1. Introduction
After more than a century, when it was first described, etiology and course of sarcoidosis remain largely unknown [
1]. Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory condition that can affect multiple organ systems. It is characterized by the formation of non-caseating granulomas in various organs, ultimately resulting in decreased organ function [
2]. The lungs, peripheral lymph nodes, central nervous system, skin, and the eye are most commonly involved [
3].
Albeit rare, cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) is potentially life-threatening. Moreover, CS patients have substantially impaired quality of life and worse clinical outcomes when compared to patients with other sarcoidosis manifestations [
4]. In CS, the formation of non-caseating granulomas can occur in all three layers of the heart although myocardial involvement is most prevalent.
Presentation of CS is heterogenous. It may be asymptomatic but may as well present as life-threatening arrythmia, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and even sudden cardiac death. This diverse presentation poses a great diagnostic challenge requiring specific diagnostic and prognostic algorithms.
2. Epidemiology
Distinct variations exist in the occurrence and frequency of sarcoidosis across various geographical regions and ethnic groups. Sarcoidosis demonstrates the highest incidence rates in Scandinavian countries, ranging from 11 to 24 cases per 100,000 individuals per year [
5,
6]. It is also prevalent among African Americans, with reported rates between 18 and 71 cases per 100,000 individuals annually [
7,
8]. In contrast, Asian countries exhibit the lowest incidence, with approximately 1 case per 100,000 individuals per year [
9,
10]. The average age of onset is 40–55 years of age, with a younger peak age at diagnosis in men (30–50 years of age) than in women (50–60 years of age) [
11]. In Serbia, an estimated incidence of sarcoidosis is 16.5 per 100,000 individuals. A retrospective study conducted in Serbia, which included PH verified sarcoidosis patients in the period from 2000. to 2023., highlighted the unique geographic and epidemiological distribution of sarcoidosis across the nation. This could be indicative of hereditary or environmental factors in the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis [
12].
An autopsy study by Iwai K et al. found that CS may be more prevalent in Japan where it seemed to be the leading cause of death among sarcoidosis patients [
13]. Clinical diagnosis of heart involvement occurs in only 5% of sarcoidosis patients. However, autopsy studies have detected cardiac involvement in up to 25% of sarcoidosis patients. In individuals with systemic sarcoidosis, the prevalence of cardiac involvement has ranged from 3.7% to 54.9% [
14]. When cardiac involvement manifests as the first or sole organ manifestation, it suggests a more severe disease course compared to CS occurring in conjunction with extracardiac disease [
15]. These findings suggest that due to suboptimal diagnostic rates, the true prevalence and incidence of CS remain to be determined. This is especially important as timely and accurate diagnosis facilitates appropriate intervention and better treatment outcomes in this patient population.
3. Risk Factors
Sarcoidosis shares a strong correlation with genetic factors, as well as environmental factors, including infectious agents and non-infectious antigens, metals, and combustible materials [
16]. As already mentioned, the risk of sarcoidosis is higher in those with African or Scandinavian descent [
5,
6]. Potential infectious exposure to mycobacteria and Propionibacterium acnes, a skin commensal bacterium, is shown to be associated with sarcoidosis [
17]. It is demonstrated that smokers are less susceptible to sarcoidosis, probably due to suppression of T-lymphocyte function and phagocytic activity of macrophages [
18]. Regarding cardiac sarcoidosis, older patients, those with diabetes mellitus, and ischemic heart disease, have higher risk of presenting with heart failure as a manifestation of CS [
19].
4. Clinical Presentation
The clinical presentation of CS is heterogenous. It can range from palpitations, syncope, orthopnea, dyspnea, and peripheral edema to sudden cardiac death. This variation of clinical presentation is dependent on the location of the granulomas within the heart and its extensivity. CS manifestations are commonly categorized into arrhythmic, cardiomyopathic, and pericardial groups [
20]. However, it should be noted that up to 37% of sarcoidosis patients with cardiac involvement exhibit no symptoms [
21].
4.1. Heart Failure
The prevalence of sarcoidosis related cardiomyopathy is increasing. It is demonstrated that the 10-year incidence of clinical heart failure among patients with sarcoidosis is 3% [
22]. Cardiomyopathy in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis can be presented as both heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction or isolated right ventricular heart failure. In early stages, reduced ventricular compliance and diastolic dysfunction can result in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, while in severe cases can be presented as restrictive cardiomyopathy [
23]. The presence of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and RV involvement is associated with poor prognosis [
24]. It is important to note that, although rare, isolated right ventricular cardiac sarcoidosis can phenotipicaly mimic arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) [
25].
4.2. Atrial Arrhythmias
Atrial arrhythmias are present in 20-30% of patients with cardiac sarcoidosis [
26]. The main pathophysiological mechanisms responsible for the occurrence of atrial arrhythmias are cardiac inflammation, granulomatous atrial involvement and fibrosis, as well as left atrial remodeling [
27]. Close monitoring, especially in symptomatic patients, and optimal anticoagulation threshold and rhythm control strategies are important part of the management.
4.3. Ventricular Tachycardia
In previous observational studies, it is shown that adverse events are mainly due to fatal ventricular arrhythmia events. Patients with low ejection fraction, high BNP levels, ventricular tachycardia or ventrucular fibrillation history, and those requiring ablation to treat VT are at highest risk of poor clinical outcome [
28]. Optimal diagnostic algorithm, especially in symtpomatic patients, and timely prevention of sudden cardiac death, are of immense importance.
4.4. Conduction Disturbances
Conduction disturbances in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis, mainly bundle branch blocks and second or third-degree AV blocks are common, having in mind the predominant involvement of interventicular septum [
29]. In observational studies, up to 30% of patients with CS can have third degree AV block, requiring permanent pacemaker implantation [
30]. In those with heart failure symptoms and reduced ejection fraction with the indication for permanent pacemaker implantation, cardiac resynchronization therapy can be an important therapeutical modality to reduce heart failure hospitalizations and mortality [
31].
5. Diagnosis
The diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) remains challenging because it lacks specific biomarkers, particularly during the early stages of the disease [
32]. Given the heterogeneous clinical manifestations (from asymptomatic to sudden cardiac arrest), establishing an early diagnosis of CS is essential [
33].
Numerous international societies have provided criteria for the diagnosis of CS, however the optimal diagnostic approach is still up for debate. Three main sets of clinical guidelines have been proposed, by the Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare (JMHW) [
34] by the World Association for Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG) [
35], and the consensus statement from the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) [
36].
The JMHW issued the first diagnostic guidelines for CS in 1993 [
37] which were later revised in 2006 [
38]. New guidelines included the utilization of novel non-invasive diagnostic methods. However, the 2006. JMHW diagnostic guidelines have not completely implemented the use of modern imaging modalities, such as FDG PET (not included in the diagnostic criteria) and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) which was included, but as minor criteria. These modalities eventually demonstrated higher diagnostic accuracy in the clinical diagnosis of CS than JMHW criteria [
39,
40,
41].
The Japanese Circulation Society released revised guidelines in 2017., highlighting the importance of CMR and FDG-PET scans [
34]
.
Societies in North America have created their own sets of CS diagnostic standards. The first algorithm was proposed by the US National Institutes of Health in 1999 [
42], and it later served as the basis for the 2014. criteria created by the WASOG [
43]. The WASOG criteria were partially referenced and built upon by a recent consensus statement from the HRS [
42], ultimately providing a more modern set of clinical criteria for the diagnosis of CS. The American guidelines stress on the need to use contemporary imaging methods to diagnose CS. In a prospective cohort from 2017. where all patients who had biopsy-confirmed extracardiac sarcoidosis and who underwent CMR, the HRS criteria were demonstrated to detect more disease than the 2006. clinical criteria by JMWH [
43]. The criteria for screening of CS with advanced cardiac imaging have been proposed by the HRS: suspected cardiac involvement in patients with biopsy-proven extracardiac sarcoidosis and one of the following symptoms (unexplained syncope/presyncope/significant palpitations lasting over 1-2 weeks) and/or abnormal ECG, and/or inconclusive echocardiogram results [
18]. Additional details of HRS and JCS criteria are shown in
Table 1.
Novel position papers from American Heart Association (AHA) and European Society of Cardiology (ESC) proposed more integrated approach to reduce morbidity and mortality in patients with CS [
44,
45]. Recently published scientific statement from the American Heart Association provide an integrated framework for the diagnosis and management of cardiac sarcoidosis. By integrating clinical data, laboratory parameters, and cardiac imaging findings, the scientific statement reffers to the diagnosis of CS in a maner of the likelihood of cardiac sarcoidosis (definite, highly probable, probable, possible, low probability, unlikely) rather than in a binary fashion. The statement emphasizes the role of CMR and PET as mandatory in all patients with clinical suspicion for CS. This approach can stratify patients into several groups and provide timely management for certain groups and more close follow up for others.
5.1. Electrocardiography
Even though considered neither sensitive nor specific enough to be a screening method for cardiac sarcoidosis, ECG is an integral part of sarcoidosis patient evaluation. In sarcoidosis patients some ECG findings may hint towards potential cardiac involvement. While a normal ECG does not rule out cardiac sarcoidosis, it suggests that severe abnormalities are less likely present [
46,
47]. Among sarcoidosis patients, plenty of ECG findings have been reported. Most described conduction abnormalities and arrythmias are right bundle branch block (RBBB), atrioventricular (AV) block of any degree and ventricular tachycardia (VT) [
48]. AV and BBBs arise due to sarcoid granuloma infiltration or consequent scaring of the interventricular septum, or involvement of the nodal artery that in turn leads to ischemia in the conduction system. In cardiac sarcoidosis, VT occurs as a re-entry mechanism that arises following granuloma scaring. These ECG findings also have a prognostic impact. Nordenswan et al. found that VT or AV block on ECG of sarcoidosis patients was associated with increased risk of sudden cardiac death during a 5-year follow-up [
49]. Sudden cardiac death due to AVB or VT accounted for 30-65% of sarcoidosis patients as per Roberts et al. [
50]. Prognosis of sarcoidosis patients with cardiac involvement is more favorable in those that present with high degree AVB as opposed to VT and heart failure [
51]. High degree AVB is reversible in about 50% of cases when treated with steroids [
52,
53]. In untreated patients, however, it is not reversible. This may be due to the underlying pathophysiology of the condition mentioned above. When sarcoid granulomas, in the active phase of the disease, cause the conduction abnormalities and not the consequent scaring, response to steroid therapy could be expected. Therefore, early recognition of cardiac sarcoidosis and its treatment is paramount. Findings of AVB, bundle branch blocks in sarcoidosis patient should raise suspicion for cardiac involvement. On the other hand, in young and middle-aged patients with these ECG findings and complaints of presyncope and syncope, sarcoidosis should be considered as a differential diagnosis. Supraventricular arrythmias, most commonly atrial fibrillation have also been described in cardiac sarcoidosis [
47]. They carry more favorable prognosis in comparison to VT and are amenable to catheter ablation [
54]. T wave abnormalities were also observed in this patient population. According to Tanaka et al. T wave in avR in conjunction with bundle branch block were independently associated with cardiac involvement in sarcoidosis patients. When combined, these ECG abnormalities showed considerable diagnostic yield for cardiac involvement with sensitivity of 94% and specificity of 89% [
55]. However, these results have not been translated into every day clinical practice due to study limitations, most notably the small sample size. The role of artefitial inteligence and machine learning could be beneficial in identifing patients with high probability for CS.
5.2. Echocardiography
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) stands out as the most accessible noninvasive method for cardiac imaging, offering crucial insights into cardiac structure and function. Echocardiographic abnormalities in sarcoidosis patients could raise suspicion of cardiac involvement. These include regional wall motion abnormalities, regional wall thickening, and valvular dysfunction, myocardial echogenicity and RV free-wall aneurysm formation [
56]. Such findings however are not sufficient to establish a diagnosis of CS but should trigger further diagnostic procedures utilizing more sensitive modalities such as positron emission tomography (PET) or cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) as per Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) consensus. The same consensus document suggests that TTE should be used as a first-line screening tool for diagnosing CS given its widespread availability [
18]. Certain echocardiographic findings may have prognostic value. The existance of basal septal thinning at the time of CS diagnosis is correlated with adverse outcomes such as increased mortality, occurrence of ventricular arrhythmias, and hospitalization due to heart failure. This association remains significant irrespective of corticosteroid therapy or cardiac resynchronization therapy [
57]. A more recent study found that basal septal thining
is associated with future development of left ventricular systolic dysfunction
even when function of the left ventricle
is preserved at time of CS diagnosis [
58]. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) remains a critical echocardiographic parameter in the evaluation of a patient with CS, as it can provide valuable insights into the long-term outcome of the condition. Individuals diagnosed with cardiac sarcoidosis and presenting with severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction (LVEF ≤ 35%) or moderate dysfunction (LVEF 36–50%) face worse prognosis compared to those with preserved LVEF (> 50%). Although patients with LVEF ≤ 35% may witness some left ventricular recovery following immunosuppression, the majority tend to persist in the severely impaired category [
59]. Novel echocardiographic parameters such as global longitudinal strain (GLS) have shown potential both in screening for CS and monitoring of these patients. Patients with systemic sarcoidosis have been found to exhibit significantly more impaired GLS [
60,
61]. Murtagh et al. found that GLS was significantly reduced in CS patients even with preserved LVEF using a cutoff of 17% [
62]. Strain has been proposed as a more sensitive measure of subclinical myocardial dysfunction than ejection fraction [
56]. Low GLS in CS patients has been associated with poor prognosis and outcomes including heart failure-related hospitalizations, need for device therapy, arrhythmias, and all-cause mortality (
Figure 1) [
63,
64]. These findings support the notion that GLS measurements should be incorporated into the TTE protocol, and patients with low GLS should be closely monitored.
5.3. Endomyocardial Biopsy (EMB)
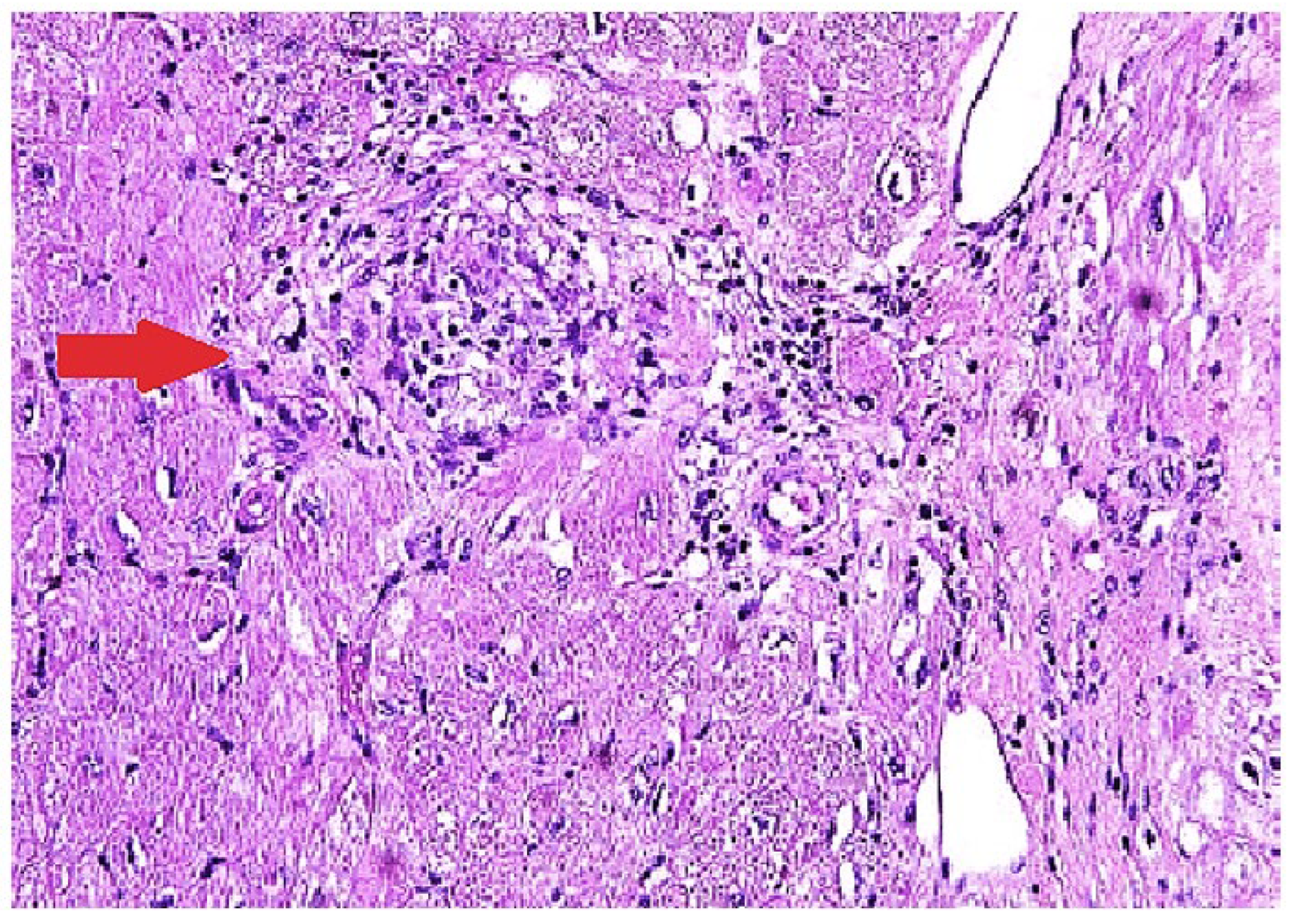
The most definitive way of diagnosing CS is through EMB showing histologic noncaseating granuloma with other causes excluded (
Figure 2) [
65]. The sensitivity of EMB for diagnosing CS was evaluated in a study that included 851 patients, and it demonstrated the sensitivity of EMB around 20% [
66]. Several other studies showed similar results [
67,
68] The low sensitivity of EMB can be partially explained by the patchy involvement of the myocardium [
69]. Higher sensitivity can be achieved with the aid of intracardiac voltage mapping or imaging guided EMB [
70]. A study from Japan revealed higher positivity of EMB in patients with reduced
left ventricular ejection fraction [
71]. This could suggest that patients with severe cardiac injury and widespread disease activity are more likely to receive a histological diagnosis via EMB due to multifocal or diffuse changes.
5.4. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR)
Over the last few years, advanced cardiac imaging which includes CMR has become the preferred way of diagnosing CS due to its non-invasiveness. [
19]. It can identify a wide range of myocardial abnormalities in patients with CS, including inflammation, fibrosis, reactive edema, and granulomatous infiltration. Kouranos et al. recently demonstrated that CMR has a significantly greater sensitivity to identify cardiac involvement in relation to echocardiography - 97% vs 27%, respectively [
43]. Conversely, in a study that analyzed explanted hearts, CS was histologically confirmed in only 1 of 8 cases presumed to have CS by CMR [
72]. The moderately low specificity of CMR had presented the biggest challenge to the diagnosis of CS [
73]. However, the specificity of CMR in diagnosing CS increased with the development of novel tissue characterization sequences. This was shown in a large meta-analysis from 2018. that included 649 patients. One group included studies between 2005. and 2011. where the overall sensitivity was 91% and specificity 80%. The second subgroup included studies between 2011. and 2017. where the overall sensitivity was 95% and specificity was even 92% [
74]. The hallmark of CS on CMR is the presence of late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) [
75]. The main principle of CMR is based on the washout of gadolinium, which is slower in edematous, inflammatory, and scarred tissues, making it visible in CMR’s delayed images [
19]. The presence of LGE is not pathognomonic for CS, as it can be seen in a variety of nonischemic cardiomyopathies. However, certain patterns of cardiac involvement are thought to be typical of CS [
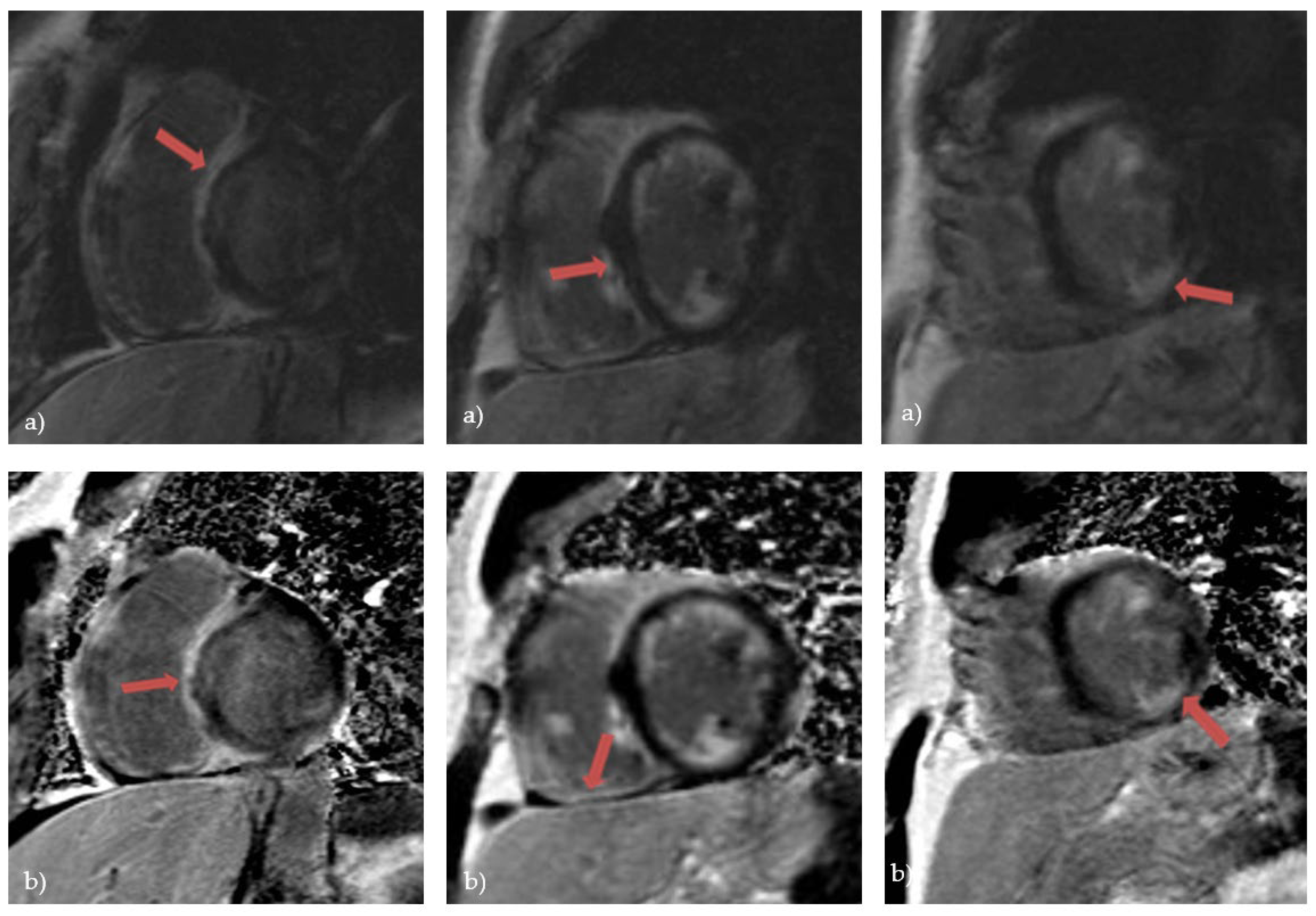
76]. A systematic review from 2019. which included patients with histologically proven CS observed that the most prevalent pattern of LGE is mid-wall or sub-epicardial enhancement in the septum, lateral wall, and basal ventricular wall (
Figure 3). However, there have also been reports of subendocardial or transmural augmentation in other myocardial regions [
77].
Additionally, a large meta-analysis demonstrated that the presence of LGE on CMR has important predictive values in patients with CS, with an increased tendency toward adverse events, including overall mortality, and heart failure hospitalization [
78].
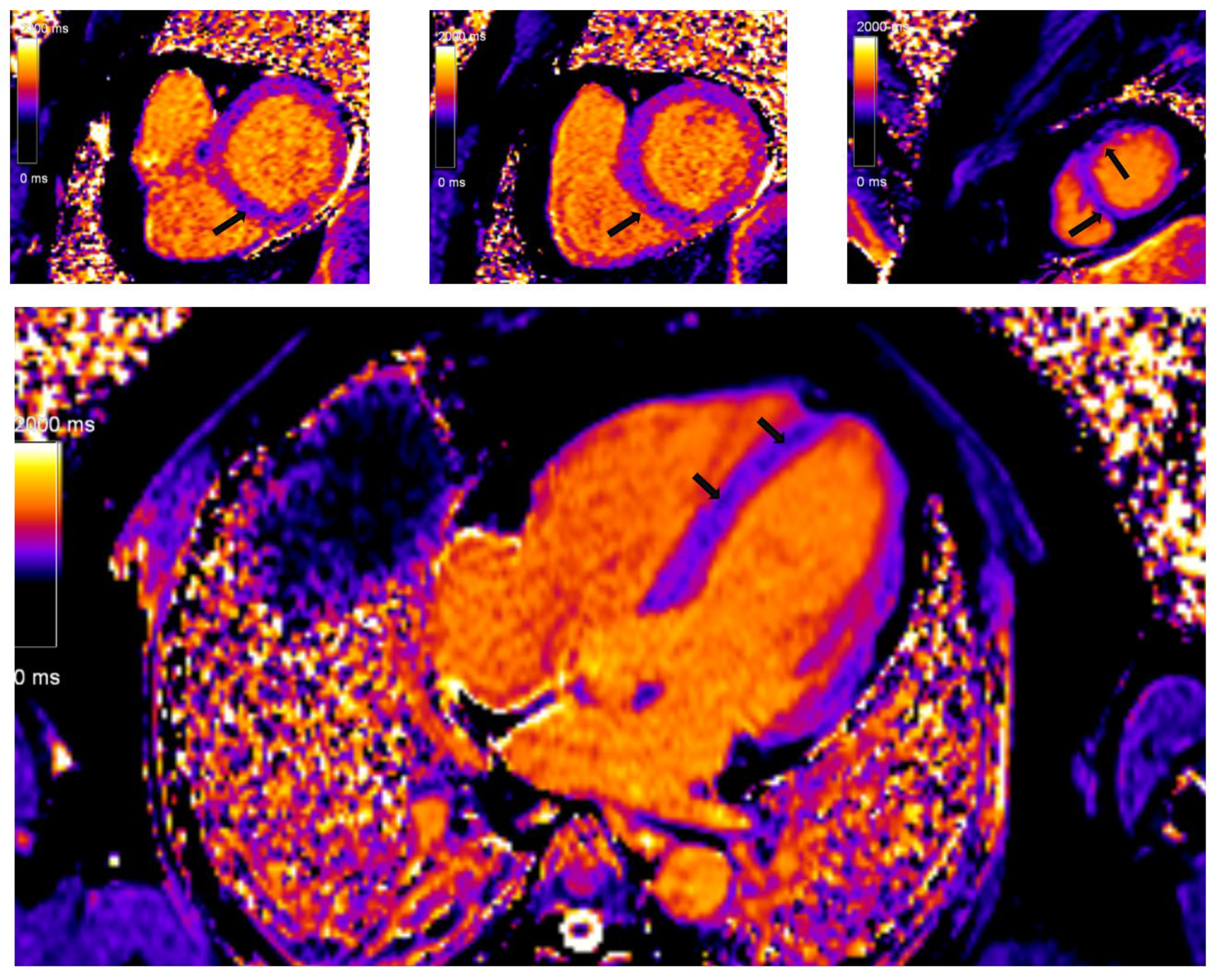
In recent years, with hardware and post-processing software improvements, predominantly driven by miltiparametric tissue mapping, the diagnosis and risk stratification of patients with CS has improved. Regional T2 mapping values are independent predictors of active myocardial inflammation in CS and may add additional discriminatory capability [
79]. Prolonged or shortened native T1 time, both focally in the septum and globally, is a significant marker of the severity of the disease, while the fraction of extracelullar volume (ECV) is an independent predictor of future serious adverse events among patients with CS (
Figure 4) [
80]. The ECV esimation is also important in differentiation of other cardiac conditions, predominanlty myocarditis. It is important to note that CS patients had higher ECV values in the areas with LGE phenomenon in comparison to patients with myocarditis.
5.5. 18Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography (FDG-PET)
Cardiac FDG-PET imaging is used in cases of suspected CS since it can identify glucose uptake by inflammatory cells in sarcoid granulomas [
81].
According to the Japanese Society of Nuclear Cardiology guidelines from 2019, it is recommended that a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet followed by fasting for a minimum of 12 hours be used to inhibit the physiologic glucose metabolism of the heart to enable diagnostic imaging [
82]
. Importantly, 25% of cardiac PET scans are not diagnostic because the physiologic glucose uptake is not sufficiently suppressed [
83]. A meta-analysis from Ontario using the JMHW guidelines as the reference standard for the diagnosis of CS reported a sensitivity of 89% and specificity of 78% for FDG PET [
84]. Those values are genuinely equivalent to the CMR’s sensitivity (75%–100%) and specificity (76.9%–78%) according to some authors [
85]. The JMHW criteria used in this meta-analysis have certain drawbacks, such as the need for extracardiac sarcoidosis in the diagnostic criteria and insufficient validation. Furthermore, these clinical criteria are insufficient for the diagnosis of isolated CS, a well-described clinical entity that may arise in about 25% of cases [
86,
87]. When a patient is adequately prepared, the normal FDG-PET shows no myocardial FDG uptake, while the predominant pathological FDG uptake patterns are focal or focal on diffuse imaging patterns [
88].
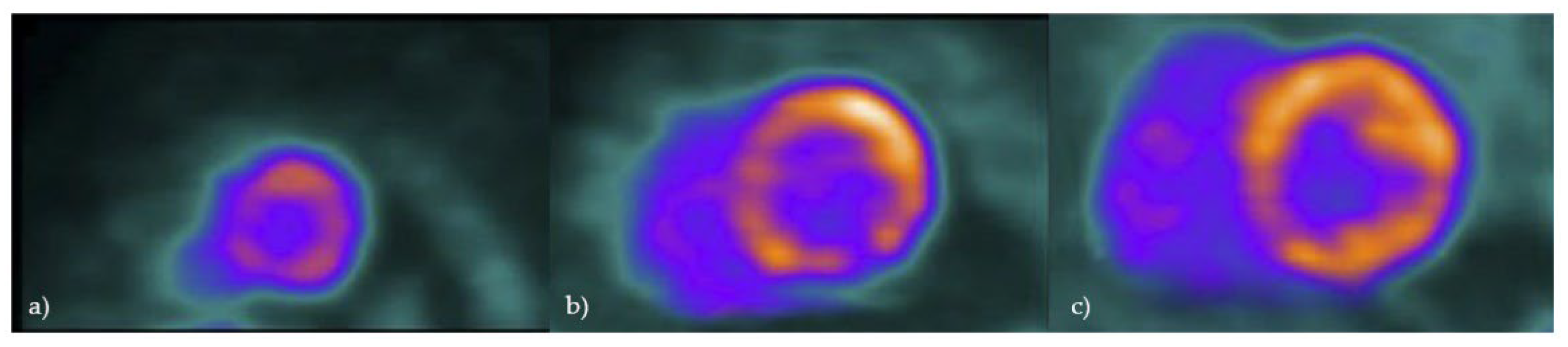
Although any part of the left ventricle can be involved, the most common place for CS to occur is the basal segments [
42]
. Besides the left ventricle, assessing for regions of localized FDG uptake in the right ventricle is particularly important, since this could be linked to a less favorable outcome (Figure 5) [
88].
Additionally, with FDG-PET it is also possible to quantify the degree of inflammation and consequently, to evaluate the outcome of anti-inflammatory treatment. According to Osborne and colleagues, a significant improvement in left ventricular ejection fraction was linked to a decrease in the intensity and extent of myocardial inflammation as determined by FDG-PET in 23 patients who had serial scans [
89]
. In a retrospective study by Blankstein and colleagues, where 118 patients with confirmed or suspected CS were assessed, it was demonstrated that the presence of focal FDG uptake on cardiac PET indicated individuals at higher risk of mortality or ventricular tachycardia [
41]
. The results of a recent meta-analysis may indicate a possible role for FDG-PET in the prognosis of CS. In this study which included 515 patients, the presence of abnormal FDG-PET pattern, especially considerable right ventricle uptake, indicated a higher risk of severe cardiac events [
90]
. Gowani et al. published some conflicting data, where FDG uptake didn’t contribute to prognostic value [
91].
5.6. The Role of Cardio-Specific Biomarkers in Patients with Cardiac Sarcoidosis: Correlation with Imaging Findings
Biomarkers can play an important diagnostic and prognostic role in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. Among routinely used biomarkers, it was shown that troponin T, NT-proBNP, and creatinine could predict clinically significant outcomes in patients with CS [
92]. These markers could indicate the disease severity and progression, but also be helpful in following the treatment response. ACE levels have good correlation with LGE registered on cardiac magnetic resonance, while 1,25-OHVit-D levels correlate with FDG-PET activity [
93]. Modified diagnostic alghorithms were developed to effectively screen for cardiac involvement in patients with sarcoidosis. Kumar et al. incorporated contemporary ehocardiographic parameters and cardiac biomarkers (NT-proBNP and troponin levels) into Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) diagnostic algorithm and increased the yield of detecting cardiac involvement by 30% [
94]. Novel markers include circulating miR-126 and miR-223 microRNAs that are significantly up-regulated in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis and have good correlation with CMR and PET findings [
95].
6. Conclusion
Cardiac sarcoidosis has a higher prevalence than previously thought. Despite significant recent advances, the diagnosis of CS still poses a challenge. Simplifying diagnostic criteria and developing new procedures is crucial not only in the diagnostic process, but also to stratify patients and follow the potential benefits of therapeutic modalities. At the same time, additional work is needed in the field of diagnosing cases of isolated CS. Nonetheless, new imaging techniques and modalities have contributed significantly to increased global awareness of CS. The formation of larger global registries can be helpful in the identification of independent predictors of adverse clinical events and development of specific diagnostic algorhithms to reduce the overal risk of this serious condition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Z. and M.S.; investigation, V.P. and I.M.; writing—original draft preparation, V.P., F. M., I.M.; writing—review and editing, M.P., A.K., and D.Z.; validation, M.S., S.P., S.J.D.; supervision, M.Z., S.P., M.S.; data curation, I.M.; methodology V.P.; project administration, D.Z.; resources, S.J.D., M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Faculty of Medicine, University of Belgrade, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia (200110).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable; the paper does not have information or images that can identify any patient.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- M. Stjepanović et al., “Neurosarcoidosis – an ever-present clinical challenge,” Srp Arh Celok Lek, vol. 149, no.
3–4, pp. 247–250, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Stjepanovic et al., “King’s Sarcoidosis Questionnaire (KSQ) – Validation study in Serbian speaking population of sarcoidosis patients,” PLoS One, vol. 18, no. 9 September, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Judson, “The Clinical Features of Sarcoidosis: A Comprehensive Review,” Clinical Reviews in Allergy and Immunology, vol. 49, no. 1. Humana Press Inc., pp. 63–78, Oct. 02, 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. Carlos Quijano-Campos, N. Sekhri, M. Thillai, and J. Sanders, “Health-related quality of life in cardiac sarcoidosis: a systematic review,” European Heart Journal Open, vol. 3, pp. 1–17, 2023. [CrossRef]
- E. V. Arkema, J. Grunewald, S. Kullberg, A. Eklund, and J. Askling, “Sarcoidosis incidence and prevalence: a nationwide register-based assessment in Sweden,” Eur Respir J, vol. 48, no. 6, pp. 1690–1699, Dec. 2016. [CrossRef]
- N. Milman and O. Selroos, “Pulmonary sarcoidosis in the Nordic countries 1950-1982. II. Course and prognosis.,” Sarcoidosis, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 113–118, 1990.
- R. P. Baughman et al., “Sarcoidosis in America: Analysis based on health care use,” Ann Am Thorac Soc, vol. 13, no. 8, pp. 1244–1252, Aug. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Y. C. Cozier, J. S. Berman, J. R. Palmer, D. A. Boggs, D. M. Serlin, and L. Rosenberg, “Sarcoidosis in Black Women in the United States: Data From the Black Women’s Health Study,” Chest, vol. 139, no. 1, p. 144, Jan. 2011. [CrossRef]
- H. Y. Yoon, H. M. Kim, Y. J. Kim, and J. W. Song, “Prevalence and incidence of sarcoidosis in Korea: a nationwide population-based study,” Respir Res, vol. 19, no. 1, Aug. 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. Morimoto et al., “Epidemiology of sarcoidosis in Japan,” European Respiratory Journal, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 372–379, Feb. 2008. [CrossRef]
- E. V. Arkema and Y. C. Cozier, “Epidemiology of sarcoidosis: current findings and future directions,” Ther Adv Chronic Dis, vol. 9, no. 11, p. 227, Nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Stjepanovic M, Maric N, Belic S, Milin-Lazovic J, Djurdjevic N, Jankovic J, Petrovic M, Peric J, Tulic I, Cvejic J, Popevic S. Characteristics of Patients with Sarcoidosis with Emphasis on Acute vs. Chronic Forms—A Single Center Experience. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024 Jun 8;14(6):616.
- K. Iwai et al., “Racial difference in cardiac sarcoidosis incidence observed at autopsy.,” Sarcoidosis, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 26–31, Mar. 1994.
- E. Hulten, S. Aslam, M. Osborne, S. Abbasi, M. S. Bittencourt, and R. Blankstein, “Cardiac sarcoidosis-state of the art review,” Cardiovasc Diagn Ther, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 50–63, 2016. [CrossRef]
- J. Lehtonen, V. Uusitalo, P. Pöyhönen, M. I. Mäyränpää, and M. Kupari, “Cardiac sarcoidosis: phenotypes,
diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis,” Eur Heart J, vol. 44, no. 17, pp. 1495–1510, May 2023. 20. [CrossRef]
- Judson, MA. Environmental Risk Factors for Sarcoidosis. Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 26;11:1340. [CrossRef]
- Swaisgood CM, Oswald-Richter K, Moeller SD, Klemenc JM, Ruple LM, Farver CF, Drake JM, Culver DA, Drake WP. Development of a sarcoidosis murine lung granuloma model using Mycobacterium superoxide dismutase A peptide. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 Feb;44(2):166-74. [CrossRef]
- Ungprasert P, Crowson CS, Matteson EL. Smoking, obesity and risk of sarcoidosis: A population-based nested case-control study. Respir Med. 2016 Nov;120:87-90. [CrossRef]
- Rossides M, Kullberg S, Grunewald J, Eklund A, Di Giuseppe D, Askling J, Arkema EV. Risk and predictors of heart failure in sarcoidosis in a population-based cohort study from Sweden. Heart. 2022 Mar;108(6):467-473. [CrossRef]
- B. A. Houston and M. Mukherjee, “Cardiac sarcoidosis: Clinical manifestations, imaging characteristics, and therapeutic approach,” Clin Med Insights Cardiol, vol. 8, pp. 31–37, Nov. 2014. [CrossRef]
- H. H. Shah et al., “Cardiac sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review of risk factors, pathogenesis, diagnosis,
clinical manifestations, and treatment strategies,” Front Cardiovasc Med, vol. 10, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yafasova A, Fosbøl EL, Schou M, Gustafsson F, Rossing K, Bundgaard H, Lauridsen MD, Kristensen SL, Torp-Pedersen C, Gislason GH, Køber L, Butt JH. Long-Term Adverse Cardiac Outcomes in Patients With Sarcoidosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Aug 18;76(7):767-777. [CrossRef]
- Gilotra NA, Griffin JM, Pavlovic N, Houston BA, Chasler J, Goetz C, Chrispin J, Sharp M, Kasper EK, Chen ES, Blankstein R, Cooper LT, Joyce E, Sheikh FH. Sarcoidosis-Related Cardiomyopathy: Current Knowledge, Challenges, and Future Perspectives State-of-the-Art Review. J Card Fail. 2022 Jan;28(1):113-132. [CrossRef]
- Smedema JP, van Geuns RJ, Ainslie G, Ector J, Heidbuchel H, Crijns HJGM. Right ventricular involvement in cardiac sarcoidosis demonstrated with cardiac magnetic resonance. ESC Heart Fail. 2017 Nov;4(4):535-544. [CrossRef]
- Waki H, Eguchi K, Toriumi S, Ikemoto T, Suzuki T, Fukushima N, Kario K. Isolated Cardiac Sarcoidosis Mimicking Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Intern Med. 2018 Mar 15;57(6):835-839. [CrossRef]
- Weng W, Wiefels C, Chakrabarti S, Nery PB, Celiker-Guler E, Healey JS, Hruczkowski TW, Quinn FR, Promislow S, Medor MC, Spence S, Odabashian R, Alqarawi W, Juneau D, de Kemp R, Leung E, Beanlands R, Birnie D. Atrial Arrhythmias in Clinically Manifest Cardiac Sarcoidosis: Incidence, Burden, Predictors, and Outcomes. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Sep;9(17):e017086. [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam Karikalan S, Yusuf A, El Masry H. Arrhythmias in Cardiac Sarcoidosis: Management and Prognostic Implications. J Clin Med. 2024 May 28;13(11):3165. [CrossRef]
- Kumar S, Barbhaiya C, Nagashima K, Choi EK, Epstein LM, John RM, Maytin M, Albert CM, Miller AL, Koplan BA, Michaud GF, Tedrow UB, Stevenson WG. Ventricular tachycardia in cardiac sarcoidosis: characterization of ventricular substrate and outcomes of catheter ablation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2015 Feb;8(1):87-93. [CrossRef]
- Nery PB, Beanlands RS, Nair GM, Green M, Yang J, McArdle BA, Davis D, Ohira H, Gollob MH, Leung E, Healey JS, Birnie DH. Atrioventricular block as the initial manifestation of cardiac sarcoidosis in middle-aged adults. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014 Aug;25(8):875-881. [CrossRef]
- Nordenswan HK, Lehtonen J, Ekström K, Kandolin R, Simonen P, Mäyränpää M, Vihinen T, Miettinen H, Kaikkonen K, Haataja P, Kerola T, Rissanen TT, Kokkonen J, Alatalo A, Pietilä-Effati P, Utriainen S, Kupari M. Outcome of Cardiac Sarcoidosis Presenting With High-Grade Atrioventricular Block. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2018 Aug;11(8):e006145. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed R, Sivasankaran K, Ahsan A, Mactaggart S, Azzu A, Dulay MS, Ramphul K, Liu A, Okafor J, Dragon M, Kouranos V, Ahmed M, Sharma R. Clinical Outcomes with Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Patients with Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Systematic Review and Proportional Meta-analysis. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Jul 13:102747. [CrossRef]
- D. H. Birnie et al., “HRS expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias associated with cardiac sarcoidosis,” Heart Rhythm, vol. 11, no. 7, pp. 1304– 1323, 2014. [CrossRef]
- A. Sharma, D. R. Okada, H. Yacoub, J. Chrispin, and S. Bokhari, “Diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis: an era of paradigm shift,” Ann Nucl Med, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 87–93, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. L. R. Neto, C. L. Jellis, E. Joyce, T. D. Callahan, R. Hachamovitch, and D. A. Culver, “Update in Cardiac Sarcoidosis,” Ann Am Thorac Soc, vol. 16, no. 11, pp. 1341–1350, 2019. [CrossRef]
- F. Terasaki and K. Yoshinaga, “New Guidelines for Diagnosis of Cardiac Sarcoidosis in Japan,” 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Judson et al., “The WASOG sarcoidosis organ assessment instrument: An update of a previous clinical tool,” Sarcoidosis Vasculitis and Diffuse Lung Diseases, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 19–27, Jan. 2014, Accessed: Feb. 20, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://pure.johnshopkins.edu/en/publications/the-wasog-sarcoidosis-organ-assessment-instrument-an-update-of-a-.
- Hiraga, H. , “The guides for the diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis,” Report of the Japanese Research Committee for Diffuse Lung Disease of Japan Ministry Welfare., pp. 23–24, 1993.
- Hiraga, H. , “Diagnostic standard and guidelines for sarcoidosis,” Jpn J Sarcoidosis and Granulomatous Disorders, pp. 27–89, 2007.
- R. J. Kim et al., “Detection of myocardial damage in patients with sarcoidosis,” Circulation, vol. 120, no. 20, pp. 1969–1977, Nov. 2009. [CrossRef]
- E. Hulten, S. Aslam, M. Osborne, S. Abbasi, M. S. Bittencourt, and R. Blankstein, “Cardiac sarcoidosis-state of the art review,” Cardiovasc Diagn Ther, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 50–63, 2016. [CrossRef]
- R. Blankstein et al., “Cardiac positron emission tomography enhances prognostic assessments of patients with suspected cardiac sarcoidosis,” J Am Coll Cardiol, vol. 63, no. 4, pp. 329–336, Feb. 2014. [CrossRef]
- B. R. T. A. T. M. Y. J. H. Judson MA, “ Defining organ involvement in sarcoidosis: the ACCESS proposed instrument. ACCESS Research Group. A Case Control Etiologic Study of Sarcoidosis,” Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 75–86, 1999.
- V. Kouranos et al., “Complementary Role of CMR to Conventional Screening in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cardiac Sarcoidosis,” JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, vol. 10, no. 12, pp. 1437–1447, Dec. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Cheng RK, Kittleson MM, Beavers CJ, et al.; American Heart Association Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology, and Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing. Diagnosis and Management of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024 May 21;149(21):e1197-e1216. [CrossRef]
- Sharma R, Kouranos V, Cooper LT, et al. Management of cardiac sarcoidosis. Eur Heart J. 2024 Jun 26:ehae356. [CrossRef]
- H. Ohira et al., “Underdiagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis by ECG and echocardiography in cases of extracardiac sarcoidosis,” ERJ Open Res, vol. 8, no. 2, Apr. 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Willy, D. G. Dechering, F. Reinke, N. Bögeholz, G. Frommeyer, and L. Eckardt, “The ECG in sarcoidosisa
marker of cardiac involvement? Current evidence and clinical implications,” 2020. [CrossRef]
- V. Sekhri, S. Sanal, L. J. Delorenzo, W. S. Aronow, and G. P. Maguire, “Cardiac sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review,” 2011. [CrossRef]
- H. K. Nordenswan et al., “Outcome of Cardiac Sarcoidosis Presenting With High-Grade Atrioventricular Block,” Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, vol. 11, no. 8, p. e006145, Aug. 2018. [CrossRef]
- W. C. Roberts, H. A. McAllister, and V. J. Ferrans, “Sarcoidosis of the heart: A clinicopathologic study of 35 necropsy patients (group I) and review of 78 previously described necropsy patients (group II),” Am J Med, vol. 63, no. 1, pp. 86–108, Jul. 1977. [CrossRef]
- Y. Takaya, K. F. Kusano, K. Nakamura, and H. Ito, “Outcomes in patients with high-degree atrioventricular block as the initial manifestation of cardiac sarcoidosis,” Am J Cardiol, vol. 115, no. 4, pp. 505–509, Feb. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Y. Kato, S. I. Morimoto, A. Uemura, S. Hiramitsu, T. Ito, and H. Hishida, “Efficacy of corticosteroids in sarcoidosis presenting with atrioventricular block.,” Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 133–137, Jun. 2003, Accessed: Feb. 20, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://europepmc.org/article/med/12870723.
- S. K. Padala, S. Peaslee, M. S. Sidhu, D. A. Steckman, and M. A. Judson, “Impact of early initiation of corticosteroid therapy on cardiac function and rhythm in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis,” Int J Cardiol, vol. 227, pp. 565–570, Jan. 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Willner, J. F. Viles-Gonzalez, J. O. Coffey, A. S. Morgenthau, and D. Mehta, “Catheter Ablation of Atrial Arrhythmias in Cardiac Sarcoidosis,” J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, vol. 25, no. 9, pp. 958–963, Sep. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Y. Tanaka et al., “T wave amplitude in lead aVR as a novel diagnostic marker for cardiac sarcoidosis,” Heart Vessels, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 352–358, Mar. 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Okafor, R. Khattar, R. Sharma, and V. Kouranos, “The Role of Echocardiography in the Contemporary Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Comprehensive Review,” Life 2023, Vol. 13, Page 1653, vol. 13, no. 8, p. 1653, Jul. 2023. [CrossRef]
- N. Nagano et al., “Association Between Basal Thinning of Interventricular Septum and Adverse Long-Term Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Cardiac Sarcoidosis,” Circulation Journal, vol. 79, no. 7, pp. 1601–1608, Jun. 2015. [CrossRef]
- K. Tanizawa et al., “Basal interventricular septum thinning and long-term left ventricular function in patients with sarcoidosis,” Respir Investig, vol. 60, no. 3, pp. 385–392, May 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Kusano et al., “Prognosis and Outcomes of Clinically Diagnosed Cardiac Sarcoidosis Without Positive Endomyocardial Biopsy Findings,” JACC: Asia, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 385–395, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. Barssoum et al., “Speckle tracking echocardiography can predict subclinical myocardial involvement in patients with sarcoidosis: A meta-analysis,” Echocardiography, vol. 37, no. 12, pp. 2061–2070, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Kusunose et al., “Deterioration of biventricular strain is an early marker of cardiac involvement in confirmed sarcoidosis,” Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, vol. 21, no. 7, pp. 796–804, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Murtagh et al., “Improved detection of myocardial damage in sarcoidosis using longitudinal strain in patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction,” Echocardiography, vol. 33, no. 9, pp. 1344–1352, Sep. 2016. [CrossRef]
- E. Joyce et al., “Subclinical left ventricular dysfunction by echocardiographic speckle-tracking strain analysis relates to outcome in sarcoidosis,” Eur J Heart Fail, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 51–62, Jan. 2015. [CrossRef]
- I. Felekos et al., “Global longitudinal strain and long-term outcomes in asymptomatic extracardiac sarcoid
patients with no apparent cardiovascular disease,” Echocardiography, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 804–808, Jun. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Judson et al., “The diagnostic pathway to sarcoidosis,” Chest, vol. 123, no. 2, pp. 406–412, Feb. 2003. [CrossRef]
- M. K. Bennett et al., “Evaluation of the role of endomyocardial biopsy in 851 patients with unexplained heart failure from 2000-2009,” Circ Heart Fail, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 676–684, Jul. 2013. [CrossRef]
- R. Kandolin et al., “Diagnosing isolated cardiac sarcoidosis,” J Intern Med, vol. 270, no. 5, pp. 461–468, Nov. 2011. [CrossRef]
- H. Ardehali et al., “A positive endomyocardial biopsy result for sarcoid is associated with poor prognosis in patients with initially unexplained cardiomyopathy,” Am Heart J, vol. 150, no. 3, pp. 459–463, Sep. 2005. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yatsynovich, N. Dittoe, M. Petrov, and N. Maroz, “Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Review of Contemporary Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment,” Am J Med Sci, vol. 355, no. 2, pp. 113–125, Feb. 2018. [CrossRef]
- F. M. Ezzeddine et al., “Electrogram-guided endomyocardial biopsy yield in patients with suspected cardiac sarcoidosis and relation to outcomes,” J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, vol. 32, no. 9, pp. 2486–2495, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Komoriyama et al., “Lower left ventricular ejection fraction and higher serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity are associated with histopathological diagnosis by endomyocardial biopsy in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis,” Int J Cardiol, vol. 321, pp. 113–117, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Divakaran et al., “Diagnostic Accuracy of Advanced Imaging in Cardiac Sarcoidosis,” Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, vol. 12, no. 6, p. e008975, Jun. 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. Smedema et al., “Evaluation of the accuracy of gadolinium-enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance in the diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis,” J Am Coll Cardiol, vol. 45, no. 10, pp. 1683–1690, May 2005. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Li, Q. Xu, B. Xu, and H. Wang, “Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Diagnosis of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Meta-Analysis,” Can Respir J, vol. 2018, 2018. [CrossRef]
- P. E. Bravo, A. Singh, M. F. Di Carli, and R. Blankstein, “Advanced cardiovascular imaging for the evaluation of cardiac sarcoidosis,” J Nucl Cardiol, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 188–199, Feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- T. Vita et al., “Complementary Value of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in the Assessment of Cardiac Sarcoidosis,” Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, vol. 11, no. 1, p. e007030, Jan. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Okasha, F. Kazmirczak, K. H. A. Chen, A. Farzaneh-Far, and C. Shenoy, “Myocardial Involvement in Patients With Histologically Diagnosed Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Gross Pathological Images From Autopsy or Cardiac Transplantation Cases,” J Am Heart Assoc, vol. 8, no. 10, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- Flamée et al., “Prognostic value of cardiovascular magnetic resonance in patients with biopsy-proven systemic sarcoidosis,” Eur Radiol, vol. 30, no. 7, pp. 3702–3710, Jul. 2020,. [CrossRef]
- Chamberlin JH, Kocher MR, Aquino G, Fullenkamp A, Dennis DJ, Waltz J, Stringer N, Wortham A, Varga-Szemes A, Rieter WJ, James WE, Houston BA, Hardie AD, Kabakus I, Baruah D, Kemeyou L, Burt JR. Quantitative myocardial T2 mapping adds value to Japanese circulation society diagnostic criteria for active cardiac sarcoidosis. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 Aug;39(8):1535-1546. [CrossRef]
- Manabe O, Oyama-Manabe N, Aikawa T, Tsuneta S, Tamaki N. Advances in Diagnostic Imaging for Cardiac Sarcoidosis. J Clin Med. 2021 Dec 11;10(24):5808. [CrossRef]
- R. H. J. A. Slart et al., “A joint procedural position statement on imaging in cardiac sarcoidosis: from the Cardiovascular and Inflammation & Infection Committees of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine, the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging, and the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology,” Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, vol. 18, no. 10, pp. 1073–1089, Oct. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Kumita et al., “Recommendations for F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Imaging for Diagnosis of Cardiac Sarcoidosis−2018 Update: Japanese Society of Nuclear Cardiology Recommendations”. [CrossRef]
- T. Osborne et al., “Patient preparation for cardiac fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography imaging of inflammation,” J Nucl Cardiol, vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 86–99, Feb. 2017. [CrossRef]
- G. Youssef et al., “The use of 18F-FDG PET in the diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis: a systematic review and metaanalysis including the Ontario experience,” J Nucl Med, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 241–248, Feb. 2012. [CrossRef]
- H. Ohira et al., “Myocardial imaging with 18F-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in sarcoidosis,” Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 933–941, May 2008. [CrossRef]
- D. R. Okada et al., “Isolated cardiac sarcoidosis: A focused review of an under-recognized entity,” J Nucl Cardiol, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 1136–1146, Aug. 2018. [CrossRef]
- B. W. Sperry, J. Oldan, R. Hachamovitch, and B. K. Tamarappoo, “Insights into biopsy-proven cardiac sarcoidosis in patients with heart failure,” J Heart Lung Transplant, vol. 35, no. 3, p. 392, Mar. 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Ishimaru et al., “Focal uptake on 18F-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography images indicates cardiac involvement of sarcoidosis,” Eur Heart J, vol. 26, no. 15, pp. 1538–1543, Aug. 2005. [CrossRef]
- M. T. Osborne et al., “Reduction in 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake on serial cardiac positron emission tomography is associated with improved left ventricular ejection fraction in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis,” J Nucl Cardiol, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 166–174, Feb. 2014. [CrossRef]
- A. I. Ahmed et al., “The prognostic role of cardiac positron emission tomography imaging in patients with sarcoidosis: A systematic review,” J Nucl Cardiol, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 1545–1552, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Z. Gowani et al., “Utility of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Versus Cardiac Positron Emission Tomography for Risk Stratification for Ventricular Arrhythmias in Patients With Cardiac Sarcoidosis,” Am J Cardiol, vol. 134, pp. 123–129, Nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Kiko T, Yoshihisa A, Kanno Y, Yokokawa T, Abe S, Miyata-Tatsumi M, Misaka T, Oikawa M, Kobayashi A, Ishida T, Takeishi Y. A Multiple Biomarker Approach in Patients with Cardiac Sarcoidosis. Int Heart J. 2018 Sep 26;59(5):996-1001. [CrossRef]
- Kolluri N, Schmidt TJ, Elwazir MY, Kapa S, Abou Ezzeddine OF, Bois JP, Schirger JA, Rosenbaum AN, Cooper LT. Routine Laboratory Biomarkers As Prognostic Indicators of Cardiac Sarcoidosis Outcomes. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2022;39(3):e2022023. [CrossRef]
- Kumar D, Madan K, Jagia P. et al. Screening for Cardiac Involvement in Patients with Sarcoidosis using AIIMS algorithm. JACC. 2024 Apr, 83 (13_Supplement) 654. doi.org/10.1016/S0735-1097(24)02644-5.
- Wong LL, Wang J, Liew OW, Richards AM, Chen YT. MicroRNA and Heart Failure. Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Apr 6;17(4):502. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Myocardial strain in a patient with cardiac sarcoidosis and reduced ejection fraction: Reduced values of GLS predominantly in basal segments of the septum.
Figure 1.
Myocardial strain in a patient with cardiac sarcoidosis and reduced ejection fraction: Reduced values of GLS predominantly in basal segments of the septum.
Figure 2.
Endomyocardial biopsy in a patient with cardiac sarcoidosis reveals a non-necrotizing granulomatous inflammation with patchy interstitial fibrosis on hematoxylin and eosin staining.
Figure 2.
Endomyocardial biopsy in a patient with cardiac sarcoidosis reveals a non-necrotizing granulomatous inflammation with patchy interstitial fibrosis on hematoxylin and eosin staining.
Figure 3.
Cardiac magnetic resonance in a patient with cardiac sarcoidosis: a) LGE MAG study, short axis: LGE in septum and inferior segments; b) LGE PSIR study, short axis: LGE changes in left and right ventricle, predominantly in septal segments (Avanto MRI, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany, 1.5T, CMR Lab University Clinical Hospital Center Bezanijska kosa, Belgrade, Serbia).
Figure 3.
Cardiac magnetic resonance in a patient with cardiac sarcoidosis: a) LGE MAG study, short axis: LGE in septum and inferior segments; b) LGE PSIR study, short axis: LGE changes in left and right ventricle, predominantly in septal segments (Avanto MRI, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany, 1.5T, CMR Lab University Clinical Hospital Center Bezanijska kosa, Belgrade, Serbia).
Figure 4.
Myocardial tissue mapping in a patient with cardiac sarcoidosis and high degree AV block: native T1 mapping revealing the areas of shortened native T1 time indicating myocardial fibrosis predominantly in the septum (Avanto MRI, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany, 1.5T, CMR Lab University Clinical Hospital Center Bezanijska kosa, Belgrade, Serbia).
Figure 4.
Myocardial tissue mapping in a patient with cardiac sarcoidosis and high degree AV block: native T1 mapping revealing the areas of shortened native T1 time indicating myocardial fibrosis predominantly in the septum (Avanto MRI, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany, 1.5T, CMR Lab University Clinical Hospital Center Bezanijska kosa, Belgrade, Serbia).
Figure 5.
Cardiac PET in a patient with cardiac sarcoidosis: 18F-FDG uptake in most of left ventricle, consistent with active inflammation; No significant uptake in apex or mid-inferolateral segment, compatible with possible fibrosis (a – apex, b – mid-ventricle, c-basal).
Figure 5.
Cardiac PET in a patient with cardiac sarcoidosis: 18F-FDG uptake in most of left ventricle, consistent with active inflammation; No significant uptake in apex or mid-inferolateral segment, compatible with possible fibrosis (a – apex, b – mid-ventricle, c-basal).
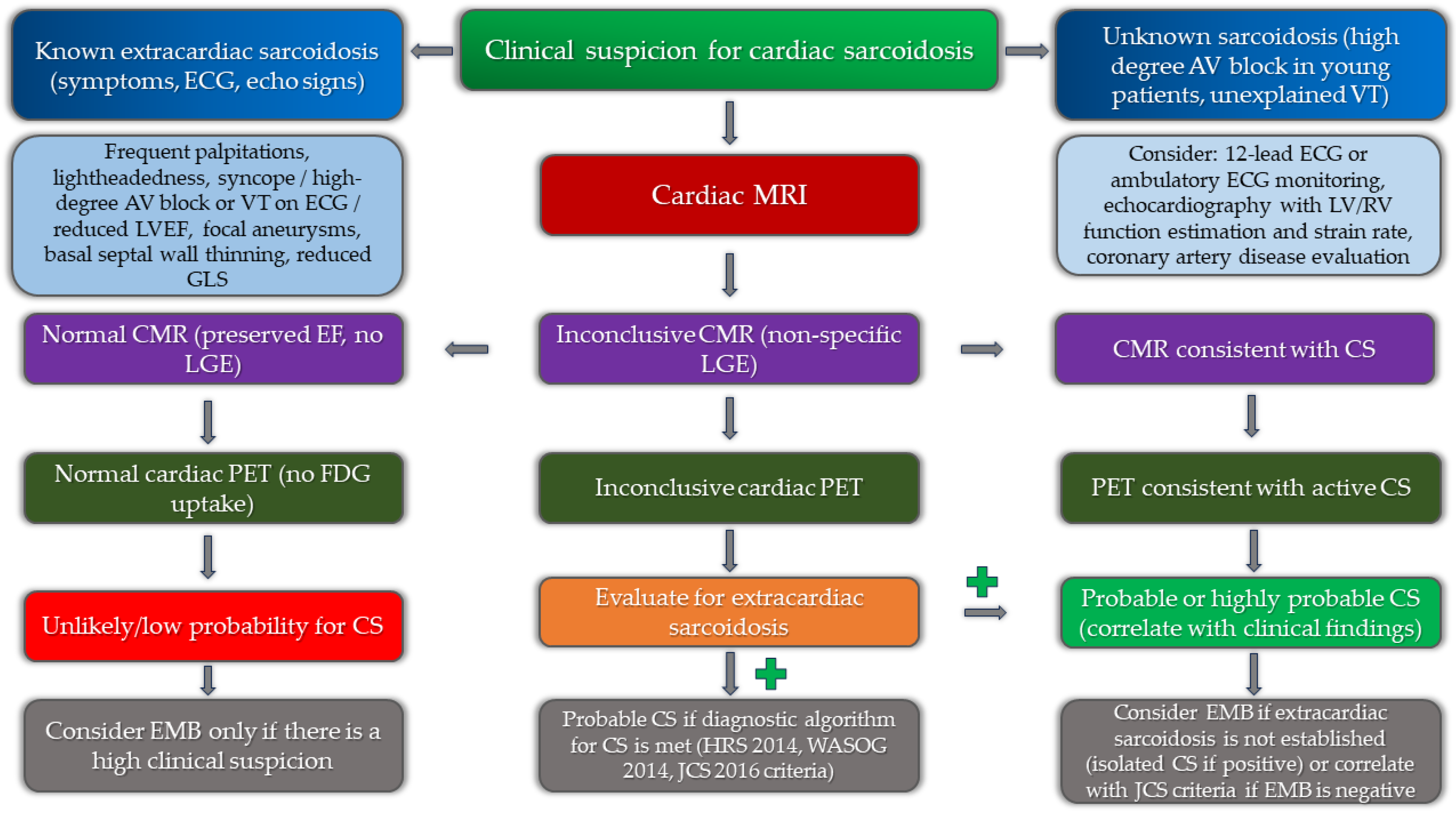
Figure 6.
Implementation of multimodality imaging into diagnostic algorithm for the diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis.
Figure 6.
Implementation of multimodality imaging into diagnostic algorithm for the diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis.
Table 1.
Japanese cardiac sarcoidosis and Heart Rhythm Society guidelines (Terasaki et al., 2017; Birnie et al. 2017).
Table 1.
Japanese cardiac sarcoidosis and Heart Rhythm Society guidelines (Terasaki et al., 2017; Birnie et al. 2017).
2017 JCS Guidelne on Diagnosis and
treatment of Cardiac Sarcoidosis |
2014 HRS expert consesus statement on the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias associated with cardiac sarcoidosis |
extracardiac sarcoidosis is confirmed and
two or more major criteria or one major and
two or more minor criteria are fullfilled
Major criteria
1. High-grade atrioventricular block (including complete atrioventricular block) or fatal ventricular arrhythmia (e.g., sustained ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation)
2. Basal thinning of the ventricular septum or abnormal ventricular wall anatomy (ventricular aneurysm, thinning of the middle or upper ventricular septum, regional ventricular wall thickening)
3. Left ventricular contractile dysfunction (left ventricular ejection fraction less than 50%) or focal ventricular wall asynergy
4. 67Ga citrate scintigraphy or FDG PET reveals abnormally high tracer accumulation in the heart
5. Gadolinium-enhanced MRI reveals delayed contrast enhancement of the myocardium
Minor criteria
1. Abnormal ECG findings: Ventricular arrhythmias (nonsustained ventricular tachycardia, multifocal or frequent premature ventricular contractions), bundle branch block, axis deviation, or abnormal Q waves
2. Perfusion defects on myocardial perfusion scintigraphy (SPECT)
3. Endomyocardial biopsy: Monocyte infiltration and moderate or severe myocardial interstitial fibrosis |
1. Unexplained reduced LVEF (<40%)
2. Corticosteroid- and/or immunosuppressant-responsive cardiomyopathy or heart block
3. unexplained sustained (spontaneous or induced) ventricular tachycardia
4. Mobitz type II second-degree AV block or third-degree AV block
5. patchy uptake of cardiac FDG-PET in a pattern consistent with cardiac sarcoidosis
6. late gadolinium enhancement on CMRI in a pattern consistent with cardiac sarcoidosis
7. positive gallium uptake in a pattern consistent with cardiac |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).