1. Introduction
Euterpe oleracea Mart. is one of the most well-known commercial plant species, native to the Eastern Amazon and very important for human populations, with the main product being the fruit (açaí), which is essential in the diet of people living in the Amazon. The production chain of açaí fruits is centered in the state of Pará, largely supplied by extractivism [
1,
2,
3].
The açaí is processed with warm water to produce a juice of high nutritional value, and the non-edible part of this fruit is the residue resulting from this processing [
4,
5]. In the city of Belém, PA alone, tons of seed from pulp processing are discarded daily, which can pose serious risks to the environment if not utilized and managed properly [
6]. Due to the gradual depletion of non-renewable energy sources and high processing costs in developing oil fields, the volume of waste generated from açaí processing could become an alternative for energy conversion, since the structure of these residues is mainly composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, and can be subjected to thermochemical processes aimed at achieving such conversion [
4,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12]
Global concern over climate change, largely associated with fossil fuel consumption, has driven increasing interest in renewable energy sources that can be derived from various oil-bearing species [
13]. The pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass is a thermochemical process with significant potential to convert waste into energy and fuel, producing primarily an aqueous phase, a gaseous phase, bio-oil, and biochar [
8]. The properties of pyrolysis products depend on the characteristics of the biomass used, reactor types, operating mode, and process parameters such as temperature and type of catalyst [
14,
15,
16].
Table 1 was synthesized based on bibliographic research covering the period from 2020 to 2024 aimed at exemplifying the published research on açaí pyrolysis [
9,
11,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. It can be observed that most studies focused on investigating the pyrolysis of comminuted seeds rather than fibers. Additionally, bio-oil was the most addressed pyrolysis product within the mentioned context, and until the moment, no research was found in the literature comparing the pyrolysis of açaí seeds with fibers or examined the influence of impregnated solution molarity on aqueous the phases composition obtained by pyrolysis of açaí fibers.
Due to the scarcity of studies characterizing the aqueous phase obtained from the pyrolysis of açaí fibers and seeds without comminution process, and recognizing that from a technical-scientific standpoint, characterizing such a product can provide a basis for new forms of reutilization of these residues, this work aims to conduct the pyrolysis of açaí seeds and fibers on a laboratory scale under different experimental conditions, and to characterize the aqueous phases physiochemically resulting from the pyrolysis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methodology
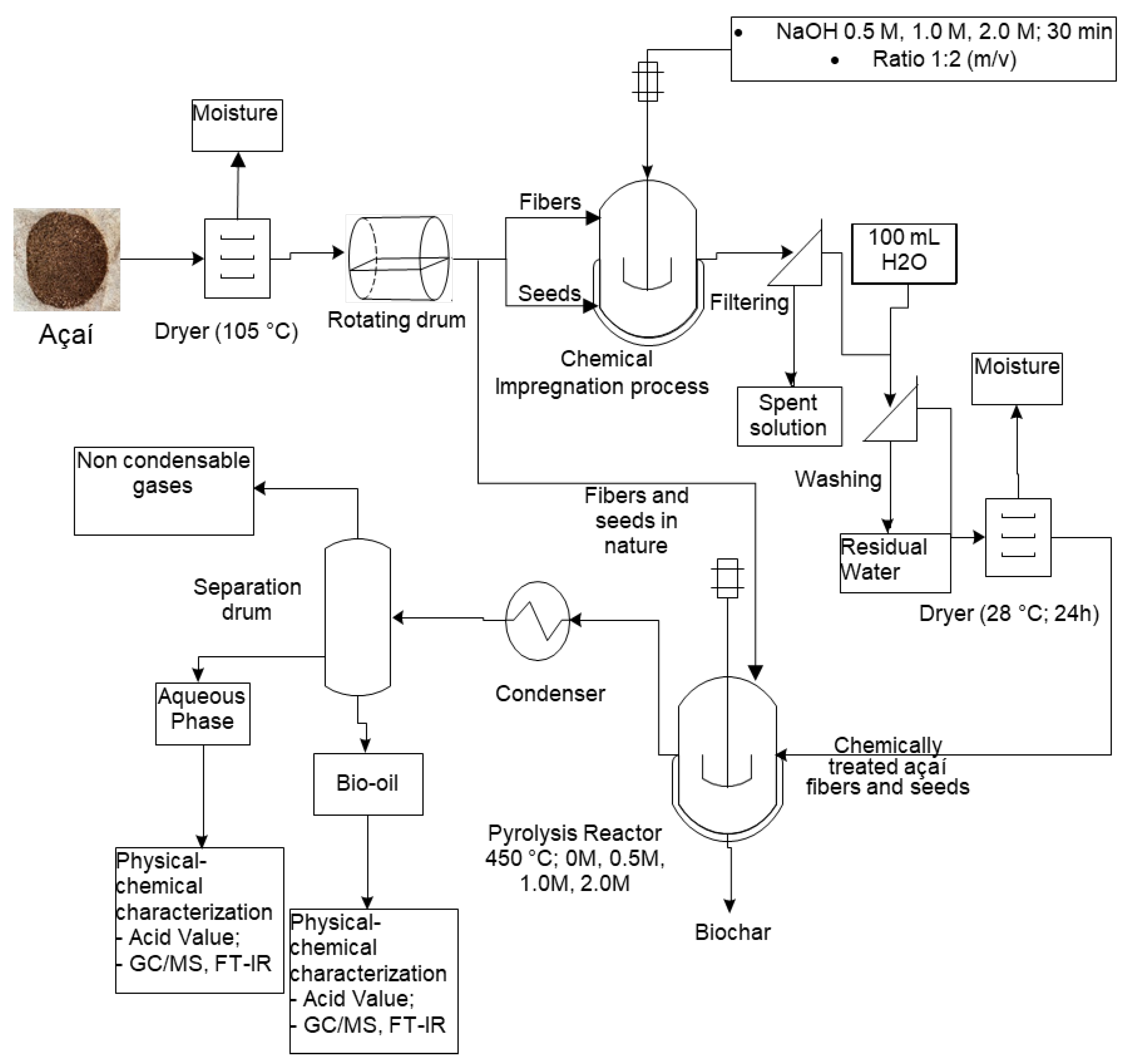
Figure 1 illustrates the entire research process methodology employed in this work. Initially, the biomass discarded after the artisanal processing was collected, and the residues were dried in an oven until constant weight. Subsequently, the fibers were separated from the seeds in a rotating drum, and the materials were impregnated with NaOH at concentrations of 0.5M, 1.0M, and 2.0M. After impregnation, the biomass was washed with distilled water, filtered, and left to dry at room temperature for 24 hours. Then, the raw and chemically treated fibers and seeds were pyrolyzed in a borosilicate glass reactor at 450 °C and 1 atm. The liquid and solid products were weighed to determine the yields. The characterization of the bio-oils and aqueous phases was conducted by determining the acidity (acid value), the chemical functions present within the liquid phase products determined by FT-IR analysis, and the chemical composition by gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry.
2.2. Collection, Drying, and Mechanical Separation of the Fibers
The açaí seeds were collected from a commercial establishment located on Cesário Alvim Street in the old town neighborhood of Belém-Pará-Brazil. After collection, the material was placed in aluminum trays and dried in an oven at 105°C until constant weight. The quantification of the biomass before and after the drying process was performed by gravimetry, and the moisture content was determined using the masses before (mi) and after drying (mf) according to the Equation (1).
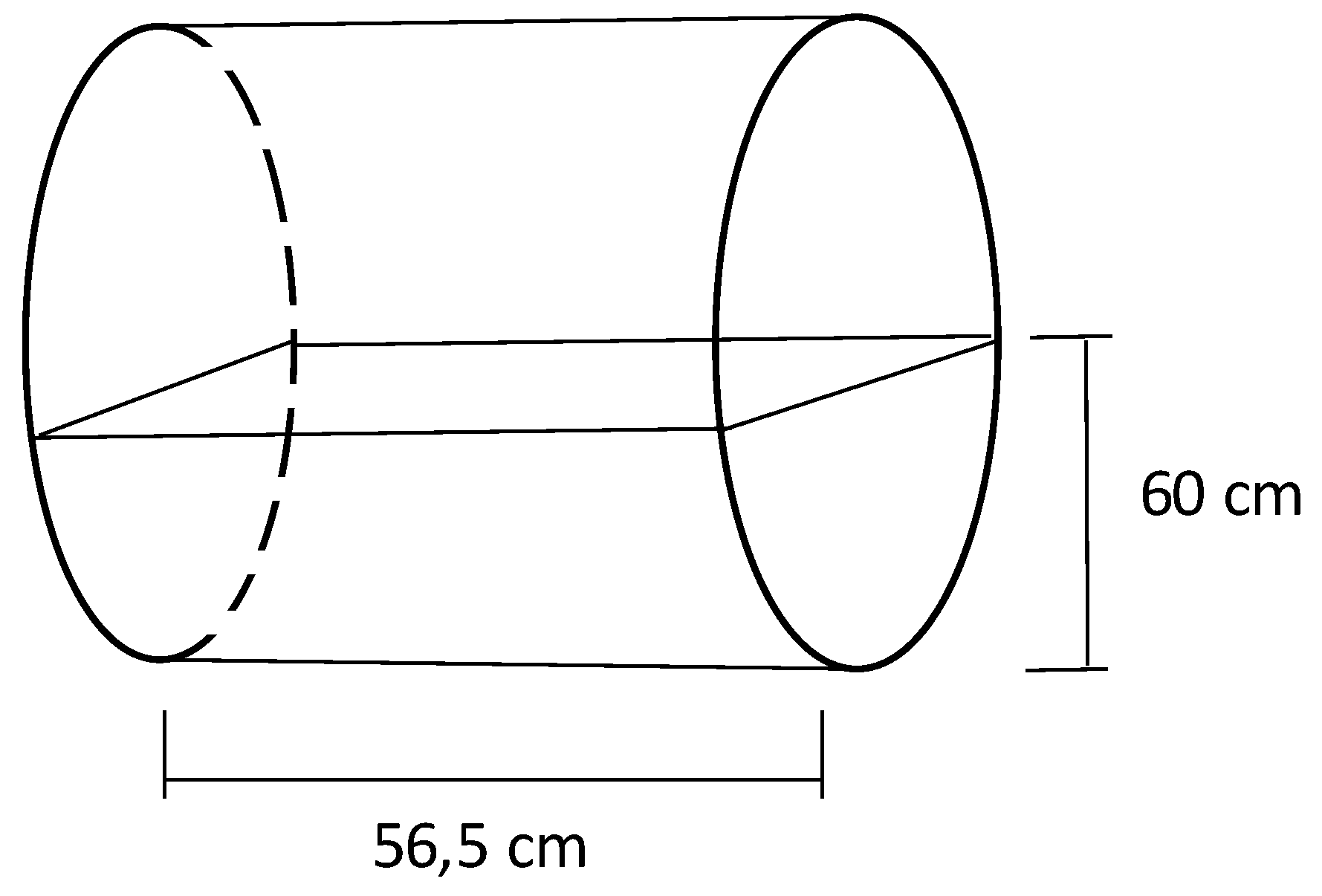
After drying in the oven, the fibers were separated from the seeds using a rotating drum (
Figure 2). The separation occurred using loads of around 1.35 kg of biomass, which was placed inside a mesh basket that was then inserted into the rotating drum at 60 rpm for 40 minutes. The yield of the process was determined by weighing the masses of the components (seed or fiber – mc) in relation to the total mass (mt), according to the Equation 2.
After determining the yield of the separation process, the samples were weighed on a Marte brand semi-analytical balance model AD330 and stored in hermetic plastic bags from Wyda Bag for later use (
Figure 3).
2.3. Determination of the volatile, Ash, and Fixed Carbon Contents of the Seeds and Fibers
2.3.1. Volatile Content
The determination of volatile content was conducted according to ASTM D 3175 07 (1993) using a muffle furnace with digital temperature and heating rate control. Approximately 1,0 g of biomass was placed in a pre-dried porcelain crucible. The material was placed on the door of the furnace, which was previously heated to 900 °C for 3 minutes. Shortly thereafter, the crucible was inserted into the furnace, where it remained for 7 minutes. After combustion, the material was placed in a desiccator until it reached room temperature and was then weighed. The entire procedure was conducted in triplicate, and the volatile content was calculated considering the total mass of residues (M) and the masses before (m2) and after (m3) calcination (Equation 3).
2.3.2. Ash Content
The determination of ash content was performed according to ASTM E 1755 01, using a muffle furnace with digital temperature and heating rate control. Approximately 2,0 g of biomass was placed in a pre-dried porcelain crucible. The material was placed in the furnace with a heating ramp. Initially, the sample was heated to 105 °C for 12 minutes, and then heated to temperatures of 250 °C and 575 °C for 30 and 180 minutes, respectively. After the burning time, the furnace was turned off, and the material was removed when the internal temperature of the equipment reached 105 °C. The crucible was placed in a desiccator until it reached room temperature before being weighed. The entire procedure was conducted in triplicate, and the volatile content was calculated using Equation 4, taking into account the mass of the crucible and ash (mcc), the mass of the crucible (mc), and the mass of the dry residue before the calcination process (Mbs).
2.3.3. Fixed Carbon Content
The fixed carbon content was obtained from the data on volatile content (MV) and ash content (CZ), using Equation 5.
2.4. Chemical Impregnation
For the chemical impregnation process of the fibers and seeds, NaOH solutions at concentrations of 0.5M, 1M, and 2M were used. Approximately 57g of biomass was placed in 600mL beakers, and the NaOH solutions were subsequently added in a ratio of 2:1 (volume of solution in mL / mass of sample). The system was stirred manually for 30 minutes with the aid of a glass rod (
Figure 4). The samples were placed in a simple filtration system and washed with 115mL of distilled water. After 24 hours, the biomass was dried in a Deleo brand oven at 105°C for an additional 24 hours.
2.5. Laboratory-Scale Pyrolysis
2.5.1. Description of the Experimental Apparatus
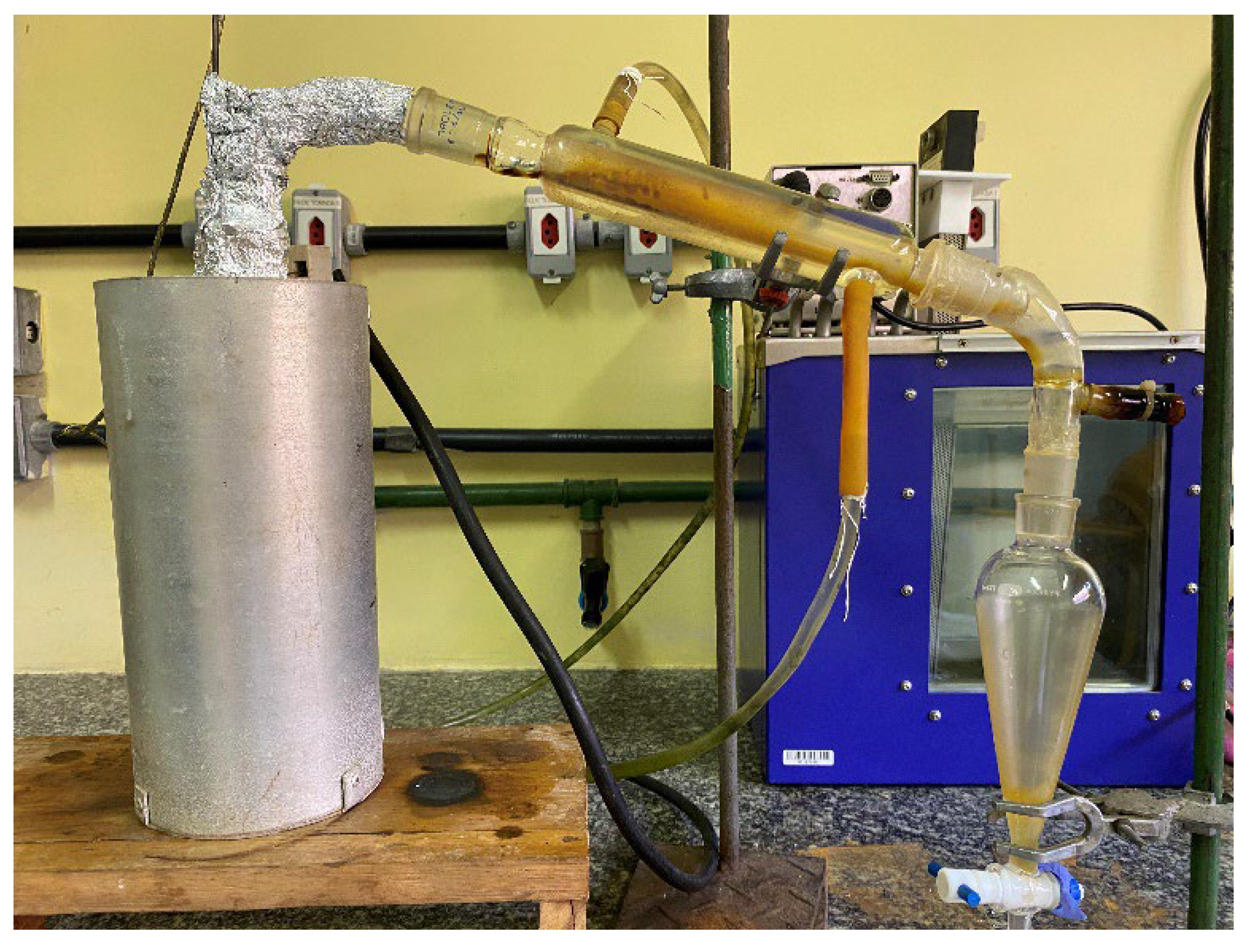
The pyrolysis unit was made up of a borosilicate reactor in a cylindrical shape with a volumetric capacity of approximately 200 ml. The reactor was placed in a cylindrical furnace with a ceramic heating element rated at 800 W. The heating element was connected to a digital temperature and heating rate controller (THERMA, Model TH90DP202 000), which had a type K temperature sensor (Ecil, Model: QK. 2). A straight borosilicate condenser (Liebig) was coupled to the reactor, connected to a cooling system consisting of a thermostatic recirculation bath (VWR), with water as the refrigerant fluid. Above the reactor, a curved connection was attached. The condensed products were collected in a borosilicate glass separation funnel. The non-condensable gaseous products and the carry-over gas were directed through an opening in the 90° curve, which was connected between the condenser and the separation funnel.
Figure 5 shows the assembled experimental setup.
2.5.2. Pyrolysis Experiments
The pyrolysis reactions were conducted using açaí fibers and seeds as feedstock. The experiments were performed at a temperature of 450 °C and 1.0 atm. Approximately 20 g of biomass was weighed for each experiment using a semi-analytical balance (Marte model AD330). Next, the reactor was inserted into the jacketed cylindrical furnace, and with the help of the temperature controller, the reaction time, heating rate, and final process temperature (set-point) were programmed, based on Equation 6. Given the established parameters, a time of 30 minutes was set to maintain each final operating temperature constant. The pyrolysis process started at room temperature with a heating rate of 10 °C/min.
The solid and liquid products from the reactions were weighed on a semi-analytical balance, and the yield per product was calculated using Equation 7, which took into account the mass of the product (mc – aqueous phase, bio-oil, or charcoal) and the biomass weighed before the pyrolysis process (mbi).
The mass of gaseous products plus the process losses was obtained through a simple mass balance using Equation 8, which considered the biomass weighed before the pyrolysis process (mbi), the mass of charcoal (mcharcoal), the mass of the aqueous phase (mfaq), and the mass of bio-oil (mbiooil) obtained.
2.6. Physicochemical Characterization of the Aqueous Fractions and Bio-Oils Obtained
The physicochemical characterization of the aqueous fractions and bio-oils produced on a laboratory scale aimed to evaluate the acidity index. The assessment was conducted through the analysis of the acidity index (AI) and the comparison of the Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra of the samples.
2.6.1. Acidity Index
The Acidity Index was determined using an adaptation of the official AOCS method Cd 3d-63 (AOCS, 2001), which is applicable to vegetable and animal oils (natural or refined), marine fats, and various derived products. Approximately 0.1 g of each oil and aqueous fraction sample were weighed in a 300 ml Erlenmeyer flask with the aid of a semi-analytical balance (Marte model AD330), where it was solubilized in 50 ml of a 1:1 solution of isopropyl alcohol and toluene. Next, titration was performed with a standardized solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH) 0.05 N, using 1% phenolphthalein as the indicator for the endpoint. The same procedure was also carried out for a blank sample under the same conditions. The Acidity Index, in mg of KOH/g of sample, was calculated using Equation 9, which took into account the volume of titrant used in the titration of the sample (VA), the volume of titrant used in the titration of the blank (VB), the normality (N), the correction factor (Cf) of the titrant solution, and the mass of the analyzed sample (mA).
2.6.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
Fourier-transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis was applied to determine which functional groups were present in the samples. The spectra were obtained using a BRUKER Fourier-transform Infrared Spectrometer (FTIR), Model: VERTEX 70v, located in the vibrational and high-pressure spectroscopy laboratory (LEVAP-PPGF/UFPA). The identification of functional groups was conducted as described in the literature [
25,
26,
27].
2.6.3. Gas Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry (CG-EM)
The chemical composition of the liquid products obtained from the pyrolysis of açaí seeds and fibers at 450°C and 1 atm was determined by GC-MS, using the equipment and procedures detailed in the literature by Castro et al. [
8,
11,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Moisture and Mechanical Separation of Fibers
Table 2 shows the yields related to the drying and mechanical separation processes of the fibers. The results indicate that the moisture content of the collected material is approximately 35% (wt.), which may be associated with the depulping process of the fruit, as well as the improper disposal of seeds that were exposed to the environment.
As expected, the yield of fibers after the mechanical separation process was significantly lower compared to the yield of seeds, as the composition of the residue indicates a smaller percentage of fibers. The losses during the mechanical separation process can be attributed to the small-sized fibers that inevitably got trapped in the mesh basket and other parts of the equipment used to assist in the separation process.
3.2. Ash Content, Volatile, and Fixed Carbon
Table 3 shows the results obtained from the physical characterization of açaí seeds and fibers. It can be observed that the volatile content for the materials in question was quite similar, with 77.39% in the seeds and 77.69% in the fibers. These values are consistent with the study by CORTEZ and LORA [
34], which describes the volatile content ranging from 65% to 83% for raw materials.
According to Barcellos et al. [
35], the ash content depends directly on the amount of inorganic compounds present in the material to be incinerated. In the present study, it was found that the ash content for the seeds was 2.77%, while for the fibers, this value was 10.92%. Seye et al. [
36], investigating açaí seeds as a source for electricity generation, found an ash content of 1.15%, while Castro [
37], studying the pyrolysis of açaí seeds, reported an ash content of 0.42% for the raw material. Santos et al. [
38], conducting the physicochemical characterization of açaí seeds and fibers from a species cultivated in Bahia, found ash contents of 1.4% and 3.41% for the fibers and seeds, respectively. Such differences can be explained by the chemical composition varying according to the cultivation region, soil types, and climatic conditions (Mesquita, [
39]).
From
Table 3, we can also observe that the fixed carbon content in the seeds was 19.84%, while in the fibers, the value was 11.39%. The fixed carbon content found by Silva [
40] for raw açaí seeds was 21.63%, while Seye et al. [
36] and Nagaishi [
41] reported values of 18.5% and 20.95%, respectively. In the present study, the fixed carbon content in raw seeds falls within the range described by the mentioned authors.
3.3. Chemical Impregnation
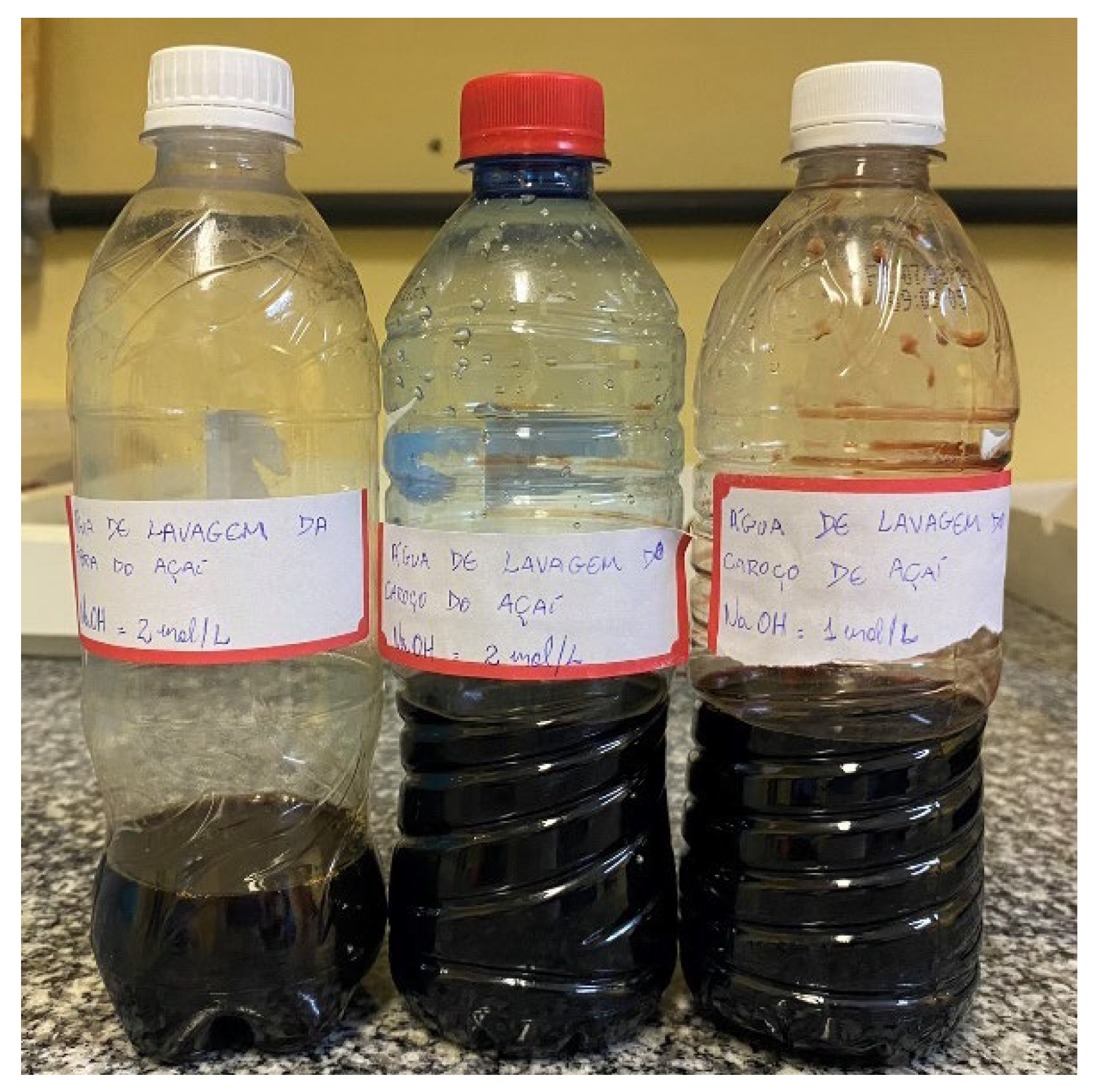
Table 4 illustrates the results after the chemical impregnation process of the seeds and fibers. With the chemical treatment, there was a mass loss in both the fibers (around 6%) and the seeds (around 4%). This process generated an aqueous phase with a characteristic color resembling the fruit pulp (
Figure 10), indicating that there was extraction and/or solubilization of chemical constituents. The variation in mass is attributed to the loss of components from the biomass structure, such as hemicellulose and lignin. According to Leão [
42], treatment with NaOH directly influences the reduction of hemicellulose and lignin by activating the hydroxyl groups of cellulose.
Figure 6.
Wash water after chemical impregnation.
Figure 6.
Wash water after chemical impregnation.
3.4. Laboratory-Scale Pyrolysis
Table 5,
Table 6 and
Table 7 show the results obtained during and after the pyrolysis process of raw seeds (S) and fibers (F), both untreated (IN) and impregnated with NaOH solutions at 0.5M, 1.0M, and 2.0M at 450 °C.
From the data in
Table 5,
Table 6 and
Table 7, and
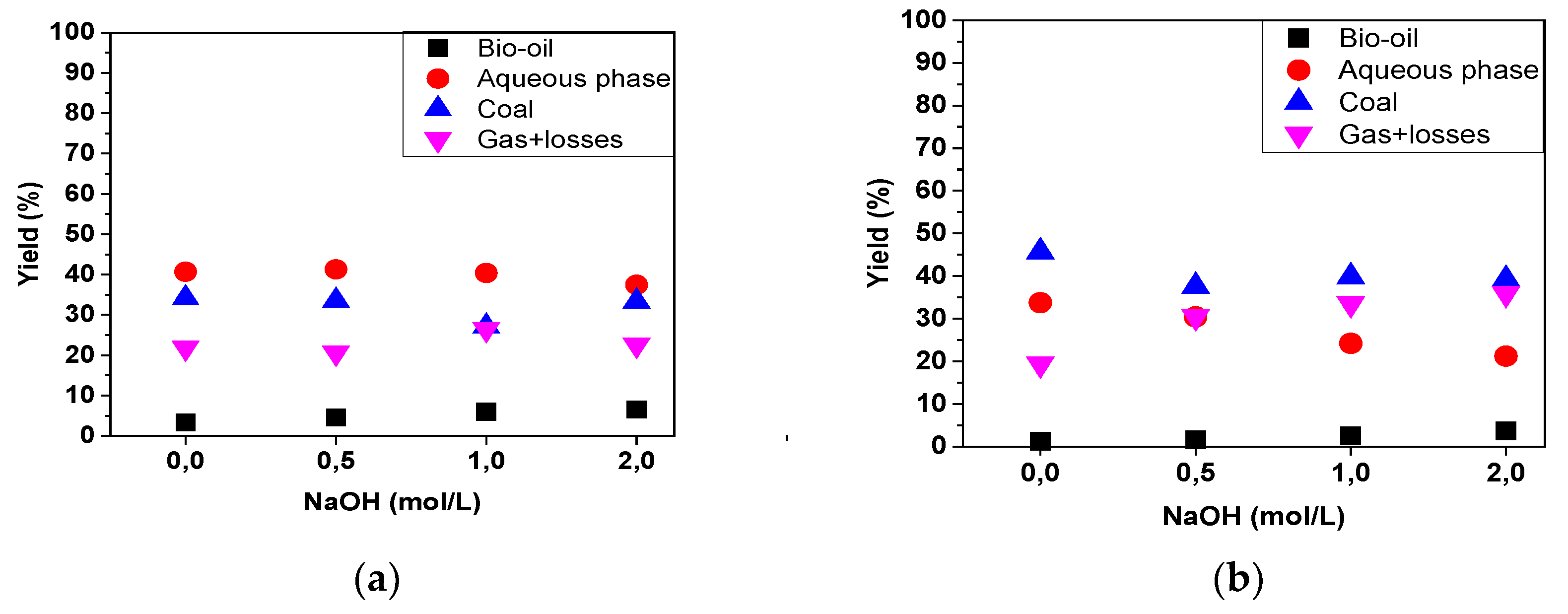
Figure 7, it is observed that there was a change in the production of some pyrolysis products. Notably, in the pyrolysis of seeds, the yield of bio-oil increased with the higher chemical impregnation of the biomass, rising from 3.3% in the raw material to 6.6% in seeds impregnated with a 2 mol/L NaOH solution. A similar trend was observed in the yields of bio-oil during the pyrolysis of fibers, increasing from 1.2% in the raw material to 3.7% in the material impregnated with 2M NaOH. Castro [
37], investigating the pyrolysis of raw açaí seeds at 450°C on bench, semi-pilot, and pilot scales, reported bio-oil yields of 13.09%, 5.6%, and 4.4%, respectively. When the same author impregnated the seeds with 2M NaOH, an increase in the yield of bio-oil was observed, reporting 15.59%, 13.38%, and 7.20% for this product obtained at the bench, semi-pilot, and pilot scales, respectively. However, when we compare the bio-oils obtained from the two experimental matrices in quantitative terms, it is evident that the seeds provided a larger quantity of this product.
It can be observed that the yield of the aqueous phase after the pyrolysis of the fibers exhibited an inverse behavior compared to the yield of bio-oil, decreasing as the concentration of the impregnating agent increased, from 33.7% (raw fiber) to 21.2% when the fiber impregnated with 2.0M NaOH was processed. After the pyrolysis of the seeds, an aqueous phase yield of around 41% was obtained for both the raw biomass and that impregnated with 0.5M NaOH, which decreased after the material was impregnated at 1.0M (40.4%) and 2M (37.5%).
In the pyrolysis of fibers, the yield of activated charcoal experienced slight variations, remaining between 33% and 34% (for raw material and that impregnated with NaOH at 0.5 and 2.0M), and decreasing to 27% in the material impregnated at 1.0M. In the pyrolysis of seeds, activated charcoal yields ranged from 38% to 40% (for material impregnated with NaOH at 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0M) and a yield of 45.7% was obtained for the raw material.
3.4. Physicochemical Characterization of the Obtained Liquid Products
3.4.1. Acidity
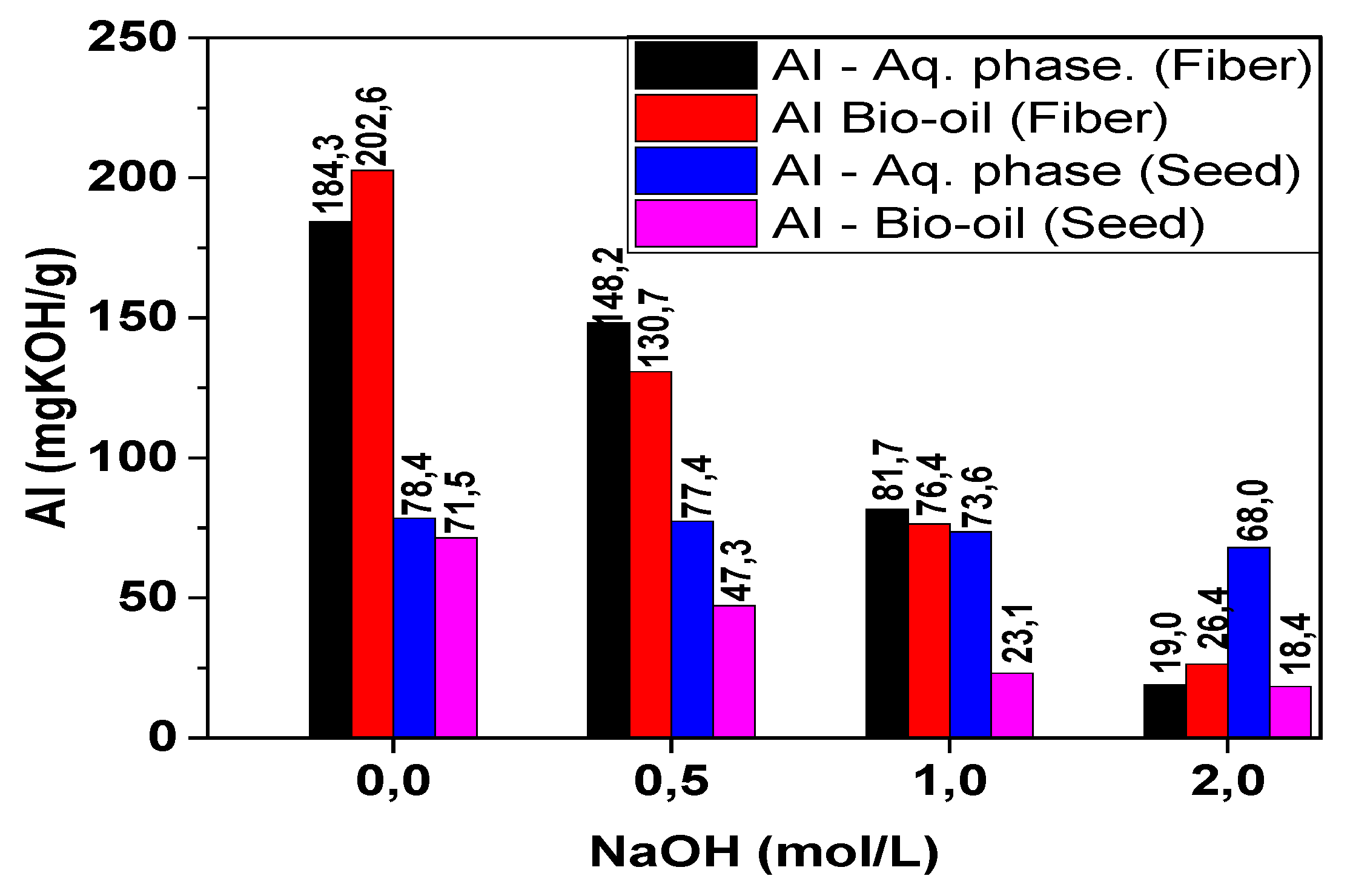
The results obtained for the acidity index in the aqueous fractions and bio-oils of the raw fibers showed high values, reaching 184.3 and 202.6 mg KOH/g sample, respectively (
Figure 8). It was observed in the fiber samples that as the concentration of the impregnating agent increased, the acidity index decreased significantly in both the aqueous fraction (a reduction of 89.6%) and in the bio-oil (a reduction of 86.9%). A similar behavior was observed in the acidity of the pyrolysis products of the seeds, decreasing from 78.4 mg KOH/g sample to 68.0 mg KOH/g sample (aqueous fraction) and from 71.5 mg KOH/g sample to 18.4 mg KOH/g sample (bio-oil).
Serrão et al. [
17], studying the pyrolysis process of açaí seeds in pilot scale at 450°C, identified an acidity index of 70.26 mg KOH/g, close to that identified in this work (71.5 mg KOH/g). Castro [
37], investigating the pyrolysis process of raw açaí seeds at bench, semi-pilot, and pilot scales, reported that at 450 °C, the acidity values found in the bio-oils were 70.25, 68.31, and 70.26 mg KOH/g, respectively. For the seeds impregnated with NaOH at 2 mol/L, the acidity values in the bio-oils obtained at bench, semi-pilot, and pilot scales were 9.21, 15.42, and 19.44 mg KOH/g, respectively.
3.4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
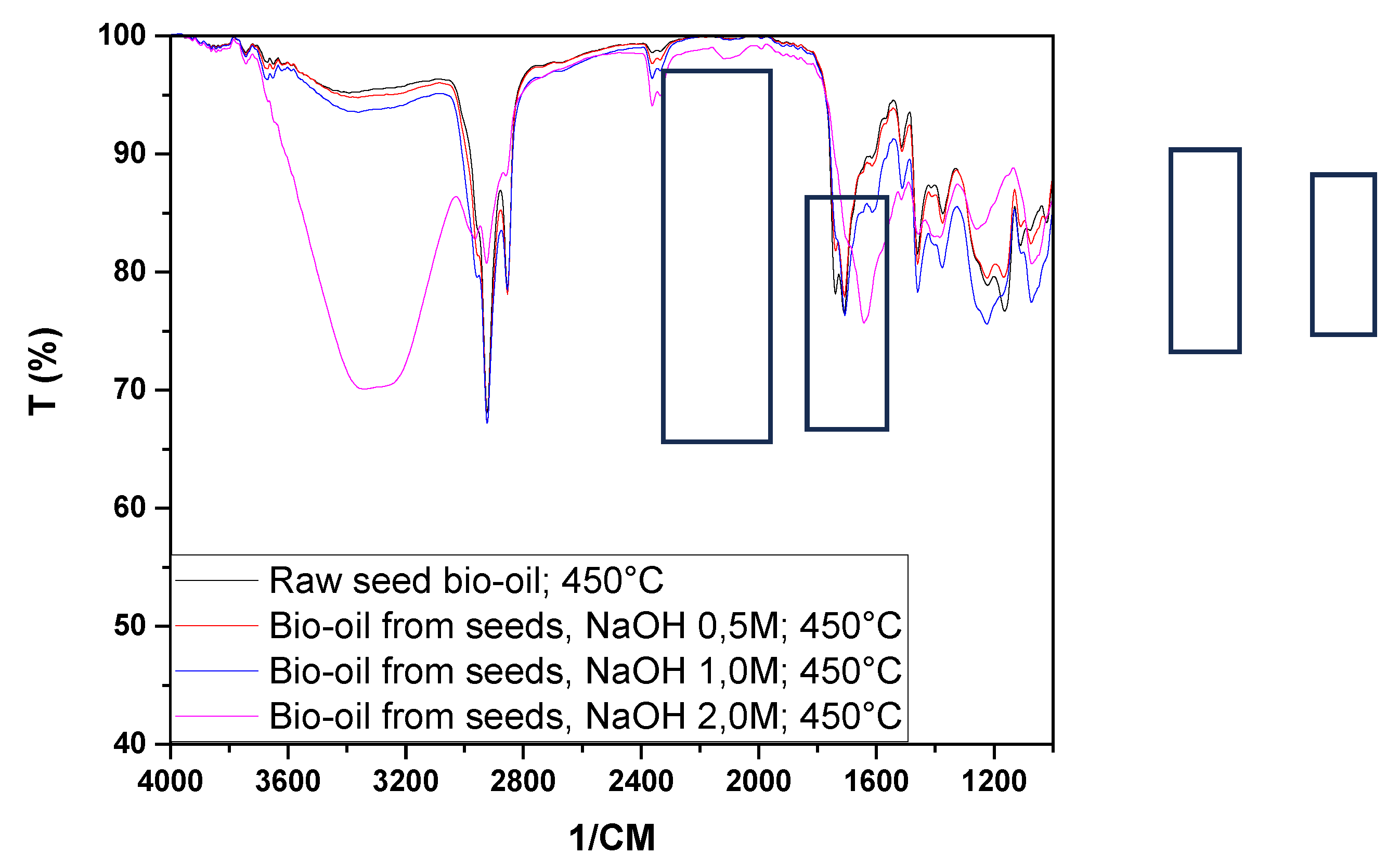
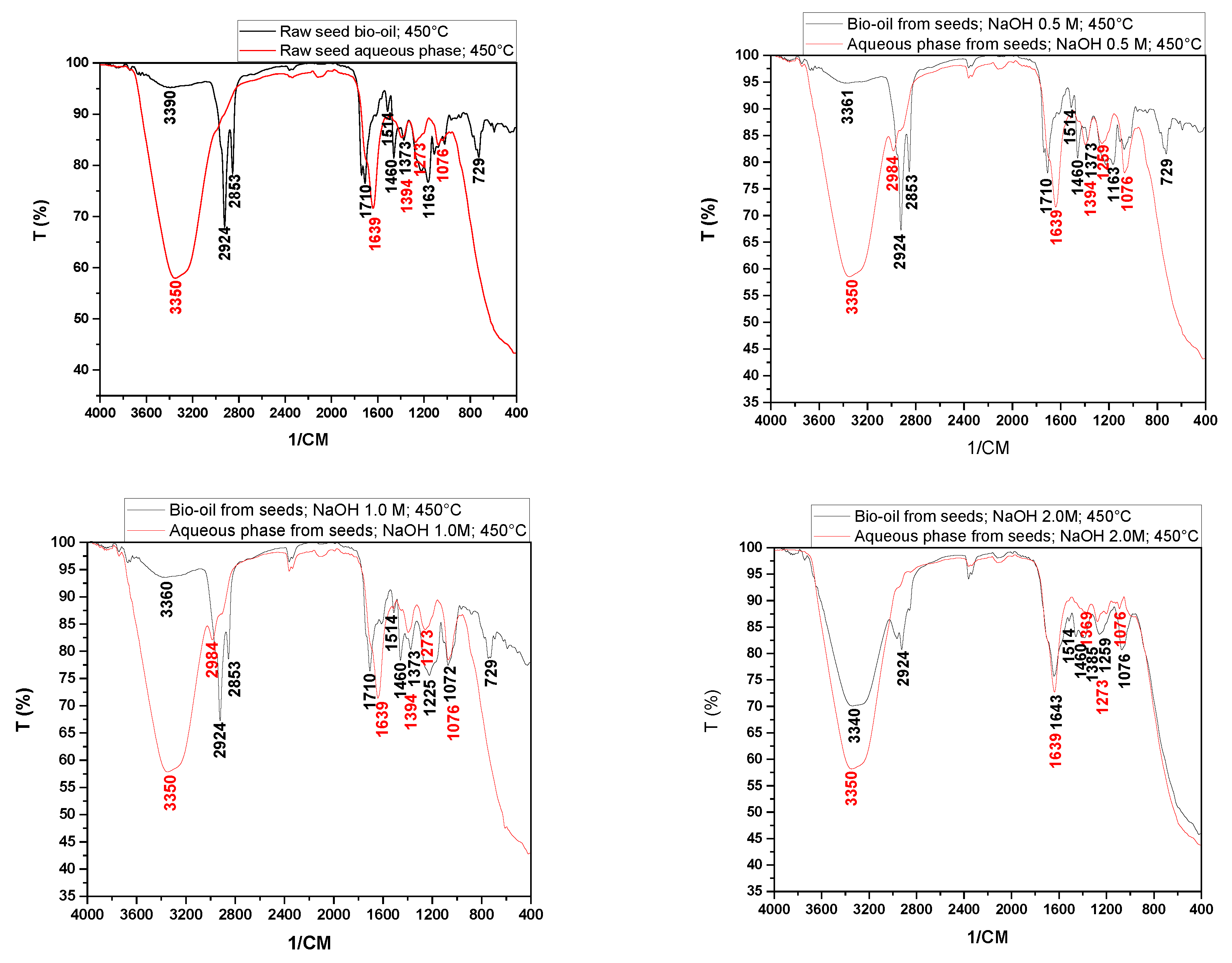
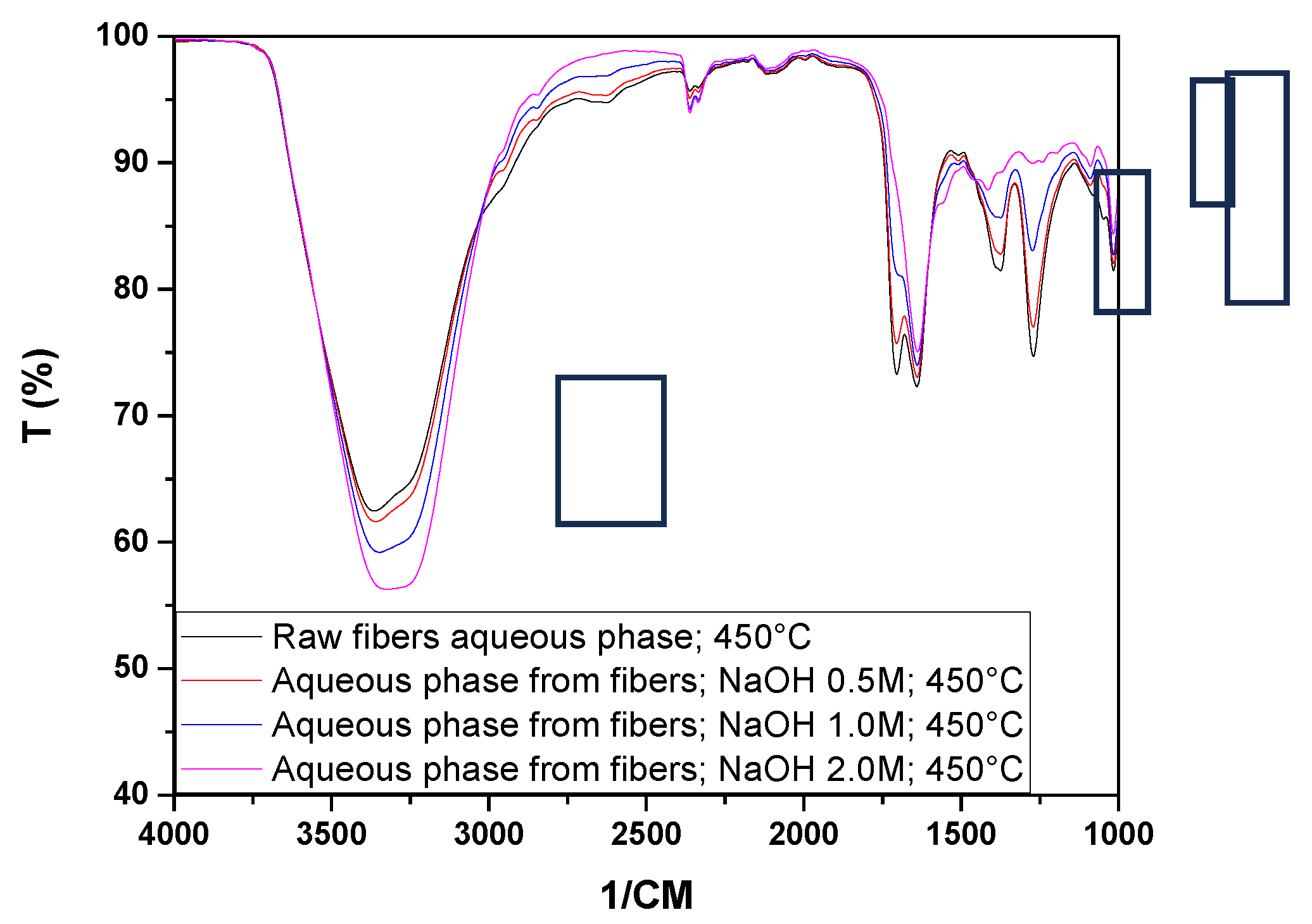
Figure 9 shows the infrared spectra of the bio-oils and aqueous phases obtained from the pyrolysis at 450 °C of raw seeds (SIN) and those impregnated with NaOH.
The bio-oil spectra showed peaks in the ranges of 2853 and 2924 cm⁻¹ associated with axial deformation vibrations, indicating the presence of hydrocarbons in all experiments. It was also observed that for the bio-oils obtained from raw seeds and those impregnated with NaOH, the spectra exhibited characteristic peaks of CO groups, which may be associated with aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, among others (1643, 1710, 3340, 3360, 3361, 3390 cm⁻¹). The peaks at 1514 cm⁻¹ and 1460 cm⁻¹ present in all bio-oils indicated the presence of aromatic nuclei (C=C) and methylene groups (CH₂)n, respectively. The peaks at 1373 cm⁻¹ correspond to the symmetric angular deformation of C-H bonds in the methyl group (CH₃). The peaks between 1072 and 1225 cm⁻¹ may be associated with the presence of alcohols, phenols, and ether and ester groups in the analyzed samples, while the peaks at 729 cm⁻¹ may be associated with methyl (CH₃, CH₂) groups.
By examining the spectra of the aqueous phases obtained from raw seeds and those impregnated with NaOH (
Figure 9), we can infer the presence of CO bonds (1639, 3350 cm⁻¹), hydrocarbons (1394 cm⁻¹), alcohols, phenols, and ether and ester groups (1076, 1273 cm⁻¹). Castro [
37], studying the pyrolysis of açaí seeds at 450°C, found bio-oil spectra similar to those shown in
Figure 9.
Through the analysis of
Figure 10, it can be observed that chemical impregnation influenced the variation in the presence of functional groups, especially in the peaks between 3200 and 3600 cm⁻¹, 2800 and 3000 cm⁻¹, 1600 and 1800 cm⁻¹, and 1200 and 1400 cm⁻¹, corroborating the data obtained from the acidity index, as the peaks observed, particularly in the range of 1710 cm⁻¹, may be associated with carboxylic acids.
Figure 10.
Comparison of the infrared spectra of bio-oils obtained by pyrolysis of in nature seeds and seeds impregnated with NaOH at 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 M.
Figure 10.
Comparison of the infrared spectra of bio-oils obtained by pyrolysis of in nature seeds and seeds impregnated with NaOH at 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 M.
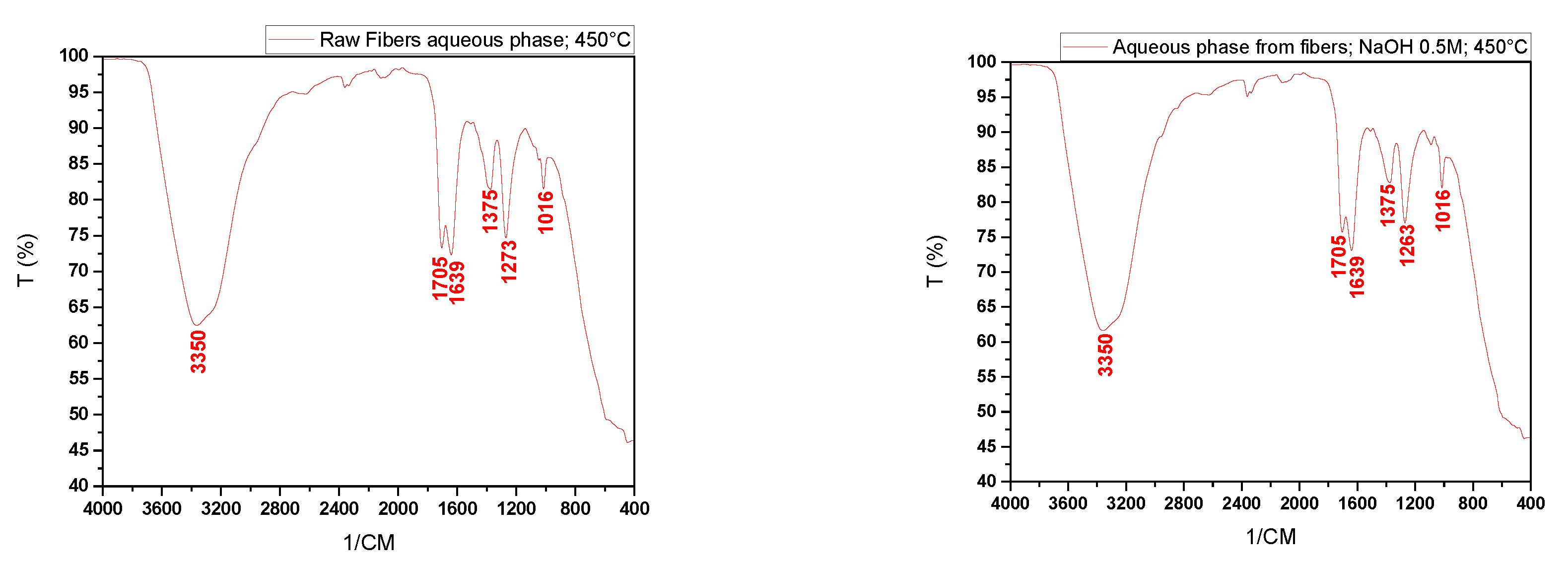
Figure 11 shows the infrared spectra of the aqueous phases and bio-oil obtained from the pyrolysis at 450 °C of raw fibers (FIN) and those impregnated with NaOH.
We can observe from the spectra of the aqueous phases peaks at 3350 cm⁻¹ indicating the presence of hydroxyl (OH) bonds that may be associated with alcohols and phenols, evidence of carbonyl (C=O) bonds at peaks of 1705 cm⁻¹ and 1639 cm⁻¹, hydrocarbons (1375 cm⁻¹), CO bonds (1263 cm⁻¹ and 1273 cm⁻¹), sulfoxide or sulfone groups (1090 cm⁻¹), as well as alkanes and ethers (1016 cm⁻¹).
Due to the low yields of bio-oil after the pyrolysis of the fibers, only the spectrum of the sample impregnated with NaOH at 1.0 mol/L could be obtained. This spectrum shows characteristic peaks of OH groups (3340 cm⁻¹), carbonyl groups (1639 cm⁻¹), hydrocarbons, and ethers (1558 cm⁻¹, 1412 cm⁻¹, 1269 cm⁻¹, 1107 cm⁻¹, and 1116 cm⁻¹).
Through the analysis of
Figure 12, it can be observed that chemical impregnation influenced the variation in the presence of functional groups in the aqueous phases obtained from the pyrolysis of the fibers, especially in the peaks between 3000 and 3500 cm⁻¹ and in the peaks indicative of the presence of hydrocarbons and carbonyls.
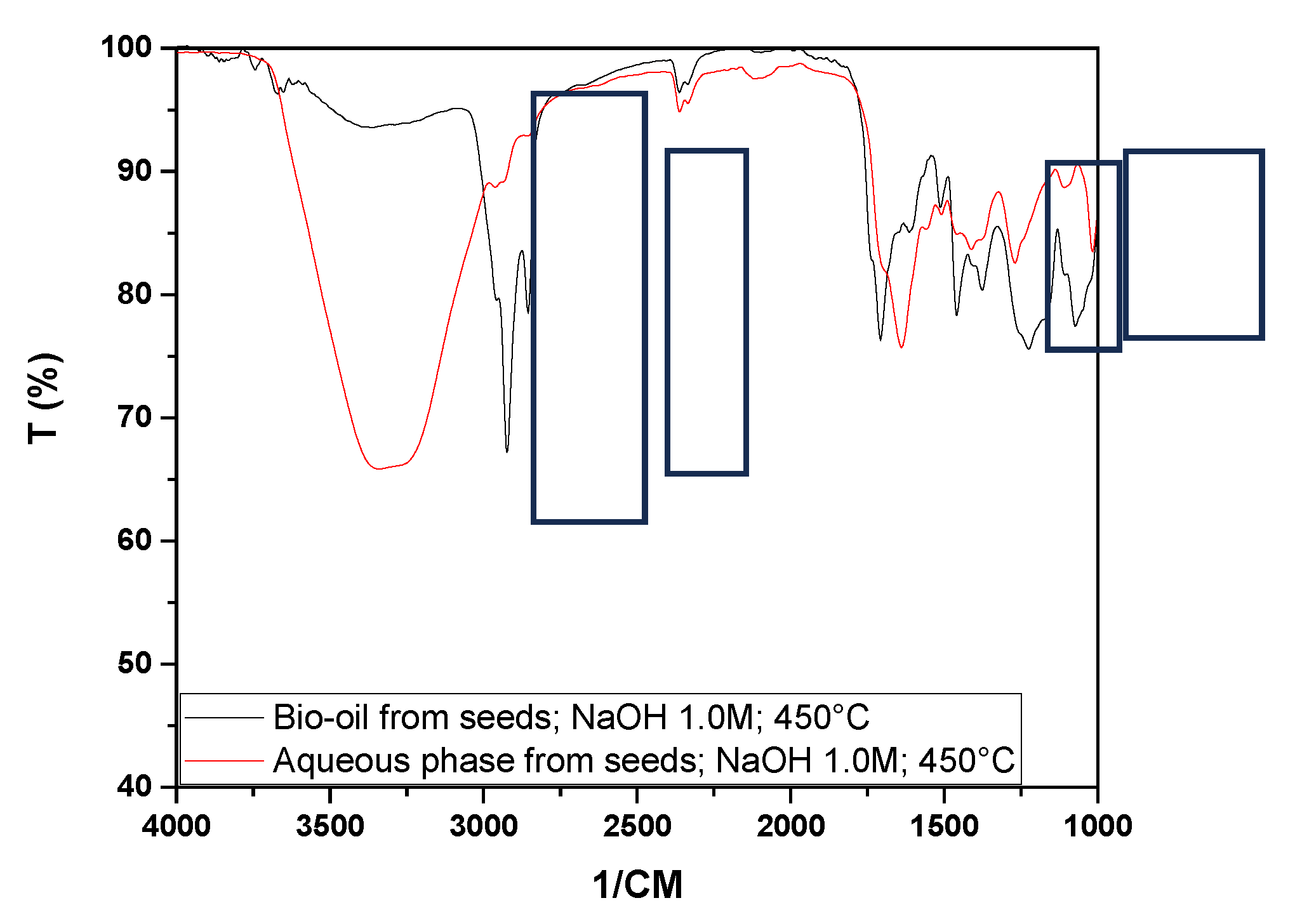
From the analysis of
Figure 13, it is possible to observe significant differences in the peaks of the bio-oil spectra obtained from the two experimental matrices (seed and fiber), especially in the characteristic regions of OH groups, hydrocarbons, and in the ranges between 1070 and 1710 cm⁻¹. This suggests a change in the chemical composition when comparing the bio-oils obtained from the seeds and fibers under the same experimental conditions.
3.4.3. Gas Chromatography
Due to the small amount of biomass used as raw material in all the pyrolysis experiments and the fact that bio-oil yield was low, it was only possible to identify the compounds present in the bio-oil from seeds impregnated with 2.0 M NaOH (S-2.0M).
Table 8 shows the chemical compounds, along with their respective retention times (RT), that are present in the oil in quantities ≥3%.
It can be observed that tetradecanoic acid was the major compound (8.91%), followed by dodecanoic acid (4.46%), n-hexadecanoic acid (3.93%), and the phenol (3.24%) and 2-furanmethanol (3.17%). Castro [
37], studying the pyrolysis of açaí residues at 450 °C, identified phenols (6.79%) as the major compound in raw seeds, followed by p-cresol (6.68%), tridecane (5.14%), and 1-tridecene (4.32%). For seeds impregnated with 2.0 M NaOH, the same author found naphthalene (7.26%) as the major compound, followed by 5-octyl-4-one, 2,2,7,7-tetramethyl (6.45%), and 7-tetradecene (5.15%).
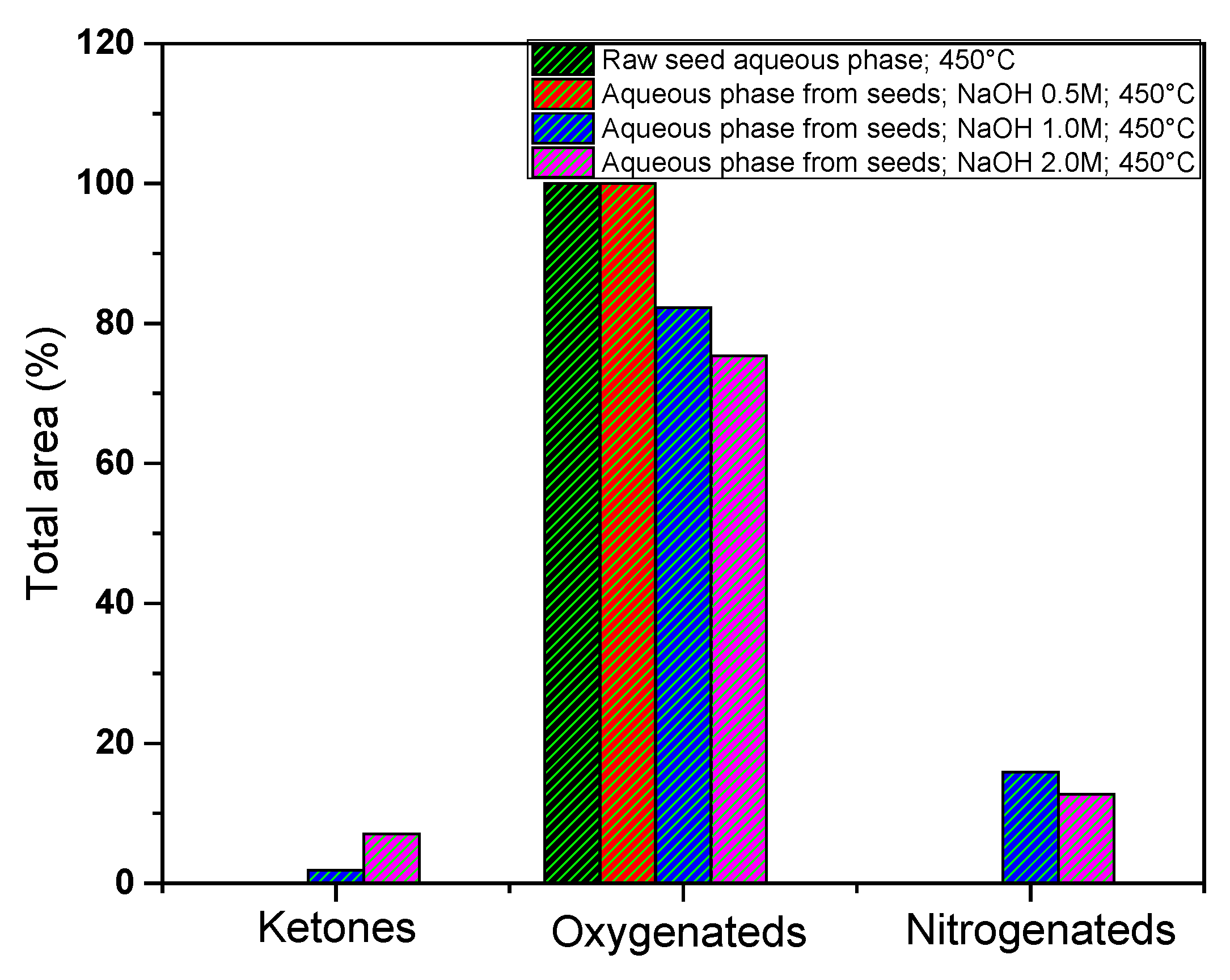
Figure 14 shows the total area percentage of the compounds identified in the aqueous phases GC-MS, obtained from pyrolysis of açaí seeds. For more details of the individual compounds see supplementary
Table S1. It can be observed that the oxygenated compounds decreased as the concentration of the impregnating agent increased. There is also a slight increase in the ketones and nitrogen-containing compounds present in the aqueous phases when the seeds were impregnated with 1.0 M and 2.0 M.
Table 9 shows the constituents ≥5%, along with their respective retention times (RT), present in the aqueous phases after the pyrolysis of the seeds. It can be observed that levoglucosan (beta-D-Glucopyranose, 1,6-anhydro-) was identified in all analyzed samples, varying between 52% and 65%. Furfural was identified in the aqueous phases of the raw seeds and those impregnated at 0.5 M with contents of 18.52% and 15.47%, respectively, while 3,5-dimethylpyrazole was identified only in the samples impregnated at 1.0 M and 2.0 M, with contents of 15.88% and 12.74%. It was observed that the constituent butyrolactone increased with the rise in chemical impregnation, from 0% in the aqueous phases of raw seeds to 12.55% when the seeds were impregnated with 2.0 M NaOH.
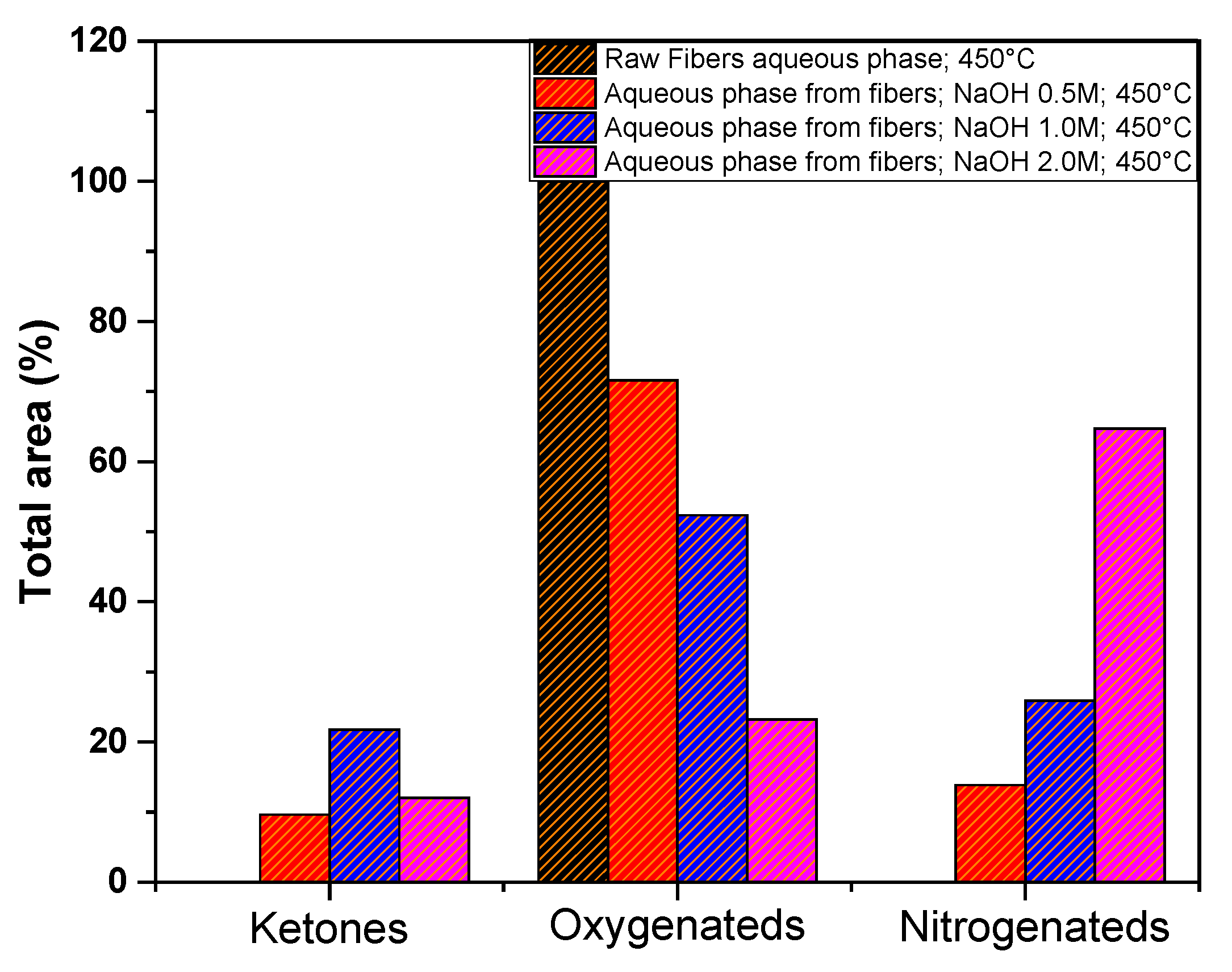
Figure 15 shows the total area percentage of the compounds identified in the aqueous phases GC-MS, obtained from pyrolysis of açaí fibers. For more details of the individual compounds see supplementary
Table S1. It can be observed that there is a significant variation in the oxygenated compounds, mainly due to the decrease of the phenol compound, which diminished as the concentration of the impregnating agent increased. This corroborates the acidity index data, as the phenolic compound imparts acidic characteristics to the aqueous phase. An inverse behavior was observed in the nitrogen-containing compounds, which increased as the concentration of NaOH increased.
Table 10 shows the constituents identified in the aqueous phases after the pyrolysis of raw fibers (F-IN) and NaOH-impregnated fibers. It can be observed that phenol was the major constituent in the aqueous phase of the raw fibers, which decreased as the concentration of the impregnating agent (NaOH) increased, from 33.08% (F-IN) to 14.86% in the fibers impregnated with 2.0 M NaOH (F-2.0M). A similar trend was observed for 2-methoxyphenol, which decreased from 11.76% (F-IN) to 8.34% (F-2.0M). Meanwhile, the concentration of 4,5-dihydro-2,4,4-trimethyl-oxazole increased from 0% (F-IN) to 48.31% in the fibers impregnated with 2.0M NaOH.
4. Conclusions
The increase in the concentration of the NaOH impregnating solutions has influenced the formation of pyrolysis products, resulting in an increase in bio-oil yield both the pyrolysis of seeds (an increase of 3.3%) and fibers (an increase of 2.5%). An inverse behavior was observed in the yield of the aqueous phases, which decreased as the concentration of NaOH increased. The yield of activated carbon showed slight variations, ranging from 27% to 34% after the pyrolysis of fibers and from 38% to 45% after the pyrolysis of seeds.
The acidity of the bio-oils decreased as the concentration of NaOH increased, with a reduction of 74.3% in the treatments of the seeds and a reduction of 86.9% in the treatment of the fibers. A similar behavior was observed in the acidity of the aqueous phases, showing a reduction of 13.3% in the products derived from the seeds and 89.6% in the aqueous phases derived from the fibers.
Chemical impregnation influenced the chemical composition of the liquid products as it causes a decrease in oxygenated compounds and an increase in nitrogen-containing compounds in the aqueous phases derived from the fibers.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
The individual contributions of all the co-authors are provided as follows: E.M.d.S. contributed with formal analysis and writing original draft preparation, investigation and methodology, K.C.A.B. contributed with formal analysis, investigation and methodology, R.M.P.S. contributed with investigation, methodology and chemical analysis, G.A.d.C.M. contributed wit investigation, methodology and chemical analysis, G.X.d.A. contributed with investigation, methodology and chemical analysis, R.B.P.F. contributed with investigation and methodology, L.P.B. contributed with formal analysis, N.M.M. contributed with resources and chemical analysis, C.G.B.T.D. contributed with investigation and methodology, D.A.R.d.C. contributed with investigation and methodology, G.d.O.R. contributed with chemical analysis, S.D.Jr. contributed with resources and chemical analysis, M.C.M. conceptualization and data curation, and N.T.M. contributed with supervision, conceptualization, and data curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Please add: This research was funded by CNPq.
Data Availability Statement
We encourage all authors of articles published in MDPI journals to share their research data. In this section, please provide details regarding where data supporting reported results can be found, including links to publicly archived datasets analyzed or generated during the study. Where no new data were created, or where data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions, a statement is still required. Suggested Data Availability Statements are available in section “MDPI Research Data Policies” at
https://www.mdpi.com/ethics.
Acknowledgments
I acknowledge the support given by Project Sustenbioenergy CNPq.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gama, M.M.; Ribeiro, G.D.; Fernandes, C.F.; Medeiros, I.M. Açaí (Euterpe spp.): características, formação de mudas e plantio para produção de frutos. Circular técnica 2005, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, D.G.; Carvalhaes, M.A.; Bezerra, V.S. Boas práticas na cadeia de produção de açaí 2021.
- Oliveira, N.P. ; Farias Neto; J.T. Euterpe oleracea e E. precatoria: açaí. Espécies nativas da flora brasileira de valor econômico atual ou potencial: plantas para o futuro: região Norte, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pompeu, D.; Silva, E.; Rogez, H. Optimisation of the solvent extraction of phenolic antioxidants from fruits of Euterpe oleracea using Response Surface Methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6076–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara Sabbe, Wim Verbeke, Rosires Deliza, Virginia Matta, Patrick Van Damme. Effect of a health claim and personal characteristics on consumer acceptance of fruit juices with different concentrations of açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.). Appetite 2009, 53, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, A.F.N.; Mattietto, R.A.; Oliveira, M.S.P. Teor de Lipídeos em Caroços de Euterpe oleracea Mart. Boletim de pesquisa e desenvolvimento.
- Ilyushin, Y.V.; Fetisov, V. Experience of virtual commissioning of a process control system for the production of high-paraffin oil. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, D.A.R.; da Silva Ribeiro, H.J.; Ferreira, C.C.; de Andrade Cordeiro, M.; Guerreiro, L.H.; Pereira, A.M.; Dos Santos, W.G.; Santos, M.C.; de Carvalho, F.B.; Junior, J.O.; et al. Fractional Distillation of Bio-Oil Produced by Pyrolysis of Açaí (Euterpe oleracea) Seeds. In Fractionation; Al-Haj Ibrahim, H., Ed.; Intechopen: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-78984-965-3. [Google Scholar]
- Guerreiro, L.H.H.; Baia, A.C.F.; Assunção, F.P.D.C.; Rodrigues, G.D.O.; e Oliveira, R.L.; Junior, S.D.; Pereira, A.M.; de Sousa, E.M.P.; Machado, N.T.; de Castro, D.A.R.; et al. Investigation of the Adsorption Process of Biochar Açaí (Euterpea olerácea Mart.) Seeds Produced by Pyrolysis. Energies 2022, 15, 6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bufalino, L.; Guimaraes, A.A.; de Silva, B.M.; de Souza, R.L.F.; de Melo, I.C.N.A.; de Oliveira, D.N.P.S.; Trugilho, P.F. Local variability of yield and physical properties of açaí waste and improvement of its energetic attributes by separation of lignocellulosic fibers and seeds. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2018, 10, 053102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, D.R.; Ribeiro, H.D.S.; Guerreiro, L.H.; Bernar, L.P.; Bremer, S.J.; Santo, M.C.; Almeida, H.D.S.; Duvoisin, S.; Borges, L.P.; Machado, N.T. Production of Fuel-Like Fractions by Fractional Distillation of Bio-Oil from Açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) Seeds Pyrolysis. Energies 2021, 14, 3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.D.M.S.D.; de Castro, D.A.R.; Santos, M.C.; Almeida, H.D.S.; Schultze, M.; Lüder, U.; Hoffmann, T.; Machado, N.T. Process Analysis of Main Organic Compounds Dissolved in Aqueous Phase by Hydrothermal Processing of Açaí (Euterpe oleraceae, Mart.) Seeds: Influence of Process Temperature, Biomass-to-Water Ratio, and Production Scales. Energies 2021, 14, 5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, A.A. Biocombustível na aviação: progressos e desafios. Monografia. Universidade do Sul de Santa Catarina. Palhoça 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinand, F.W.; Van de Steene, L.; Blaise, K.K.; Siaka, T. Prediction of pyrolysis oils higher heating value with gas chromatography– mass spectrometry. Fuel 2012, 96, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernar, L.P.; Ferreira, C.C.; Costa, A.F.d.F.; Ribeiro, H.J.D.S.; dos Santos, W.G.; Pereira, L.M.; Pereira, A.M.; Moraes, N.L.; Assunção, F.P.D.C.; da Mota, S.A.P.; et al. Catalytic Upgrading of Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Carbon Pellets into Hydrocarbons-like Fuels in a Two-Stage Reactor: Analysis of Hydrocarbons Composition and Physical-Chemistry Properties. Energies 2022, 15, 4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.C.; Bernar, L.P.; Costa, A.F.d.F.; Ribeiro, H.J.D.S.; Santos, M.C.; Moraes, N.L.; Costa, Y.S.; Baia, A.C.F.; Mendonça, N.M.; da Mota, S.A.P.; et al. Improving Fuel Properties and Hydrocarbon Content from Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Red Mud Pellets in Two-Stage Reactor: Optimization of Reaction Time and Catalyst Content. Energies 2022, 15, 5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrão, A.C.M.; Silva, C.M.S.; Assunção, F.P.C.; Ribeiro, H.J.S.; Santos, M.C.; Almeida, H.S.; JR, S.D.; Borges, L.E.P.; CASTRO, D.A.R.; Machado, N.T. Análise do processo de pirólise de sementes de Açaí (Euterpe Oleracea, Mart): Influência da temperatura no rendimento dos produtos de reação e nas propriedades físico-químicas do BioÓleo. Brazilian Journal of Development. 2021, 7, 18200–18220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.L.; Guerreiro, L.H. H, Bernar, L.P.; Ribeiro, H.J.S.; Oliveira, R.L.; Santos, M.C.; Almeida, H.S.; Jr, S.D.; Borges, L.E.P.; Castro, D.A.R.; Machado, N.T. Análise da composição química do Bio-Óleo produzido via pirólise de sementes de Açaí (Euterpe Oleracea, Mart). Brazilian Journal of Development. 2021, 7, 15549–15565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, F.S.; Bernar, L.P.; Ribeiro, Ferreira, C.C, H.J.S.; Assunção, F.P.C.; Pereira, L.M..; Almeida, H.S.; Jr, S.D.; Borges, L.E.P.; Castro, D.A.R.; Machado, N.T. Purificação do Bio-Óleo produzido via pirólise de sementes de Açaí (Euterpe Oleracea, Mart). Brazilian Journal of Development. 2021, 7, 18260–18277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitoza, U.S.; Thue, P.S.; Lima, E.C.; Reis, G.S.; Rabiee, N.; Alencar, W.S.; Mello, B.L.; Dehmani, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; Dias, S.L. Use of Biochar Prepared from the Açaí Seed as Adsorbent for the Uptake of Catechol from Synthetic Effluents. Molecules 2022, 27, 7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, W.M.; Assunção, F.P.C.; Castro, D.A.R.; Guerreiro, L.H.H; Machado, N.T. Estudo do processo de produção de biochar via pirólise da semente de açaí visando à remediação do solo. Revista DAE 2024, 72, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valois, F.P.; Bezerra, K.C.A.; Assunção, F.P.C.; Bernar, L.P.; Paz, S.P.A.; Santos, M.C.; Feio, W.P.; Silva, R.M.P.; Mendonça, N.M.; Castro, D.A.R.; Jr. S.D.; Gomes, A.R.Q.; Sousa, V.R.C.; Monteiro, M.C.; Machado, N.T. Improving the Antioxidant Activity, Yield, and Hydrocarbon Content of Bio-Oil from the Pyrolysis of Açaí Seeds by Chemical Activation: Effect of Temperature and Molarity. Catalysts 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valois, F.P.; Valdez, G.D.; Bezerra, K.C.A.; Bremer, S.J.; Bernar, L.P.; Paz, S.P.A.; Santos, M.C.; Feio, W.P.; Silva, R.M.P.; Mendonça, N.M.; Castro, D.A.R. ; Jr. S.D.; Monteiro, M.C.; Machado, N.T. Effect of temperature and molarity on the bio-oil yield and quality by pyrolysis of Açaí seeds (Euterpe Oleraceae, Mart.) activated with KOH. Preprints.org. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Valdez, D.G.; Valois, F.P.; Bremer, S.J.; Bezerra, K.C.A.; Hamoy Guerreiro, L.H.; Santos, M.C.; Bernar, L.P.; Feio, W.P.; Moreira, L.G.S.; Mendonça, N.M.; et al. Improving the Bio-Oil Quality of Residual Biomass Pyrolysis by Chemical Activation: Effect of Alkalis and Acid Pre-Treatment. Energies 2023, 16, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, H.D.S.; Corrêa, O.; Eid, J.; Ribeiro, H.; de Castro, D.; Pereira, M.; Pereira, L.; Mâncio, A.D.A.; Santos, M.; Souza, J.D.S.; et al. Production of biofuels by thermal catalytic cracking of scum from grease traps in pilot scale. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 118, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, H.D.S.; Corrêa, O.; Eid, J.; Ribeiro, H.; de Castro, D.; Pereira, M.; Pereira, L.; Aâncio, A.D.A.; Santos, M.; da Mota, S.; et al. Performance of thermochemical conversion of fat, oils, and grease into kerosene-like hydrocarbons in different production scales. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 120, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Mota, S.; Mancio, A.; Lhamas, D.; de Abreu, D.; da Silva, M.; dos Santos, W.; de Castro, D.; de Oliveira, R.; Araújo, M.; Borges, L.E.; et al. Production of green diesel by thermal catalytic cracking of crude palm oil (Elaeis guineensis Jacq) in a pilot plant. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 110, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernar, L.P.; Ferreira, C.C.; Costa, A.F.d.F.; Ribeiro, H.J.D.S.; dos Santos, W.G.; Pereira, L.M.; Pereira, A.M.; Moraes, N.L.; Assunção, F.P.D.C.; da Mota, S.A.P.; et al. Catalytic Upgrading of Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Carbon Pellets into Hydrocarbons-like Fuels in a Two-Stage Reactor: Analysis of Hydrocarbons Composition and Physical-Chemistry Properties. Energies 2022, 15, 4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.C.; Bernar, L.P.; Costa, A.F.d.F.; Ribeiro, H.J.D.S.; Santos, M.C.; Moraes, N.L.; Costa, Y.S.; Baia, A.C.F.; Mendonça, N.M.; da Mota, S.A.P.; et al. Improving Fuel Properties and Hydrocarbon Content from Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Red Mud Pellets in Two-Stage Reactor: Optimization of Reaction Time and Catalyst Content. Energies 2022, 15, 5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancio, A.; da Mota, S.; Ferreira, C.; Carvalho, T.; Neto, O.; Zamian, J.; Araújo, M.; Borges, L.; Machado, N. Separation and characterization of biofuels in the jet fuel and diesel fuel ranges by fractional distillation of organic liquid products. Fuel 2018, 215, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mâncio, A.; da Costa, K.; Ferreira, C.; Santos, M.; Lhamas, D.; da Mota, S.; Leão, R.; de Souza, R.; Araújo, M.; Borges, L.; et al. Process analysis of physicochemical properties and chemical composition of organic liquid products obtained by thermochemical conversion of palm oil. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 123, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.C.; Lourenço, R.M.; de Abreu, D.H.; Pereira, A.M.; de Castro, D.A.R.; Pereira, M.S.; Almeida, H.S.; Mâncio, A.A.; Lhamas, D.E.L.; da Mota, S.A.P.; et al. Gasoline-like hydrocar-bons by catalytic cracking of soap phase residue of neutralization process of palm oil (Elaeis guineensis Jacq). J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 71, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Costa, E.; de Castro, D.; Pereira, M.; Mâncio, A.; Santos, M.; Lhamas, D.; da Mota, S.; Leão, A.; Duvoisin, S.; et al. Deacidification of organic liquid products by fractional distillation in laboratory and pilot scales. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 127, 468–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, L.A.B.; Lora, E.E.S.; Ayarza, J.A.C. Biomassa no Brasil e no mundo: biomassa para energia. UNICAMP, 2008.
- Barcellos, D.C.; et al. O estado da arte das plantações de florestas de rápido crescimento para produção de Biomassa para energia em Minas Gerais: aspectos técnicos, econômicos, sociais e ambientais. . 1. ed., 2000, 1, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Seye, O.; Souza, R. C. R.; Bacellar, A. A.; Morais, M. R. Caracterização do caroço de açaí como insumo para geração de eletricidade via gaseificação. In: CONGRESSO INTERNACIONAL SOBRE GERAÇÃO DISTRIBUÍDA E ENERGIA NO MEIO RURAL, 7, 2008. Anais... Fortaleza, 2008.
- Castro, D.A.R. Estudo do processo de pirólise de sementes de açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) para produção de biocombustíveis. Tese de doutorado, Universidade Federal do Pará, Belém-Pa, Brasil, 2019.
- Santos, M.M.; Pasolini, F.S.; Costa, A.P.O. Caracterização físico-química do caroço e da fibra do açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) via métodos clássicos e instrumentais. Brasilian Journal of Production Engineering 2023, 9, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, A.L. Estudos de processos de extração e caracterização de fibras do fruto de açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) da Amazônia para produção de ecopainel de partículas de média densidade. Tese de doutorado, Universidade Federal do Pará, Belém-Pa, Brasil, 2013.
- Silva, T.F. Caroço de açaí: uma alternativa bioenergética. Dissertação de mestrado. Programa de Pós-graduação em Ciências Florestais. Universidade de Brasília. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nagaishi, T. Y. R. Açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart): extrativismo, características, energia e renda em uma comunidade na ilha de Marajó/PA. Dissertação de Mestrado em Ciências Florestais. Universidade Federal Rural da Amazônia. Belém. 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Leão, R. M. Tratamento superficial de fibra de coco e aplicação em materiais compósitos como reforço do polipropileno. 2012. Dissertação (Mestrado em Engenharia Mecânica) – Universidade de Brasília, Brasília-DF. 2012. [Google Scholar]
Figure 1.
Methodology used for obtaining and characterizing the liquid products from the pyrolysis of açaí seeds and fibers. Source: adapted from Valdez [
24].
Figure 1.
Methodology used for obtaining and characterizing the liquid products from the pyrolysis of açaí seeds and fibers. Source: adapted from Valdez [
24].
Figure 2.
Schematic of the rotating drum used for fiber separation.
Figure 2.
Schematic of the rotating drum used for fiber separation.
Figure 3.
Seeds and fibers after the separation process.
Figure 3.
Seeds and fibers after the separation process.
Figure 4.
(a) Chemical impregnation of açaí fibers with NaOH solution; (b) Chemical impregnation of açaí seeds with NaOH solution.
Figure 4.
(a) Chemical impregnation of açaí fibers with NaOH solution; (b) Chemical impregnation of açaí seeds with NaOH solution.
Figure 5.
Experimental setup of the pyrolysis process.
Figure 5.
Experimental setup of the pyrolysis process.
Figure 7.
(a) Yield of reaction products by pyrolysis of açaí seeds; (b) Yield of reaction products by pyrolysis of açaí fibers.
Figure 7.
(a) Yield of reaction products by pyrolysis of açaí seeds; (b) Yield of reaction products by pyrolysis of açaí fibers.
Figure 8.
Acidity index of the aqueous fractions and bio-oils from açaí seeds and fibers.
Figure 8.
Acidity index of the aqueous fractions and bio-oils from açaí seeds and fibers.
Figure 9.
Infrared spectra of bio-oils and aqueous phases by pyrolysis of in nature seeds and NaOH-impregnated seeds.
Figure 9.
Infrared spectra of bio-oils and aqueous phases by pyrolysis of in nature seeds and NaOH-impregnated seeds.
Figure 11.
Infrared spectra of the aqueous phases and bio-oil obtained by pyrolysis of in nature fibers and NaOH-impregnated fibers.
Figure 11.
Infrared spectra of the aqueous phases and bio-oil obtained by pyrolysis of in nature fibers and NaOH-impregnated fibers.
Figure 12.
Comparison of the infrared spectra of the aqueous phases obtained by pyrolysis of in nature fibers and fibers impregnated with NaOH at 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 M.
Figure 12.
Comparison of the infrared spectra of the aqueous phases obtained by pyrolysis of in nature fibers and fibers impregnated with NaOH at 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 M.
Figure 13.
Comparison of the infrared spectra of bio-oils obtained by pyrolysis of açaí seeds and fibers impregnated with NaOH at 1.0 M.
Figure 13.
Comparison of the infrared spectra of bio-oils obtained by pyrolysis of açaí seeds and fibers impregnated with NaOH at 1.0 M.
Figure 14.
Total area percentage sum of the compounds identified in the aqueous phases obtained by pyrolysis of in nature seeds and NaOH-impregnated seeds.
Figure 14.
Total area percentage sum of the compounds identified in the aqueous phases obtained by pyrolysis of in nature seeds and NaOH-impregnated seeds.
Figure 15.
Total area percentage sum of the compounds identified in the aqueous phases obtained by pyrolysis of in nature fibers and NaOH-impregnated fibers.
Figure 15.
Total area percentage sum of the compounds identified in the aqueous phases obtained by pyrolysis of in nature fibers and NaOH-impregnated fibers.
Table 1.
Studies reported in the literature on açaí pyrolysis between 2020 and 2024 [
9,
11,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24].
Table 1.
Studies reported in the literature on açaí pyrolysis between 2020 and 2024 [
9,
11,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24].
| publications |
experimental
matrix |
impregnating
agent |
pyrolysis
temperature |
biomass
comminution |
Featured products |
| [9] |
Seeds |
NaOH 2M |
400°C, 450°C |
Yes |
biochar |
| [11] |
Seeds |
- |
450°C |
Yes |
bio-oil |
| [17] |
Seeds |
- |
350°C, 400°C, 450°C |
Yes |
bio-oil |
| [18] |
Seeds |
- |
350°C, 400°C, 450°C |
Yes |
bio-oil |
| [19] |
Seeds |
- |
450°C |
Yes |
bio-oil |
| [20] |
Seeds |
ZnCl2 |
650°C |
Yes |
biochar |
| [21] |
Seeds |
- |
400°C, 450°C |
Yes |
biochar |
| [22] |
Seeds |
KOH 0.5M, 1.0M, 2.0M |
350°C, 400°C, 450°C |
Yes |
bio-oil, aqueous phase |
| [23] |
Seeds |
KOH 0.5M, 1.0M, 2.0M |
350°C, 400°C, 450°C |
Yes |
bio-oil, aqueous phase, biochar |
| [24] |
Seeds |
HCl, KOH |
350°C, 450°C |
Yes |
bio-oil, aqueous phase, biochar |
Table 2.
Yields after the pre=treatment of drying and mechanical separation processes of the fibers.
Table 2.
Yields after the pre=treatment of drying and mechanical separation processes of the fibers.
| Data |
Drying |
Separation-Seeds |
Separation-Fibers |
| Initial mass (kg) |
7.35 |
1.35 |
1.35 |
| Final mass (kg) |
4.80 |
1.10 |
0.20 |
| Yield (%) |
65.31 |
81.48 |
14.54 |
| Moisture (%) |
34.69 |
- |
- |
Table 3.
Physical-chemical characterization of raw açaí seeds and fibers.
Table 3.
Physical-chemical characterization of raw açaí seeds and fibers.
| Data |
Seeds |
Fibers |
| Ash content (%) |
2.77 |
10.92 |
| Volatile content (%) |
77.39 |
77.69 |
| Fixed carbon (%) |
19.84 |
11.39 |
Table 4.
Yields after chemical treatment of seeds and fibers with NaOH.
Table 4.
Yields after chemical treatment of seeds and fibers with NaOH.
| Material |
NaOH (mol/L) |
Initial mass (g) |
Final mass (g) |
Mass loss (%) |
| Fiber |
0.5 |
57.500 |
53.853 |
6.343 |
| Fiber |
1.0 |
57.500 |
53.729 |
6.558 |
| Fiber |
2.0 |
57.500 |
54.160 |
5.809 |
| Seed |
0.5 |
57.500 |
55.187 |
4.023 |
| Seed |
1.0 |
57.500 |
55.558 |
3.377 |
| Seed |
2.0 |
57.500 |
55.086 |
4.198 |
Table 5.
Process parameters, mass balances, and product yields by pyrolysis of açaí fibers activated with NaOH at 450°C, 1 atm, in laboratory scale.
Table 5.
Process parameters, mass balances, and product yields by pyrolysis of açaí fibers activated with NaOH at 450°C, 1 atm, in laboratory scale.
| Process parameters |
450 °C |
| NaOH 0.5M |
NaOH 1.0M |
NaOH 2.0M |
| Mass of Açaí fibers (g) |
20.003 |
20.007 |
20.007 |
| Cracking time (min) |
70 |
70 |
70 |
| Initial cracking temperature (°C) |
285 |
278 |
218 |
| Mass of Solid (Coke) (g) |
7.519 |
7.967 |
7.841 |
| Mass of Liquid (Bio-oil) (g) |
0.303 |
0.491 |
0.741 |
| Mass of H2O (g) |
6.089 |
4.843 |
4.242 |
| Mass of gas (g) |
6.092 |
6.706 |
7.183 |
| Bio-oil yield (wt.%) |
1.51 |
2.45 |
3.70 |
| Aqueous phase yield (wt.%) |
30.44 |
24.21 |
21.20 |
| Biochar yield (wt.%) |
37.59 |
39.82 |
39.19 |
| Gas yield (wt.%) |
30.46 |
33.52 |
35.90 |
| Acidity H2O (mg KOH/g) |
148.2 |
81.7 |
19 |
| Acidity Bio-oil (mg KOH/g) |
130.7 |
76.4 |
26.4 |
Table 6.
Process parameters, mass balances, and product yields by pyrolysis of açaí seeds activated with NaOH at 450 °C, 1 atm, in laboratory scale.
Table 6.
Process parameters, mass balances, and product yields by pyrolysis of açaí seeds activated with NaOH at 450 °C, 1 atm, in laboratory scale.
| Process parameters |
450 °C |
| NaOH 0.5M |
NaOH 1.0M |
NaOH 2.0M |
| Mass of Açaí seeds (g) |
20.008 |
20,074 |
20,066 |
| Cracking time (min) |
70 |
70 |
70 |
| Initial cracking temperature (°C) |
255 |
270 |
280 |
| Mass of Solid (Coke) (g) |
6.710 |
5.450 |
6.696 |
| Mass of Liquid (Bio-oil) (g) |
0.910 |
1.202 |
1.322 |
| Mass of H2O (g) |
8.264 |
8.107 |
7.519 |
| Mass of gas (g) |
4.124 |
5.315 |
4.529 |
| Bio-oil yield (wt.%) |
4.55 |
5.99 |
6.59 |
| Aqueous phase yield (wt.%) |
41.30 |
40.39 |
37.47 |
| Biochar yield (wt.%) |
33.54 |
27.15 |
33.37 |
| Gas yield (wt.%) |
20.61 |
26.48 |
22.57 |
| Acidity H2O (mg KOH/g) |
77.4 |
73.6 |
68 |
| Acidity Bio-oil (mg KOH/g) |
47.3 |
23.1 |
18.4 |
Table 7.
Process parameters, mass balances, and yields of reaction products (liquids, solids, H2O, and gas) by pyrolysis of açaí fibers and açaí seeds in nature at 450 °C, 1.0 atmosphere, in laboratory scale.
Table 7.
Process parameters, mass balances, and yields of reaction products (liquids, solids, H2O, and gas) by pyrolysis of açaí fibers and açaí seeds in nature at 450 °C, 1.0 atmosphere, in laboratory scale.
| Process parameters |
450°C |
| Fibers |
Seeds |
| Mass of Açaí seeds (g) |
20.000 |
20.034 |
| Cracking time (min) |
70 |
70 |
| Initial cracking temperature (°C) |
300 |
290 |
| Mass of Solid (Coke) (g) |
9.134 |
6.836 |
| Mass of Liquid (Bio-oil) (g) |
0.245 |
0.663 |
| Mass of H2O (g) |
6.747 |
8.155 |
| Mass of gas (g) |
3.874 |
4.380 |
| Bio-oil yield (wt.%) |
1.23 |
3.31 |
| Aqueous phase yield (wt.%) |
33.74 |
40.71 |
| Biochar yield (wt.%) |
45.67 |
34.12 |
| Gas yield (wt.%) |
19.37 |
21.86 |
| Acidity H2O (mg KOH/g) |
184.3 |
78.4 |
| Acidity Bio-oil (mg KOH/g) |
202.6 |
71.5 |
Table 8.
Compounds ≥3% identified in the bio-oil after pyrolysis at 450°C of açaí seeds impregnated with 2.0 M NaOH.
Table 8.
Compounds ≥3% identified in the bio-oil after pyrolysis at 450°C of açaí seeds impregnated with 2.0 M NaOH.
| RT |
Compounds |
S-2.0M |
| 4041 |
2-Furanmethanol |
3.17 |
| 6689 |
Phenol |
3.24 |
| 22845 |
Dodecanoic acid |
4.46 |
| 27619 |
Tetradecanoic acid |
8.91 |
| 32124 |
n-Hexadecanoic acid |
3.93 |
Table 9.
Compounds ≥5% identified in the aqueous phases after pyrolysis at 450 °C of raw seeds and NaOH-impregnated seeds with 2.0 mol/L.
Table 9.
Compounds ≥5% identified in the aqueous phases after pyrolysis at 450 °C of raw seeds and NaOH-impregnated seeds with 2.0 mol/L.
| RT |
Compounds |
S-IN |
S-0.5M |
S-1.0M |
S-2.0M |
| 3.742 |
Furfural |
18.52 |
15.47 |
|
|
| 3.746 |
3,5-Dimethylpyrazole |
|
|
15.88 |
12.74 |
| 5.119 |
Butyrolactone |
|
6.4 |
9.57 |
12.55 |
| 20.820 |
beta,-D-Glucopyranose, 1,6-anhydro- |
55.43 |
65.53 |
59.04 |
52.34 |
Table 10.
Compounds ≥ 5% identified in the aqueous phases after pyrolysis at 450 °C of NaOH-impregnated fibers.
Table 10.
Compounds ≥ 5% identified in the aqueous phases after pyrolysis at 450 °C of NaOH-impregnated fibers.
| IR |
Compounds |
F-IN |
F-0.5M |
F-1.0M |
F-2.0M |
| 3.134 |
Oxazole, 4,5-dihydro-2,4,4-trimethyl- |
|
5.01 |
16.76 |
48.31 |
| 6.702 |
Phenol |
33.08 |
37.28 |
28.19 |
14.86 |
| 9.613 |
Phenol, 2-methoxy- |
11.76 |
26.11 |
15.86 |
8.34 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).