1. Introduction
Water pollution is actual and increasing every day [
1,
2], therefore, the presence of metals, dyes, and pharmaceuticals, among other compounds, in untreated industrial effluent that ends up in our rivers, lakes, and oceans represent alarming environmental pollution. Many process industries from different sectors produce a large quantity of coloured wastewater [
3]. In particular, the dyeing and finishing processes in the textile industries are an important pollution source of their wastewaters, discharging significant amounts of coloured compounds [
4], and presenting high suspended solids content, chemical oxygen demand, biochemical oxygen demand, pH changes, and other inorganic contaminants. The existence of colour reduces aquatic biodiversity by interfering the transit of light through the water, consequently, avoiding the photosynthesis of aqueous flora [
5]. In some cases, dye concentration lower than 1 mg L−1 is enough to produce an evident water coloration. Moreover, most of these compounds can cause skin irritation [
6] and are toxic, carcinogenic, and mutagenic to human beings [
7,
8]. Consequently, different treatments of effluents containing dyes were developed to reduce the adverse conditions due to the release of untreated effluents directly into the environment and the concern for human health [
5].
In this way, various physical and physicochemical processes as coagulation, flocculation, biodegradation, adsorption, membrane separation, ion exchange, oxidation, and advanced oxidation process have been widely used for dyes removal [
5,
9,
10]. However, dyes are highly resistant to degradation due to their complex chemical structures [
11]. Among existing technologies, those based on adsorption are the most common and have shown good efficiencies for dye removal [
12]. Many studies on finding the best adsorbent materials have been carried out in recent decades. In this respect, carbons are the most extensively used with good results [
13]. Their behaviour can be hydrophobic or organophilic depending on the polarity on their surface, which arises from the complexity of the surface chemical groups and thus they are widely used in the adsorption of organic compounds, as dyes, in water recovery and purification systems. Another important factor, in addition to the surface chemistry of the adsorbent, is its internal porous structure that directly affects the dye capture. Also, the precursor used for carbon manufacturing is very important because affects its internal structure. As an example,
Table 1 shows representative precursors to obtain carbons and their adsorption capacities for common dyes, observing that the use of lignocellulosic materials is common due to their low cost. However, their main disadvantage is the impossibility of controlling the internal structure of the carbonaceous matrix. On the other hand, the use of polymers allows to control the pore size and provides larger surface areas.
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) is used as a good precursor for producing carbon materials with an extraordinary graphitization degree and a high surface area but relatively low porosity. These characteristics are owing to the formation of a tightly stacked and low-defect structure during the PAN pre-oxidation process. Moreover, PAN is a polymer with nitrogen atoms, which can contribute to proportionate functionalities into the carbon structure [
22,
23]. Also, doping with heteroatoms (N, S, B, P, Se) causes structural changes modifying the carbon physicochemical properties, which is used to provide carbon materials with adjustable functions for different applications [
24]. In particular, the incorporation of sulphur to the carbon frameworks can play a double role, acting both as a morphology stabilizer and as a dopant, facilitating the formation of N, S-co-doped nanocarbons with a great specific surface area and controlled pore size [
25]. Moreover, it has been found that the sulphur doping provides to the carbons of appropriate characteristics to be used as heavy metals or dyes adsorbents and supercapacitors. [
26,
27]. In addition, physical or chemical activation increases the porosity and specific surface of the porous carbon [
14,
28], which together with the surface chemistry of the activated carbon, has a significant effect on the adsorption process.
In this work, three doped porous carbons manufactured from polyacrylonitrile, N-doped carbon (PAN-C), N-doped activated carbon (PAN-C-Act) and N, S-co-doped carbon (PAN-S-C) were used as adsorbents of an industrial wood dye. The influence of pH, initial dye concentration and solid/liquid ratio was analysed on the adsorption capacity of each carbon. Kinetics and diffusion mechanisms were also evaluated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Porous Carbons
Three porous carbons were manufactured using the same experimental procedure than a previous work [
29] using PAN as precursor (150,000 g mol−1): N-doped carbon (PAN-C), N-doped activated carbon with 4-fold excess of KOH (PAN-C-Act) and N, S-co-doped carbon with sulphur in a 1:1 weight ratio (PAN-S-C). The carbonization process consisted of two continuous stages, one at 553 K which stabilizes the PAN structure, and another at 1073 K where the polymer was completely pyrolyzed. For activation, PAN-C was ground with KOH (1:4 w/w) and carbonized in an inert N
2 atmosphere at 1073 K for 2 hours. In addition, commercial activated carbon (CAC) was used as a reference material (Merck, Kenilworth, NJ, USA). Porous carbons characterization including textural properties and morphological features can be found in the previous work [
29].
2.2. Wood Red Dye
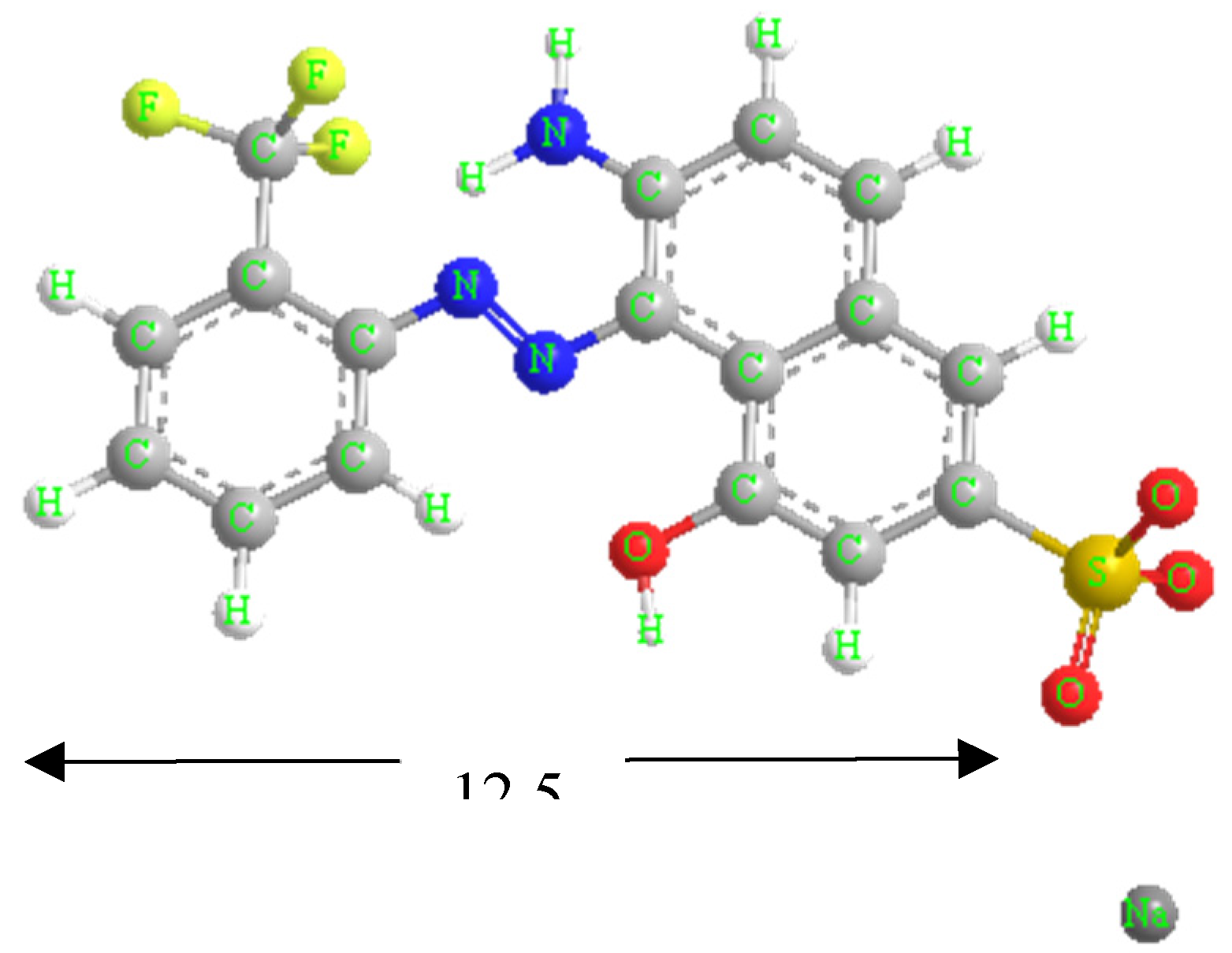
Red GRA 200% (433.34 g mol-1) is an industrial acidic and anionic wood dye provided by ASERPAL S.A. company (Grupo Losán S.A., Galicia, Spain) specialized in the preparation of wood veneers boards.
Figure 1 shows the structural formula of the dye. A stock aqueous solution (500 mg L−1) was prepared by dissolving the red dye in distilled water, which was diluted to obtain the working solutions at required concentration. To adjust pH, 1 mol L−1 NaOH or HCl aqueous solutions were used. A scan of red dye solutions (10 mg L-1) between pH 1.5 - 12.5 was performed by UV/VIS spectroscopy, obtaining the maximum wavelength (λ
max) at 506 nm for pH from 1.5 to 8. At pH 8, the red dye solution changed to yellow at λ
max of 505 nm, and finally, the λ
max was 482 nm from pH 11.5. A previous study confirmed that dye solutions at all conditions of initial concentration and pH used were stable over time (48 h). The determination of the acid dissociation constant (pK
a) of the Red GRA-200% dye was previously performed by an UV–Visible spectroscopic method [
30]. pK
a, which predicts the ionization state of the molecule concerning pH, is 10.6.
2.3. Adsorption Kinetic Experiments
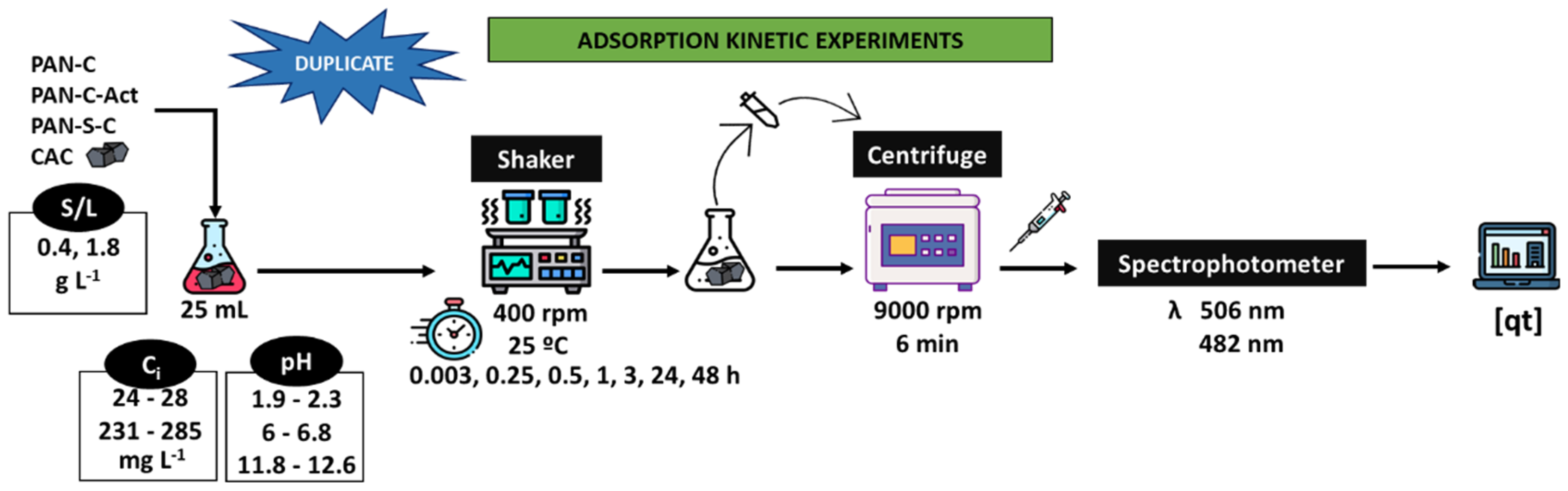
Figure 2 shows a scheme of the process followed to carry out the adsorption kinetics experiments using PAN-C, PAN-S-C, PAN-C-Act and CAC as adsorbents. For studying the dye adsorption, various batch experiments were carried out in 25 mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The suspensions were kept in an orbital mini shaker (VWR, Cienytech) with temperature control at 400 rpm, 25 ºC and at different times (up 48 h), pH (acidic, 1.9-2.3; natural, 6-6.8; alkaline, 11.8-12.6), adsorbent dosage (S/L, 0.43-0.53 and 1.73-1.91 g L−1) and initial dye concentration (
Ci, 24 - 28 mg L−1 and 231 - 285 mg L−1). Finally, samples were centrifuged (Alresa Microcen) at 9,000 rpm for 6 min. The supernatant was collected, and the dye concentration was measured at the λ
max previously indicated using an UV-Vis spectrophotometer (V-630 Jasco). All the experiments were done in duplicate. For comparison, a commercial carbon was used for dye adsorption experiments under the same conditions.
The adsorption capacity,
qt (mg g−1), was calculated as the amount of dye adsorbed at time t per mass unit of carbon following Equation (1):
where
Ci is the initial dye concentration (mg L−1),
Ct is the dye concentration at any time
t (h),
V is the volume of solution (L), and
m is the mass of adsorbent (g of oven dried (o.d.) carbon). The maximum
qt is referred to as
qmax and corresponds with the experimental maximum adsorption capacity.
The dye removal efficiency was determined as Equation (2):
Lagergren’s first order model, Equation (3) [
31] and Ho’s pseudo-second-order model, Equation (4) [
32] were used to describe dye kinetic adsorption:
where
qt and
qe are the amounts of dye adsorbed (mg g−1) at time t and equilibrium (h), respectively.
k1 (h−1) and
k2 (g mg−1 h−1) represent the rate constants for pseudo-first and pseudo-second order models, respectively. The adsorption mechanism was also evaluated by the intra-particle diffusion model, Equation (5) [
33].
where
I (mg g−1) is the intercept and
Kid is the rate constant of intra-particle diffusion (mg g−1 h−0.5).
3. Results and Discussion
Adsorbents characterization was carried out in a previous work [
29]. BET surface areas, S
BET, of PAN-C, PAN-S-C, PAN-C-Act and CAC were 36.3, 150.5, 3154.9 and 1059.9 m2 g-1, respectively, determined from N
2 adsorption isotherms at 77 K. The nitrogen sorption isotherms for PAN-C and PAN-S-C carbons were type I isotherms. PAN-C-Act showed a combination of type I and IV isotherms and CAC presented a type II isotherms adsorption. XPS analysis was also performed to determine the presence of nitrogen and sulphur-containing functional groups, resulting that the porous carbons fabricated from polyacrylonitrile had N groups in their structure such as pyrrolic N and pyridinic N, as well as C-N bonds. However, PAN-C-Act lost pyridinic N-groups during activation. PAN-C-S also showed S-rich groups, C-SO
2-C, sulphur and disulfide bonds. Moreover, the oxidation and activation stages provided a higher formation of carbonyl and hydroxyl groups. CAC showed only C=O and COOH groups.
The presence of hydroxyl groups determines the carbon acid-base character and reactivity. Moreover, the surface of carbon materials containing other surface groups, such as carboxylic, lactonic, phenolic, carbonyl, and etheric types makes their surface chemistry much more versatile than that of other adsorbents [
34]. As consequence the pollutants adsorption from aqueous solutions using activated carbons is complex and involves many parameters as solution pH, ionic strength, solute-solute and solute-solvent interactions [
35]. In this way, several series of dye adsorption experiments using the manufactured carbons and the commercial one have been carried out as a function of time at different conditions (
Table 2).
3.2. Effect of Initial pH
Dye solution pH affects notably to the entire adsorption process and particularly to the adsorption capacity of the materials [
15]. Hence, adsorption of red dye on carbons was studied as a function of pH at acid (1.9 – 2.3), natural (6 – 6.8) and alkaline pH (11.8 – 12.6) at the range of two initial concentrations (24 – 28 mg L−1 and 231 – 285 mg L−1) and carbon dosages essayed (0.43-0.53 and 1.73-1.91 g L−1) at 298 K and 48 h.
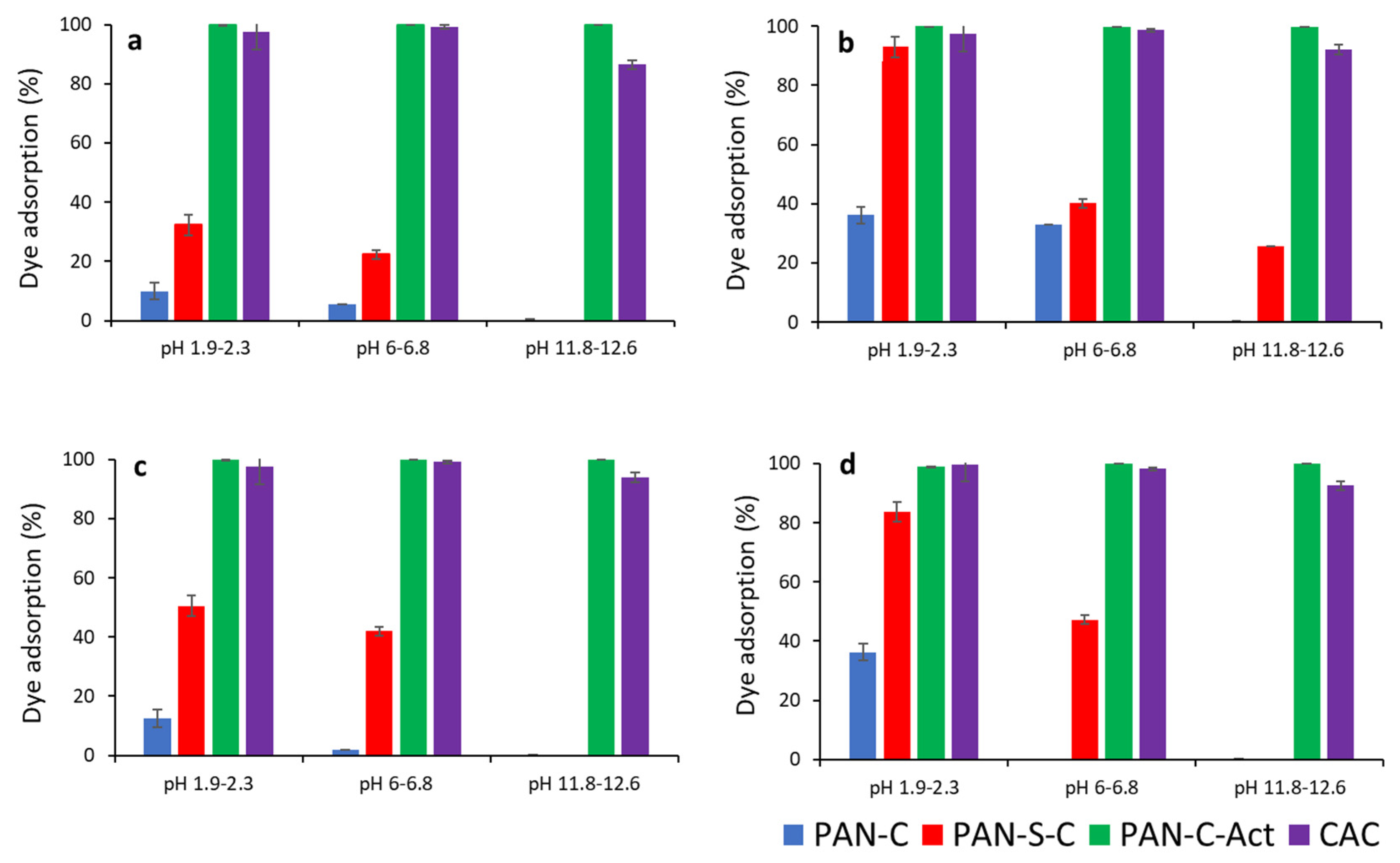
Figure 3 compares the effect of pH on dye removal efficiency for PAN-C, PAN-S-C, PAN-C-Act and CAC. pH affected the maximum adsorption efficiency for all carbons, especially for PAN-C and PAN-S-C, and the higher adsorption percentages were obtained at acid pH. Moreover, the PAN-C-Act carbon showed the best removal performance, even better than the commercial one, with adsorption yield (%) of approximately 100%. Considering the point of zero charge of carbons, at acid and natural pH, lower than pH
PZC (8.3 and 8.2 for PAN-C and PAN-S-C, respectively, and 7.4 for both PAN-C-Act and CAC) [
29], cationic functional groups predominate on the carbon surface while the surface is negatively charged at an alkaline pH. In addition, as found previously [
30], the dye is a weak acid (pK
a of 10.6), therefore, it, is greater adsorbed on cationic surfaces due to its anionic form in aqueous solution. This behaviour has also been evidenced by Al-Degs et al. [
36] with a commercial activated carbon F-400. Furthermore, the presence of oxygen functional groups, such as ketone and hydroxyl groups, gives basicity to the carbons surface with PAN-C-Act showing an increase in the oxygen content after KOH activation respect to the other two carbons [
29]. By the contrary, PAN-C is the carbon with the lowest removal efficiency, being the higher yield of 36.2% (5.1 mg g−1) at pH 2, adsorbent dosage (S/L = 1.7 g L−1) and initial concentration of 24 mg L−1. Besides this carbon has the lower BET surface area (36.3 m2 g−1) and pore volume (0.018 cm3 g−1) [
29], which can indicate that these characteristics are directly related to the adsorption capacity. The pH variations observed (
Table 2) are because as the dye concentration was increased the solution became slightly alkaline.
3.3. Effect of Carbon Structural Properties
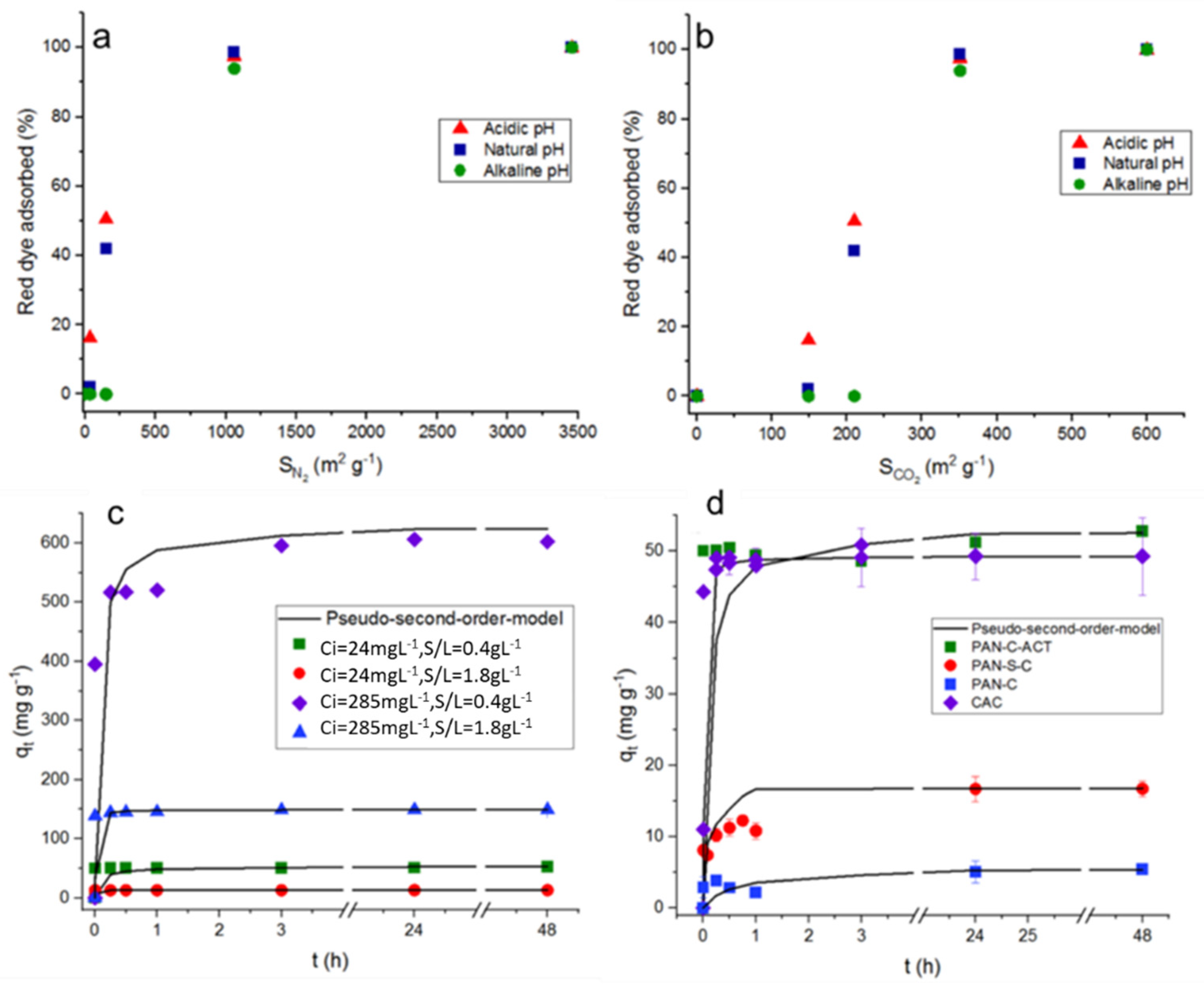
In general, it is usually considered that the materials with a greater surface area tend to adsorb better the molecules under study. To analyse more carefully the effect of surface area (measured by CO
2 at 273 K and N
2 at 77 K, [
29]) on dye adsorption, the surface areas of each carbon (PAN-C, 36.3; PAN-S-C, 150.5; PAN-C-Act, 3154.9; and CAC, 1059.9 m2 g-1) were related to the red dye adsorption percentages at acid, natural and basic pH (1.9 - 2.3; 6 - 6.8; 11.8 - 12.6), higher initial concentration (C
i, 231 - 285 mg L
−1) and lower carbon dosage (S/L, 0.43-0.53 g L
−1), as shown in
Figure 4a,b.
It can be observed that, in general, the adsorption percentage increases with the surface area increasing, independently of pH. As a result, in
Figure 4a it was observed that as the N
2 surface area tends to very low values, the adsorption efficiency tends to zero, however, the results in
Figure 4b indicate that the CO
2 surface area doesn’t contribute to the dye adsorption. So, adsorption percentages almost nil will be obtained, especially at alkaline pH, even with surface areas of nearly 150 m2 g−1. From previous studies [
37], it was concluded that the surface area determined with CO
2 at 273 K is generated by those pores in the ultramicroporosity range (d
p < 0.7 nm). Therefore, the results found would agree that a part of the surface area is not available for the dye adsorption due to a size exclusion phenomenon. This fact is very clearly observed for PAN-C (36.3 m2 g−1 with N
2 at 77 K and 148.7 m2 g−1 with CO
2 at 273 K) for which the surface area due to ultramicropores represents the 80 % of the total area [
29], and it is not available for dye access, showing low adsorption percentages in all conditions (
Table 2). By the contrary, PAN-S-C, which is also a non-activated carbon, but doped with sulphur, showed higher adsorption percentages, being the highest value, 92.0% (q
max, 11.9 mg g−1) at pH 2, S/L 1.9 g L−1 and 24 mg L−1 of initial dye concentration. The presence of S causes the formation of mesopores (68% of total pore volume) [
29] allowing the access of dye. As mentioned before, PAN-C-Act with a very large surface area containing high mesopore volume almost completely adsorbed the dye in all conditions essayed (
Table 2). From
Figure 4a, it possible to conclude that the results of dye adsorption correlate with the surface area determined with N
2 (without considering the area due to ultramicroporosity), and, therefore, making in a variable of major importance.
3.4. Effect of Initial Concentration and Adsorbent Dosage
The effect of initial dye concentration, which was varied from 24-28 mg L−1 to 231-285 mg L−1 depending on the carbon, affected to their adsorption performance (
Table 2). As it can be observed, for a fixed pH and adsorbent dosage (S/L), an increase of the dye initial concentration increased, in general, the adsorption capacity of all carbons with values up to 70.5, 252.7, 602.3 and 556.1 mg g−1 for PAN-C, PAN-S-C, PAN-C-Act and CAC, respectively, at pH ~ 2 and S/L ~ 0.5 g L−1 and C
i = 231-285 mg L−1. This behaviour is also showed in function of time for PAN-C-Act at the initial dye concentrations and adsorbent doses essayed (
Figure 4c).
The adsorbent dosage had a positive effect on the adsorption percentage of the dye increasing these values as shown in
Figure 3. If
Figure 3a is compared with 3b and 3c is compared with 3d, a general improvement of the adsorption percentages is observed for PAN-C and PAN-C-S at acid and natural pH, and even at alkaline pH for lower initial concentration (Ci, 24 – 28 mg L-1). Increasing of adsorbent dosage provides more active sites for dye to be adsorbed and increases the adsorption percentage as observed in
Table 2. On the contrary, the adsorption capacity of porous carbons decreases with increasing adsorbent dosage, as observed as well in
Table 2 and, specifically, for PAN-C-Act adsorption in
Figure 4c.
Figure 4d shows the red dye adsorption kinetic data for all carbons and the effect of type of adsorbent on dye adsorption at 298 K and 48 h (C
i, 24 - 28 mg L−1 and 0.43-0.53 g L−1). The use of PAN-C-Act together the CAC led to the better adsorption performance.
3.5. Adsorption Kinetic Modelling
Kinetic studies are important because they provide valuable information on the mechanism of the adsorption process [
38].
Figure 4d shows the influence of time on the red dye adsorption capacity of the porous carbons at pH ~ 2, observing a fast adsorption of the dye during the first minutes and reaching the maximum adsorption capacity after 24 h, 3 h and 15 minutes for PAN-C, PAN-S-C and PAN-C-Act, respectively, for all experiments performed. Moreover, although the PAN-C-Act reaches a slightly higher dye adsorption capacity than CAC,
Figure 4d shows that the CAC has a more favourable kinetic. This fact is probably due to the presence of smaller porous inside PAN-C-Act [
29] which significantly decreases the diffusivity of the dye in its porous structure.
Table 2 shows the kinetics parameters for the pseudo-second order and
Table 3 shows the intraparticle diffusion models together with the corresponding coefficients of determination for all experiments performed. For all carbons essayed, the pseudo-first-order model did not fit well to the experimental data with low R2 values. On the contrary, the pseudo-second order kinetic model explained better the adsorption behaviour, except for PAN-C at natural pH, obtaining determination coefficients higher than 0.96 (
Table 2). The dye diffusion mechanism into PAN-C and PAN-S-C has two simultaneous stages, external mass transfer followed by intraparticle diffusion as demonstrated by the fitting to the intraparticle diffusion model (
Table 3). PAN-C-Act and commercial activated carbon show a two-step adsorption mechanism, where in the first step there is a fast adsorption of the dye by the carbon. In the case of these materials do not fit well to the intraparticle diffusion model since in many cases the determination coefficients are lower than 0.5. In general, it is observed a good agreement between the calculated and experimental adsorption capacities for the pseudo-second order kinetic model (
Table 2 and
Figure 4c,d).
The adsorption process can be controlled by many factors including the nature of the functional groups present in the adsorbate and adsorbent, the textural and surface properties of the adsorbent, the diffusion behaviour of the adsorbate into the adsorbent, and the mechanism of the adsorbate-adsorbent interaction. In this work, the results suggested that the overall rate of red wood dye adsorption could be controlled by chemical processes between dye and carbons.
Table 4 shows dye adsorption capacities for commercial activated carbons published by other authors. It can be observed that the activated carbon PAN-C-Act prepared in this work showed, in general, higher adsorption capacity that those commercial ones and those prepared from other precursors (
Table 1), although, obviously, these values can be dependent on the type of dye used and the conditions applied.
4. Conclusions
Three porous carbons produced using PAN as precursor were used as adsorbents of a red wood dye present in aqueous solutions. pH affected the dye adsorption and, in general, the adsorption capacity for all carbons increased at acid pH. In addition, the initial dye concentration and carbon dosage affected considerably only the adsorption performance of N-doped carbon (PAN-C) and N,S co-doped carbon with sulphur (PAN-S-C). In case of N-doped activated carbon (PAN-C-Act) the maximum sorption yield (approximately 100%) was reached for all conditions essayed, with values higher than those obtained for the commercial activated carbon (CAC). This achievement was probably due to the development of porosity and a higher specific surface area. The pseudo-second order model fitted better the adsorption kinetics and the existence of external mass transfer followed by intra-particle diffusion was confirmed by the intraparticular diffusion model.
In general, the results obtained in the present work allow to conclude that the presence of microporosity in the materials, especially in the range of ultramicroporosity, has a negative effect on the dye adsorption since the size exclusion was observed. Despite the availability of surface area (mainly into the solid particles), adsorption is not attained because dye molecules do not have access to the carbon porous structure. Therefore, selection of carbons for the red dye removal must be done based not only in the chemical characteristics of the carbon surface and the total surface area available but also on pore size distribution to avoid dyes size exclusion.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation: M.S. Freire (M.S.F.), D.Gómez-Díaz (D.G.D.), J. González-Álvarez (J.G.A.) and M. Lazzari (M.L.); investigation: L. Domínguez-Ramos (L.D.R.), I. Tejado (I.T.); writing—original draft preparation: L.D.R.; writing—review and editing: M.S.F, D.G.D., J.G.A and M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades, grant number PGC2018-101047-B-I00 and Consellería de Educación, Universidade e Formación Profesional, grants number ED431B 2020/39 and ED431B 2020/13.
Additional Information Data Availability
All data regarding the work presented here is available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Bao, C.;Fang, C. L. Water resources flows related to urbanization in China: Challenges and perspectives for water management and urban development. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 531–552. [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R. P.; Egli, T.; Hofstetter, T. B.; Von Gunten, U.;Wehrli, B. Global water pollution and human health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 109–136. [CrossRef]
- Litefti, K.; Freire, M. S.; Stitou, M.;González-Álvarez, J. Adsorption of an anionic dye (Congo red) from aqueous solutions by pine bark. Sci. Reports 2019, 9, 16530. [CrossRef]
- Hessel, C.; Allegre, C.; Maisseu, M.; Charbit, F.;Moulin, P. Guidelines and legislation for dye house effluents. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 83, 171–180. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M. D.; Singh, A.; Khan, M. Z.; Tabraiz, S.; Sheikh, J. Current perspectives, recent advancements, and efficiencies of various dye-containing wastewater treatment technologies. J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 53, 103579. [CrossRef]
- Brookstein, D. S. Factors associated with textile pattern dermatitis caused by contact allergy to dyes, finishes, foams, and preservatives. Dermatol. Clin. 2009, 27, 309–322. [CrossRef]
- de Lima, A.; Bazo, A.P.; Fávero, D. M.; Rech, C. M.; de Palma, D.; de Aragão, G. Mutagenic and carcinogenic potential of a textile azo dye processing plant effluent that impacts a drinking water source. Mutat. Res. 2007, 626, 53–60. [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, P. A.; Umbuzeiro, G. A.; Oliveira, D. P.;Zanoni, M. V. B. Assessment of water contamination caused by a mutagenic textile effluent/dyehouse effluent bearing disperse dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 694–699. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.;Liu, Y. Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 352-365. [CrossRef]
- Garg, V. K., Amita, M., Kumar, R.;Gupta, R. Basic dye (methylene blue) removal from simulated wastewater by adsorption using Indian Rosewood sawdust: a timber industry waste. Dyes Pigment. 2004, 63, 243–250. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, E.; Alavi, M. R.;Hashemi, S. H. Investigation of decolorization kinetics and biodegradation of azo dye Acid Red 18 using sequential process of anaerobic sequencing batch reactor/moving bed sequencing batch biofilm reactor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 71, 43–49. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Jiang, X.; Tian, L. Adsorption behavior of direct red 80 and congo red onto activated carbon/surfactant: Process optimization, kinetics and equilibrium. Spectroc. Acta P.t. A- Molec. Biomolec. Spectr. 2015, 137, 1126–1143. [CrossRef]
- Al-Degs, Y.; Khraisheh, M. A. M.; Allen, S. J.; Ahmad, M. N.;Walker, G. M. Competitive adsorption of reactive dyes from solution: Equilibrium isotherm studies in single and multisolute systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 128, 163–167. [CrossRef]
- Munagapati, V. S.; Yarramuthi, V.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K. M.; Kim, D. S. Removal of anionic dyes (Reactive Black 5 and Congo Red) from aqueous solutions using banana peel powder as an adsorbent. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2018, 148, 601–607. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y-d.; Lin, Y-C.; Ho, S-H.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, N-q. Highly efficient adsorption of dyes by biochar derived from pigments-extracted macroalgae pyrolyzed at different temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 104–110. [CrossRef]
- Sangon, S.; Hunt, A. J.; Attard, T. M.; Mengchang, P.; Ngernyen, Y.; Supanchaiyamat, N.Valorisation of waste rice straw for the production of highly effective carbon based adsorbents for dyes removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1128–1139. [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B. H..; Din, A.T.M.; Ahmad, A. L. Adsorption of methylene blue onto bamboo-based activated carbon: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 819–825. [CrossRef]
- Mingjie, M.; Ying, H.; Cao, F.; Wang, Q.; Ai, N. Adsorption of Congo red on mesoporous activated carbon prepared by CO2 physical activation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 1069-1076. [CrossRef]
- Mohebali, S.; Bastani, D.; Shayesteh, H. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of a low-cost biosorbent for the removal of Congo red dye: Acid and CTAB-acid modified celery (Apium graveolens). J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1176, 181-193. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, X.; Hu, M.; Hu, X.; Zhou, M. Adsorption of Congo red from aqueous solution using ZnO-modified SiO2 nanospheres with rough surfaces. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 772-778. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen T. T. T.; Thien, T.V.; Du, P. D.; Chau, T. T.; Mau, T. X.; Khieu, D. Q. Adsorptive removal of Congo red from aqueous solution using zeolitic imidazolate framework–67. J Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2269-2280. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Hu, H.; Dong, H.; Zheng, M.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y. KNO3-mediated synthesis of high-surface-area polyacrylonitrile-based carbon material for exceptional supercapacitors. Carbon 2019, 152, 120–127. [CrossRef]
- Kim, B. H.; Yang, K. S.; Woo, H. G. Thin, bendable electrodes consisting of porous carbon nanofibers via the electrospinning of polyacrylonitrile containing tetraethoxy orthosilicate for supercapacitor. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 1042–1046. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shao, Y.; Mei, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Sun, J-k; Matyjaszewski, K.; Antonietti, M.; Yuan, J. Polymer-derived heteroatom-doped porous carbon materials. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9363–9419. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Wang, H.; Sun, M.; Damodaran, K.; Gottlieb, E.; Kopeć, M.; Eckhart, K.; Li, S.; Whitacre, J.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Kowalewski, T. Well-defined N/S co-doped nanocarbons from sulfurized PAN- b-PBA block copolymers: structure and supercapacitor performance. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 2467–2474. [CrossRef]
- Manoukian, M.; Tavakol, H.; Fashandi, H. Synthesis of highly uniform sulfur-doped carbon sphere using CVD method and its application for cationic dye removal in comparison with undoped product. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6904-6915. [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A. B. Highly porous S-doped carbons. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2012, 158, 318-323. [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, C. H.; Díaz-Fernández, L.; Gómez-Díaz, D.; Freire, M. S.; González-Álvarez, J. Separation of CO2 using biochar and KOH and ZnCl2 activated carbons derived from pine sawdust. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111378. [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Ramos, L.; Prieto-Estalrich, A.; Malucelli, G.; Gómez-Díaz, D.; Freire, M. S.; Lazzari, M.; González-Álvarez, J. N- and S-doped carbons derived from polyacrylonitrile for gases separation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3760. [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, C. H.; Freire, M. S.; Gómez-Díaz, D.; González-Álvarez, J. Removal of wood dyes from aqueous solutions by sorption on untreated pine (Pinus pinaster) sawdust. Cellulose 2023, 30, 4587-4608. [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe. K. Sven. Vetenskapsakademiens 1898, 24, 1–39.
- Ho, Y. S.;McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process. Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [CrossRef]
- Weber, W. J;Morris, J. C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31-59. [CrossRef]
- Carlos, A.; Leon y Leon, D.; Radovic, L. R. Interfacial chemistry and electrochemistry of carbon surfaces. Chem. Phys. Carb. 1994, 24, 213-310.
- Mattson, J. S.;Mark, H. B. Activated carbon: surface chemistry and adsorption from solution. Marcel Dekker, New York, 1971.
- Al-Degs, Y.; Khraisheh, M. A.; Allen, S. J.; Ahmad, M. N. Effect of carbon surface chemistry on the removal of reactive dyes from textile effluent. Water Res. 2000, 34, 927–935. [CrossRef]
- Kim, K. Ch.; Yoon, T-U.; Bae, Y-S. Applicability of using CO2 adsorption isotherms to determine BET surface areas of microporous materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 224, 294-301. [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, N. F.; Lima, E. C.; Royer, B.; Bach, M. V.; Dotto, G. L.; Pinto, L. AA.; Calvete, T. Comparison of Spirulina platensis microalgae and commercial activated carbon as adsorbents for the removal of Reactive Red 120 dye from aqueous effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241-242, 146–153. [CrossRef]
- Ribas, M. C.; Adebayo, M. A.; Prola, L. DT.; Lima, E.C.; Cataluña, R.; Feris, L.A.; Puchana-Rosero, M.J.; Machado, F.M.; Pavan, F. A.; Calvete, T. Comparison of a homemade cocoa shell activated carbon with commercial activated carbon for the removal of reactive violet 5 dye from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 248, 315–326. [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.;Nunes, N. Adsorption of a textile dye on commercial activated carbon: A simple experiment to explore the role of surface chemistry and ionic strength. J. Chem. Educ. 2015, 92, 143–147. [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D. A., Kyzas, G. Z., Avranas, A.;Lazaridis, N. K. Multi-parametric adsorption effects of the reactive dye removal with commercial activated carbons. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 213, 381–389. [CrossRef]
- Choy, K. K., Porter, J. F.; McKay, G. Langmuir isotherm models applied to the multicomponent sorption of acid dyes from effluent onto activated carbon. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2000, 45, 575–584. [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z.;Tezer, S. Biosorption of reactive dyes on the green alga Chlorella vulgaris. Process. Biochem. 2005, 40, 1347–1361. [CrossRef]
- Venkata Mohan, S., Chandrasekhar Rao, N.; Karthikeyan, J. Adsorptive removal of direct azo dye from aqueous phase onto coal based sorbents: a kinetic and mechanistic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 90, 189–204. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Structural formula of dye red GRA-200%.
Figure 1.
Structural formula of dye red GRA-200%.
Figure 2.
Scheme of the batch adsorption kinetic experiments carried out with PAN-C, PAN-S-C, PAN-C-Act and CAC.
Figure 2.
Scheme of the batch adsorption kinetic experiments carried out with PAN-C, PAN-S-C, PAN-C-Act and CAC.
Figure 3.
Effect of pH on dye adsorption (%) for PAN-C, PAN-S-C, PAN-C-Act and CAC. a) Ci, 24-28 mg L-1, S/L, 0.43-0.53 g L-1; b) Ci, 24-28 mg L-1, S/L, 1.73-1.91 g L-1, c) Ci, 230 – 285 mg L-1, S/L, 0.43-0.53 g L-1 and d) Ci, 230 – 285 mg L-1, S/L, 1.73-1.91 g L-1.
Figure 3.
Effect of pH on dye adsorption (%) for PAN-C, PAN-S-C, PAN-C-Act and CAC. a) Ci, 24-28 mg L-1, S/L, 0.43-0.53 g L-1; b) Ci, 24-28 mg L-1, S/L, 1.73-1.91 g L-1, c) Ci, 230 – 285 mg L-1, S/L, 0.43-0.53 g L-1 and d) Ci, 230 – 285 mg L-1, S/L, 1.73-1.91 g L-1.
Figure 4.
Top plots: Influence of surface area determined in PAN-C, PAN-S-C, PAN-C-Act and CAC with a) N2 at 77 K and b) CO2 at 273 K, on dye adsorption at 48 h (pH, 1.9 - 2.3; 6 - 6.8; 11.8 - 12.6, Ci, 230 - 285 mg L−1 and S/L, 0.43-0.53 g L−1). Plots below: Red dye adsorption kinetic data. The lines correspond to pseudo-second-order model. c) Effect of dye initial concentration (Ci, 24 and 285 mg L−1) and adsorbent dosage (0.45-0.47 and 1.86-1.89 g L−1) on adsorption capacity for PAN-C-Act at pH ~ 2 and 298 K. d) Effect of adsorbent on adsorption kinetics at 298 K (Ci, 24 - 28 mg L−1 and 0.43-0.53 g L−1).
Figure 4.
Top plots: Influence of surface area determined in PAN-C, PAN-S-C, PAN-C-Act and CAC with a) N2 at 77 K and b) CO2 at 273 K, on dye adsorption at 48 h (pH, 1.9 - 2.3; 6 - 6.8; 11.8 - 12.6, Ci, 230 - 285 mg L−1 and S/L, 0.43-0.53 g L−1). Plots below: Red dye adsorption kinetic data. The lines correspond to pseudo-second-order model. c) Effect of dye initial concentration (Ci, 24 and 285 mg L−1) and adsorbent dosage (0.45-0.47 and 1.86-1.89 g L−1) on adsorption capacity for PAN-C-Act at pH ~ 2 and 298 K. d) Effect of adsorbent on adsorption kinetics at 298 K (Ci, 24 - 28 mg L−1 and 0.43-0.53 g L−1).
Table 1.
Dyes adsorption capacities for carbon materials made from different precursors.
Table 1.
Dyes adsorption capacities for carbon materials made from different precursors.
| Precursor |
Activation |
Surface area (m2 g−1) |
Dye |
Adsorption capacity (mg g−1) |
Source |
| Banana peel |
--- |
--- |
Reactive Black 5 |
26.9 |
[14] |
| Congo red |
46.7 |
| Macroalgae (Ulothrix zonata) |
--- |
133.2 |
Malachite green |
5306.2 |
[15] |
| Crystal violet |
1222.5 |
| Congo red |
345.2 |
| Rice straws |
KOH |
1973.0 |
Methylene blue |
527.6 |
[16] |
| Congo red |
44.2 |
| H3PO4
|
392.6 |
Methylene blue |
34.7 |
| Congo red |
67.1 |
| CO2
|
214.7 |
Methylene blue |
44.2 |
| Congo red |
253.9 |
| Bamboo |
KOH |
1896.0 |
Methylene blue |
454.2 |
[17] |
| Sargassum fusiforme |
CO2
|
1329 |
Congo red |
234.0 |
[18] |
| H2SO4 modified celery residue |
--- |
24.93 |
Congo red |
238.09 |
[19] |
| ZnO-modified SiO2 nanospheres |
--- |
34.5 |
Congo red |
83.0 |
[20] |
| Zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 |
--- |
1388 |
Congo red |
714.3 |
[21] |
Table 2.
Experimental conditions essayed and kinetic parameters of the pseudo-second order and intra-particle diffusion models for the removal of red wood dye with CAC, PAN-C, PAN-S-C and PAN-C-Act carbons. *fits better for the first-order model (aqmax corresponds with the experimental maximum adsorption capacity and bqe are the amounts of dye adsorbed (mg g−1) at equilibrium time (h) according to model fit).
Table 2.
Experimental conditions essayed and kinetic parameters of the pseudo-second order and intra-particle diffusion models for the removal of red wood dye with CAC, PAN-C, PAN-S-C and PAN-C-Act carbons. *fits better for the first-order model (aqmax corresponds with the experimental maximum adsorption capacity and bqe are the amounts of dye adsorbed (mg g−1) at equilibrium time (h) according to model fit).
| Sample |
Experimental conditions |
Adsorbed dye percentage
(%) |
qmaxa
(mg g-1) |
Pseudo-second-order model |
|
| pH |
S/L
(g L-1) |
Ci
(mg L-1) |
|
k2
(g mg-1 h-1) |
qeb
(mg g-1) |
R2
|
|
| CAC |
2.0 |
0.53 |
24 |
97.4 |
43.7 |
1.733 |
43.9 |
1 |
|
| 2.0 |
0.44 |
250 |
97.5 |
556.1 |
0.032 |
555.6 |
0.99 |
|
| 2.0 |
1.76 |
24 |
97.4 |
13.3 |
11.772 |
13.0 |
0.99 |
|
| 2.0 |
1.91 |
250 |
99.8 |
130.3 |
0.593 |
129.87 |
1 |
|
| 6.1 |
0.5 |
25 |
99.2 |
55.2 |
0.550 |
54.9 |
0.99 |
|
| 6.5 |
0.46 |
234 |
99.1 |
506.6 |
0.01 |
500 |
0.99 |
|
| 6.0 |
1.75 |
24 |
98.6 |
13.5 |
1.663 |
13.5 |
0.99 |
|
| 6.5 |
1.74 |
236 |
98.2 |
133.2 |
1.186 |
129.9 |
1 |
|
| 12.6 |
0.43 |
25 |
86.4 |
49.9 |
0.260 |
49.5 |
0.99 |
|
| 12.1 |
0.45 |
259 |
93.9 |
545.8 |
0.012 |
526.3 |
0.99 |
|
| 12.6 |
1.74 |
26 |
92.1 |
13.8 |
15.093 |
12.9 |
0.99 |
|
| 12.1 |
1.78 |
260 |
92.6 |
135.0 |
0.047 |
133.3 |
0.99 |
|
| PAN-C |
2.0 |
0.44 |
24 |
9.9 |
5.4 |
0.351 |
5.4 |
0.99 |
|
| 2.3 |
0.45 |
256 |
12.5 |
70.5 |
0.008 |
67.1 |
0.96 |
|
| 2.0 |
1.70 |
24 |
36.2 |
5.1 |
0.254 |
4.9 |
0.98 |
|
| 2.0 |
1.87 |
256 |
35.8 |
49.0 |
0.029 |
47.8 |
0.99 |
|
| 6.0 |
0.44 |
24 |
5.5 |
0.3 |
0.307 |
2.3 |
0.99 |
|
| 6.5 |
0.48 |
231 |
2.0 |
9.6 |
— |
— |
— |
|
| 6.1* |
1.87 |
24 |
32.8 |
4.2 |
0.06
*k1 0.06 (h-1) |
3.6
*20.7 |
0.73
*0.93 |
|
| 6.5 |
1.80 |
231 |
0 |
0 |
— |
— |
— |
|
| 11.9 |
0.40 |
28 |
0 |
0 |
— |
— |
— |
|
| 11.8 |
0.40 |
278 |
0 |
0 |
— |
— |
— |
|
| 11.8 |
1.80 |
28 |
0 |
0 |
— |
— |
— |
|
| 11.8 |
1.80 |
259 |
0 |
0 |
— |
— |
— |
|
| PAN-S-C |
2.0 |
0.46 |
24 |
32.3 |
16.7 |
0.314 |
16.8 |
0.99 |
|
| 2.0 |
0.46 |
247 |
47.1 |
252.7 |
0.8 |
250.0 |
1 |
|
| 2.0 |
1.86 |
24 |
92.0 |
11.9 |
0.923 |
11.9 |
0.99 |
|
| 2.0 |
1.84 |
256 |
80.9 |
112.7 |
0.792 |
112.6 |
1 |
|
| 6.0 |
0.47 |
25 |
22.3 |
11.9 |
0.472 |
12.2 |
0.97 |
|
| 6.8 |
0.40 |
252 |
42.0 |
57.4 |
0.303 |
57.5 |
1 |
|
| 6.1 |
1.90 |
25 |
40.2 |
5.3 |
4.163 |
5.3 |
1 |
|
| 6.8 |
1.84 |
252 |
47.2 |
64.5 |
0.343 |
64.5 |
1 |
|
| 12.0 |
0.40 |
25 |
0 |
0 |
— |
— |
— |
|
| 12.1 |
0.40 |
258 |
0 |
0 |
— |
— |
— |
|
| 12.0 |
1.85 |
28 |
25.7 |
3.9 |
94.413 |
3.4 |
0.99 |
|
| 12.1 |
1.80 |
244 |
0 |
0 |
— |
— |
— |
|
| PAN-C-Act |
1.9 |
0.45 |
24 |
100.0 |
52.8 |
0.226 |
52.6 |
0.99 |
|
| 1.9 |
0.47 |
285 |
99.9 |
602.3 |
0.026 |
625.0 |
1 |
|
| 1.9 |
1.86 |
24 |
100.0 |
12.9 |
29.954 |
12.9 |
1 |
|
| 1.9 |
1.89 |
285 |
99.0 |
149.1 |
0.748 |
149.3 |
1 |
|
| 6.1 |
0.46 |
25 |
99.6 |
53.6 |
0.161 |
53.2 |
0.99 |
|
| 6.7 |
0.49 |
246 |
100.0 |
505.0 |
0.800 |
500.0 |
1 |
|
| 6.1 |
1.86 |
25 |
99.8 |
13.4 |
6.300 |
13.3 |
1 |
|
| 6.7 |
1.88 |
246 |
100.0 |
130.7 |
0.593 |
129.9 |
1 |
|
| 11.9 |
0.47 |
25 |
99.1 |
52.8 |
1.191 |
52.9 |
1 |
|
| 12.0 |
0.48 |
265 |
100.0 |
549.5 |
0.324 |
555.6 |
1 |
|
| 11.9 |
1.85 |
25 |
99.8 |
13.5 |
0.898 |
13.4 |
1 |
|
| 12.0 |
1.90 |
265 |
100.0 |
139.4 |
5.184 |
138.9 |
1 |
|
Table 3.
Experimental conditions essayed and intra-particle diffusion models for the removal of red wood dye with CAC, PAN-C, PAN-S-C and PAN-C-Act carbons.
Table 3.
Experimental conditions essayed and intra-particle diffusion models for the removal of red wood dye with CAC, PAN-C, PAN-S-C and PAN-C-Act carbons.
| Sample |
Experimental conditions |
Intra-particle-difussion model |
| pH |
S/L
(g L-1) |
Ci
(mg L-1) |
First stage |
Second stage |
K1d
(mg g-1 h-0.5) |
I1
(mg g-1) |
R2
|
K2d
(mg g-1 h-0.5) |
I2
(mg g-1) |
R2
|
| CAC |
2.0 |
0.53 |
24 |
61.35 |
18.24 |
0.50 |
0.06 |
44.78 |
0.03 |
| 2.0 |
0.44 |
250 |
503.67 |
190.16 |
0.55 |
6.02 |
516.29 |
0.79 |
| 2.0 |
1.76 |
24 |
16.53 |
5.63 |
0.44 |
0.11 |
12.45 |
0.41 |
| 2.0 |
1.91 |
250 |
176.73 |
59.34 |
0.44 |
0.12 |
128.92 |
0.02 |
| 6.1 |
0.5 |
25 |
80.07 |
20.36 |
0.58 |
0.06 |
54.34 |
0.14 |
| 6.5 |
0.46 |
234 |
553.11 |
66.56 |
0.85 |
25.43 |
362.05 |
0.67 |
| 6.0 |
1.75 |
24 |
19.001 |
5.47 |
0.47 |
0.04 |
13.23 |
0.59 |
| 6.5 |
1.74 |
236 |
175.85 |
59.12 |
0.44 |
0.05 |
130.55 |
0.01 |
| 12.6 |
0.43 |
25 |
79.60 |
16.14 |
0.54 |
0.67 |
45.06 |
0.19 |
| 12.1 |
0.45 |
259 |
317.18 |
114.40 |
0.76 |
24.67 |
371.74 |
0.77 |
| 12.6 |
1.74 |
26 |
71.14 |
16.97 |
0.61 |
0.86 |
44.12 |
0.29 |
| 12.1 |
1.78 |
260 |
378.18 |
98.76 |
0.80 |
24.70 |
371.14 |
0.77 |
| PAN-C |
2.0 |
0.44 |
24 |
5.51 |
1.23 |
0.57 |
0.51 |
2.15 |
0.93 |
| 2.3 |
0.45 |
256 |
89.38 |
10.25 |
0.84 |
6.49 |
21.47 |
0.90 |
| 2.0 |
1.70 |
24 |
47.13 |
8.62 |
0.67 |
3.06 |
26.87 |
0.99 |
| 2.0 |
1.87 |
256 |
20.32 |
2.94 |
0.95 |
0.10 |
20.62 |
0.03 |
| 6.0 |
0.44 |
24 |
0.28 |
0.01 |
0.96 |
0.02 |
0.35 |
0.92 |
| 6.5 |
0.48 |
231 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
| 6.1* |
1.87 |
24 |
0.47 |
0.27 |
0.85 |
— |
— |
— |
| 6.5 |
1.8 |
231 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
| 11.9 |
0.4 |
28 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
| 11.8 |
0.4 |
278 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
| 11.8 |
1.8 |
28 |
— |
— |
|
— |
— |
— |
| 11.8 |
1.8 |
259 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
0.92 |
| PAN-S-C |
2.0 |
0.46 |
24 |
11.68 |
3.77 |
0.62 |
1.28 |
10.35 |
0.93 |
| 2.0 |
0.46 |
247 |
355.72 |
93.88 |
0.52 |
0.72 |
249.18 |
0.99 |
| 2.0 |
1.86 |
24 |
13.22 |
1.05 |
0.96 |
0.47 |
10.80 |
0.72 |
| 2.0 |
1.84 |
256 |
258.27 |
41.39 |
0.42 |
1.08 |
107.45 |
0.94 |
| 6.0 |
0.47 |
25 |
8.04 |
1.62 |
0.91 |
— |
— |
— |
| 6.8 |
0.4 |
252 |
89.38 |
0.76 |
0.99 |
11.15 |
43.40 |
0.56 |
| 6.1 |
1.90 |
25 |
9.04 |
0.31 |
0.93 |
0.73 |
4.25 |
0.73 |
| 6.8 |
1.84 |
252 |
102.09 |
4.50 |
0.88 |
1.07 |
58.28 |
0.63 |
| 12.0 |
0.4 |
25 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
| 12.1 |
0.4 |
258 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
| 12.0 |
1.85 |
28 |
3.49 |
1.01 |
0.67 |
0.02 |
3.54 |
0.04 |
| 12.1 |
1.8 |
244 |
68.53 |
14.13 |
0.63 |
0.03 |
44.08 |
0.09 |
| PAN-C-Act |
1.9 |
0.45 |
24 |
44.81 |
23.55 |
0.38 |
0.41 |
49.65 |
0.89 |
| 1.9 |
0.47 |
285 |
736.27 |
168.26 |
0.56 |
12.85 |
529.11 |
0.60 |
| 1.9 |
1.86 |
24 |
11.39 |
6.01 |
0.38 |
0.02 |
12.83 |
0.84 |
| 1.9 |
1.89 |
285 |
181.03 |
60.86 |
0.37 |
0.59 |
145.57 |
0.65 |
| 6.1 |
0.46 |
25 |
48.72 |
23.48 |
0.42 |
0.15 |
51.4 |
0.12 |
| 6.7 |
0.49 |
246 |
351.37 |
223.0 |
0.48 |
1.93 |
515.53 |
0.27 |
| 6.1 |
1.86 |
25 |
16.28 |
5.8 |
0.34 |
0.01 |
13.28 |
0.04 |
| 6.7 |
1.88 |
246 |
115.07 |
58.85 |
0.39 |
0.20 |
129.25 |
0.49 |
| 11.9 |
0.47 |
25 |
65.86 |
23.11 |
0.35 |
0.09 |
52.48 |
0.32 |
| 12.0 |
0.48 |
265 |
552.79 |
274.65 |
0.25 |
0.28 |
560.43 |
0.30 |
| 11.9 |
1.85 |
25 |
16.12 |
5.83 |
0.34 |
0.09 |
12.92 |
0.34 |
| 12.0 |
1.90 |
265 |
140.21 |
69.01 |
0.25 |
0.01 |
139.09 |
0.47 |
Table 4.
Reported dye adsorption capacities for azo dyes for commercial activated carbons.
Table 4.
Reported dye adsorption capacities for azo dyes for commercial activated carbons.
| Supplier |
Dye |
qmax (mg g−1) |
Source |
| PAN-C |
Red GRA 200% |
70.5 |
This study |
| PAN-S-C |
252.7 |
| PAN-C-Act |
606.3 |
| CAC |
551.1 |
| Chemviron F-400 |
Remazol Golden Yellow |
714 |
[38] |
| Remazol Red |
278 |
| Remazol Black B |
213 |
| Merck |
Reactive Red 120 (RR-120) |
267 |
[38] |
| Reactive Violet f |
517 |
[39] |
| Panreac |
Mordant Blue 9 |
213 |
[40] |
| Fagron |
221 |
| Norit Darco |
Reactive Black 5 |
564 |
[41] |
| Norit R008 |
796 |
| Norit PK |
474 |
| Filtrasorb Corp E-400 |
Acid Yellow 117 |
156 |
[42] |
| Reactive Red |
112 |
[43] |
| Calgon Corp F-400 |
Direct Brown 1 |
8 |
[44] |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).