Submitted:
31 July 2024
Posted:
02 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
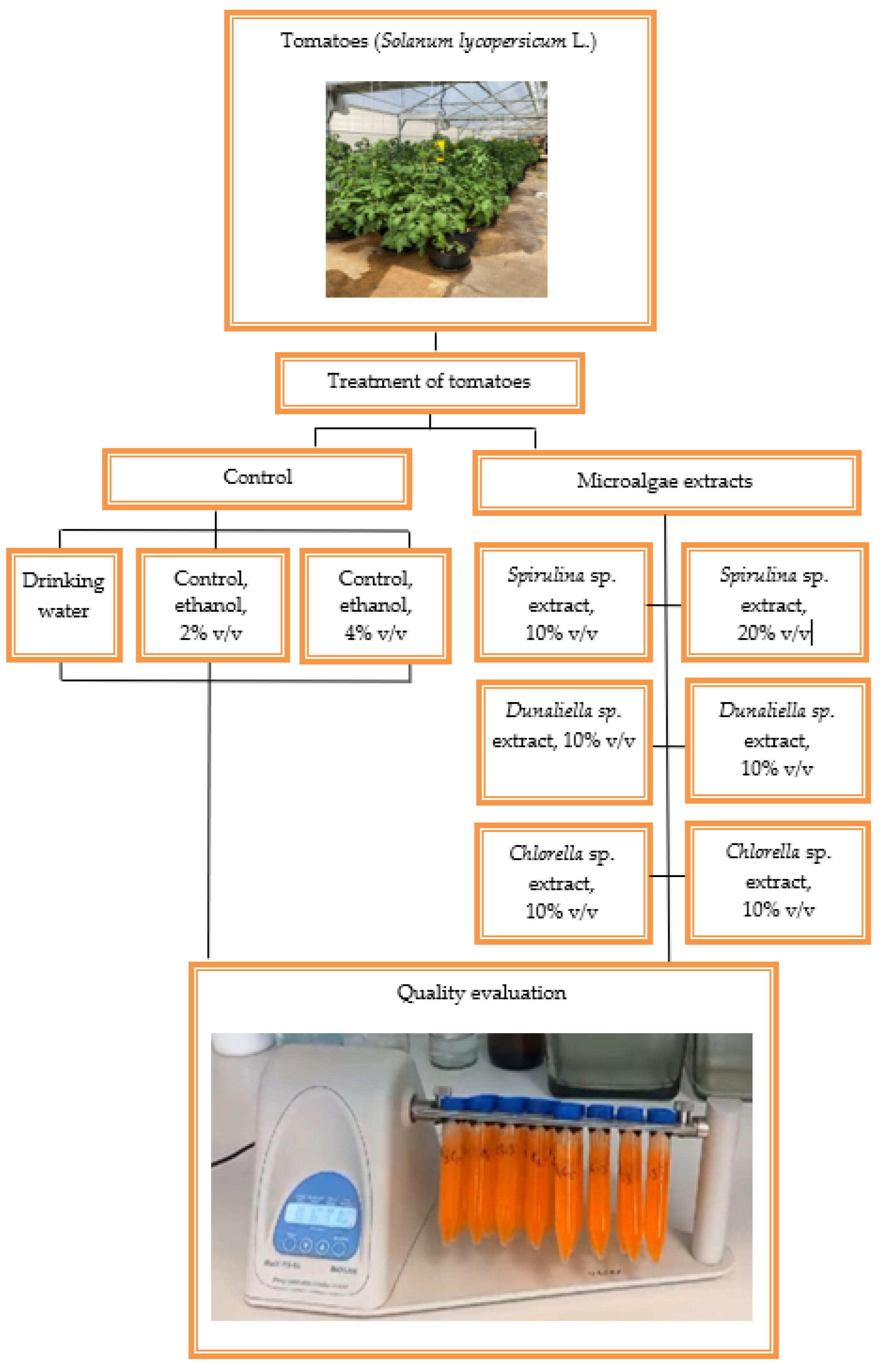
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the microalgae extractions
2.2. Plant material and sampling
2.3. Determination of vitamin C content
2.4. Determination of titratable acidity (TA)
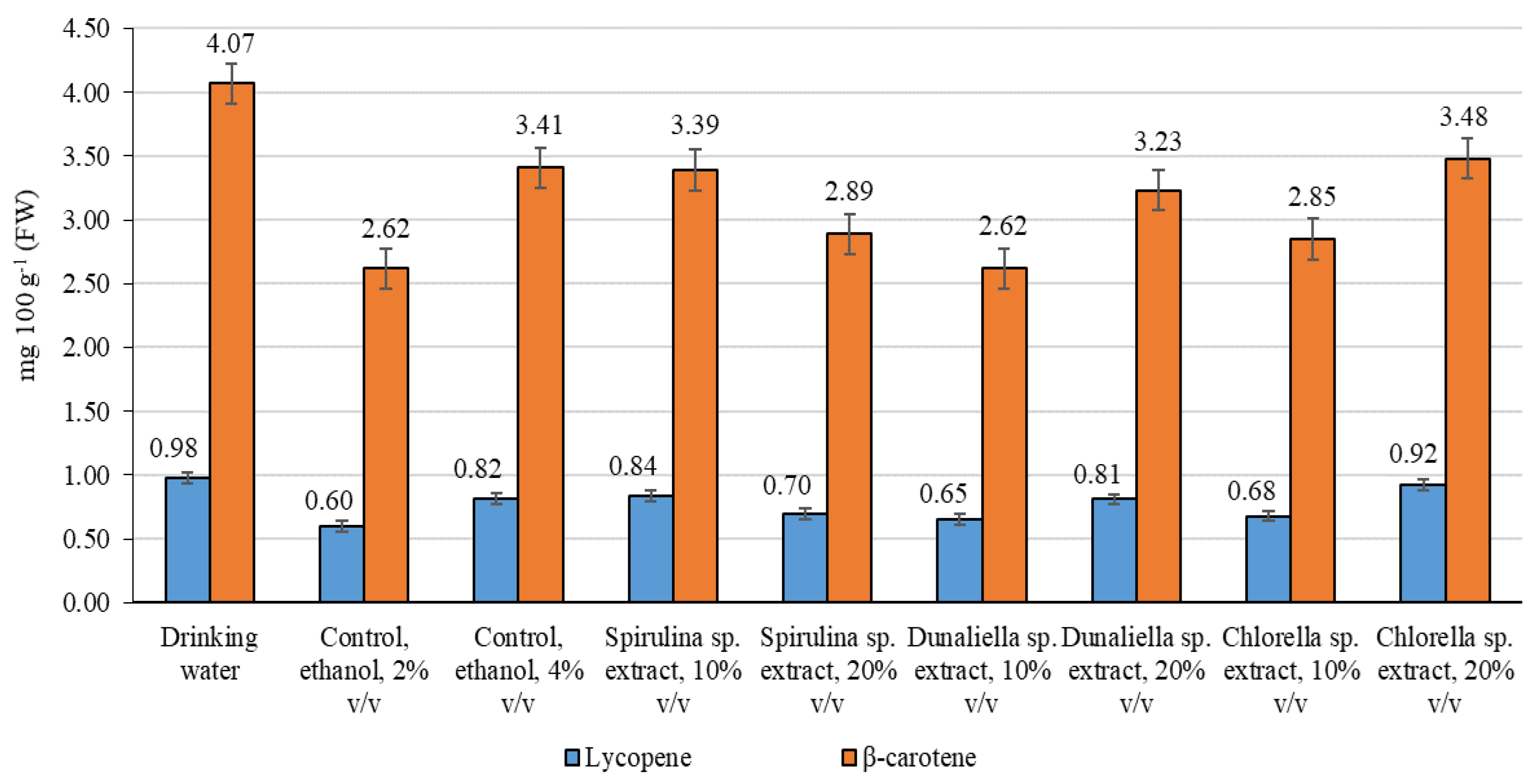
2.6. Determination of lycopene and β-carotene
2.7. Determination of anthocyanins content
2.8. Determination of total phenols content
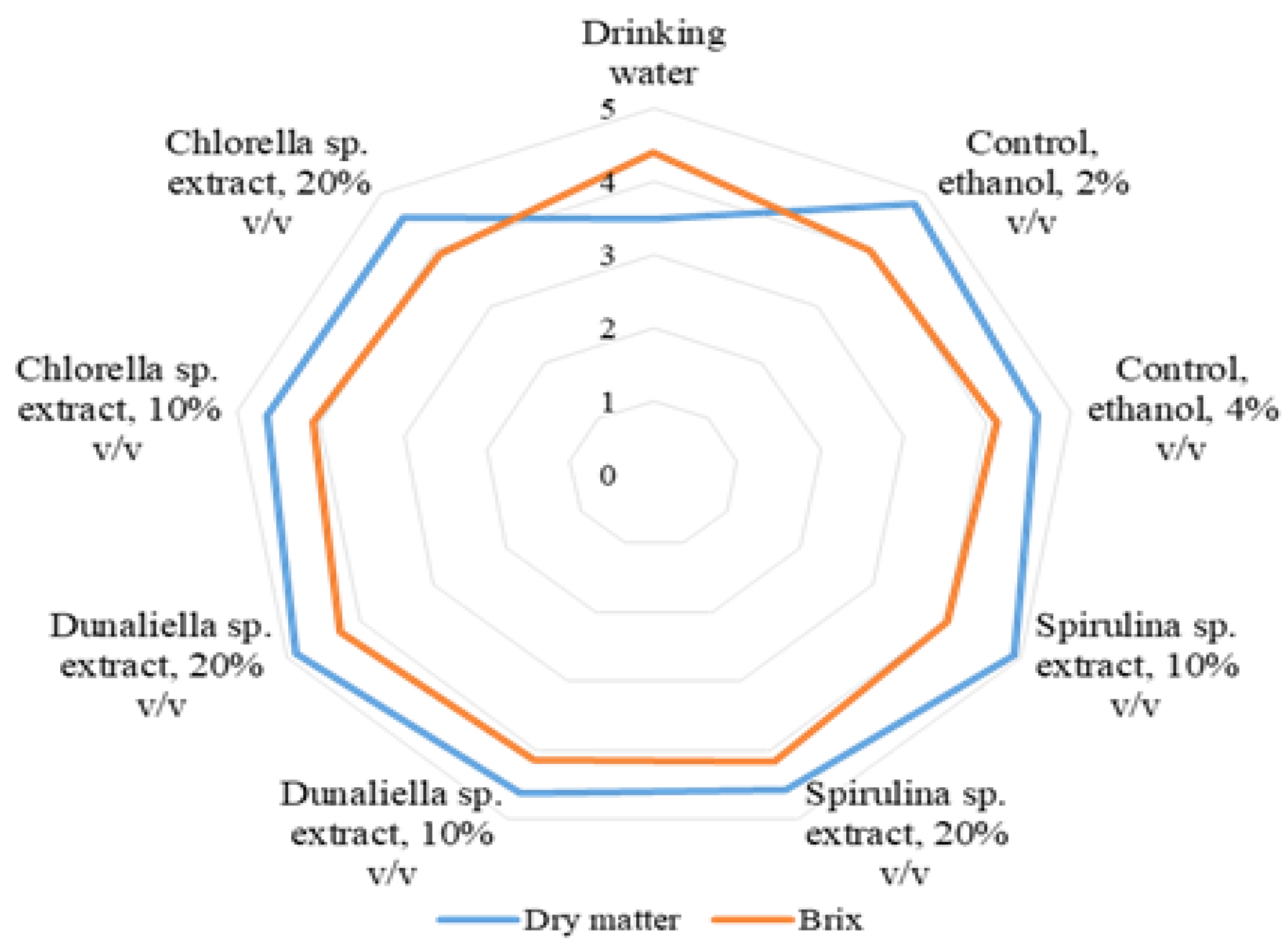
2.9. Determination of dry matter and total soluble solids
2.10. Determination of fruits mass and taste index
2.11. Statistical analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sousa, V.; Marques, P.R.A.; Vicente, A.M.; Dias, O.; Geada, P. Microalgae biomass as an alternative source of biocompounds: new insights and future perspectives of extraction methodologies. Food Res. Int., 2023, 173, pp. 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Gharib, F. A. E. L. , Osama, K., Sattar, A. M. A. E., & Ahmed, E. Z. (2024). Impact of Chlorella vulgaris, Nannochloropsis salina, and Arthrospira platensis as bio-stimulants on common bean plant growth, yield and antioxidant capacity. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 1398. [CrossRef]
- Montuori, E.; Lima, S.; Marchese, A.; Scargiali, F.; Lauritano, C. Lutein production and extraction from microalgae: recent. [CrossRef]
- Gharib, F.A.E.L.; Osama, K.; Sattar, A.M.A.E.; Ahmed, E.Z. Impact of Chlorella vulgaris, Nannochloropsis salina, and Arthrspira insights and bioactive potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2024, 25, 2892, pp.1–33.
- Ronga, D.; Biazzi, E.; Parati, K.; Carminati, D., Carminati, E.; Tava, A. Microalgal bio-stimulants and biofertilisers in crop productions. Agronomy, 2019, 9, 192, pp. 1–22.
- Mapelli-Brahm, P.; Gómez-Villegas, P.; Gonda, M.L; León-Vaz, A.; León, R.; Mildenberger, J.; Rebours, C.; Saravia, V.; Vero, S., Vila, E.; Meléndez-Martínez, A. J. Microalgae, seaweeds and aquatic bacteria, archaea, and yeasts: sources of carotenoids with potential antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory health-promoting actions in the sustainability era. Mar. Drugs, 2023; 21(6), 340, pp. 1–45. [CrossRef]
- Spolaore, P.; Joannis-Cassan, C.; Duran, E; Isambert, A. Commercial applications of microalgae. J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2006, 101(2), pp. 87–96. [CrossRef]
- Nemani, N.; Dehnavi, S. M.; Pazuki, G. Extraction and separation of astaxanthin with the help of pre-treatment of Haematococcus pluvialis microalgae biomass using aqueous two-phase systems based on deep eutectic solvents. Sc. Rep., 2024, 14:5420, pp. 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahim, H.; Eladel, H.; Battah, M.; Radwan, A.; Saber, A.A. Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer activity of an extract of two pollution-tolerant green microalgae. Benha J. of Appl. Sc., 2024, 9(3), pp. 187–196. [CrossRef]
- Mularczyk, M.; Michalak, I.; Marycz, K. Astaxanthin and other nutrients from haematococcus pluvialis—multifunctional applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18(9), pp. 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Di Lena, G.; Casini, I.; Lucarini, M.; Lombardi-Boccia, G. Carotenoid profiling of five microalgae species from large-scale production. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, pp. 810–818. [CrossRef]
- Coppens, J.; Grunert, O.; Hende, S.V.D.; Vanhoutte, I.; Boon, N.; Haesaert, G.; Gelder, L.D. The use of microalgae as a high-value organic slow-release fertilizer results in tomatoes with increased carotenoid and sugar levels. J. of App. Phyc., 2016, 28, pp. 2367–2377. [CrossRef]
- Dudina, I.; Kalashnikova, E.; Kirakosyan, R. Green microalgae chlorella in the study of the biosynthetic potential of higher plants in vitro. BIO Web of Conferences, 2024, pp.1–8. [CrossRef]
- Geada, P.; Loureiro, L.; Teixeira, J. A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Vicente, A. A.; Fernandes, B. D. Evaluation of disruption/permeabilization methodologies for Microcystis aeruginosa as alternatives to obtain high yields of microcystin release. Algal Res., 2019, 42, 101611, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Caroppo, E.; Mazza, M.; Sannella, A.; Marano, G.; Avallone, C.; Claro, A. E.; Sani, G. Will nothing be the same again?: changes in lifestyle during COVID-19 pandemic and consequences on mental health. Int. J. of Env. Res. and Pub. Health, 2021,. 18(16), 8433, pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Cotas, J.; Valado, A. Antioxidants from microalgae and their potential impact on human well-being. Expl. of Drug Sc., 2024, 2, pp. 292–321. [CrossRef]
- Cunha, E.; Sousa, V.; Geada, P.; Teixeira, J. A.; Vicente, A. A.; Dias, O. Systems biology’s role in leveraging microalgal biomass potential: current status and future perspectives. Alg. Res., 2023, 69 (December 2022), 102963, pp. 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Urcera, J.; Romero, A.; Cruz, P.; Vasconcelos, V.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B.; Rodríguez, F. Screening of microalgae for bioactivity with antiviral, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer assays. Biol., 2024, 13(4), 255–pp.1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadi., Z.; Jalali, H.; Safavi, M. Izadi. Z.; Jalali, H.; Safavi, M. Protective activity of Chlorella vulgaris microalgae extract on the in vitro cultured oocytes, Iran. J. of Fish. Sc., 2024, 23(4), pp. 589–602.
- Morón-Ortiz, Á.; Karamalegkos, A.A.; Mapelli-Brahm, P.; Ezcurra, M.; Meléndez-Martínez, A.J. Phytoene and phytoene-rich microalgae extracts extend lifespan in C. elegans and protect against amyloid-β toxicity in an Alzheimer’s disease model. The Prepr. Ser. for Biol. 2024, pp.1–16. [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, G.; Moovendhan, M.; Arumugam, A.; Matharasi, A.; Dineshkumar, R.; Sampathkumar, P. Evaluation of chemical composition and in vitro anti-inflammatory effect of marine microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Waste. and Biom. Valor., 2018, 10, pp. 3263–3270.
- Sudhakar, M.P.; Ramesh Kumar, B.; Mathimani, T.; Arunkumar, K.A. Review on bioenergy and bioactive compounds from microalgae and macroalgae-sustainable energy perspective. J. Clean. Prod., 2019, 228, pp. 1320–1333. [CrossRef]
- Siddhnath, K.; Surasani, V.K.R.; Singh, A., Singh S.M., Hauzoukim, Narasimha Murthy L., Baraiya K.G., Bioactive compounds from micro-algae and its application in foods: a review. Disc. Food, 2024, 4:27, pp.1–20. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.P.; Regueiras, A.; Lopes, G.; Matos, G.; Silva, L.P.; Cerqueira, M.T.; Cardoso, H.; Correia, N.; Saraiva, J.A.; Silva, J.L.; Martins, R.; Marques, A.P. Nonthermal high-pressure microalgae extracts: A new source of natural ingredients for cosmetics. Alg. Res., 2024, 81, 103591, pp. 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Eze, C.N.; Onyejiaka, C.K.; Ihim, S.A.; Ayoka, T.O.; Aduba, C.C.; Ndukwe, J.K.; Nwaiwu, O.; Onyeaka, H. Bioactive compounds by microalgae and potentials for the management of some human disease conditions. AIMS Microb., 2023, 9(1), pp. 55–74. [CrossRef]
- Mtaki, K.; Kyewalyanga, M.S.; Mtolera, M.S.P. Assessment of antioxidant contents and free radical-scavenging capacity of chlorella vulgaris cultivated in low cost media. App. Sc., 2020, 10, pp. 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Widowati, I.; Zainuri, M.; Kusumaningrum, P.H.; Susilowati, R.; Hardivillier, Y.; Leignel, V.; Bourgougnon, N.; Mouget, J.L. Antioxidant activity of three microalgae Dunaliella salina, Tetraselmis chuii and Isochrysis galbana clone Tahiti. Earth and Env. Sc., 2017, 55, 012067, pp.1–6.
- Kampuss, K.; Semjonovs, P.; Koļesovs, S.; Afoņina, K.; Bāliņš, A. Response of raspberries to treatments with Spirulina sp., Dunaliella sp. and Chlorella sp. extractions. Res. J. of Biot., 2024, 19(3), pp. 51–57. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Kaur, I.; Bhatnagar, A.K. Effect of aqueous extract of Sargassum johnstonii Setchell & Gardner on growth, yield and quality of Lycopersicon esculentum. Mill. J Appl. Phycol., 2011, 23, pp. 623–633. [CrossRef]
- Mulbry, W.; Kondrad, S.; Pizarro, C. Biofertilizers from algal treatment of dairy and swine manure effluents. J. Veg. Sci., 2007, 12, pp. 107–125. [CrossRef]
- Conti, V.; Parrotta, L.; Romi, M.; Del Duca, S.; Cai, G. Tomato biodiversity and drought tolerance: a multilevel review. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2023, 24, 10044, pp. 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Cavallaro, V.; Santoro, P.; Mori, J.; Ferrante, A.; Cocetta, G. Quality and physiological evaluation of tomato subjected to different supplemental lighting systems. Sci. Hort., 2024, 323, pp.1–12. [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.Y.; Sina, A.A.I.; Khandker, S.S.; Neesa, L.; Tanvir, E.M.; Kabir, A.; Khalil, I.; Gan, S. H. Nutritional composition and bioactive compounds in tomatoes and their impact on human health and disease: a review. Foods, 2020, 10, 45, pp. 1–32. [CrossRef]
- Lima, G.P.P.; Gomez, H.A.G.; Seabra, S.; Maraschin, M.; Tecchio, M.A.; Borges, C.V. Functional and nutraceutical compounds of tomatoes as affected by agronomic practices, postharvest management, and processing methods: a mini review. Front. Nutr., 2022, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, N.; Basit, A.; Ahmad, I.; Ullah, I.; Shah, S.T.; Mohamed, H.I.; Javed, S. Mitigation the adverse effect of salinity stress on the performance of the tomato crop by exogenous application of chitosan. Bulletin of the Nat. Res. Centre, 2020, pp. 3–11. [CrossRef]
- Martí, R.; Roselló, S.; Cebolla-Cornejo, J. Tomato as a source of carotenoids and polyphenols targeted to cancer. Prev. Cancers, 2016, 8, 58, pp. 1–28. [CrossRef]
- Tamasi, G.; Pardini, A.; Bonechi, C.; Donati, A.; Pessina, F.; Marcolongo, P.; Gamberucci, A.; Leone, G.; Consumi, M.; Magnani, A. et al. Characterization of nutraceutical components in tomato pulp, skin and locular gel. Eur. Food Res. Techn.., 2019, 245, pp. 907–918. [CrossRef]
- Antal-Tremurici, A.; Ambăruş, S.; Bute, A.; Brezeanu, P.M.; Iosob, G.-A.; Brezeanu, C. Preliminary study on the fruit morphology, agronomic, and physio-chemical characteristics of tomato varieties in greenhouse conditions. Scien. Papers. Series B, Horticulture, 2023, LXVII, 1, pp. 511–518.
- Raza, B.; Hameed, A.; Saleem, M.Y. Fruit nutritional composition, antioxidant and biochemical profiling of diverse tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) genetic resource. Front. in Plant Sc., 2022, October 13, pp. 1–35. [CrossRef]
- Erdberga, I.; Alsiņa, I.; Dubova, L.; Dūma, M.; Sergejeva, D.; Augšpole, I.; Avotiņš, A. Changes in the biochemical composition of tomato fruit under the influence of illumination quality. Key Eng. Mat. Subm., 2019, 850, pp. 172–178. [CrossRef]
- Vox, G.; Teitel, M.; Pardossi, A.; Minuto, A.; Tinivella, F.; Schettini, E. Sustainable greenhouse systems. In Sustainable agriculture: technology, planning and management, Nova Science Publishers: New York, 2010, pp. 1–79.
- Duma, M.; Alsina, I.; Dubova, L.; Erdberga, I. Quality of tomatoes during storage. In Conference: 11th Baltic Conference on Food Science and Technology “Food science and technology in a changing world”, 2017, pp.130–133.
- Dūma, M.; Alsiņa, I.; Dubova, L.; Gavare, D.; Erdberga, I. Quality of different coloured tomatoes depending on the growing season. Proceedings of the Latvian Academy of Sciences, Section B, 2022, 76(1), pp. 89–95. [CrossRef]
- Duma, M; Alsina, I. The content of plant pigments in red and yellow bell peppers. Sci. Pap. B Hortic., 2012, 56:10, pp. 5–8.
- Nagata, M; Yamashita, I. Simple method for simultaneous determination of chlorophyll and carotenoids in tomato fruit. J. Jpn. Food Sci. Technol., 1992, 39(10), pp. 922–928. [CrossRef]
- Kerch, G.; Sabovics, M.; Kruma, Z.; Kampuse, S.; Straumite, E. Effect of chitosan and chitooligosaccharide on vitamin C and polyphenols contents in cherries and strawberries during refrigerated storage. Eur. Food Res. Technol., 2011, 233(2), pp. 351–358. [CrossRef]
- Moor, U.; Karp, K.; Põldma, P.; Pae, A. Cultural systems affect content of anthocyanins and vitamin C in strawberry fruits. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci., 2005, 70(4), pp. 195–201.
- Ozola, L.; Kampuse, S.; Galoburda, R. The effect of high-pressure processing on enteral food made from fresh or semi-finished ingredients. In 11th Baltic Conference on Food Science and Technology, Jelgava: Latvia University of Agriculture, 2017, pp. 80–85.
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.M.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioksidants by means of Folin – Ciocalteu reagent. Method Enzymol., 1999, 299, pp. 152–178.
- Narvez, B.; Letard, M.; Graselly, D.; Jost, M. Les criteres de qualite de la tomate. Infos Ctifl, 1999, 155, pp. 41–47.
- Nielsen, S. Food analysis, 3rd ed. New-York, Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, 2003, 534 p.
- Dobrin, A.; Nedeluș, O.; Bujor, A.; Mot, M.; Zugravu, L.; Bădulescu, T.A. Nutritional quality parameters of the fresh red. Sc. Papers. Series B, Horticulture, 2019, LXIII, No. 1, pp. 439–443.
- Kantoğlu, K.Y.; Iҫ, E.; Özmen, D.; Bulut, F.S.; Ergun, E.; Kantoğlu, Ö.; Özcoban, M. Gamma rays induced enhancement in the phytonutrient capacities of tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum L.), Front. Hortic., 2023, 2:1190145, pp. 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Anthon, G.E.; LeStrange, M.; Barrett, D.M.; Changes in pH, acids, sugars and other quality parameters during extended vine holding of ripe processing tomatoes. J. Sci. Food Agric., 2011, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Astuti, S.D.; Salengke, S.; Lagac, A.; Bilangd, M.; Mochtar, H.; Waris A. Characteristics of pH, Total Acid, Total Soluble Solid on Tomato Juice by Ohmic Heating Technology. IJSBAR, 2018, 39(2), pp. 21–28.
- Yong, K.T.; Yong, P.H.; Ng, Z.H. Tomato and human health: A perspective from post-harvest processing, nutrient bio-accessibility, and pharmacological interaction. Food Front., 2023, 4, pp. 1702–1719.
- Fenni, S.; Hammou, H.; Astier, J.; Bonnet, L.; Karkeni, E.; Couturier, C.; Tourniaire, F.; Landrier, J.F. Lycopene and tomato powder supplementation similarly inhibit high-fat diet induced obesity, inflammatory response, and associated metabolic disorders. Mol. Nutr. Food Res., 2017, 61(9), 1601083, pp. 1–29. [CrossRef]
- Alda, L.M.; Gogoaşă, I.; Gogoaşă, D.M.; Gergen, I.; Alda, S.; Moldovan, C.; Niţă, L. Lycopene content of tomatoes and tomato products. J. Agroaliment. Process Technol., 2009, 15(4), pp. 540–542.
- Perez-Esteve, E.; Salata, A.; Barat, J.M.; Stepniowska, A.; Lopez-Galarza, S.; NurzynskaWierdak, R. Polyphenolic composition of spanish cultivars of globe artichoke (Cynara cardunculus L. var. Scolymus (L.) Fiori. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus, 2018, 17(2), pp. 177–184.
- Soare, R.; Dinu, M.; Apahidean, A.I.; Soare, M. The evolution of some nutritional parameters of the tomato fruit during the harvesting stages. Hortic. Sci. (Prague), 2019, 3, pp. 132–137. [CrossRef]
- Valsikova, M.; Komár, P.; Rehušs, M. The effect of varieties and degree of ripeness to vitamin C content in tomato fruits. Acta Hortic. Regiotecturae, 2017, 2, pp. 44–48.
- Dūma, M.; Alsiņa, I.; Dubova, L.; Erdberga, I. Bioactive compounds in tomatoes at different stages of maturity. Proceedings of the Latvian Academy of Sciences. Section B, 2018, 72, 2, 713, pp. 85–90. [CrossRef]
- Duma, M.; Alsina, I.; Dubova, L.; Augspole, I.; Erdberga, I. Suggestions for consumers about suitability of differently coloured tomatoes in nutrition. In: FoodBalt 20019: 13th Baltic conference on food science and technology “Food. Nutrition. Well-Being”: conference proceedings, 2019, Jelgava: LLU, pp. 261–264.
- Augšpole, I.; Dūma, M.; Alsiņa, I.; Dubova, L.; Sergejeva, D. Changes in tomato quality under different growing conditions. Proceedings of the Scientific and Practical Conference on Harmonious Agriculture, 2019, LLU, Jelgava, Latvia, pp. 137–142.
- Matejkova, J.; Petrikova, K. Variation in Content of Carotenoids and Vitamin C in Carrots. Not. Sci. Biol., 2010, 2(4), pp. 88–91. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez–Concepcion, M.; Stange, C. Biosynthesis of carotenoids in carrot: An underground story comes to light. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2013, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Fikselová, M.; Mareĉek, J.; Mellen, M. Carotenes content in carrot roots (Daucus Carota L.) as affected by cultivation and storage. Veg. Crop Prod., 2010, 73, pp. 47–54.
- Duckena, L.; Alksnis, R.; Erdberga, I.; Alsiņa, I.; Dubova, L.; Duma, M. Non-Destructive Quality Evaluation of 80 Tomato Varieties Using Vis-NIR Spectroscopy. Foods, 2023, 12(10), 1990, pp. 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Mendelová, A.; Fikselová, M.; Mendel, Ľ. Carotenoids and lycopene content in fresh and dried tomato fruits and tomato juice. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun., 2013, 61(5), pp. 1329–1337. [CrossRef]
- Biesiada, A.; Tomczak, A. Biotic and abiotic factors affecting the content of the chosen antioxidant compounds in vegetables. J. Veg. Crop Prod., 2012, 76(1), pp. 55–78. [CrossRef]
- Bramley, P.M. Is lycopene beneficial to human health? Phytoch., 2000, 54, 3, pp. 233–236.
- Fraser, P.D.; Bramley, P.M. The biosynthesis and nutritional uses of carotenoids. Prog. Lipid Res., 2004, 43, 3, pp. 228–265. [CrossRef]
- Moneruzzaman, K.M.; Hossain, A.B.M.S.; Sani, W.; Saifuddin, M. Effect of stages of maturity and ripening conditions on the biochemical characteristics of tomato. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol., 2008, 4(4), pp. 329–335. [CrossRef]
- Vinha, A.F.; Barreira, S.V.P.; Castro, A.; Costa, A.; Oliveira, B.P.P. Influence of the storage conditions on the physicochemical properties, antioxidant activity and microbial flora of different tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum L.) cultivars. J. Agric. Sci., 2013, 5, 2, pp. 118–128. [CrossRef]
- Gajewski, M.; Szymczak, P.; Radzanowska, J. Sensory Quality of Orange, Purple and Yellow Carrots Stored under Controlled Atmosphere. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot., 2010, 38(3), pp. 169–176.
- Rashidi, M. Modeling of carrot firmness based on water content and total soluble solids of carrot. JABS, 2011, 6(8), pp. 62–65.
- Atallah, M.M. Physical and mechanical properties of tomato plant to Designa harvest machine. Bull. Fac, Agric., Cairo Univ., 2012, 63, pp. 8–18. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, W.A.; Elwakeel, A.E. Study on some Properties of Tomato Fruits for Natural Sun Drying, J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng., Mansoura Univ., 2021, 12(11), pp. 763–767.
- Li, H.; Hou, X.; Bertin, N.; Ding, R.; Du, T. Quantitative responses of tomato yield, fruit quality and water use efficiency to soil salinity under different water regimes in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manage, 2023, 277, 108134, pp. 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahim, H.; Eladel, H.; Battah, M.; Radwan, A.; Saber, A.A. Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer activity of an extract of two pollution-tolerant green microalgae. Benha J. Appl. Sci., 2024, 9, 3, pp. 187–196. [CrossRef]

| Plant material | Vitamin C mg 100 g-1 (in fresh matter) |
Titratable acidity g 100 g-1 (in fresh matter) |
pH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drinking water | 17.96 ± 0.89a | 0.33 ± 0.02a | 4.21 ± 0.14a |
| Control, ethanol, 2% v/v | 16.32 ± 0.64a | 0.45 ± 0.03a | 4.24 ± 0.11abc |
| Control, ethanol, 4% v/v | 15.68 ± 0.56a | 0.31 ± 0.03a | 4.25 ± 0.14bc |
| Spirulina sp. extract, 10% v/v | 16.17 ± 0.98a | 0.32 ± 0.02a | 4.23 ± 0.16ab |
| Spirulina sp. extract, 20% v/v | 15.68 ± 0.94a | 0.27 ± 0.02a | 4.22 ± 0.10a |
| Dunaliella sp. extract, 10% v/v | 18.55 ± 0.74a | 0.28 ± 0.01a | 4.25 ± 0.15bc |
| Dunaliella sp. extract, 20% v/v | 17.21 ± 0.58a | 0.25 ± 0.02a | 4.25 ± 0.10bc |
| Chlorella sp. extract, 10% v/v | 17.47 ± 0.82a | 0.32 ± 0.03a | 4.30 ± 0.11d |
| Chlorella sp. extract, 20% v/v | 15.47 ± 0.83a | 0.28 ± 0.01a | 4.27 ± 0.12c |
| Plant material | Anthocyanins mg 100 g-1 (in fresh matter) |
Total phenols mg 100 g-1 (in fresh matter) |
|---|---|---|
| Drinking water | 0.42 ± 0.04a | 166.93 ± 2.01c |
| Control, ethanol, 2% v/v | 0.09 ± 0.01a | 137.59 ± 1.34a |
| Control, ethanol, 4% v/v | 0.07 ± 0.01a | 142.21 ± 1.53ab |
| Spirulina sp. extract, 10% v/v | 0.12 ± 0.02a | 144.21 ± 1.87ab |
| Spirulina sp. extract, 20% v/v | 0.11 ± 0.01a | 142.23 ± 1.33ab |
| Dunaliella sp. extract, 10% v/v | 0.14 ± 0.02a | 142.22 ± 2.02ab |
| Dunaliella sp. extract, 20% v/v | 0.09 ± 0.01a | 143.33 ± 1.22ab |
| Chlorella sp. extract, 10% v/v | 0.11± 0.01a | 145.96 ± 2.04ab |
| Chlorella sp. extract, 20% v/v | 0.12± 0.01a | 145.49 ±2.25 ab |
| Plant material | Tomato fruit mass, g | Taste index |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average p=0.673 |
Minimum | Maximum | S.D. | ||
| Drinking water | 92.49a | 43.05 | 200.01 | 44.81 | 0.31 |
| Control, ethanol, 2% v/v |
95.11a | 45.08 | 170.00 | 40.47 | 0.38 |
| Control, ethanol, 4% v/v |
115.21a | 37.89 | 325.76 | 67.09 | 0.34 |
|
Spirulina sp. extract, 10% v/v |
101.66a | 39.25 | 185.73 | 46.71 | 0.57 |
|
Spirulina sp. extract, 20% v/v |
116.15a | 40.34 | 213.28 | 47.77 | 0.54 |
|
Dunaliella sp. extract, 10% v/v |
129.33a | 55.71 | 273.75 | 68.08 | 0.37 |
|
Dunaliella sp. extract, 20% v/v |
102.52a | 39.45 | 218.00 | 59.36 | 0.39 |
|
Chlorella sp. extract, 10% v/v |
94.85a | 34.7 | 188.75 | 48.63 | 0.33 |
|
Chlorella sp. extract, 20% v/v |
104.78a | 55.27 | 195.21 | 42.02 | 0.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





