Submitted:
02 August 2024
Posted:
02 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
The Gut Microbiota and HD
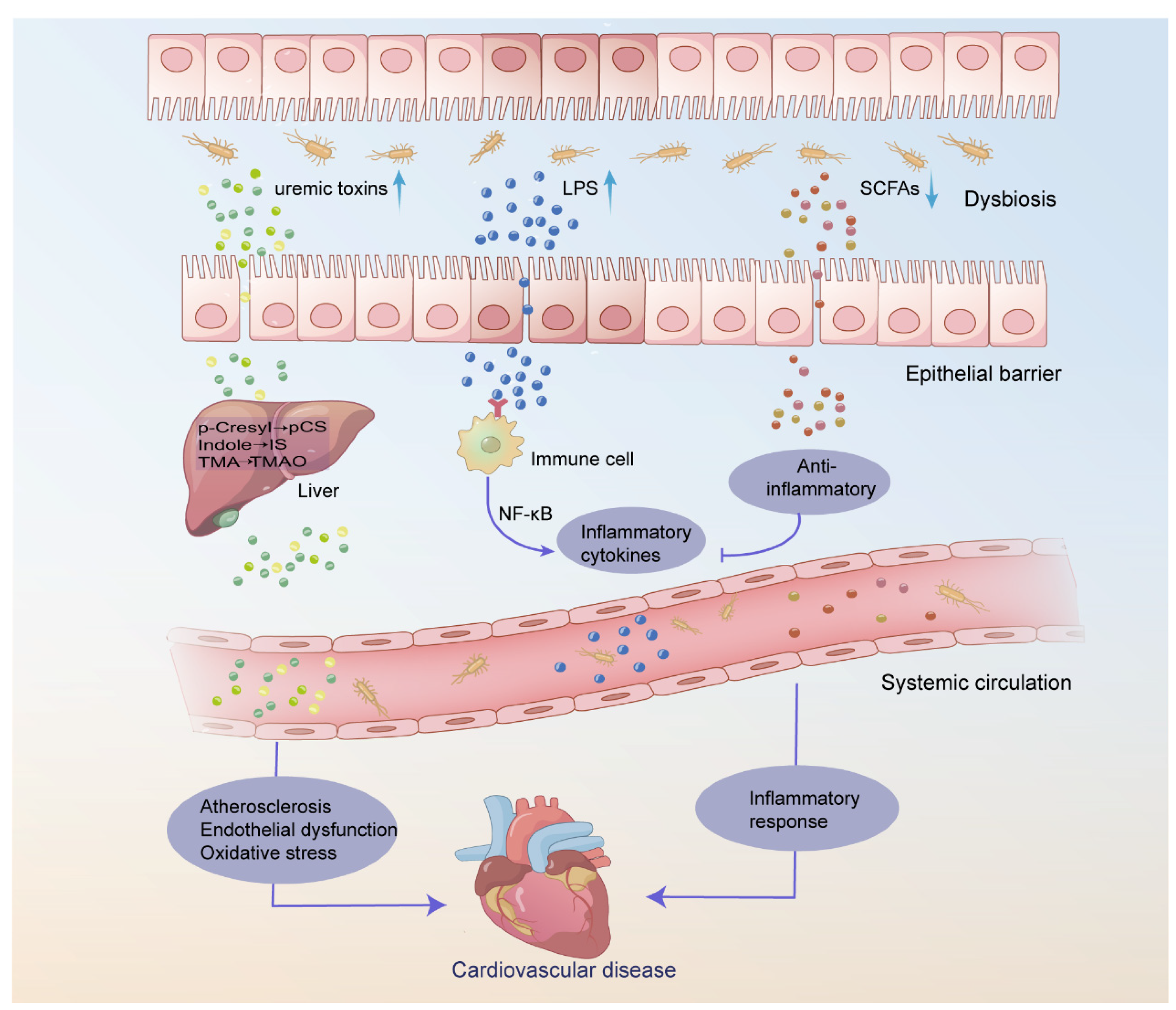
The Gut Microbiota and CVD
The Gut Microbiota and Infection
The Gut Microbiota and Anemia
The Gut Microbiota and Malnutrition
Strategies to Attenuate Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in HD
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; et al. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2021, 398, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liyanage, T.; et al. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet, 2015, 385, 1975–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, A.; et al. Survival advantage of planned haemodialysis over peritoneal dialysis: a cohort study. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 2018, 33, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelfarb, J. Hemodialysis complications. Am J Kidney Dis, 2005, 45, 1122–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saran, R.; et al. US Renal Data System 2016 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis, 2017, 69, A7–a8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature, 2012, 486, 207–14. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemurno, E.; et al. What would you like to eat, Mr CKD Microbiota? A Mediterranean Diet, please! Kidney Blood Press Res, 2014, 39, 114–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galla, S.; et al. Microbiotal-Host Interactions and Hypertension. Physiology (Bethesda), 2017, 32, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, A.; et al. Role of the Gut Microbiome in Uremia: A Potential Therapeutic Target. Am J Kidney Dis, 2016, 67, 483–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulou, E.; et al. Focus on the Gut-Kidney Axis in Health and Disease. Front Med (Lausanne), 2020, 7, 620102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D.; et al. Chronic kidney disease alters intestinal microbial flora. Kidney Int, 2013, 83, 308–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenepoel, P. , Poesen, R. ; Meijers, B., The gut–kidney axis. Pediatric Nephrology, 2016, 32, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosola, C.; et al. Microbiota metabolites: Pivotal players of cardiovascular damage in chronic kidney disease. Pharmacol Res, 2018, 130, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; et al. Gut microbiota as a key regulator of intestinal mucosal immunity. Life Sci, 2024, 345, 122612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mörbe, U.M.; et al. Human gut-associated lymphoid tissues (GALT); diversity, structure, and function. Mucosal Immunology, 2021, 14, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourlioux, P.; et al. he intestine and its microflora are partners for the protection of the host: report on the Danone Symposium “The Intelligent Intestine,” held in Paris, June 14, 2002. Am J Clin Nutr 2003, 78, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature, 2011, 473, 174–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourountzis, T.; et al. Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease. Life (Basel), 2022, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, W.L.; Vaziri, N.D. The Leaky Gut and Altered Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease. J Ren Nutr, 2017, 27, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.; et al. Expansion of urease- and uricase-containing, indole- and p-cresol-forming and contraction of short-chain fatty acid-producing intestinal microbiota in ESRD. Am J Nephrol, 2014, 39, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, T.; et al. The gut-kidney axis in chronic renal failure: A new potential target for therapy. Hemodial Int, 2017, 21, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Zhao, Y-Y.; Pahl, M.V. Altered intestinal microbial flora and impaired epithelial barrier structure and function in CKD: the nature, mechanisms, consequences and potential treatment. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 2016, 31, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões-Silva, L.; et al. The microbiome in chronic kidney disease patients undergoing hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Pharmacological Research, 2018, 130, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, R.D. , Wommack, E. ; Deitch, E.A., Immunosuppression and intestinal bacterial overgrowth synergistically promote bacterial translocation. Arch Surg, 1988, 123, 1359–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; et al. Gut bacterial translocation may aggravate microinflammation in hemodialysis patients. Dig Dis Sci, 2014, 59, 2109–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, C.W.; et al. Circulating endotoxemia: a novel factor in systemic inflammation and cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2011, 6, 133–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blikslager, A.T.; et al. Restoration of barrier function in injured intestinal mucosa. Physiol Rev, 2007, 87, 545–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.Y.; et al. Microbiota analysis in the hemodialysis population—Focusing on Enterobacteriaceae. J Microbiol Immunol Infect, 2023, 56, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo-Salgado, J.; et al. Intestinal microbiota in pediatric patients with end stage renal disease: a Midwest Pediatric Nephrology Consortium study. Microbiome, 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; et al. The Effects of Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis on the Gut Microbiota of End-Stage Renal Disease Patients, and the Relationship Between Gut Microbiota and Patient Prognoses. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11, 579386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, A.K.; Yu, Z. , Genomic Insights into the Distribution of Peptidases and Proteolytic Capacity among Prevotella and Paraprevotella Species. Microbiol Spectr, 2022, 10, e0218521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morotomi, M.; et al. Paraprevotella clara gen. nov., sp. nov. and Paraprevotella xylaniphila sp. nov., members of the family ‘Prevotellaceae’ isolated from human faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2009, 59, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A. The determination of urea, ammonia, and urease. Methods Biochem Anal, 1969, 17, 311–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila is a promising probiotic. Microb Biotechnol, 2019, 12, 1109–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; et al. Alterations to the Gut Microbiota and Their Correlation With Inflammatory Factors in Chronic Kidney Disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2019, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visca, P. , Seifert, H. ; Towner, K.J., Acinetobacter infection--an emerging threat to human health. IUBMB Life, 2011, 63, 1048–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, A.L.; et al. Proteus spp. as Putative Gastrointestinal Pathogens. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2018, 31, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; et al. Unilateral ureteral obstruction causes gut microbial dysbiosis and metabolome disorders contributing to tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Exp Mol Med, 2019, 51, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; et al. Gut bacterial translocation is associated with microinflammation in end-stage renal disease patients. Nephrology (Carlton), 2012, 17, 733–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Xie, Y. , Effect of Different Hemodialysis Methods on Microbiota in Uremic Patients. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020, 6739762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassabi, A.; et al. Potential contribution of the immune system to the emergence of renal diseases. Immunology Letters, 2022, 248, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- March, D.S.; et al. Intestinal Barrier Disturbances in Haemodialysis Patients: Mechanisms, Consequences, and Therapeutic Options. Biomed Res Int, 2017, 2017, 5765417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Pahl, M.V. , Altered intestinal microbial flora and impaired epithelial barrier structure and function in CKD: the nature, mechanisms, consequences and potential treatment. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2016, 31, 737–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; et al. Immunosenescence, gut dysbiosis, and chronic kidney disease: Interplay and implications for clinical management. Biomed J, 2023, 47, 100638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, K.; Lehmann, C. , Inflammatory Response to Different Toxins in Experimental Sepsis Models. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, H.J.; Andersen, K.; Stecher, B. , The intestinal microbiota, a leaky gut, and abnormal immunity in kidney disease. Kidney Int, 2013, 83, 1010–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; et al. Expansion of Urease- and Uricase-Containing, Indole- and p-Cresol-Forming and Contraction of Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Producing Intestinal Microbiota in ESRD. American Journal of Nephrology, 2014, 39, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.H.; et al. Relationship between gut microbiota and vascular calcification in hemodialysis patients. Ren Fail, 2023, 45, 2148538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roediger, W.E. , Utilization of nutrients by isolated epithelial cells of the rat colon. Gastroenterology, 1982, 83, 424–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segain, J.P.; et al. Butyrate inhibits inflammatory responses through NFkappaB inhibition: implications for Crohn’s disease. Gut, 2000, 47, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Their Association with Signalling Pathways in Inflammation, Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Besten, G.; et al. Gut-derived short-chain fatty acids are vividly assimilated into host carbohydrates and lipids. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2013, 305, G900–G910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, S.E.; et al. Production and utilization of acetate in mammals. Biochem J, 1974, 142, 401–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; et al. The role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Adv Immunol, 2014, 121, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.J.; et al. The Orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short chain carboxylic acids. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278, 11312–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirich, T.L.; et al. Prominent accumulation in hemodialysis patients of solutes normally cleared by tubular secretion. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2014, 25, 615–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenepoel, P.; Poesen, R.; Meijers, B. The gut-kidney axis. Pediatr Nephrol, 2017, 32, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.C.; Sirich, T.L. , Indoxyl Sulfate-Review of Toxicity and Therapeutic Strategies. Toxins (Basel), 2016, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.B.; et al. Advanced chronic kidney disease populations have elevated trimethylamine N-oxide levels associated with increased cardiovascular events. Kidney Int, 2016, 89, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; et al. Association of trimethylamine N-Oxide with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients. Ren Fail, 2020, 42, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agus, A.; Clément, K.; Sokol, H. , Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as central regulators in metabolic disorders. Gut, 2021, 70, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, X.; et al. Mechanism of Prominent Trimethylamine Oxide (TMAO) Accumulation in Hemodialysis Patients. PLoS One, 2015, 10, e0143731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, J.R.; et al. Serum Trimethylamine-N-Oxide is Elevated in CKD and Correlates with Coronary Atherosclerosis Burden. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2016, 27, 305–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; et al. Association of Circulating Trimethylamine-N Oxide With Malnutrition and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients With Maintenance Hemodialysis. J Ren Nutr, 2023, 33, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bammens, B.; et al. Free serum concentrations of the protein-bound retention solute p-cresol predict mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int, 2006, 69, 1081–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadmehrabi, S.; Tang, W.H.W. Hemodialysis-induced cardiovascular disease. Semin Dial, 2018, 31, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echefu, G.; et al. Pathophysiological concepts and screening of cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Front Nephrol, 2023, 3, 1198560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, M.; et al. Cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2018, 33, iii28–iii34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; et al. Gut Bacterial Translocation May Aggravate Microinflammation in Hemodialysis Patients. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 2014, 59, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Meier, D.T.; Böni-Schnetzler, M. Inflammation in the Pathophysiology and Therapy of Cardiometabolic Disease. Endocr Rev, 2019, 40, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, K.; et al. Circulating Microbial Signatures and Cardiovascular Death in Patients With ESRD. Kidney Int Rep, 2021, 6, 2617–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinakaran, V.; et al. Elevated levels of circulating DNA in cardiovascular disease patients: metagenomic profiling of microbiome in the circulation. PLoS One, 2014, 9, e105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, S.; Gupta, D. , Crosstalk of toll-like receptors signaling and Nrf2 pathway for regulation of inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 108, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; et al. Bacteroides vulgatus and Bacteroides dorei Reduce Gut Microbial Lipopolysaccharide Production and Inhibit Atherosclerosis. Circulation, 2018, 138, 2486–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao-Kitamoto, H.; et al. Interleukin-22-mediated host glycosylation prevents Clostridioides difficile infection by modulating the metabolic activity of the gut microbiota. Nat Med, 2020, 26, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, V.; et al. A Possible Link between Gut Microbiome Composition and Cardiovascular Comorbidities in Psoriatic Patients. J Pers Med, 2022, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; et al. Trimethylamine-N-oxide is an independent risk factor for hospitalization events in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis. Ren Fail, 2020, 42, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, T.; et al. Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Cardiovascular Events in Hemodialysis Patients. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017, 28, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, T.; et al. Diverse roles of macrophages in atherosclerosis: from inflammatory biology to biomarker discovery. Mediators Inflamm, 2012, 2012, 693083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; et al. Implication of Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020, 2020, 5394096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeth, R.A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med, 2013, 19, 576–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gérard, P. Diet-gut microbiota interactions on cardiovascular disease. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2022, 20, 1528–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seldin, M.M.; et al. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Promotes Vascular Inflammation Through Signaling of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and Nuclear Factor-κB. J Am Heart Assoc, 2016, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide induces inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via activating ROS-TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2016, 481, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, J.; et al. The gut microbial metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide and cardiovascular diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14, 1085041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.Y.; et al. Serum Trimethylamine N-Oxide Level Is Positively Associated with Aortic Stiffness Measured by Carotid-Femoral Pulse Wave Velocity in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis. Toxins (Basel), 2023, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; et al. Higher serum trimethylamine-N-oxide levels are associated with increased abdominal aortic calcification in hemodialysis patients. Ren Fail, 2022, 44, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, M.; et al. Cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2018, 33, iii28–iii34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanholder, R.; et al. The uremic toxicity of indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate: a systematic review. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2014, 25, 1897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; et al. Serum total indoxyl sulfate and clinical outcomes in hemodialysis patients: results from the Japan Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study. Clin Kidney J, 2021, 14, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; et al. Serum total indoxyl sulfate levels and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients: a prospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol, 2022, 23, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.J.; et al. Serum p-cresyl sulfate predicts cardiovascular disease and mortality in elderly hemodialysis patients. Arch Med Sci, 2013, 9, 662–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, I.-W.; et al. Serum free p -cresyl sulfate levels predict cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in elderly hemodialysis patients—a prospective cohort study. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 2011, 27, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.S.; et al. Association of indoxyl sulfate with heart failure among patients on hemodialysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2015, 10, 111–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, T.; et al. Results of the HEMO Study suggest that p-cresol sulfate and indoxyl sulfate are not associated with cardiovascular outcomes. Kidney Int, 2017, 92, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; et al. Indoxyl Sulfate and Incident Peripheral Artery Disease in Hemodialysis Patients. Toxins (Basel) 2020, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, M.L.; et al. Retained organic solutes, patient characteristics and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hemodialysis: results from the retained organic solutes and clinical outcomes (ROSCO) investigators. BMC Nephrol, 2013, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarnak, M.J.; Jaber, B.L. , Mortality caused by sepsis in patients with end-stage renal disease compared with the general population. Kidney Int, 2000, 58, 1758–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powe, N.R.; et al. Septicemia in dialysis patients: incidence, risk factors, and prognosis. Kidney Int, 1999, 55, 1081–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; et al. Risk factors for catheter-associated bloodstream infection in hemodialysis patients: A meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2024, 19, e0299715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descamps-Latscha, B. The immune system in end-stage renal disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens, 1993, 2, 883–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.; Hörl, W.H. Immune dysfunction in uremia—an update. Toxins (Basel), 2012, 4, 962–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shorr, A.F.; et al. Prediction of infection due to antibiotic-resistant bacteria by select risk factors for health care-associated pneumonia. Arch Intern Med, 2008, 168, 2205–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; et al. Aspects of immune dysfunction in end-stage renal disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2008, 3, 1526–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchetti, M.T.; et al. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins and Immunity. Methods Mol Biol, 2021, 2325, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, T.; et al. Free and total p-cresol sulfate levels and infectious hospitalizations in hemodialysis patients in CHOICE and HEMO. Medicine (Baltimore), 2017, 96, e5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.J.; et al. Serum protein-bound uraemic toxins and clinical outcomes in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2010, 25, 3693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Yassin, H.M. Infection and Hemodialysis Access: An Updated Review. Infectious Disorders—Drug Targets, 2013, 13, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.B.; et al. National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Dialysis Event Surveillance Report for 2014, Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017, 12, 1139–1146.
- Gupta, V.; Yassin, M.H. Infection and hemodialysis access: an updated review. Infect Disord Drug Targets, 2013, 13, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, G.; et al. Association of Kidney Function with Infections by Multidrug-Resistant Organisms: An Electronic Medical Record Analysis. Sci Rep, 2018, 8, 13372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharioudakis, I.M.; et al. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci colonization among dialysis patients: a meta-analysis of prevalence, risk factors, and significance. Am J Kidney Dis, 2015, 65, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, N.B.; et al. CDC National Health Report: leading causes of morbidity and mortality and associated behavioral risk and protective factors--United States, 2005-2013. MMWR Suppl, 2014, 63, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; et al. Alterations of gut microbial pathways and virulence factors in hemodialysis patients. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12, 904284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitão, J.H. Microbial Virulence Factors. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; et al. Anemia Management in the China Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study. Blood Purif, 2016, 42, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, S.; et al. Indole 3-acetic acid, indoxyl sulfate and paracresyl-sulfate do not influence anemia parameters in hemodialysis patients. BMC Nephrol, 2017, 18, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madai, S.; et al. Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway protects against acute ischemic stroke by reprogramming central carbon metabolism. Theranostics, 2024, 14, 2856–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.K.; et al. Indoxyl sulfate, a representative uremic toxin, suppresses erythropoietin production in a HIF-dependent manner. Lab Invest, 2011, 91, 1564–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; et al. Indoxyl sulfate signals for rapid mRNA stabilization of Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator with Glu/Asp-rich carboxy-terminal domain 2 (CITED2) and suppresses the expression of hypoxia-inducible genes in experimental CKD and uremia. Faseb j, 2013, 27, 4059–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, T.; et al. The drug-specific properties of hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors in mice reveal a significant contribution of the kidney compared to the liver to erythropoietin induction. Life Sci, 2024, 346, 122641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.S.; et al. Triggering of suicidal erythrocyte death by uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate. BMC Nephrol, 2013, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capo-Chichi, J.C.C.; et al. Is there an association between the plasma levels of uremic toxins from gut microbiota and anemia in patients on hemodialysis? Int Urol Nephrol, 2022, 54, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcelli, D.; et al. Dynamics of the erythropoiesis stimulating agent resistance index in incident hemodiafiltration and high-flux hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int, 2016, 90, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdougall, I.C.; Cooper, A.C. Erythropoietin resistance: the role of inflammation and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2002, 17, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; et al. The prebiotic effects of soluble dietary fiber mixture on renal anemia and the gut microbiota in end-stage renal disease patients on maintenance hemodialysis: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Transl Med, 2022, 20, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota Correlates With Clinical Responsiveness to Erythropoietin in Hemodialysis Patients With Anemia. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12, 919352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K. , Maintenance of Skeletal Muscle to Counteract Sarcopenia in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease and Especially Those Undergoing Hemodialysis. Nutrients, 2021, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing, 2010, 39, 412–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-L.; et al. Impact of sarcopenia and its diagnostic criteria on hospitalization and mortality in chronic hemodialysis patients: A 3-year longitudinal study. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association, 2020, 119, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, S.; et al. The gut microbiota influences skeletal muscle mass and function in mice. Sci Transl Med, 2019, 11, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; et al. Characterization of the gut microbiota in hemodialysis patients with sarcopenia. Int Urol Nephrol, 2022, 54, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; et al. The gut microbiota from maintenance hemodialysis patients with sarcopenia influences muscle function in mice. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2023, 13, 1225991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.S.; et al. Differences in the gut microbiome and reduced fecal butyrate in elders with low skeletal muscle mass. Clin Nutr, 2022, 41, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, W.Q.; et al. Human gut microbiome impacts skeletal muscle mass via gut microbial synthesis of the short-chain fatty acid butyrate among healthy menopausal women. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2021, 12, 1860–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, E.; et al. Metabolic alterations by indoxyl sulfate in skeletal muscle induce uremic sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease. Sci Rep, 2016, 6, 36618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changchien, C.Y.; et al. Indoxyl sulfate induces myotube atrophy by ROS-ERK and JNK-MAFbx cascades. Chem Biol Interact, 2019, 304, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouque, D.; et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int, 2008, 73, 391–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herselman, M.; et al. Protein-energy malnutrition as a risk factor for increased morbidity in long-term hemodialysis patients. J Ren Nutr, 2000, 10, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Hung, S.C. , Association of subjective global assessment of nutritional status with gut microbiota in hemodialysis patients: a case-control study. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2021, 36, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Mitch, W.E. Mechanisms of muscle wasting in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2014, 10, 504–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; et al. Correlation between intestinal flora disruption and protein-energy wasting in patients with end-stage renal disease. BMC Nephrol, 2022, 23, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis and protein energy wasting in patients on hemodialysis: an observational longitudinal study. Front Nutr, 2023, 10, 1270690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; et al. Correlation between serum trimethylamine-N-oxide concentration and protein energy wasting in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Ren Fail, 2022, 44, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.; et al. The effect of probiotic supplementation on systemic inflammation in dialysis patients. Kidney Res Clin Pract, 2022, 41, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, A.; et al. Probiotic supplementation in diabetic hemodialysis patients has beneficial metabolic effects. Kidney Int, 2017, 91, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Nutrient Intake, Ghrelin, and Adiponectin Concentrations in Diabetic Hemodialysis Patients. Altern Ther Health Med, 2023, 29, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; et al. Clostridium butyricum affects nutrition and immunology by modulating gut microbiota. Biosci Microbiota Food Health, 2022, 41, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belova, I.V.; et al. Colon Microbiocenosis and Its Correction in Patients Receiving Programmed Hemodialysis. Sovrem Tekhnologii Med, 2021, 12, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamanadze, A.; et al. IMPACT OF MICROBIOME COMPOSITION ON QUALITY OF LIFE IN HEMODIALYSIS PATIENTS. Georgian Med News 2022, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Eidi, F.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus on serum uremic toxins (phenol and P-Cresol) in hemodialysis patients: A double blind randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr ESPEN, 2018, 28, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, N.A.; et al. Probiotic Supplementation in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial. J Ren Nutr, 2018, 28, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, H.S.; Paik, K.H.; Cho, H.Y. p-Cresyl sulfate and indoxyl sulfate in pediatric patients on chronic dialysis. Korean J Pediatr, 2013, 56, 159–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavin, J. , Fiber and prebiotics: mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients, 2013, 5, 1417–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salarolli, R.T.; et al. Can curcumin supplementation reduce plasma levels of gut-derived uremic toxins in hemodialysis patients? A pilot randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Int Urol Nephrol, 2021, 53, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kemp, J.A.; et al. The Impact of Enriched Resistant Starch Type-2 Cookies on the Gut Microbiome in Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2021, 65, e2100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirich, T.L.; et al. Effect of increasing dietary fiber on plasma levels of colon-derived solutes in hemodialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2014, 9, 1603–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esgalhado, M.; et al. Could resistant starch supplementation improve inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers and uremic toxins levels in hemodialysis patients? A pilot randomized controlled trial. Food Funct, 2018, 9, 6508–6516. [Google Scholar]
- Tayebi Khosroshahi, H.; et al. Effect of high amylose resistant starch (HAM-RS2) supplementation on biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in hemodialysis patients: a randomized clinical trial. Hemodial Int, 2018, 22, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosroshahi, H.T.; et al. Effects of fermentable high fiber diet supplementation on gut derived and conventional nitrogenous product in patients on maintenance hemodialysis: a randomized controlled trial. Nutr Metab (Lond), 2019, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, J.A.; et al. Resistant Starch Type-2 Supplementation Does Not Decrease Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) Plasma Level in Hemodialysis Patients. J Am Nutr Assoc, 2022, 41, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, M.; et al. Synbiotics Improved Stool Form via Changes in the Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Hemodialysis Patients. Kobe J Med Sci, 2021, 67, E112–e118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lopes, R.; et al. Synbiotic meal decreases uremic toxins in hemodialysis individuals: A placebo-controlled trial. Food Res Int, 2019, 116, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighat, N.; et al. Effects of Synbiotics and Probiotics Supplementation on Serum Levels of Endotoxin, Heat Shock Protein 70 Antibodies and Inflammatory Markers in Hemodialysis Patients: a Randomized Double-Blinded Controlled Trial. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins, 2020, 12, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighat, N.; et al. The Effect of Synbiotic and Probiotic Supplementation on Mental Health Parameters in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial. Indian J Nephrol, 2021, 31, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




