1. Introduction
Sinkholes and land subsidence are dangerous natural (or human-induced) hazards resulting in fatalities and property loss, often affecting transportation and other infrastructure networks in regions under soluble bedrock. In recent decades, an increase in sinkhole-related damage has been reported globally, and this has been attributed to human activities that initiate mobilising agents or to the development of sinkhole-prone terrain [
1,
2,
3].
In urban environments, sinkholes and subsidence pose a significant risk to the affected communities and infrastructure [
2,
4,
5,
6,
7]. Examination of recent instances is drawn from various countries and locations, including the USA, Florida [
8] and Virginia [
9]; Italy [
10,
11,
12]; Turkey [
13]; China [
14]; Saudi Arabia [
15]; the Dead Sea [
16], and South Africa [
17,
18,
19].
These incidents frequently manifest suddenly with minimal or no advance notice and can cause devastating impacts without readily detectable forewarnings. The primary financial burden is linked to the remediation, mitigation, and closure of the revealed cavity, followed by the secondary costs of repairing the impacted infrastructure or property. Sinkhole-related losses can be classified as either direct or indirect. Direct losses relate to fatalities and damage to property and infrastructure (for example, damage to service lines, roads and pipelines, and differential settlements in building support foundations). In contrast, indirect losses extend on a larger scale and can impact entire communities or businesses, reaching beyond the immediate vicinity. This includes disturbances to business operations, transportation, and communication networks. The associated costs encompass assistance, temporary storage, and accommodation for individuals displaced by the event. Additionally, intangible losses are challenging to quantify monetarily, such as disruptions in daily commuting, mental health impacts, and, ultimately, the expenses tied to relocating the population from high-risk areas [
12].
Between 2000 and 2015 in the USA, the average cost of sinkhole-associated damage was estimated at least US
$300 million per year, with the total probably much higher [
20]. Located on expansive gypsum formations, the Spanish cities of Oviedo (1998) and Calatayud (2003) experienced significant economic setbacks due to individual collapse incidents, amounting to 18 million and 4.8 million euros, respectively [
21]. Furthermore, around 30,000 households were moved to a more secure location on dolomite terrain west of Johannesburg, incurring a substantial expense exceeding US
$600 million [
1].
Sinkholes can be classified into three main categories based on the processes leading to their formation [
4]: collapse sinkholes, characterised by the brittle gravitational deformation of cover, bedrock, or caprock material; sagging sinkholes, where ductile sediments sag due to the differential lowering of the cover deposit, bedrock, or caprock; and suffusion sinkholes, involving the migration of cover deposits downward through dissolution conduits accompanied by ductile settling. In practical terms, many sinkholes emerge due to a combination of these processes: solution sinkholes, collapse sinkholes, caprock sinkholes, dropout sinkholes, suffusion sinkholes, and buried sinkholes [
4].
The mechanism behind the formation of sinkholes involves the ongoing dissolution of subsurface soluble rocks, gradually giving rise to voids. As the soil above these voids reaches a critical state, marked by the surpassing of shear strength by soil material, it undergoes collapse due to diminished vertical soil stress. Primary contributors to underground voids' formation include water infiltration, groundwater table reduction, or extensive pumping resulting in dewatering [
12,
17].
Drawing insights from South African dolomites, Jennings et al. [
30] elucidated the geotechnical failure mechanism of sinkholes, attributing it to the collapse of an arch or dome spanning an air-filled void. The collapse is characterised by an "onionskin" peeling of the intrados, causing the material to fall into the void, subsequently moving the void toward the ground surface. The culmination of this process results in the manifestation of a sinkhole. Jennings outlines five requirements for sinkhole formation:
Sturdy material supports the soil covering the dome, functioning as essential support for the void's roof. The span should fall within limits conducive to arch formation.
The development of an arching mechanism within the residuum material.
The formation of a void beneath the arch in the residuum.
The requirement for a reservoir below the arch to accumulate the material resulting from the arch's collapse.
The initiation of a disruptive factor occurs when a void of adequate size forms in the residuum, leading to the collapse of the arch's roof. Typically, the triggering factor is water infiltration, causing a weakening of the arching soils.
Water infiltration into the soil serves as a trigger, increasing the load of soil material deposited in the vadose zone. Consequently, this has the potential to diminish the geomechanical strength of the soil and facilitate internal erosion and dissolution processes [
21].
The present study investigates the propagation of a sinkhole caused by a leaking pipe in dense sand. It analyses the significance and methods used in sinkhole monitoring, introduces optical fibre sensing with FBGs, describes the experimental setup and data collection approach, presents and discusses the findings, and concludes on the effectiveness and potential applications of FBG sensors in geotechnical monitoring and mitigation.
2. Sinkhole Monitoring Methods and Previous Investigations
2.1. Methods of Sinkhole Monitoring
The techniques and technologies commonly employed for monitoring sinkhole deformations have undergone extensive testing and application in other geohazard monitoring domains. However, when dealing with cavity propagation, there are inherent challenges compared to landslide hazards [
12]. One challenge is the sudden manifestation of the phenomenon without any warning, particularly in the case of sinkhole caprock collapse [
4]. According to Intrieri et al. [
12], measurable plastic deformation may occur days before the failure, ranging from a few millimetres to a few centimetres. Observations from numerical simulations and physical model experiments by [
16,
25,
27,
28] suggest that while surface subsidence accelerates during the precursory period, the width of the subsiding area remains unchanged. This indicates that the upward propagation and breakthrough of the cavity do not necessarily occur during the precursory period.
Over the past few decades, various detection and monitoring methods have been extensively employed to investigate sinkholes and subsidence. These approaches include GPS and geophysical techniques such as electrical resistivity tomography (ERT), ground-penetrating radar (GPR), cross-hole electrical resistivity tomography (CHERT), and seismic refraction (SR) [
6,
31,
32,
33,
34]. Another widely used method is the Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR), which utilises satellite radar images to create interferograms that are analysed to detect changes in the earth's surface. Recently, optical fibre sensing technology has been proposed for detecting and monitoring sinkhole formation [
3,
27,
28,
29,
35].
In many sinkhole locations, gradual land subsidence persists for weeks to years following the collapse. Therefore, a quantitative assessment of subsidence rates and their spatial and temporal extents provides valuable insights into subsurface sinkhole formation processes. It enables the evaluation of activity levels at specific sites and distinguishes between active and inactive areas.
2.2. Previous Investigation of Sinkhole
The available literature shows that various researchers have investigated soil behaviour and sinkhole formation through analytical, physical, and numerical modelling. Terzaghi [
22] investigated stress distribution in the sand over a yielding trap door, finding stress transfer away from the trap door under pressure. Costa et al. [
23] examined failure mechanisms in granular soil simulating deep and shallow conditions over a deep trap door. Among their findings was that the relative density influences the surficial settlement of the soil. Alrowaimi et al. [
24]used physical models to show a groundwater cone of depression to indicate imminent sinkhole collapse. Jacobsz [
25] found that the zone of influence of a trap door matches its width, indicating sinkhole diameters are like the arch width. Al-Naddaf et al. [
26] demonstrated that geosynthetics stabilise soil arching and increase load capacity under surface loading. Labuschagne et al. [
27] and Ferentinou [
28] used fibre Bragg grating sensors to monitor sinkhole propagation, with findings highlighting these sensors' sensitivity to sand relative density's effect on failure patterns. Möller et al. [
29] showed that distributed fibre optic sensing could allow for sinkhole prediction formation, suggesting its potential for early warning systems in critical infrastructure.
The literature on sinkhole monitoring has garnered increasing interest due to the growing need to understand the mechanisms of incipient collapse and monitor ground displacement rates for effective risk management. Reliable spatial and temporal hazard mapping, supported by monitoring programs, can enhance sinkhole risk management by adopting sinkhole protocols, land zoning, remedial measure design, and performance assessment of these solutions. Analysing research trends highlights the need for future studies to advance sensor technologies, enhance understanding of sinkhole and soil behaviour, integrate physical models, examine environmental impacts, and apply these findings to critical infrastructure to improve early detection and mitigation of sinkhole risks.
3. Introduction to the Optical Fibre Sensing Using Fibre Bragg Gratings (FBGs)
Optical fibre sensing (OFS) technology employs optical fibres as sensors to measure diverse physical quantities like strain, temperature, pressure, and vibration. Optical fibre sensors present several advantages compared to conventional sensing technologies, including high sensitivity, immunity to electromagnetic interference, and the capacity to cover extensive distances without signal degradation. OFS utilises dielectric devices that confine and guide light [
36]. The optical fibre comprises a glass core surrounded by a glass cladding with a refractive index lower than the core, facilitating the propagation of light waves within the core. The buffer coating safeguards the glass fibre, and, at times, an outer jacket provides mechanical protection to the fibre.
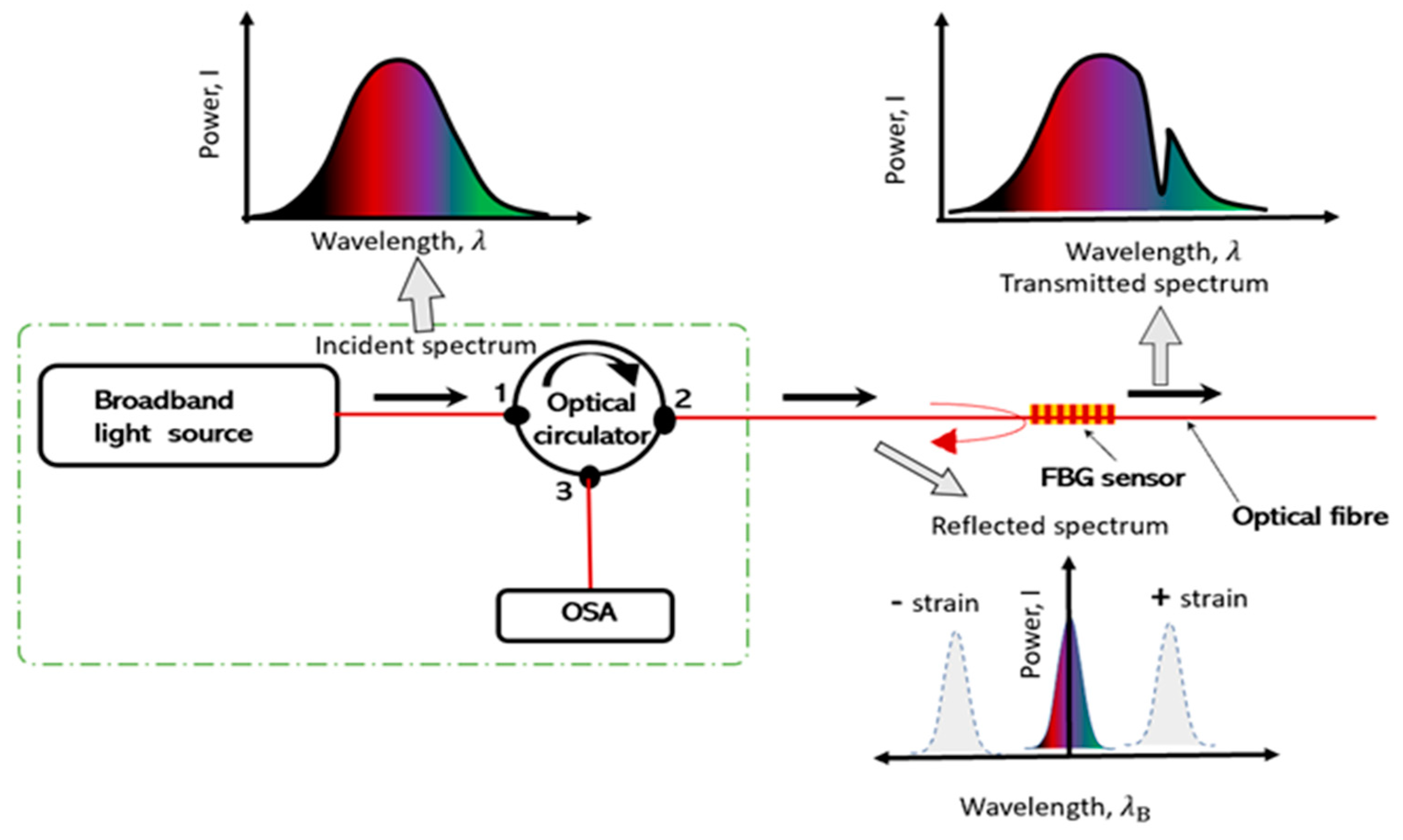
Fibre Bragg gratings (FBGs) represent a category of optical fibre sensors widely applied in geotechnical and structural monitoring applications. FBGs consist of an optical fibre section with a periodically changing refractive index. These periodic variations result in a wavelength-specific reflection of incident light known as the Bragg wavelength.
Figure 1 illustrates a single-mode fibre with a printed FBG sensor.
An FBG sensor monitoring system can determine strain or temperature change based on the wavelength change of the reflected light signal at the grating position [
37,
38]. The reflected Bragg wavelength is shown in equation (1):
In the given expression, where λ
B represents the Bragg wavelength,
denotes the effective refractive index of the optical fibre core, and Λ represents the grating period. When strain is applied to the sensor, causing a change in the grating period (Λ), there is a corresponding shift in the reflected Bragg wavelength, as indicated in equation (1). The fundamental detection principle of the FBG sensor is expressed by equation (2):
In the given expression, ∆λ
B is the change in the reflected wavelength, λ
B denotes the initial Bragg wavelength, p
e stands for the photoelastic coefficient, ε represents the strain,
is the thermal coefficient,
is the thermal modulation of the core refractive index, and
is the temperature change [
38].
If we replace
by
and
by
, equation (2) can be written in a simplified form as equation (3):
The coefficients related to strain and temperature and can be found by calibration.
When the FBG sensor is stretched or compressed, the reflected Bragg wavelength of the FBG varies. It is, nevertheless, also sensitive to changes in temperature. As a result, strain and temperature fluctuations affect the FBG.
Figure 2 illustrates the pathway of an incident spectrum from the broadband source as it travels through the optical fibre with an FBG sensor, and the reflected spectrum subsequently being [
37].
4. Materials and Methods
Physical modelling in geotechnical engineering is a physical representation of a field prototype in an investigation. A scaling law maintains the similarity between the field prototype and the physical laboratory model. The parameters for 1-g proposed by Park and Kim [
39] were utilised to scale down the model. This model was built from Perspex material with 500 x 350 x 80 mm inner dimensions. The model represents a field prototype of 15 x 8.1 x 2.4 m. A scaling factor (N) of 30 was used to model the characteristic parameters of the field prototype, as applied by Labuschagne et al. [
27] and Ferentinou [
28] and shown in
Table 1.
Fine silica sand (Cullinan sand) was used in this experiment and was obtained from the Cullinan mine, a commercial source near Pretoria in Gauteng province, South Africa. The properties of Cullinan sand are described in
Table 2. The soil was mixed with 10% water, placed in layers, and compacted to a thickness of 30 mm, achieving a density of 1548.8 kg/m³ and a relative density of 60.7%, which classifies it as dense.
The phase mask technique was used to print the FBG sensors for this study in the University of Johannesburg Photonics Laboratory. The fourth harmonic (266 nm) of a Nd: YAG laser was used to print the gratings in the wavelength range of 1550 nm to 1560 nm. The FBGs were calibrated to determine the strain and temperature coefficients (β and ξ) as stated in equation (3). The coefficients β and ξ of the FBG sensors were found to be 7.06 x 10-7 and 7.14 x 10-6 /⁰C.
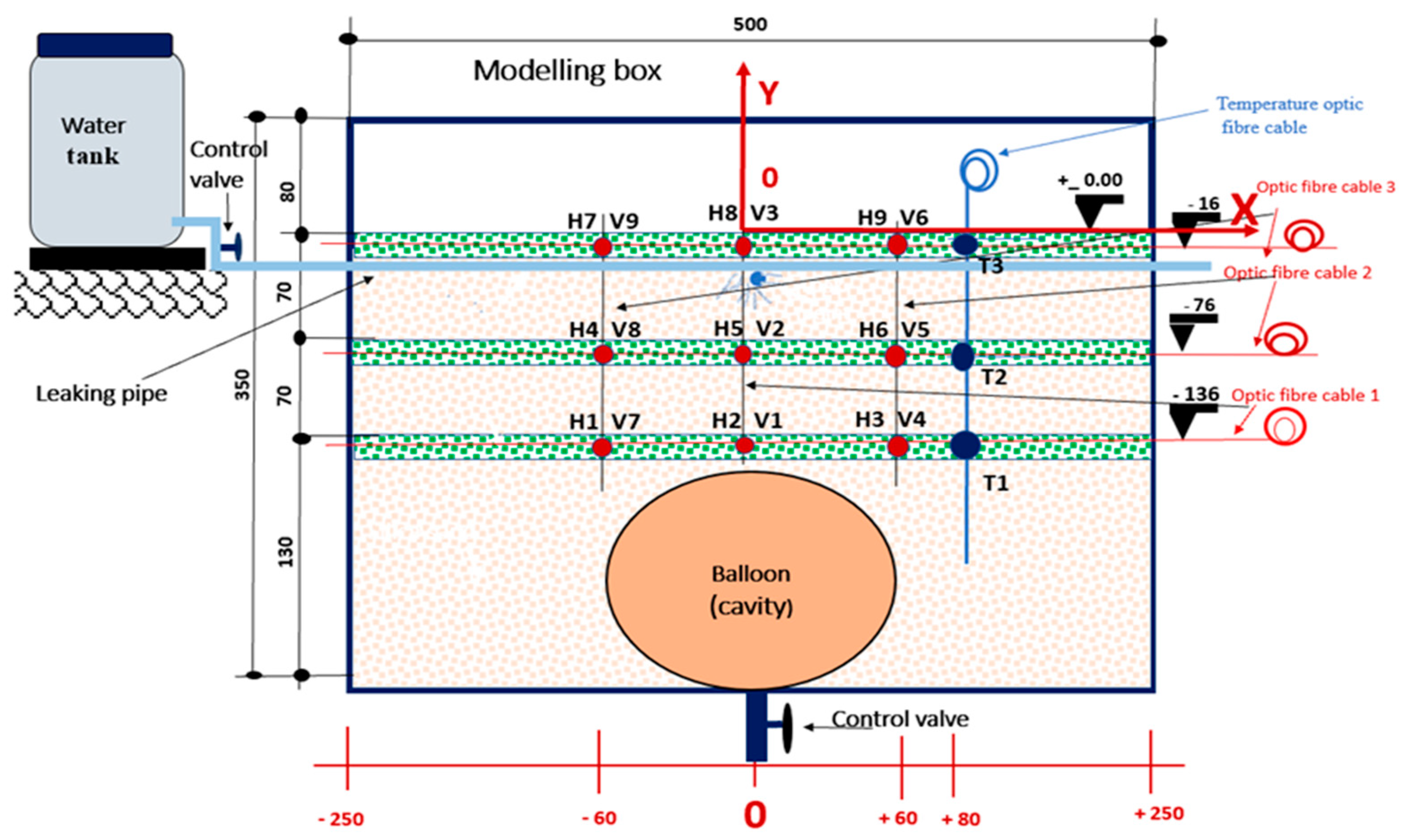
FBGs were printed on seven (7) different optical fibre cables. Each optical fibre had three printed sensors with a 60 mm interval between the sensors, corresponding to a 1.8 m interval in the field prototype. One fibre was used to measure temperature to allow for temperature compensation. Three fibres were placed in horizontal positions, and three were placed in vertical positions above the cavity to measure strain.
The optical fibre temperature was encased in an aluminium tube to isolate temperature sensors from strain or vibration disturbances during the experiment. This setup also allowed for temperature compensation in determining strain values measured by strain sensors, as shown in
Figure 3a.
Figure 3b illustrates a cross-section of the vertical support structure to which the optical fibre cables were attached and maintained vertically. The cables were fixed at both ends to the support structure using superglue, and their bodies were coated with silicone and rolled in sand to create an adhesive surface, ensuring strong adherence to the sand.
The container (experimental box) was constructed from Perspex material (
Figure 3c), enabling the complete burial of the optical fibre sensors in the soil. This design ensured efficient soil deformation detection without compromising measurement accuracy due to structural influence.
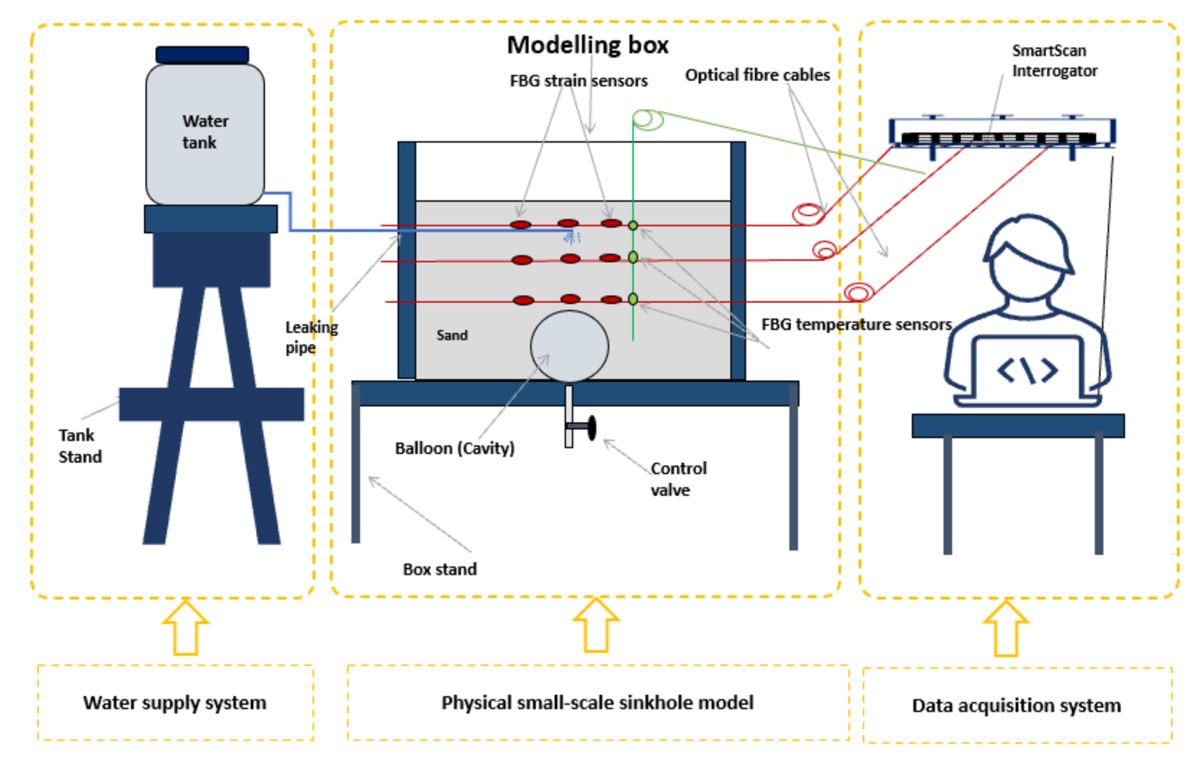
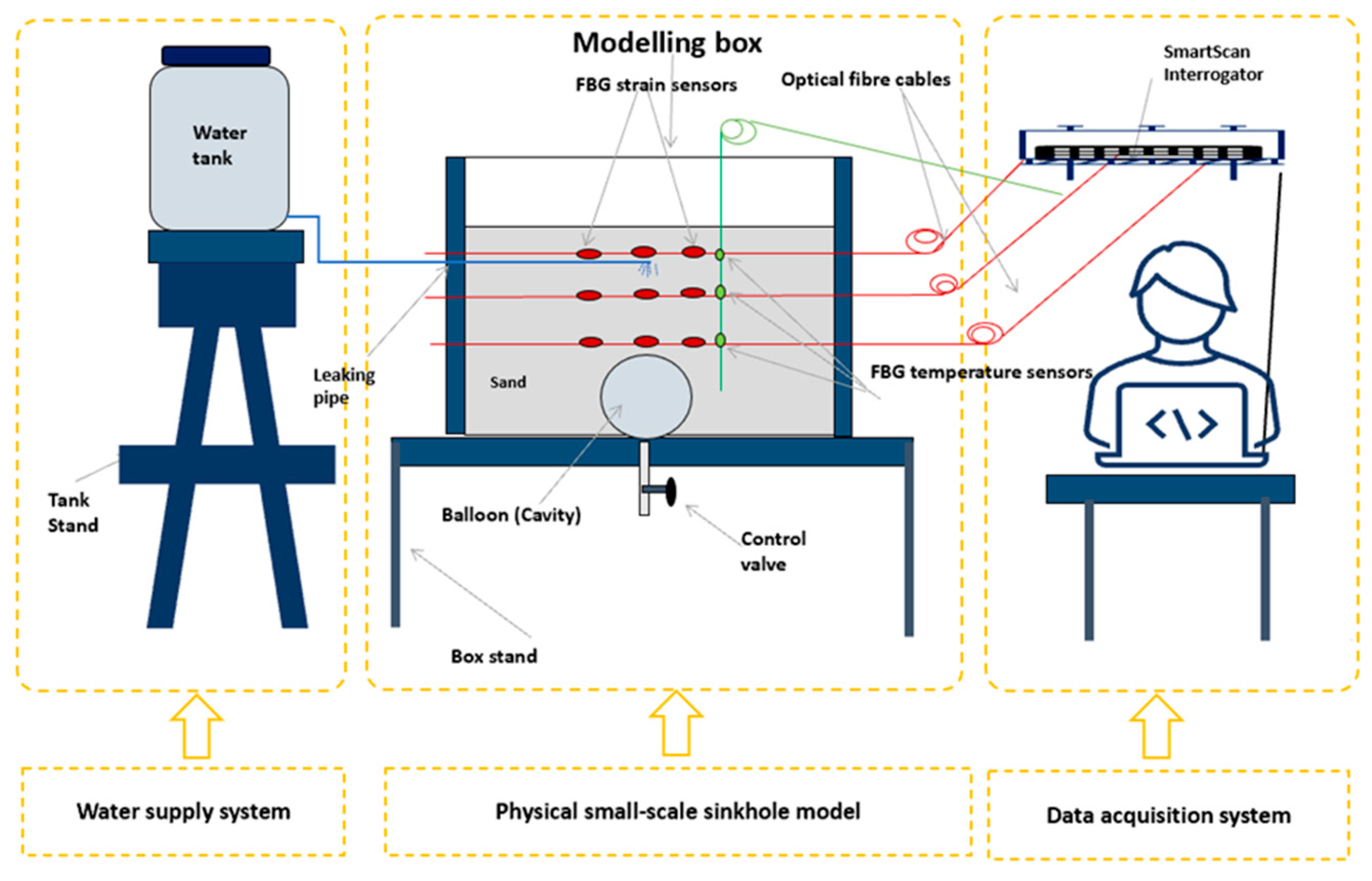
The experimental setup consisted of three main parts: the water supply system, the container, the data acquisition system, and the instrumentation, as illustrated in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5. The water tank served as a source for the water. A control valve was mounted at the bottom of the tank to regulate the flow rate. The fibre optic sensors were placed at specific locations in the model to monitor deformation, as shown in
Figure 4. In the vertical direction, optical fibre sensors were placed 16 mm below the surface in the model, corresponding to a depth of 0.5 m in the field prototype; the second set of optical fibre sensors was placed at a depth of 76 mm, corresponding to a depth of 2.3 m in the field prototype; and finally, the third set of optical fibre sensors was placed at a depth of 136 mm, corresponding to a depth of 4.1 m in the field prototype. The balloon was positioned at a depth of 150 mm, equivalent to 4.5 m in the field, with a diameter of 120 mm, corresponding to 3.6 m.
A water-filled balloon was used to create a cavity at the bottom of the model. The balloon was inflated to a volume of 550 ml with a horizontal diameter of 115 mm. The balloon's volume and diameter defined the dimensional characteristics of the cavity formed in the soil mass after compaction, corresponding to the void of a volume of 14.85 m
3 and a diameter of 3.45 m in the field. A sinkhole that can form with this diameter of two to five metres can be classified as medium size [
40].
A leaky pipe was placed 30 mm below the soil's surface according to the South African specifications of trench requirements for flexible pipes [
41]. The cavity formation period was the period it took to deflate the balloon at a flow rate of 55 ml/m. After the cavity was formed, water was leaked into the model through the buried leaky pipe at a flow rate of 40 ml per minute, calibrated for inducing the collapse of the cavity arch in a control condition and allowing the proper collection and analysis of the data during this period, while the FBGs were interrogated with a SmartScan interrogator.
5. Results
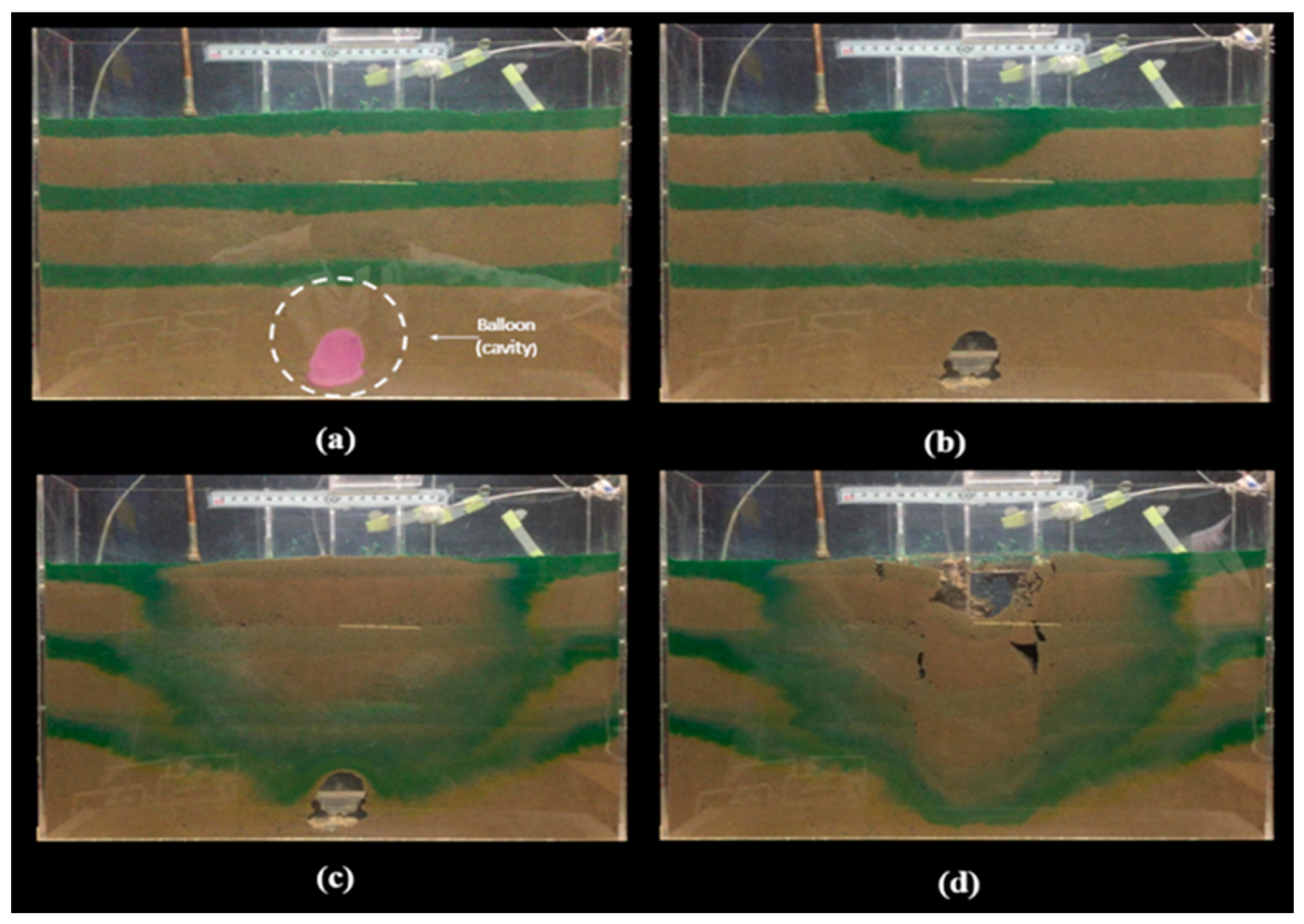
Figure 6 depicts the progression of a sinkhole, starting from cavity formation, followed by the weathering and erosion of the soil mass, and culminating in the collapse of the cavity and its upward propagation. The dyed soil layer indicates water infiltration from a leaking pipe, which triggers the cavity's collapse. In
Figure 6a, a balloon is inflated with water to create a cavity in the soil mass.
Figure 6b shows the balloon's deflation and the cavity's formation. In
Figure 6c, water leaks into the soil mass, causing the cavity to collapse and form a sinkhole. Finally, figure 6d shows the sinkhole's development and upward propagation to the ground surface.
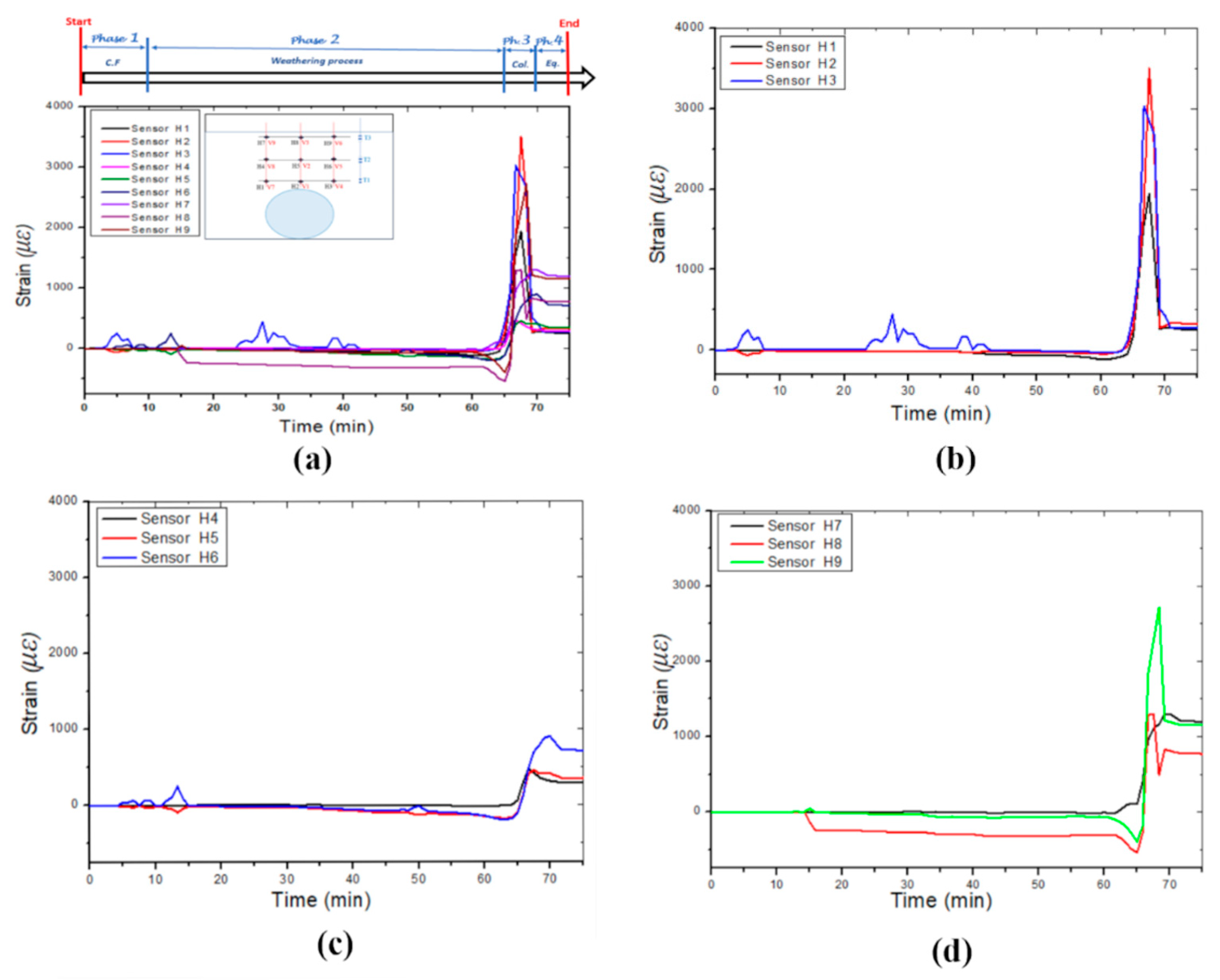
Figure 7a illustrates the horizontal strain signatures measured by the horizontally positioned FBG sensors and highlights the boundaries of the four identified phases. The overall trend of the strain signatures in this model indicates that the FBG sensors experienced tensile deformation during the collapse period. FBGs H1, H2, and H3, placed above and closer to the cavity, recorded the highest strains due to their proximity (
Figure 7b). FBG H2 measured the maximum strain of approximately 3.5 x 10³ με. FBGs H4, H5, and H6 recorded lower strain values (
Figure 7c). During the weathering period, FBGs H5, H6, H8, and H9 displayed strain variations before the collapse, likely due to the leak orientation affecting the right-hand side of the model more than the left.
Figure 8 illustrates the strain variation observed in the four identified phases of the failure collapse process.
Figure 8a shows the strain variation during cavity formation, i.e. while the balloon deflates.
Figure 8b displays the strain variation while water was leaked into the soil mass (during the weathering and erosion process); most of the FBGs were in a small compression state before the failure occurred. The strain variation measured during the collapse of the cavity is displayed in
Figure 8c, and the post-collapse phase is represented in
Figure 8d, where the variation of the strain is relatively constant.
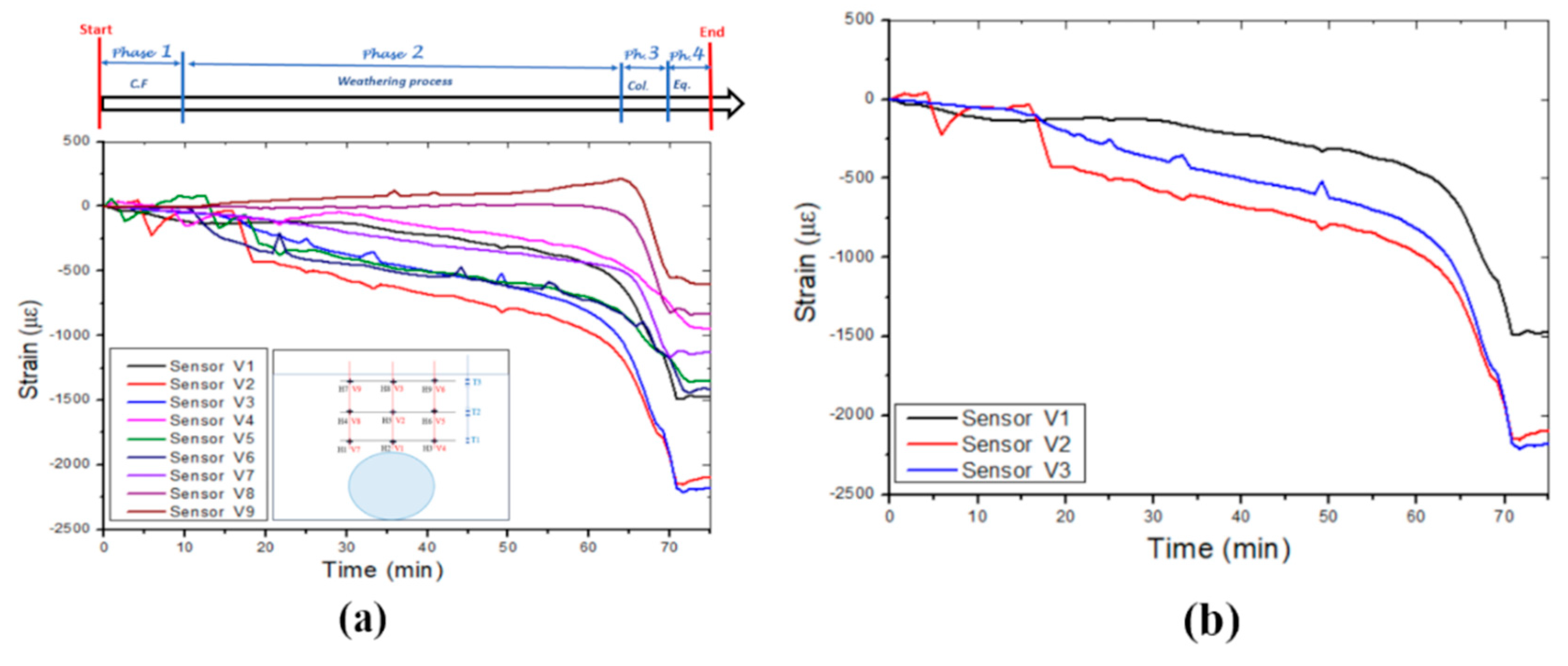
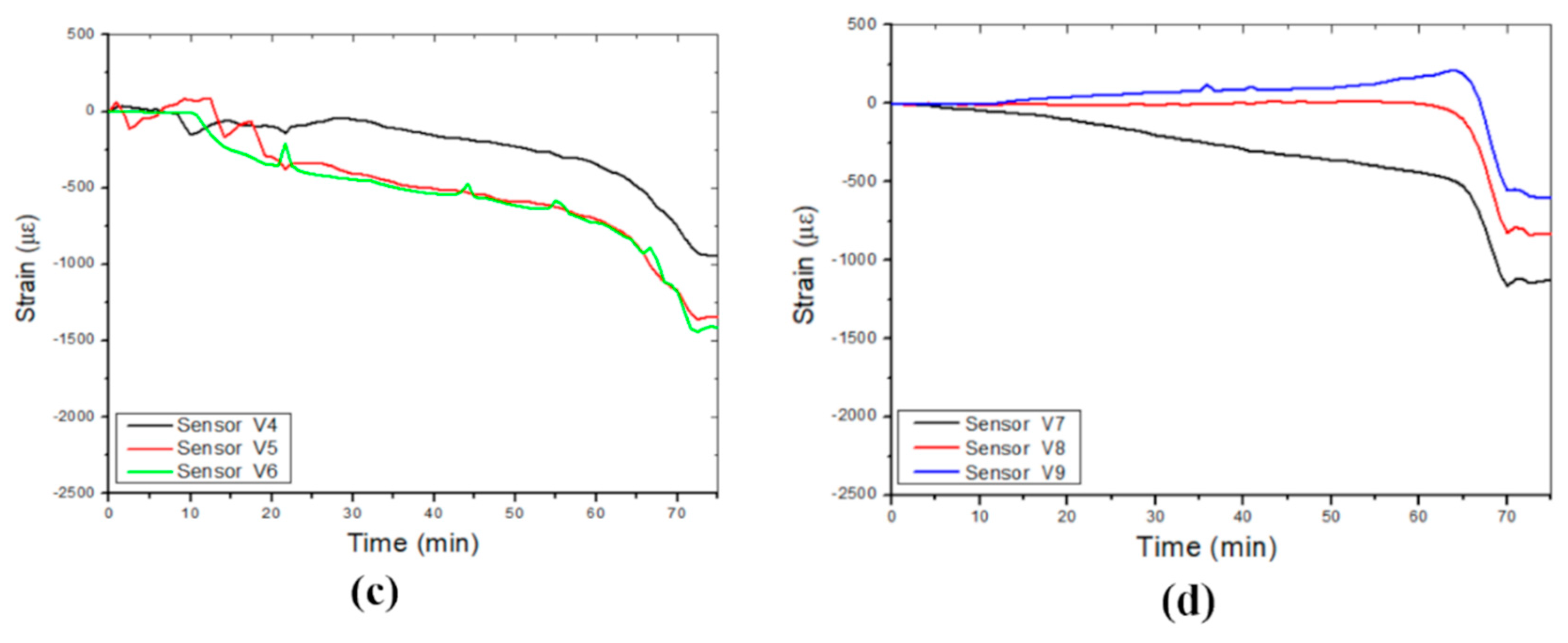
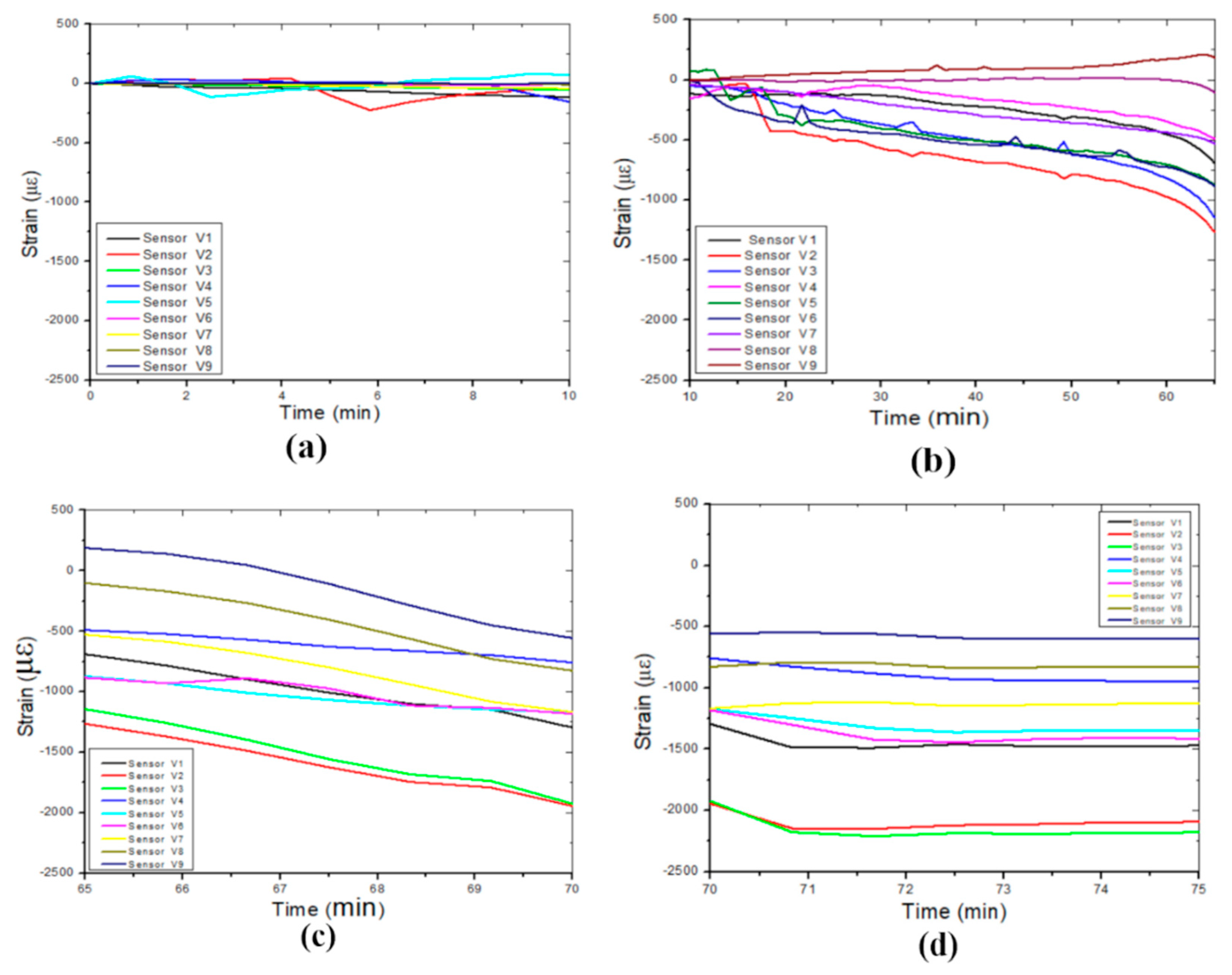
Figure 9a displays the strain variations measured by all vertically positioned FBG sensors and the boundaries of the four identified phases. The strain level is lower than those measured by the horizontally positioned sensors except for FBGs V2 and V3. FBGs V2 and V3 measured the highest strain variation (maximum strain, approximately 2.25 x 103 με) on cable one (1) owing to its location in the central axis above the cavity, as shown in
Figure 9b. The strain variation on the right side of the cavity is presented
Figure 9c, and FBG V6, located in the middle, measured the maximum strain value, approximately 1.5 x 103 με. However, the strain variation on the left side of the cavity is represented in
Figure 9d, where V7 measured a maximum strain of approximately 1.15 x 103 με at the cavity roof. Moreover, the cable on the left side of the cavity detected lower strain values. The vertical strain variation due to the leaking water that induced the collapse of the cavity is also shown in
Figure 9d.
Figure 10 shows the strain variation during the four identified phases of the failure process.
Figure 10a shows the strain variation during the cavity formation (while the balloon was deflating), and
Figure 10b displays the strain variation while water leaked into the soil mass (during the weathering and erosion process). During this period, the FBGs experienced a gradual compressive deformation until failure occurrence. The strain variation measured during the cavity collapse is displayed in
Figure 10c, and the post-collapse phase is illustrated in
Figure 10d, where the strain variation is relatively constant.
6. Discussion
The reduced-scale physical model developed to investigate the sinkhole propagation in partially saturated dense sand corresponds closely to the reality of the field prototype since, in most cases, the subsoil is in a wet or partially saturated state. Five conditions must be met for a sinkhole to form, as described by Jennings et al. [
30]. These conditions were considered during the experimental design process.
The results reveal that the formation and the upward propagation of the sinkhole pass through four phases: underground cavity formation, a weathering process accompanied by an erosion process, a collapsing process, and an equilibrium process. The period to deflate the balloon (10 minutes) determined the underground cavity formation period. The cavity was formed according to the volume/diameter of the inflated balloon. The FBGs detected the movement of the induced internal deformation of the soil mass when the arch formed. Usually, a trigger weakens the arch until it collapses [
42].
Weathering is the deterioration of rock by chemical, physical, or biological processes [
43]. In this experiment, this period was characterised by the erosion time (55 minutes) just after the cavity formed. The water leaked into the soil mass during the period when water was leaked from the pipe. This overburden-soil sank into the cavity, changing the bonding strength between soil grains and decreasing the mass of the soil at the surface [
42]. This process continued upward in the shape of an arch until the soil remaining in the arch eventually collapsed and sank into the cavity [
42]. The flow rate was 40 ml/min, equivalent to approximately 7.27% of the original cavity volume per minute. The leaking pipe leaked water into the soil for 55 minutes. The total amount of water that induced collapse was 2200 ml, compared to the original cavity volume of 550 ml, representing a ratio of 1:4.
Both horizontally and vertically positioned FBG sensors experienced compressive deformation during the leaking period, particularly the vertically positioned sensors. During the collapse period, the strains measured by the FBGs increased significantly to a maximum value. Vertical sensors experienced compressive deformation, while horizontal sensors experienced tension deformation during the collapse of the cavity.
The finding revealed that the internal deformation mechanism's distribution was not symmetrical, implying that the strain distribution is not similar on both sides (the left and right sides of the cavity). This could be due to the orientation of the leak point in the soil mass, the infiltration of the water, and the compaction mode, as this was affected by the arrangement of the sensors and their different support devices in the model.
In the last phase, identified as the equilibrium process, the graphs showed no strain variations for all the sensors. The soil reached a balanced state.
However, horizontal installation of optical fibre cables at significant depths in urban environments can pose considerable challenges. Conversely, vertical installations can offer advantages by simply requiring a small borehole for inserting the sensing cable attached to its anchor or vertical support system (smart anchoring system). For future research in this field, we can recommend the following:
Addressing noise issues in interrogator resolution is crucial to avoid false alarms in the sensing network and to ensure the reliability of collected data. It is essential to recoat the optical fibre cable with a recoating material that can enhance its adhesion to the surrounding soil, which plays a significant role in the overall performance and longevity of the monitoring system.
Future work can also focus on developing real-time monitoring and remote sensing by incorporating cloud computing of data and the Internet of Things. These monitoring systems can also be tested in large-scale or site-field models.
7. Conclusions
The study promoted the integrated science of geotechnical engineering and photonics. A small-scale sinkhole model was designed as a representation of a field sinkhole. A leaking pipe was used to induce the collapse of a cavity, and FBG sensors were placed above the cavity in horizontal and vertical positions to measure the resulting strain variations.
The experimental results suggest that the upward propagation of the sinkhole processes could be divided into phases:
Phase 1: Underground cavity formation, determined by the balloon deflation time, produces a stable arch supporting the soil.
Phase 2: Weathering process characterised by the leaking time (water infiltration) after forming the cavity.
Phase 3: Collapsing process, during which time the failure was induced.
Phase 4: Equilibrium period, where the soil mass falls over the sensors and reaches equilibrium.
FBG sensors are sensitive to ground movement and can identify collapse failure before it becomes visible. Efficient integration of an IoT-enabled FBG sensing system could detect precursor movement of soil mass due to leaking pipes to guide decision-making and more efficient risk management. The findings also show the viability of OFS for developing an early warning system.
The practical application of OFS technology should be fostered in future monitoring efforts in geohazard-prone areas.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, MF and MG; methodology, JY; validation, MF, MG and JY; formal analysis, JY; investigation, JY; resources, MF; data curation, MG; writing—original draft preparation, JY; writing—review and editing, MG; visualisation.; supervision; project administration; funding acquisition, MF All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been supported by Telkom, the National Laser Centre (NLC), the Water Research Commission (WRC), the African Laser Centre (ALC), and the Photonics Research Centre at the University of Johannesburg.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Buttrick, D.B.; Trollip, N.Y.G.; Gerber, A.A. A Performance Based Approach to Dolomite Risk Management. 2011, 1127–1138. [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, F.; Parise, M.; Waele, J. De; Jourde, H.; De Waele, J.; Jourde, H.; Waele, J. De; Jourde, H. A Review on Natural and Human-Induced Geohazards and Impacts in Karst. Earth-Science Rev. 2014, 138, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Qiao, L.; Liu, X.; Wei, C.; Zhang, W. Feasibility Study on Sinkhole Monitoring with Fiber Optic Strain Sensing Nerves. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, F.; Cooper, A.H.; Johnson, K.S. Identification, Prediction, and Mitigation of Sinkhole Hazards in Evaporite Karst Areas. In Proceedings of the Environmental Geology; January 2008; Vol. 53, pp. 1007–1022.
- Zhou, W.; Beck, B.F. Management and Mitigation of Sinkholes on Karst Lands: An Overview of Practical Applications. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, F.; Zarroca, M.; Linares, R.; Roqué, C.; Carbonel, D.; Guerrero, J.; McCalpin, J.P.; Comas, X.; Cooper, A.H. Identifying the Boundaries of Sinkholes and Subsidence Areas via Trenching and Establishing Setback Distances. Eng. Geol. 2018, 233, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, M. A Procedure for Evaluating the Susceptibility to Natural and Anthropogenic Sinkholes. Georisk 2015, 9, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, R.; Wilson, K.; Elko, N.; Seale, L.D.; Florea, L.; Vacher, H.L. Sinkhole Distribution Based on Pre-Development Mapping in Urbanised Pinellas County, Florida, USA. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2007, 279, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, A.; Stuecheli, M.; Bruckno, B.; Hoppe, E.; Acton, S.T. Detection of Geophysical Features in InSAR Point Cloud Data Sets Using Spatiotemporal Models. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 8215–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prete, S.; Di Crescenzo, G.; Santangelo, N.; Santo, A. Collapse Sinkholes in Campania (Southern Italy): Predisposing Factors, Genetic Hypothesis and Susceptibility. Zeitschrift fur Geomorphol. 2010, 54, 259–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, M.; Lollino, P. A Preliminary Analysis of Failure Mechanisms in Karst and Man-Made Underground Caves in Southern Italy. Geomorphology 2011, 134, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intrieri, E.; Gigli, G.; Nocentini, M.; Lombardi, L.; Mugnai, F.; Fidolini, F.; Casagli, N. Sinkhole Monitoring and Early Warning: An Experimental and Successful GB-InSAR Application. Geomorphology 2015, 241, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doǧan, U.; Yilmaz, M. Natural and Induced Sinkholes of the Obruk Plateau and Karapidotlessnar-Hotami{dotless}ş Plain, Turkey. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 40, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Luo, W.; Jiang, X.; Lei, M.; Dai, J. Investigations of Large Scale Sinkhole Collapses, Laibin, Guangxi, China. In Proceedings of the Full Proceedings of the Thirteenth Multidisciplinary Conference on Sinkholes and the Engineering and Environmental Impacts of Karst; National Cave and Karst Research Institute, 2013; pp. 327–331.
- Youssef, A.M.; Al-Harbi, H.M.; Gutiérrez, F.; Zabramwi, Y.A.; Bulkhi, A.B.; Zahrani, S.A.; Bahamil, A.M.; Zahrani, A.J.; Otaibi, Z.A.; El-Haddad, B.A. Natural and Human-Induced Sinkhole Hazards in Saudi Arabia: Distribution, Investigation, Causes and Impacts. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 24, 625–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, G.; Magen, Y.; Nof, R.N.; Raz, E.; Lyakhovsky, V.; Shalev, E. InSAR Measurements and Viscoelastic Modeling of Sinkhole Precursory Subsidence: Implications for Sinkhole Formation, Early Warning, and Sediment Properties. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2018, 123, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippenaar, M.A.; Swart, D.; Van Rooy, J.L. The Karst Vadose Zone : Influence on Recharge , Vulnerability. South Africa, Water Reseach Commission (Report No. Tt 109/99); 2019; Vol. 3.
- Theron, A.; Engelbrecht, J.; Kemp, J.; Kleynhans, W.; Turnbull, T. Detection of Sinkhole Precursors Through SAR Interferometry: Radar and Geological Considerations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinou, S.; Van Rooy, J.L. Sinkhole and Subsidence Size Distribution across Dolomitic Land in Gauteng. J. South African Inst. Civ. Eng. 2018, 60, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weary, D. The Cost of Karst Subsidence and Sinkhole Collapse in the United States Compared with Other Natural Hazards. In Proceedings of the Sinkholes and the Engineering and Environmental Impacts of Karst: Proceedings of the Fourteenth Multidisciplinary Conference; University of South Florida Tampa Library, 2015; pp. 433–446.
- Gutiérrez, F.; Guerrero, J.; Lucha, P. A Genetic Classification of Sinkholes Illustrated from Evaporite Paleokarst Exposures in Spain. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi Stress Distribution in Dry Ans in Saturated Sand above a Yielding Trap-Door. 1936, Internatio.
- Costa, Y.D.; Zornberg, J.G.; Asce, M. ; Benedito, ; Bueno, S.; Costa, C.L. Failure Mechanisms in Sand over a Deep Active Trap-door. 2009, 1741–1753.
- Alrowaimi, M.; Yun, H.-B.; Chopra, M. Sinkhole Physical Models to Simulate and Investigate Sinkhole Collapses. In Proceedings of the Sinkholes and the Engineering and Environmental Impacts of Karst: Proceedings of the Fourteenth Multidisciplinary Conference; University of South Florida Tampa Library, 2015; pp. 559–568.
- Jacobsz, S.W. Trap-door Experiments Studying Cavity Propagation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the fi rst Southern African Geotechnical Conference; Group, T.& F., Ed.; Proceedings of the fi rst Southern African Geotechnical Conference –: Suncity, 2016; pp. 159–165.
- Al-Naddaf, M.; Han, J.; Jawad, S.; Abdulrasool, G.; Xu, C. Investigation of Stability of Soil Arching under Surface Loading Using Trap-door Model Tests. In Proceedings of the ICSMGE 2017 - 19th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering; 2017; Vol. 2017-Septe, pp. 889–892.
- Labuschagne, J.; Ferentinou, M.; Grobler, M.; Jacobsz, S.W. Smart Monitoring of Sinkhole Formation Using Optic Fibre Technology. In Proceedings of the Springer Series in Geomechanics and Geoengineering; Springer, 2019; Vol. 1, pp. 763–773.
- Ferentinou, M. Sinkhole Collapse Propagation Studies through Instrumented Small-Scale Physical Models. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences; Copernicus GmbH, April 22 2020; Vol. 382, pp. 71–76.
- Möller, T.; da Silva Burke, T.S.; Xu, X.; Ragione, G. Della; Bilotta, E.; Abadie, C.N. Distributed Fibre Optic Sensing for Sinkhole Early Warning: Experimental Study. Géotechnique 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, J.E. , Brink, A.B.A., Louw, A. & Gowan, G.. Sinkholes and Subsidences in the Transvaal Dolomite of SouthAfrica. Int. Soc. Soil Mech. Geotech. Eng. 1965, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Argentieri, A.; Carluccio, R.; Cecchini, F.; Chiappini, M.; Ciotoli, G.; De Ritis, R.; Di Filippo, M.; Di Nezza, M.; Marchetti, M.; Margottini, S.; et al. Early Stage Sinkhole Formation in the Acque Albule Basin of Central Italy from Geophysical and Geochemical Observations. Eng. Geol. 2015, 191, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzi, V.; Di Filippo, M.; Di Nezza, M.; Carlà, T.; Bardi, F.; Marini, F.; Fontanelli, K.; Intrieri, E.; Fanti, R. Integrated Geophysical Survey in a Sinkhole-Prone Area: Microgravity, Electrical Resistivity Tomographies, and Seismic Noise Measurements to Delimit Its Extension. Eng. Geol. 2018, 243, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevil, J.; Gutiérrez, F.; Carnicer, C.; Carbonel, D.; Desir, G.; García-Arnay, Á.; Guerrero, J. Characterizing and Monitoring a High-Risk Sinkhole in an Urban Area Underlain by Salt through Non-Invasive Methods: Detailed Mapping, High-Precision Leveling and GPR. Eng. Geol. 2020, 272, 105641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Sun, H.; Qin, J.; Zheng, Z. A Multi-Geophysical Approach to Assess Potential Sinkholes in an Urban Area. Eng. Geol. 2023, 318, 107100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, F.; Sevil, J.; Sevillano, P.; Preciado-Garbayo, J.; Martínez, J.J.; Martín-López, S.; González-Herráez, M. The Application of Distributed Optical Fiber Sensors (BOTDA) to Sinkhole Monitoring. Review and the Case of a Damaging Sinkhole in the Ebro Valley Evaporite Karst (NE Spain). Eng. Geol. 2023, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bado, M.F.; Casas, J.R. A Review of Recent Distributed Optical Fiber Sensors Applications for Civil Engineering Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.-S.; Dong, L.-J.; Borana, L.; Liu, H.-B. Early-Warning System With Quasi-Distributed Fiber Optic Sensor Networks and Cloud Computing for Soil Slopes. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 25437–25444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hong, L.; Zhou, Z. Optical Fiber Technology Investigation of Sensitivity Enhancing and Temperature Compensation for Fi Ber Bragg Grating ( FBG ) -Based Strain Sensor. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2019, 48, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Kim, D.S. Centrifuge Modelling for Evaluation of Seismic Behaviour of Stone Masonry Structure. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 53, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttrick, D.B.; Van Schalkwyk, A. The Method of Scenario Supposition for Stability Evaluation of Sites on Dolomitic Land in South Africa, Technical Paper. J. South African Inst. Civ. Eng. 1995, 37, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- SABS SANS 2001-DP1 : Construction Works Part DP1 : Earthworks for Buried Pipelines and Prefabricated Culverts; Edition1.1.; South African Bureau of Standards: Pretoria:, 2011. ISBN 9780626251604.
- Heath, G.J.J.; Oosthuizen, A.C.C. A Preliminary Overview of the Sinkhole Record of South Africa. SAICE Conf. Probl. Soils South Africa 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sverdrup, H. Chemical Weathering of Soil Minerals and the Role of Biological Processes. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2009, 23, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Depiction of a single-mode optical fibre.
Figure 1.
Depiction of a single-mode optical fibre.
Figure 2.
Working principle of an FBG sensor .
Figure 2.
Working principle of an FBG sensor .
Figure 3.
Model preparation: (a) Isolation of temperature cable with three printed FBGs, (b) Vertical support design of the optical fibre sensors mounted in the modelling, (c) Container with optical fibre sensors mounted.
Figure 3.
Model preparation: (a) Isolation of temperature cable with three printed FBGs, (b) Vertical support design of the optical fibre sensors mounted in the modelling, (c) Container with optical fibre sensors mounted.
Figure 4.
Horizontal and vertical position of FBG sensors in the sinkhole model.
Figure 4.
Horizontal and vertical position of FBG sensors in the sinkhole model.
Figure 5.
Experimental setup consisted of a water supply system, the physical small-scale model of the sinkhole and the data acquisition system.
Figure 5.
Experimental setup consisted of a water supply system, the physical small-scale model of the sinkhole and the data acquisition system.
Figure 6.
Development of the sinkhole: (a)The balloon is inflated with water to create a cavity in the soil mass, (b) The ballon is deflected, and the cavity is created, (c) water leaks into the soil mass to induce the collapse and form the sinkhole, (d) the sinkhole is developed and propagated upward the ground surface.
Figure 6.
Development of the sinkhole: (a)The balloon is inflated with water to create a cavity in the soil mass, (b) The ballon is deflected, and the cavity is created, (c) water leaks into the soil mass to induce the collapse and form the sinkhole, (d) the sinkhole is developed and propagated upward the ground surface.
Figure 7.
The horizontal strain was measured in different layers by three optic fibre sensor cables: (a) Strain-induced by leaking water, (b) Optic fibre cable 1, (c) Optic fibre cable 2 and (d) Optic fibre cable 3.
Figure 7.
The horizontal strain was measured in different layers by three optic fibre sensor cables: (a) Strain-induced by leaking water, (b) Optic fibre cable 1, (c) Optic fibre cable 2 and (d) Optic fibre cable 3.
Figure 8.
Horizontal strain variation during the four identified phases in the failure process of the sinkhole, (a) Cavity formation process, (b) Weathering or erosion process, (c) Collapsing process and (d) Equilibrium process.
Figure 8.
Horizontal strain variation during the four identified phases in the failure process of the sinkhole, (a) Cavity formation process, (b) Weathering or erosion process, (c) Collapsing process and (d) Equilibrium process.
Figure 9.
Vertical strains were measured in different layers by the three optic fibre sensor cables: (a) Strain-induced by leaking water, (b) Optic fibre cable 1, (c) Optic fibre cable 2 and (d) Optic fibre cable 3.
Figure 9.
Vertical strains were measured in different layers by the three optic fibre sensor cables: (a) Strain-induced by leaking water, (b) Optic fibre cable 1, (c) Optic fibre cable 2 and (d) Optic fibre cable 3.
Figure 10.
Vertical strain variation during the four identified phases in the failure process of a sinkhole, (a) Cavity formation process, (b) Weathering or erosion process, (c) Collapsing process and (d) Equilibrium process.
Figure 10.
Vertical strain variation during the four identified phases in the failure process of a sinkhole, (a) Cavity formation process, (b) Weathering or erosion process, (c) Collapsing process and (d) Equilibrium process.
Table 1.
Scaling factor.
| Parameter |
Scaling factor (prototype/model) |
| |
|
Centrifuge physical modelling |
|
1-g physical modelling |
|
| Displacement, Length |
N |
N |
| Mass |
N3
|
N3
|
| Density |
1 |
1 |
| Stress |
1 |
N |
| Strain |
1 |
1 |
Table 2.
Fundamental engineering properties of Cullinan silica sand.
Table 2.
Fundamental engineering properties of Cullinan silica sand.
| Engineering Property |
Value |
| Compaction density |
1548.8 kg m-3
|
| Relative density |
60% |
| Specific gravity, Gs |
2.67 |
| Particle shape |
Angular to sub-rounded |
| Cohesion, C' |
0 kPa |
| Angle of repose (ϕ) |
370
|
| D50 particle diameter |
0.15 mm |
| Moisture content |
10% |
| Unified soil classification system (USCS) |
SP. |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).