1. Introduction
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) represents a significant global public health concern. The prevalence of CKD is on an upward trajectory, exacerbated by demographic aging, escalating environmental pollution, and shifts in lifestyle patterns. The Global Burden of Disease Consortium predicts that CKD will become the top five leading diseases leading to life lost by 2040 [
1]. Beyond its direct impact on renal function, CKD substantially elevates the risk of myriad complications; notably, cardiovascular mortality rates in CKD patients are estimated to be 2 to 3 times higher than in the general population [
2], with hypertension prevalence ranging from 65% to 95% [
3]. Furthermore, diabetes emerges as the etiology for half of all end-stage renal disease (ESRD) cases [
4]. The current approach to the diagnosis of CKD predominantly encompasses traditional methodologies, including but not limited to blood and urine analyses, as well as imaging procedures (e.g., ultrasound, computed tomography [CT], magnetic resonance imaging [MRI]), renal biopsy, and histopathological examination [
5]. Nevertheless, it is observed that the precision of conventional diagnostic practices for CKD typically hovers around the 70% mark [
6]. The indistinct early symptomatology of CKD significantly enhances the risk of misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis, underscoring the imperative for more streamlined, rapid, and efficacious diagnostic approaches [
7].
The ancient Chinese medical book,
Huangdi Neijing (Inner Canon of Yellow Emperor), posits that “the kidney manifests in the ear,” suggesting a potential intimate link between ear health and kidney function. The nexus between CKD and auditory anomalies has garnered scholarly attention since the onset of the 20th century, with observational studies delving into the link between CKD and auditory function. These studies report an increased prevalence of sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) among patients with CKD, a type of hearing loss directly related to damage within the inner ear or auditory nerve [
8,
9,
10,
11]. However, research assessing the correlation between CKD and hearing loss has primarily focused on hearing loss at different frequencies, with insufficient consideration of other ear-related factors such as tympanic chamber measurements and otoscopic examinations. The variability in study outcomes may be attributed to differences in hearing assessment methodologies (pure-tone audiometry, threshold determination, surveys, etc.) and the influence of confounding factors [
12,
13]. Current research predominantly scrutinizes the correlation between CKD and auditory impairment without a unified stance on the sequential development of CKD and hearing loss or establishing a definitive causal relationship. To delve deeper into this domain, it is imperative to employ Mendelian randomization analysis to investigate the causal relationships between CKD-related factors and hearing disorders. We investigate the causal relationships between other specified disorders of kidney and ureter and age-related hearing impairment (MTAG), as well as the causality between kidney injury molecule levels and MTAG. Molecular markers of kidney injury have been identified as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of CKD, predicting the presence of CKD [
14], while other specified disorders of kidney and ureter are classified as subtypes of chronic kidney disease [
15].
In the realm of epidemiological research, Mendelian randomization stands as a formidable methodology, wherein genetic variability is leveraged to probe the causal linkage between risk elements and specific health conditions [
16]. The presence of confounders significantly impedes the process of causal deduction within these studies. Conversely, genetic variants utilized in Mendelian randomization investigations adhere to the principle of the stochastic allocation of alleles to progeny, mirroring the methodology intrinsic to randomized controlled trials [
17]. This technique effectively mitigates the influence of confounding variables and the issue of reverse causality that are prevalent in observational research, while also addressing concerns related to the representativeness and applicability seen in randomized controlled experiments [
18]. Consequently, the Mendelian randomization methodology was employed in this investigation to assess the association between factors related to chronic kidney disease and hearing impairment.
The investigation delved into the putative link between otologic indicators and CKD, further scrutinizing the causative associations between subtypes of CKD and auditory impairment. With the advent of information technology, an extensive compilation of clinical data has been amassed and analyzed, furnishing novel insights for the prognostication and diagnosis of ailments. Notably, the deployment of machine learning algorithms has manifested substantial benefits in enhancing diagnostic precision and forecasting disease susceptibility through the adept handling of voluminous linear and nonlinear datasets. Within the domain of CKD diagnosis, the precision of machine learning models has been documented to range between 80 and 90%, markedly surpassing that of conventional diagnostic techniques. Presently, an array of machine learning models, leveraging algorithms such as support vector machines, random forests, and artificial neural networks, are employed in the prediction of CKD. The datasets for these models are typically sourced from IBM Explorys, hospital records, and other repositories [
19,
20,
21,
22,
23].
This investigation represents the inaugural effort to assess the prognostic utility of otologic indicators for CKD. Employing multiple machine learning (ML) methodologies sourced from NHANES, which encompassed 12,392 participants, a novel predictive model for early detection of CKD based on auricular metrics was developed and validated. The predictive efficacy of this model was juxtaposed with that of pre-existing models to underscore the enhanced accuracy afforded by the ML algorithm, grounded in a data-driven otologic examination. It is anticipated that the fusion of TCM principles with contemporary medical technologies will pave the way for novel strategies and methodologies in the early detection of CKD, ameliorating patient outcomes, alleviating suffering, and enhancing quality of life.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
The NHANES, conducted by the United States National Health Statistics Service (NCHS), represents a pivotal cross-sectional survey designed to amass data regarding the health and nutritional status of the U.S. populace. This endeavor facilitates the acquisition of critical insights into the health conditions prevalent within the nation, thereby underpinning the formulation of informed policies by governmental entities. Endorsement of the NHANES survey protocol by the NCHS Research Ethics Review Board was secured, accompanied by the provision of informed written consent from all participants. Accessibility to the entire database (
https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/Default.aspx) has rendered the requirement for an ethics review in our research exempt [
24].
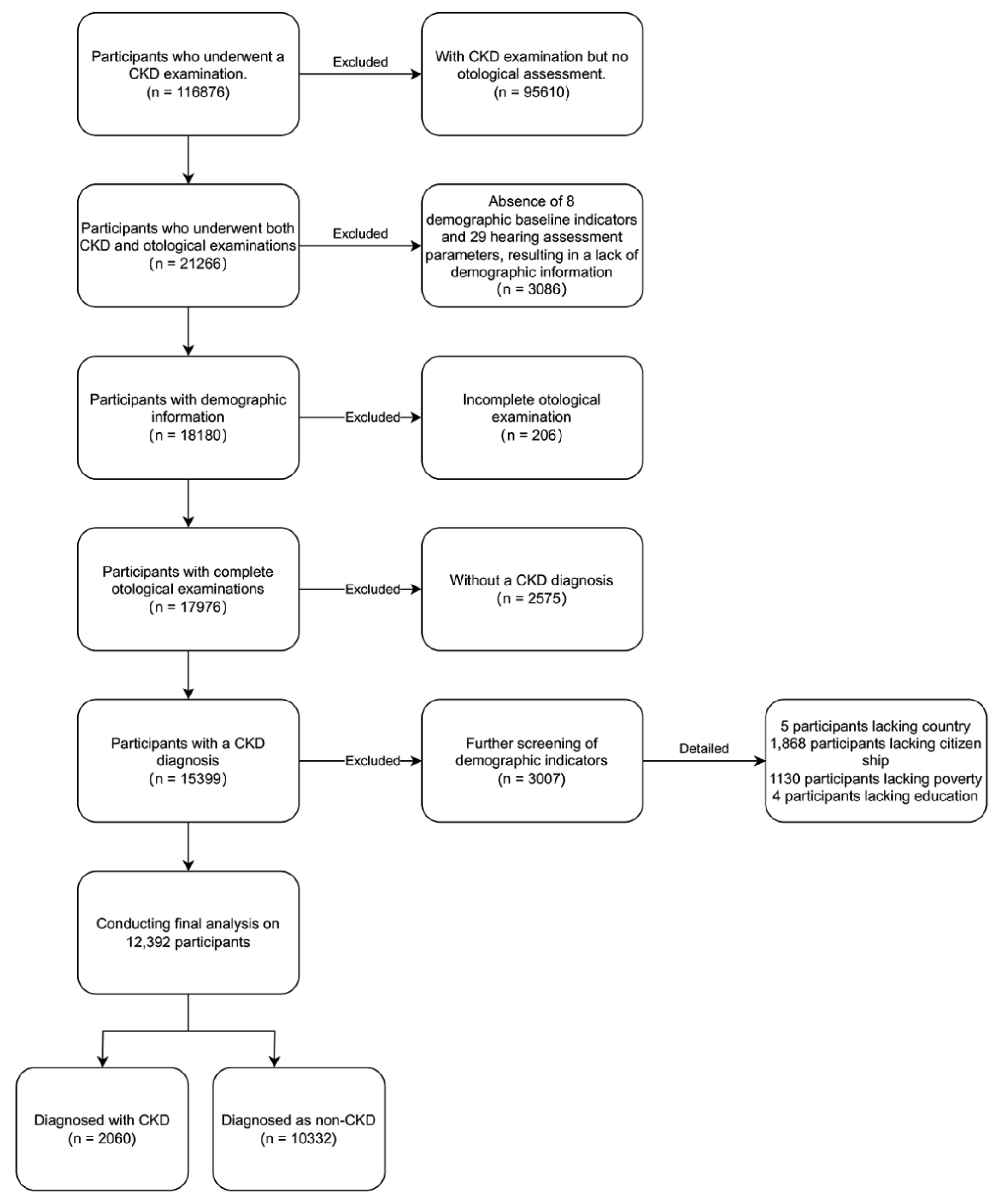
The cohort for this investigation was derived from NHANES dataset, covering the period from 2000 to 2020. Inclusion criteria mandated a diagnosis of CKD and the availability of comprehensive otology examination data. Individuals lacking complete baseline demographic information or missing audiological test results were systematically excluded (
Figure 1). Following rigorous selection criteria focused on extensive exposure assessment, a total of 12,392 participants were incorporated into the final analysis. This meticulous approach ensured the integrity and relevance of the data, which underpin further conclusions.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
In this study, a complex sampling design along with sampling weights, in alignment with the guidelines for analysis set forth by NHANES, was meticulously applied to ensure that the findings accurately reflect the demographic composition of the U.S. populace. This methodology facilitated precise estimations of the prevalence of CKD and its associated health metrics within the general population. For the initial data assessment, the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test was employed to elucidate disparities in the distribution of categorical variables, namely sex, race, and citizenship status, between individuals diagnosed with CKD and those without, while accommodating for stratification effects. Moreover, differences in continuous variables such as age and the poverty index between these groups were scrutinized using the t-test.
Subsequently, logistic regression was applied to identify auditory test measures associated with CKD. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was employed to ascertain the factors correlated with CKD. This methodology facilitated the discovery of specific variables significantly associated with an increased risk of CKD, allowing for the isolation of these effects from other confounding factors. Through this analytical approach, factors that maintained a significant association with CKD risk were identified, with the provision of corresponding odds ratios (ORs) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs), thereby enhancing the accuracy and relevance of the study’s outcomes.
Furthermore, Pearson’s correlation analysis was applied across 37 variables within the CKD dataset to quantify the extent of their influence on the condition’s presence or absence, with the correlation coefficients indicating the degree of association. This comprehensive analysis underscored the intricate interplay between various factors and CKD, thereby contributing to a deeper understanding of its epidemiology.
2.3. Mendelian Randomization Analysis
2.3.1. Data Sources
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have collated data on hearing impairment, various kidney and ureteral diseases, and kidney injury at the molecular level through the MRC IEU OpenGWAS data infrastructure [
25]. This research predominantly utilized exposure and outcome data derived from the UK Biobank (
http://www.nealelab.is/uk-biobank) and FinnGen Biobank (
https://www.finngen.fi/fi). Exposure data included 330,759 cases from the UK Biobank [
26]. Outcome data included 1301 cases from the UK Biobank [
27] and 424 cases alongside 217,185 controls from the FinnGen Biobank. (
Supplementary Table S1) Ethical clearance was secured for each component study prior to conducting the Mendelian Randomization (MR) Analysis. The UK Biobank, a forward-looking study, encompasses over half a million UK residents aged 40 to 69 at enrollment (2006-2010), and has amassed genome-wide genotyping and phenotypic data on a broad spectrum of traits.
2.3.2. Instrumental Variables
In this analysis, three sets of GWAS summary data for exposures were extracted (
Supplementary Table S1). Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the designated loci, exhibiting significance levels of 5 × 10
−8, were selected as instrumental variables. A fundamental principle of Mendelian Randomization (MR) dictates the absence of linkage disequilibrium (LD) among the chosen instrumental variables to preclude the emergence of biased outcomes. Accordingly, to evaluate LD among SNPs, cluster processing was undertaken with a stringent threshold (
R2 < 0.001 and a cluster distance of 10,000 kb), ensuring the reliability and integrity of the instrumental variables employed in this study.
2.3.3. Hypotheses
This two-sample Mendelian Randomization (MR) study is predicated on three foundational assumptions to mitigate bias. Firstly, the genetic instruments employed exhibit significant associations with the exposure. Secondly, the instrumental variables are not correlated with confounders influencing both exposure and outcome, ensuring their independence. Lastly, the instrumental variables exert influence on the outcomes solely via the exposure pathway, indicating the absence of horizontal pleiotropy wherein the instrumental variables would have effects on the outcomes that are not mediated through exposure [
28].
2.3.4. Data Analysis
A variety of analytical techniques were employed to explore potential causal inferences, encompassing inverse variance weighting (IVW) [
29], MR-Egger, weighted mode [
30], weighted median [
31], and simple mode [
32]. In scenarios devoid of horizontal pleiotropy, IVW findings were deemed robust [
33]. Heterogeneity was assessed utilizing the ‘mr_heterogeneity’ function within the “TwoSampleMR” R package, applying Cochran’s Q test for the IVW method and MR-Egger regression. Horizontal pleiotropy was examined through the ‘mr_pleiotropy_test’ function, also in the “TwoSampleMR” package, leveraging the MR-Egger approach. MR-Egger regression was then used to estimate the impact of pleiotropy, providing more reliable causal estimates after adjusting for pleiotropy under the presumption of no measurement errors and instrument strength being independent of direct effects [
34]. Should MR-Egger indicate pleiotropy, MR-PRESSO [
35] was employed to adjust for outliers. Leave-one-out analysis determined the causal influence of individual SNPs. The
F-statistic was calculated to ascertain the presence of weak instrument bias within the chosen instrumental variables, with
F > 10 suggesting the absence of such bias, thereby reinforcing the hypothesis of association. The formula for the
F-statistic is
, where ‘N’ represents the sample size of the exposure, and ‘R
2’ denotes the proportion of exposure variation explained by the instrumental variable [
36].
2.4. Construction of Machine Learning Model
Initially, data from NHANES underwent a cleaning process to extract relevant feature indicators and predictors. This process involved segregating features into continuous and categorical variables, applying one-hot encoding to categorical variables, and scaling continuous variables for normalization [
37].
Within the Python (Version 3.8) programming environment, the Scikit-learn library [
38] was utilized to construct nine machine learning models: Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random Forest Classifier (RF), Logistic Regression Classifier (LR), Gradient Boosting Classifier (GB), K-Nearest Neighbors Classifier (KNN), Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LGBM), CatBoost (CATB), Decision Tree (DT), and AdaBoost (AD). Hyperparameter optimization for these models was conducted using GridSearchCV, a method that combines grid search with cross-validation, to identify and store each model’s optimal settings. This optimization process employed a ten-fold cross-validation approach to assess model performance, ultimately selecting the combination of parameters that exhibited the best performance.
Following the principle of random stratified sampling, the dataset was partitioned into a training set and a test set in an 8:2 ratio. Subsequently, nine machine learning models were trained using this data partitioning.
2.5. Evaluation of Machine Learning Models
Utilizing the optimized parameters, the models were trained, and their performance metrics were computed, including the generation and comparison of classification reports and confusion matrices [
39]. Precision, recall, accuracy, F1 score, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) served as the evaluation criteria for the machine learning models [
40]. Additional analyses, such as precision-recall, decision boundary analysis, and Bootstrap ROC analysis, were conducted to further assess model performance [
39].
The Shapley Additive exPlanation (SHAP), a framework introduced by Lundberg and Lee [
41] for elucidating machine learning predictions, offers a novel approach to interpreting various complex models, providing interpretable insights that has been substantiated in prior research [
42]. In our study, SHAP values were employed to highlight critical features for the prediction of early-stage CKD, facilitating an examination of the pivotal factors that influence outcome predictions. This analysis delineated the impact of each significant feature on the predictive performance of the final machine learning model, enhancing our understanding of the model’s decision-making process.
2.6. Creation of Interactive Web Interface
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
A cohort comprising 12,392 individuals was recruited, with an average age of 43.3 years; among these, 2,060 were diagnosed with CKD while 10,332 were not, as summarized in
Table 1. Preliminary analysis of the baseline data revealed that the mean age of patients with CKD was significantly greater compared to those without CKD, with the majority of participants being non-Hispanic white. Regarding gender distribution, the non-CKD group exhibited a balanced ratio of male to female participants, whereas the CKD group had a predominance of female patients. Furthermore, notable disparities were observed between the CKD and non-CKD groups in terms of demographic characteristics, including economic status, race, citizenship, level of education, and household size, with all differences achieving statistical significance (
P < 0.05).
In the self-reported data (
Table 2), 84.1% of participants indicated either no perceived difference in hearing between their ears or were unaware of any disparity. The analysis of otoscopic screening data revealed a statistically significant variation in the incidence of excessive cerumen between the left and right ears among individuals with and without CKD, and the proportion of patients with cerumen excess in the CKD group was higher than that in the non-CKD group. Furthermore, significant discrepancies were noted in the outcomes of normal otoscopic examinations between the two groups (P<0.05), with a greater proportion of individuals in the non-CKD group exhibiting normal otoscopic findings compared to those in the CKD group.
AUX_G Hearing data file is displayed in
Table 3, (1) Analysis of bilateral tympanic chamber measurement data: there were significant differences in tympanic volume and compliance between CKD group and CKD group (
P < 0.05), but there was no statistical significance in middle ear pressure and tympanic width between subjects with and without CKD (
P > 0.05). (2) Analysis of hearing threshold data of pure tone air conduction measurement: The test thresholds of the left and right ears of the CKD group and the non-CKD group at all frequencies are significantly different, and the test results all show that the average hearing threshold of the CKD group is higher than that of the non-CKD group, that is, the average hearing loss of the CKD group is greater in different frequency groups.
3.2. Logistic Regression Analysis of Hearing Indicators
Upon examining the baseline data, we incorporated all pertinent data into the logistic regression analysis to identify factors contributing to CKD and their 95% CIs (
Table 4). The logistic regression model revealed:
(1) A negative correlation between the tympanic volume and compliance in both ears and CKD, indicating that as tympanic volume and compliance decrease, the odds of CKD increase (OR < 1, P < 0.05).
(2) No significant association was observed between tympanic pressure and width with CKD [OR = 1.00, 95% CI = (1.00, 1.00), P > 0.05].
(3) Hearing thresholds at various frequencies in both ears exhibited a positive correlation with CKD, implying that higher hearing thresholds are associated with an increased risk of CKD [OR = 1.02/1.03, P < 0.0001].
3.3. Correlation Analysis
Table 5 presents the ten most significant features as delineated by their correlation coefficients. The magnitude of the coefficient’s absolute value is directly proportional to the feature’s impact on the model’s predictive outcome. Specifically, a positive coefficient signifies a direct correlation with an increase in the feature value leading to a higher likelihood of the positive class, exemplified by the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease, whereas a negative coefficient denotes an inverse relationship. The elucidated correlation coefficients suggest that variables including citizenship, hearing threshold, and age possess considerable potential to influence the progression of CKD.
3.4. Mendelian Randomization Analysis
Following the clustering of SNPs and data harmonization, a total of 29 SNPs were identified as being associated with all outcomes.
Table S3 encapsulates the R2 and F-statistics pertaining to exposure, with all exposures demonstrating F-statistics greater than 10. This absence of weak instrument bias underscores the robust validity of all SNPs under consideration. (
Supplementary Table S3)
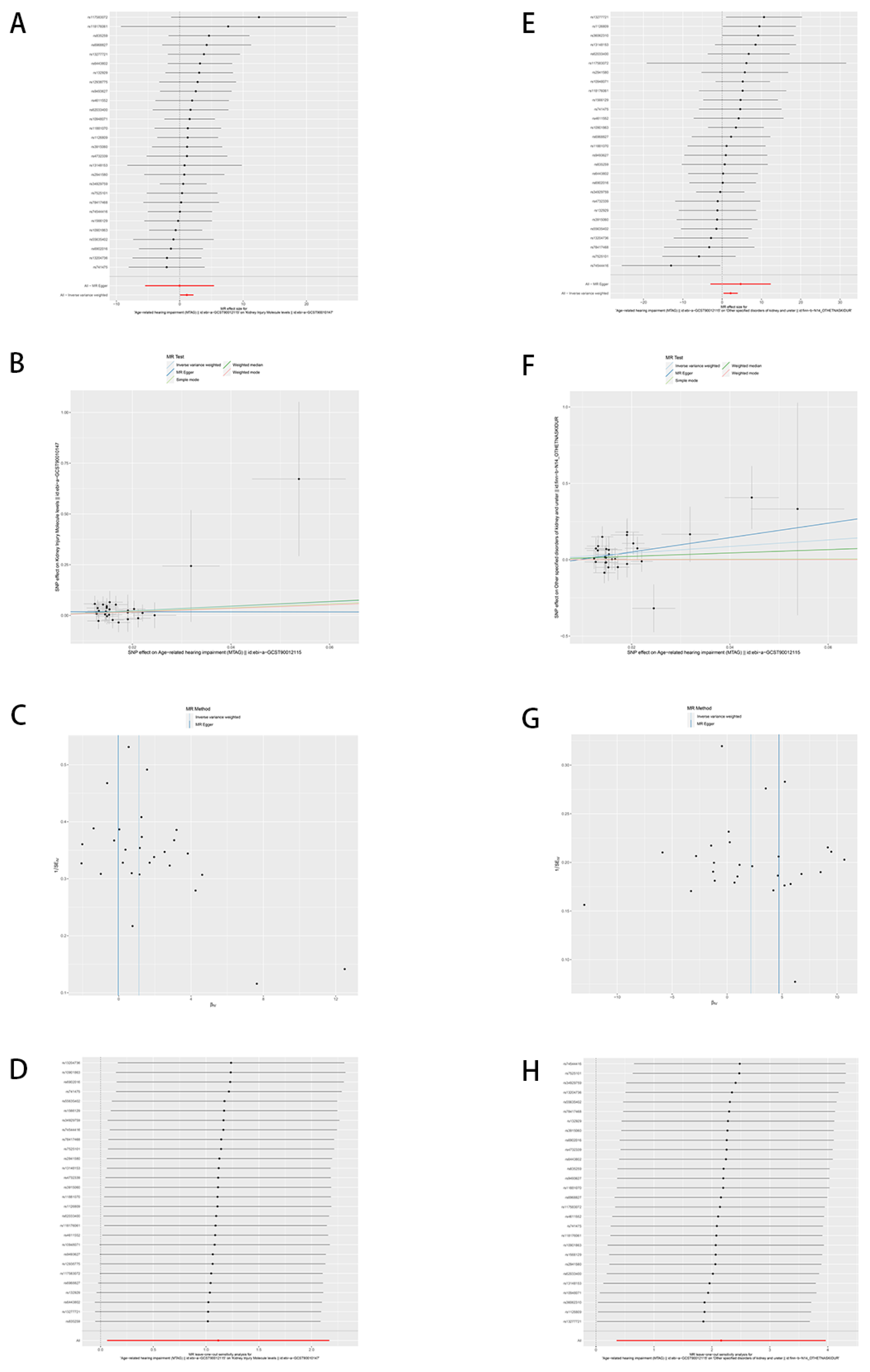
In our investigation of the causal relationships between certain chronic kidney disease factors and hearing impairment, as illustrated by scatter plots and forest plots (
Figure 2), the results indicate a significant positive correlation. The Inverse Variance Weighted (IVW) method reveals a causal relationship between MTAG and kidney injury molecule levels, demonstrating a significant positive correlation (
Figure 2, A) (β = 1.116, OR = 3.051, 95%CI: (1.064, 8.748),
P = 0.0379). This finding suggests that an increase in hearing impairment is associated with elevated levels of kidney injury markers. Despite an overarching positive trend across all five analytical methods (inverse variance weighting, MR Egger, simple mode, weighted median, and weighted mode) (
Figure 2, B), the wide confidence intervals introduce some uncertainty regarding the specific magnitude of this effect. Nonetheless, they uniformly affirm a statistically significant connection between MTAG and the kidney injury molecule levels. Furthermore, MTAG exhibited a causally significant and positive association with other specified disorders of kidney and ureter (
Figure 2E) (β = 2.160, OR = 8.673, 95% CI: (1.427, 52.728),
P = 0.0190), intimating that worsening hearing impairment is closely and significantly linked to an augmented risk of these conditions. While the five methodologies similarly indicate an overall positive correlation (
Figure 2, F), their extensive confidence intervals reveal some ambiguity regarding the impact’s definitive extent. (
Supplementary Table S4)
To assess the robustness of our study findings, further analyses were conducted on the included SNPs using MR-Egger and MR-PRESSO tests. These analyses did not detect any potential horizontal pleiotropy (
P > 0.05), (
Supplementary Table S5) indicating an absence of pleiotropic effects among the SNPs. However, it is noteworthy that funnel plots revealed a slight asymmetry (
Figure 2, C and G). Such asymmetry within the funnel plots suggests the presence of some degree of potential bias or heterogeneity among the study outcomes. While this does not directly undermine our findings, it prompts consideration of the possibility of unexplained minor biases or variations present in the data.
Adjusted Cochran Q statistics for the current analysis indicate significant heterogeneity among the SNP effects included in our study. (
Supplementary Table S5) Furthermore, leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was employed to assess the impact of each individual SNP on the overall causal relationship. (
Figure 2, D and H) As illustrated, the outcomes of this analysis demonstrate that systematically excluding each SNP and repeating the MR analysis does not result in any significant alterations to the observed causal relationship. This consistency across various iterations of the analysis reinforces the conclusion that the estimated effects are not driven by any single genetic variant. This finding substantiates the robustness of the causal inferences drawn from our data, suggesting that the genetic instruments constitute a well-distributed set that collectively contributes to the analysis.
3.5. Machine Learning model Construction
Nine machine learning models were developed, encompassing Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random Forest (RF), Logistic Regression (LR), Gradient Boosting (GB), K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LGBM), CatBoost (CATB), Decision Tree (DT), and AdaBoost (AD). Following the optimization of hyperparameters, the optimal settings for each model were determined. (
Supplementary Table S6)
3.6. Machine Learning Model Comparison and Evaluation
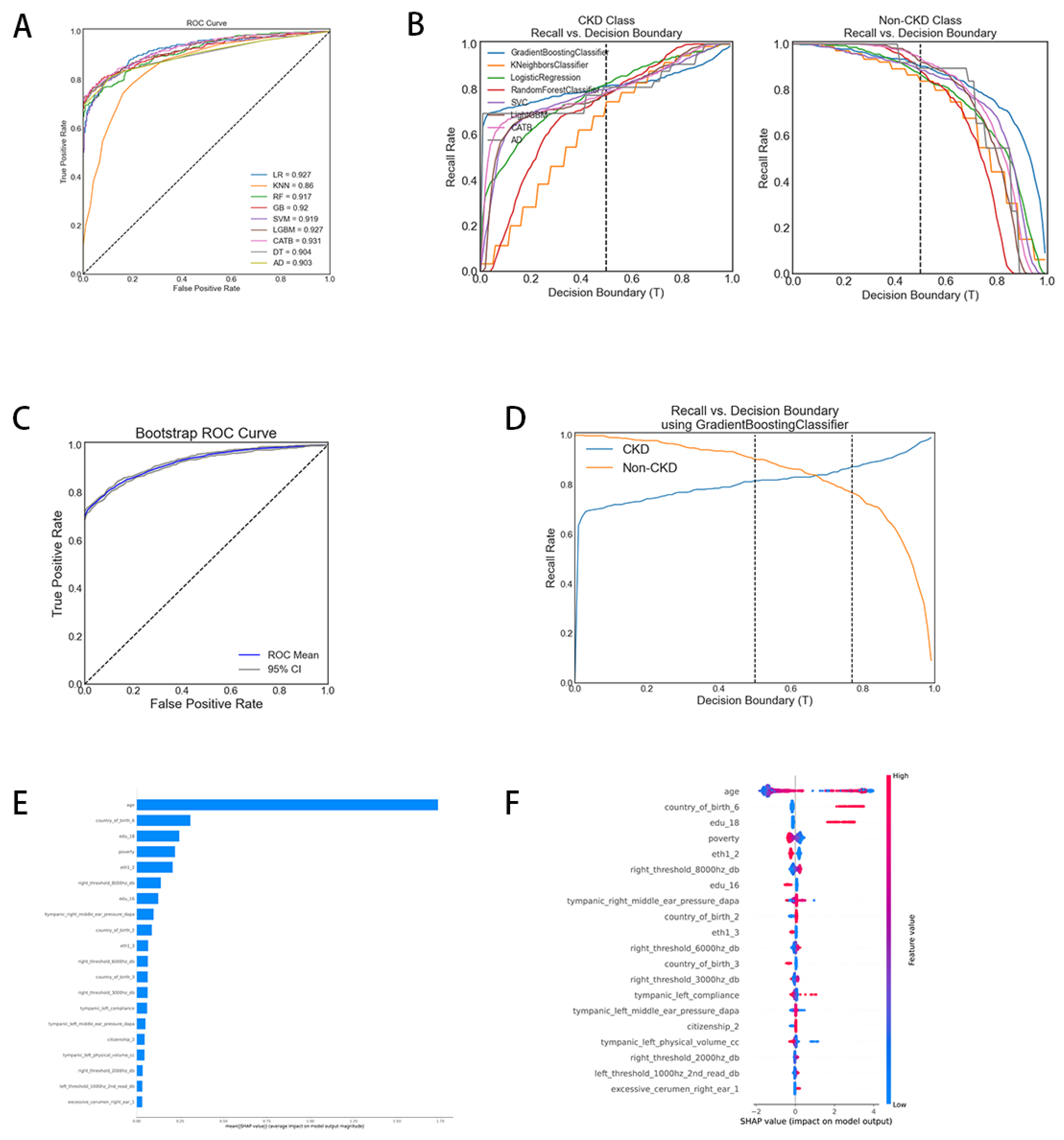
We embarked on a comparison and evaluation of various machine learning models for the binary classification of CKD, utilizing two distinct performance assessment methodologies. Initially, the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves during the training process were plotted (
Figure 3). This figure displays the ROC curve for each model, with the Area Under the Curve (AUC) scores provided in the legend. The AUC score quantifies the two-dimensional area beneath the entirety of the ROC curve, offering a comprehensive measure of performance across all classification thresholds. The proximity of the ROC curve to the top left corner of the chart signifies greater test accuracy. Correspondingly, an AUC score nearing 1 indicates the model’s proficiency in predicting positive cases while minimizing false positives. The figure illustrates our ROC curves closely aligned with the upper left corner, denoting high accuracy. CatBoost emerged with the highest AUC at 0.931, marking it as the most effective among the evaluated models. In contrast, the K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) model had the lowest AUC at 0.860, reflecting its poor trade-off between true positive and false positive rates. Subsequently, recall and decision boundary graphs were delineated (
Figure 3B), comprising separate charts for the CKD and non-CKD classes. Each line within these graphs represents the recall rate of distinct models across various decision boundary thresholds (T). For the CKD class (left graph), recall rates ascend with increasing decision boundaries, whereas for the non-CKD class (right graph), most models initially exhibit high recall rates, which then progressively diminish. This pattern indicates a trade-off in accurately classifying CKD versus non-CKD cases. The ideal threshold for balancing recall rates between these categories lies near the convergence or closest approach of the curves. The adjustment of recall rates is tailored to the specific requirements of the task at hand. CatBoost, Logistic Regression, and Light Gradient Boosting models notably achieve an optimal balance in overall performance.
Subsequently, we compared various metrics across nine machine learning models (Table 6). Accuracy, defined as the ratio of correct predictions to total predictions, indicates the model’s efficacy in correctly predicting labels. A higher accuracy denotes a greater number of correctly predicted labels. According to the results, the CatBoost model achieved the highest accuracy (0.862), signifying it had the highest percentage of correctly classified instances. Conversely, the KNN model exhibited the lowest accuracy, indicating the highest number of classification errors.
Regarding the AUC, the CatBoost model demonstrated superior performance, closely followed by Logistic Regression and Light Gradient Boosting Machine, suggesting these models excel in distinguishing between categories. When assessing accuracy, the CatBoost model also ranked highest, with Decision Tree and Gradient Boosting models trailing closely behind.
Further analysis of model performance, as per Table 6, reveals that among all models, CatBoost exhibits an exceptionally high recall rate for the non-CKD class and the best precision for the CKD class, with high F1 scores for both categories. CatBoost appears to maintain the optimal overall balance between accuracy and recall across these two categories. The KNN model underperforms in predicting CKD, manifesting the lowest F1 score for this category. The Decision Tree model shows a very high recall for the non-CKD class, indicating a potential overprediction of this category at the expense of precision for the CKD class. When considering both macro and weighted averages, CATB also performs well in terms of accuracy, recall and F1 scores. It was positioned as a potentially superior model for this dataset based on these metrics. GB and DT also demonstrate strong performance, albeit slightly inferior to CATB.
Consequently, considering its superior overall performance, we have selected CatBoost as our preferred model, characterized by an AUC of 0.931 and an accuracy of 0.862. The stability and discriminative capacity of the model are further corroborated by the Bootstrap ROC curve (
Figure 3, C), with the 95% confidence interval closely hugging the mean line, indicating consistent model performance across different samples. The recall versus decision boundary graph (
Figure 3, D) illustrates that within the threshold range of 0.5 to 0.75, the model achieves an optimal balance between identifying CKD cases and maintaining a low false-positive rate. These findings underscore the CatBoost model’s capability to accurately identify positive cases while minimizing misdiagnoses, making it particularly well-suited for scenarios requiring precise identification of CKD cases.
Subsequently, we employed SHAP values to elucidate how various variables influence CKD predictions within the model.
Figure 3E illustrates the top 20 risk factors assessed by average absolute SHAP values.
Figure 3F highlights the 20 most significant features within our model. It was observed that age stands out as the most critical feature, exerting a substantial average impact on the model’s output magnitude. Additionally, several demographic factors, such as place of birth, education level, poverty status, and ethnicity, also significantly influence the model. Hearing-related variables, like “right_threshold_8000hz_db” and “tympanic_right_middle_ear_pressure_dapa,” play an important role in the model’s decision-making process.
Ultimately, we have established a website that utilizes the CatBoost algorithm to predict CKD from auditory and demographic data, available at (
https://guanmiao.shinyapps.io/machinelearningckd88/). This platform features a user-friendly interface that permits the entry of clinical characteristics for new samples. This web application also offers predictions regarding the likelihood of CKD presence or absence, tailored to the specifics of the user-provided information.
4. Discussion
In this study, we explored interpretable ML approaches utilizing auditory and demographic indicators from the US NHANES data spanning from 2000 to 2020, aimed at identifying CKD. The study encompassed 12,392 participants, including 2,060 individuals diagnosed with CKD. By comparing the baseline characteristics of the CKD and non-CKD groups, we observed that individuals with CKD were, on average, older and that there was a higher proportion of females among these patients. Additionally, significant correlations were identified between CKD and various demographic factors such as economic status, race, citizenship, level of education, and household size, underscoring the importance of considering demographic characteristics in CKD research and management. Most participants perceived their hearing in both ears to be similar. However, otoscopic examinations revealed significant differences between the CKD and non-CKD groups in terms of cerumen excess and otoscopic results. Furthermore, a positive correlation was observed between hearing thresholds and CKD, indicating greater average hearing loss within the CKD group. These results suggest that auditory indicators may serve as critical health markers for individuals with CKD. Through Mendelian randomization analysis, we discovered causal relationships between certain factors of CKD and hearing impairment. Significantly, our research elucidated substantial causal associations between other specified disorders of kidney and ureter and age-related hearing impairment, as well as establishing the causality between kidney injury molecule levels and MTAG. These findings, based on extensive clinical data, not only reinforce the potential biological connection between CKD and hearing but also represent a pioneering investigation into the causal relationship between factors associated with CKD and hearing impairment. Additionally, they provide a theoretical foundation for ML models that use auditory and demographic indicators for the early prediction of CKD.
Among nine ML models, the CATB model achieved the best performance, ultimately being selected to identify CKD. Tested across various metrics, the CATB model demonstrated an average AUC of 0.931, indicating efficient and stable classification capabilities, coupled with a high accuracy of 0.862, as well as superior F1-score, recall, and other metrics. Nevertheless, different models possess distinct advantages; some may excel in identifying CKD patients, while others may be better at confirming non-CKD cases. The choice of model might depend on clinical requirements. If minimizing false negatives is paramount, models with a high recall rate for the CKD category at the selected threshold would be preferable. Conversely, if reducing false positives is more critical, models with a high recall rate for the non-CKD category would be favored. The CATB model demonstrates robust and stable performance in classifying diseases such as CKD, striking an excellent balance between identifying actual cases and avoiding false positives. Yet, the precise balance between recall and precision can be adjusted according to the specific costs associated with false negatives and false positives in the application domain, allowing for fine-tuning of decision thresholds to achieve the balance required for practical use [
43].
In
Table 7, we catalog a range of machine learning models previously employed for predicting CKD. Comparative analysis reveals that our model exhibits a higher AUC, denoting a superior capability in distinguishing between CKD and non-CKD instances. This elevated discriminative proficiency not only underscores the model’s robustness but also its reliability in generating predictions. Moreover, the balanced performance of our model across accuracy, recall, and F1 scores highlights its efficacy in managing the binary classification of CKD and non-CKD categories. Notably, a high recall rate for the positive category ensures that the model rarely overlooks actual cases of CKD, a critical requirement for medical diagnostics. The considerable size of our dataset offers multiple advantages. It mitigates the risk of overfitting, a common challenge in machine learning models, thereby enhancing the model’s ability to generalize well to new data. Additionally, it addresses issues related to class imbalance, a frequently encountered concern in medical datasets where one category may disproportionately represent. The extensive dataset also diminishes the impact of noise or incorrect data, contributing to the robustness of our predictive model.
CKD is defined as persistent abnormalities in kidney structure or function for more than three months [
44]. Diagnosis primarily relies on routine screening or incidental findings through serum chemistry features and urinalysis, followed by confirmatory imaging studies (e.g., ultrasound, CT, MRI), renal biopsy, and histopathological examination [
5]. Traditional machine learning (ML) models for early diagnosis of CKD typically utilize predictors derived from blood and urine tests along with demographic indicators. Our methodology introduces a pioneering approach by integrating auditory examination indicators with demographic predictors for CKD forecasting. These predictive markers are more readily accessible than traditional blood and urine analyses, requiring merely an ear examination and
Supplementary Information gathered through a brief survey. Consequently, this predictive model can be broadly applied across various levels of medical institutions, from primary care to specialized clinics. Our research delves deeper into the association and causality between auditory indicators and CKD, pioneering a CKD prediction model based on auditory metrics. We assessed the significance of auditory indicators within the model using SHAP values, revealing their notable importance. This innovative approach to CKD detection offers enhanced convenience, cost-effectiveness, and accuracy, presenting a valuable instrument poised to advance early and broader CKD screening, particularly in environments where conventional methods are less accessible.
The model, leveraging data from the NHANES, principally mirrors the demographic characteristics of the U.S. population, including a higher proportion of African American and Hispanic individuals [
24]. However, it does not comprehensively encompass global diversity, which may limit its applicability worldwide. The reliance on auditory examination metrics may overlook other critical medical indicators essential for the diagnosis of CKD. Clinical validation emerges as a pivotal next step, necessitating the testing of the model within clinical settings to ensure the reliability and adaptability of its predictions.
In summary, we have employed innovative otologic indicators in conjunction with demographic indicators as predictors, subsequently transforming them into a promising tool for the expedited screening of CKD. It is meritorious for future studies to test the model incorporating ear examinations in actual clinical settings, thereby enhancing its potential for wider application and adoption. More importantly, further investigations into whether interventions targeting these factors could reduce the incidence of CKD are warranted, thereby facilitating precise early-stage prevention and intervention.
5. Conclusions
Our investigation leverages NHANES data spanning from 2000 to 2020, with a focus on otologic indicators and demographic factors to identify CKD. The study elucidates the correlation and causation between CKD and auditory impairments, serving as the foundation for the development of a robust machine learning model. Notably, the CatBoost algorithm emerged as the most efficacious, exhibiting an average AUC of 0.931. Compared to traditional blood and urine tests, this novel approach herald new avenues for CKD screening, minimizing the risk of misdiagnoses or overlooked cases, and demonstrating potential for broader application across various medical settings. However, further clinical validation is required to ensure the predictive relevance of the model and its adaptability in real-world healthcare environments. This study synergizes traditional medical theories with contemporary technology, offering a simplified and more effective tool for the early detection of CKD.
6. Patents
There are no patents resulting from the work reported in this manuscript.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org. Table S1: Summary of the GWAS included in this study; Table S2: Quantization rule; Table S3: Details of each SNP in Mendelian randomization; Table S4: Causal evaluation results of five methods of Mendelian randomization; Table S5: Mendelian randomization results for heterogeneity and horizontal pleiotropy; Table S6: Optimal parameters of nine machine learning models after hyperparameter optimization.
Author Contributions
Y.Y. and L.Y. contributed equally and were responsible for the conception and design. N.Z., J.X., and Y.Z. provided important guidance for the design of the research. Y.Y. primarily handled data analysis and interpretation, drafting the article, and critical revision. L.Y. was mainly responsible for data acquisition, data analysis, and approval of the final manuscript. H.Z., L.R., C.Z. participated in parts of the manuscript writing and data preparation, and manuscript review. Z.N. was involved in the review of the manuscript. N.Z., J.X., and Y.Z. offered multiple critical suggestions for the writing of the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part or in whole by grants from the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (RCBS20200714114820147); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M670051); Shenzhen Postdoctoral Fellowship (S229201013); National Natural Science Foundation of China (82100506, 22307083); Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2023A1515010816) and Guangzhou Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2024A04J4983).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chen, T.K.; Hoenig, M.P.; Nitsch, D.; E Grams, M. Advances in the management of chronic kidney disease. BMJ 2023, 383, e074216. [CrossRef]
- Gansevoort, R.T.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Jafar, T.H.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Mann, J.F.; Matsushita, K.; Wen, C.P. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet 2013, 382, 339–352. [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, R.; Suhail, F.; Lerma, E.V. Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease. Disease-a-Month 2015, 61, 387–395.
- Ling, J.; Ng, J.K.C.; Chan, J.C.N.; Chow, E. Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Assessment and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 869899. [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Jafar, T.H.; Nitsch, D.; Neuen, B.L.; Perkovic, V. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2021, 398, 786–802. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, X.; Luo, J.; Chen, W.; Yang, M.; Wang, L.; Zhu, N.; Yuan, W.; Gu, L. Choosing an appropriate glomerular filtration rate estimating equation: role of body mass index. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, D.; He, W.; Liu, Y.; Jin, J.; He, Q.; Lin, B. Misdiagnosis of chronic kidney disease and parathyroid hormone testing during the past 16 years. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Boateng, J.O.; Boafo, N.; Osafo, C.; Anim-Sampong, S. Hearing impairment among chronic kidney disease patients on haemodialysis at a tertiary hospital in Ghana. Ghana Med J. 2019, 53, 197–203. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, B.; Lim, S.H.; Ahn, Y.H.; Kang, H.G.; Ha, I.-S.; Cheong, H.I. Renal Syndromic Hearing Loss Is Common in Childhood-onset Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Korean Med Sci. 2020, 35, e364. [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.J.; Choi, H.G.; Wee, J.H. Association between Chronic Kidney Disease and Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Studies Using ICD-10 Codes in a National Health Screening Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2861. [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-L.; Shih, C.-P.; Chan, J.-S.; Chung, C.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Tsao, C.-H.; Lin, F.-H.; Chien, W.-C.; Hsiao, P.-J. Investigation of the relationship between sensorineural hearing loss and associated comorbidities in patients with chronic kidney disease: A nationwide, population-based cohort study. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0238913. [CrossRef]
- Sarin, V.; Sharma, A.; Chopra, I. High Frequency Hearing Loss in Chronic Renal Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 74, 4046–4052. [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Singh, C.V. Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e48244. [CrossRef]
- Rysz, J.; Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Franczyk, B.; Jabłonowski, Z.; Ciałkowska-Rysz, A. Novel Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease and the Prediction of Its Outcome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1702. [CrossRef]
- ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N28.89 - Other Specified Disorders of Kidney and Ureter Available online: https://icdlist.com/icd-10/N28.89#google_vignette (accessed on 8 April 2024).
- Titova, O.E.; Michaëlsson, K.; Larsson, S.C. Sleep Duration and Stroke: Prospective Cohort Study and Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Stroke 2020, 51, 3279–3285. [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Smith, G.D. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ 2018, 362, k601. [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [CrossRef]
- Ravizza, S.; Huschto, T.; Adamov, A.; Böhm, L.; Büsser, A.; Flöther, F.F.; Hinzmann, R.; König, H.; McAhren, S.M.; Robertson, D.H.; et al. Predicting the early risk of chronic kidney disease in patients with diabetes using real-world data. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 57–59. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, P.; Wu, H.; Su, G. A nomogram to predict the in-hospital mortality of patients with congestive heart failure and chronic kidney disease. ESC Hear. Fail. 2022, 9, 3167–3176. [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Zhang, X.; He, K.; Chen, Y.; Wu, N. Individualized prediction of chronic kidney disease for the elderly in longevity areas in China: Machine learning approaches. Front. Public Heal. 2022, 10, 998549. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Ding, R.; Xu, X.; Guan, H.; Feng, X.; Sun, T.; Zhu, S.; Ye, Z. Comparison and development of machine learning tools in the prediction of chronic kidney disease progression. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hong, Q.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Xi, Y.; Shi, J.; et al. Prediction of 3-year risk of diabetic kidney disease using machine learning based on electronic medical records. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- National Center for Health Statistics. NHANES - About the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. [Accessed 2023 Dec 8].;
- The MRC IEU OpenGWAS Data Infrastructure. bioRxiv https://www.biorxiv.org/ content/10.1101/2020.08.10.244293v1 (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Kalra, G.; Milon, B.; Casella, A.M.; Herb, B.R.; Humphries, E.; Song, Y.; Rose, K.P.; Hertzano, R.; Ament, S.A. Biological insights from multi-omic analysis of 31 genomic risk loci for adult hearing difficulty. PLOS Genet. 2020, 16, e1009025. [CrossRef]
- Gilly, A.; Park, Y.-C.; Png, G.; Barysenka, A.; Fischer, I.; Bjørnland, T.; Southam, L.; Suveges, D.; Neumeyer, S.; Rayner, N.W.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing analysis of the cardiometabolic proteome. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Coneys, R.; Storm, C.S.; Kia, D.A.; Almramhi, M.; Wood, N.W. Mendelian Randomisation Finds No Causal Association between Urate and Parkinson’s Disease Progression. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2182–2187. [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian Randomization Analysis With Multiple Genetic Variants Using Summarized Data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Smith, G.D.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiology 2016, 40, 304–314. [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Timpson, N.; Smith, G.D. Mendelian randomization: Using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 1133–1163. [CrossRef]
- Yavorska, O.O.; Burgess, S. MendelianRandomization: An R Package for Performing Mendelian Randomization Analyses Using Summarized Data. Int J Epidemiol 2017, 46, 1734–1739. [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting Findings from Mendelian Randomization Using the MR-Egger Method. Eur J Epidemiol 2017, 32, 377–389. [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, N.; Dimou, N.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Banbury, B.; Martin, R.M.; Lewis, S.J.; Kazmi, N.; Robinson, T.M.; Albanes, D.; Aleksandrova, K.; et al. Physical activity and risks of breast and colorectal cancer: a Mendelian randomisation analysis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, P.; Bautista, M.A.; Gonzàlez, J.; Escalera, S. Beyond one-hot encoding: Lower dimensional target embedding. Image Vis. Comput. 2018, 75, 21–31. [CrossRef]
- Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python | The Journal of Machine Learning Research Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/1953048.2078195 (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Fawcett, T. An Introduction to ROC Analysis. Pattern Recognition Letters 2006, 27, 861–874. [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M.W. Evaluation: From Precision, Recall and F-Measure to ROC, Informedness, Markedness and Correlation 2020.
- A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions | Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/ 10.5555 /3295222.3295230 (accessed on 30 March 2024).
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.G.; Lee, S.-I. Consistent Individualized Feature Attribution for Tree Ensembles 2019. [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Goadrich, M. The Relationship between Precision-Recall and ROC Curves. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on Machine learning; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, June 25 2006; pp. 233–240. [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E.; Bilous, R.W.; Coresh, J.; Francisco, A.L.M.D.; Jong, P.E.D.; Griffith, K.E.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Iseki, K.; Lamb, E.J.; et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney International Supplements 2013, 3, 1–150. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).