1. Introduction
Drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), are aircraft that do not require an onboard human pilot [
1]. These vehicles can be operated remotely by a human pilot or autonomously without a remote pilot [
1,
2]. UAV technology encompasses the vehicles themselves, as well as the supporting hardware and software, sensors, microcontrollers, ground control stations, communication protocols, and user interfaces [
1,
2].
According to Gupta et al. [
3], the application fields of drones are growing exponentially, with the transportation sector being one of the most promising applications of UAVs. Additionally, various fields are highlighted in numerous studies where UAVs can be applied. UAVs can be used for meteorological purposes [
4], geodetic surveys [
5], infrastructure monitoring [
6,
7], wildfire observation [
8], rescue operations [
9], and cargo transportation [
10]. Furthermore, regarding a study by Ju and Son [
11], the agricultural use of UAVs has significantly reduced labor time and workforce requirements while also improving the efficiency of agricultural operations.
It is emphasized in the literature that researchers are currently seriously concerned with increasing the autonomy of UAVs. The use of autonomous aerial vehicles eliminates the need for human intervention, which reduces the risk of accidents caused by human error and inaccuracies due to disturbances during flight maneuvers [
12,
13,
14].
According to the study of Elmokadem and Savkin [
15], challenges are continually increasing with the development of UAV technology, particularly as these systems perform increasingly complex tasks and move towards fully autonomous operations that minimize human intervention. UAVs are often required to operate autonomously in unknown environments, relying solely on their onboard sensors to map their surroundings [
15]. Furthermore, it is stated by Elmokadem and Savkin [
15] that the challenge of autonomous navigation lies in the ability of the UAV to reach its target position without colliding with environmental obstacles. This challenge is particularly significant as safe navigation is essential to avoid damages and injuries [
15,
16].
It is emphasized by Saavedra-Ruiz et al. [
17] that autonomous landing is a capability essential for fully exploiting the potential of UAVs in various applications. According to Badakis et al. [
18], in order to move towards full autonomy of UAVs, the drone must be capable of autonomous takeoff and landing. Landing is a more complex process [
18]. Despite the ability of the drone to navigate based on its onboard GPS, the landing accuracy is typically within 1-2 meters [
18]. This is generally not satisfactory, for instance, when the drone needs to land on a hangar platform or a battery charging platform [
18].
In the study by Yang et al. [
19], the importance of the safe landing of drones is highlighted. A monocular vision-based autonomous landing system is proposed that uses optical equipment and image recognition technology to detect the position and environment of the drone. This system is particularly useful in the absence of GPS signals, when drones would be unable to land properly [
19]. The robustness of the system is confirmed by experiments, ensuring safe landings in unknown environments [
19].
The low interference tolerance of GPS systems is also highlighted by Yang et al [
19], meaning that onboard GPS receivers in drones can easily malfunction due to electronic interference. Consequently, drones may lose their navigation and positioning functions, which may result in an inability to land safely [
19]. According to Yang et al. [
19] there are other problems with GPS systems, such as weather factors and sunspots that can reduce signal strength, electromagnetic interference, strong magnetic fields, and the shielding effects of buildings, vehicles, trees, and metal parts, as well as high-rise buildings and densely packed building blocks. Due to the susceptibility of GPS signals to interference, further research is needed to improve UAV positioning and safe landing in situations where GPS signals are unavailable [
19]. This is crucial for both autonomous operations and remote pilot control [
19].
It is highlighted by Grlj et al. [
20] that despite continuous improvements in batteries, UAV flight time is still heavily limited by the constraints of lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries. A flight time of only 30 minutes per battery charge is mentioned by De Silva et al [
21]. This problem is partially solved by using docking stations [
20,
21,
22]. These platforms can be used to ensure safe landing, battery charging (or replacement), takeoff, and secure storage for UAVs [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. Additionally, the use of docking stations represents an advancement in the automation of UAV systems [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26]. Docking stations can also store UAVs, protecting them from adverse weather conditions [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26]. The takeoff and landing, as well as the flight maneuvers on the docking station, must be autonomous to minimize the need for human intervention [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26]. Therefore, UAV docking stations enable longer working hours for drones without requiring the operator to manually replace the battery [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26].
According to Grlj et al. [
20], precise positioning is crucial for accurate landings on a docking station due to constrained dimensions of the platform. The landing phase consists of several stages [
20]. The first is the approach phase [
20]. Generally, systems using the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) are sufficient to approach the docking station [
20].
Before landing, the next phase is the precise positioning of the UAV [
20]. This phase is crucial for a successful landing with minimal error [
20]. UAVs are typically positioned using markers placed on the docking station; however, other methods are also available for this purpose [
20,
27,
28,
29]. The primary goal of docking stations is often to charge the battery of the UAV. One possible solution for this is the use of wireless power transfer (WPT) systems [
20,
21].
According to Grlj et al. [
20], once a UAV has landed on the landing platform, further fine-tuning may be required to achieve the most accurate final position. This can be accomplished, for example, using some kind of mechanical system [
20]. The more accurately a UAV lands using visual and landing algorithms, the less mechanical fine-tuning is needed after landing [
20]. Therefore, developing and researching more accurate landing algorithms can minimize the mechanical adjustments required in docking stations for final positioning after landing [
20,
21].
It is also mentioned by Grlj et al. [
20] that Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) can also be used as moving landing platforms for UAVs.
Landing on moving platforms presents numerous technical challenges, including the limited size of the landing area (such as the roof of a car or the bed of a truck), the accuracy of speed estimation methods, and handling environmental disturbances, all of which affect the success of the landing [
30,
31,
32].
Several studies address the use of UAVs in maritime applications, where continuous research is needed to solve the landing of UAVs on moving marine vehicles. The research of Borowczyk et al. [
31] is also extended to UAV landings on marine vehicles. It is mentioned that the aim is to achieve extremely high precision during landing, given the limited dimensions of the ship deck. Additional challenges for UAV landings on ship decks are discussed by Wang and Bai [
33], such as the effects of wind and large ocean waves.
The importance of WPT systems is highlighted in the studies of Grlj et al. [
20] and De Silva et al. [
21]. As previously mentioned, the possibility of wireless charging is of great significance for drone autonomy, for example, following a landing on a docking station. According to Rohan et al. [
34], it is relatively difficult to autonomously land a drone on a charging station to achieve maximum efficiency in battery charging. It is highlighted in the research that wireless battery charging is less efficient if the drone is unable to land exactly within 100 mm of the target.
Achieving full autonomy in UAV flights requires high precision, even for wireless battery charging [
30,
34].
The WPT system uses electromagnetic coils on both the quadcopter and the charging station, which need to be aligned for efficient energy transfer [
30,
34]. Inaccurate landings of UAVs cause misalignment of the coils, resulting in energy loss and affecting the efficiency of the charging system [
30,
34].
A DJI Mavic Pro drone was tested during the research of Yoakum and Cerreta [
30]. Regarding the study, this type of drone is capable of precision landing if the feature is activated on the device. The precision landing feature enables the drone to land autonomously by taking an image of its surroundings during takeoff [
30,
35,
36]. This image is used as a reference during landing, and if the terrain features match the image taken during takeoff, the drone lands safely [
30,
35,
36].
It is mentioned by Yoakum and Cerreta [
30] that, based on information published by DJI, the accuracy of the Mavic Pro's precision landing is unknown. There is no public data available on the accuracy of precision or non-precision automated landings [
30]. It is also unknown whether the DJI Mavic Pro can land within 100 mm of the target, ensuring wireless charging of the drone [
30]. Moreover, it is unclear whether precision landings are more accurate or require smaller landing areas than non-precision landings [
30].
The following questions are sought to be answered in the research of Yoakum and Cerreta [
30]:
"Do the precision landing systems of the DJI Mavic Pro improve the accuracy of autonomous landing [
30]?"
"Is the DJI Mavic Pro able to land autonomously with a precision that allows wireless charging, which necessitates a tolerance of 100 mm [
30]?"
According to Yoakum and Cerreta [
30], the answers to these questions can determine whether the DJI Mavic Pro is suitable for applications requiring landing in confined spaces, such as wireless charging, emergency landings, or the use of small docking stations.
A total of 128 measurements were conducted by Yoakum and Cerreta [
30], with 64 measurements performed with the precision landing function enabled (PLON) and 64 measurements with the precision landing function disabled (PLOFF). In the latter case, only the initial home position GPS data was used as a reference for landing at the starting location. In the experiments, the drone was always launched from the same starting point (Home Position) on a platform, then the drone followed a path, and subsequently the Return-to-Home (RTH) command was issued, allowing the UAV to land autonomously. The landing position was compared with the initial position. A two-tailed, two-sample t-test was used to examine whether there was a statistically significant difference between the PLON and PLOFF states, and a one-tailed, one-sample t-test was used to examine whether the DJI Mavic Pro could land exactly within 100 mm of the target. According to Yoakum and Cerreta [
30], the tests were conducted in calm, sunny weather.
The research results of Yoakum and Cerreta [
30] demonstrated that the DJI Mavic Pro is able to land within 100 mm of the target in calm weather conditions, making it suitable for wireless charging based on the hypothesis of Rohan et al. [
34]. Additionally, it can be derived from the results that there is a statistically significant difference between the PLON and PLOFF states, meaning that the PLON state improves the accuracy of the autonomous landing of the DJI Mavic Pro [
30].
The experiments of Yoakum and Cerreta [
30] were conducted in calm weather, using the DJI Mavic Pro drone. In their work, it was suggested to conduct the experiment with other types of drones and in harsher weather conditions.
Measurements were conducted using a DJI Mavic 2 Pro UAV by the authors of this article. The aim of the research is to examine whether, based on the methods mentioned by Yoakum and Cerreta [
30], the precision landing systems of the DJI Mavic 2 Pro improve the accuracy of autonomous landing in constant wind and strong gusts, and whether there is a significant difference between the PLON and PLOFF states during landing in windy conditions. Additionally, the study aimed to determine whether the DJI Mavic 2 Pro is able to land autonomously with the accuracy required for wireless charging, even on a docking station, with a tolerance of 100 mm in strong winds.
The results of the authors of this article were also compared with those of Yoakum and Cerreta [
30] to see how the newer, wind-tested DJI Mavic 2 Pro performs compared to the older, calm-weather-tested DJI Mavic Pro. This allows for assessing the impact of technological advancements and whether the newer model performs better in windy conditions than the older model in calm weather.
No similar measurements have previously been conducted in windy conditions to examine the landing accuracy of the DJI Mavic 2 Pro. Similar to the DJI Mavic Pro, public data is not available on the accuracy of precision or non-precision automated landings for the DJI Mavic 2 Pro. As with the DJI Mavic Pro, it is unknown whether the DJI Mavic 2 Pro can land within 100 mm of the target, ensuring wireless charging for the drone. It is also unknown whether precision landings are more accurate or require smaller landing areas than non-precision landings for the DJI Mavic 2 Pro.
For more accurate comparison, 64 measurements were also conducted by the authors of this article each in PLON and PLOFF states, similar to the study by Yoakum and Cerreta [
30].
The new findings of this research on the DJI Mavic 2 Pro allow for assessing the impact of technological advancements and how much better the newer models perform under challenging weather conditions. Additionally, based on the research results, it is possible to conclude to what extent the DJI Mavic 2 Pro drones can be applied in various industries where autonomous landing and accuracy are of paramount importance. Moreover, the results can provide valuable information for developers to further refine and optimize precision landing systems.
2. Introduction to the DJI Mavic 2 Pro
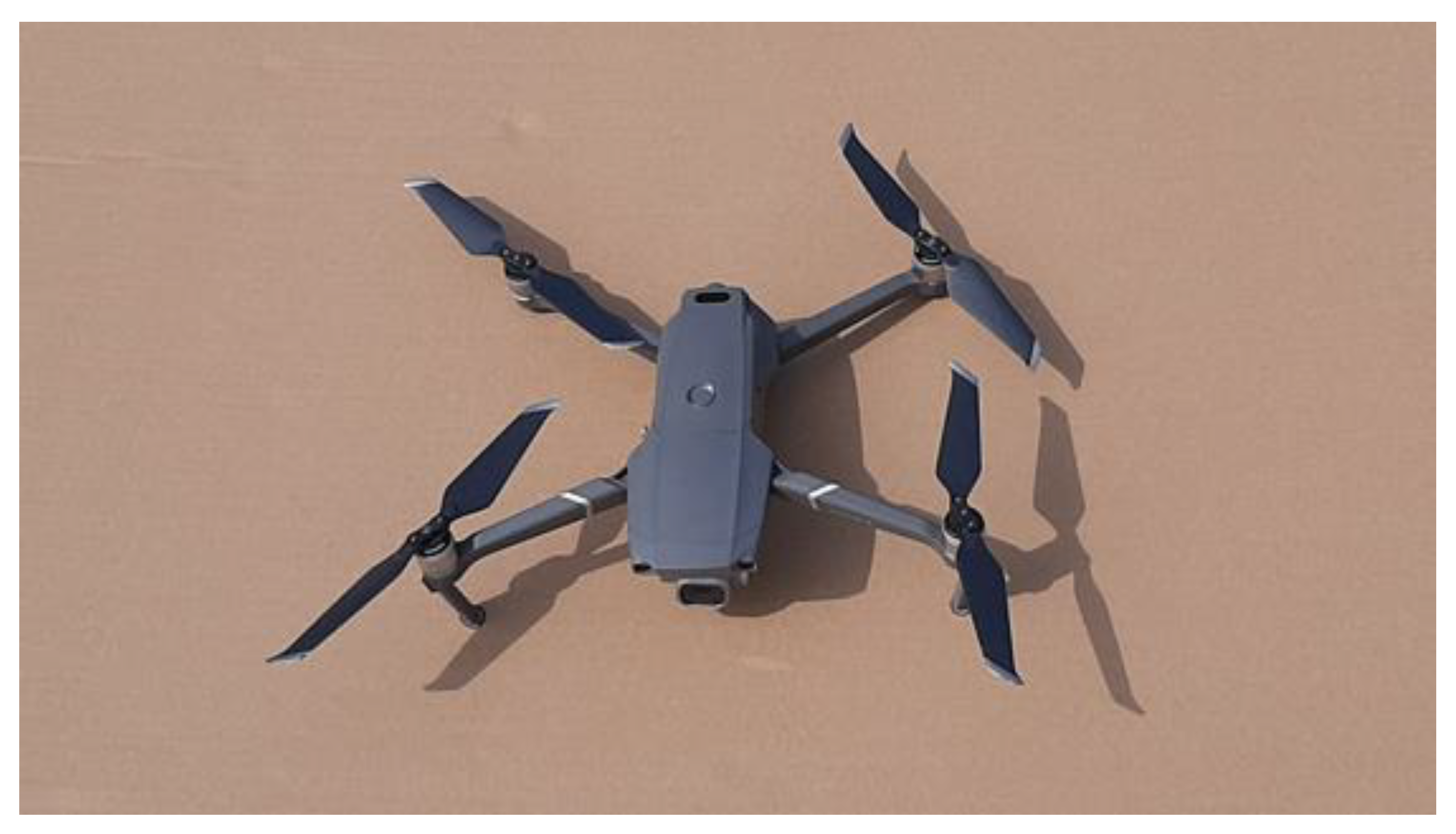
The DJI Mavic 2 Pro is among the low-cost drones and is becoming increasingly popular in various application areas [
36]. The DJI Mavic 2 Pro UAV is shown in
Figure 1.
This type of quadcopter weighs 907 grams [
37]. The device is equipped with a sophisticated gimbal that stabilizes the camera [
36]. The DJI Mavic 2 Pro uses built-in sensors to detect and avoid obstacles and automatically returns to the starting point before the battery runs out or, for example, after issuing the RTH (Return-to-Home) command [
36,
37].
The DJI Mavic 2 Pro quadcopter is fast (with a maximum speed of 72 km/h), quiet, and can fly up to 8 km horizontally from the remote controller [
37,
38,
39]. According to Vellemu et al. [
38], the DJI Mavic 2 Pro is equipped with obstacle sensors on all six sides, with front and rear collision avoidance technology, enabling it to easily avoid obstacles in an autonomous way. The DJI Mavic 2 Pro uses the dual satellite system, for example, for precision flight, homing, and obstacle avoidance [
38]. This is important, for instance, during UAV landing to avoid accidents [
38]. The Mavic 2 Pro uses a four-cell lithium polymer (LiPo) battery with a capacity of 3850 mAh, which can last up to 31 minutes of flight time in calm weather, at a constant flight speed of 25 km/h [
37,
38,
39].
The DJI Mavic 2 Pro is capable of using the precision landing function. It is mentioned in the user manual issued by DJI [
37] that DJI Mavic 2 Pro drones use advanced terrain mapping technology, which automatically compares the current terrain features with the home position data during the return process. If the terrain features match, the drone initiates the landing [
37]. The DJI GO 4 app provides an error message if the matching fails [
37]. To achieve precise landing, it is necessary to ensure that the home position is recorded at takeoff and that the terrain features there remain unchanged. Additionally, the drone must ascend at least 7 meters vertically before horizontal movement, and the terrain features must be distinctive, with lighting conditions not being too bright or too dark [
37]. During the precision landing process, it is possible to accelerate the landing by moving the throttle stick downward or stop the landing by moving the control sticks in any direction; in the latter case, the drone will land vertically if the control sticks are released [
37].
The DJI Mavic 2 Pro is compatible with the DJI GO 4 application [
37,
39]. The application allows users to control the drone directly through their smartphone or tablet, as well as record videos and take photos [
40,
41,
42]. Data in the application, such as GPS position, altitude, speed, and other flight data, help users track the movement and status of their drones. The DJI GO 4 also plays an important role in managing the data captured by the drone, including videos and photos, which can be edited and shared through the application [
37,
40,
41,
42].
The purpose of this article is to conduct measurements with the DJI Mavic 2 Pro in windy conditions. Therefore, the most important data from the device for the measurements was the maximum wind speed at which it can be flown. According to information published by DJI, the maximum wind speed the drone can withstand is 29-38 km/h [
36,
39]. The measurements were carried out in constant 19 km/h wind, with gusts reaching 38 km/h during the test. This is the limit that the DJI Mavic 2 Pro can withstand, according to DJI.
3. Presentation of the Measurement Conditions
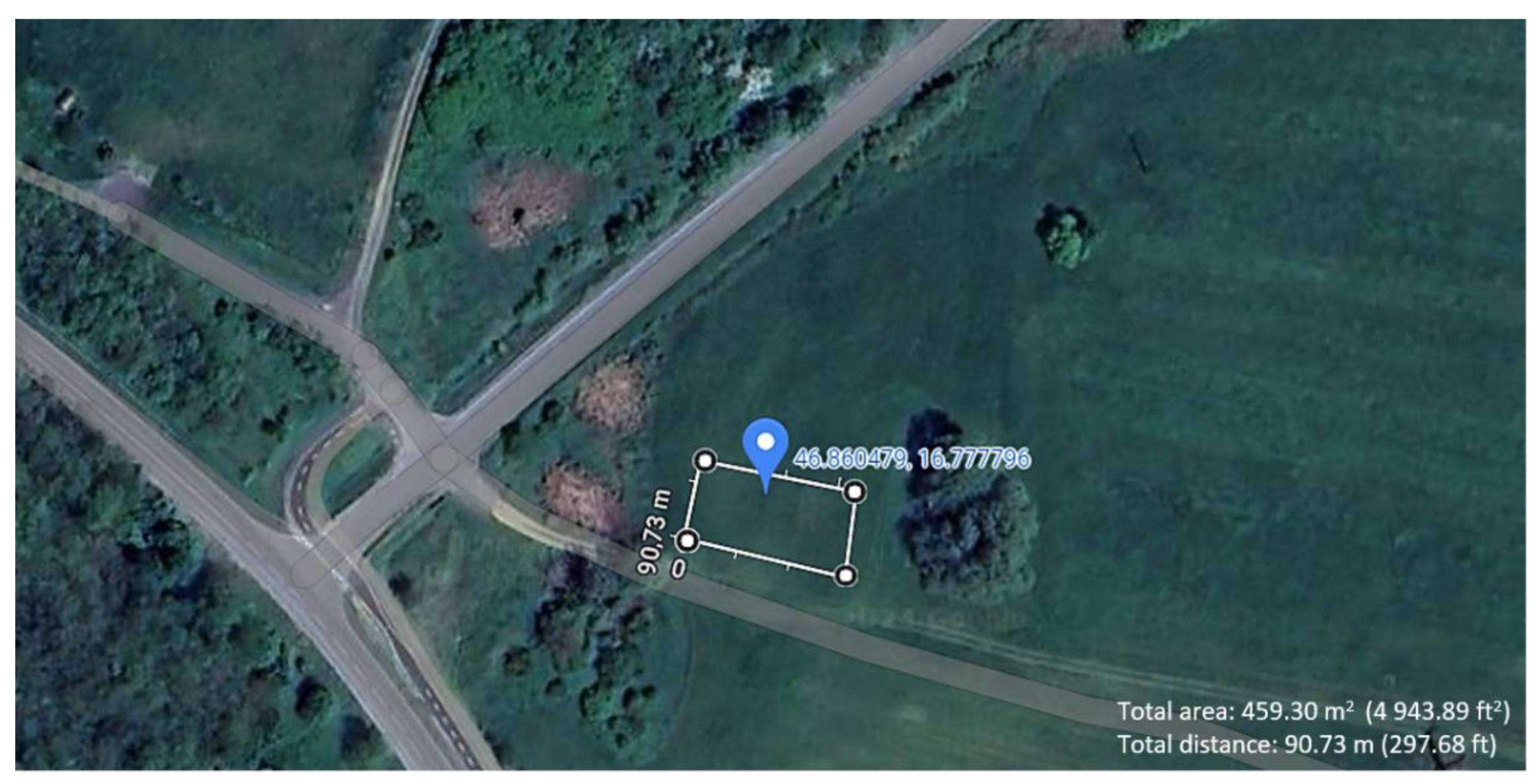
The measurements were carried out in the outskirts of the village of Teskánd, in Zala County, Hungary. The primary criteria for selecting the measurement location were the presence of few environmental obstacles, ample space, and distance from densely populated areas. The measurement site is illustrated in
Figure 2 below.
In
Figure 2 above, the coordinates of the location (46.86°N and 16.78°E) are provided, as well as the size of the area designated for drone operations.
Figure 2 was created using Google Maps [
43].
The essence of the measurements was to conduct the tests in windy conditions; therefore, it was challenging to pre-select a guaranteed suitable occasion. It was crucial that the wind speed posed a challenge to the UAV, approaching the specified limits (29-38 km/h) of the manufacturer, but not so strong as to make the flight operation difficult or even impossible. The measurements were conducted on Sunday, April 21, 2024, between 2:00 PM and 8:00 PM.
During the measurements, it was ensured that all 128 measurements were performed on the same day. This was to assure that all measurements were carried out under the same environmental conditions for more accurate and reliable results.
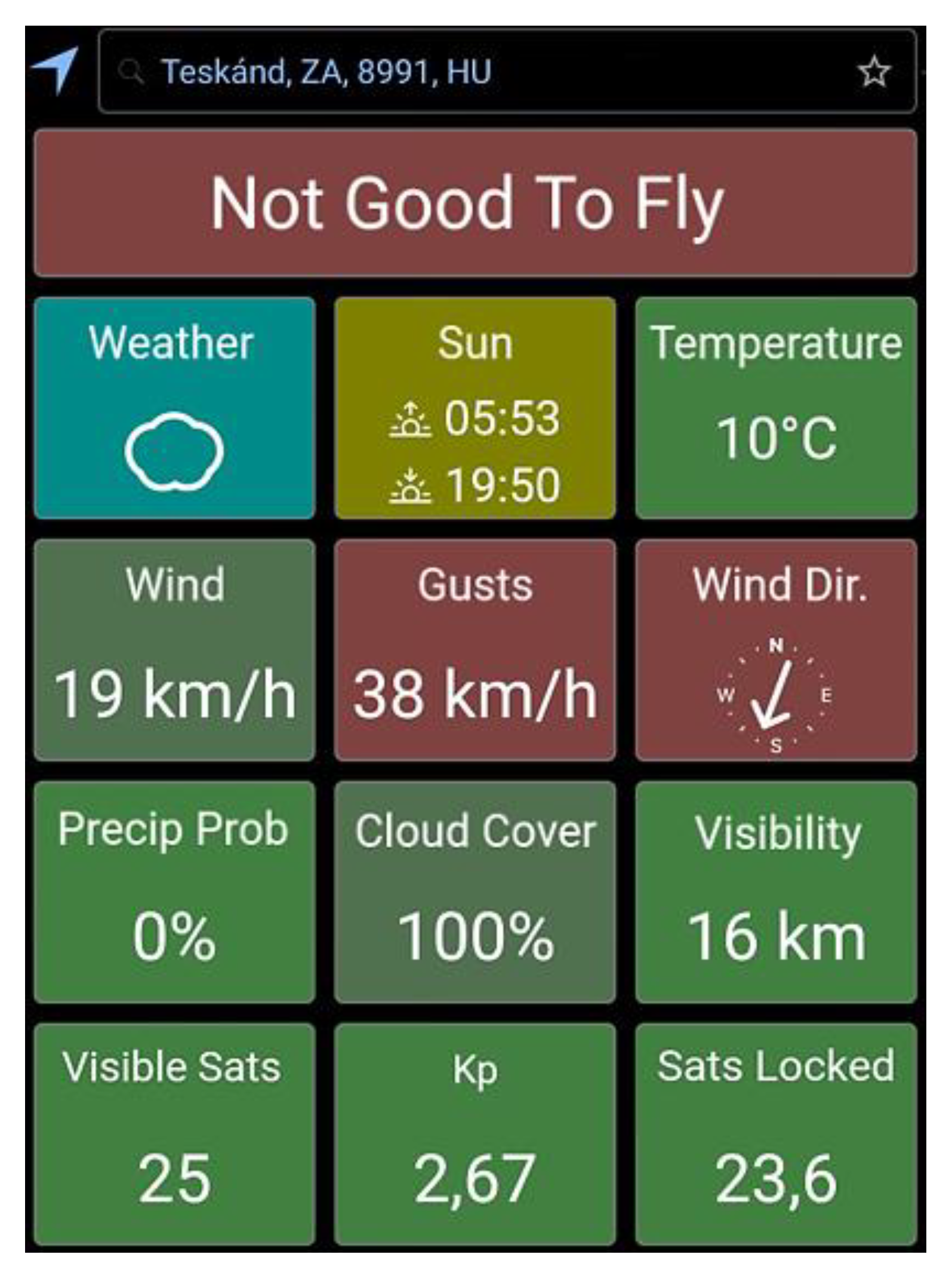
On the specified day, the wind strength was checked using the UAV Forecast application. A screenshot of this can be seen in
Figure 3 below.
On the day of the measurement, the temperature was 10°C, the wind speed was 19 km/h, with gusts up to 38 km/h. The sky was clear, and the weather was sunny. Due to the wind strength, the UAV Forecast application did not recommend flying, and the DJI GO 4 application used during the flight continuously issued warnings because of the strong wind.
The constant wind speed of 19 km/h was from the north-northeast direction towards the south-southwest direction, according to the UAV Forecast application. This wind direction had less influence on the movement of the drone. However, the 38 km/h gusts, which hit the drone from the side, significantly displaced the drone during landing, especially if the gust occurred at the moment of landing.
4. Preparations and Measurements for Executing the Test
At the beginning of the drone operation, a 195×173 cm cardboard sheet (serving as a landing platform) was fixed on grassy ground to examine the landing of the UAV on a homogeneous surface. Due to the strong wind, six metal stakes were used to secure the cardboard sheet. If the cardboard sheet moves because of the strong wind, the measurement would be invalidated. In such a case, the results measured up to that point would need to be considered null and void due to the displacement of the measured positions and the home position recorded by the drone before the first takeoff.
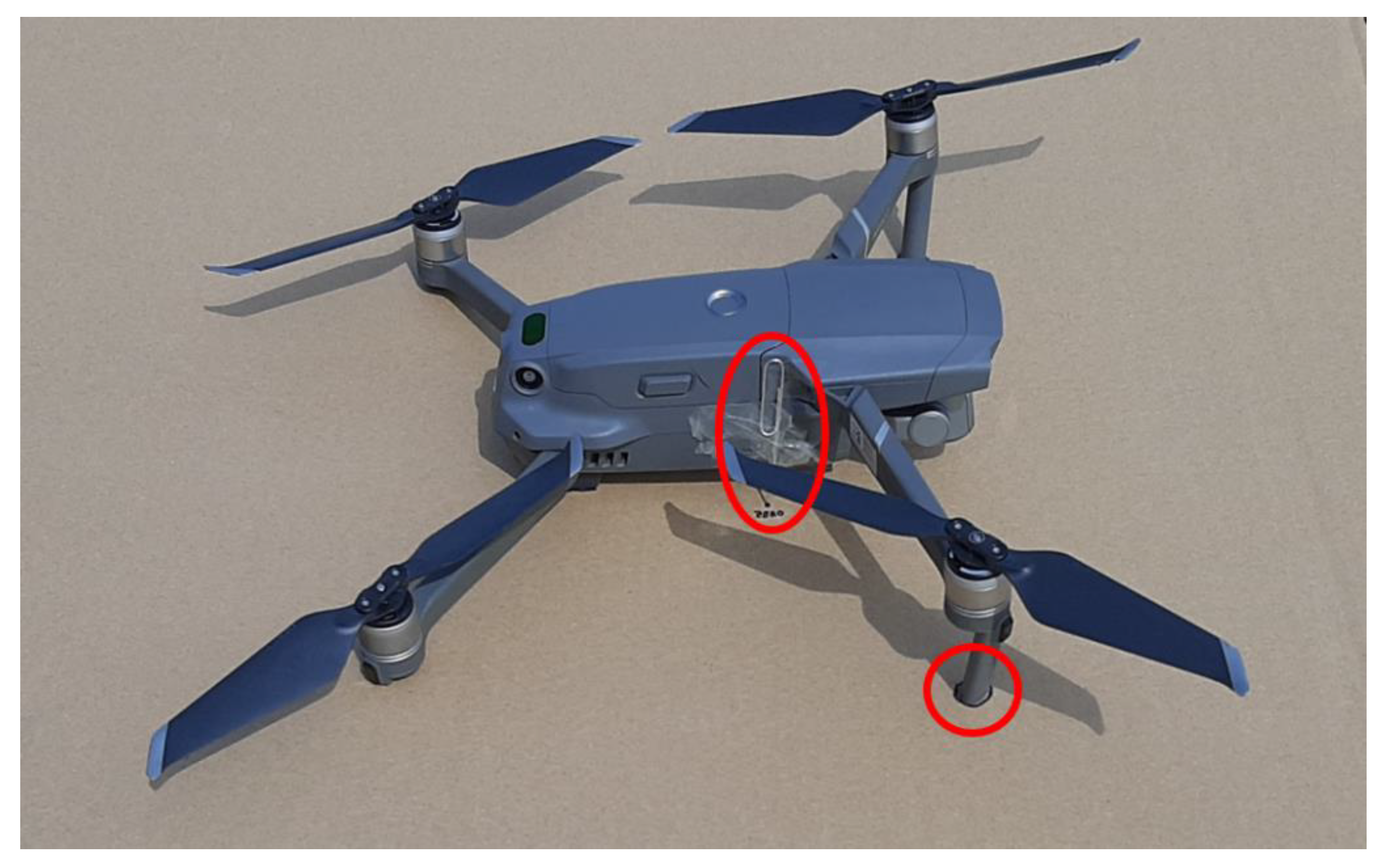
An important element in preparation of the measurements was determining the starting point of the UAV. Before each measurement, the drone needed to be placed precisely at this initial point, which would serve as the home position of the drone. The first two landing legs of the drone, as well as a paperclip marker attached to the drone, were marked on the cardboard sheet. This ensured that the starting point for all measurements would always be the same initial home position. This is illustrated in
Figure 4, which shows one of the landing legs of the drone as it was plotted on the landing platform. The figure also shows the metal paperclip attached to the drone body, which was used to mark the landing positions.
Since the paperclip marker was attached to the side of the drone body, as shown in
Figure 4, it is offset both longitudinally and laterally from the center of the drone. Considering the front camera position as the front of the UAV, the paperclip marker was displaced by 1.7 cm longitudinally and 3 cm laterally. Therefore, after landings, the measurement points on the cardboard must be corrected both longitudinally and laterally to recalibrate the measurement results to the center of the UAV. Naturally, the position of the marker must also be recalibrated at the starting home position to ensure all measurements are referenced to the center of the UAV. To facilitate the measurement process, the drone always faced the same direction during flight, meaning no rotation around the vertical axis was performed during the flights. This does not affect the measurement results but makes it easier to recalibrate the measurement points to the center of the drone.
Takeoffs were always performed from the same initial position. Throughout all measurements, the UAV was under the control of a remote pilot, except during landings when the drone landed autonomously upon issuing the RTH command. A relatively simple flight path was chosen for the test, which could be easily followed by the remote pilot.
First, 64 measurements were conducted with the precision landing function enabled. According to the user manual issued by DJI for the DJI Mavic 2 Pro [
37], the UAV automatically scans and attempts to identify terrain features for using the precision landing function. When the terrain matches the takeoff terrain of the UAV, the drone initiates landing upon issuing the RTH command [
37]. If terrain matching fails, the DJI GO 4 application displays an error message for the remote pilot [
37]. In the PLON state, the UAV must ascend vertically by 7 meters at takeoff before moving horizontally [
37]. During this maneuver, the UAV records the terrain features using its sensors [
37]. The terrain features of the starting point must remain relatively unchanged for the UAV to use the precision landing function to return to the home position [
37]. It is important that the environment is neither too dark nor too brightly lit [
37].
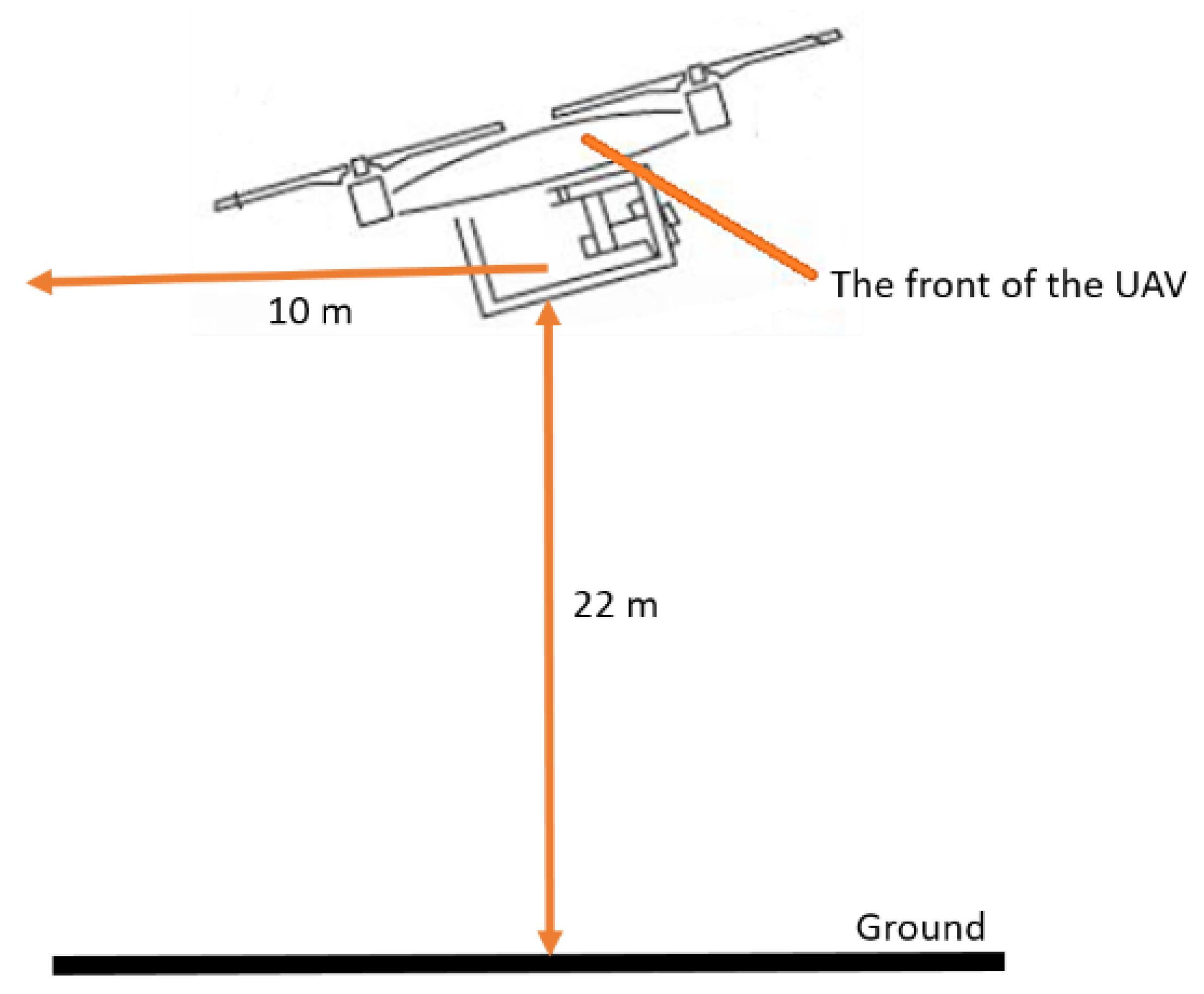
During the tests, when using the precision landing function, the UAV was always elevated to 22 meters above the starting point by the remote pilot. No horizontal displacement occurred during this maneuver. Subsequently, the drone was moved 10 meters backward by the remote pilot. The drone operation is illustrated in
Figure 5.
When the drone reached the end of the route, the RTH command was issued, initiating the autonomous landing of the drone towards the initial home position. Since the drone was only displaced backward, no vertical axis rotation was necessary; the drone proceeded forward and then descended towards the home position. After landing, the position of the marker paperclip was flagged on the cardboard, and then this point was recalibrated according to the center of the drone. Subsequently, the central position obtained during landing could be measured relative to the initial starting point. On the cardboard used to record the landing, a note was made next to each recorded point indicating the number of measurements performed. Thus, 64 measurement results were recorded during the examination.
Subsequently, additional measurements were conducted with the precision landing function disabled.
According to the DJI Mavic 2 Pro user manual [
37] published by DJI, to disable the precision landing function, the drone must be displaced horizontally while ascending, before reaching a height of 7 meters [
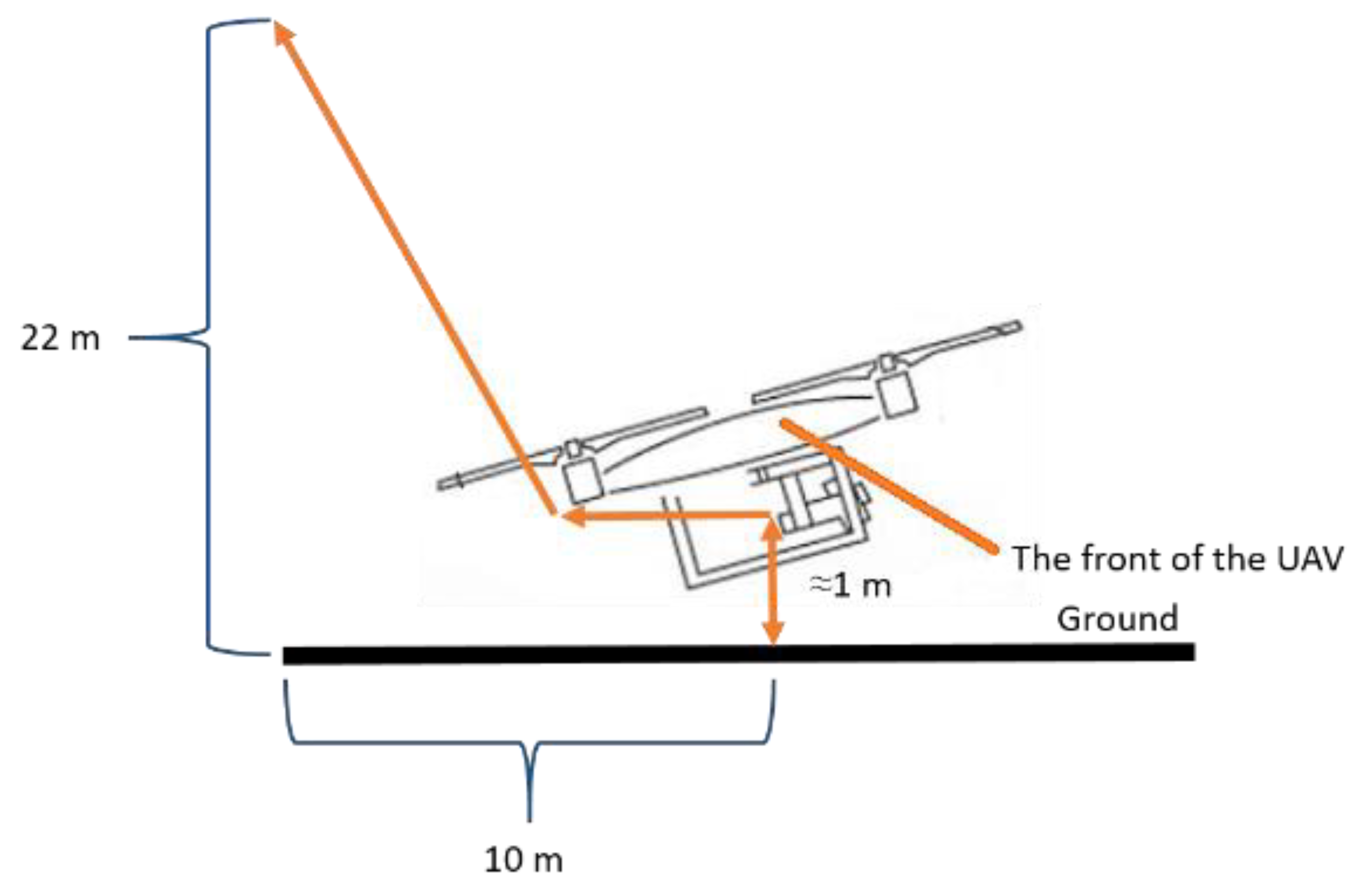
37]. In the PLOFF state, the remote pilot controlled the drone as shown in
Figure 6.
After takeoff, when the drone was approximately 1 meter above the ground, the UAV was displaced horizontally, backward from the vertical position, so the UAV was unable to map its surroundings and the precision landing function was deactivated. Subsequently, the remote pilot began the ascent of the drone to a height of 22 meters, while continuing the horizontal, backward movement for a distance of 10 meters. Then the RTH command was issued, and the drone landed in the vicinity of the home position relying on the GNSS positioning system.
The measurement of the landing point from the starting position is the same as in the PLON case. In the PLOFF state, 64 measurement points were also recorded, which were marked in a different color on the landing platform compared to the previous measurement results.
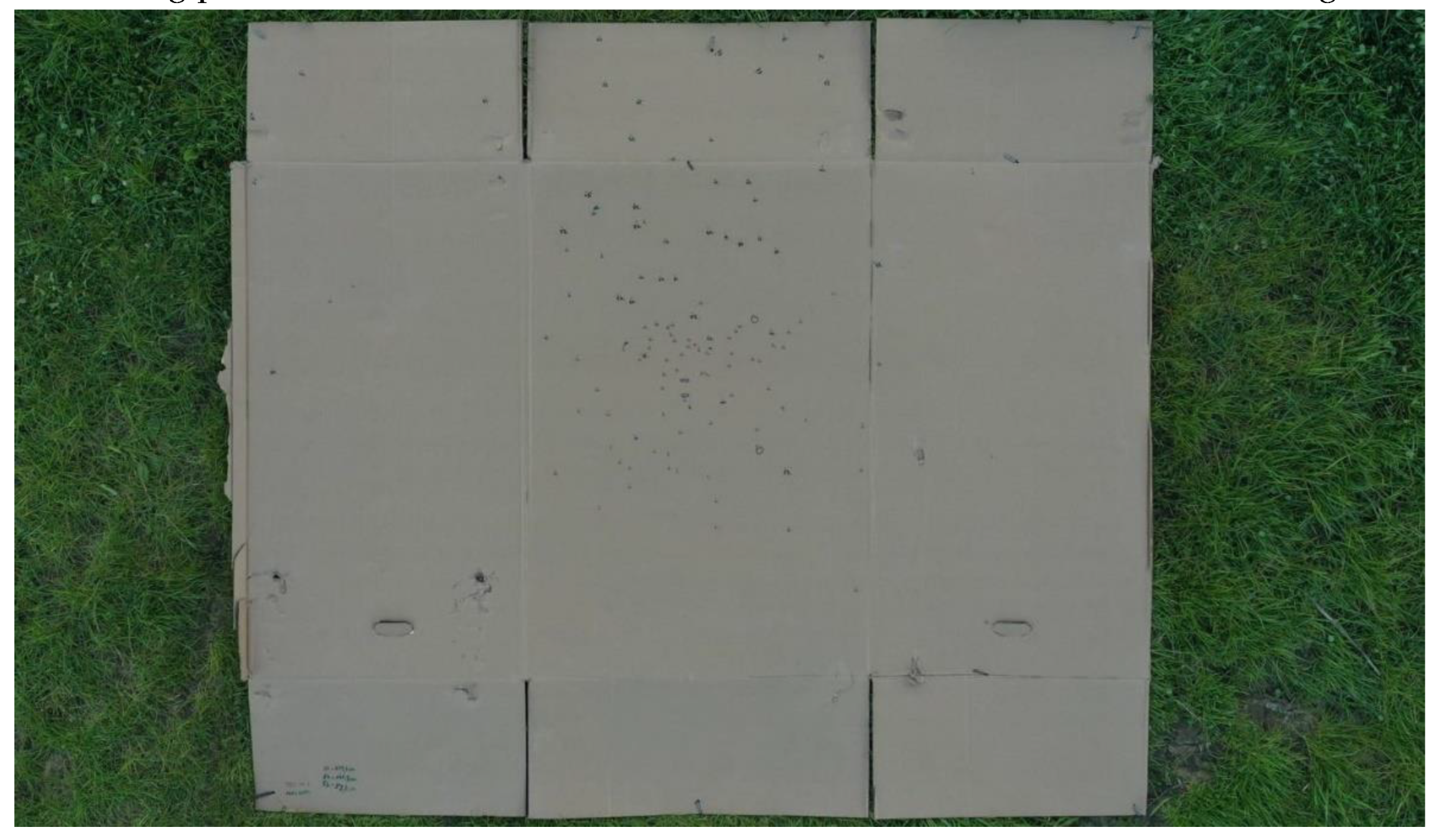
The landing platform after the PLON and PLOFF measurements is illustrated in
Figure 7.
The majority of the measurement results fell within the middle third of the landing platform. More measurement results fell in the upper section of the platform in the PLOFF state.
5. Presentation and Analysis of Measurement Results
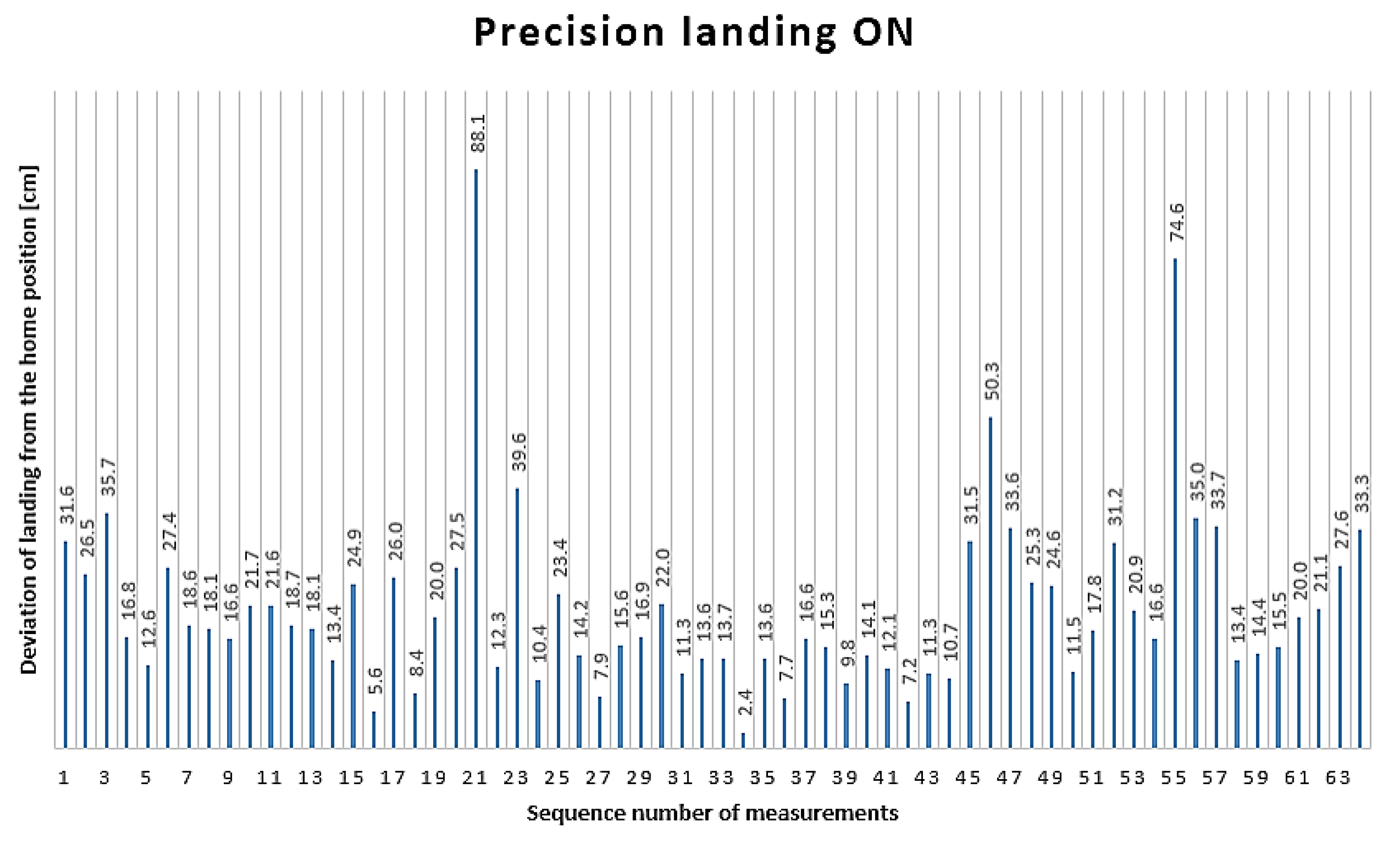
All 64 measurement results obtained in the PLON state are illustrated in
Figure 8. The horizontal axis of the graph shows the measurement number. The distance of the landing from the home position, measured in centimeters, is indicated by the values on the bars.
The farthest landing from the home position was 88.1 cm, recorded during the 21st landing, whereas the closest landing to the home position was 2.4 cm, recorded during the 34th measurement.
The average deviation from the home position in the PLON state was 21.4 cm, with a standard deviation (SD) of ±14.2 cm. The 95% confidence interval (CI) ranges from 17.9 to 24.9 cm.
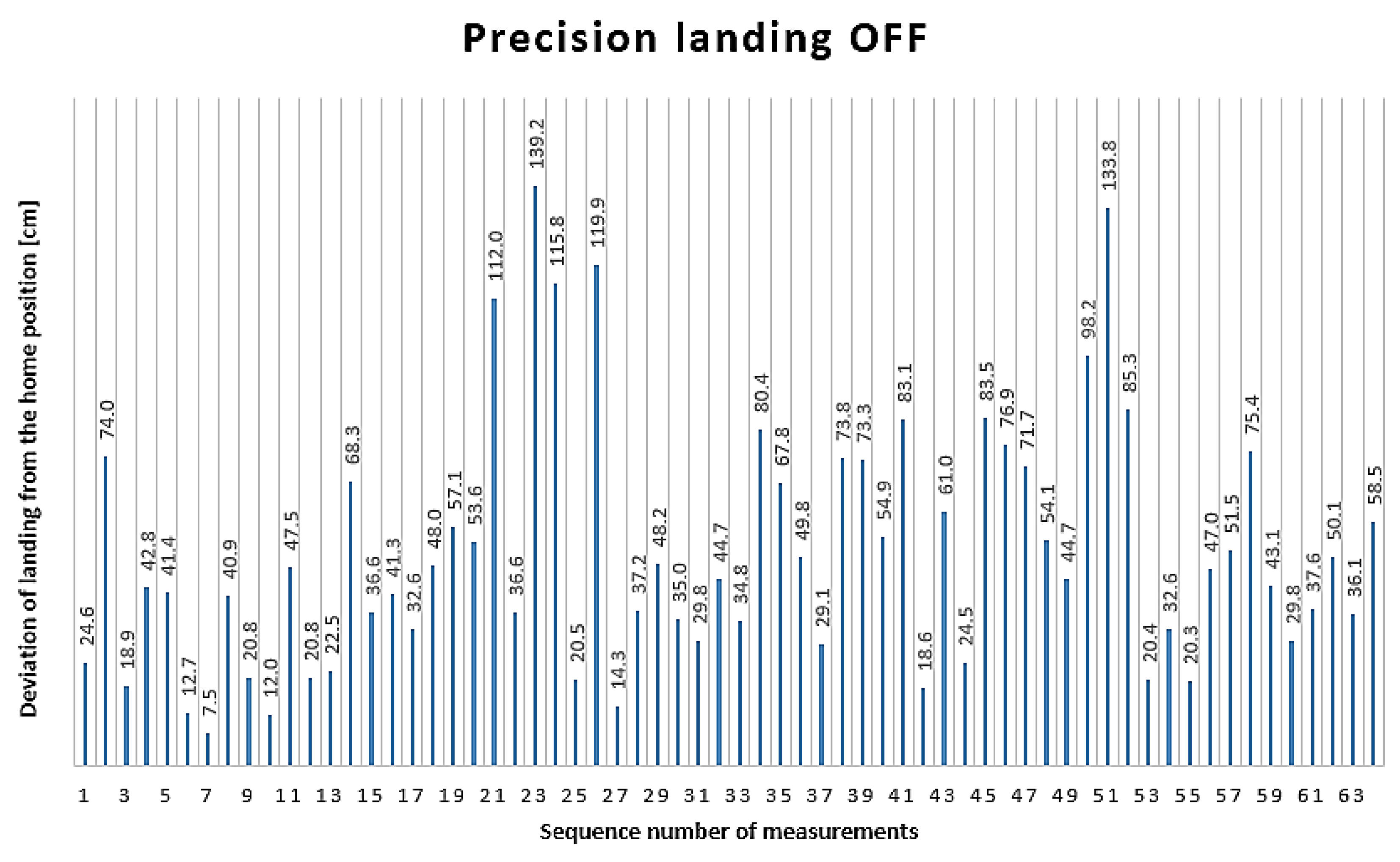
All 64 measurement results obtained during the PLOFF state are illustrated in
Figure 9. In this case, the horizontal axis of the graph also shows the measurement numbers. The distance of the landing from the home position, measured in centimeters, is indicated by the values on the bars.
The farthest landing from the home position was 139.2 cm, recorded during the 23rd landing, while the closest landing to the home position was 7.5 cm, recorded during the 7th measurement.
The average deviation from the home position in the PLOFF state was 51.2 cm, with a standard deviation of ±30.1 cm. The 95% confidence interval ranges from 43.9 to 58.6 cm.
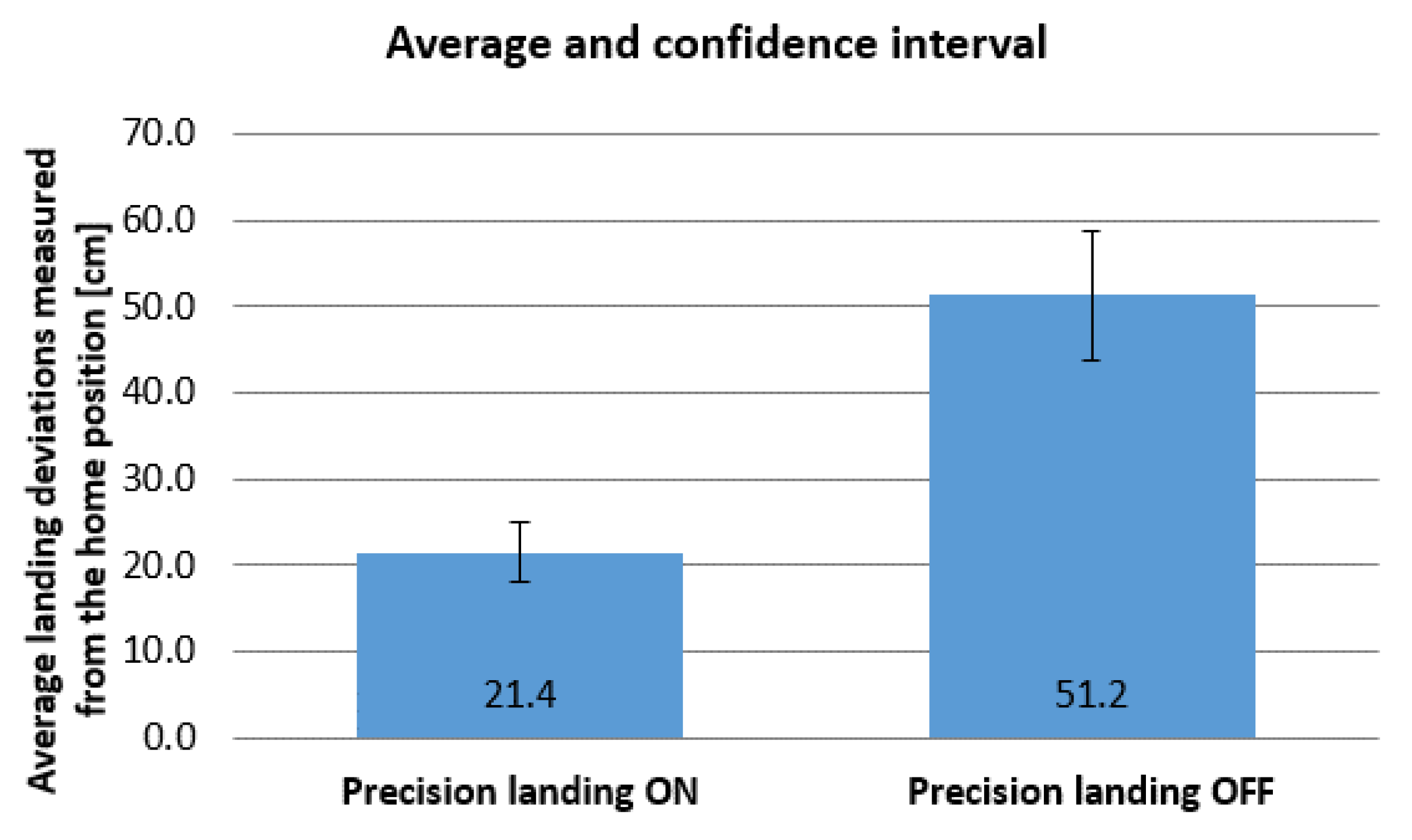
The average and confidence interval values are illustrated in
Figure 10 on a bar chart for the cases when the precision landing function is enabled and disabled. The average deviations from the home position, measured in centimeters, are shown on the vertical axis. The confidence intervals are represented by the sections indicated on the bar charts.
Based on the above graphs, it can be stated that activating the precision landing function results in more reliable and accurate landings, even when the UAV flies in 19 km/h wind with gusts up to 38 km/h.
Based on the measurement data, it was examined whether there is a statistically significant difference between PLON and PLOFF when the tests are conducted in a constant wind speed of 19 km/h with gusts up to 38 km/h.
According to the H10 null hypothesis, there is no statistically significant difference in landing accuracy between PLON and PLOFF under a constant wind speed of 19 km/h with gusts up to 38 km/h.
Conversely, it is stated in the H11 alternative hypothesis that there is a statistically significant difference in landing accuracy between PLON and PLOFF under a constant wind speed of 19 km/h with gusts up to 38 km/h.
To conduct this test, a two-tailed, two-sample t-test was used to statistically compare the average distances between landings in PLON and PLOFF states. The result is considered significant for p≤0,05.
The t-test value is p=2·10-10, so the null hypothesis is rejected as p<0.001. Based on the result, it can be stated that there is a statistically significant difference in landing accuracy between PLON and PLOFF under a constant wind speed of 19 km/h with gusts up to 38 km/h.
With the precision landing function enabled, further examination was conducted based on the measurement data in this state. The objective was to determine whether the DJI Mavic 2 Pro can autonomously land with sufficient accuracy to enable wireless charging, which requires the drone to be able to land within 100 mm of the designated landing site [
30,
34].
The H20 null hypothesis is that the DJI Mavic 2 Pro is able to land within 100 mm of the designated landing site for wireless charging under a wind speed of 19 km/h with gusts up to 38 km/h.
The H21 alternative hypothesis is that the DJI Mavic 2 Pro UAV is unable to land within 100 mm of the designated landing site for wireless charging under a wind speed of 19 km/h with gusts up to 38 km/h.
To conduct the examination, a one-tailed, one-sample t-test was used, also with a significance level of p≤0.05. In this case, the one-sample t-test value is p=1·10-8, thus the p-value is significant, p<0.001, providing sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis. As a result, it can be stated that the DJI Mavic 2 Pro UAV is unable to land within 100 mm of the designated landing site for wireless charging under a wind speed of 19 km/h with gusts up to 38 km/h.
It is indicated by the result that under such wind conditions, the DJI Mavic 2 Pro UAV is unable to land within 100 mm of the designated landing site for wireless charging, even with the precision landing function enabled.
7. Conclusion
New findings on the landing performance of the DJI Mavic 2 Pro in strong winds were presented in this article. It was established that there is a statistically significant difference in landing accuracy between the PLON and PLOFF functions under constant wind speeds of 19 km/h and gusts up to 38 km/h. Furthermore, based on the measurement results, it was determined that the DJI Mavic 2 Pro UAV is not suitable for the 100 mm precision landing required for wireless charging in such strong winds, even in the PLON state. The results were compared with experimental results obtained by other authors using the DJI Mavic Pro drone in calm and clear weather.
Based on the examination results, it can be stated that wind conditions critically impact the operational efficiency and safe operation of drones.
In subject to the results of this paper, it is recommended to further investigate the precision landing capabilities of the DJI Mavic 2 Pro and other types of drones in different wind conditions. In this way, the data obtained from the measurement results presented in this article can be validated and detailed guidelines can be developed for the efficient and safe use of drones, including for wireless charging on a docking station in strong winds. Additionally, it is important to reproduce the results of this study under similar conditions to compare the obtained data with the measurement results of this article.
Further research is also recommended to examine the effects of different lighting conditions, both with the precision landing function enabled and disabled. These studies would significantly contribute to the advancement of drone technology and the broader application of precision landings.
Further aim of the authors is to conduct the above-mentioned measurements with the DJI Mavic 2 Pro in calm weather and compare them with the behavior observed in strong winds. Based on previous research by other authors, the DJI Mavic Pro was able to land accurately under calm conditions, effectively performing wireless charging. Since the DJI Mavic 2 Pro is a newer model, it is likely that this type will also be able to land within 100 mm of the target in calm weather. The assumption could be confirmed by tests conducted in calm weather with the DJI Mavic 2 Pro, providing further evidence of the accuracy and reliability of the drone.
In addition, examining the distribution function of the measurement results could provide further valuable information for analyzing the landing accuracy and reliability of drones. The distribution function could help to explore the behavior of drones under different environmental conditions and identify the factors that most significantly affect landing accuracy. However, the current 64-64 measurement results in PLON and PLOFF states are probably insufficient to obtain a reliable distribution function. Therefore, further measurements with larger sample sizes (e.g., 500 measurements) are recommended to achieve more accurate and statistically significant results.
Such research could also significantly contribute to the development of drone technology and the broader application of precision landings, particularly for purposes like wireless charging or landing in confined spaces in strong winds.
It is important to note, however, that the limited battery capacity of drones poses a challenge for conducting a larger number of measurements. Frequent battery replacement or recharging is required, which significantly increases the measurement duration. During this time, weather conditions may change, potentially reducing the accuracy and reliability of the results. Considering these limitations, further research and development are needed to ensure optimal measurement conditions for testing the precision landing capabilities of drones.