Introduction
Sarcopenia is a widespread, advancing condition that impacts skeletal muscles, resulting in reduced muscle bulk and performance, thereby heightening the risk of significant complications. It is widely recognized that a decline in muscle tissue and capability can present as symptoms in various major illnesses, such as cancer, endocrine disorders, rheumatologic diseases, and other systemic conditions. With the rise in life expectancy, sarcopenia is increasingly seen in general practice as an age-related issue, contributing to higher mortality and disability rates. Various international research organizations have created definitions, screening techniques, and diagnostic standards for sarcopenia [
1].
The term "sarcopenia" was first introduced in the 1990s. In a 1997 essay, Irwin H. Rosenberg discusses its origins and contemporary importance, highlighting a lecture he gave at a symposium called "Sarcopenia: Diagnosis and Mechanisms" on April 17, 1996, in Washington, DC. The word "sarcopenia" is derived from the Greek words "sarx" (meaning "flesh") and "penia" (meaning "loss") [
2].
Sarcopenia is classified as "primary" (age) when age is the sole contributing factor. However, when additional variables are evident, it is categorized as "secondary". The EWGSOP describes three conceptual stages: "presarcopenia," "sarcopenia," and "severe sarcopenia." The "presarcopenia" stage involves a reduction in muscle mass without affecting strength or physical performance, detectable only through techniques that accurately measure muscle mass relative to populations. The "sarcopenia" stage is characterized by a loss of muscle tissue, decreased muscle strength, or reduced physical function. Severe sarcopenia is defined when there is a simultaneous presence of decreased muscle mass, reduced muscle strength, and impaired physical performance [
3]. Sarcopenia associated with hospitalization, acute sarcopenia, and induced sarcopenia are not attributed to age. Instead, these conditions arise from factors such as activity levels, diet, or illness [
4].
Sarcopenia may be caused by systemic illnesses, notably inflammatory conditions like cancer or organ failure. Physical inactivity, whether due to a sedentary lifestyle, immobility, or disability resulting from illness, can also contribute to sarcopenia. Furthermore, insufficient intake of protein or calories, which may arise from conditions like anorexia, malabsorption, restricted eating patterns, or inadequate access to nutritious foods, can play a role in the development of sarcopenia [
5].
Sarcopenia is associated with several risk factors, including age, gender, and physical activity levels. Resistance exercise is particularly effective in mitigating the skeletal muscle loss associated with aging. Additionally, sarcopenia is linked to major co-morbidities such as osteoporosis, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and obesity [
6]. Sarcopenia has been linked to increased risks of cardiovascular disease, mortality, physical disability, and metabolic dysfunction. It often coexists with obesity, leading to a condition known as sarcopenic obesity. This condition primarily affects older individuals who have elevated body fat percentages alongside reduced muscle mass, strength, or quality. Consequently, there appears to be a significant correlation between obesity, metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in individuals with sarcopenia [
7].
Aging is accelerating globally, especially among those over 60. By 2050, the percentage of people over 60 worldwide is expected to increase significantly, rising from 10% to 16% [
8]. Between 1990 and 2010, the population over 60 increased by 75.1%, and by 2025, it is predicted to have doubled to 11% [
9]. In 1985, the global population consisted of about 9 percent elderly women [
10]. By 2015, the number of senior females in Europe had increased by less than 40% [
11]. Musculoskeletal problems among the elderly vary by age, geography, and personal circumstances. These issues are prevalent globally but exhibit significant differences between countries. In 2017, musculoskeletal diseases imposed a significant burden, with an estimated 1.3 billion prevalent cases and 138.7 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). Age-standardized death rates were reported at 1,720 per 100,000 individuals. Since 1990, there has been a slight decrease in age-standardized prevalence (-1.6 percent) and DALY rates (-3.5 percent) [
12].
Sarcopenia becomes more prevalent with age, affecting approximately 14% of individuals aged 65 to under 70, and about 53% of those over 80. According to published definitions, sarcopenia's prevalence ranges from 5% to 14% among people aged 61 to 71, and from 12% to 52% in those aged 80 and above. In the year 2000, there were 600 million adults aged over 60 worldwide. By 2050, the global population is expected to be reached two billion, up from 1.2 billion in 2025. Currently, sarcopenia affects more than 50 million people, with projections indicating that this number will be surpassed by 200 million in the next 40 years based on standard prevalence estimates [
13].
The hormonal changes during menopause adversely affect women's musculoskeletal health, heightening their vulnerability to health issues during midlife and beyond. Conditions like osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and sarcopenia, which involve reduced muscle mass and function, are all associated with estrogen deficiency typical of menopause [
14]. Reduced estrogen levels also contribute to decreases in both bone density and muscle strength [
15]. As the global population ages, the prevalence of osteoporosis is on the rise. Complications from osteoporosis can lead to significant social and financial burdens, underscoring the importance of early identification. While other imaging modalities allow for the quantification of bone loss, assessment of fracture presence, and study of bone quality, conventional radiography enables semi-qualitative and qualitative evaluation of osteoporosis. In efforts to detect osteoporosis early, advanced imaging techniques such as high-resolution MRI and micro-CT are being utilized [
16].
Materials and Method
This cross-sectional study was conducted at Ali Fatima hospital, Lahore. We enrolled 370 postmenopausal women aged between 55 to 75 years who had been diagnosed with osteoporosis Patients with other types of osteoporosis (i.e., osteoporosis caused by malignant tumors, steroids, hyperthyroidism, and metabolic diseases) were excluded. We also excluded patients with reduced postural stability due to specific diseases, such as cardiovascular disease and vestibular nerve disorders. The study was conducted from 12 February to 5 July 2024, as the frequency of regular visits to Ali Fatima hospital, Lahore, physiotherapy department is generally three months for osteoporosis patients. The inclusion criteria were female sex, age between 55 to 75 years, and ability to fill a self-descriptive questionnaire.
The Chair Stand Test: The Chair Stand test, which involves repeatedly standing up from a seated position within a specified time frame, was utilized to gauge lower body strength and endurance [
17].
The EuroQol-5D (EQ-5D) questionnaire was used to evaluate patients' health-related quality of life (QOL) at Jinnah Hospital, Mayo Hospital, and Ali Fatima Hospital. The EuroQoL Group developed this questionnaire, which provides a comprehensive assessment of health-related QOL in several domains, such as mobility, regular activities, self-care, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression. There are three degrees of difficulty for each dimension: no issues, moderate problems, and severe problems. Each level is denoted by a distinct five-digit code that represents the person's current state of health. A code such as 1-2-2-3-3, for example, denotes no functional limitations, moderate difficulties with self-management and daily tasks, and significant difficulties with pain/discomfort and anxiety/depression. These five-digit codes are added together to get the EQ-5D index score, which is a value between 5 and 15 that gives a general idea of the patient's overall.
The Berg Balance Scale: This scale is a popular instrument for assessing balance in elderly people and people with balance problems. It comprises of a set of exercises designed to evaluate a person's ability to stay balanced while engaging in a variety of functional motions, including sitting, standing, reaching, and turning [
18].
The Romberg Test: An individual's ability to remain balanced while standing still with their feet together and their eyes closed is assessed using the Romberg test. This test can identify anomalies in sensory or proprioceptive function that may impact postural stability. It depends on proprioception and vestibular input to maintain balance [
19].
Results
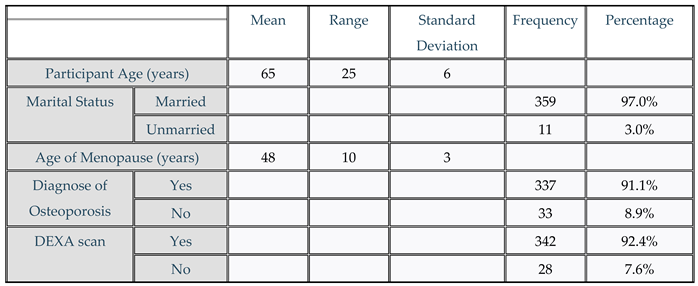
The characteristics of the study participants are summarized in
Table 1. A total of 370 women aged between 55 to 75 years (mean age: 64.59 years) were recruited.
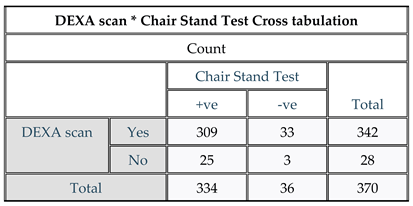
Figure 1.
DEXA Scan and Chair stand test. Result: The results of the correlation analysis between DEXA scan and Chair Stand Test revealed that 342 participants had osteoporosis, while 309 participants tested positive for sarcopenia. Notably, the results indicated that approximately 90.35% of the participants (309 out of 342) had sarcopenia.
Figure 1.
DEXA Scan and Chair stand test. Result: The results of the correlation analysis between DEXA scan and Chair Stand Test revealed that 342 participants had osteoporosis, while 309 participants tested positive for sarcopenia. Notably, the results indicated that approximately 90.35% of the participants (309 out of 342) had sarcopenia.
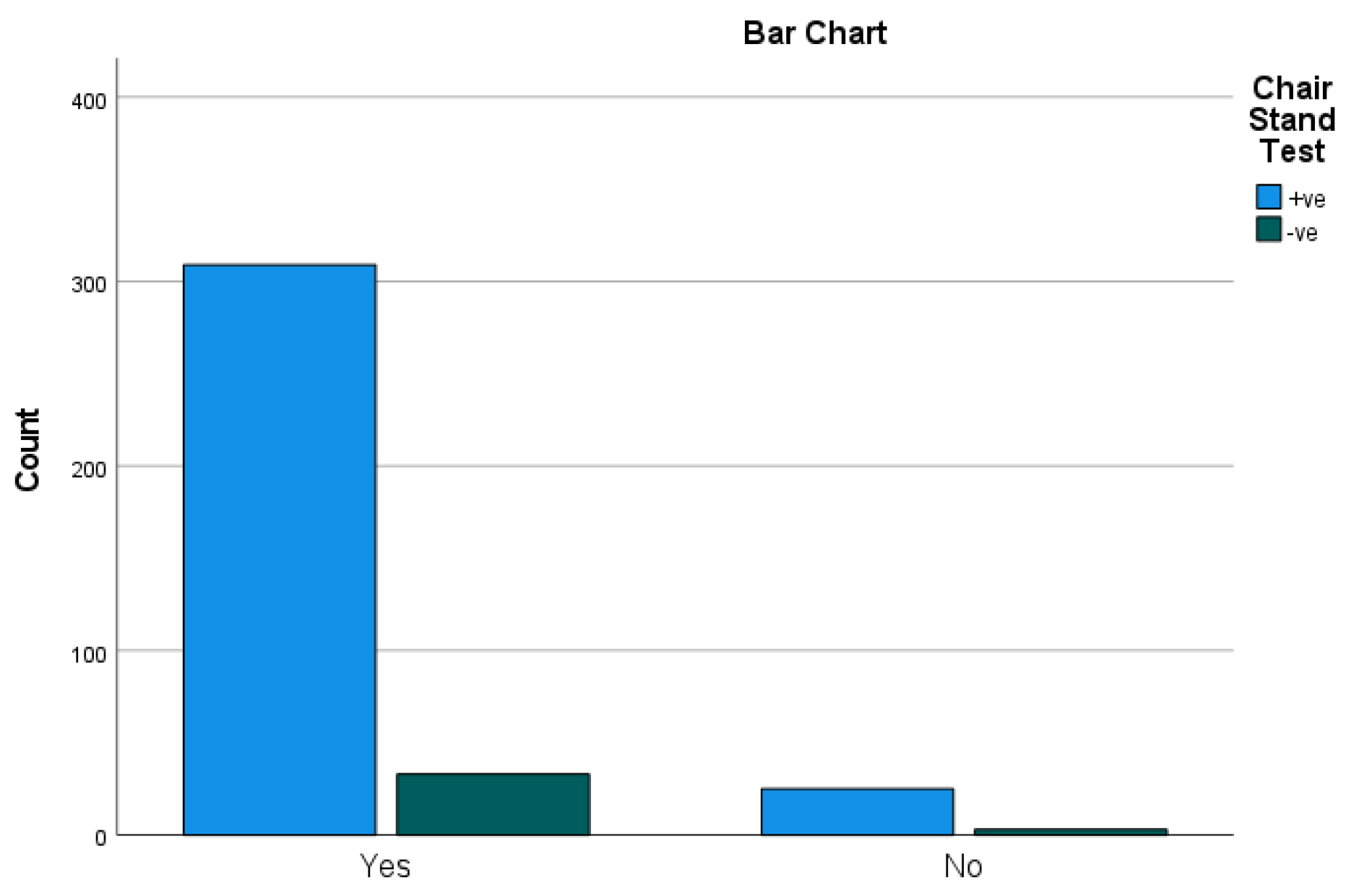
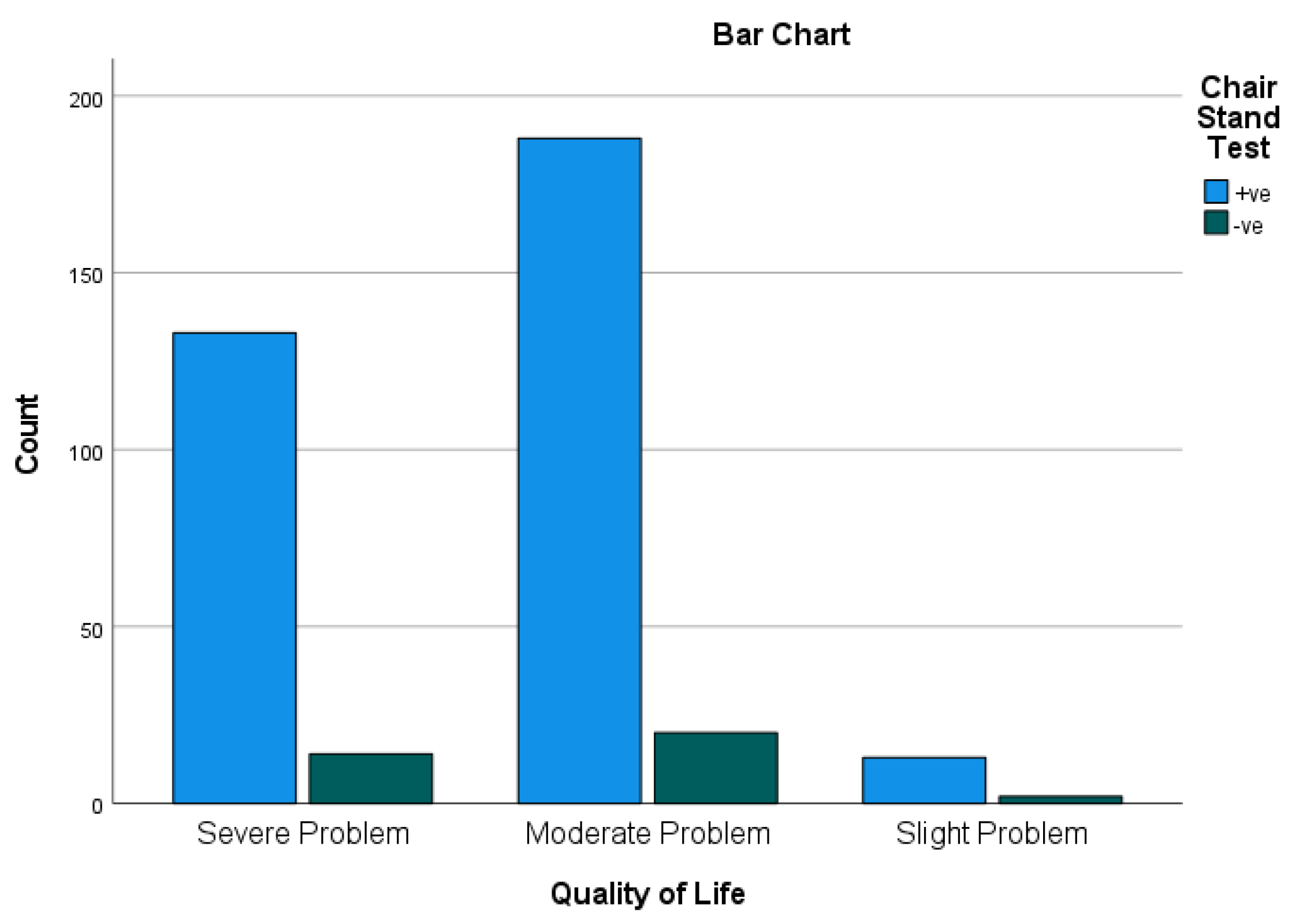
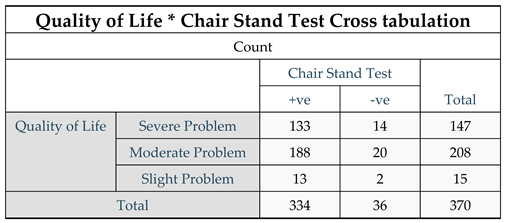
Figure 4.
Quality of Life * Chair Stand Test Cross tabulation. Result: The results of the correlation analysis between Quality of life and Chair Stand Test revealed that 133 participants had severe problem Notably, the results indicated that approximately 39.82% of the participants (133 out of 334) had affect the quality of life.
Figure 4.
Quality of Life * Chair Stand Test Cross tabulation. Result: The results of the correlation analysis between Quality of life and Chair Stand Test revealed that 133 participants had severe problem Notably, the results indicated that approximately 39.82% of the participants (133 out of 334) had affect the quality of life.
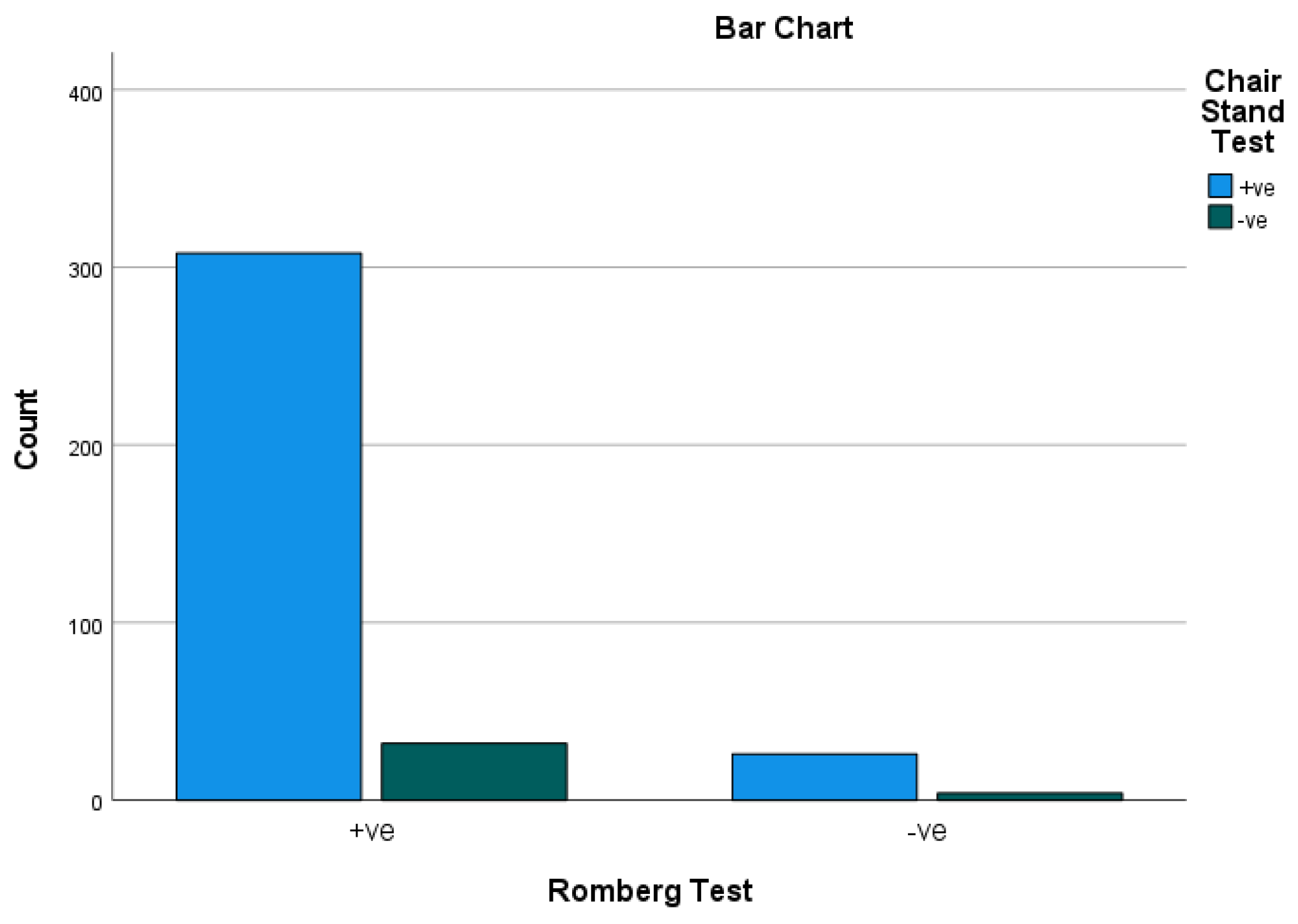
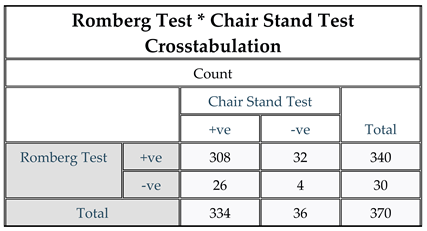
Figure 5.
Romberg Test * Chair Stand Test Crosstabulation. Result: The results of the correlation analysis between Romberg test and Chair Stand Test revealed that 308 participants had postural instability. Notably, the results indicated that approximately 92.21% of the participants (308 out of 334) had postural instability.
Figure 5.
Romberg Test * Chair Stand Test Crosstabulation. Result: The results of the correlation analysis between Romberg test and Chair Stand Test revealed that 308 participants had postural instability. Notably, the results indicated that approximately 92.21% of the participants (308 out of 334) had postural instability.
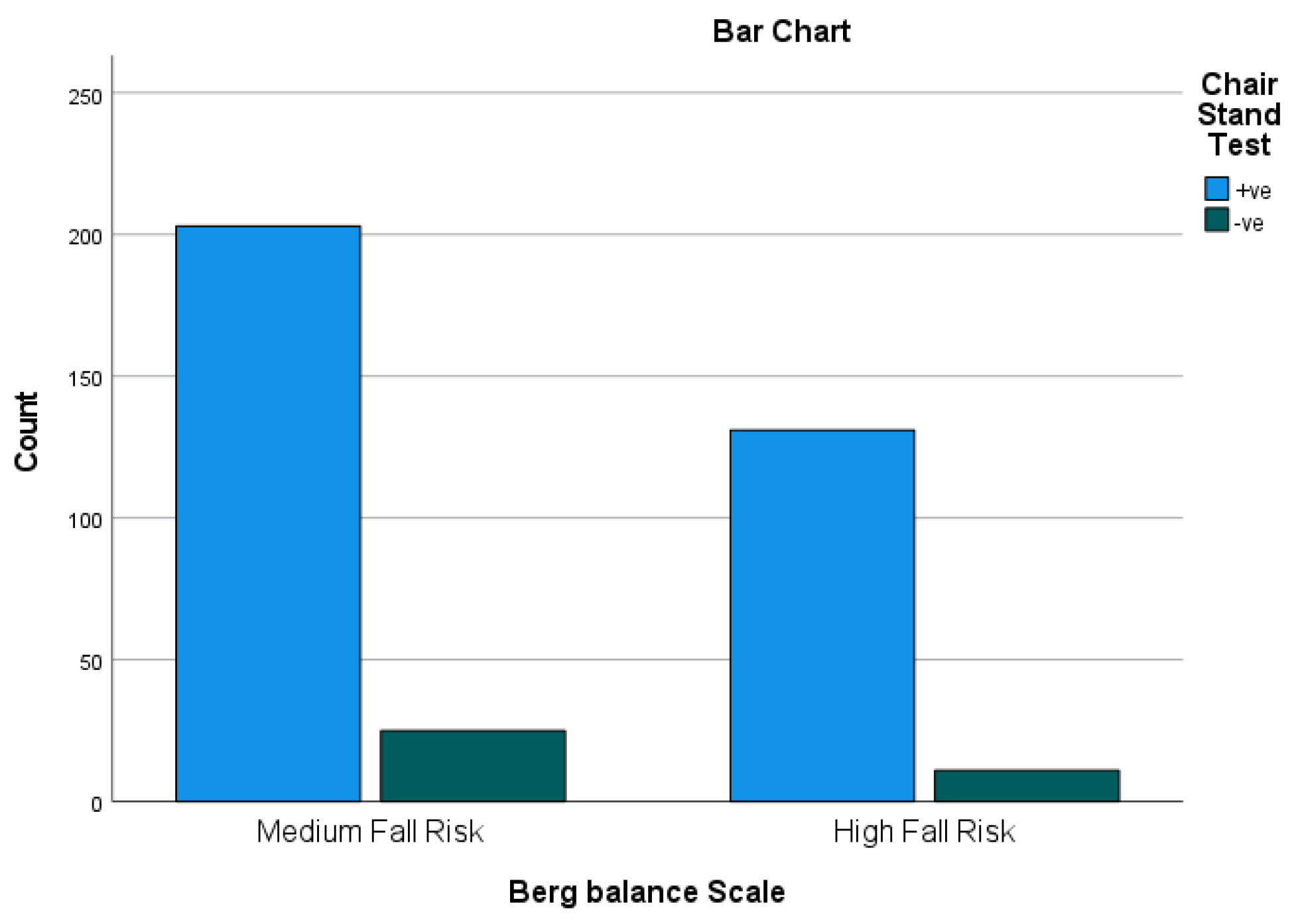
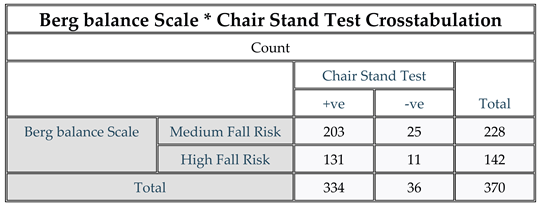
Figure 6.
Berg balance Scale * Chair Stand Test Crosstabulation. Result: The results of the correlation analysis between Berg balance scale and Chair Stand Test revealed that 131 participants had high fall risk. Notably, the results indicated that approximately 39.22% of the participants (131 out of 334) had balance issues.
Figure 6.
Berg balance Scale * Chair Stand Test Crosstabulation. Result: The results of the correlation analysis between Berg balance scale and Chair Stand Test revealed that 131 participants had high fall risk. Notably, the results indicated that approximately 39.22% of the participants (131 out of 334) had balance issues.
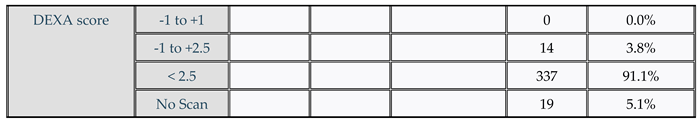
Table 1.
Characteristics of the study population (n = 370), Marital status, Diagnose of Osteoporosis, DEXA scan, DEXA score.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the study population (n = 370), Marital status, Diagnose of Osteoporosis, DEXA scan, DEXA score.
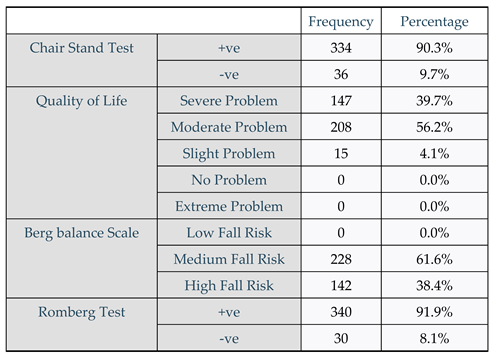
Table 2.
Chair Stand Test, Quality of life, Berg Balance Scale, Romberg Test.
Table 2.
Chair Stand Test, Quality of life, Berg Balance Scale, Romberg Test.
Table 3.
DEXA Scan and Chair stand test cross tabulation.
Table 3.
DEXA Scan and Chair stand test cross tabulation.
Table 4.
Quality of Life * Chair Stand Test Cross tabulation.
Table 4.
Quality of Life * Chair Stand Test Cross tabulation.
Table 5.
Romberg Test * Chair Stand Test Crosstabulation.
Table 5.
Romberg Test * Chair Stand Test Crosstabulation.
Table 6.
Berg balance Scale * Chair Stand Test Crosstabulation.
Table 6.
Berg balance Scale * Chair Stand Test Crosstabulation.
Discussion
Research conducted at the physiotherapy department of the Ali Fatima Hospital in Lahore revealed that sarcopenia was often observed in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis and that it was linked to a history of falls, postural stability, nutrition, and quality of life. The primary cause of musculoskeletal deterioration and loss of functional ability in older adults is sarcopenia. The condition is characterised by a decrease in the amount and quality of skeletal muscle. The frequency of sarcopenia varies by age group [
20].
The age range of our study was 55–75, with a mean age of 65. This is in line with other research on sarcopenic older adult populations. Akira Okayama et alstudy .'s from 2022 found sarcopenia in postmenopausal women in several randomly selected age groups. The mean age of the 61 patients was 77.6 ± 8.1 years [
21].
The majority of participants in our study were between the ages of 58 and 71, according to the standard deviation of six years, which is also in line with other studies [
22].
According to our research, the menopausal mean age in our population was 49 years, with a 3-year standard deviation. This result is in line with earlier research that suggested the average menopausal age was around 46 years [
23].The results of this investigation are consistent with other studies showing that osteoporosis and osteopenia are highly prevalent in comparable groups [
24]. The majority of patients (90.8%) had DEXA values below 2.5, which is indicative of osteoporosis. This finding is in line with other research that found a significant incidence of osteoporosis in this age range [
25]. Additionally, the percentage of patients with osteopenia (3.8%) is consistent with earlier findings [
26].
The study's conclusions show that a vast majority of individuals—93.0 percent—did not have any comorbidities, whereas just 6.7% of participants did—having one or more. This implies that most of the subjects had minimal underlying medical issues and were generally in good health.
According to the findings of the Chair Stand Test, a sizable majority of participants (90.0 percent, n=334) had positive test results, suggesting insufficient functional ability and lower extremity strength. This implies that the majority of individuals lacked the functional ability and physical power necessary to get up from a sitting posture on their own.
However, a lesser percentage of subjects (10.0 percent, n=36) had negative test results, meaning that their lower extremity strength and functional ability were unaffected.
The results of this study are in line with earlier studies that have demonstrated lower extremity weakness and functional limits in older persons, which can have major effects on day-to-day functioning [
27].
The EQ-5D quality of life assessment results show that among postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, there is a worrying prevalence of severe difficulties in at least one dimension. A considerable influence on their day-to-day life was shown by the almost 40% (39.6%) of individuals who reported having serious issues with their mobility, self-care, pain, regular activities, or sadness.
Furthermore, a majority of the participants (56.1%) reported experiencing moderate problems, suggesting a significant number of symptoms and functional limitations. The low percentage of respondents (4.0%) who expressed modest worries demonstrates how prevalent these issues are in this group of people. These results are in line with other studies that shown osteoporosis in postmenopausal women increases the likelihood of sarcopenia, a disorder marked by a gradual loss of muscular mass, strength, and function [
28].
With 91.9 percent (340/370) of the subjects testing positive, the Romberg test findings show a high prevalence of positive results among the participants. On the other hand, 8.1 percent (30/370) of the subjects had negative Romberg test results, which suggests that their proprioception and balance are unharmed.
Most subjects showed deficits in proprioception and balance, which are essential for mobility, postural stability, and functional ability [
19].
The high percentage of positive Romberg test findings is in line with other studies that have demonstrated the danger of balance and mobility problems in older persons with osteoporosis [
19]. The study's findings emphasise how crucial it is to identify and treat this population's balance and proprioception issues in order to stop falls and the damage they cause.
The Berg Balance Scale results show a worrisome prevalence of postural instability and fall risk among the participants, with 38.5 percent (142/370) and 61.5 percent (228/370) respectively categorised as moderate and medium fall risk. According to these results, a sizable fraction of participants may be at danger of falling, which can result in severe injuries and disabilities.
This is in line with other studies that have demonstrated that osteoporosis in older persons increases the risk of falls because of decreased muscular strength, mobility, and balance [
29].
This research is subject to many limitations. In order to be included, postmenopausal women had to fulfil two requirements: they needed to be older (55–75 years old) and osteoporotic. As a result, women in various age groups might not be able to utilise the findings. Women who need walking assistance were included; however, women who were completely unable to walk or who had other concurrent diseases that may affect muscle mass or function (such as advanced cancer or end-stage renal illness) were excluded. Our study participants Each participant was chosen from the "Ali Fatima Hospital, Lahore" physiotherapy department.
This study has additional benefits. This large group includes over 370 elderly postmenopausal women who have Type-1 osteoporosis. By verifying each and every osteoporosis diagnosis using DEXA scan results, the high calibre of the osteoporosis data was guaranteed. This is the first investigation of the clinical traits linked to the incidence of sarcopenia in postmenopausal women with Type-1 osteoporosis. More studies of this sort will be required to ascertain the frequency of sarcopenia in postmenopausal women with Type-1 osteoporosis and the clinical characteristics linked to it in various age groups and research scenarios.
Conclusions
This study concluded that the prevalence of sarcopenia was 90.35% with affected quality of life in 39.82%, postural instability in 92.21% patients and balance in 39.92% patients respectively.
References
- Golounina O, Fadeev V, Belaya Zh. Modern recommendations for the diagnosis of sarcopenia. Clinical medicine. 2023;101(4-5):198-207.
- Roman D, Mahoney K, Mohamadi A. Sarcopenia: What's in a name? Journal of the American Medical Directors Association. 2013;14(2):80-2. [CrossRef]
- Santilli V, Bernetti A, Mangone M, Paoloni M. Clinical definition of sarcopenia. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2014;11(3):177-80.
- Wakabayashi, H. Hospital-associated sarcopenia, acute sarcopenia, and iatrogenic sarcopenia: Prevention of sarcopenia during hospitalization. Journal of General and Family Medicine. 2023;24(3):146-7. [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age and ageing. 2010;39(4):412-23. [CrossRef]
- Janssen I, Shepard DS, Katzmarzyk PT, Roubenoff R. The healthcare costs of sarcopenia in the United States. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52(1):80-5. [CrossRef]
- Atkins JL, Wannamathee SG. Sarcopenic obesity in ageing: cardiovascular outcomes and mortality. British Journal of Nutrition. 2020;124(10):1102-13. [CrossRef]
- Ferrara N, Komici K, Rengo G, Corbi G. Aging: from Demography to Epidemiology. In: Crucitti A, editor. Surgical Management of Elderly Patients. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2018. p. 3-8.
- Sixsmith, A. Technology and the Challenge of Aging. In: Sixsmith A, Gutman G, editors. Technologies for Active Aging. Boston, MA: Springer US; 2013. p. 7-25.
- Rix SE. Older women: Making a difference in development. Ageing International. 1992;19(1):1-11. [CrossRef]
- Kunugi, T. Women and population aging. Asia Pac Popul J. 1989;4(2):75-9.
- Safiri S, Kolahi AA, Cross M, Hill C, Smith E, Carson-Chahhoud K, et al. Prevalence, deaths, and disability-adjusted life years due to musculoskeletal disorders for 195 countries and territories 1990–2017. Arthritis & rheumatology. 2021;73(4):702-14. [CrossRef]
- Morley JE. Sarcopenia: diagnosis and treatment. J Nutr Health Aging. 2008;12(7):452-6. [CrossRef]
- Khadilkar, SS. Musculoskeletal Disorders and Menopause. The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India. 2019;69(2):99-103. [CrossRef]
- Zumwalt M, Dowling B. Prevention and Management of Common Musculoskeletal Injuries in the Aging Female Athlete. In: Robert-McComb JJ, Norman RL, Zumwalt M, editors. The Active Female: Health Issues Throughout the Lifespan. New York, NY: Springer New York; 2014. p. 261-74.
- Guglielmi G, Muscarella S, Bazzocchi A. Integrated imaging approach to osteoporosis: state-of-the-art review and update. Radiographics. 2011;31(5):1343-64. [CrossRef]
- Mehmet H, Yang AW, Robinson SR. What is the optimal chair stand test protocol for older adults? A systematic review. Disability and rehabilitation. 2020;42(20):2828-35. [CrossRef]
- Berg, T. Berg balance scale. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2009;73:2-5.
- Khasnis A, Gokula R. Romberg′ s Test. Journal of postgraduate medicine. 2003;49(2):169.
- Chen L-K, Liu L-K, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung T-W, Bahyah KS, et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association. 2014;15(2):95-101. [CrossRef]
- Okayama A, Nakayama N, Kashiwa K, Horinouchi Y, Fukusaki H, Nakamura H, et al. Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Its Association with Quality of Life, Postural Stability, and Past Incidence of Falls in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Healthcare. 2022;10(2):192. [CrossRef]
- Teraž K, Marusic U, Kalc M, Šimunič B, Pori P, Grassi B, et al. Sarcopenia parameters in active older adults – an eight-year longitudinal study. BMC Public Health. 2023;23(1):917. [CrossRef]
- Singh P, Vyas S, Vallabh V, Nautiyal R, Srivastava A. Age at natural menopause and factors affecting its onset: A cross-sectional study among postmenopausal females in District Dehradun. Indian Journal of Community Health. 2022;34(2):241-7. [CrossRef]
- Shankam LP, Kothandan D, Tukivakam A, Pamidi D. Natural menopausal age: Correlation with body mass index and various reproductive factors in postmenopausal women. National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2018;8(6):887-. [CrossRef]
- Anupama DS, Noronha JA, Acharya KKV, Prabhu MM, Shetty J, Shankar R, et al. Burden of Osteopenia and Osteoporosis Among Postmenopausal Women in India: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Mid-life Health. 2022;13(2):107-14. [CrossRef]
- Khinda R, Valecha S, Kumar N, Walia JPS, Singh K, Sethi S, et al. Prevalence and Predictors of Osteoporosis and Osteopenia in Postmenopausal Women of Punjab, India. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022;19(5):2999. [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro PA, Carneiro JAO, Coqueiro RS, Pereira R, Fernandes MH. “Chair stand testˮ as simple tool for sarcopenia screening in elderly women. The journal of nutrition, health & aging. 2016;20(1):56-9. [CrossRef]
- Ciubean AD, Ungur RA, Irsay L, Ciortea VM, Borda IM, Onac I, et al. Health-related quality of life in Romanian postmenopausal women with osteoporosis and fragility fractures. Clinical interventions in aging. 2018:2465-72. [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi H, Ashraf A, Zeynali N, Ebrahimi B, Jehu DA. Balance and functional mobility predict low bone mineral density among postmenopausal women undergoing recent menopause with osteoporosis, osteopenia, and normal bone mineral density: A cross-sectional study. Geriatric Nursing. 2021;42(1):33-6. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).