Submitted:
30 July 2024
Posted:
30 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Traditional Methods
1.2. Deep Learning-Based Methods
1.3. Motivation and Contribution
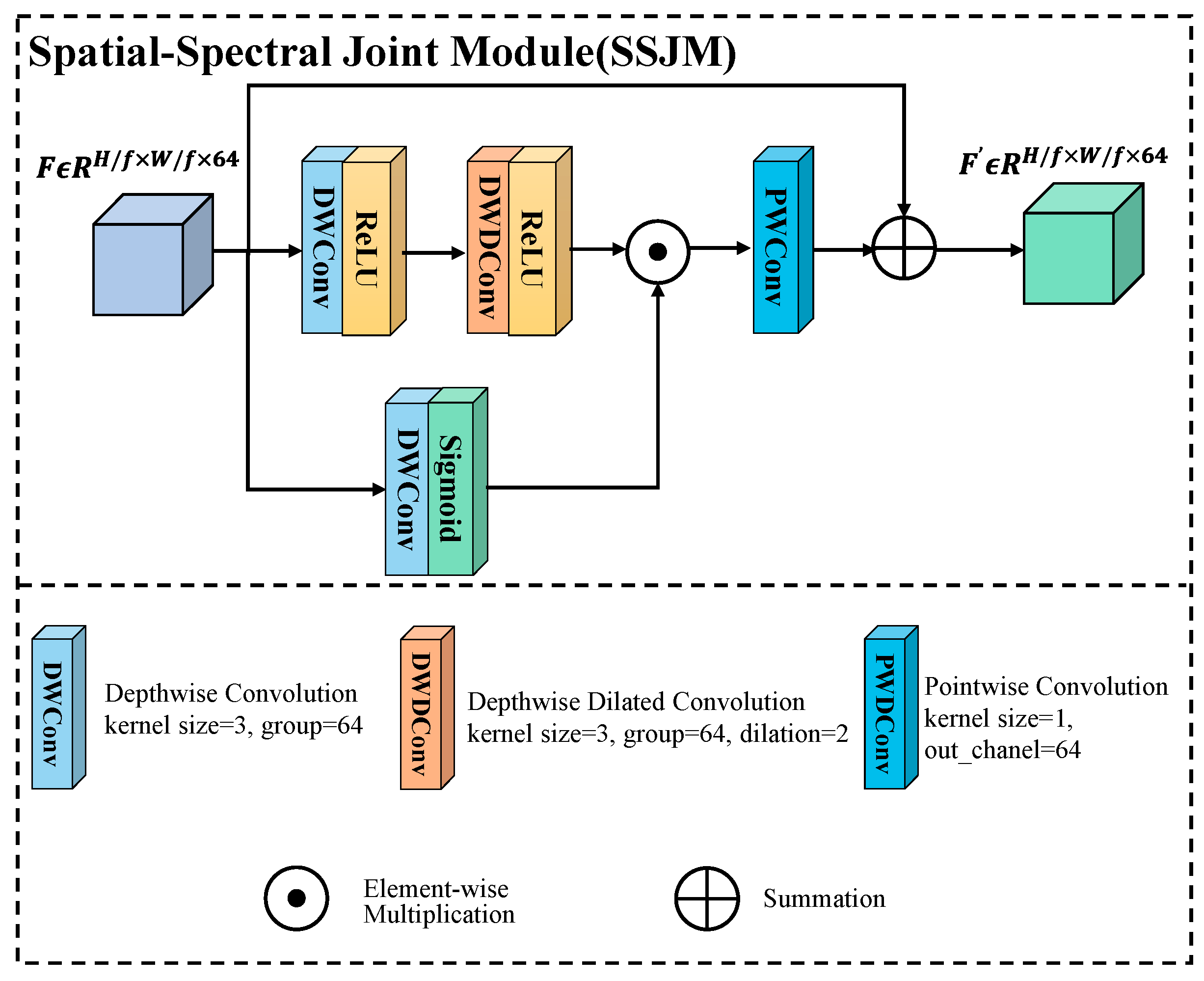
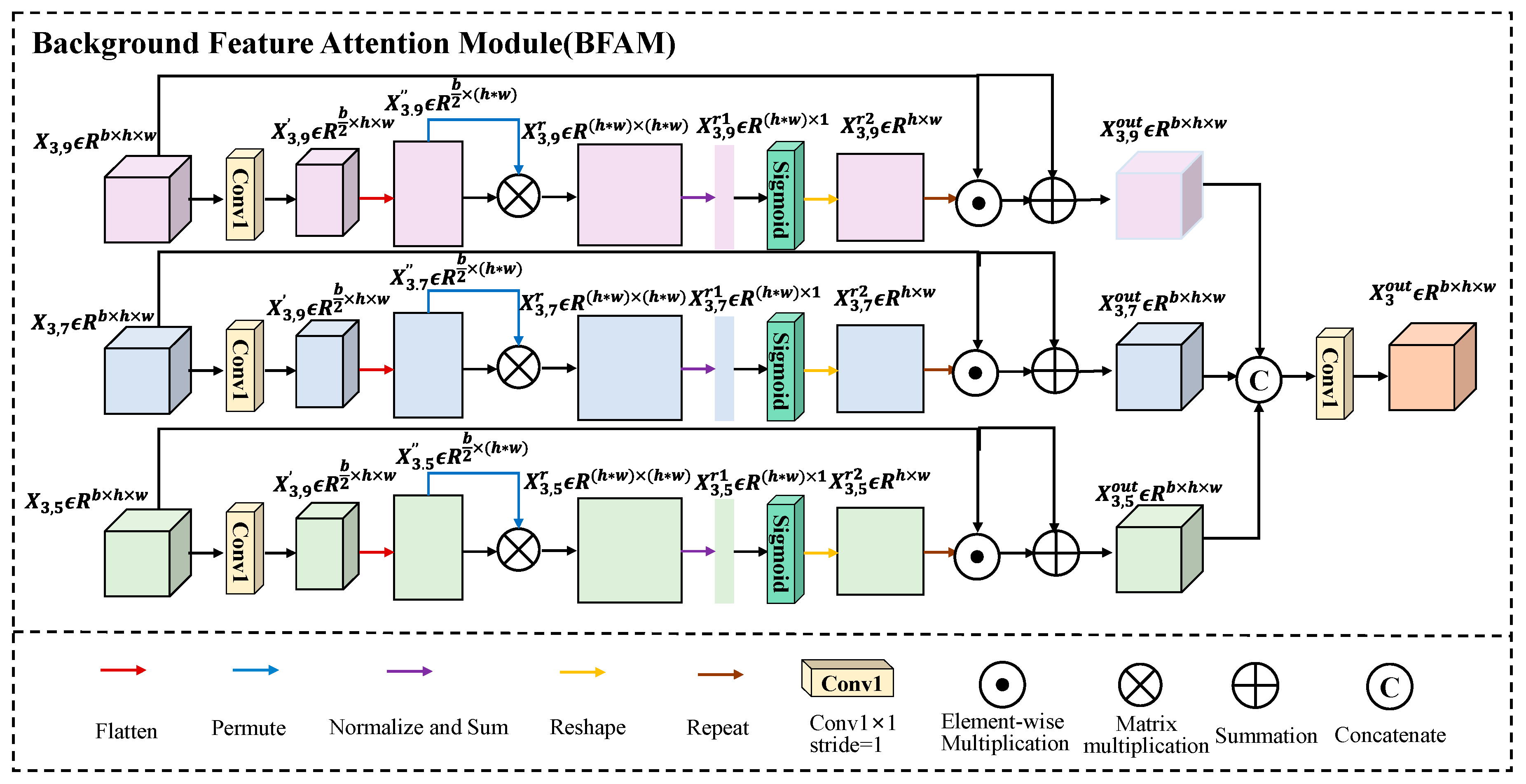
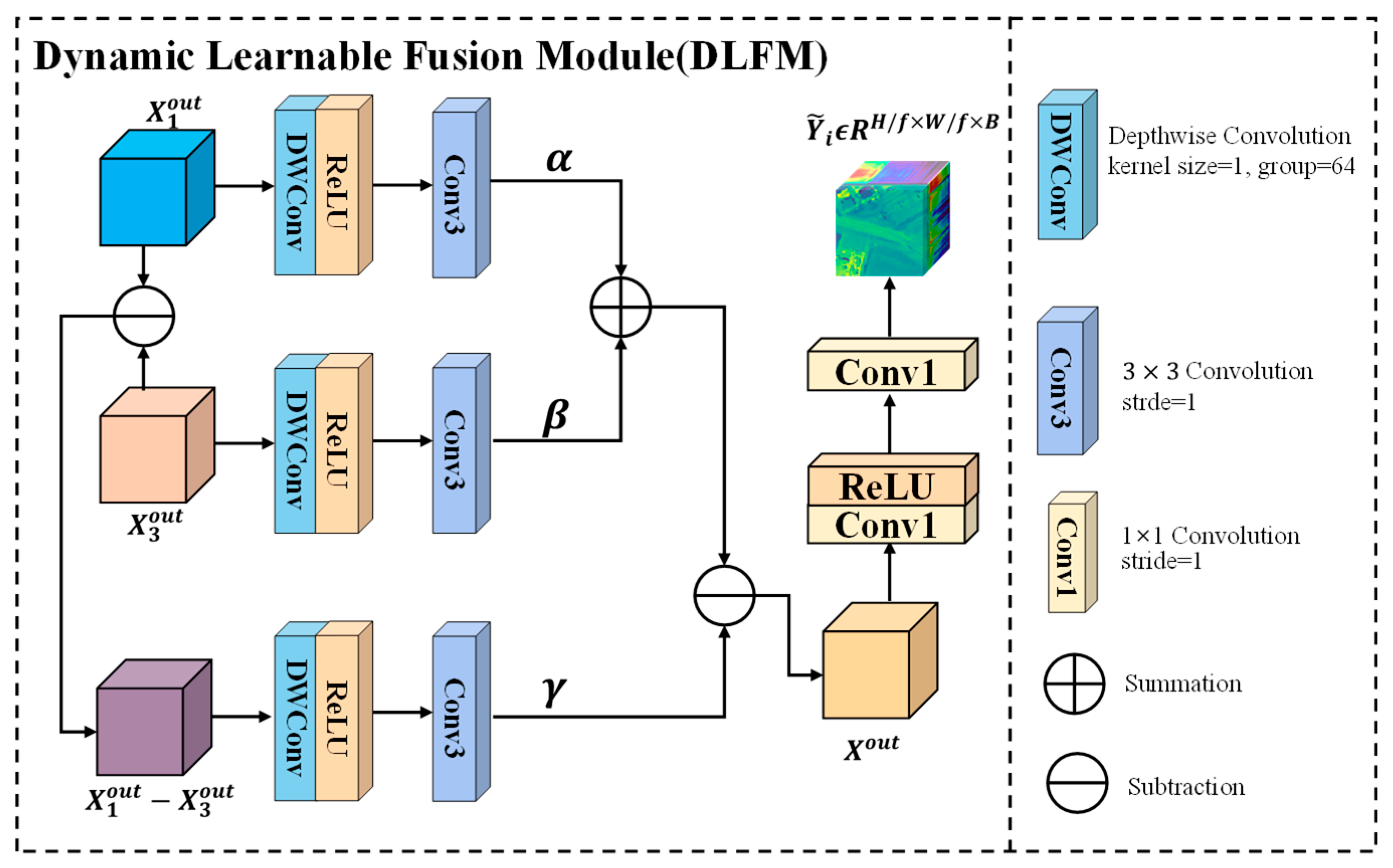
2. Proposed Method: MMBSN
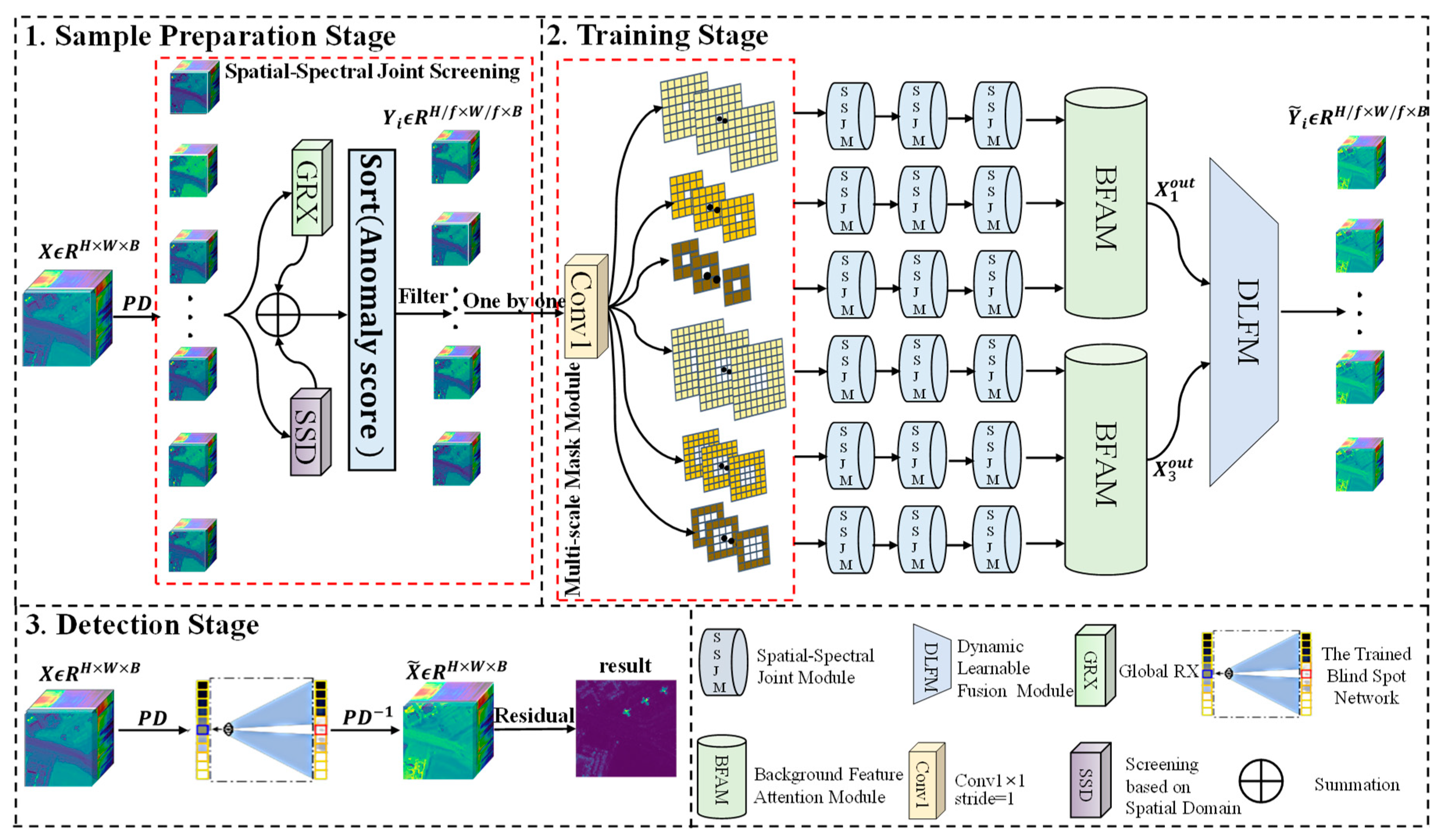
2.1. Overview
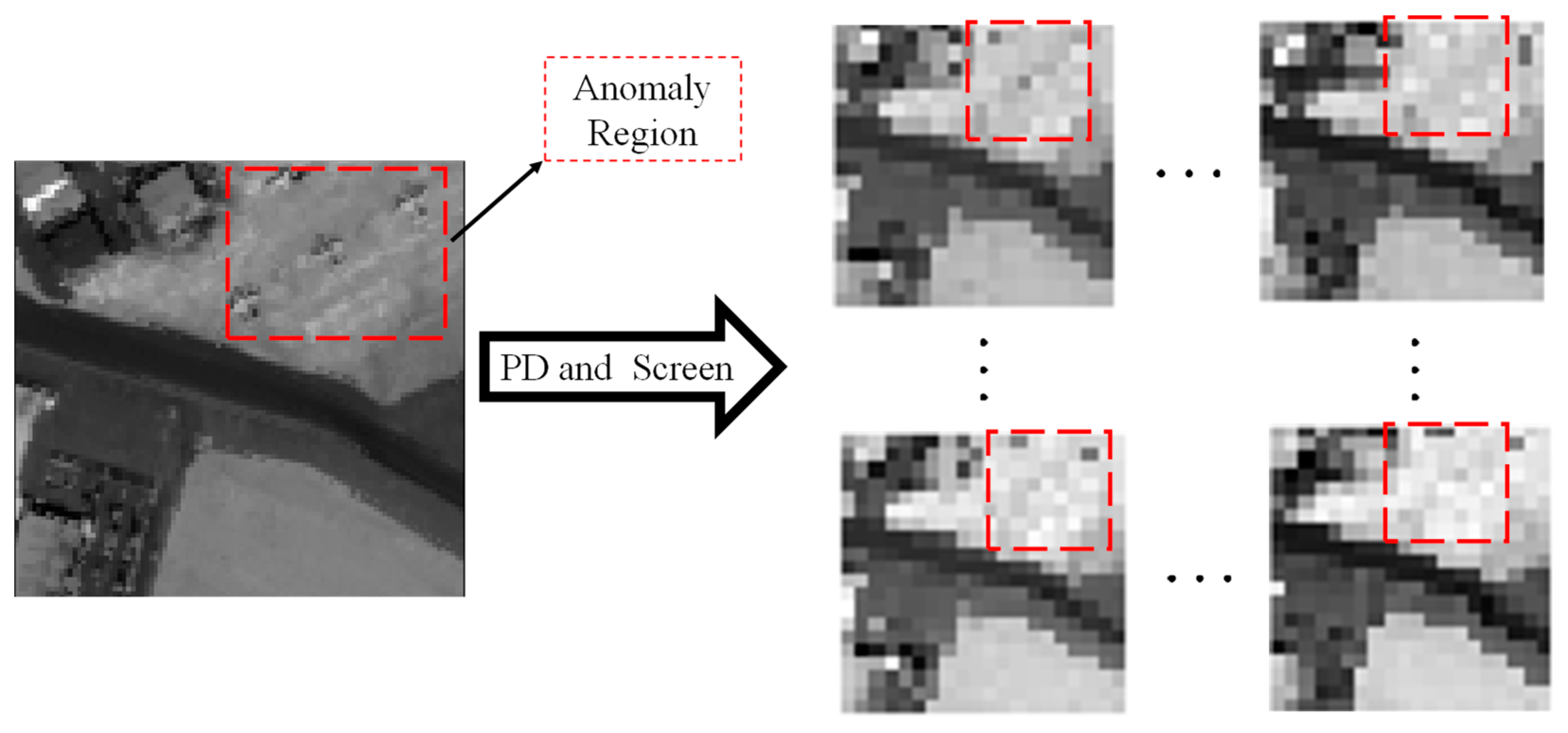
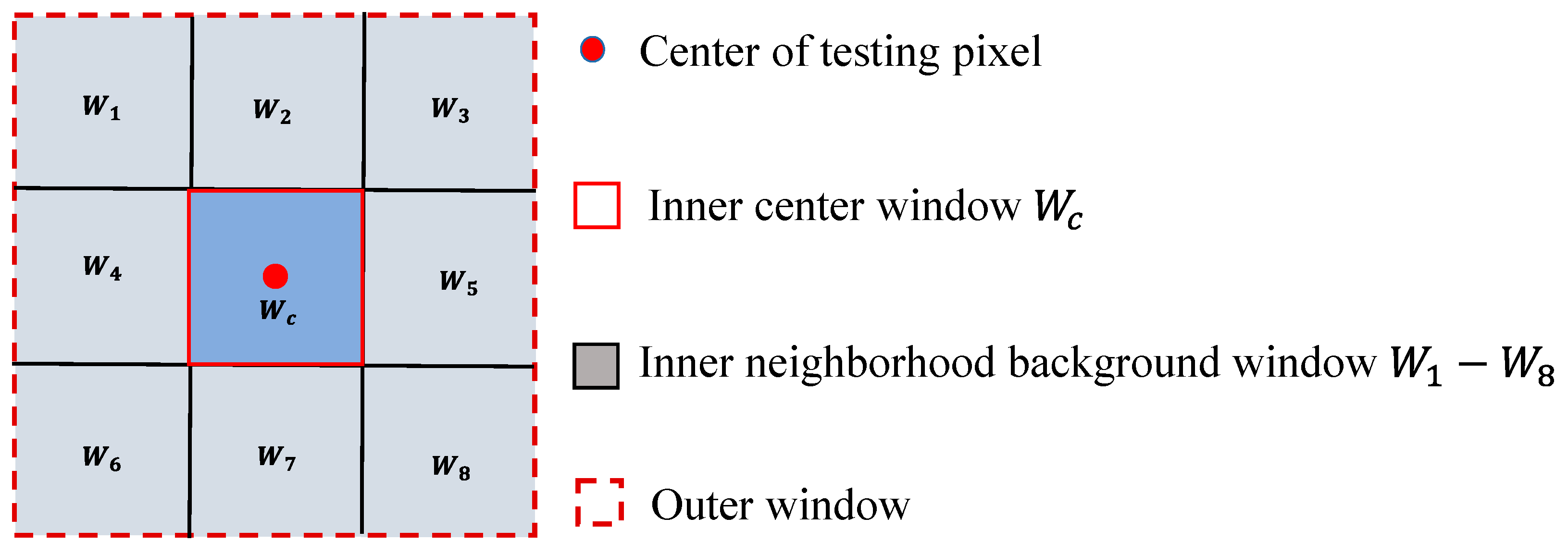
2.2. Sample Preparation Stage
2.3. Training Stage
2.4. Detection Stage

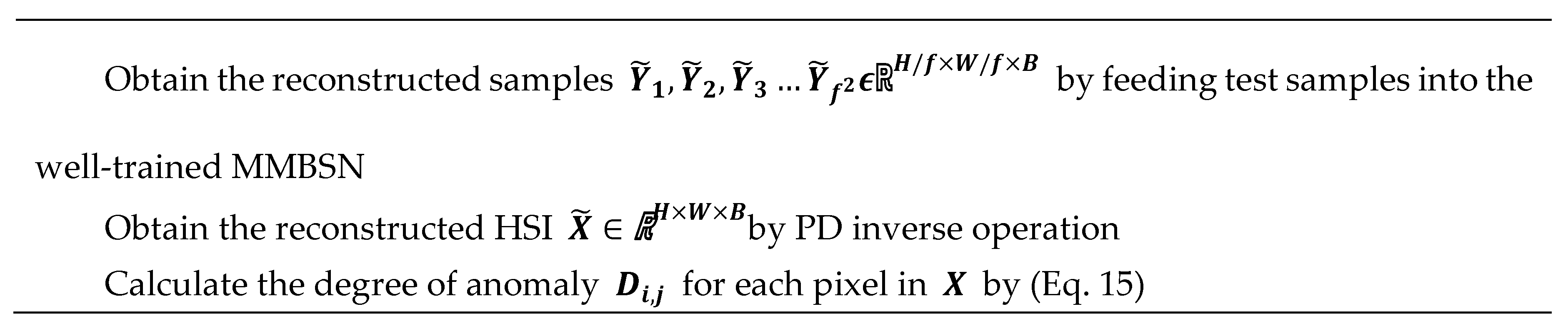
3. Experiments and Analysis
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Evaluation Metrics
3.3. Comparison Algorithms and Evaluation Metrics
3.4. Detection Performance for Different Methods
3.5. Parameter Analysis
3.6. Ablation Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- X. Sun, Y. Qu, L. Gao, X. Sun, H. Qi, B. Zhang, T. J. I. T. o. G. Shen, and R. Sensing, "Target detection through tree-structured encoding for hyperspectral images," vol. 59, no. 5, pp. 4233-4249, 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Gao, X. Sun, X. Sun, L. Zhuang, Q. Du, B. J. I. T. o. G. Zhang, and R. Sensing, "Hyperspectral anomaly detection based on chessboard topology," vol. 61, pp. 1-16, 2023.
- X. Cheng, M. Zhang, S. Lin, K. Zhou, S. Zhao, H. J. I. G. Wang, and R. S. Letters, "Two-stream isolation forest based on deep features for hyperspectral anomaly detection," 2023.
- G. Tejasree, L. J. M. T. Agilandeeswari, and Applications, "An extensive review of hyperspectral image classification and prediction: techniques and challenges," pp. 1-98, 2024. [CrossRef]
- H. Su, Z. Wu, H. Zhang, Q. J. I. G. Du, and R. S. Magazine, "Hyperspectral anomaly detection: A survey," vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 64-90, 2021. [CrossRef]
- I. Racetin and A. J. A. S. Krtalić, "Systematic review of anomaly detection in hyperspectral remote sensing applications," vol. 11, no. 11, p. 4878, 2021. [CrossRef]
- I. S. Reed, X. J. I. t. o. a. Yu, speech,, and s. processing, "Adaptive multiple-band CFAR detection of an optical pattern with unknown spectral distribution," vol. 38, no. 10, pp. 1760-1770, 1990. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Molero, E. M. Garzon, I. Garcia, A. J. I. j. o. s. t. i. a. e. o. Plaza, and r. sensing, "Analysis and optimizations of global and local versions of the RX algorithm for anomaly detection in hyperspectral data," vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 801-814, 2013. [CrossRef]
- H. Kwon, N. M. J. I. t. o. G. Nasrabadi, and R. Sensing, "Kernel RX-algorithm: A nonlinear anomaly detector for hyperspectral imagery," vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 388-397, 2005.
- A. Schaum, "Joint subspace detection of hyperspectral targets," in 2004 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No. 04TH8720), 2004, vol. 3: IEEE.
- W. Li, Q. J. I. T. o. g. Du, and r. sensing, "Collaborative representation for hyperspectral anomaly detection," vol. 53, no. 3, pp. 1463-1474, 2014.
- B. Tu, N. Li, Z. Liao, X. Ou, and G. J. R. S. Zhang, "Hyperspectral anomaly detection via spatial density background purification," vol. 11, no. 22, p. 2618, 2019.
- M. Vafadar, H. J. I. G. Ghassemian, and R. S. Letters, "Anomaly detection of hyperspectral imagery using modified collaborative representation," vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 577-581, 2018.
- Q. Ling, Y. Guo, Z. Lin, W. J. I. T. o. G. An, and R. Sensing, "A constrained sparse representation model for hyperspectral anomaly detection," vol. 57, no. 4, pp. 2358-2371, 2018.
- L. Ren, Z. Ma, F. Bovolo, L. J. I. T. o. G. Bruzzone, and R. Sensing, "A nonconvex framework for sparse unmixing incorporating the group structure of the spectral library," vol. 60, pp. 1-19, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yuan, D. Ma, and Q. J. I. A. Wang, "Hyperspectral anomaly detection via sparse dictionary learning method of capped norm," vol. 7, pp. 16132-16144, 2019. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhuang, M. K. Ng, Y. J. I. T. o. G. Liu, and R. Sensing, "Cross-track illumination correction for hyperspectral pushbroom sensor images using low-rank and sparse representations," vol. 61, pp. 1-17, 2023.
- T. Cheng, B. J. I. T. o. G. Wang, and R. Sensing, "Graph and total variation regularized low-rank representation for hyperspectral anomaly detection," vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 391-406, 2019.
- Y. Yang, J. Zhang, S. Song, and D. J. R. s. Liu, "Hyperspectral anomaly detection via dictionary construction-based low-rank representation and adaptive weighting," vol. 11, no. 2, p. 192, 2019.
- Y. Qu, W. Wang, R. Guo, B. Ayhan, C. Kwan, S. Vance, H. J. I. T. o. G. Qi, and R. Sensing, "Hyperspectral anomaly detection through spectral unmixing and dictionary-based low-rank decomposition," vol. 56, no. 8, pp. 4391-4405, 2018.
- X. Cheng, R. Mu, S. Lin, M. Zhang, and H. J. R. S. Wang, "Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection via Low-Rank Representation with Dual Graph Regularizations and Adaptive Dictionary," vol. 16, no. 11, p. 1837, 2024. [CrossRef]
- C. Zhang, H. Su, X. Wang, Z. Wu, Y. Yang, Z. Xue, Q. J. I. T. o. G. Du, and R. Sensing, "Self-paced Probabilistic Collaborative Representation for Anomaly Detection of Hyperspectral Images," 2024. [CrossRef]
- X. Kang, X. Zhang, S. Li, K. Li, J. Li, J. A. J. I. T. o. G. Benediktsson, and R. Sensing, "Hyperspectral anomaly detection with attribute and edge-preserving filters," vol. 55, no. 10, pp. 5600-5611, 2017.
- W. Xie, T. Jiang, Y. Li, X. Jia, J. J. I. T. o. G. Lei, and R. Sensing, "Structure tensor and guided filtering-based algorithm for hyperspectral anomaly detection," vol. 57, no. 7, pp. 4218-4230, 2019.
- Z. Wang, X. Wang, K. Tan, B. Han, J. Ding, and Z. J. P. R. Liu, "Hyperspectral anomaly detection based on variational background inference and generative adversarial network," vol. 143, p. 109795, 2023.
- S. Zhang, X. Meng, Q. Liu, G. Yang, and W. J. R. S. Sun, "Feature-Decision Level Collaborative Fusion Network for Hyperspectral and LiDAR Classification," vol. 15, no. 17, p. 4148, 2023. [CrossRef]
- X. Cheng, Y. Huo, S. Lin, Y. Dong, S. Zhao, M. Zhang, H. J. I. T. o. I. Wang, and Measurement, "Deep Feature Aggregation Network for Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection," 2024. [CrossRef]
- P. Xiang, S. Ali, J. Zhang, S. K. Jung, H. J. I. J. o. A. E. O. Zhou, and Geoinformation, "Pixel-associated autoencoder for hyperspectral anomaly detection," vol. 129, p. 103816, 2024.
- D. Wang, L. Zhuang, L. Gao, X. Sun, X. Zhao, A. J. I. T. o. G. Plaza, and R. Sensing, "Sliding Dual-Window-Inspired Reconstruction Network for Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection," 2024.
- J. Lian, L. Wang, H. Sun, H. J. I. T. o. N. N. Huang, and L. Systems, "GT-HAD: Gated Transformer for Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection," 2024.
- T. Jiang, Y. Li, W. Xie, Q. J. I. T. o. G. Du, and R. Sensing, "Discriminative reconstruction constrained generative adversarial network for hyperspectral anomaly detection," vol. 58, no. 7, pp. 4666-4679, 2020.
- P. Xiang, S. Ali, S. K. Jung, H. J. I. T. o. G. Zhou, and R. Sensing, "Hyperspectral anomaly detection with guided autoencoder," vol. 60, pp. 1-18, 2022. [CrossRef]
- G. Fan, Y. Ma, X. Mei, F. Fan, J. Huang, J. J. I. T. o. G. Ma, and R. Sensing, "Hyperspectral anomaly detection with robust graph autoencoders," vol. 60, pp. 1-14, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Wang, X. Wang, L. Zhang, Y. J. I. T. o. G. Zhong, and R. Sensing, "Auto-AD: Autonomous hyperspectral anomaly detection network based on fully convolutional autoencoder," vol. 60, pp. 1-14, 2021.
- S. Wang, X. Wang, L. Zhang, Y. J. I. T. o. G. Zhong, and R. Sensing, "Deep low-rank prior for hyperspectral anomaly detection," vol. 60, pp. 1-17, 2022.
- X. Cheng, M. Zhang, S. Lin, Y. Li, H. J. I. T. o. I. Wang, and Measurement, "Deep Self-Representation Learning Framework for Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection," 2023.
- L. Wang, X. Wang, A. Vizziello, P. J. I. T. o. G. Gamba, and R. Sensing, "RSAAE: Residual self-attention-based autoencoder for hyperspectral anomaly detection," 2023.
- D. Wang, L. Zhuang, L. Gao, X. Sun, M. Huang, A. J. I. T. o. G. Plaza, and R. Sensing, "PDBSNet: Pixel-shuffle down-sampling blind-spot reconstruction network for hyperspectral anomaly detection," 2023.
- D. Wang, L. Zhuang, L. Gao, X. Sun, M. Huang, A. J. I. T. o. G. Plaza, and R. Sensing, "BockNet: Blind-block reconstruction network with a guard window for hyperspectral anomaly detection," vol. 61, pp. 1-16, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Gao, D. Wang, L. Zhuang, X. Sun, M. Huang, and A. Plaza, "BS 3 LNet: A new blind-spot self-supervised learning network for hyperspectral anomaly detection," IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, vol. 61, pp. 1-18, 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. Manolakis and G. Shaw, "Detection algorithms for hyperspectral imaging applications," IEEE signal processing magazine, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 29-43, 2002. [CrossRef]
- A. P. Bradley, "The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms," Pattern recognition, vol. 30, no. 7, pp. 1145-1159, 1997. [CrossRef]
- C. Ferri, J. Hernández-Orallo, and P. A. Flach, "A coherent interpretation of AUC as a measure of aggregated classification performance," in Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-11), 2011, pp. 657-664.
- D. Manolakis and G. J. I. s. p. m. Shaw, "Detection algorithms for hyperspectral imaging applications," vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 29-43, 2002.
- Y. Xu, Z. Wu, J. Li, A. Plaza, Z. J. I. T. o. G. Wei, and R. Sensing, "Anomaly detection in hyperspectral images based on low-rank and sparse representation," vol. 54, no. 4, pp. 1990-2000, 2015. [CrossRef]
- A. P. J. P. r. Bradley, "The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms," vol. 30, no. 7, pp. 1145-1159, 1997.
- C.-I. J. I. T. o. G. Chang and R. Sensing, "An effective evaluation tool for hyperspectral target detection: 3D receiver operating characteristic curve analysis," vol. 59, no. 6, pp. 5131-5153, 2020.

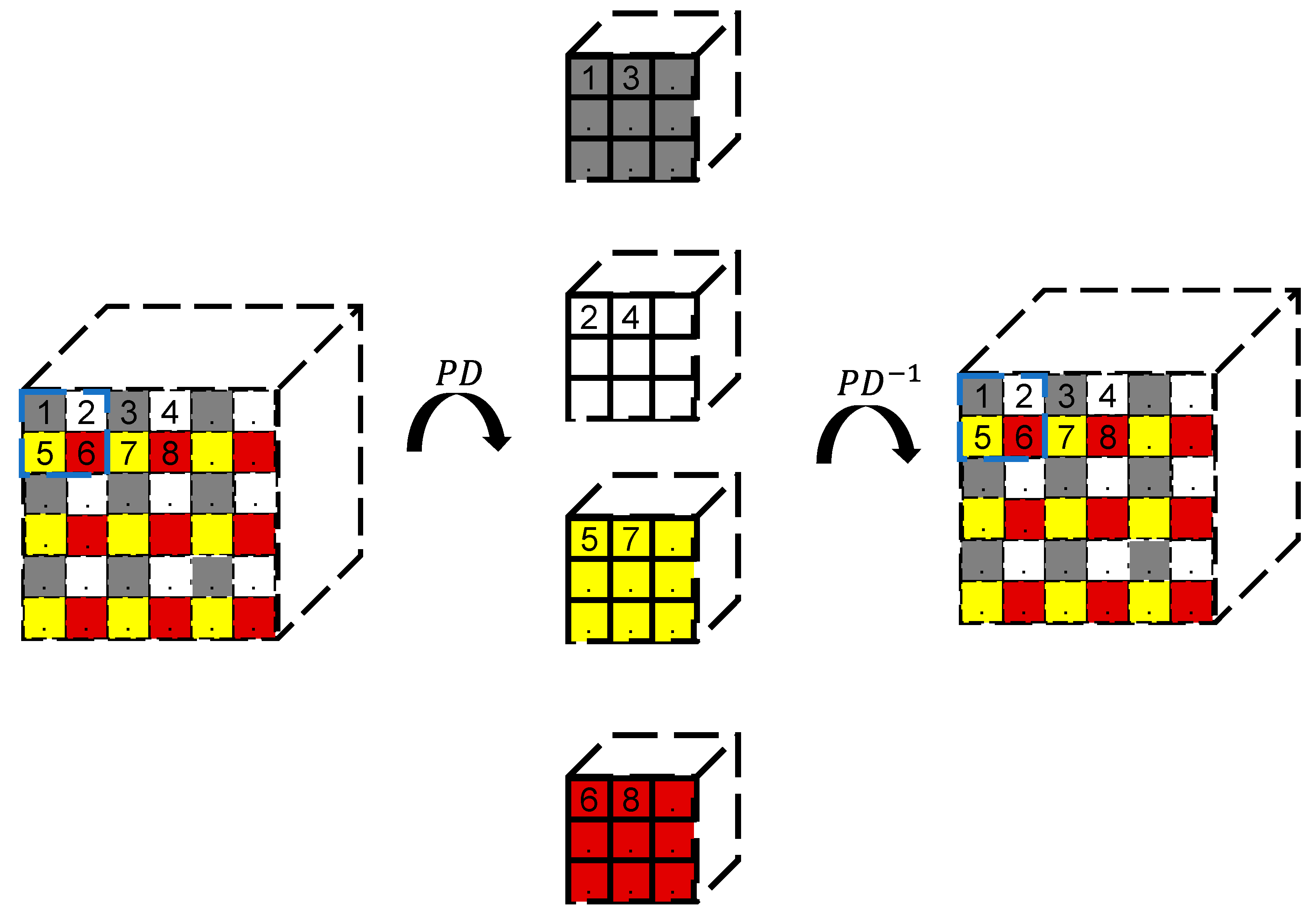
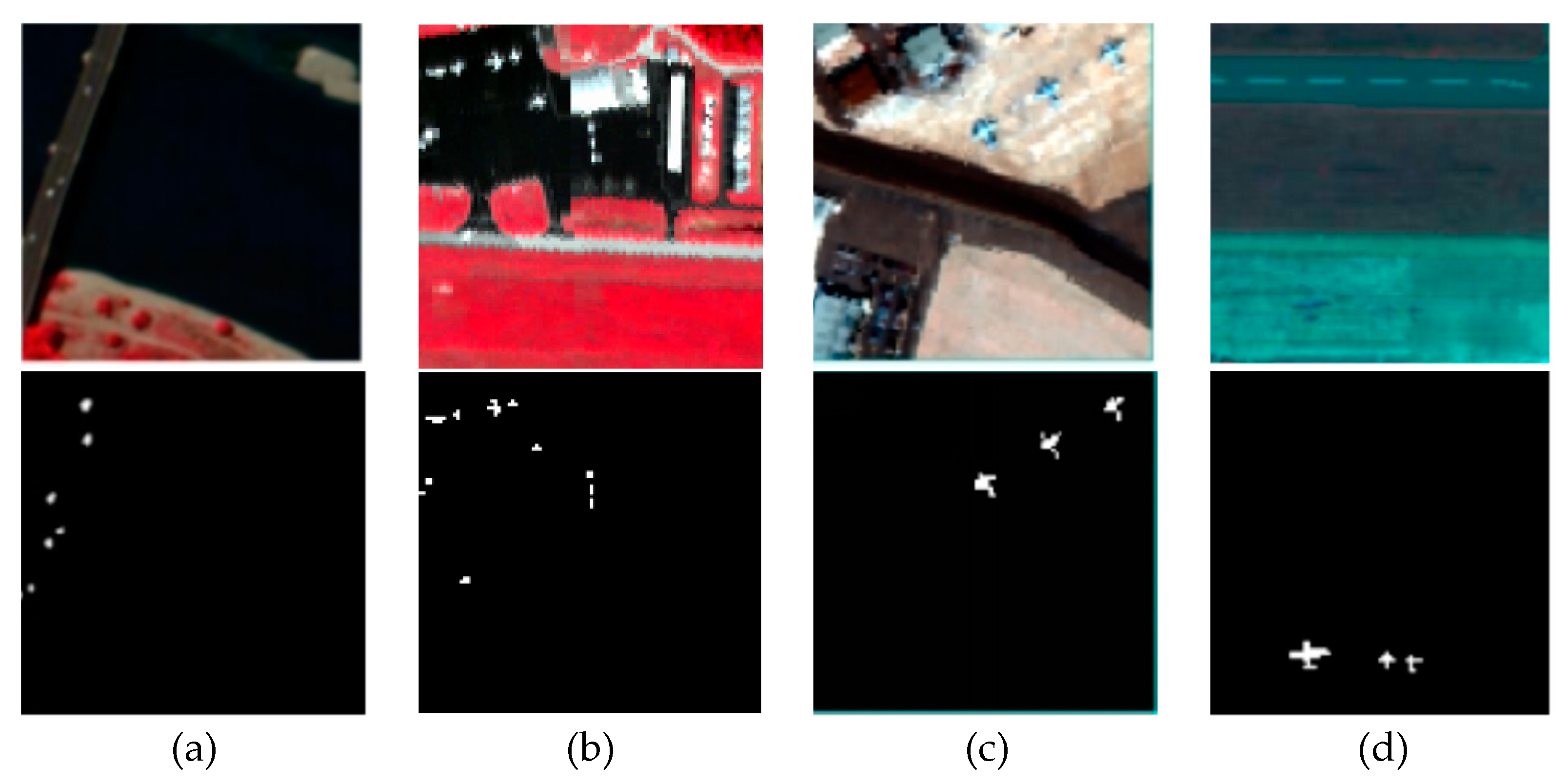
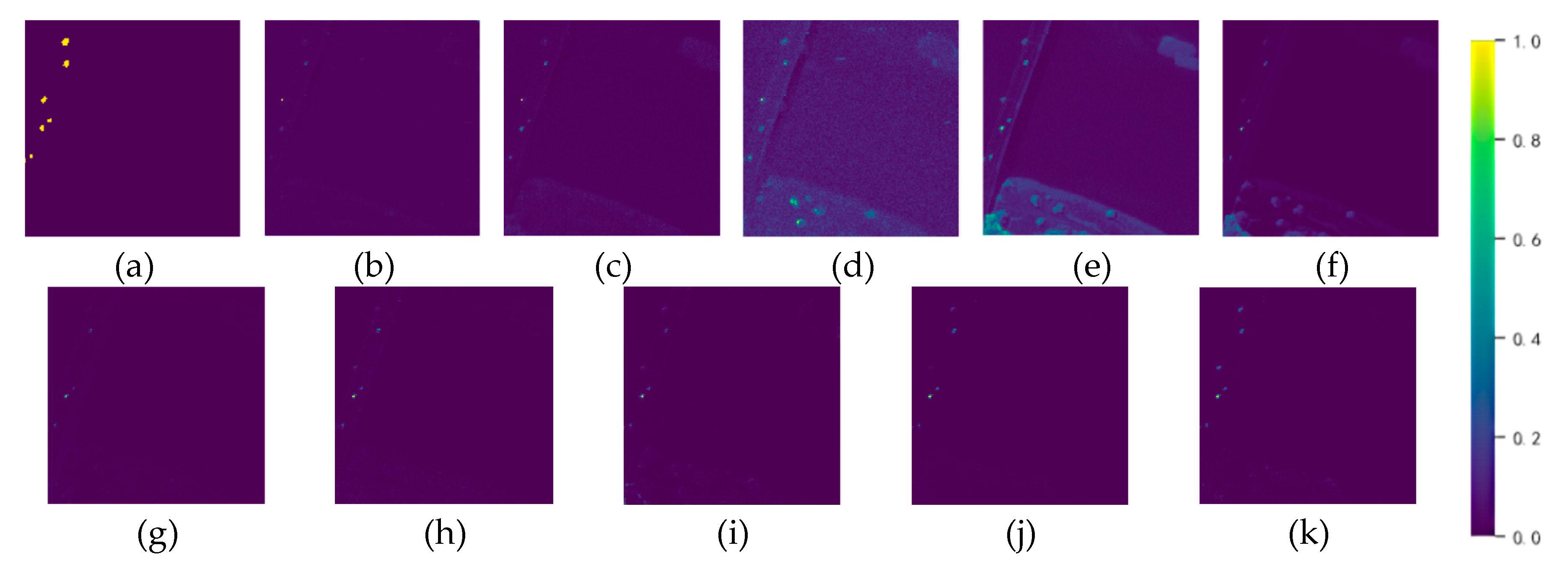
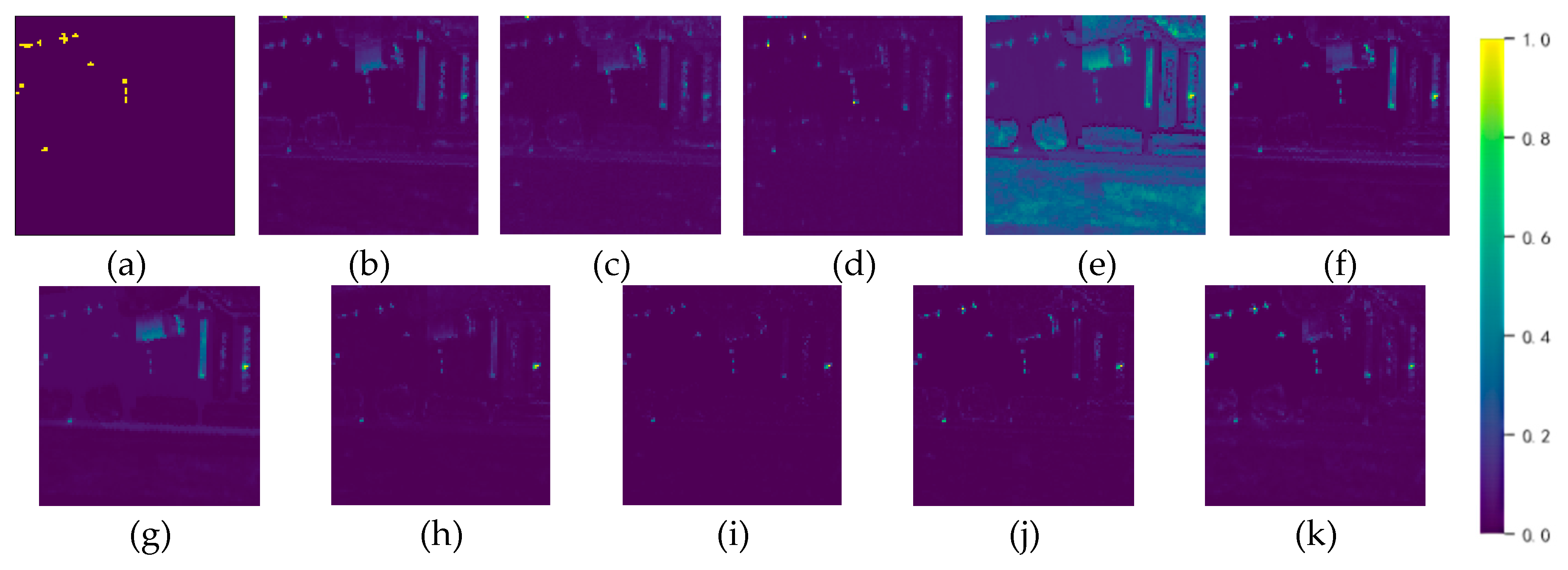
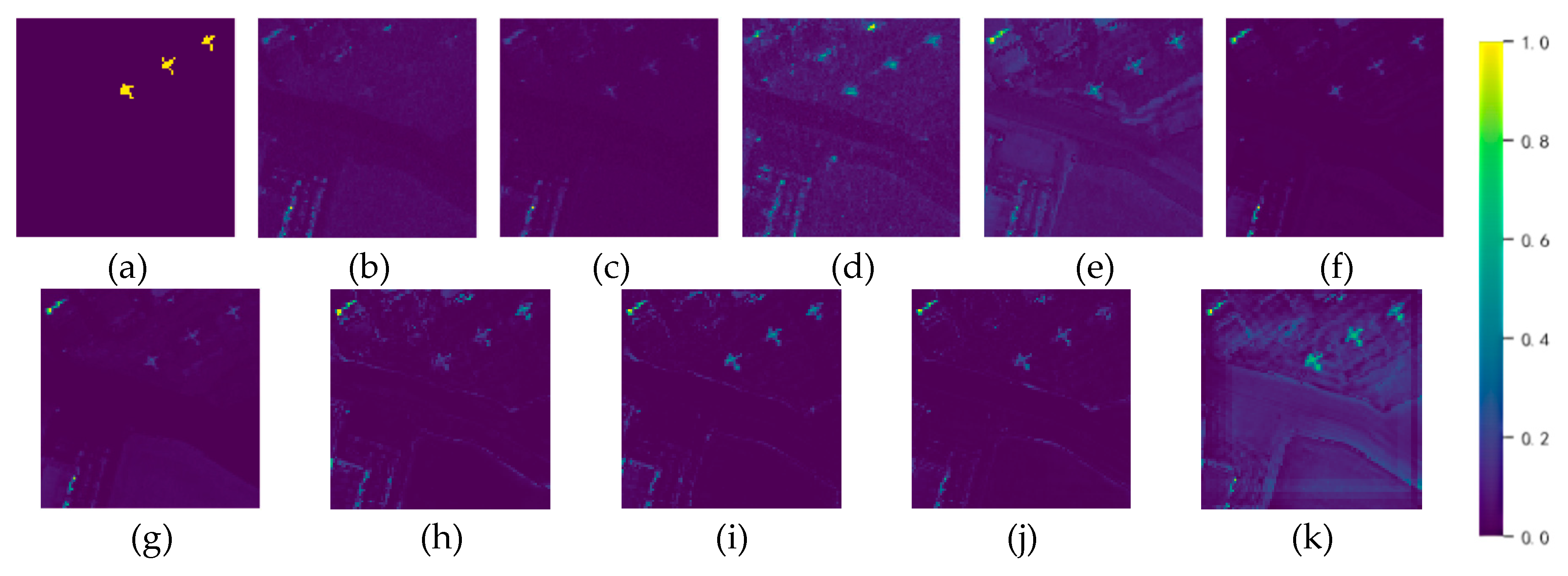
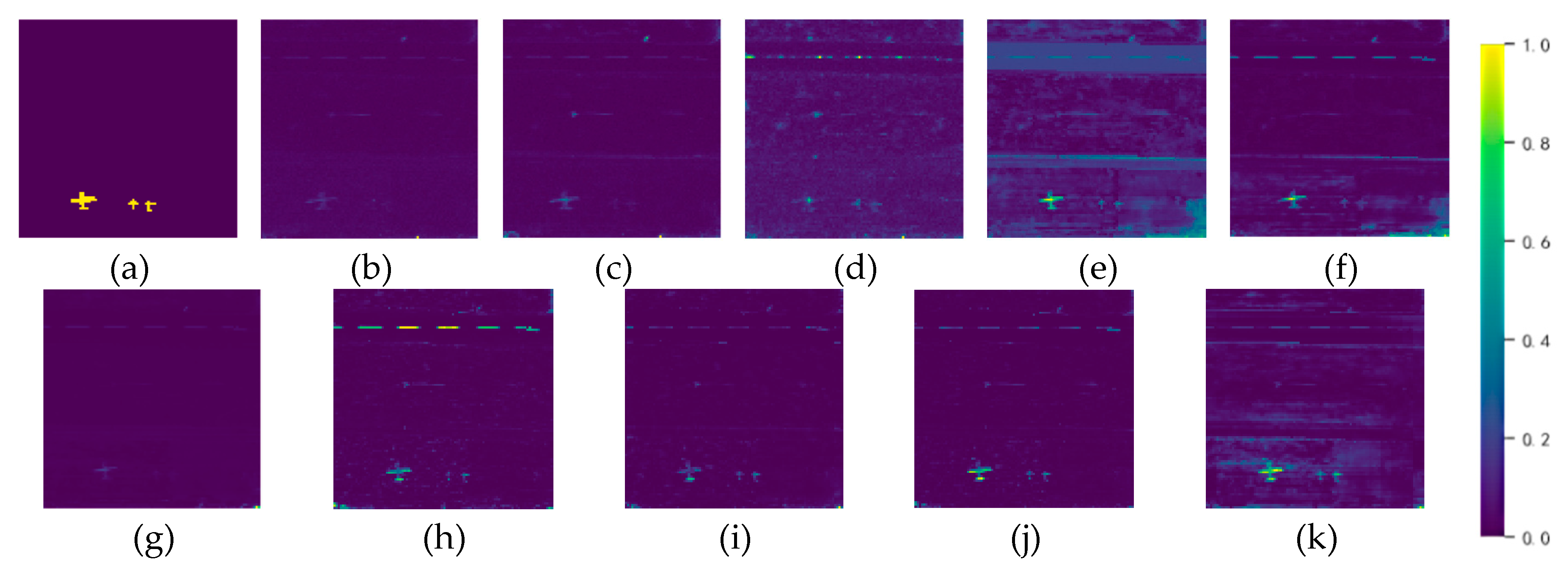
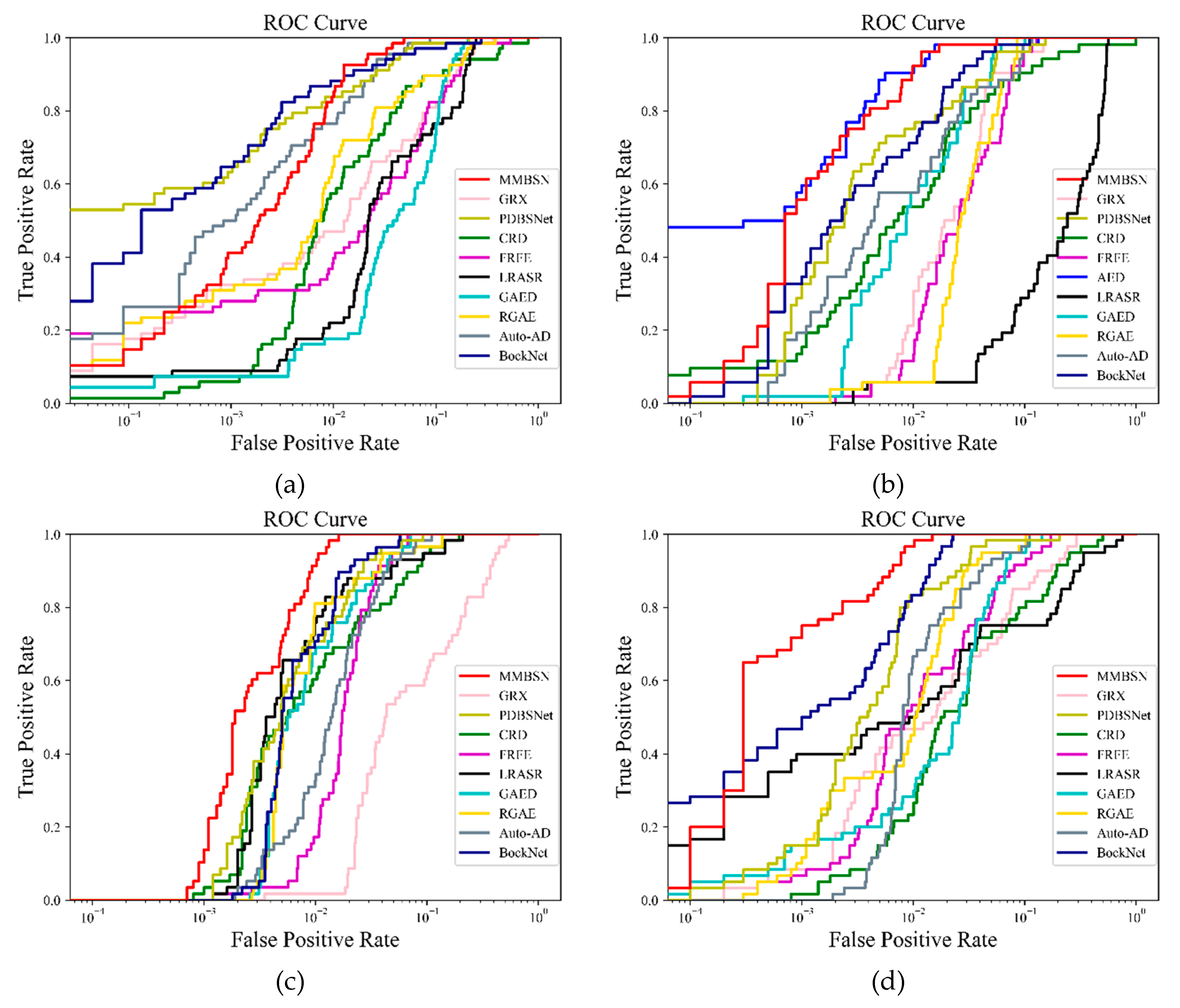
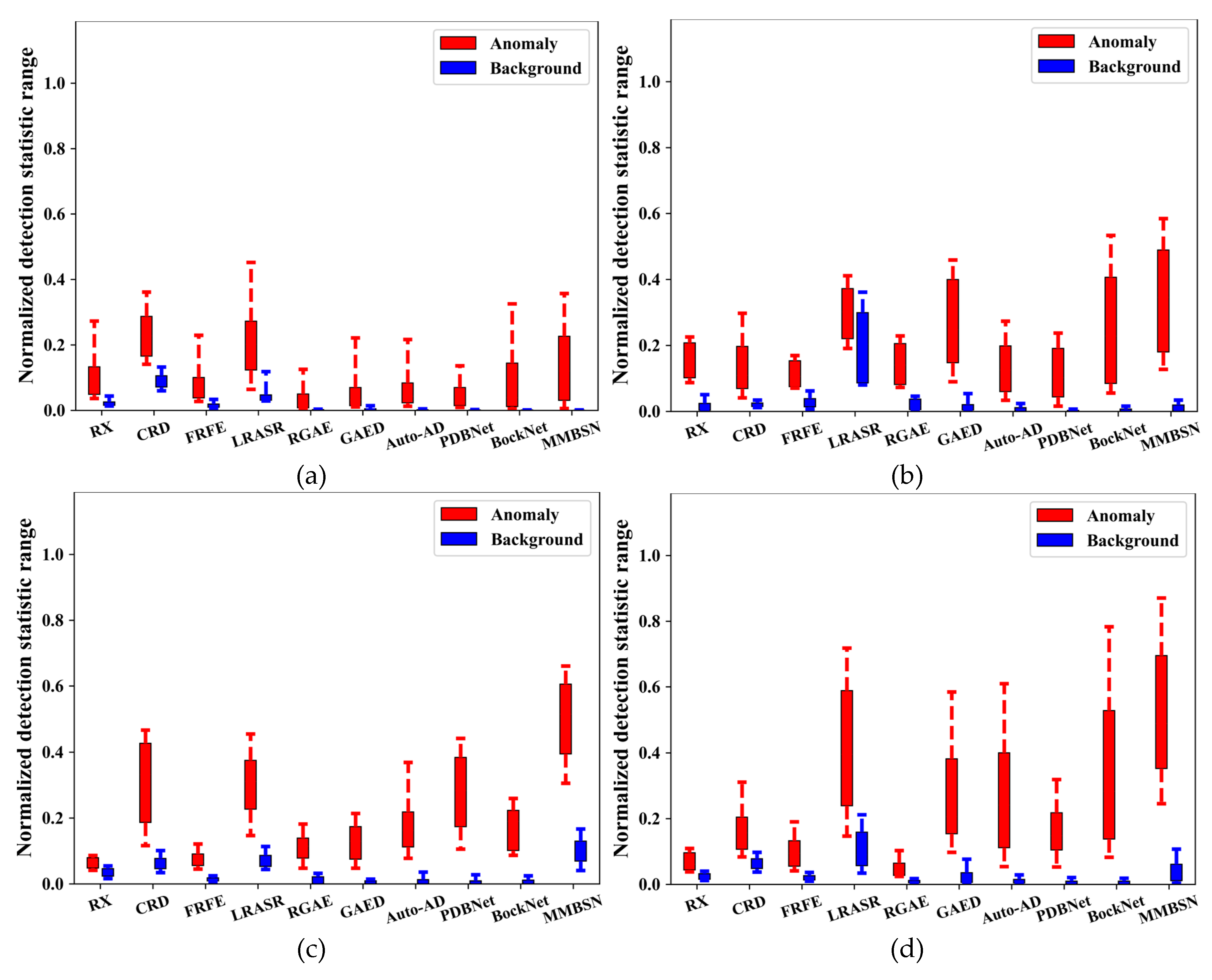
| Dataset | Sensor | Image size | resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pavia | ROSIS | 150×150×102 | 1.3m |
| Gainesville | AVIRIS | 100×100×191 | 3.5m |
| San Diego | AVIRIS | 100×100×189 | 3.5m |
| Gulfport | AVIRIS | 100×100×191 | 3.4m |
| Dataset | of Different Methods | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRX | FRFE | CRD | LRASR | GAED | RGAE | Auto-AD | PDBSNet | BockNet | MMBSN | |
| Pavia | 0.9538 | 0.9457 | 0.9510 | 0.9380 | 0.9398 | 0.9688 | 0.9925 | 0.9915 | 0.9905 | 0.9945 |
| Gainesville | 0.9684 | 0.9633 | 0.9536 | 0.7283 | 0.9829 | 0.9647 | 0.9808 | 0.9863 | 0.9901 | 0.9963 |
| San Diego | 0.8736 | 0.9787 | 0.9768 | 0.9824 | 0.9861 | 0.9854 | 0.9794 | 0.9892 | 0.9901 | 0.9961 |
| Gulfport | 0.9526 | 0.9722 | 0.9342 | 0.9120 | 0.9705 | 0.9842 | 0.9825 | 0.9895 | 0.9955 | 0.9983 |
| Average | 0.9371 | 0.9650 | 0.9539 | 0.8902 | 0.9698 | 0.9758 | 0.9838 | 0.9891 | 0.9916 | 0.9963 |
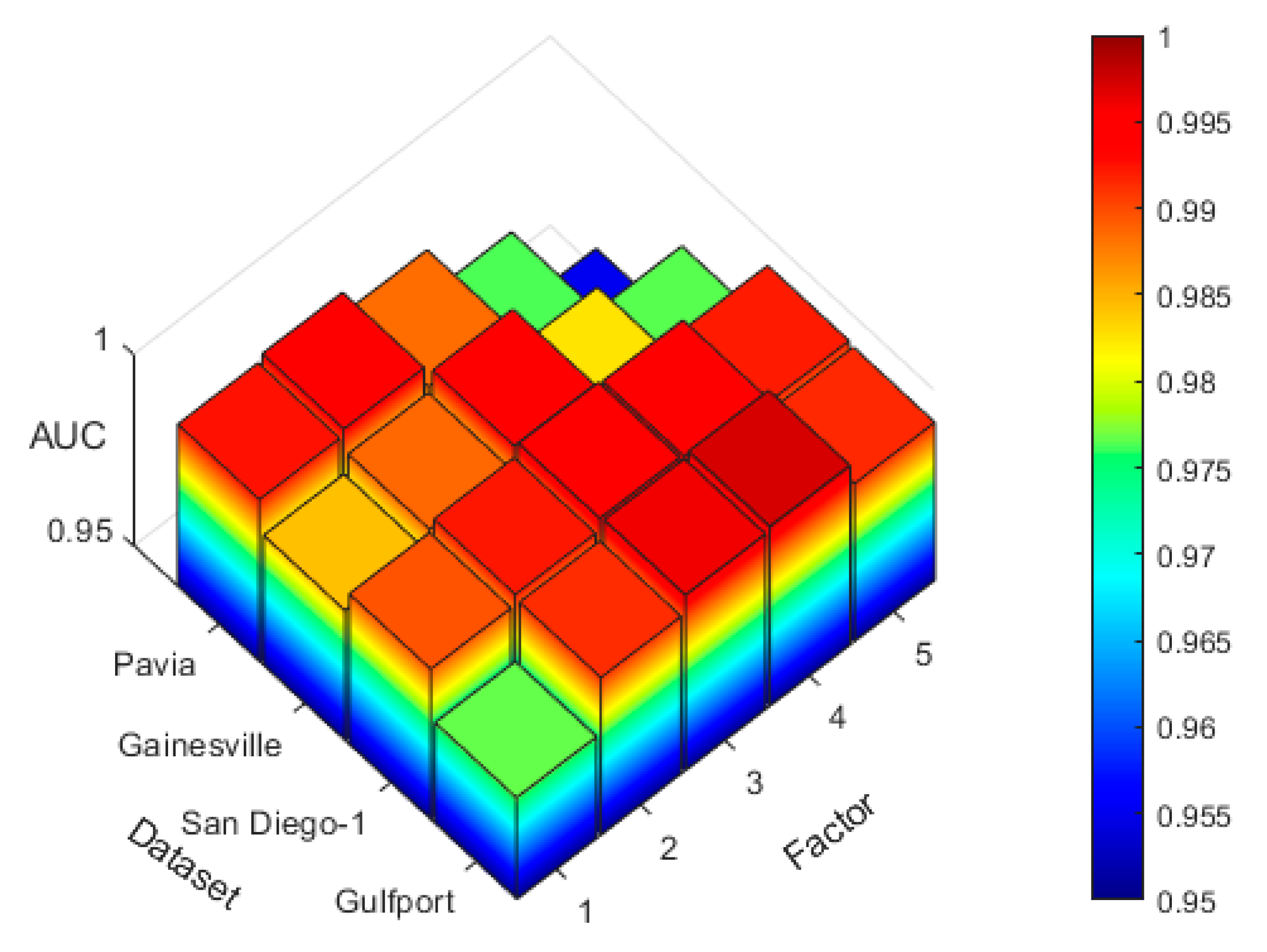
| Factor | The AUC of different factors on four datasets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pavia | Gainesville | San Diego | Gulfport | |
| 1(Rate=1.0) | 0.9925 | 0.9842 | 0.9896 | 0.9767 |
| 2(Rate=0.5) | 0.9941 | 0.9886 | 0.9923 | 0.9913 |
| 3(Rate=0.5) | 0.9884 | 0.9936 | 0.9953 | 0.9960 |
| 4(Rate=0.5) | 0.9763 | 0.9826 | 0.9947 | 0.9971 |
| 5(Rate=0.5) | 0.9552 | 0.9765 | 0.9921 | 0.9915 |
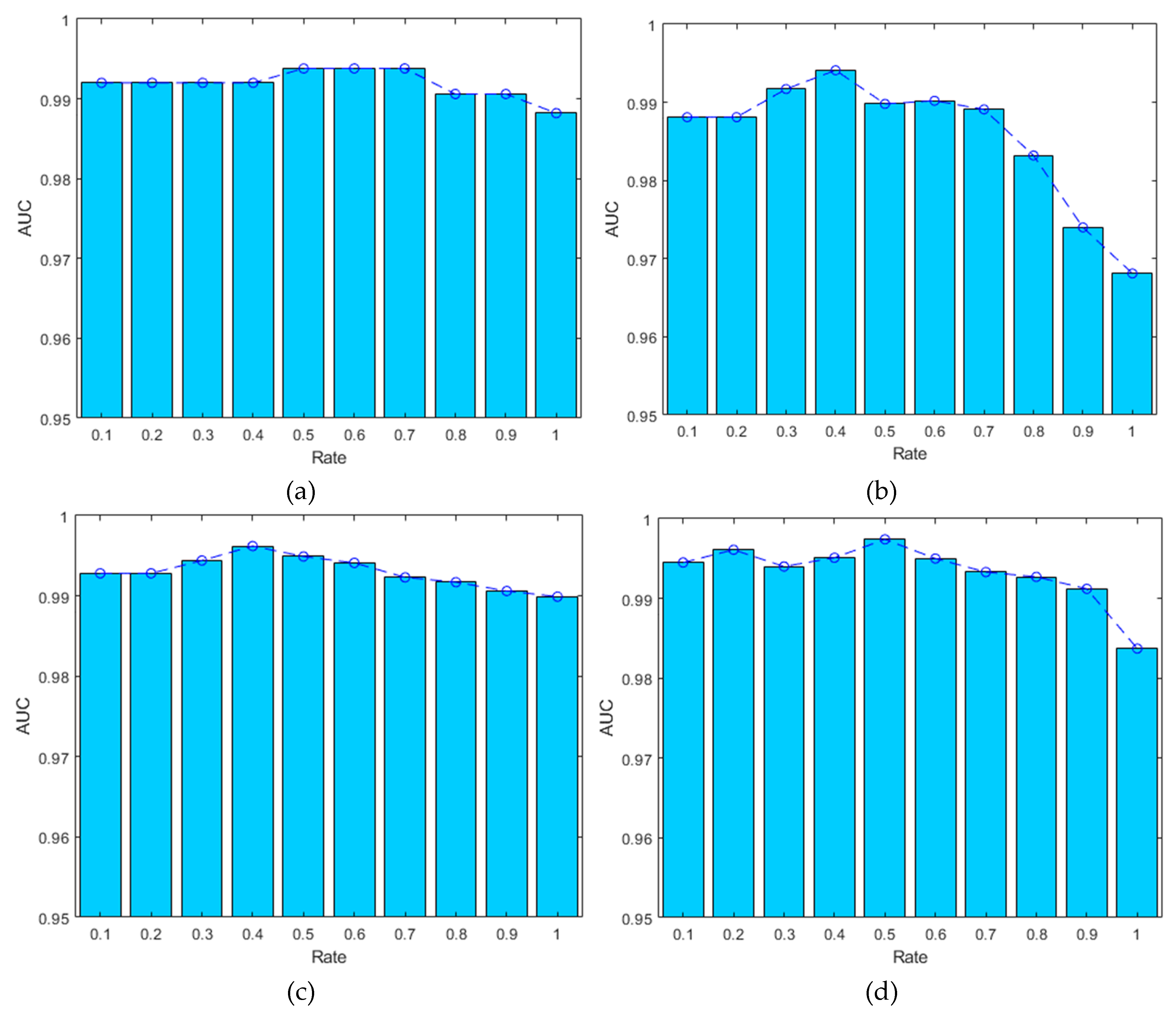
| Rate | The AUC of different rates on four datasets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pavia (Factor=2) |
Gainesville (Factor=3) |
San Diego (Factor=3) |
Gulfport (Factor=4) |
|
| 0.1 | 0.9920 | 0.9881 | 0.9928 | 0.9945 |
| 0.2 | 0.9920 | 0.9881 | 0.9928 | 0.9961 |
| 0.3 | 0.9920 | 0.9917 | 0.9944 | 0.9940 |
| 0.4 | 0.9920 | 0.9941 | 0.9962 | 0.9951 |
| 0.5 | 0.9938 | 0.9898 | 0.9949 | 0.9974 |
| 0.6 | 0.9938 | 0.9902 | 0.9941 | 0.9950 |
| 0.7 | 0.9938 | 0.9891 | 0.9923 | 0.9933 |
| 0.8 | 0.9906 | 0.9832 | 0.9917 | 0.9927 |
| 0.9 | 0.9906 | 0.9740 | 0.9906 | 0.9912 |
| 1.0 | 0.9882 | 0.9681 | 0.9899 | 0.9837 |
| Component | Case1 | Case2 | Case3 | Case4 | Case5 |
| MMCM | × | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| SSJM | √ | × | √ | √ | √ |
| BFAM | √ | √ | × | √ | √ |
| DLFM | √ | √ | √ | × | √ |
| Dataset | The AUC of different cases | ||||
| Pavia | 0.9862 | 0.9923 | 0.9901 | 0.9938 | 0.9943 |
| Gainesville | 0.9772 | 0.9920 | 0.9882 | 0.9923 | 0.9960 |
| San Diego | 0.9820 | 0.9929 | 0.9910 | 0.9927 | 0.9952 |
| Gulfport | 0.9667 | 0.9917 | 0.9889 | 0.9911 | 0.9976 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





