Submitted:
06 August 2024
Posted:
08 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Highlights
1. Introduction

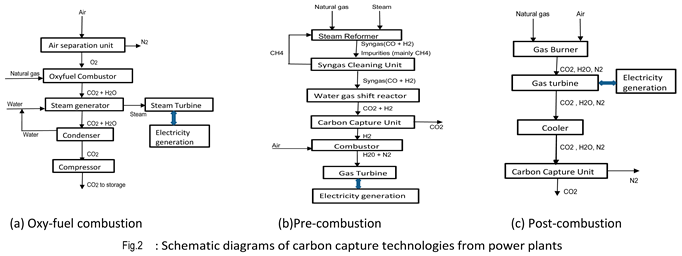
2. Methodology
- 2S-AB +AD: Two-stage Absorption + Adsorption hybrid
- 2S-AB +MB: Two-stage Absorption + Membrane hybrid
- 2S-AD +AB: Two-stage Adsorption + Absorption hybrid
- 2S-AD +MB: Two-stage Adsorption + Membrane hybrid
- 2S-MB +AB: Two-stage Membrane + Absorption hybrid
- 2S-MB +AD: Two-stage Membrane + Adsorption hybrid
- Total investment cost (TIC)
- Total Product cost (TPC)
- Net present value (NPV)
- Rate of return on investment (ROI)
- Discounted Cash-Flow Rate of Return (DCFRR)
- Levelized cost of electricity (LCOE)
- Carbon emission intensity (CEI)
- Cost of carbon avoidance (COA)
2.1. Total Investment Cost
2.2. Operating Costs
2.3. Net Present Value (NPV)
2.4. Discounted Cash-Flow Rate of Return
2.5. Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE)
2.6. CO2 Emission Intensity
2.7. Cost of CO2 Avoidance (COA)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Discussion and Analyses
3.2. Dimensional Analysis
| 7. Levelized cost of electricity (LCOE): $/MWh | 582.9698033 | 651.1117874 | 503.4920413 | 545.5409734 | 721.2756674 | 606.9620734 |
| 8. Total carbon emissions | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 |
| 9. Carbon emissions intensity (CEI): kg CO2/kWh | 0.167045455 | 0.18375 | 0.147 | 0.159782609 | 0.204166667 | 0.175 |
| 10. Cost of avoided carbon (COA): $/ton CO2 | 3489.887258 | 3543.465509 | 3425.115927 | 3414.270038 | 3532.778779 | 3468.354705 |
4. Conclusions and future direction
- 2S-AB +AD: Two-stage Absorption + Adsorption hybrid
- 2S-AB +MB: Two-stage Absorption + Membrane hybrid
- 2S-AD +AB: Two-stage Adsorption + Absorption hybrid
- 2S-AD +MB: Two-stage Adsorption + Membrane hybrid
- 2S-MB +AB: Two-stage Membrane + Absorption hybrid
- 2S-MB +AD: Two-stage Membrane + Adsorption hybrid
- Total investment cost (TIC)
- Total Product cost (TPC)
- Net present value (NPV)
- Discounted Cash-Flow Rate of Return (DCFRR)
- Levelized cost of electricity (LCOE)
- Carbon emission intensity (CEI)
- Cost of carbon avoidance (COA)
Nomenclature
| 2S-AB +AD: | Two-stage Absorption + Adsorption hybrid |
| 2S-AB +MB: | Two-stage Absorption + Membrane hybrid |
| 2S-AD +AB: | Two-stage Adsorption + Absorption hybrid |
| 2S-AD +MB: | Two-stage Adsorption + Membrane hybrid |
| 2S-MB +AB: | Two-stage Membrane + Absorption hybrid |
| 2S-MB +AD: | Two-stage Membrane + Adsorption hybrid |
| APC | Annual Product cost |
| CCS | Carbon capture and storage |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| CEI | Carbon emission intensity |
| COA | Cost of carbon avoidance |
| DCFRR | Discounted Cash-Flow Rate of Return |
| H2 | Hydrogen |
| KgCO2 | Kilogram of CO2 captured |
| KWh | Kilowatt-hour |
| LCOE | Levelized cost of electricity |
| MWh | Megawatt-hour |
| NGPPs | Natural gas power plants |
| NCF | Net cash flow |
| NPV | Net present value |
| NOx | Nitrogen oxides |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| PCC | Post-combustion carbon capture |
| PEC | Purchased Equipment cost |
| SO2 | Sulfur dioxide |
| tCO2/ton | Tons of CO2 captured |
| TIC | Total investment cost |
| TCI | Total capital investment |
References
- A.G. Olabi, Khaled Obaideen, Khaled Elsaid, Tabbi Wilberforce, Enas Taha Sayed, Hussein M. Maghrabie, Mohammad Ali Abdelkareem, Assessment of the pre-combustion carbon capture contribution into sustainable development goals SDGs using novel indicators, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Volume 153, 2022, 111710, ISSN 1364-0321. [CrossRef]
- Adamu, Abdullahi & Russo Abegão, Fernando & Boodhoo, Kamelia. Process intensification technologies for CO2 capture and conversion – a review. BMC Chemical Engineering. 2020, 2. [CrossRef]
- Bahman, N., Al-Khalifa, M., Al Baharna, S. et al. Review of carbon capture and storage technologies in selected industries: potentials and challenges. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 22, 451–470 (2023). [CrossRef]
- CHAPTER 10 - Discounted Cash Flow Rate of Return, Editor(s): GEORGE S. KOCH, Computer Methods in the Geosciences, Pergamon, Volume 8, 1990, Pages 119-127, ISSN 1874-561X, ISBN 9780080402819. [CrossRef]
- Church, J. A., Clark, P. U., Cazenave, A., Gregory, J. M., Jevrejeva, S., Levermann, A., ... & Zicker, S. S. Sea level change. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (pp. 1137-1216). Cambridge University Press. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Cong Chao, Yimin Deng, Raf Dewil, Jan Baeyens, Xianfeng Fan, Post-combustion carbon capture, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Volume 138, 2021, 110490, ISSN 1364-0321. [CrossRef]
- EPA. Air Pollution and Health. United States Environmental Protection Agency, 2022.
- Hansen, J., Sato, M., Ruedy, R., Lo, K., Lea, D. W., & Medina-Elizondo, M. Ice melt, sea level rise and superstorms: Evidence from paleoclimate data, climate modeling, and modern observations that 2°C global warming above the preindustrial level would be dangerous. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 2020, 20(19), 10655-10665. [CrossRef]
- Hospital-Benito, D. & Lemus, Jesus & Moya, Christine & Santiago, Rubén & Paramio, C. & Palomar, J.. Aspen Plus supported design of pre-combustion CO2 capture processes based on ionic liquids. Separation and Purification Technology. 2022, 290. 12084. [CrossRef]
- . [CrossRef]
- Huang, Xiaoting & Ai, Ning & Li, Lan & Jiang, Quanda & Wang, Qining & Ren, Jie & Wang, Jiawei. Simulation of CO2 Capture Process in Flue Gas from Oxy-Fuel Combustion Plant and Effects of Properties of Absorbents. Separations. 2022, 9. 95. [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press. 2021.
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change and Land: an IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems. Cambridge University Press. 2022.
- International Energy Agency (IEA) (2022). Global Energy Review 2022.).
- IPCC Emission Factor Database (2023). IPCC Emissions Factor Database | GHG Protocol.
- Li et al. Hybrid post-combustion carbon capture process for natural gas power plants. Journal of Cleaner Production 2022, 377, 134111, Wang et al. Optimization of hybrid post-combustion carbon capture process for natural gas combined cycle power plants. Fuel 2022, 324, 123264.
- Li, J. Li, J., Wang, T., Liu, P. et al. Dynamic modelling and simulation of a post-combustion CO2 capture process for coal-fired power plants. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 16, 198–209 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Max Peters. Plant Design and Economics for Chemical Engineers 5th Edition. Google book. WEB Jan 16, 2019. https://archive.org/details/plantdesignecono0000pete.
- Moro, A., Helmers, E. A new hybrid method for reducing the gap between WTW and LCA in the carbon footprint assessment of electric vehicles. Int J Life Cycle Assess 22, 4–14 (2017). [CrossRef]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Global CO2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion, 2022. Boot-Handford et al. Carbon capture and storage: A review of the current state of the art. Energy & Environmental Science 2020, 13(10), 2831-2851).
- Obi, D., Onyekuru, S., & Orga, A. Review of recent process developments in the field of carbon dioxide (CO2) capture from power plants flue gases and the future perspectives. International Journal of Sustainable Energy 2024, 43(1). [CrossRef]
- Peters et al. Plant design and economics for chemical engineers. McGraw-Hill, Liu et al. (2022). Cost optimization of carbon capture processes using dimensional analysis. Energy 2020, 238, 122102).
- Roussanaly, S. Calculating CO2 avoidance costs of Carbon Capture and Storage from industry. Carbon Management 2019, 10(1), 105–112. [CrossRef]
- Sujeet Yadav, S.S. Mondal, A review on the progress and prospects of oxy-fuel carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) technology, Fuel, Volume 308, 2022, 122057, ISSN 0016-2361. [CrossRef]
- Swanson, Norman R. (editor), Yang, Xiye. Recent Advances in Theory and Methods for the Analysis of High Dimensional and High Frequency Financial Data- from Econometrics (MDPI); 2020, 9783036508528, 9783036508535. [CrossRef]
- Wai Lip Theo, Jeng Shiun Lim, Haslenda Hashim, Azizul Azri Mustaffa, Wai Shin Ho, Review of pre-combustion capture and ionic liquid in carbon capture and storage, Applied Energy, Volume 183, 2016, Pages 1633-1663, ISSN 0306-2619. [CrossRef]
- Wall Street Prep. Net Present Value (NPV) | Formula + Calculator. Retrieved from (Return on Assets (ROA) | Formula + Calculator (wallstreetprep.com)), 2024.
- WallStreetMojo. DCFROr (Discounted Cash Flow Rate of Return). 2024. Retrieved from (https://www.wallstreetmojo.
- Zhang et al. Recent advances in hybrid carbon capture technologies. Chemical Engineering Journal 2022, 427, 131921, Smith et al. Dimensional analysis for process intensification and optimization. Chemical Engineering Research and Design 2022, 177, 102-115.
- Zohuri, B. Principles of the Dimensional Analysis. In: Dimensional Analysis Beyond the Pi Theorem, 2017.
| Direct Cost | ||
|---|---|---|
| Item | $ | |
| f1 | Purchased Equipment cost: from Aspen Plus flowsheet simulation | PEC |
| F2 | Purchased Equipment installations | 12% of PEC |
| F3 | Instrumentation and control (installed) | 12% of PEC |
| F4 | Piping (installed) | 20% of PEC |
| F5 | Electrical (installed) | 10% of PEC |
| F6 | Buildings (including process/services) | 18% of PEC |
| F7 | Yard improvement | 10% of PEC |
| F8 | Service facilities(installed) | 20% of PEC |
| F9 | Land | 5% of PEC |
| TOTAL DIRECT COST:∑(f1---f9) | DC | |
| Indirect Cost | ||
| f10 | Items | $ |
| F11 | Engineering Supervision | 12% of PEC |
| F12 | Construction expenses: EC | 15% of PEC |
| TOTAL INDIRECT COST:∑(f10---f12) | IC | |
| Other costs ($) | ||
| Items | $ | |
| F13 | Contractors’ fee | 10% of (DC +IC) |
| F14 | Contingency | 15% of (DC + IC) |
| TOTAL OTHER COSTS:∑(f13—f14) | OC | |
| Fixed Project Cost: DC + IC + OC | FPC | |
| Working Capital: 15% of FPC | WC | |
| Total Capital Investment: FPC + WC | TCI |
| Operating/Production Cost | ||
|---|---|---|
| Variable Operating Cost | ||
| Items | Cost ($) | |
| F1 | Raw materials | 15% of TCI |
| F2 | Utilities | 5% of TCI |
| F3 | Miscellaneous materials | 1% of FPC |
| Total Variable Cost:∑(f1---f3) | VC | |
| Fixed Operating Capital | ||
| F4 | Maintenance cost (MC) | 10% of FPC |
| F5 | Operating Labour cost (OLC) | 50% of TCI |
| F6 | Laboratory Cost (LC) | 21% of OLC |
| F7 | Supervision Cost (SC) | 10% of OLC |
| F8 | Plant Overheads cost (POC) | 65% of OLC |
| F9 | Insurance Costs (IC) | 1% of FWC |
| F10 | Local taxes | 2% of FPC |
| Total Fixed Costs:∑(f4---f10) | FC | |
| General Overheads Cost: 8.5% of (VC + FC) | GOC | |
| Operating cost/ Production Cost: VC + FC + GOC | OPS | |
| 1: Molar composition | |
| Chemical Compound | % mole |
| Methane | 90.19 |
| Ethane | 6.94 |
| Propane | 2.09 |
| N-butane | 0.361 |
| I-butane | 0.414 |
| N-pentane | 0.005 |
| I-pentane | 0.007 |
| 2. Operating conditions | |
| Gas flow rate, MMSCFD | 7498656 |
| Inlet temperature, °C | 45.94 |
| Inlet pressure, bar | 147.5 |
| 3. Gas properties | |
| Gas gravity, kg/m³ | 0.182 |
| Gas specific heat capacity, J/kgK | 2170 |
| Thermal capacity, MW | 1470 |
| 4. Ambient conditions | |
| Ambient pressure, bar | 143.27 |
| Ambient temperature, °C | 15 |
| 2S-AB +AD | 2S-AB +MB | 2S-AD +AB |
| Two-stage absorber: | Two-stage absorber: | Adsorber Stage 1 |
| Solvent: MEA (monoethanolamine) | Solvent: MEA (monoethanolamine) | Adsorbent: Zeolite 13X |
| Flow rate: 550 kg/s | Flow rate: 500 kg/s | Bed dimensions: 7 m diameter, 15 m height |
| Column dimensions: 12 m diameter, 25 m height | Column dimensions: 10 m diameter, 20 m height | Adsorption cycle: 3 hours |
| Operating conditions: 45°C, 1.8 bar | Operating conditions: 40°C, 1.5 bar | Desorption cycle: 2 hours |
| Inlet CO2 concentration: 12% (v/v) | ||
| Adsorber: | Membrane: | Outlet CO2 concentration: 6% (v/v) |
| Adsorbent: Zeolite 13X | Type: Polyamide | |
| Bed dimensions: 6 m diameter, 12 m height | Surface area: 1000 m² | Adsorber Stage 2 |
| Adsorption cycle: 2.5 hours | Selectivity: CO2/N2 = 50 | Adsorbent: Zeolite 13X |
| Desorption cycle: 1.5 hours | Permeance: 100 GPU (gas permeance unit) | Bed dimensions: 7 m diameter, 15 m height |
| Capture efficiency: 92% | Capture efficiency: 90% | Adsorption cycle: 3 hours |
| CO2 purity: 96% | CO2 purity: 95% | Desorption cycle: 2 hours |
| Membrane area: 5000 m² | Inlet CO2 concentration: 6% (v/v) | |
| Integration | Outlet CO2 concentration: 3% (v/v) | |
| Flue gas flow rate: 2200 kg/s | Integration | |
| - CO2 concentration: 11% (v/v) | Flue gas flow rate: 2000 kg/s | Absorber |
| Capture system energy consumption: 11% of power plant output | CO2 concentration: 10% (v/v) | Solvent: MEA (monoethanolamine) |
| Recycle ratio: 0.6 (absorber outlet to adsorber inlet) | Capture system energy consumption: 10% of power plant output | Flow rate: 600 kg/s |
| - CO2 capture rate: 1.3 million tons per year | Recycle ratio: 0.5 (absorber outlet to membrane inlet) | Column dimensions: 15 m diameter, 30 m height |
| Power plant efficiency penalty: 11.2% | CO2 capture rate: 1.2 million tons per year | Operating conditions: 50°C, 2.0 bar |
| Power Generation $ 1. Gas Turbine: 120,000,000 2. Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG): 80,000,000 3. Steam Turbine: 50,000,000 4. Generator: 20,000,000 Carbon Capture System 1. Absorption Stage: Absorber Column: 2,500,000 Lean Amine Tank: 1,500,000 Rich Amine Tank: 1,000,000 Heat Exchangers: 2,000,000 Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 2. Adsorption Stage: Adsorber Vessels (2-3): 2,250,000 Zeolite or Activated Carbon Adsorbent: 1,000,000 Desorption Heat Exchangers: 1,150,000 Pumps and Valves: 700,000 : 3. Hybrid System Components: Inter-stage Heat Exchanger: 1,000,000 Flash Tank: 500,000 Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 |
Power plant efficiency penalty: 10.5% | Inlet CO2 concentration: 3% (v/v) |
| Power Generation $ 1. Gas Turbine: 120,000,000 2. Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG): 80,000,000 3. Steam Turbine: 50,000,000 4. Generator: 20,000,000 Carbon Capture System 1. Absorption Stage: - Absorber Column: 2,500,000 - Lean Amine Tank: 1,500,000 - Rich Amine Tank: 1,000,000 - Heat Exchangers: 2,000,000 - Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 2. Membrane Stage: Membrane Modules: 1,800,000 Compressors: 1,350,000 Heat Exchangers: 500,000 Pumps and Valves: 700,000 3. Hybrid System Components: Inter-stage Heat Exchanger: 1,000,000 Flash Tank: 500,000 Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 |
Outlet CO2 concentration: 0.5% (v/v) | |
| Integration | ||
| CO2 capture rate: 1.5 million tons per year | ||
| Power plant efficiency penalty: 12.5% | ||
| Capture system capital cost: $600 million | ||
| Operating cost: $150 million per year | ||
| CO2 purity: 98% | ||
| Capture efficiency: 95% | ||
| Power Generation $ 1. Gas Turbine: 120,000,000 2. Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG): 80,000,000 3. Steam Turbine: 50,000,000 4. Generator: 20,000,000 Carbon Capture System 1. Adsorption Stage: Adsorber Vessels (2-3): 4,500,000 Zeolite or Activated Carbon Adsorbent: 2,000,000 Desorption Heat Exchangers: 2,300,000 Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 2. Absorption Stage: Absorber Column: 1,250,000 Lean Amine Tank: 750,000 Rich Amine Tank: 500,000 Heat Exchangers: 1,000,000 Pumps and Valves: 700,000 3. Hybrid System Components: Inter-stage Heat Exchanger: 1,000,000 Flash Tank: 500,000 Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 | ||
| 2S-AD +MB | 2S-MB +AB | 2S-MB +AD |
| Two-stage adsorber: | Two-stage membrane: | Two-stage membrane: |
| Adsorbent: Zeolite 13X | Type: Polyamide | Type: Polyamide |
| Bed dimensions: 8 m diameter, 18 m height | Surface area: 1500 m | Surface area: 1800 m |
| Adsorption cycle: 3.5 hours | Selectivity: CO2/N2 = 70 | Selectivity: CO2/N2 = 80 |
| Desorption cycle: 2.5 hours | Permeance: 150 GPU (gas permeance unit) | Permeance: 180 GPU (gas permeance unit) |
| Membrane: | Absorber: | Adsorber: |
| Type: Polyamide | Solvent: MEA (monoethanolamine) | Adsorbent: Zeolite 13X |
| Surface area: 1200 m² | Flow rate: 700 kg/s | Bed dimensions: 10 m diameter, 20 m height |
| Selectivity: CO2/N2 = 60 | Column dimensions: 18 m diameter, 35 m height | Adsorption cycle: 4 hours |
| Permeance: 120 GPU (gas permeance unit) | Operating conditions: 55°C, 2.2 bar | Desorption cycle: 3 hours |
| Capture efficiency: 96% | Capture efficiency: 97% | Capture efficiency: 98% |
| -CO2 purity: 99% | CO2 purity: 99.5% | CO2 purity: 99.8% |
| Integration_ | Integration | Integration |
| Flue gas flow rate: 2600 kg/s | Flue gas flow rate: 2800 kg/s | Flue gas flow rate: 3000 kg/s |
| CO2 concentration: 13% (v/v) | CO2 concentration: 14% (v/v) | CO2 concentration: 15% (v/v) |
| Capture system energy consumption: 13% of power plant output | Capture system energy consumption: 14% of power plant output | Capture system energy consumption: 15% of power plant output |
| Recycle ratio: 0.8 (adsorber outlet to membrane inlet) | - Recycle ratio: 0.9 (membrane outlet to absorber inlet) | Recycle ratio: 0.95 (membrane outlet to adsorber inlet) |
| - CO2 capture rate: 1.9 million tons per year | CO2 capture rate: 2.1 million tons per year | |
| - Power plant efficiency penalty: 15.2% | Power plant efficiency penalty: 16.5% | |
| Power Generation $ 1. Gas Turbine: 120,000,000 2. Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG): 80,000,000 3. Steam Turbine: 50,000,000 4. Generator: 20,000,000 Carbon Capture System 1. Adsorption Stage: Adsorber Vessels (2-3): 4,500,000 Zeolite or Activated Carbon Adsorbent: 2,000,000 Desorption Heat Exchangers: 2,300,000 Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 2. Membrane Stage: Membrane Modules: 1,800,000 Compressors: 1,350,000 Heat Exchangers: 500,000 Pumps and Valves: 700,000 3. Hybrid System Components: Inter-stage Heat Exchanger: 1,000,000 Flash Tank: 500,000 Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 |
Power Generation $ 1. Gas Turbine: 120,000,000 2. Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG): 80,000,000 3. Steam Turbine: 50,000,000 4. Generator: 20,000,000 Carbon Capture System 1. .Membrane Stage: Membrane Modules: 3,600,000 Compressors: 2,700,000 Heat Exchangers: 1,000,000 Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 2. Absorption Stage: Absorber Column: 1,250,000 Lean Amine Tank: 750,000 Rich Amine Tank: 500,000 Heat Exchangers: 1,000,000 Pumps and Valves: 700,000 3. Hybrid System Components: Inter-stage Heat Exchanger: 1,000,000 Flash Tank: 500,000 Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 |
Two-stage membrane: |
| Type: Polyamide | ||
| Surface area: 1800 m | ||
| Selectivity: CO2/N2 = 80 | ||
| Permeance: 180 GPU (gas permeance unit) | ||
| Adsorber: | ||
| Adsorbent: Zeolite 13X | ||
| Bed dimensions: 10 m diameter, 20 m height | ||
| Adsorption cycle: 4 hours | ||
| Desorption cycle: 3 hours | ||
| -Capture efficiency: 98% | ||
| Power Generation $ 1. Gas Turbine: 120,000,000 2. Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG): 80,000,000 3. Steam Turbine: 50,000,000 4. Generator: 20,000,000 Carbon Capture System 1. . Membrane Stage: Membrane Modules: 3,600,000 Compressors: 2,700,000 Heat Exchangers: 1,000,000 Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 2. Adsorption Stage: Adsorber Vessels (2-3): 2,250,000 Zeolite or Activated Carbon Adsorbent: 1,000,000 Desorption Heat Exchangers: 1,150,000 Pumps and Valves: 700,000 3. Hybrid System Components: Inter-stage Heat Exchanger: 1,000,000 Flash Tank: 500,000 Pumps and Valves: 1,400,000 |
| Table 5a: Purchased cost of major equipment for the three capture technologies | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | 2S-AB +AD | 2S-AB +MB | 2S-AD +AB | 2S-AD +MB | 2S-MB +AB | 2S-MB +AD |
| Power Generation | ||||||
| 1. Gas Turbine: | 120,000,000 | 120,000,000 | 120,000,000 | 120,000,000 | 120,000,000 | 120,000,000 |
| 2. Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG): | 80,000,000 | 80,000,000 | 80,000,000 | 80,000,000 | 80,000,000 | 80,000,000 |
| 3. Steam Turbine: | 50,000,000 | 50,000,000 | 50,000,000 | 50,000,000 | 50,000,000 | 50,000,000 |
| 4. Generator: | 20,000,000 | 20,000,000 | 20,000,000 | 20,000,000 | 20,000,000 | 20,000,000 |
| Carbon Capture System | ||||||
| 1. Absorption Stage: | ||||||
| - Absorber Column: | 2,500,000 | 2,500,000 | 1,250,000 | 1,250,000 | ||
| - Lean Amine Tank: | 1,500,000 | 1,500,000 | 750,000 | 750,000 | ||
| - Rich Amine Tank: | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 500,000 | 500,000 | ||
| - Heat Exchangers: | 2,000,000 | 2,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | ||
| - Pumps and Valves: | 1,400,000 | 1,400,000 | 700,000 | 700,000 | ||
| 2. Adsorption Stage: | ||||||
| - Adsorber Vessels (2-3): | 2,250,000 | 4,500,000 | 4,500,000 | 2,250,000 | ||
| - Zeolite or Activated Carbon Adsorbent: | 1,000,000 | 2,000,000 | 2,000,000 | 1,000,000 | ||
| - Desorption Heat Exchangers: | 1,150,000 | 2,300,000 | 2,300,000 | 1,150,000 | ||
| - Pumps and Valves: | 700,000 | 1,400,000 | 1,400,000 | 700,000 | ||
| 3. Membrane Stage: | ||||||
| - Membrane Modules: | 1,800,000 | 1,800,000 | 3,600,000 | 3,600,000 | ||
| - Compressors: | 1,350,000 | 1,350,000 | 2,700,000 | 2,700,000 | ||
| - Heat Exchangers: | 500,000 | 500,000 | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | ||
| - Pumps and Valves: | 700,000 | 700,000 | 1,400,000 | 1,400,000 | ||
| 4. Hybrid System Components: | ||||||
| - Inter-stage Heat Exchanger: | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 |
| - Flash Tank: | 500,000 | 500,000 | 500,000 | 500,000 | 500,000 | 500,000 |
| - Pumps and Valves: | 1,400,000 | 1,400,000 | 1,400,000 | 1,400,000 | 1,400,000 | 1,400,000 |
| TOTAL PURCHASED COST OF MAJOR EQUIPMENT (PCE | 286,400,000 | 285,650,000 | 287,300,000 | 287,450,000 | 285,800,000 | 286,700,000 |
| Table 5b: Total investment cost determination by factorial method. | ||||||
| Direct Cost | 2S-AB +AD | 2S-AB +MB | 2S-AD +AB | 2S-AD +MB | 2S-MB +AB | 2S-MB +AD |
| Item | Cost ($) | |||||
| Purchased Equipment cost (PEC) | 286400000 | 285650000 | 287300000 | 287450000 | 285800000 | 286700000 |
| Purchased Equipment installations: 12% of PEC | 34368000 | 34278000 | 34476000 | 34494000 | 34296000 | 34404000 |
| Instrumentation(installed) and control: 12% of PEC | 34368000 | 34278000 | 34476000 | 34494000 | 34296000 | 34404000 |
| Piping (installed): 20% of PEC | 57280000 | 57130000 | 57460000 | 57490000 | 57160000 | 57340000 |
| Electrical (installed): 10% of PEC | 28640000 | 28565000 | 28730000 | 28745000 | 28580000 | 28670000 |
| Buildings (including process/services): 18% of PEC | 51552000 | 51417000 | 51714000 | 51741000 | 51444000 | 51606000 |
| Yard improvement: 10% of PEC | 28640000 | 28565000 | 28730000 | 28745000 | 28580000 | 28670000 |
| Service facilities(installed): 20% of PEC | 57280000 | 57130000 | 57460000 | 57490000 | 57160000 | 57340000 |
| Land: 5% of PEC | 14320000 | 14282500 | 14365000 | 14372500 | 14290000 | 14335000 |
| TOTAL DIRECT COST (DC) | 592848000 | 591295500 | 594711000 | 595021500 | 591606000 | 593469000 |
| Indirect Cost | ||||||
| Items | Cost ($) | Cost ($) | Cost ($) | Cost ($) | Cost ($) | Cost ($) |
| Engineering Supervision; 12% of PEC | 34368000 | 34278000 | 34476000 | 34494000 | 34296000 | 34404000 |
| Construction expenses: 15% of PEC | 42960000 | 42847500 | 43095000 | 43117500 | 42870000 | 43005000 |
| TOTAL INDIRECT COST(IC) | 77328000 | 77125500 | 77571000 | 77611500 | 77166000 | 77409000 |
| DC + IC | 670176000 | 668421000 | 672282000 | 672633000 | 668772000 | 670878000 |
| Other costs ($) | ||||||
| Items | Cost ($) | Cost ($) | Cost ($) | Cost ($) | Cost ($) | Cost ($) |
| Contractors’ fee: 10% of (DC +IC) | 73719360 | 73526310 | 73951020 | 73989630 | 73564920 | 73796580 |
| Contingency: 15% of (DC + IC) | 100526400 | 100263150 | 100842300 | 100894950 | 100315800 | 100631700 |
| TOTAL OTHER COSTS (OC) | 174245760 | 173789460 | 174793320 | 174884580 | 173880720 | 174428280 |
| Fixed Project Cost (FPC): DC + IC + OC | 844421760 | 842210460 | 847075320 | 847517580 | 842652720 | 845306280 |
| Working Capital (WC): 15% of FPC | 126663264 | 126331569 | 127061298 | 127127637 | 126397908 | 126795942 |
| Total Capital Investment (TCI): FPC + WC | 971,085,024.00 | 968,542,029.00 | 974,136,618.00 | 974,645,217.00 | 969,050,628.00 | 972,102,222.00 |
| Table 5c: Operating/Production Cost | ||||||
| Variable Operating Cost | ||||||
| Items | 2S-AB +AD | 2S-AB +MB | 2S-AD +AB | 2S-AD +MB | 2S-MB +AB | 2S-MB +AD |
| Raw materials: 15% of TCI | 145662753.6 | 145281304.4 | 146120492.7 | 146196782.6 | 145357594.2 | 145815333.3 |
| Utilities: 5% of TCI | 48554251.2 | 48427101.45 | 48706830.9 | 48732260.85 | 48452531.4 | 48605111.1 |
| Miscellaneous materials: 1% of FPC | 18999489.6 | 18949735.35 | 19059194.7 | 19069145.55 | 18959686.2 | 19019391.3 |
| Total Variable Cost (A) | 213216494.4 | 212658141.2 | 213886518.3 | 213998189 | 212769811.8 | 213439835.7 |
| Fixed Operating Capital | ||||||
| Maintenance cost (MC): 10% of FPC | 84442176 | 84221046 | 84707532 | 84751758 | 84265272 | 84530628 |
| Operating Labour cost (OLC): 50% of TCI | 485542512 | 484271014.5 | 487068309 | 487322608.5 | 484525314 | 486051111 |
| Laboratory Cost (LC): 21% of OLC | 101963927.5 | 101696913 | 102284344.9 | 102337747.8 | 101750315.9 | 102070733.3 |
| Supervision Cost (SC): 10% of OLC | 48554251.2 | 48427101.45 | 48706830.9 | 48732260.85 | 48452531.4 | 48605111.1 |
| Plant Overheads cost (POC): 65% of OLC | 315602632.8 | 314776159.4 | 316594400.9 | 316759695.5 | 314941454.1 | 315933222.2 |
| Insurance Costs (IC): 1% of FWC | 8444217.6 | 8422104.6 | 8470753.2 | 8475175.8 | 8426527.2 | 8453062.8 |
| Local taxes: 2% of FPC | 16888435.2 | 16844209.2 | 16941506.4 | 16950351.6 | 16853054.4 | 16906125.6 |
| Total Fixed Costs (B) | 591095232 | 589547322 | 592952724 | 593262306 | 589856904 | 591714396 |
| Direct Operating Cost (DOC): A + B | 804311726.4 | 802205463.2 | 806839242.3 | 807260495 | 802626715.8 | 805154231.7 |
| General Overheads Cost(C): 8.5% of DOC | 68366496.74 | 68187464.37 | 68581335.6 | 68617142.07 | 68223270.84 | 68438109.69 |
| Annual Production Cost (APC): A + B + C | 1085894718 | 1083051069 | 1089307096 | 1089875826 | 1083619798 | 1087032177 |
| Table 5d: Annual sales revenue/ assessment factors determination | ||||||
| Unit output kW,q | 1470 | 1470 | 1470 | 1470 | 1470 | 1470 |
| Forecast sales volume(yearly) kW, (Q) | 12877200 | 12877200 | 12877200 | 12877200 | 12877200 | 12877200 |
| Forecast sales prize($/Kw-hr.)) SP | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Annual sales revenue (ASR): Q x SP | 1287720000 | 1287720000 | 1287720000 | 1287720000 | 1287720000 | 1287720000 |
| Net Cash flow (NCF): ASR – APC | 201825282.5 | 204668931.3 | 198412903.8 | 197844174 | 204100201.6 | 200687822.9 |
| Rate of Return (ROR) | ||||||
| ROR = (NCF)/(TCI) | 0.207834821 | 0.21131652 | 0.203680778 | 0.202990966 | 0.210618719 | 0.206447242 |
| %ROR = ROR x 100 | 20.78348213 | 21.13165203 | 20.36807776 | 20.29909659 | 21.06187186 | 20.64472422 |
| Net Present Value (NPV) | ||||||
| Project life, n: | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| NPV= n x NCF/(1+ROR) − TCI, $ | 3,206,333,917.99 | 3,255,558,936.82 | 3,146,825,257.93 | 3,136,860,597.13 | 3,245,740,503.51 | 3,186,550,885.23 |
| Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) | ||||||
| Net annual electricity generation/consumption(E), MW: | 220,000 | 200,000 | 250,000 | 230,000 | 180,000 | 210,000 |
| LCOE = NPV/ (n x E): | 582.9698033 | 651.1117874 | 503.4920413 | 545.5409734 | 721.2756674 | 606.9620734 |
| Carbon emission intensity (CEI) | ||||||
| Total CO2 Emissions(@300Kg/MW-hr) by IPCC | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 |
| CEI = Total CO2 Emissions/E | 0.167045455 | 0.18375 | 0.147 | 0.159782609 | 0.204166667 | 0.175 |
| Cost of CO2 Avoidance (COA) | ||||||
| COA = LCOE / CEI, $/ton (IPCC) | 3489.887258 | 3543.465509 | 3425.115927 | 3414.270038 | 3532.778779 | 3468.354705 |
| Item | 2S-AB + AD | 2S-AB + MB | 2S-AD + AB | 2S-AD + MB | 2S-MB + AB | 2S-MB + AD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Total investment cost (TIC): $ million | 971,085,024.00 | 968,542,029.00 | 974,136,618.00 | 974,645,217.00 | 969,050,628.00 | 972,102,222.00 |
| 2. Total product cost or operating capital (TPC): $ million/year | 1085894718 | 1083051069 | 1089307096 | 1089875826 | 1083619798 | 1087032177 |
| 3. Net present value (NPV): $ million | 3,206,333,917.99 | 3,255,558,936.82 | 3,146,825,257.93 | 3,136,860,597.13 | 3,245,740,503.51 | 3,186,550,885.23 |
| 4. Return on investment (ROI): % | 20.78348213 | 21.13165203 | 20.36807776 | 20.29909659 | 21.06187186 | 20.64472422 |
| 5. Discounted cash flow return on investment (DCFROI) or discounted cash flow return on rate (DCFRR): % | 12.15 | 10.14 | 8.12 | 7.11 | 8.12 | 6.1 |
| 6. Net annual electricity consumption kWh/ton | 220 | 200 | 250 | 230 | 180 | 210 |
| 7. Levelized cost of electricity (LCOE): $/MWh | 582.9698033 | 651.1117874 | 503.4920413 | 545.5409734 | 721.2756674 | 606.9620734 |
| 8. Total carbon emissions | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 | 36750 |
| 9. Carbon emissions intensity (CEI): kg CO2/kWh | 0.167045455 | 0.18375 | 0.147 | 0.159782609 | 0.204166667 | 0.175 |
| 10. Cost of avoided carbon (COA): $/ton CO2 | 3489.887258 | 3543.465509 | 3425.115927 | 3414.270038 | 3532.778779 | 3468.354705 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





