Submitted:
05 August 2024
Posted:
06 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
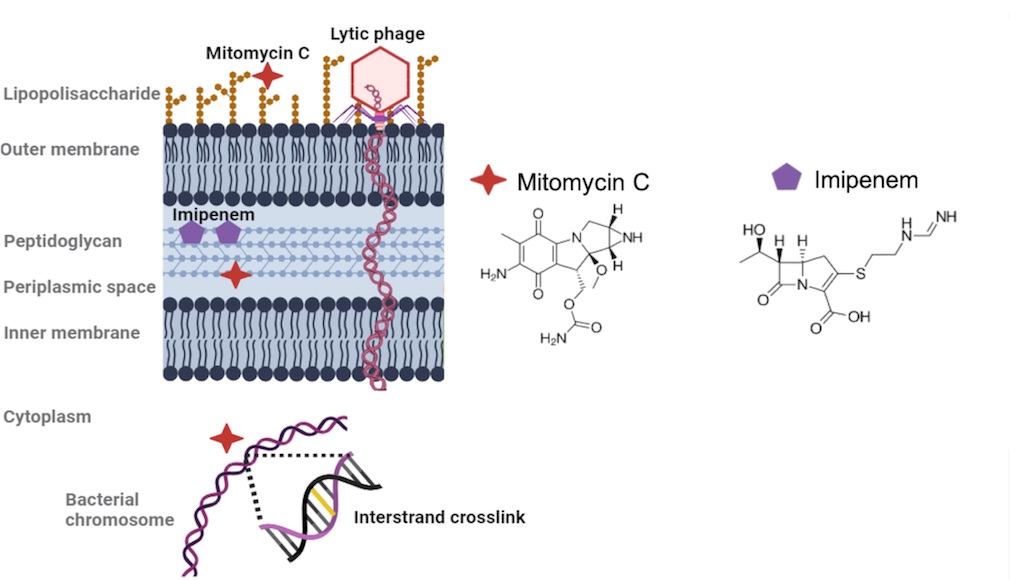
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
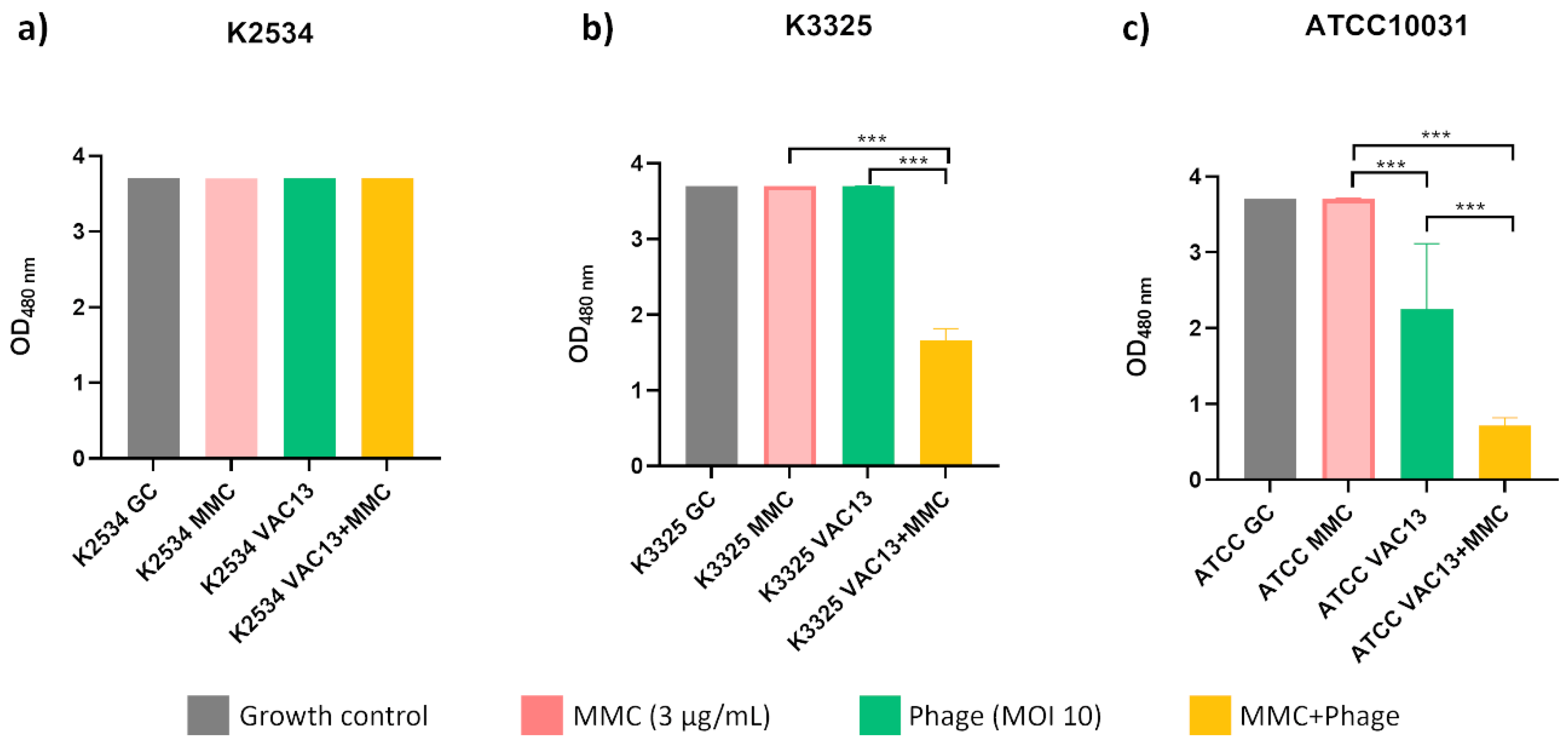
2.1. Synergy Studies
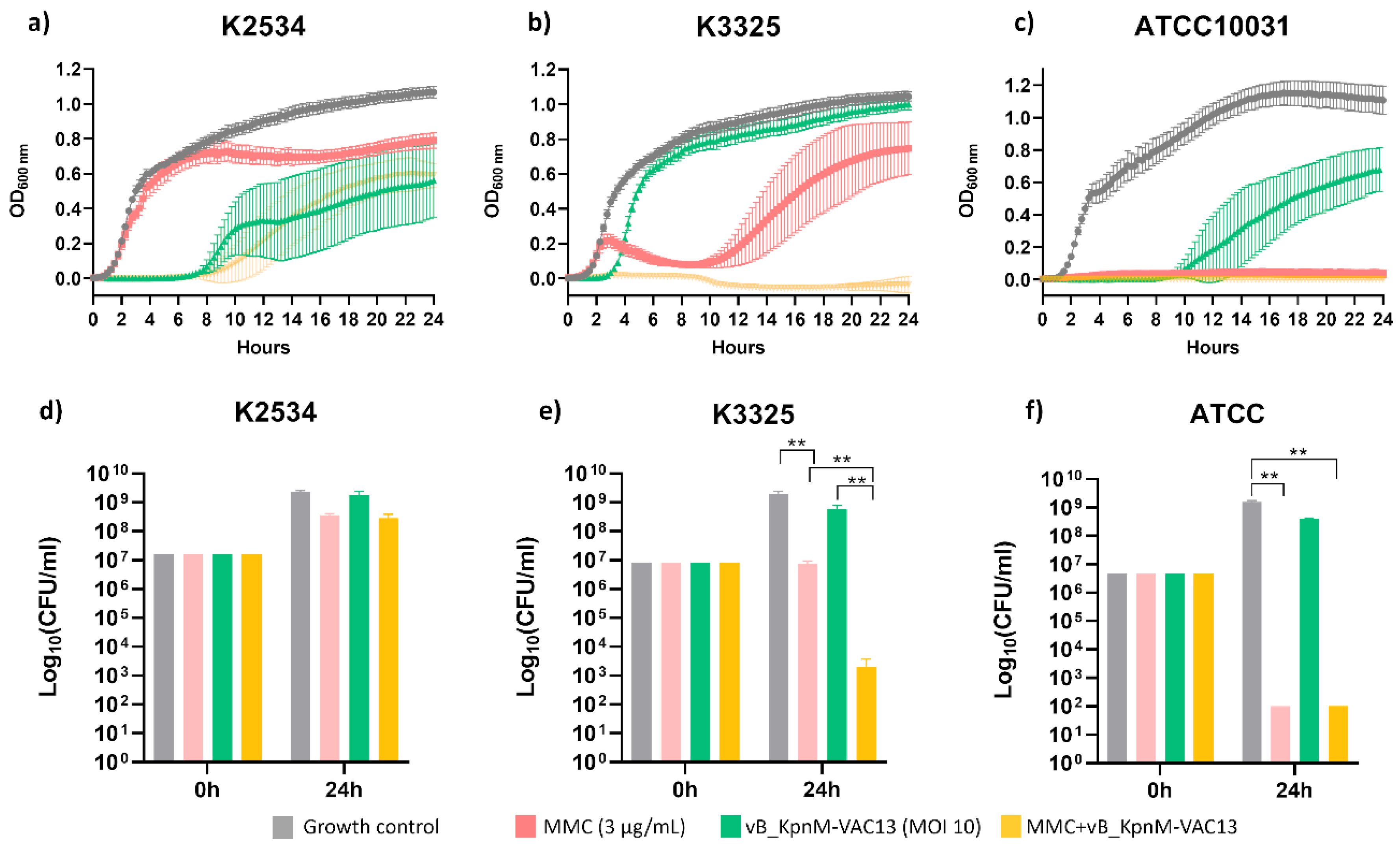
2.1.1. Optical Density Growth Curves and Viability Assay
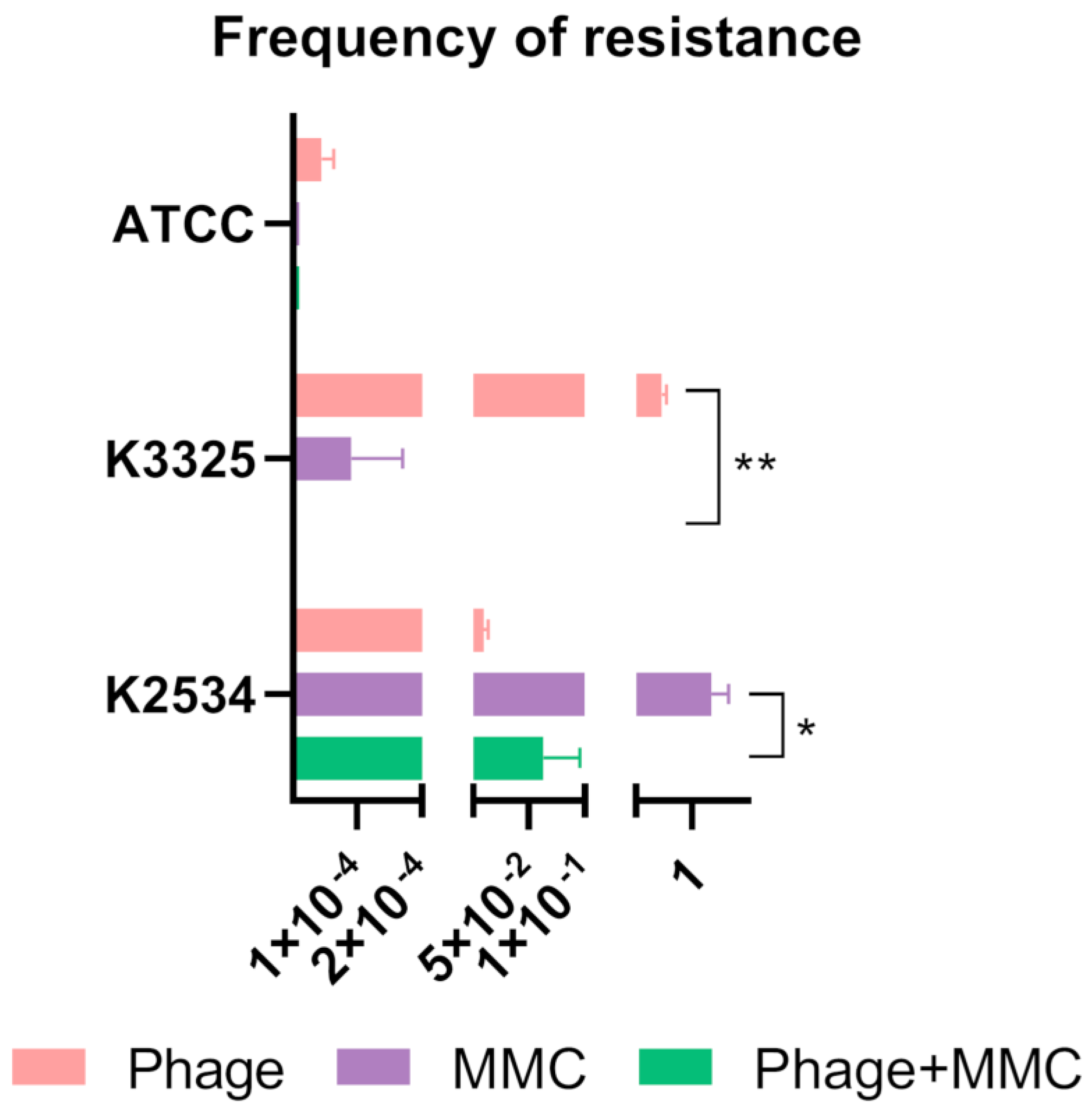
2.1.2. Frequency of Phage-Resistant Mutants
2.1.3. Assessment of the Cellular Respiration In Vitro
2.2. Toxicity Studies
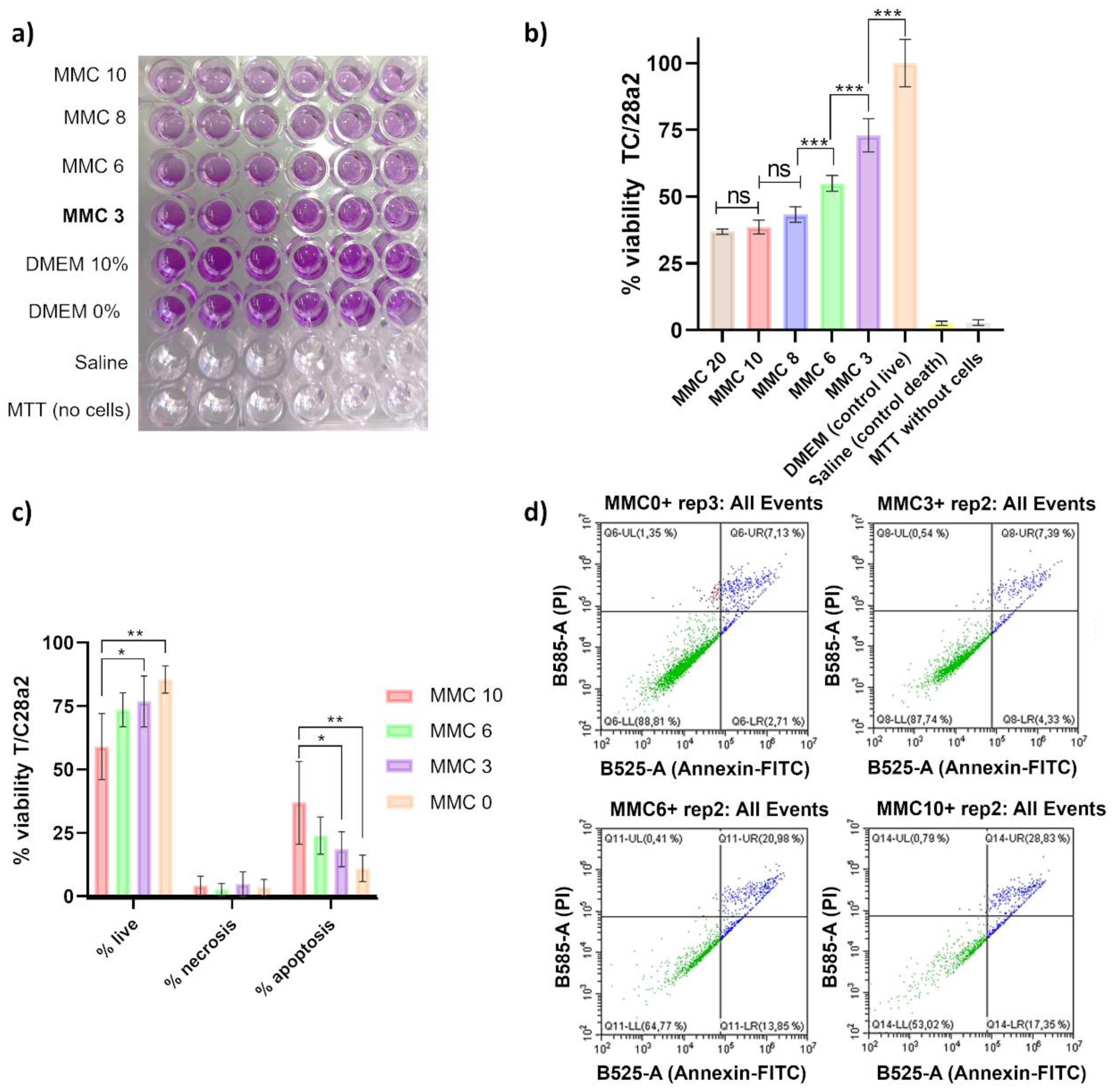
2.2.1. In Vitro: Metabolic Activity and Apoptosis Study
2.2.2. In vivo toxicity assay: murine model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Phage and Growth Culture Conditions
4.2. Optical Density Growth Curves
4.3. Time-Kill Curves Assay
4.4. Frequency of Resistant Mutants
4.5. Respiration Assay Using the Tetrazolium Salt WST-1
4.6. Cytotoxicity Assay Using Human Chondrocytes T/C28a2 Cell Line
4.6.1. MTT-Cytotoxic Assay
4.6.2. Apoptosis Study Using Flow Cytometry
4.7. Acute and Cumulative of MMC and Lytic Bacteriophage vB_KpnM-VAC13 in Healthy Female C57BL6/J Mice
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clegg, S.; Murphy, C.N. Epidemiology and Virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol Spectr 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Dong, N.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, D.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Chan, E.W.; Shu, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; et al. A fatal outbreak of ST11 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Chinese hospital: a molecular epidemiological study. Lancet Infect Dis 2018, 18, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, K.; Zou, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Yin, L.; Zhang, X. An Outbreak of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in an intensive care unit of a major teaching hospital in Chongqing, China. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021, 11, 656070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, Y.; Ersoy, Y.; Gursoy, N.C.; Altunisik Toplu, S.; Otlu, B. A silent outbreak due to Klebsiella pneumoniae that co-produced NDM-1 and OXA-48 carbapenemases, and infection control measures. Iran J Basic Med Sci 2020, 23, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pilato, V.; Principe, L.; Andriani, L.; Aiezza, N.; Coppi, M.; Ricci, S.; Giani, T.; Luzzaro, F.; Rossolini, G.M. Deciphering variable resistance to novel carbapenem-based β-lactamase inhibitor combinations in a multi-clonal outbreak caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae resistant to ceftazidime/avibactam. Clin Microbiol Infect 2023, 29, 537.e531–537.e538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, M.; Mairpady Shambat, S.; Brugger, S.D.; Zinkernagel, A.S. Antibiotic resistance and persistence-Implications for human health and treatment perspectives. EMBO Rep 2020, 21, e51034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaban, N.Q.; Merrin, J.; Chait, R.; Kowalik, L.; Leibler, S. Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch. Science 2004, 305, 1622–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, R. Bacterial persistence: some new insights into an old phenomenon. J Biosci 2008, 33, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, T.K.; Knabel, S.J.; Kwan, B.W. Bacterial persister cell formation and dormancy. Appl Environ Microbiol 2013, 79, 7116–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helaine, S.; Cheverton, A.M.; Watson, K.G.; Faure, L.M.; Matthews, S.A.; Holden, D.W. Internalization of Salmonella by macrophages induces formation of nonreplicating persisters. Science 2014, 343, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeva, M.; Gutu, A.D.; Hebert, W.; Wager, J.D.; Yonker, L.M.; O'Toole, G.A.; Ausubel, F.M.; Moskowitz, S.M.; Joseph-McCarthy, D. An Antipersister Strategy for Treatment of Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goneau, L.W.; Yeoh, N.S.; MacDonald, K.W.; Cadieux, P.A.; Burton, J.P.; Razvi, H.; Reid, G. Selective target inactivation rather than global metabolic dormancy causes antibiotic tolerance in uropathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014, 58, 2089–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Xie, X.; Tian, W.; Bahar, A.A.; Lin, N.; Song, F.; An, J.; Ren, D. (Z)-4-bromo-5-(bromomethylene)-3-methylfuran-2(5H)-one sensitizes Escherichia coli persister cells to antibiotics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2013, 97, 9145–9154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windels, E.M.; Michiels, J.E.; Fauvart, M.; Wenseleers, T.; Van den Bergh, B.; Michiels, J. Bacterial persistence promotes the evolution of antibiotic resistance by increasing survival and mutation rates. Isme j 2019, 13, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacios, O.; Blasco, L.; Bleriot, I.; Fernandez-Garcia, L.; Gonzalez Bardanca, M.; Ambroa, A.; Lopez, M.; Bou, G.; Tomas, M. Strategies to Combat Multidrug-Resistant and Persistent Infectious Diseases. Antibiotics (Basel) 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyttebroek, S.; Chen, B.; Onsea, J.; Ruythooren, F.; Debaveye, Y.; Devolder, D.; Spriet, I.; Depypere, M.; Wagemans, J.; Lavigne, R.; et al. Safety and efficacy of phage therapy in difficult-to-treat infections: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis 2022, 22, e208–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirnay, J.P.; Djebara, S.; Steurs, G.; Griselain, J.; Cochez, C.; De Soir, S.; Glonti, T.; Spiessens, A.; Vanden Berghe, E.; Green, S.; et al. Retrospective, observational analysis of the first one hundred consecutive cases of personalized bacteriophage therapy of difficult-to-treat infections facilitated by a Belgian consortium. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Bradner, W.T. Mitomycin C: a clinical update. Cancer Treat Rev 2001, 27, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, J.; Pinedo, H.M. Mitomycin C: mechanism of action, usefulness and limitations. Anticancer Drugs 1990, 1, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Muñiz, M.Y.; López-Jacome, L.E.; Hernández-Durán, M.; Franco-Cendejas, R.; Licona-Limón, P.; Ramos-Balderas, J.L.; Martinéz-Vázquez, M.; Belmont-Díaz, J.A.; Wood, T.K.; García-Contreras, R. Repurposing the anticancer drug mitomycin C for the treatment of persistent Acinetobacter baumannii infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2017, 49, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, B.W.; Chowdhury, N.; Wood, T.K. Combatting bacterial infections by killing persister cells with mitomycin C. Environ Microbiol 2015, 17, 4406–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Z.; Luo, D.; Li, T.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, S.L. Design and synthesis of TPP+-Mitomycin C conjugate with reduced toxicity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2022, 77, 129036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacios, O.; Fernández-García, L.; Bleriot, I.; Blasco, L.; González-Bardanca, M.; López, M.; Fernández-Cuenca, F.; Oteo, J.; Pascual, Á.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; et al. Enhanced Antibacterial Activity of Repurposed Mitomycin C and Imipenem in Combination with the Lytic Phage vB_KpnM-VAC13 against Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2021, 65, e0090021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleriot, I.; Blasco, L.; Pacios, O.; Fernández-García, L.; Ambroa, A.; López, M.; Ortiz-Cartagena, C.; Cuenca, F.F.; Oteo-Iglesias, J.; Pascual, Á.; et al. The role of PemIK (PemK/PemI) type II TA system from Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical strains in lytic phage infection. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L, F.-G.; M, T.; TK, W. Ribosome inactivation by Escherichia coli GTPase RsgA inhibits T4 phage. 2023, 14. [CrossRef]
- Farha, M.A.; Brown, E.D. Drug repurposing for antimicrobial discovery. Nat Microbiol 2019, 4, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tong, Z.; Shi, J.; Li, R.; Upton, M.; Wang, Z. Drug repurposing for next-generation combination therapies against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4910–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug repurposing: progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.; Guarner, F.; Bustos Fernandez, L.; Maruy, A.; Sdepanian, V.L.; Cohen, H. Antibiotics as Major Disruptors of Gut Microbiota. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020, 10, 572912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, V.W.; Kwan, B.W.; Quezada, H.; Castillo-Juárez, I.; Pérez-Eretza, B.; García-Contreras, S.J.; Martínez-Vázquez, M.; Wood, T.K.; García-Contreras, R. Repurposing of Anticancer Drugs for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Curr Top Med Chem 2017, 17, 1157–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domalaon, R.; Ammeter, D.; Brizuela, M.; Gorityala, B.K.; Zhanel, G.G.; Schweizer, F. Repurposed Antimicrobial Combination Therapy: Tobramycin-Ciprofloxacin Hybrid Augments Activity of the Anticancer Drug Mitomycin C Against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Espejo, S.; Del Barrio-Tofiño, E.; Cebrero-Cangueiro, T.; López-Causapé, C.; Álvarez-Marín, R.; Cisneros, J.M.; Pachón, J.; Oliver, A.; Pachón-Ibáñez, M.E. Carbapenem Combinations for Infections Caused by Carbapenemase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Experimental In Vitro and In Vivo Analysis. Antibiotics (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayerbe-Algaba, R.; Gil-Marqués, M.L.; Jiménez-Mejías, M.E.; Sánchez-Encinales, V.; Parra-Millán, R.; Pachón-Ibáñez, M.E.; Pachón, J.; Smani, Y. Synergistic Activity of Niclosamide in Combination With Colistin Against Colistin-Susceptible and Colistin-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2018, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, M.W.; Zheng, Y.; Jasti, V.P.; Champeil, E.; Tomasz, M.; Wang, Y.; Basu, A.K.; Tang, M.S. Repair of mitomycin C mono- and interstrand cross-linked DNA adducts by UvrABC: a new model. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38, 6976–6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Wood, T.L.; Martínez-Vázquez, M.; García-Contreras, R.; Wood, T.K. DNA-crosslinker cisplatin eradicates bacterial persister cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 2016, 113, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton-Brown, C.E.; Friman, V.P. Rapid evolution of generalized resistance mechanisms can constrain the efficacy of phage-antibiotic treatments. Evol Appl 2018, 11, 1630–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Vega, A.; Bernstein, L.R.; Mandujano-Tinoco, E.A.; García-Contreras, S.J.; García-Contreras, R. Drug repurposing as an alternative for the treatment of recalcitrant bacterial infections. Front Microbiol 2015, 6, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyclit, L.; Baron, S.A.; Rolain, J.M. Drug Repurposing to Fight Colistin and Carbapenem-Resistant Bacteria. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2019, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacios, O.; Fernández-García, L.; Bleriot, I.; Blasco, L.; Ambroa, A.; López, M.; Ortiz-Cartagena, C.; Cuenca, F.F.; Oteo-Iglesias, J.; Pascual, Á.; et al. Phenotypic and Genomic Comparison of Klebsiella pneumoniae Lytic Phages: vB_KpnM-VAC66 and vB_KpnM-VAC13. Viruses 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://genomes.atcc.org/genomes/f629ae6e6bcd483e (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Abedon, S.T.; Yin, J. Bacteriophage plaques: theory and analysis. Methods Mol Biol 2009, 501, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raya, R.R.; H'bert, E.M. Isolation of Phage via Induction of Lysogens. Methods Mol Biol 2009, 501, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.; Pereira, C.; Almeida, A. Sequential Combined Effect of Phages and Antibiotics on the Inactivation of Escherichia coli. Microorganisms 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| K. pneumoniae clinical strain | Sequence-type | Carbapenemase | Biological origin | GenBank acc. Number | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K2534 | ST437 | OXA-245 | Rectal | WRXG00000000.1 | [23] |
| K3325 | ST42 | - | Blood | SAMEA3649525 | [23] |
| ATCC | ST131 | - | Commercial | [40] | |
| K. pneumoniae lytic bacteriophage | Morphotype | Genus | Genome size (bp) | GenBank accession number | Characterization (reference) |
| vB_KpnM-VAC13 | Myoviridae | Slopekvirus | 174826 | MZ322895.1 | [23] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





