generalized to pediatric or adolescent populations, which is a significant gap considering the rising prevalence of obesity in younger age groups.
Third, our review was limited to freely accessible articles. This restriction may have resulted in the exclusion of pertinent studies published in subscription-based journals, potentially introducing a selection bias. Freely accessible articles may not represent the entirety of available research, potentially impacting the comprehensiveness of our review.
Fourth, the search was confined to articles published in the English language. This linguistic limitation may have led to the exclusion of relevant studies published in other languages, thereby limiting the global applicability and generalizability of our findings.
Fifth, our review specifically targeted the efficacy and safety of GLP-1RAs, including tirzepatide, in the management of obesity in nondiabetic patients. This specific focus means that our review did not consider other pharmacological or non-pharmacological interventions for obesity, which may provide a more holistic view of the available treatment landscape.
Furthermore, while the existing data provide promising insights into the use of GLP-1RAs for the management of obesity in nondiabetic patients, there is a need for more extensive, long-term studies to better understand their efficacy, safety, and potential side effects. Current studies often have limited follow-up periods, which may not fully capture the long-term outcomes and risks associated with GLP-1RA treatment.
Finally, potential conflicts of interest and funding sources of the included studies were not systematically analyzed in this review. These factors could influence study outcomes and interpretations, underscoring the need for cautious interpretation of the results.
In summary, while our review sheds light on the potential of GLP-1RAs, including tirzepatide, for managing obesity in nondiabetic patients, these limitations highlight the need for further comprehensive and methodologically rigorous studies to deepen our understanding in this field.
Conclusions:
With acceptable safety and high compliance, exenatide, liraglutide, semaglutide, and tirzepatide can effectively improve the health and quality of life of obese patients without diabetes by significantly reducing body weight, BMI, and WC. They also have a positive effect on heart-related risk factors like blood pressure, glycemic control, nephropathy, lipid levels, serum insulin levels, and CRP profiles. Finally, they can decrease the risk of a composite of death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke among individuals with preexisting cardiovascular disease.
References
- Obesity. Accessed: November 20, 2023. https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity.
- American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines For Medical Care of Patients with Obesity - Endocrine Practice. Accessed: November 20, 2023. https://www.endocrinepractice.org/article/S1530-891X(20)44630-0/fulltext.
- Yumuk V, Tsigos C, Fried M, Schindler K, Busetto L, Micic D, Toplak H: European Guidelines for Obesity Management in Adults. Obes Facts. 2015, 8:402–24. 10.1159/000442721.
- Obesity: The New Global Epidemic Pharmacological Treatment, Opportunities and Limits for Personalized Therapy | Bentham Science. Accessed: November 20, 2023. https://www.eurekaselect.com/article/106651.
- Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N Engl J Med. 2017, 377:13–27. 10.1056/NEJMoa1614362.
- World Obesity Day Atlases | Obesity Atlas 2023. World Obes. Fed. Glob. Obes. Obs. Accessed: November 20, 2023. https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/?cat=19.
- NHLBI Obesity Education Initiative Expert Panel on the Identification E: Overweight and Obesity: Background. In: Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: The Evidence Report. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; 1998.
- Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association | Circulation. Accessed: November 20, 2023. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000973.
- Bessesen DH, Gaal LFV: Progress and challenges in anti-obesity pharmacotherapy. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6:237–48. 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30236-X.
- Dombrowski SU, Knittle K, Avenell A, Araújo-Soares V, Sniehotta FF: Long term maintenance of weight loss with non-surgical interventions in obese adults: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. The BMJ. 2014, 348:g2646. 10.1136/bmj.g2646.
- Webb VL, Wadden TA: Intensive Lifestyle Intervention for Obesity: Principles, Practices, and Results. Gastroenterology. 2017, 152:1752–64. 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.01.045.
- Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, et al.: 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS Guideline for the Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. Circulation. 2014, 129:S102–38. 10.1161/01.cir.0000437739.71477.
- Pharmacological Management of Obesity: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline | The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism | Oxford Academic. Accessed: November 20, 2023. https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/100/2/342/2813109?login=false.
- Nauck MA, Quast DR, Wefers J, Meier JJ: GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes – state-of-the-art. Mol Metab. 2020, 46:101102. 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101102.
- Ard J, Fitch A, Fruh S, Herman L: Weight Loss and Maintenance Related to the Mechanism of Action of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists. Adv Ther. 2021, 38:2821–39. 10.1007/s12325-021-01710-0.
- Mathiesen DS, Bagger JI, Bergmann NC, Lund A, Christensen MB, Vilsbøll T, Knop FK: The Effects of Dual GLP-1/GIP Receptor Agonism on Glucagon Secretion—A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20:4092. 10.3390/ijms20174092.
- Zhang F, Tong Y, Su N, Li Y, Tang L, Huang L, Tong N: Weight loss effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 mimetics on obese/overweight adults without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Diabetes. 2015, 7:329–39. 10.1111/1753-0407.12198.
- O’Neil PM, Birkenfeld AL, McGowan B, et al.: Efficacy and safety of semaglutide compared with liraglutide and placebo for weight loss in patients with obesity: a randomised, double-blind, placebo and active controlled, dose-ranging, phase 2 trial. The Lancet. 2018, 392:637–49. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31773-2.
- Guo X, Zhou Z, Lyu X, et al.: The Antiobesity Effect and Safety of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist in Overweight/Obese Patients Without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Horm Metab Res. 2022, 54:458–71.
- FDA Approves Novel, Dual-Targeted Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes | FDA. Accessed: November 22, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-novel-dual-targeted-treatment-type-2-diabetes.
- Willard FS, Douros JD, Gabe MBN, et al.: Tirzepatide is an imbalanced and biased dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist. JCI Insight. 5:e140532. 10.1172/jci.insight.140532.
- Dutta D, Surana V, Singla R, Aggarwal S, Sharma M: Efficacy and safety of novel twincretin tirzepatide a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist in the management of type-2 diabetes: A Cochrane meta-analysis. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2021, 25:475–89. 10.4103/ijem.ijem_423_21.
- Efficacy and safety of a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial - The Lancet. Accessed: December 4, 2023. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)01324-6/fulltext.
- Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes |, N.E.J.M. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes |, N.E.J.M. Accessed: December 4, 2023. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2107519?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200pubmed.
- Jastreboff AM, Aronne LJ, Ahmad NN, et al.: Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022, 387:205–16. 10.1056/NEJMoa2206038.
- Chou C, Chuang S: Evaluation of the efficacy of low-dose liraglutide in weight control among Taiwanese non-diabetes patients. J Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11:1524–31. 10.1111/jdi.13314.
- Gao X, Hua X, Wang X, Xu W, Zhang Y, Shi C, Gu M: Efficacy and safety of semaglutide on weight loss in obese or overweight patients without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 13:935823. 10.3389/fphar.2022.935823.
- Rubino DM, Greenway FL, Khalid U, et al.: Effect of Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Daily Liraglutide on Body Weight in Adults With Overweight or Obesity Without Diabetes: The STEP 8 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2022, 327:138–50. 10.1001/jama.2021.23619.
- Wilding JP, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al.: Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021, 384:989–1002.
- Zhang P, Liu Y, Ren Y, Bai J, Zhang G, Cui Y: The efficacy and safety of liraglutide in the obese, non-diabetic individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Afr Health Sci. 2019, 19:2591–9. 10.4314/ahs.v19i3.35.
- Lautenbach A, Wernecke M, Huber TB, et al.: The Potential of Semaglutide Once-Weekly in Patients Without Type 2 Diabetes with Weight Regain or Insufficient Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery—a Retrospective Analysis. Obes Surg. 2022, 32:3280–8. 10.1007/s11695-022-06211-9.
- Liu Y, Ruan B, Jiang H, et al.: The Weight-loss Effect of GLP-1RAs Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Non-diabetic Individuals with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2023, 118:614–26. 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.04.017.
- Garvey WT, Batterham RL, Bhatta M, et al.: Two-year effects of semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: the STEP 5 trial. Nat Med. 2022, 28:2083–91. 10.1038/s41591-022-02026-4.
- Lincoff AM, Brown-Frandsen K, Colhoun HM, et al.: Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2023, NEJMoa2307563. 10.1056/NEJMoa2307563.
- Anne Ottney: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for weight loss in adult patients without diabetes. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2013, 70:2097–103. 10.2146/ajhp130081.
- Zander M, Madsbad S, Madsen JL, Holst JJ: Effect of 6-week course of glucagon-like peptide 1 on glycaemic control, insulin sensitivity, and β-cell function in type 2 diabetes: a parallel-group study. The Lancet. 2002, 359:824–30. 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07952-7.
- Coskun T, Sloop KW, Loghin C, et al.: LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Mol Metab. 2018, 18:3–14. 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.09.009.
- Seino Y, Fukushima M, Yabe D: GIP and GLP-1, the two incretin hormones: Similarities and differences. J Diabetes Investig. 2010, 1:8–23. 10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00022.x.
- Healthcare G: EASD 2023: meta-analysis shows tirzepatide superiority to semaglutide. Clin. Trials Arena. 2023.
- Garvey WT, Frias JP, Jastreboff AM, et al.: Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity in people with type 2 diabetes (SURMOUNT-2): a double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. The Lancet. 2023, 402:613–26. 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01200-X.
- Del Olmo-Garcia MI, Merino-Torres JF: GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018:1–12. 10.1155/2018/4020492.
- Nauck MA, Kemmeries G, Holst JJ, Meier JJ: Rapid Tachyphylaxis of the Glucagon-Like Peptide 1–Induced Deceleration of Gastric Emptying in Humans. Diabetes. 2011, 60:1561–5. 10.2337/db10-0474.
-
Neuropsychiatric safety with liraglutide 30 mg for weight management: Results from randomized controlled phase, 2.; 3a trials -, P. M.C. Accessed: December 28, 2023.
- Wadden TA, Bailey TS, Billings LK, et al.: Effect of subcutaneous semaglutide vs placebo as an adjunct to intensive behavioral therapy on body weight in adults with overweight or obesity: the STEP 3 randomized clinical trial. Jama. 2021, 325:1403–13.
- A Randomized, Controlled Trial of 3.0 mg of Liraglutide in Weight Management | NEJM. Accessed: December 28, 2023. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa1411892?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Once-weekly tirzepatide versus once-daily insulin degludec as add-on to metformin with or without SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3): a randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 trial - The Lancet. Accessed: December 28, 2023. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)01443-4/fulltext.
- Full article: Managing the gastrointestinal side effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists in obesity: recommendations for clinical practice. Accessed: December 28, 2023. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00325481.2021.2002616.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).