1. Introduction
Stem cell transplantation (SCT) is the standard and potentially curative treatment for a diverse spectrum of malignancies and bone marrow failure syndromes [
1]. Witnessing a steady raise, the number of transplants surpassed 1.29 million in 2016 worldwide [
2]. For years, UAE residents facing the difficult journey of transplant have opted for overseas options, seeking care in countries like the United States, India, Turkey, Egypt, Korea and Europe. This "transplant tourism," while offering access to potentially life-saving SCT procedure, often translates to fragmented post-transplant care riddled with challenges. The long-distance travel exposes patients to increased infection risks, treatment interruptions, and inconsistent pre- and post-transplant protocols [
3].
Published literature surrounding SCT and its associated complications in the UAE remains scarce. The Department of Health provides a glimpse into the magnitude of this phenomenon, reporting 325 patients (161 adults and 164 pediatrics) who underwent SCT outside the UAE between 2016 and 2018 [
4]. However, in July 2020 a first successful bone marrow transplant was performed within UAE borders [
5]. Unfortunately, the SCT program's progress was halted by the global COVID pandemic, further highlighting the nation's reliance on transplant tourism.
Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD) is the most common and formidable post-transplant complication, impacting morbidity, mortality, and quality of life [
6,
7]. With its diverse manifestations often targeting the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and liver [
8], GVHD casts a shadow of uncertainty over the transplant journey even in optimal settings [
9,
10]. Estimates of GVHD incidence can range from 30% to 80%, influenced by factors like related or unrelated donors [
11,
12], HLA-matching between donor and recipient [
13], recipient age [
14], and even gender disparities [
15]. The complexity extends beyond these classic elements, encompassing minor histocompatibility antigens [
16], and GVHD prophylaxis protocols [
17,
18].
Furthermore, the quality of pre- and post-transplant care intricately intertwines with GVHD outcomes. This care hinges on access to detailed pre-transplant information, the transplant center's experience, expertise, and the accessibility of evolving medications. Unfortunately, these elements often fall short in transplant tourism scenarios, where fragmented care and geographical barriers impede optimal post-transplant support. Although extensive data have been published on GVHD and its risk factors, information on international SCT patients returning to home countries that lack transplant facilities and expertise is scarce and not well documented.
Our retrospective observational study, encompassing patients from diverse backgrounds who underwent transplants abroad and receiving post-transplant care within the UAE, aims to report the nuances of GVHD in this unique population. We also investigated the well-known GVHD risk factors and their potential variation in this context, with a particular focus on organ-specific GVHD. We hope to pave the way for multicenter and well directed studies studying the impact of factors related to travel on international stem cell transplant outcomes.
2. Materials and Methods
A retrospective analysis was conducted at our healthcare institution in Abu Dhabi, UAE. A total of 91 SCT recipients (both adults and children) out of 149 transplant recipients receiving follow-up care at our institution between January 2019 and December 2022 were included. Patients with incomplete medical records or fewer than three post-transplant clinic visits were excluded to ensure data reliability and completeness. Data were collected from transplant centre reports and clinical documents, covering recipient and donor demographics, transplant indications, pre-SCT chemotherapy lines, transplant timing, recipient blood group, donor-recipient relationships, conditioning regimens, and GVHD severity/type/organ involvement.
Descriptive statistics and inferential tests (two-sample tests, variance equality, Chi-square) were applied. Relative risk was calculated for key risk factors and presented as forest plots. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered significant. Due to missing data, bivariate analysis was preferred over multivariate analysis to maintain statistical power. Variables with significant missing data (e.g., donor age, HLA alleles) were excluded from the analysis. Subgroup analyses were infeasible due to data gaps, which limited detailed stratification of the data
3. Results
3.1. Age, Gender and Pre-Transplant Timing
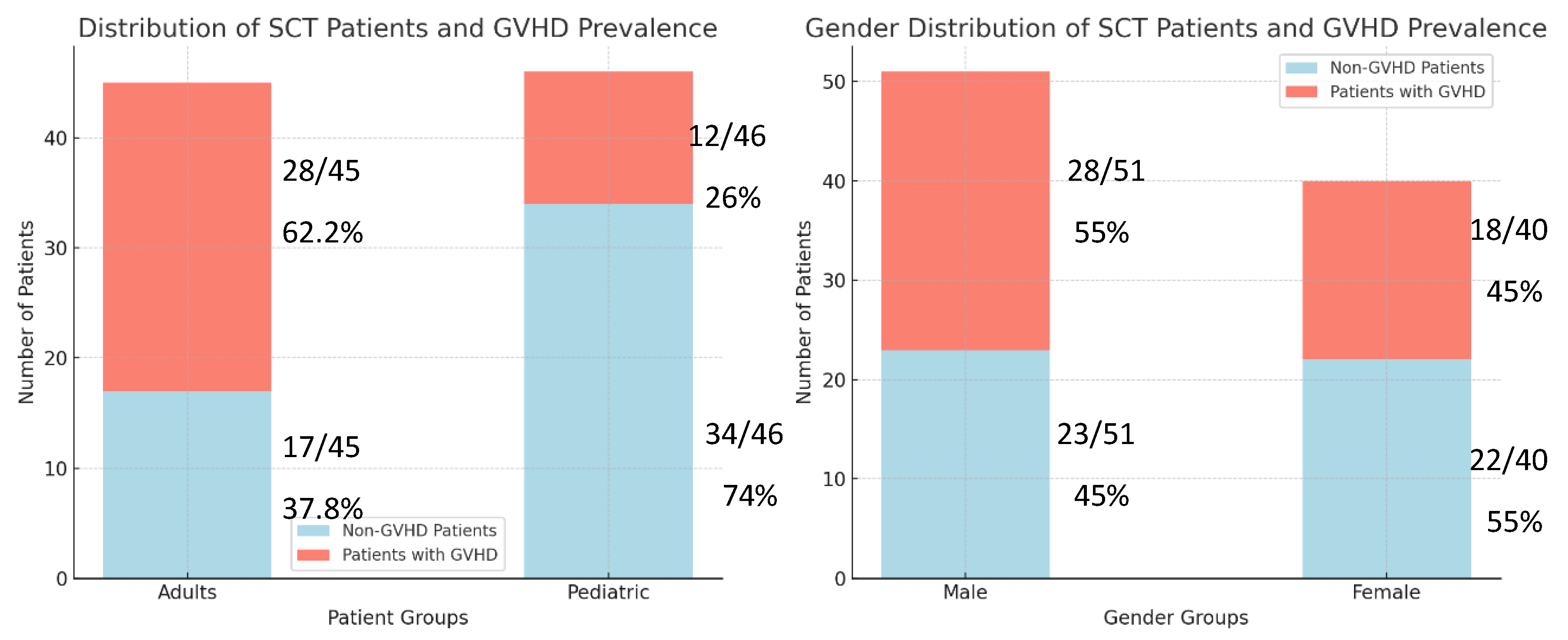
Among the 91 SCT recipients in our study, 87.9% (n=80) received allogeneic transplants. Of these, 50% (n=40) developed Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD). Among overall SCT recipients, adults (70%, 28) comprised a larger proportion of GVHD cases compared to pediatric recipients (30%, 12). Within each group, GVHD prevalence was higher in adults (62.2%, 28/45) than in children (26%, 12/46) as shown in left panel of
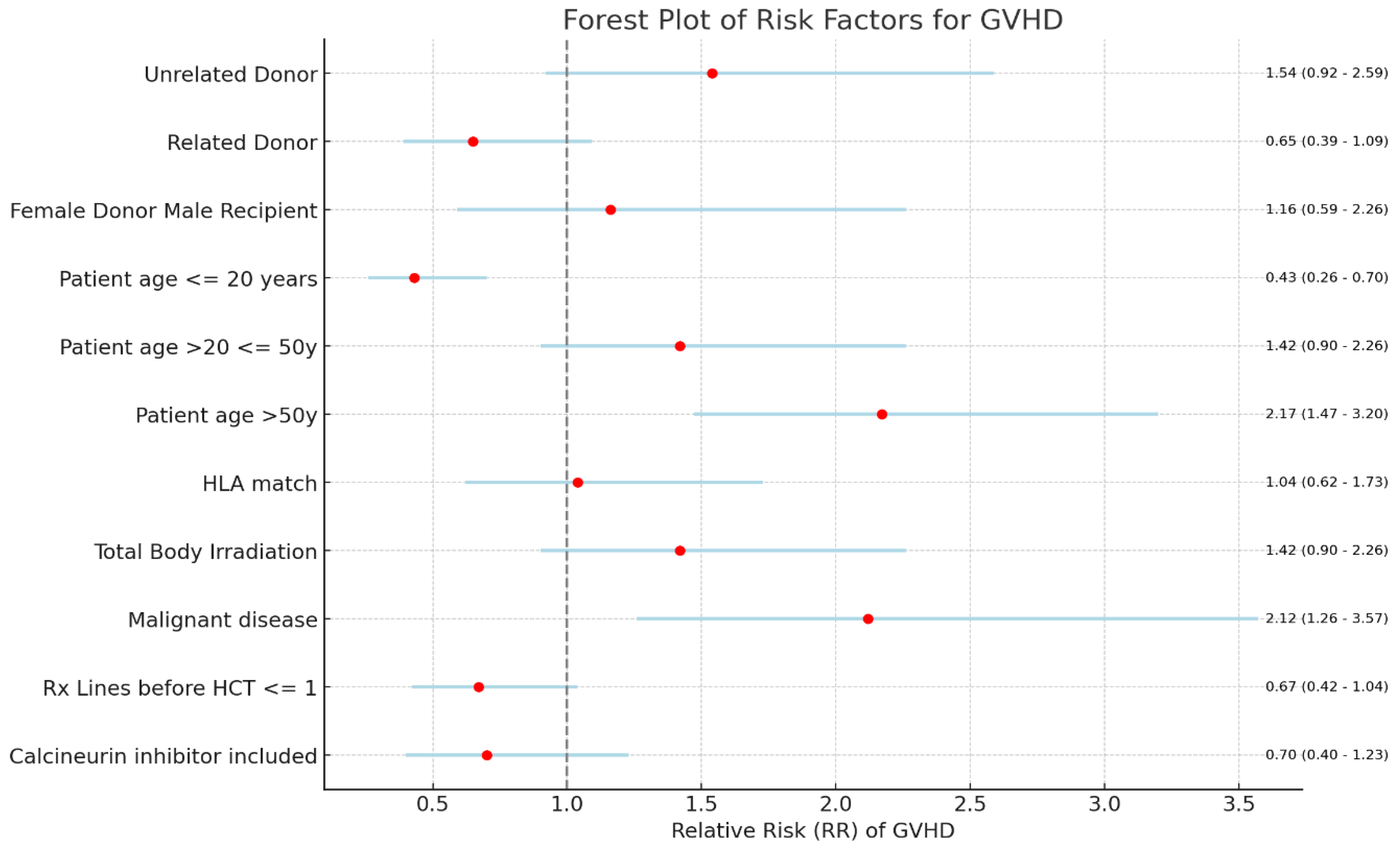
Figure 1. While the distribution of pediatric recipients slightly exceeded adults (51.65% vs. 48.35%), the overall mean age was 24.47 years. Recipient age showed a significant correlation with GVHD (p=0.004). Compared to adults, pediatric recipients exhibited a reduced GVHD risk (RR 0.43, 95% CI 0.27-0.7), while adults greater than fifty years of age faced an elevated risk (RR 2.17, 95% CI 1.47-3.2) (
Figure 2).
Among total, 51 were male and 40 were female. While males exhibited a slightly higher GVHD prevalence (55% vs 45%) as shown in right panel of
Figure 1, recipient gender did not show a statistically significant correlation with GVHD (p > 0.05). Similarly, no significant association was observed between donor gender and GVHD (p = 0.8).
Acute GVHD and chronic GVHD occurred in 52.5% and 47.5% of GVHD cases, respectively. The Severity distribution was 41.6% severe, 22.2% moderate, and 36.1% mild cases.
The mean time from diagnosis to hematopoietic cell transplantation (SCT) in our study was 47.8 months, with recipients averaging 19.2 years old at the time of SCT. This timeframe did not demonstrate a significant correlation with GVHD occurrence (p = 0.98).
3.2. Diverse Backgrounds and Blood Groups
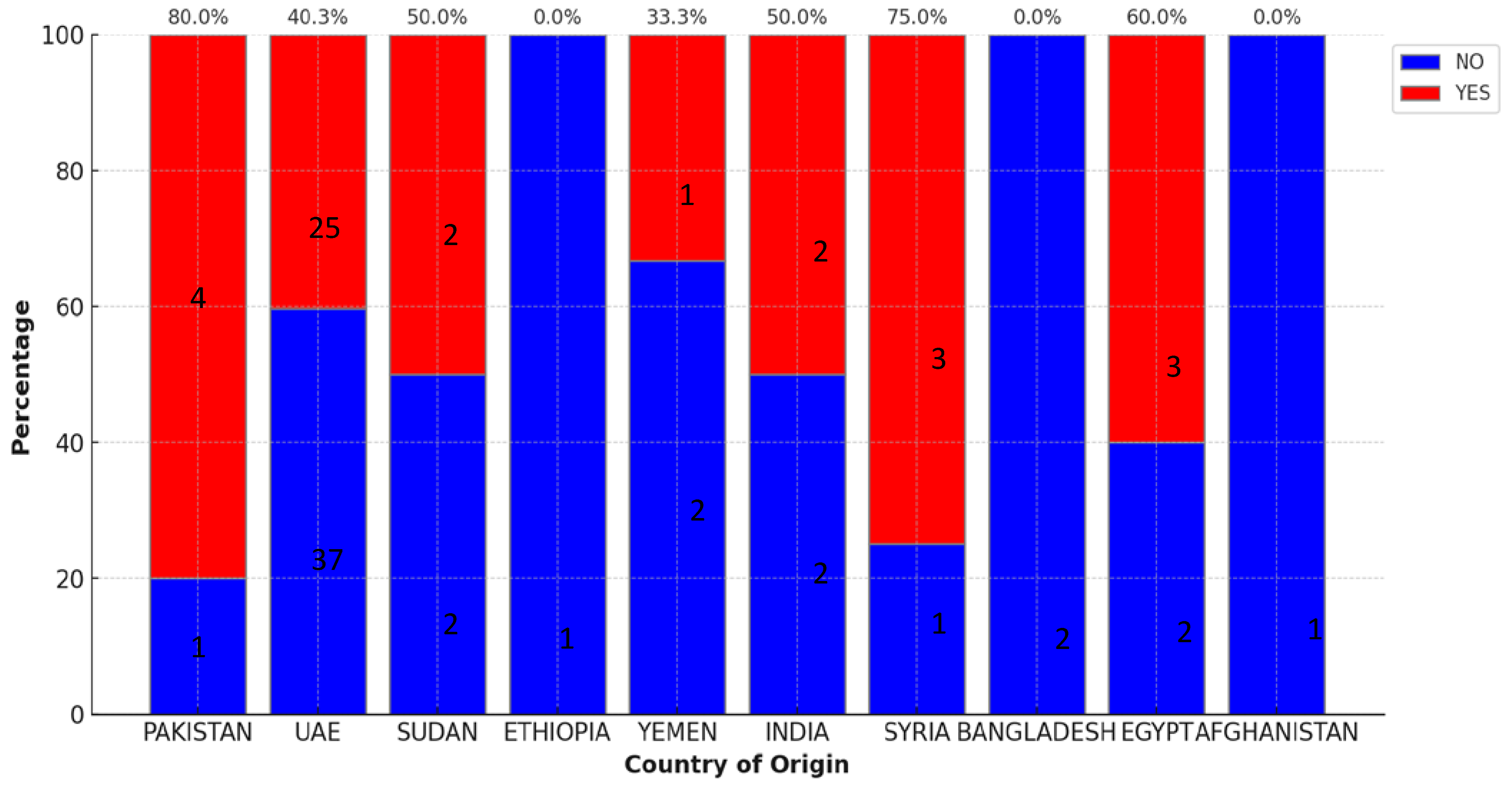
Among the recipients, 31.8% hailed from diverse backgrounds, with Pakistan (5%), Egypt (5%), and Sudan (4%) constituting the next highest populations after native UAE patients. The GVHD prevalence among SCT recipients from Pakistan, Egypt, and Syria showed higher percentages as indicated in
Figure 3.
Regarding blood groups, O positive was the most frequent (39.5%), followed by A+ (28.5%), B+ (17.5%), and O- (4.4%). No statistically significant association was observed between recipient blood group and GVHD occurrence (p = 0.1).
3.3. Donor Relationship
Siblings formed the majority of donors (52.6%), followed by related donors (23.09%), with smaller proportions of self and unrelated donors (12.09%). GVHD prevalence with unrelated donors exhibited the highest GVHD rate (63.4%), followed by siblings (58.3%) and then related donors (23.8%). A significant association noted between overall donor-recipient relationship and GVHD occurrence (p=0.04). Due to the limited sample size, further analysis of association strength within donor relationship subcategories was not feasible.
3.4. Transplant Indication
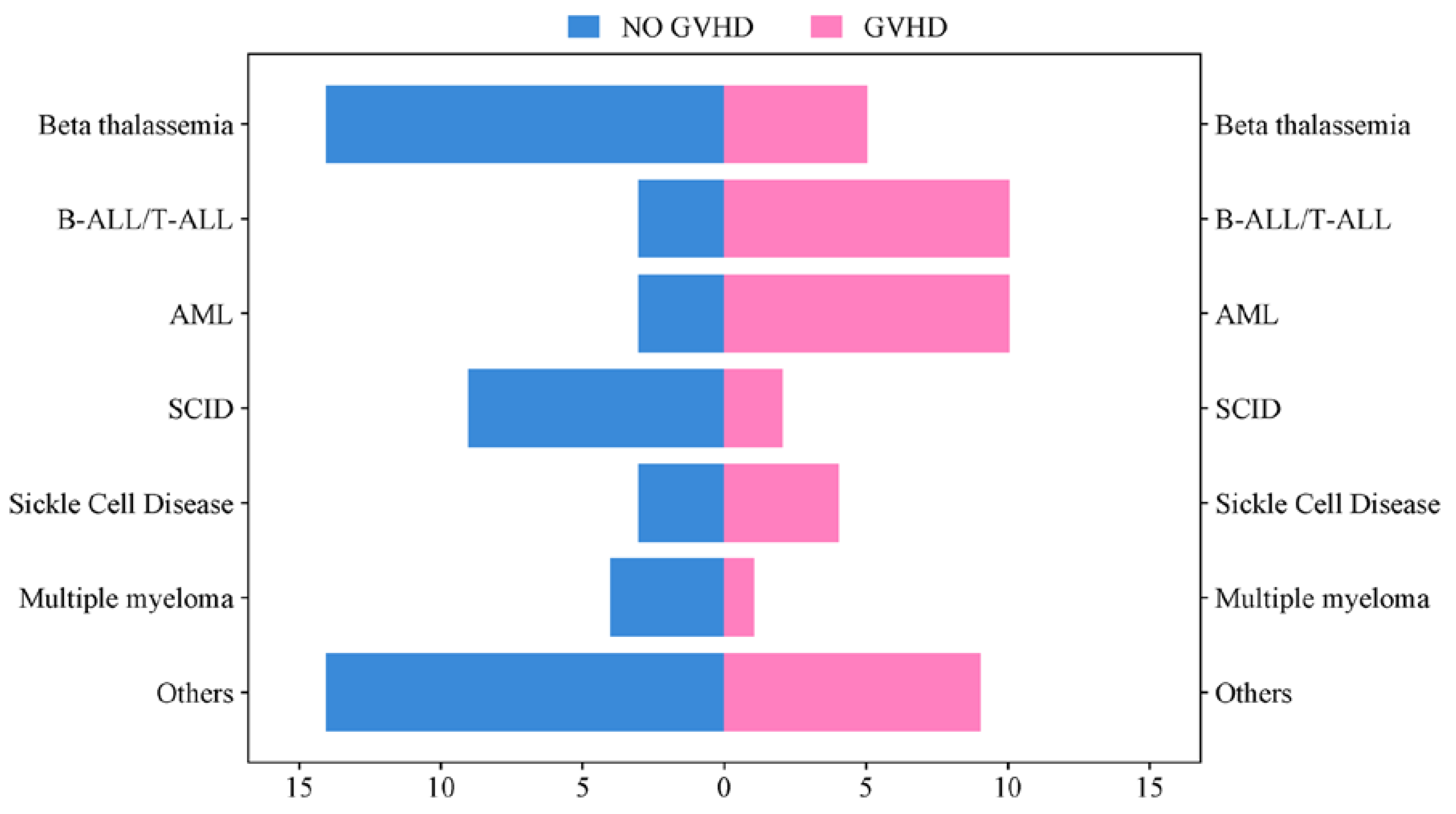
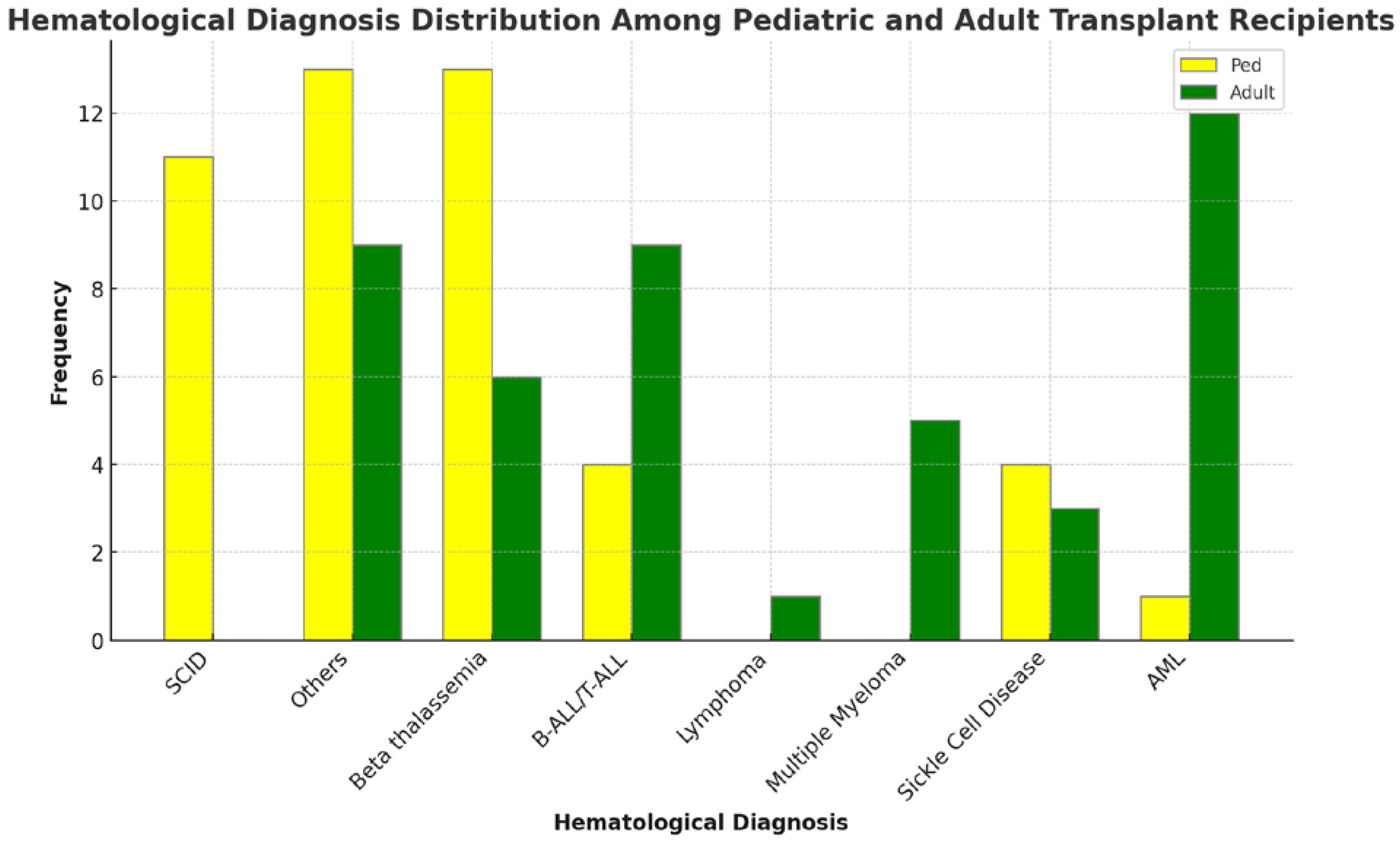
Common transplant indications included Beta thalassemia (20.8%), Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (14.2% each), Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) (12%), and Sickle Cell Disease (SCID) (7.6%). Moreover, the frequency of distribution of GVHD and no GVHD based on hematological conditions is represented in
Figure 4. Benign hematological conditions were more frequent in pediatric recipients, while malignant hematological conditions predominated in adults, as shown in
Figure 5. The indication for SCT influenced GVHD occurrence (p=0.007). Recipients with benign hematological disorders exhibited a markedly reduced risk of GVHD compared to those with malignant conditions (RR 0.47, 95% CI 0.28-0.79 vs. RR 2.12, CI 1.26-3.57) as indicated in
Figure 2.
3.5. Stem Cell Source, Pre-Transplant Chemotherapy and Conditioning Regimens
Among stem cell sources, bone marrow dominated (36%), followed by peripheral blood (26.3%) and cord blood (4%). GVHD prevalence varied: 58% with peripheral blood, 49% with bone marrow, and 4% with cord blood. Pre-transplant chemotherapy: 42% did not receive any chemotherapy, 15% received one or three lines each and 25% received two lines.
GVHD prevalence was higher in recipients who received total body irradiation (TBI) as part of the conditioning regimen (69.2%) compared to those who did not (31.9%). Moreover, a lower relative risk of GVHD among ATG recipients (RR = 0.79; CI, 0.37-1.6) was reported.
3.6. HLA Match, GVHD Prophylaxis, and Mortality
Among SCT recipients, 69.2% received HLA-identical transplants, 21.9% haploidentical, and 8.9% unidentical. GVHD prevalence varied: 60% in unidentical, 44% in identical, and 42% in haploidentical cases. Within the identical donor group, related donors exhibited GVHD in 50% compared to 71% in unrelated donors. However, HLA match did not demonstrate a statistically significant association with overall GVHD (p=0.66), shown in
Figure 2.
Regarding GVHD prophylaxis, cyclosporin was the primary agent in 34.6% of cases, followed by calcineurin inhibitors in 25%. The use of these agents showed a significant correlation with GVHD occurrence (p=0.03). Unfortunately, 10% of recipients had passed away at data collection, predominantly adults (77%). This mortality rate was associated with GVHD occurrence (p=0.009).
3.7. Organ-Specific GVHD
Skin was the primary organ involved, affecting 35.5% of recipients. Subsequent organs in descending order of involvement were gastrointestinal tract (including oral) (25.5%), ocular (16.6%), liver (14.4%), and lungs (11.1%). Notably, risk factors for organ-specific GVHD largely mirrored those for overall GVHD, with the exception of lung involvement. Significant correlations were observed among all affected organs (p<0.05), except for lung and eye GVHD (p=0.45)
Table 1.
4. Discussion
Our study provides a comprehensive perspective on the prevalence of GVHD in SCT recipients who have returned to the UAE after receiving transplants at international centres. Among the 91 recipients, a significant majority (87.9%, n=80) underwent allogeneic transplants, with half of these patients (50%, n=40) developing GVHD. Notably, adult recipients exhibited a higher prevalence of GVHD (62.2%) as anticipated. Contrary to expectations, recipients with related HLA-identical donors exhibited higher GVHD rates (50%).
The study also assessed well-known risk factors such as the age and gender of both recipients and donors, haematological diseases, chemotherapy regimens, donor-recipient relationships, conditioning regimens with or without TBI, stem cell sources, and GVHD prophylaxis. These risk factors influenced GVHD prevalence as expected; however, lung GVHD did not show a clear association with these factors. Additionally, the prevalence of ocular GVHD was lower than that reported in the literature.
4.1. GVHD
While the overall GVHD rate of 43.9% aligns with established literature, the 62.2% prevalence in adult recipients stands out. This observed rate surpasses the 28% GVHD reported in a large-scale study of allogeneic transplants over two decades (1990-2015) [
19]. Our GVHD prevalence of 71% surpasses the 44-50% GVHD prevalence reported in the National Marrow Donor Program for unrelated donors. The prevalence of 50% GVHD remains significantly higher than the 28% observed in HLA-matched sibling transplants too [
20]. Higher GVHD prevalence in this cohort even when majority were pediatric recipients (52%), had HLA identical donor (69.2%), and over half of the donors being siblings (52.6%) is concerning [
20]. These characteristics, associated with lower GVHD, might mask the full impact of potential factors such as travel complexities and disruptions in post-transplant care.
4.2. Recipient and Donor Age
Recipient age emerged as the most influential risk factor for GVHD in our cohort, echoing established literature [13,20]. As expected, a strong correlation was observed between adult recipients and higher GVHD rates (p=0.004), as illustrated in Figure 2. Compared to adults, pediatric patients exhibited a substantially lower relative risk of GVHD (RR=0.43; CI, 0.27-0.7), highlighting the significant impact of age on GVHD development. While existing studies suggest an increased risk with donors older than 30 [21], our analysis couldn't explore this relationship due to missing data.
4.3. SCT Indication
The underlying disease requiring SCT significantly impacted GVHD development. Benign hematological conditions, predominantly affecting pediatric recipients as shown in
Figure 5, exhibited a markedly lower GVHD risk compared to malignant hematological diseases, which are more prevalent in adults [
19]. This observation aligns with the broader literature, where primary transplant indications often include hemoglobinopathies followed by malignancies like leukemia [
2]. SCT indication remained important risk factor, with a significantly higher relative risk of GVHD associated with malignant conditions (RR=2.12; CI, 1.26-3.57) as illustrated in
Figure 2. This disparity in risk likely stems from a complex interplay of factors, including variations in conditioning regimens [
22], the potential use of total body irradiation (TBI), and differences in pre-transplant treatment strategies [
23].
4.4. Sibling/Related donors
Our findings align with the established preference for matched sibling or related donors over matched unrelated donors to mitigate GVHD risk [
18,
24]. This trend emerges in our data too, as unrelated donors exhibited a higher relative risk of GVHD (RR=1.4; CI, 0.9-2.6) compared to related or sibling donors (p=0.04). Further echoing existing literature, our analysis revealed a potential association between donor gender and GVHD prevalence when the recipient is male [
25]. While the relative risk in such cases was modest (RR=1.1; CI, 0.59-2.26), it adds to the ongoing investigation of gender-specific factors in GVHD development. However, consistent with broader research, our study did not identify donor gender as a significant overall risk factor for GVHD (p=0.8) [
26]. These findings highlight the complex interplay of donor characteristics and their impact on GVHD risk. While certain relationships and donor gender may exhibit subtle or context-dependent associations, further research is needed to elucidate their precise role in influencing GVHD development and inform optimal donor selection strategies.
4.5. Pre-SCT Chemotherapy
The number of pre-SCT chemotherapy regimens displayed a significant association with GVHD occurrence (p=0.03). Recipients who received one or fewer lines of chemotherapy exhibited a lower relative risk of GVHD compared to those receiving multiple lines (RR=0.67; CI, 0.42-1.04), as illustrated in Figure 2. This finding suggests that minimizing pre-transplant chemotherapy intensity might offer a potential strategy for mitigating the GVHD risk.
4.6. HLA Compatibility
Contrary to expectations and established literature highlighting the importance of HLA matching, we did not find a significant association between HLA matching and GVHD in our cohort (p=0.66) as shown in Figure 2. This finding aligns with existing research suggesting a lower susceptibility to GVHD among pediatric recipients, even in the context of HLA mismatch or non-identical transplants [19,27]. Given the high proportion of pediatric patients in our study (52%), this factor could potentially explain the observed lack of a strong correlation between HLA matching and GVHD [28].
4.7. Stem Cell Source
Our findings align with established literature by demonstrating a higher relative risk of GVHD associated with peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs) compared to bone marrow (BM) as the stem cell source [
29,
30]. Within our cohort, 58% of PBSC recipients developed GVHD compared to 49% of BM recipients. However, it's important to acknowledge that our data lacks information on the specific proportion of PBSCs mobilized using colony-stimulating factors (CSFs). As CSF mobilization has also been linked to GVHD risk, further analysis with this information could provide deeper insights into the interplay between stem cell sources and mobilization techniques.
4.8. Conditioning Regimens with or without TBI and GVHD Prophylaxis
Within our cohort, 69% of recipients who underwent TBI conditioning developed GVHD, aligning with earlier studies reporting a higher chronic GVHD prevalence with TBI [21,22,31]. Conversely, the inclusion of Anti-Thymocyte Globulin (ATG) during conditioning has been associated with reduced GVHD risk [22]. Consistent with this trend, our analysis revealed a lower relative risk of GVHD among ATG recipients (RR=0.79; CI, 0.37-1.6). These findings highlight the potential trade-offs involved in selecting conditioning regimens, emphasizing the need for careful consideration of both GVHD risk and disease control efficacy.
The type of GVHD prophylaxis also emerged as a significant factor (p=0.03). Specifically, regimens containing calcineurin inhibitors seemed to be associated with a higher risk of GVHD, calling for further investigation into their role and potentially influencing future prophylaxis selection [19]. 4.9. Organ GVHD
Aligning with literature, skin remained the most common site of GVHD manifestation [32,33]. Recipient age emerged as a key factor influencing organ involvement, mirroring Inamoto et al.'s findings [34]. Ocular GVHD, however, appeared less prevalent in our cohort (16%) compared to reported ranges of 60-90% [35]. While organ GVHD exhibited significant correlations with other organ involvement, lung GVHD did not (Table 1).
At 11%, lung GVHD prevalence in our study was slightly higher than previously reported 3-10% ranges [36]. Unlike overall GVHD, our analysis of lung GVHD risk factors revealed no significant correlations, aligning to study by Rabanus et al. [37]. Notably, our data also showed significant correlations between manifestations in various organs (p<0.05), except for the absence of a link between lung and eye GVHD (p=0.45) as seen in Table 1 [33]. 5. Limitations
Our cohort of 91 recipients restricts the subgroup analyses, potentially masking nuanced associations within specific demographic or clinical subgroups. The diverse origins of transplant centers and recipients introduce heterogeneity in treatment approaches and data collection practices. We initially assumed consistent methodologies across centers, but limitations in accessing their specific protocols hindered our ability to account for potential variations. Additionally, gaps in data, including missing donor information and ambiguous clinical records, further challenged precise GVHD categorization (acute vs. chronic) and treatment analysis. The UAE's demographic composition, with a large expatriate population (88%), presents additional complications. Many patients seek post-diagnosis treatment abroad, leading to fragmented medical records and incomplete follow-up data. This hinders our ability to comprehensively track disease trajectories and treatment outcomes within this specific population.
6. Conclusions
This study highlights a higher prevalence of GVHD among adult international SCT recipients who return home for post-transplant care. Despite favorable factors, such as matched related donors, particularly siblings, the prevalence of GVHD remains elevated. While the overall and organ-specific GVHD risk factors generally align with existing literature, lung GVHD showed no clear association with these established risk factors, and ocular GVHD had a lower-than-expected prevalence. To better understand and identify the contributing factors to the higher GVHD rates in this unique population, large multicenter studies are necessary. Our study serves as a pilot project and, to our knowledge, is the first study from the UAE to report findings on stem cell transplantation and graft-versus-host disease.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S. and S.H.; methodology, N.S.; formal analysis, N.S. and S.H.; investigation, N.S. and S.H.; resources, I.A., F.A.M., A.A.K.,N.J.M.H., H.A.S., H.S.,A.U.C., A.H., and G.E.G.; data curation, N.S., F.A.M., and I.A.; writing—original draft preparation, N.J.M.H. and I.A.; writing—review and editing, N.S., G.E.G., and S.H.; supervision, S.H.; funding acquisition, N.S. and S.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was funded by Department of Health, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Sheikh Shakbout Medical City (No. SSMCREC-444, Date:30-11-2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to retrospective observational study that included data extraction from medical records.
Data Availability Statement
De-identified data underlying the results presented in this study are openly available in Mendeley Data at DOI: 10.17632/svwnp5kkrz.1
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- E. D. Thomas, H. L. Lochte, W. C. Lu, and J. W. Ferrebee, ‘Intravenous Infusion of Bone Marrow in Patients Receiving Radiation and Chemotherapy’, New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 257, no. 11, pp. 491–496, Sep. 1957. [CrossRef]
- D. Niederwieser et al., ‘One and a half million hematopoietic stem cell transplants: continuous and differential improvement in worldwide access with the use of non-identical family donors’, Haematologica, vol. 107, no. 5, pp. 1045–1053, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Humaid O. Al-Shamsi, ‘Establishing and Launching a Comprehensive Bone Marrow Transplant Unit in the UAE Amidst the COVID-19 Pandemic: Overcoming Barriers Through International Collaboration and Resilience’, in https://connection.asco.org/blogs/establishing-and-launching-comprehensive-bone-marrow-transplant-unit-uae-amidst-covid-19, Abu Dhabi: American Society of Clinical Oncology, Dec. 2021.
- H. O. Al-Shamsi et al., ‘Challenges for cancer patients returning home during SARS-COV-19 pandemic after medical tourism - a consensus report by the emirates oncology task force’, BMC Cancer, vol. 20, no. 1, p. 641, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Shireena Al Nowais, ‘UAE’s first bone marrow transplant patient tells of life-saving treatment’. https://www.thenationalnews.com/uae/health/uae-s-first-bone-marrow-transplant-patient-tells-of-life-saving-treatment-1.
- G. Socié et al., ‘Long-Term Survival and Late Deaths after Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation’, New England journal of medicine, vol. 341, no. 1, pp. 14–21, 1999. [CrossRef]
- T. L. Kiss, M. Abdolell, N. Jamal, M. D. Minden, J. H. Lipton, and H. A. Messner, ‘Long-term medical outcomes and quality-of-life assessment of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia followed at least 10 years after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation’, J Clin Oncol, vol. 20, no. 9, pp. 2334–2343, 2002. [CrossRef]
- D. A. Jacobsohn, ‘Acute graft-versus-host disease in children’, Bone Marrow Transplant, vol. 41, no. 2, pp. 215–221, 2007. [CrossRef]
- H. T. Greinix et al., ‘Incidence of Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease and Survival after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation over Time: A Study from the Transplant Complications and Chronic Malignancies Working Party of the EBMT’, Blood, vol. 132, no. Supplement 1, pp. 2120–2120, Nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Arai et al., ‘Increasing Incidence of Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease in Allogeneic Transplantation: A Report from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research’, Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 266–274, Feb. 2015. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Nash et al., ‘Phase 3 study comparing methotrexate and tacrolimus with methotrexate and cyclosporine for prophylaxis of acute graft-versus-host disease after marrow transplantation from unrelated donors’, Blood, vol. 96, no. 6, pp. 2062–2068, 2000. [CrossRef]
- M. Mohyeddin Bonab, K. Alimoghaddam, S. Vatandoust, F. Forouzia, M. Jahani, and A. Ghavamzadeh, ‘Are HLA antigens a risk factor for acute GVHD in thalassemic patients receiving HLA-identical stem cell transplantation?’, Transplant Proc, vol. 36, no. 10, pp. 3190–3193, Dec. 2004. [CrossRef]
- M. E. D. Flowers et al., ‘Comparative analysis of risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease and for chronic graft-versus-host disease according to National Institutes of Health consensus criteria’, Blood, vol. 117, no. 11, pp. 3214–3219, 2011. [CrossRef]
- A. Urbano-Ispizua et al., ‘Risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease in patients undergoing transplantation with CD34+ selected blood cells from HLA-identical siblings’, Blood, vol. 100, no. 2, pp. 724–727, Jul. 2002. [CrossRef]
- R. P. Gale et al., ‘Risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease’, Br J Haematol, vol. 67, no. 4, pp. 397–406, 1987. [CrossRef]
- D. WEISDORF et al., ‘RISK FACTORS FOR ACUTE GRAFT-VERSUS-HOST DISEASE IN HISTOCOMPATIBLE DONOR BONE MARROW TRANSPLANTATION’, Transplantation, vol. 51, no. 6, pp. 1197–1202, 1991. [CrossRef]
- C. G. DiRienzo, G. F. Murphy, S. C. Jones, R. Korngold, and T. M. Friedman, ‘T-Cell Receptor Vα Spectratype Analysis of a CD4-Mediated T-Cell Response against Minor Histocompatibility Antigens Involved in Severe Graft-versus-Host Disease’, Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, vol. 12, no. 8, pp. 818–827, Aug. 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. Jagasia et al., ‘Risk factors for acute GVHD and survival after hematopoietic cell transplantation’, Blood, vol. 119, no. 1, pp. 296–307, Jan. 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. Zecca, ‘Chronic graft-versus-host disease in children: incidence, risk factors, and impact on outcome’, Blood, vol. 100, no. 4, pp. 1192–1200, 2002. [CrossRef]
- K. Atkinson et al., ‘Risk factors for chronic graft-versus-host disease after HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation’, Blood, vol. 75, no. 12, pp. 2459–2464, 1990. [CrossRef]
- S. Ozawa et al., ‘Chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation from an unrelated donor: incidence, risk factors and association with relapse. A report from the Japan Marrow Donor Program’, Br J Haematol, vol. 137, no. 2, pp. 142–151, 2007. [CrossRef]
- W. E. Beschorner, K. A. Di, A. D. Hess, and G. W. Santos, ‘Cyclosporine and the thymus: Influence of irradiation and age on thymic immunopathology and recovery’, Cell Immunol, vol. 110, no. 2, pp. 350–364, 1987. [CrossRef]
- S. M. Davies et al., ‘Recent Decrease in Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease in Children with Leukemia Receiving Unrelated Donor Bone Marrow Transplants’, Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 360–366, 2009. [CrossRef]
- D’Souza et al., ‘Current Use of and Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in the United States’, Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, vol. 26, no. 8, pp. e177–e182, Aug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Eisner and C. S. August, ‘Impact of donor and recipient characteristics on the development of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease following pediatric bone marrow transplantation.’, PubMed, vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 663–668, 1995.
- A. W. Loren et al., ‘Impact of Donor and Recipient Sex and Parity on Outcomes of HLA-Identical Sibling Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation’, Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, vol. 12, no. 7, pp. 758–769, Jul. 2006. [CrossRef]
- L. Ochs et al., ‘Predictive factors for chronic graft-versus-host disease after histocompatible sibling donor bone marrow transplantation.’, PubMed, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 455–460, 1994.
- A. Nagler, C. Brautbar, S. Slavin, and A. Bishara, ‘Bone marrow transplantation using unrelated and family related donors: the impact of HLA-C disparity.’, PubMed, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 891–897, 1996.
- C. Anasetti et al., ‘Peripheral-Blood Stem Cells versus Bone Marrow from Unrelated Donors’, New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 367, no. 16, pp. 1487–1496, Oct. 2012. [CrossRef]
- C. Cutler, S. Giri, S. Jeyapalan, D. Paniagua, A. Viswanathan, and J. H. Antin, ‘Acute and Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease After Allogeneic Peripheral-Blood Stem-Cell and Bone Marrow Transplantation: A Meta-Analysis’, Journal of Clinical Oncology, vol. 19, no. 16, pp. 3685–3691, 2001. [CrossRef]
- T. Shinozawa, W. E. Beschorner, and A. D. Hess, ‘THE THYMUS AND PROLONGED ADMINISTRATION OF CYCLOSPORINE’, Transplantation, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 106–111, 1990. [CrossRef]
- V. Bhushan, ‘Chronic Graft-vs-Host Disease’, JAMA, vol. 290, no. 19, p. 2599, Nov. 2003. [CrossRef]
- Y. Inamoto et al., ‘Failure-free survival after initial systemic treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease’, Blood, vol. 124, no. 8, pp. 1363–1371, Aug. 2014. [CrossRef]
- J. Pidala et al., ‘Analysis of Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Chronic Grant-versus-Host Disease Manifestations on Major Outcomes: A Chronic Grant-versus-Host Disease Consortium Study’, Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 784–791, May 2013. [CrossRef]
- E. M. Espana, S. Shah, M. R. Santhiago, and A. D. Singh, ‘Graft versus host disease: clinical evaluation, diagnosis and management’, Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology, vol. 251, no. 5, pp. 1257–1266, May 2013. [CrossRef]
- G. C. Hildebrandt et al., ‘Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary chronic GVHD: report from the consensus conference on clinical practice in chronic GVHD’, Bone Marrow Transplant, vol. 46, no. 10, pp. 1283–1295, Oct. 2011. [CrossRef]
- R. Rabanus, J. Hahn, R. Andreesen, E. Holler, and G. C. Hildebrandt, ‘11: Risk Factor Analysis for the Development of Restrictive and Obstructive Pulmonary Function Changes After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation’, Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, vol. 14, no. 2, p. 6, Feb. 2008. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).