1. Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrably increased public awareness of personal hygiene and its role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases [
1]. This heightened awareness is reflected in the increased use of personal protective equipment such as disposable masks, gloves, and hand sanitizers [
2] For example, one survey documented an almost 9,000% increase in the proportion of face masks found in litter within a year of the pandemic’s start [
3]. Additionally, the demand for multipurpose disposable wet wipes has surged globally since the recent pandemic [
4]. For instance, the occurrence of these wipes on beaches increased by 94% in 2016 alone, marking a 400% rise over the past decade. On a single stretch of the Thames shoreline in the UK, over 23,000 wet wipes were collected [
5,
6,
7].
While these practices significantly contribute to reducing viral transmission and protecting public health, it is crucial to acknowledge that the disposable products market was already experiencing growth before the pandemic due to various factors such as increased urbanization, rising disposable income, and changing lifestyles.
A survey conducted by Evey at the California State Science Fair in 2015 [
8] indicated that 51 percent of respondents used a paper toilet seat cover, with an average usage of 14 sheets of toilet paper per flush. It is worth noting that one toilet seat cover is approximately equivalent to seven sheets of toilet paper. Concerning the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the global disposable toilet seat cover sheet market size was estimated to be USD 525.7 million in 2022, and it is projected to reach a revised size of USD 602.5 million by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate of 2.3 percent during the review period, as demonstrated by 360 Research Reports [
9].
The increased use of disposable toilet seat covers after the pandemic can be attributed to several factors: firstly, the pandemic heightened awareness about the importance of maintaining cleanliness and hygiene to prevent the spread of infectious diseases. Toilet plumes could play a contributory role to the transmission of enteric diseases. Common toilet hygiene measures include handwashing, hand drying, disinfecting, or covering the toilet seat surface before use, and flushing the toilet with the lid closed [
10]. In addition, it was recognized that outpatients were sharing toilet facilities with other patients, potentially staff and visitors, in some areas of the hospital. This raised the possibility that vector transmission could occur due to contact with the toilet seat [
11]. As such, disposable toilet seat covers offer individuals a convenient way to protect themselves from potential contaminants in public restrooms, thus addressing heightened hygiene concerns. Secondly, disposable toilet seat covers are convenient and easy to use. They offer a quick and hassle-free solution for individuals who prefer not to make direct contact with toilet seats in public restrooms. The convenience factor likely plays a significant role in their widespread adoption. Thirdly, the pandemic has spurred cultural shifts towards a greater emphasis on personal hygiene and cleanliness. Public toilets are a potential source of infection because they are contaminated with microbes from the gut every time they are used for defection. Being wet provides ideal conditions for the survival and growth of microbes, these microbes are clear vectors for disease transmission [
12]. As a result, individuals may be more inclined to use disposable toilet seat covers as part of their efforts to maintain hygiene standards in public settings. Therefore, the combined effect of the pandemic-induced hygiene awareness and pre-existing growth trends likely led to the widespread use of disposable toilet seat covers observed after the pandemic.
While flushing disposable toilet seat covers might seem ideal, it is not recommended due to the materials they’re made of. These seat covers typically consist of paper or non-woven fabric [
13]. Non-woven fabric is extensively used in the medical field and in protection against biological agents in other sectors [
14]. Even though paper is hydrophilic, it may not disintegrate quickly enough in water to avoid clogging, especially without additional aggressive treatment. Nonwoven materials with improved finishes such as liquid repellent, virus proof and bacterial resistance have been developed for applications such as surgical masks, gowns, drapes etc [
14]. On the other hand, non-woven fabric is relatively hydrophobic and non-wettable with water
[15], does not break down in water at all and can contribute significantly to plumbing problems. Therefore, discarding disposable toilet seat covers in a designated waste receptacle is better than flushing them down the toilet [
16].
Disposing the toilet cover in a separate waste receptacle after use could worsen the environmental impact by increasing household waste. A more sustainable solution is to use toilet covers made from biodegradable cellulose fibers rather than non-degradable materials. Furthermore, the most desirable option is to flush the used toilet cover paper, minimizing both waste and environmental impact.
For disposable toilet cover paper to be discarded with water and avoid clogging, it must possess specific properties. Like toilet paper, the cover sheet must absorb water fast enough and disintegrate well in water, ensuring effective breakdown during flushing and preventing blockages in the toilet or pipes. Additionally, it should possess sufficient physical strength to withstand the weight movement of toilet users on the toilet cover. ISO 12625-17 [
17,
18] describes a standard test method for evaluating the disintegration rate of tissue products by placing the tissue product in deionized water under specified conditions, agitating it, and then pouring it onto a sieve of specified size to measure the weight of the residue [
19].
This study aimed to develop a flushable toilet seat cover sheet as a more environmentally friendly alternative to disposable covers, replacing both non-biodegradable plastic and paper options requiring separate waste disposal. To achieve this, it was necessary to enhance the water absorption capability and the durability of the paper material compared to current products on the market. By doing so, the intention is to reduce the volume of waste generated from toilet seat covers that cannot be disposed of via flushing, thereby minimizing the environmental impact by ensuring the covers can be safely and conveniently disposed of within the restroom facilities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Meterials
Bleached hardwood kraft pulp (Hw-BKP) of Moorim P&P Co. Ltd in Korea was used to make a base paper for a disposable toilet cover sheet. Hw-BKP was beaten up to 300-500 mL CSF using a laboratory single disk refiner (KOS1 Co., Gimhae, Korea). According to ISO 5269-1, laboratory handsheets with a basis weight of 22±2 g/m
2 were prepared for physical and antibacterial testing. The types and amounts of chemicals used to improve the water resistance, antibacterial properties, and retention of pulp fibers and an antibacterial agent are summarized in
Table 1.
2.2. Antibacterial Test
Specimens with a diameter of 1 cm were collected from the antibacterial cover sheets. These were placed on agar previously inoculated with the test bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli). If the discs of the cover sheets have high antibacterial activity, a transparent zone or ring will form around them. The larger the zone of inhibition, the greater the antibacterial effect of the cover sheet.
2.3. Water Resistance Test
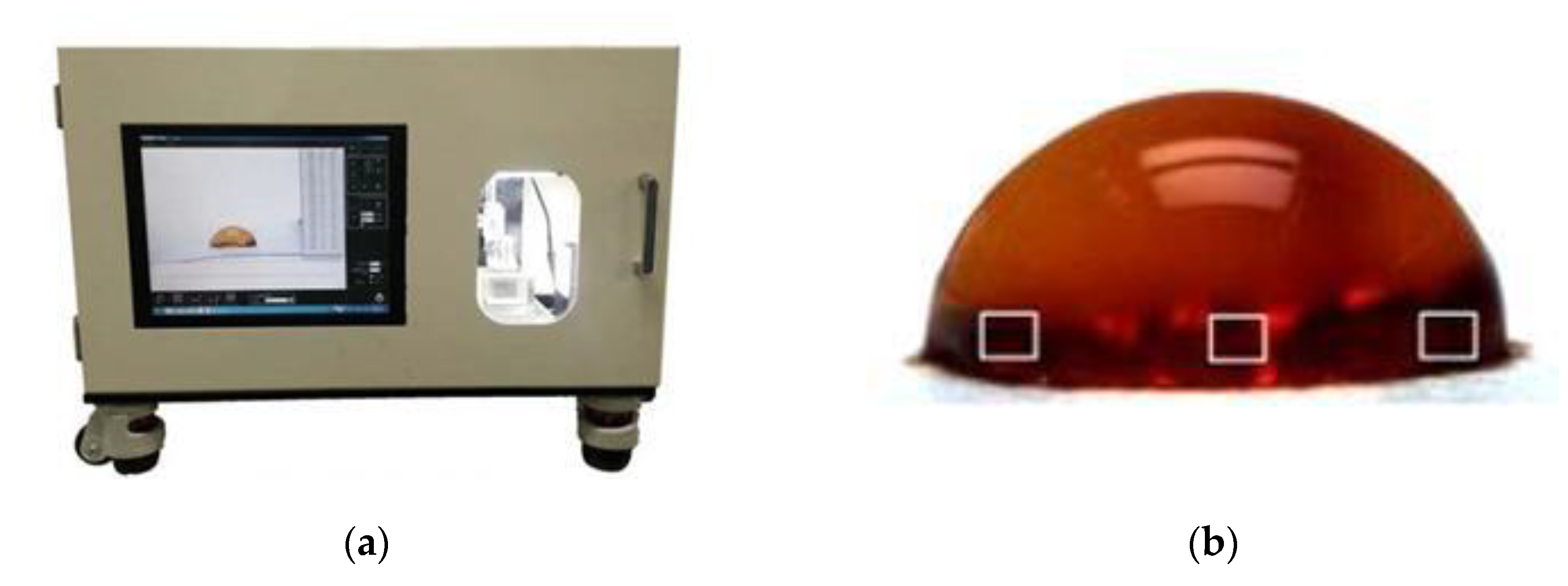
The self-developed device that simultaneously measures sizing degree and contact angle was used to evaluate the water resistance of disposable toilet seat covers [
20,
21]. As shown in
Figure 1, this automatic device helps assess liquid penetration into the specimens and hydrophobic properties on the specimen surface.
The device comprises a liquid droplet dispenser, a digital camera, and analysis software. The dispenser is used to drop around 18.5 mg of 6% FeCl3 (II) onto the surface of the toilet seat cover sheet on the solution of 6% NH4SCN. The digital camera is used to record the color change of the liquid droplet. The software measures the change in the droplet’s contact angle and the end point at which the droplet turns reddish-brown [
22].
2.4. SEM Image
Images were taken with FE-SEM (scanning electron microscope, JSM-7610F, JEOL, Japan) to observe the surface structure of the cover sheet made of refined pulp fibers. Through image analysis taken with SEM, how the refining process increases the interfiber bonding was identified.
2.5. Physical Properties
Tensile strength, tear strength, and surface roughness were measured according to ISO 1924-3, ISO 1974, and ISO 8791-4.
To evaluate the suitability of a disposable toilet cover sheet for disposal via flushing, an 11.4 cm x 10 cm sample was placed in 500 mL of distilled water within a beaker. The water was agitated at 600 revolutions per minute (rpm) using a three-winged propeller. Subsequently, the disintegration time of the toilet cover sheet was determined and compared to that of conventional toilet paper under identical conditions.
3. Results and Disscusion
3.1. Disintegration Rate
The disintegration rate of disposable toilet seat cover sheets is a critical parameter influencing both user comfort and the environmental impact of the product [
23].
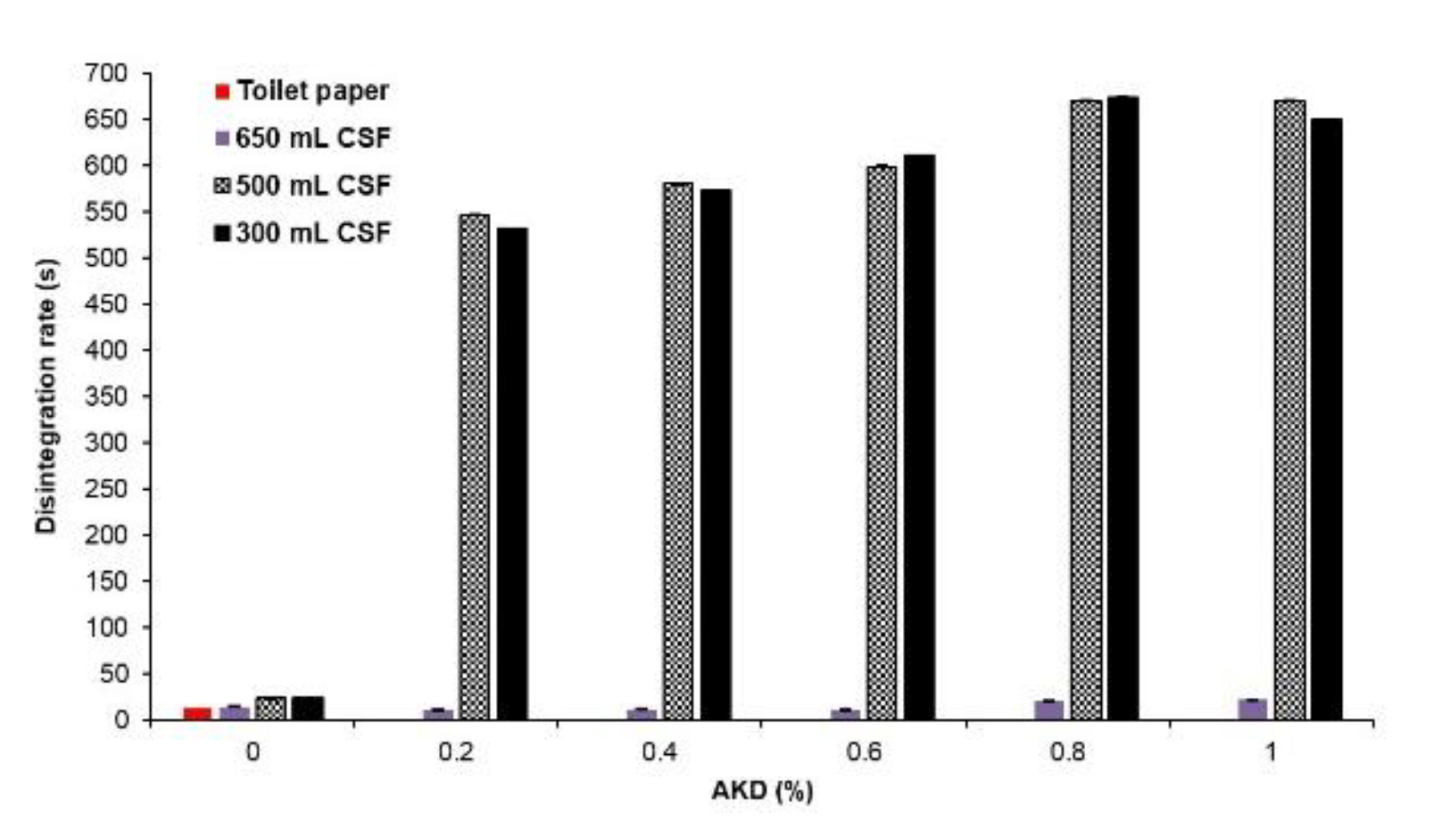
Figure 2 illustrates how the disintegration rate varies with different levels of freeness and the addition of AKD (alkyl ketene dimer). This study investigates the effects of refining and AKD addition on the disintegration rate, aiming to optimize the balance between product performance and user convenience.
The study examined disposable toilet seat cover sheets prepared with varying levels of pulp freeness and AKD addition. AKD was incorporated into the pulp stock to enhance the hydrophobic properties of the cover sheets, thereby preventing liquids from being readily absorbed and improving user comfort [
24]. The disintegration rate was measured by the time taken for the sheets to fully break down in water, compared to standard toilet tissue paper.
The results indicate that non-sized cover sheets (without AKD) disintegrated in approximately 23 seconds, which is about 10 seconds longer than the disintegration time for standard toilet tissue paper (13 seconds). The refining process, which subjects the fibers to compression and shear forces, appears to impact the disintegration rate negatively. The morphological changes in pulp fibers during refining enhance interfiber bonding, making the cover sheets more resistant to disintegration. Interestingly, the difference in freeness after refining did not significantly affect the disintegration rate of the cover sheets. The addition of AKD was found to be a more significant factor. Increased levels of AKD led to slower disintegration rates, as the cover sheets became more resistant to water absorption [
25,
26]. However, when AKD was added to unrefined pulp stock, there was a slight improvement in the disintegration rate, although this effect was not substantial compared to the impact on refined pulp stocks.
The findings highlight the complex interplay between fiber morphology, refining, and chemical additives in determining the disintegration rate of disposable toilet cover sheets. Non-sized cover sheets, while quicker to disintegrate, do not provide the same level of user comfort due to their higher water absorption. On the other hand, cover sheets with higher levels of AKD, while more comfortable, disintegrate more slowly, posing potential issues for disposal in toilets.
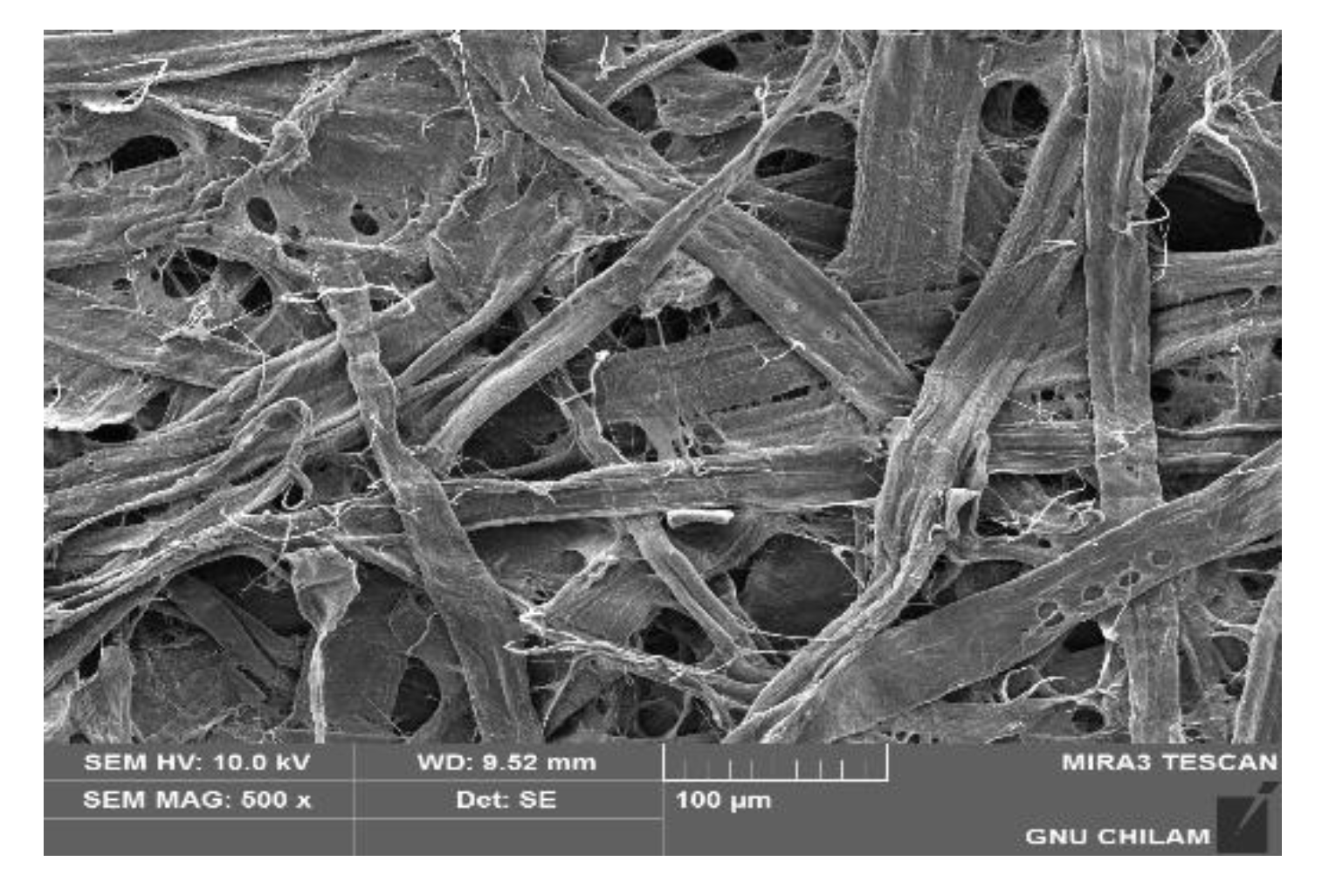
As shown in
Figure 3, the SEM image displaying the surface structure of the cover sheet made from refined pulp fibers illustrates how the refining process increases interfiber bonding [
27]. This enhancement contributes to the durability and structural integrity of the cover sheets but comes at the expense of disintegration efficiency [
28]. This emphasizes the need for a balanced production approach, where the benefits of refining and AKD addition are carefully weighed against the disintegration requirements.
3.2. Sizing Degree and Contact Angle
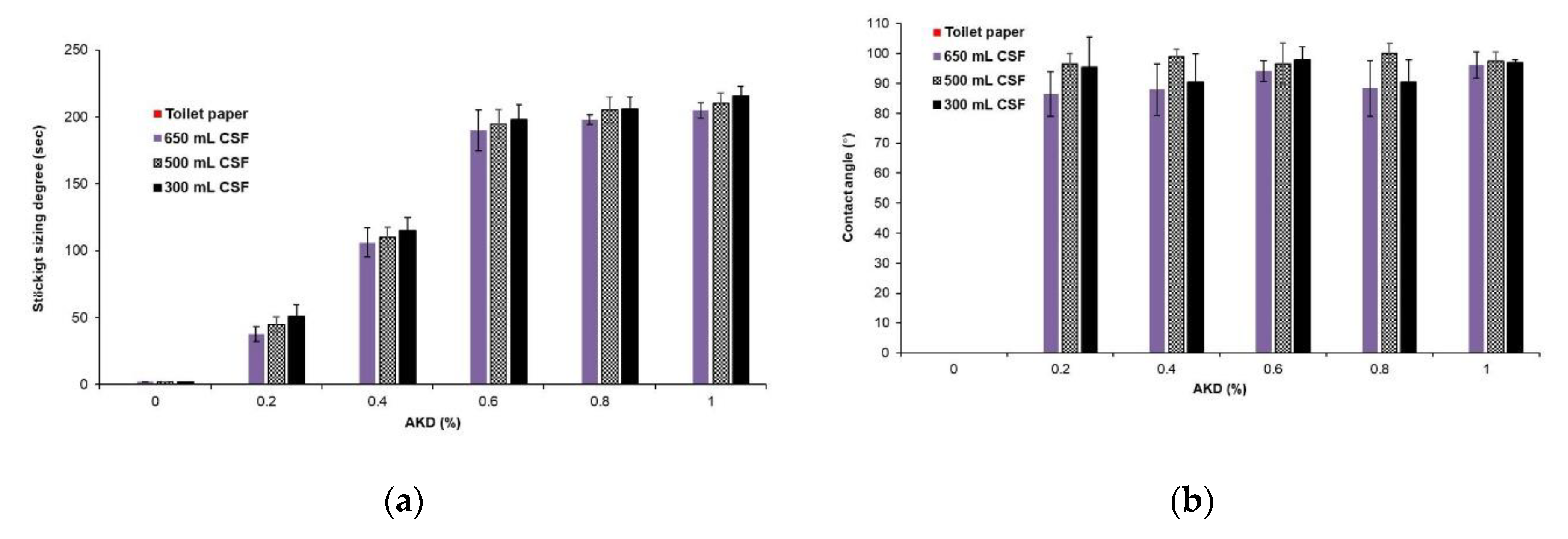
Figure 4 compares the Stöckigt sizing degree and the contact angle of the disposable toilet cover sheets based on different levels of freeness and AKD addition. The Stöckigt sizing degree is a measure of how long it takes for a specific solution to penetrate the paper. A higher sizing degree indicates that the paper takes longer to absorb the solution, meaning it’s more resistant to water. On the other hand, the contact angle is a direct measure of the wettability of the material surface. A high contact angle (above 90 degrees) typically indicates that the surface is hydrophobic (water-repellent), whereas a low contact angle suggests that the surface is hydrophilic (water-attractive).
The cover seat must immediately resist the absorption or penetration of moisture from the toilet seat surface but must not maintain this resistance for too long after being submerged in water within the plumbing system. Without a sizing agent, liquid readily penetrated the cover sheets irrespective of freeness levels. As AKD was added, the time it took for the liquid to penetrate the cover sheet began to lengthen, and when more than 0.4% AKD was added, the penetration time took over 100 seconds [
29,
30]. Therefore, to alleviate users’ discomfort caused by moisture absorption in the cover sheet, adding 0.2% AKD or less was found ideal to sufficiently delay absorption or penetration.
The contact angles of disposable toilet cover sheets made of disintegrated pulp fibers were lower (85-95°) than those made from refined pulp fibers [
31,
32]. The difference in contact angles between cover sheets made from disintegrated and refined pulp fibers could also be linked to fixing AKD onto the cellulose fibers. AKD, which imparts hydrophobicity to paper, more significantly adhered to refined pulp fibers with more fibrils, resulting in a greater contact angle [
33] Variations in AKD retention levels between the two types of pulp fibers could affect the surface wettability and hydrophobicity of the cover sheets, leading to differences in contact angles.
In conclusion, the disposable toilet cover sheets prepared from disintegrated pulp fibers displayed lower contact angles, signifying a slightly greater affinity for water interaction than those from refined pulp fibers. This attribute suggests that they may be better suited for disposal through a toilet system when compared to cover sheets made from refined pulp fibers. The enhanced water interaction implies easier disintegration in water, as shown in
Figure 2, potentially leading to more efficient disposal and reduced environmental impact. At the same time, the cover sheet with only 0.2% AKD will not readily absorb moisture from the toilet cover surface, contributing to lowering the discomfort of toilet users caused by contact with moisture.
3.3. Physical Properties
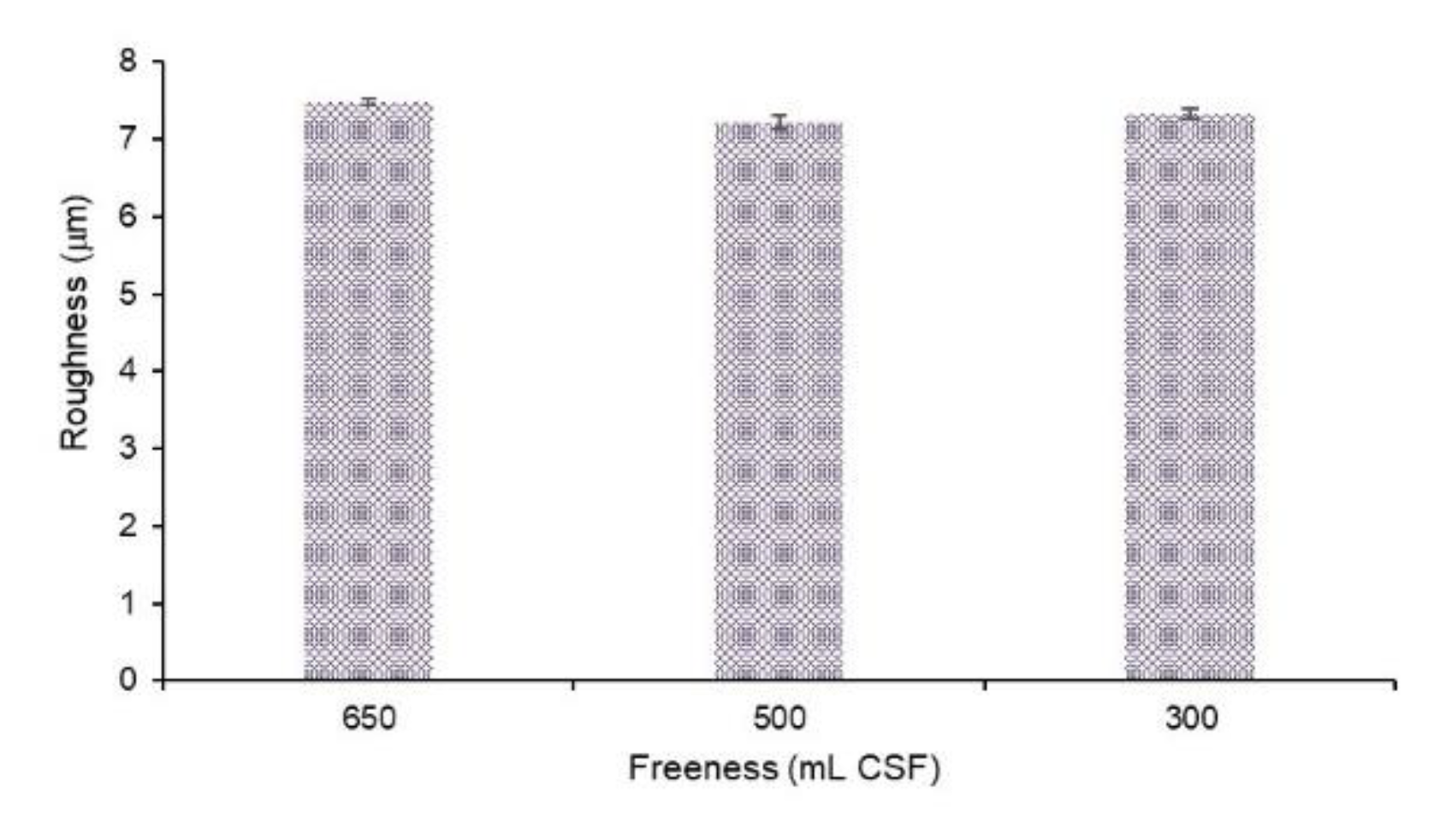
The surface roughness and tensile strength of toilet seat cover sheets containing 0.2% AKD, which exhibited a disintegration rate comparable to toilet paper and water-repellent properties, were compared under different freeness conditions.
Surface roughness is a critical attribute of toilet seat cover sheets that directly affects user comfort. This study investigates the impact of pulp freeness on the surface roughness of toilet seat cover sheets containing 0.2% AKD (alkyl ketene dimer).
Figure 5 illustrates the surface roughness of these sheets prepared under different freeness conditions.
Toilet seat cover sheets were prepared by incorporating 0.2% AKD into pulp stocks with varying levels of freeness. The surface roughness of the sheets was measured to assess the tactile smoothness perceived by users. Freeness, a measure of the drainage rate of a pulp slurry, was adjusted through refining processes, which fibrillate the fibers and potentially alter the surface characteristics of the final product.
The results indicate that refining slightly improved the surface roughness of the toilet seat cover sheets, making them marginally smoother. However, no significant difference in surface roughness was observed based on changes in freeness levels. This suggests that the tactile smoothness of the cover sheets, as perceived by users, remains almost identical regardless of the freeness of the pulp used. The slight improvement in surface roughness with refining can be attributed to the mechanical processing of fibers, which creates a more uniform and less coarse fiber network. Refining causes fibers to undergo compression and shear forces, leading to fibrillation and the creation of finer fiber elements that contribute to a smoother surface. Despite this, the study found that variations in freeness did not significantly impact the surface roughness. The consistent tactile smoothness across different freeness levels suggests that users will have a similar sensory experience with the toilet seat cover sheets, irrespective of the processing variations in pulp freeness. This uniformity in surface roughness is beneficial from a manufacturing perspective, as it allows for flexibility in the refining process without compromising user comfort.
The findings have practical implications for the production of toilet seat cover sheets. Manufacturers can achieve the desired surface smoothness without heavily focusing on adjusting freeness levels. This can streamline the production process, reduce costs associated with extensive refining, and ensure consistent product quality. The slight improvements in surface roughness due to refining are beneficial but not critical, allowing for greater flexibility in manufacturing parameters.
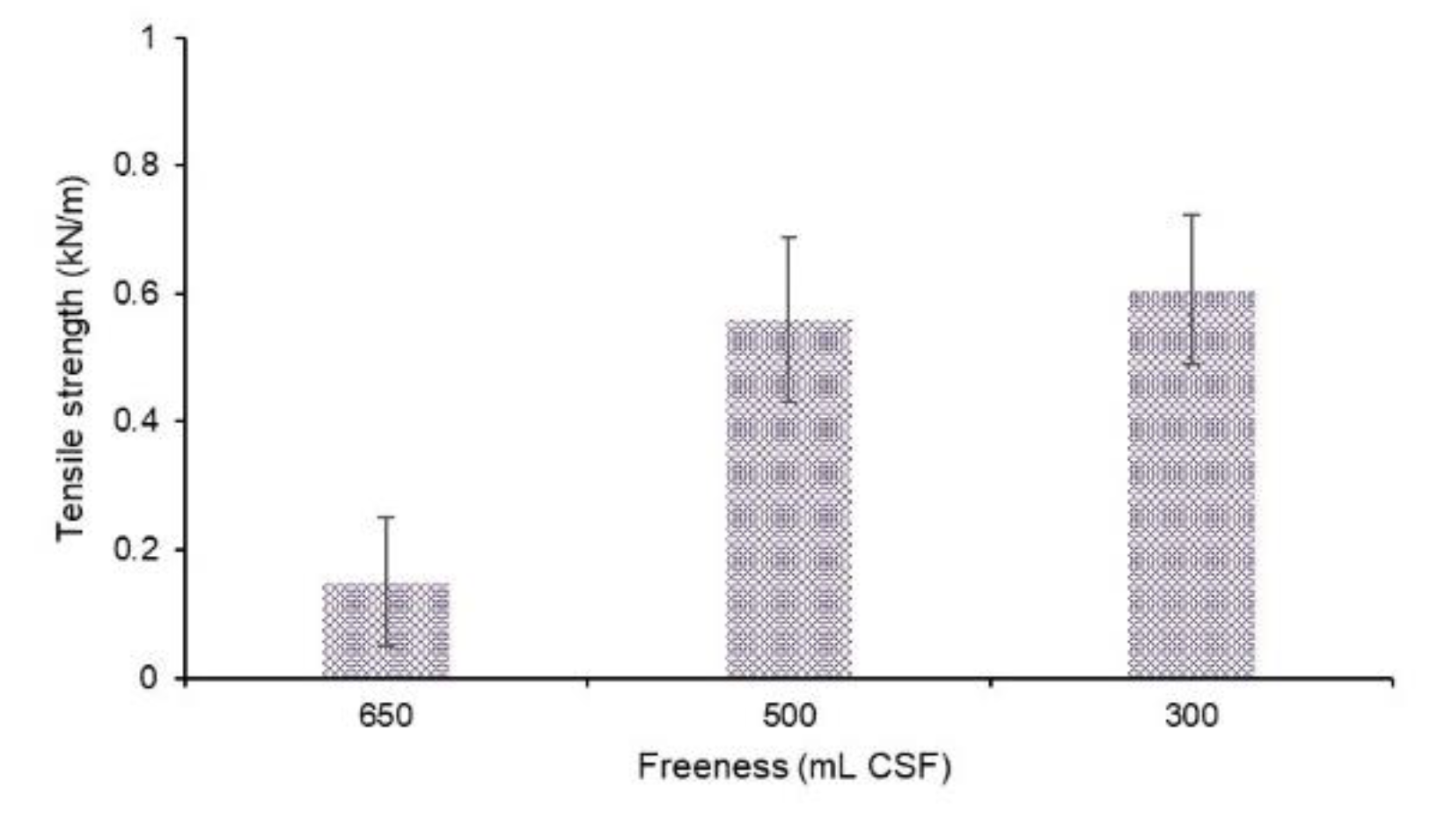
Tensile strength is a key mechanical property that determines the durability and performance of toilet seat cover sheets. This study investigates the impact of pulp freeness on the tensile strength of these sheets [
34,
35]. Toilet seat cover sheets were prepared from pulp stocks with different levels of freeness, which were adjusted through refining processes. Freeness, measured as the drainage rate of a pulp slurry, influences the extent of fiber bonding and network cohesion [
36]. Refining involves mechanical processing that fibrillates the fiber surfaces, increasing their surface area and creating a more entangled and interconnected fiber network. As shown in
Figure 6, the results indicated that cover sheets made from unrefined fibers exhibited fewer contact points and entanglements between neighboring fibers, resulting in weaker bonds and a less cohesive network. Consequently, the tensile strength of these unrefined sheets was similar to that of 2-ply toilet tissue paper with a basis weight of 28 g/m
2, approximately 0.13 kN/m. In contrast, refining significantly enhanced the tensile strength of the cover sheets. The mechanical processing during refining increased the fiber surface area and created a more uniform, entangled, and interconnected fiber network. This enhanced bonding capability resulted in a much stronger and more cohesive fiber network, leading to a meaningful increase in tensile strength.
The study highlights the crucial role of refining in improving the tensile strength of toilet seat cover sheets. Unrefined fibers, with their limited contact points and weak bonding, result in lower tensile strength, comparable to standard 2-ply toilet tissue paper. The lack of sufficient fiber entanglement and bonding leads to a less cohesive fiber network, reducing the mechanical robustness of the cover sheets. Refining significantly alters the fiber morphology by applying compression and shear forces that fibrillate the fibers [
37,
38] . This increases their surface area and creates a more interconnected and entangled network, enhancing the bonding capability between fibers and resulting in a stronger and more cohesive fiber network [
39,
40]. The improved tensile strength of the refined cover sheets demonstrates the effectiveness of refining in enhancing the mechanical properties of the product.
From a practical standpoint, refining is a critical step in the production of high-strength toilet seat cover sheets. Manufacturers can optimize the refining process to achieve the desired tensile strength, ensuring that the cover sheets are durable and capable of withstanding the mechanical stresses encountered during use. The enhanced tensile strength also contributes to user satisfaction by providing a more reliable and robust product.
3.4. Antibacterial Test
The incorporation of antibacterial agents into toilet seat cover sheets can provide significant hygiene benefits, particularly in public or high-traffic restrooms where the risk of bacterial contamination is higher [
41].
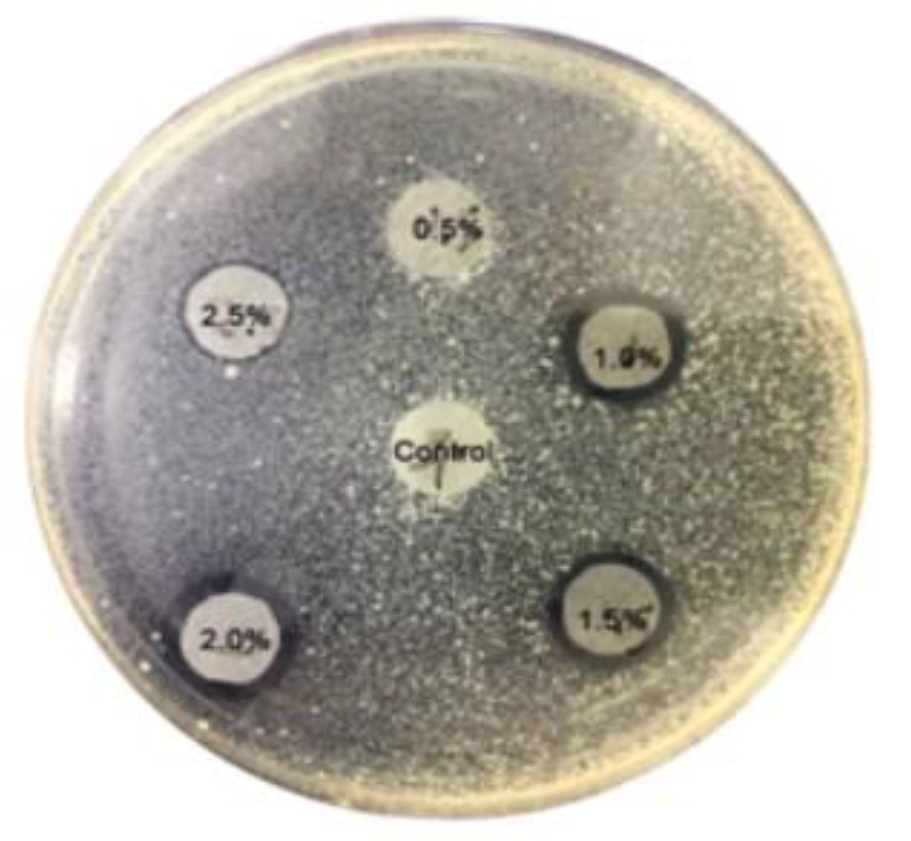
Figure 7 highlights the antibacterial properties of toilet seat cover sheets containing 0.2% AKD (alkyl ketene dimer) and an organic antibacterial agent. This study examines the efficacy of these agents and their potential impact on public health.
A powder-type organic antibacterial agent was chosen to enhance the retention and efficacy of the antibacterial properties within the fiber network. The toilet seat cover sheets were prepared with varying concentrations of the antibacterial agent to determine the minimum effective concentration.
The findings indicate that toilet seat cover sheets made solely from pulp fibers or with antibacterial agents added at concentrations below 1% showed no noticeable antibacterial effect. The antibacterial activity was significant only when the added antibacterial agent constituted at least 1.0% of the total dry weight of the pulp fibers. This threshold concentration is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of the antibacterial properties in practical applications.
The results underscore the importance of the concentration of antibacterial agents in achieving significant antibacterial activity. At concentrations below 1%, the antibacterial agents are insufficient to provide any noticeable effect, likely due to inadequate coverage and interaction with bacteria. However, when the concentration reaches or exceeds 1%, the antibacterial agents are more effectively retained within the fiber network, providing a robust antibacterial effect. The use of powder-type organic antibacterial agents is particularly advantageous for this application. The powder form enhances the retention of the agent within the fiber network, ensuring sustained antibacterial efficacy [
42]. This is essential for maintaining the hygiene benefits of the toilet seat cover sheets over time.
The incorporation of antibacterial agents in toilet seat cover sheets offers additional hygiene benefits in environments with high bacterial contamination risks. Public and high-traffic restrooms, in particular, can benefit from this added layer of protection. The antibacterial properties help reduce the spread of germs, promoting a cleaner environment and providing peace of mind for users with health concerns or heightened awareness of hygiene.
4. Conclusions
Disposable toilet seat covers for public restrooms must be flushable, durable, water resistant, and soft. This study explored optimal stock preparation by varying pulp freeness, adding 0.2% AKD for water resistance, and incorporating a 1% organic antibacterial agent for hygiene, Non-sized cover sheets disintegrate more slowly than toilet tissue paper. Refining enhances interfiber bonding but negatively impacts disintegration. Increased AKD levels improve water resistance but slow down disintegration rates. Adding AKD to unrefined pulp slightly boosts disintegration. A balance between refining and AKD levels is necessary to ensure efficient disintegration while maintaining user comfort. Refining slightly improves the surface roughness of the toilet seat cover sheets, making them marginally smoother. Changes in freeness levels do not significantly impact tactile smoothness. This suggests that manufacturers can achieve the desired smoothness without heavily focusing on freeness adjustments, simplifying the production process while ensuring user comfort. Unrefined fibers result in weaker bonds and a less cohesive network, leading to lower tensile strength. Refining increases fiber surface area and creates a more entangled and interconnected network, significantly enhancing tensile strength. These finding emphasize the importance of refining in producing durable and robust toilet seat cover sheets, ensuring high mechanical agent is necessary to achieve significant antibacterial activity. Lower concentrations or the absence of the antibacterial agent resulted in no noticeable antibacterial effect. The use of antibacterial agents provides additional hygiene benefits, particularly in public or high-traffic restrooms, by reducing the spread of germs and promoting a cleaner environment. The optimal preparation involves a freeness of 650 mL CSF, 0.2% AKD, and 1% antibacterial agent, ensuring flushability, strength, water resistance, and hygiene.
Author Contributions
Research and investigation, C.-H.K., J.-H.P., H.-H.P., T.-K.L., M.-S.P. and J.-S.L.; tables and figures preparation, J.-H.P. and H.-H.P.; data curation, T.-K.L., M.-S.P. and J.-S.L.; writing—review and editing, J.-H.P. and C.-H.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Basic Science Research Program via the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education (Grant No. 2022R1I1A3053045). It was also supported by the Korea Basic Science Institute (National Research Facilities and Equipment Center) grant funded by the Ministry of Education (Grant No. 2022R1A6C101B724).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hadley, T., Hickey, K., Lix, K., Sharma, S., Berretta, T., & Navessin, T. (2023). Flushed but not forgotten: The rising costs and opportunities of disposable wet wipes. BioResources, 18(1), 2271. [CrossRef]
- Rizan, C., Reed, M., & Bhutta, M. F. (2021). Environmental impact of personal protective equipment distributed for use by health and social care services in England in the first six months of the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 114(5), 250-263.
- Roberts, K.P.; Phang, S.C.; Williams, J.B.; Hutchinson, D.J.; Kolstoe, S.E.; Bie, J.; Williams, I.D.; Stringfellow, A.M. Increased personal protective equipment litter as a result of COVID-19 measures. Nature Sustainability 2022, 5, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M. A., Khan, M. Q., Salam, A., & Ahmad, A. (2020). Cotton in nonwoven products. Cotton Science and Processing Technology: Gene, Ginning, Garment and Green Recycling, 305-332.
- Allison, T.; Ward, B.D.; Harbottle, M.; Durance, I. Do flushed biodegradable wet wipes really degrade? Science of the Total Environment 2023, 164912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasağun, H. G., & Bhat, G. S. (2020). Advancement in flushable wipes: Modern technologies and characterization. Journal of Industrial Textiles, 49(6), 722-747.
- Joksimovic, D., Khan, A., & Orr, B. (2020). Inappropriate disposal of ‘flushable’consumer products–reasons for concern. Water Science and Technology, 81(1), 102-108.
- Evey, G.A. Paper toilet seat covers: health necessity or environmental detriment? California State Science Fair Project Summary 2015.
- Research Reports. Disposable Toilet Potty Seat Covers Market Size: Analyzing Trends and Projected Outlook for 2023-2030. 2023.
- Sun, K.S.; Lam, T.P.; Tang, W.S.; Chan, H.Y.; Lam, K.F.; Chow, E.C.Y.; Ho, P.L. Improving public toilet environment and hygiene practices in an Asian city: Voices from Hong Kong residents. Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health 2021, 33, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, M.A.; Nance, D.; McCullers, J.A. Are toilet seats a vector for transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus? American Journal of Infection Control 2009, 37, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Chanchal, M.W. Anti-Odour Finished Disposable Toilet Seat Cover: An Innovative Approach.
- Raipale, N., & Heikkilä, P. (2024). SUSTAFIT–Sustainability Strategies for Nonwovens.
- Abel, O.T.; Ogundana, A.K. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology 2014, 3, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.H.; Yang, F.L.; Wang, W.J.; Chen, B. Preparation and characterization of hydrophilic modification of polypropylene non-woven fabric by dip-coating PVA (polyvinyl alcohol). Separation and Purification Technology 2008, 61, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja Munoz, L., Gonzalez Baez, A., McKinney, D., & Garelick, H. (2018). Characterisation of “flushable” and “non-flushable” commercial wet wipes using microRaman, FTIR spectroscopy and fluorescence microscopy: to flush or not to flush. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 20268-20279.
- ISO 12625-17. Tissue paper and tissue products - Part 17: Determination of disintegration in water.
- Park, N.; Lee, J.; Yoo, S.; Woo, K.; Kim, H. Evaluation of water release characteristics of domestically distributed tissue products. Pulp and Paper Technology 2021, 53, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Penn, R., Schuetze, M., Jens, A., & Friedler, E. (2018). Tracking and simulation of gross solids transport in sewers. Urban Water Journal, 15(6), 584-591.
- Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, G.-C.; Kim, V.; Sheikh, M.I.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Sim, S.-W.; Cho, H.-S. Automated test method of sizing degree by analysis of liquid penetration and its surface behavior. Journal of Korea TAPPI 2012, 44, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, C.-H.; Lee, J.; Nam, H.-G.; Lee, G.-S.; Jo, H.-S.; Park, H.-H. Evaluation of reliability of the automatic system for measuring sizing degree by basis weight variation of paper. Journal of Korea TAPPI 2014, 46, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Kim, C.-H.; Moon, S.-O. Automatic Stöckigt sizing test using an automatic recognition principle of color expression. Appita Journal 2006, 59, 396–400. [Google Scholar]
- De Assis, T., Reisinger, L. W., Pal, L., Pawlak, J., Jameel, H., & Gonzalez, R. W. (2018). Understanding the effect of machine technology and cellulosic fibers on tissue properties–A review. BioResources, 13(2), 4593-4629.
- Korpela, A.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Asikainen, J. Effects of hydrophobic sizing on paper dry and wet-strength properties: A comparative study between AKD sizing of NBSK handsheets and rosin sizing of CTMP handsheets. BioResources 2021, 16, 5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H., Okayama, T., Arai, R., & Ohtani, H. (2011). Relationship between wettability and sizing degree of paper containing bulking agent. Journal of wood science, 57, 34-39.
- Taniguchi, R., Isogai, A., Onabe, F., & Usuda, M. (1993). Sizing mechanism of alkylketene dimers: Part 3. Appearance of sizing features of AKD-sized sheets. Nordic Pulp & Paper Research Journal, 8(4), 352-357a.
- Lee, J. Y., Kim, C. H., Kwon, S., Lee, M. S., & Min, B. G. (2016). Representative effects of Valley beater and disk refiner on pulp fibers. Journal of Korea TAPPI, 48(5), 37-44.
- Gharehkhani, S.; Sadeghinezhad, E.; Kazi, S.N.; Yarmand, H.; Badarudin, A.; Safaei, M.R.; Zubir, M.N.M. Basic effects of pulp refining on fiber properties—A review. Carbohydrate Polymers 2015, 115, 785–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochaeni, H., Irawan, C., Nurfitri, M., Lestari, P. S., & Rosdianan, U. (2018, December). The Influence and The Analysis Of Alkyl Ketene Dimers (AKD) to Paper Resistance in Water Absorption and Chemical Solution Penetration. In International Conference on Science and Technology (ICST 2018) (pp. 298-300). Atlantis Press.
- Kumar, Y. S., Mahavir, S., Santosh, G., Rami Reddy, S., Sarvjeet, S., Reddy, K. P., & Rajinder, S. (2007). An Experience of Alkaline Sizing with AKD. IPPTA, 19(4), 85.
- Atasağun, H. G., & Bhat, G. S. (2020). Assessing the structural, mechanical and dispersible characteristics of flushable nonwovens. Textile research journal, 90(5-6), 581-592.
- Zhang, Y., Xu, Y., Zhao, Y., Huang, C., & Jin, X. (2019). Effects of short-cut fiber type and water-jet pressure sum on wet strength and dispersibility of wood pulp-based wetlaid/spunlace wipes. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, 77, 33-43.
- Seppänen, R., Tiberg, F., & Valignat, M. P. (2000). Mechanism of internal sizing by alkyl ketene dimers (AKD): The role of the spreading monolayer precursor and autophobicity. Nordic Pulp & Paper Research Journal, 15(5), 452-458.
- Joutsimo, O., Wathén, R., & Tamminen, T. (2005). Effects of fiber deformations on pulp sheet properties and fiber strength. Paperi ja puu, 87(6), 392.
- Wathén, R. (2006). Studies on fiber strength and its effect on paper properties.
- Borodulina, S., Motamedian, H. R., & Kulachenko, A. (2018). Effect of fiber and bond strength variations on the tensile stiffness and strength of fiber networks. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 154, 19-32.
- Min, B. G., Lee, J. Y., Kim, C. H., Park, S. H., Lee, M. S., Gu, H. G., & Lee, C. Y. (2020). New technology for developing a lightweight refiner plate for hardwood kraft pulp fibers. BioResources, 15(4), 9128.
- Ryu, J. H., Kim, C. H., Lee, J. Y., Lee, J. S., Lee, C. H., & Park, J. H. (2022). Study of refining effect of mixed pulps using refiner plates with different bar patterns. Applied Sciences, 12(22), 11445.
- Park, H. H., Kim, C. H., Lee, J. S., & Lee, C. H. (2023). Effects of Refiner Plates with Different Fillings on TMP Properties. Applied Sciences, 13(8), 5091.
- Gu, H. G., Min, B. G., Lee, J. Y., Park, S. H., Lee, M. S., Lee, C. Y., & Kim, C. H. (2021). Mechanical modification of softwood pulp fibers using a novel lightweight vertical bar plate.
- Pasquale, T. R., & Tan, J. S. (2005). Nonantimicrobial effects of antibacterial agents. Clinical infectious diseases, 40(1), 127-135.
- Ahmad, H. (2021). Celluloses as support materials for antibacterial agents: a review. Cellulose, 28(5), 2715-2761.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).