1. Introduction
The latest change in European Union (EU) pharmacovigilance legislation (Regulation (EU) No 1027/2012 and Directive 2012/26/EU 2012) highlighted the importance of strengthening public participation in drug and vaccine safety monitoring [
1]. Indeed, the legislation introduced the opportunity and right for European citizens to report any suspected Adverse Events related to drugs or vaccines (i.e., Adverse Events Following Immunization - AEFI) directly to national medicine regulatory authorities and marketing-authorization holders [
2,
3]. Patient engagement in vaccinovigilance activities offers several advantages, such as ensuring more timely detection of potential unknown threats, enhancing the system's reliability through a more comprehensive understanding of vaccine safety, and fostering public confidence in regulatory authorities and vaccines [
4,
5]. Concerns about vaccine safety and potential adverse reactions are primary determinants of vaccine hesitancy. Establishing open and transparent communication regarding safety issues raised by the public can contribute to bolstering confidence in vaccination and enhancing adherence rates [
6].
However, underreporting and low patient participation in post-marketing surveillance are well-known limitations of passive surveillance systems, potentially undermining the validity of collected data and negatively impacting benefit/risk assessment evaluation [
7,
8]. According to a recent study, the reporting rate (RR) for AEFI in Italy over a 10-year period (2008–2017) was 17.1 per 100,000 distributed doses [
9]. The analysis showed a progressive increase over time, with notable peaks attributed to the implementation of active surveillance projects. However, the overall proportion of reports from citizens was low (4.4%), with nearly half collected in 2017, suggesting the need for the further promotion of citizen engagement in vaccinovigilance activities.
In a recent systematic review, the lack of competence in identifying/recognizing adverse reactions, lack of knowledge regarding the reporting process, as well as time constraints have been identified as the motivations or obstacles influencing patient reporting. Furthermore, another contributing factor identified was patient-healthcare provider communication issues, highlighting instances where Healthcare Professionals (HCP) may not adequately inform patients about reporting procedures or may even discourage patient reporting [
10]. Simplifying the reporting process and promoting citizens’ awareness of their potential valuable contribution to drug safety monitoring are essential steps to increase patient engagement. Various digital solutions, such as the utilization of short message service (SMS), have been implemented in recent years to enhance the quantity and quality of spontaneous reporting, facilitating active patient-centered surveillance projects and complementing passive surveillance data [
11,
12,
13]. Moreover, many recent projects have been developed to apply Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning and Natural Language Processing (NLP) not only in pharmacovigilance data collection but also in the processing, identification and analysis of safety-relevant data [
14,
15]. Despite the promising nature of these systems in facilitating vaccine safety surveillance, they face challenges in ensuring the easy and feasible collection of all necessary data for both patients and HCPs. Balancing the need for comprehensive data collection by minimizing the burden on operators and ensuring user-friendly interfaces is crucial for maximizing participation and avoiding dropouts from surveillance.
The main aim of this study is to enhance vaccine safety surveillance by integrating the use of SMS to prompt citizens’ reporting with data from electronic immunization registries (IRs) available in Local Health Units (LHUs) across Italian regions. The secondary aim is to provide safety surveillance data on consistent serious adverse reactions following paediatric vaccinations.
2. Materials and Methods
The Italian Pharmacovigilance system encompasses both drugs and vaccine surveillance; reports of AEFI are submitted to the Local Responsible for Pharmacovigilance (LRPV) and collected in the National Pharmacovigilance Network (NPN), managed by the Italian Medicines Agency (Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco - AIFA). This project was coordinated by the Regional Pharmacovigilance Center (RPVC) of the Veneto Region of Italy in collaboration with AIFA. Eleven Italian regions, each with a computerized IRs, agreed to take part in the project (
Table S1). The number of participating vaccination centers varied among regions, depending on local organization. All parents of children aged 2 years or younger who received compulsory and/or recommended vaccinations according to the regional vaccination plan aligned with the Preventive National Vaccination Plan (PNVP 2017-2019) [
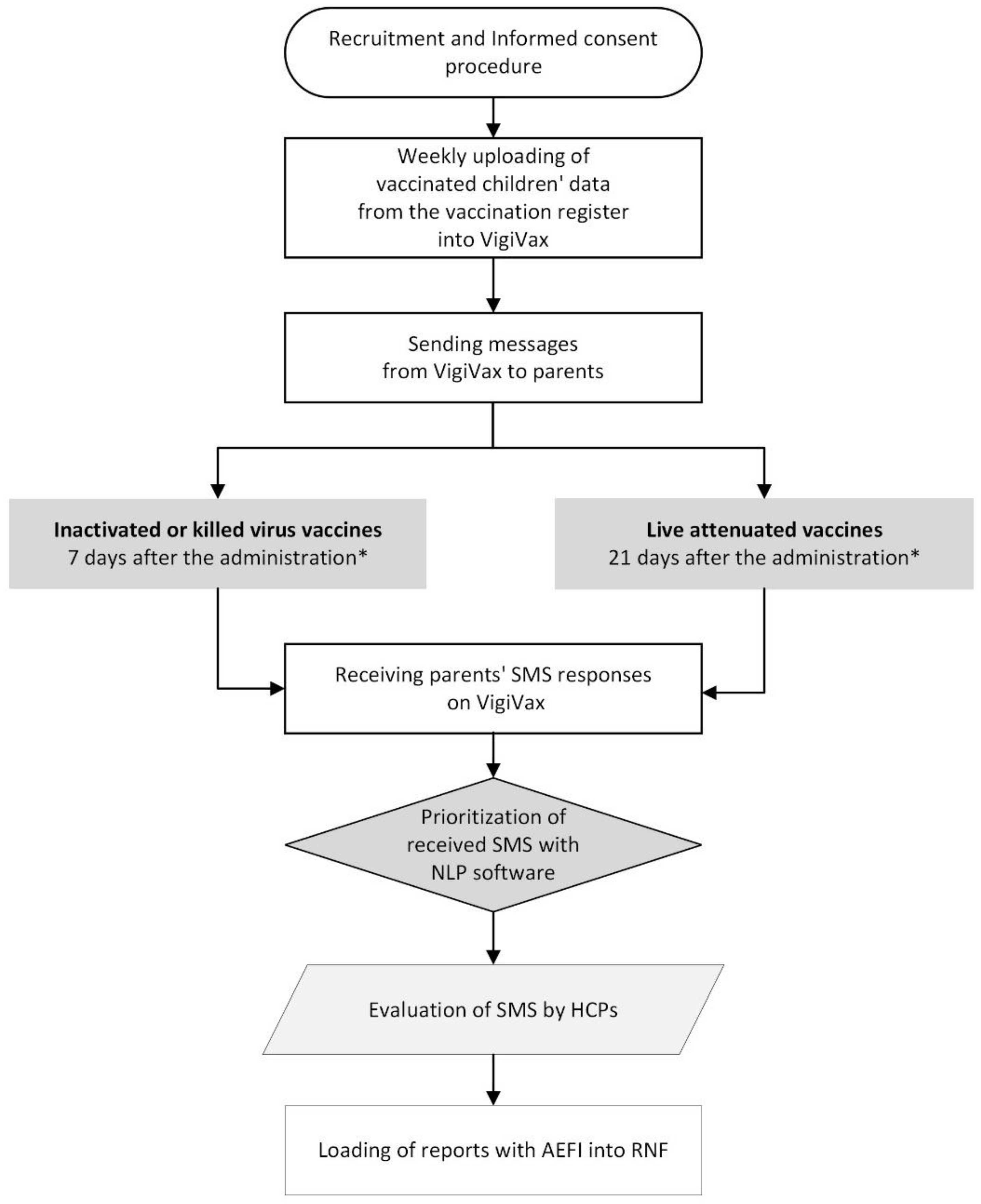
16], at one of the participating centers between March 1st 2021 and May 31st 2022, were considered eligible to participate in the study. A specific software, named 'VigiVax,' was developed by the RPVC of the Veneto Region. Personal data regarding patient initials, sex, date of birth, vaccine administration date, type of vaccine and mobile phone number of parents were extracted from the IRs and automatically uploaded on a weekly basis in VigiVax. Further step consisted in the automatic generation and sending of one SMS to the parents of vaccinated children, asking whether any AEFI have has occurred. The parents' responses sent to the system by SMS were automatically integrated by VigiVax with the previously uploaded individual data. The software also included an NLP algorithm to prioritize the evaluation of SMS with any potential serious events. Sensitive data, such as the phone number, were automatically deleted 30 days after SMS sending; however, parents still had the possibility to respond within a reasonable timeframe, considering the occurrence of any adverse reactions.
The data collection procedure involved several steps (
Figure 1). Initially, all participating vaccination centers registered on VigiVax, and HCPs underwent training on software usage through video tutorials, online learning sessions, and instruction manuals. Subsequently, HCPs were tasked with recruiting all eligible patients during routine vaccination sessions, informing them about the study’s main purpose and data collection methods. Parents willing to participate in the project agreed to receive the SMS. In our study, less than 0.2% of parents declined participation. The SMSs were sent 7 or 21 days after vaccination, with inactivated or live attenuated vaccines, respectively. If a child received both a live and an inactivated vaccine, the messages were sent after 21 days.
Supplementary Table 2 specifies the types of vaccines and the timing for SMS delivery. The SMS text inquired whether any AEFIs had occurred after the vaccine administration and eventually asked to describe symptoms and their onset date.
The response SMS messages from parents collected in VigiVax were reviewed by expert HCPs of the vaccination center who preliminary assessed the seriousness of the reported AEFIs and could request additional information or outcomes for serious cases. SMS messages without any reported AEFIs were archived. Furthermore, SMS reporting any AEFI, that were evaluated by HCPs and deemed by the coordinating center as definitely unrelated to vaccine administration due to incompatible time of onset or a definite relationship with other causes, were discarded. Finally, all SMS reporting an AEFI, at least potentially related to vaccination, were entered into the NPN.
The reported adverse reactions were coded using the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) while vaccines were categorized based on national terminology and classification.
Reports were sent and classified according to seriousness in the pharmacovigilance system, starting from the judgement of the reporter, based on standardized criteria. Serious adverse reactions are defined as “any untoward medical occurrence that at any dose results in death, is life-threatening, requires inpatient hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization, results in persistent or significant disability or incapacity, or is a congenital anomaly/birth defect” [
17]. Moreover, reporters can classify an event as serious if they judge it to be clinically relevant. However, this approach may not always align with the actual clinical severity of the event [
18]. All received reports were subsequently reevaluated, and their seriousness was reclassified by the coordinating center personnel based on clinical severity criteria [
19]. The coordinating center also assessed the causal relationship between AEFIs and the suspected vaccine for all the reports defined as serious by the reporters or during the revaluation. This assessment involves estimating the probability that the reported event may or may not be causally related to the vaccination and is carried out based on the WHO standardized algorithm [
20]. The evaluation of the causal relationship considered factors such as temporal interval, presence of alternative causes, biological plausibility, epidemiological data, diagnostic investigations, therapy, duration, and clinical progression. The final classification includes the categories 'consistent' (when a causal association to immunization is established), 'indeterminate' (when the relationship cannot be definitively established or excluded), 'inconsistent' (when the causal relationship is excluded), or 'unclassifiable' (when there is insufficient data to determine the causal relationship).
The overall RR per administered doses (AD) was calculated as the number of reports submitted online per 100,000 AD. Based on the causality assessment, the RR for severe consistent and indeterminate AEFIs per 100.000 AD was provided.
3. Results
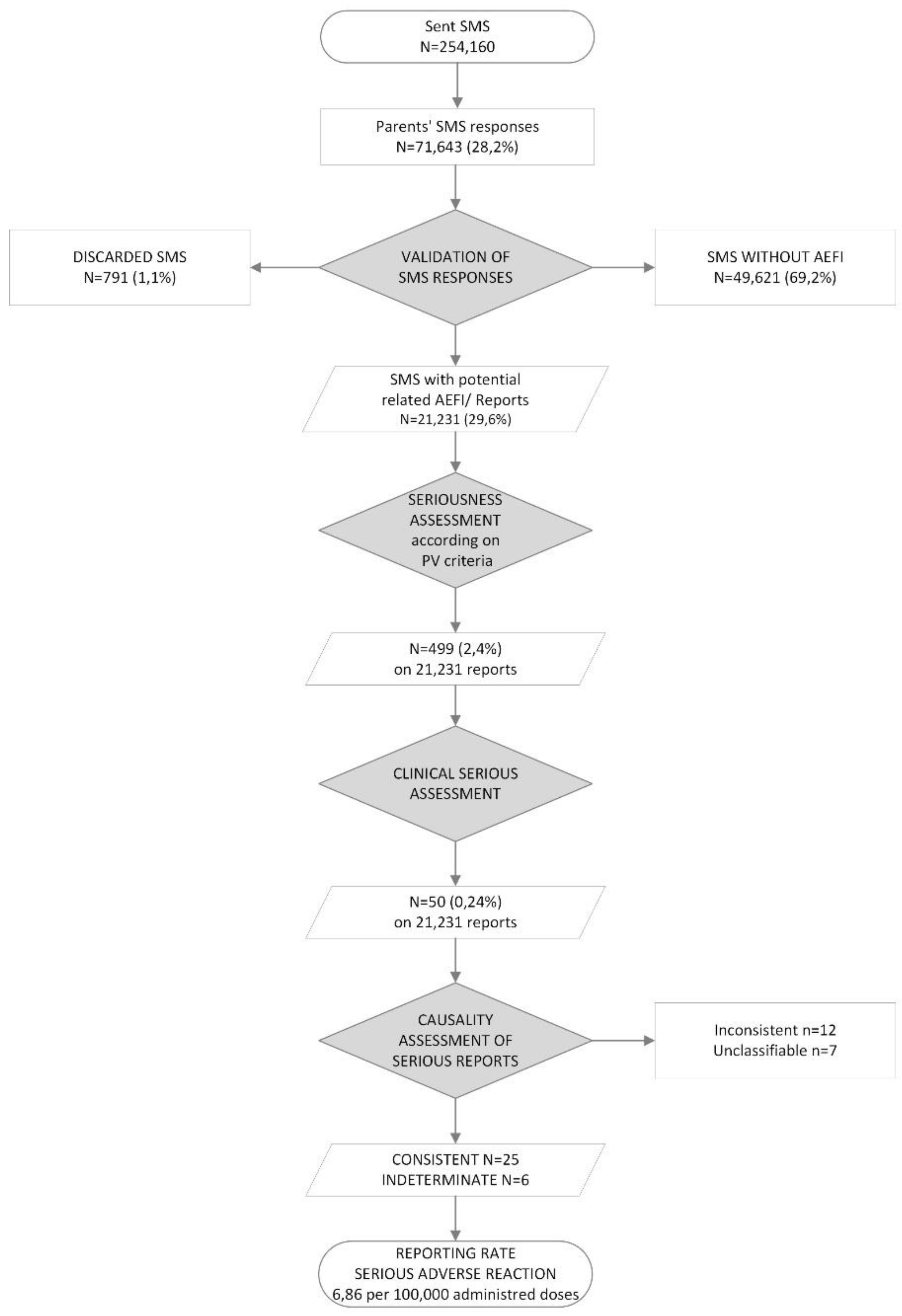
During the study, 254,160 SMS messages were sent, for a total of 451,656 vaccine AD. There was significant variability among participating regions according to the number of involved vaccinations centers, with 66% of SMS messages sent from the Piemonte region and 20% from Friuli Venezia Giulia region (
Table 1s). In terms of sex distribution, 51.3% of SMSs referred to vaccinated male children.
An overall response rate of 28.2% was achieved (number of returned SMS = 71,643), with a distribution of 28.8% for males and 27.6% for females. Among all received responses 1.1% (791/71,643) of SMS were discarded after evaluation by the HCP. Furthermore, 69.3% (49,621/71,643) of responses affirmed the absence of any adverse event. Finally, 29.6% (21,231/71,643) reported at least one AEFI equivalent to 8.3% of the total number of sent SMS messages. Considering sex distribution, the proportions were 29.8% for males and 29.3% for females of SMS responses (M/F RR Ratio 1.07, 95% CI 1.04-1.10), equivalent to 8.58% for males and 8.08% for females of sent SMS.
Figure 2.
Flowchart illustrating the steps and results of the study.
Figure 2.
Flowchart illustrating the steps and results of the study.
Vaccines administered in each vaccination session with a number of doses higher than 200 are listed in
Table 1
The 20 most frequently reported AEFIs among the 21,231 notifications are shown in
Table 2.
All cases reviewed and submitted by the HCPs were evaluated as serious according to pharmacovigilance criteria, with 499 out of 21,231 reports (2.35%) classified as 'serious. These mostly referred to clinically significant events but generally resolved spontaneously. The majority of these events included hyperpyrexia (54%), a combination of non-serious events (33%) or reactions that resulted in unnecessary emergency department visits. According to the seriousness assessment based on actual clinical criteria, 50 reports (0,24% of SMS responses with AEFI) were evaluated as serious, corresponding to an RR per 100,000 AD of 11,07 (RR per 100,000 vaccination session=19,67). The causality assessment was inconsistent in 12 reports, while in 7 cases, despite the follow-up, it remained unclassifiable (
Table 3).
Finally, a total of 31 reports were classified as either “consistent” (N=25, RR per 100.000 AD =5.54) or indeterminate (N=6, RR per 100.000 AD =1.33), accounting for a proportion of 0,15% among all received SMS responses with AEFI and an overall RR per 100.000 AD of 6.86 (RR per 100.000 vaccination session=12.2) (
Table 4). Considering sex distribution, the incidence proportion of consistent /indeterminate reports was respectively 0,014% for males and 0,011% for females of sent SMS (M:F RR Ratio 1.31, 95% CI 0.64-2.68).
The majority of serious AEFIs refers to febrile seizures following MMRV vaccination (n=11), with an incidence of 32.35 per 100.000 doses (11/34008). Of these reported cases, 73% were male (8 cases for males compared to 3 cases for females) with a RR Ratio M:F of 2.53 (95% CI 0.67-9.53). The RR for specific vaccines for other notable adverse events include 3.93 cases per 100.000 doses of febrile seizures after the MenB vaccine (4/101,829), 3.17 cases per 100.000 doses of intussusception after the rotavirus vaccine (2/63,028), 2.79 cases per 100.000 doses of thrombocytopenia after the MMRV and MenC-con vaccine (1/35,884) and 0.98 cases per 100.000 doses of thrombocytopenia after the MenB vaccine (1/101,829).
Regarding the outcome of reported AEFIs, 77.4% (24 out of 31) cases resulted in complete recovery or improvement, while data for the remaining cases was either not available at follow-up or was unknown at time of follow up. No fatal outcomes were reported.
4. Discussion
This study, conducted on a large sample of vaccinated children, confirms the excellent safety profile of vaccines and underscores the importance of integrating digital tools into vaccine surveillance.
Digital technology and mobile systems to enhance post-marketing surveillance of vaccines and drugs has been widely implemented in many countries. A recent scoping review, including twenty-seven publications, focused on the effectiveness of interventions like SMS, emails, etc. to enhance public participation in AEFI surveillance [
11]. Most of the studies came from Australia and Canada, with the seasonal influenza vaccine being the most frequently monitored. Considering only publications comparable to our study (i.e., studies covering all vaccines scheduled for the pediatric population), we observed a notably lower response rate (28%), in contrast to response rates ranging from 70% to 90% in other studies [
21,
22]. However, it’s important to note that response rates are usually calculated based on the initial contact with vaccinees. Indeed, digital AEFI surveillance systems typically rely on an initial SMS or e-mail to inquire about the occurrence of an AEFI and if a positive answer is received, more specific information is gathered through subsequent e-questionnaires. In our study, both the occurrence of AEFIs and all necessary information were collected via a single SMS contact thanks to the integration with data from the IR. Actually, when considering the proportion of responses reporting at least one AEFI, our study obtained similar or even higher proportions. Specifically, Gold and colleagues [
22] conducted a randomized controlled trial (RCT) to assess the efficacy of the Stimulated Telephone Assisted Rapid Safety Surveillance (STARSS) System. This initiative utilizes repetitive SMS messages sent to adult vaccinees or parents of children receiving a vaccine and obtained an AEFI detection rate of 4,3%. In our study, the proportion of AEFI reports per total SMS messages sent was approximately twofold higher (8.3%). Similarly, a study focused on the implementation of a vaccine safety monitoring tool based on SMS (SmartVax), to prompt AEFI reporting after childhood vaccination (<5 years), obtained a proportion of AEFI reports similar to our study (i.e. 8,2%; 239 out of 2897 vaccination visits) over a 44-month period [
21].
It’s important to consider that our study is temporally positioned during the pandemic period and throughout the entire COVID-19 vaccination campaign, which was characterized by a decrease in AEFI reporting for no-COVID-19 vaccine [
23,
24]. Indeed, HCPs and the general population primarily focused their efforts on the global emergency and on monitoring the COVID-19 vaccine rather than the more established childhood vaccines analyzed in our project. Additionally, the increased workload brought by the pandemic may have adversely affected the time dedicated to the project by HCPs, potentially resulting in less effort put into promoting the project to parents. To confirm the negative impact of the pandemic on vaccine surveillance not related to COVID-19, an RCT study conducted around the same time as our research aimed at testing vaccine safety surveillance through SMS and computer-assisted telephone interviews (i.e., the Zimbabwe Stimulated Telephone Assisted Rapid Safety Surveillance - Zm-STARSS), achieved a response rate of 31% (704 out of 2280), comparable to our study. These findings confirm that VigiVax represents an efficient and effective method for enhancing the surveillance of vaccine adverse events [
25].
Although the pandemic may have negatively affected the participation, it’s worth noticing that national AEFIs RR of non-COVID-19 vaccines per 100.000 AD was higher in the year 2021 during the project's occurrence (i.e., 78 per 100.000 AD) compared to spontaneous reporting in the previous years (17.9 and 22 per 100.000 AD in 2020 and 2019, respectively) [
24,
26]. These results suggest that the implementation of feasible active surveillance of AEFIs ensured the maintenance of an adequate level of safety monitoring during the pandemic when the spontaneous reporting system experienced a significant decline, both in the context of drugs and vaccines.
One of our study's strengths was its integration with information from regional IRs. This simplified parents’ participation by requiring responses via a single SMS and reduced the workload for HCPs, who no longer needed to collect patient data. In fact, data from the IRs, combined with AEFIs descriptions provided by parents via SMS, allowed for the automatic generation of reports submitted to the NPN.
The timing for sending SMS messages was also adapted to the type of vaccine, differentiating between live and inactivated vaccines, which enabled a higher likelihood of capturing AEFI with respective timeframes of 21 and 7 days. For comparison, other similar active surveillance systems were designed to receive responses within a few hours after vaccination, potentially leading to the loss of relevant data [
21]. It is noteworthy that in our system, parents had the opportunity to send SMS even outside the 7 or 21-day window with any further information automatically collated into the same report. Moreover, the minimal rate of discarded messages (1.1%) by HCPs indicates the reliability and credibility of the patient-reported data, which is crucial in the context of vaccine surveillance where there is a risk of receiving numerous reports of unrelated adverse events. This underscores the importance of involving patients in the adverse events reporting system, as they often provide insights into adverse reactions that may differ from those reported by HCPs. Furthermore, this highlights the crucial role of easily accessible surveillance systems that can facilitate public participation [
27].
Additionally, the proportion of SMS messages reporting at least one AEFI was highly relevant, confirming the system's usefulness in collecting valuable information for vaccine safety monitoring. It's important to note that all discharged SMS messages were confirmed by the coordinating center to avoid loss of pertinent information.
Finally, the population sample recruited for our project was notably larger than in other published initiatives for active surveillance based on SMS [
11]. This substantial volume allowed us to thoroughly test the effectiveness of such a system, demonstrating its potential for routine implementation. Notably, a high proportion of responses were received even when no AEFI occurred. A separate analysis of these responses revealed that participating parents highly valued the system.
The most frequently reported MedDRA PTs such as fever, irritability, and pain at the injection site, are well-known and considered mild vaccine reactions for the pediatric population. Data presented in
Table 1 suggests that vaccines administered during the same session are reported more frequently than those administered separately. For instance, the co-administration of MenB + PNEUMO-con13 and MenB + ROTAVIRUS shows greatly higher reporting rates compared to individual vaccines such as MenB and MMRV. However, the sum of individual RR for each type of vaccine administered separately is similar or even lower than the RR for the same vaccines administered during the same session, suggesting that there is no increase in risk when vaccines are co-administered compared to when they are administered separately. In an immunization schedule rich in co-administrations, active surveillance becomes crucial to ascertain whether there is a difference in risk associated with vaccine co-administration.
Borsari and colleagues [
28] conducted a study comparing the agreement between Classification of AEFI Seriousness as defined according to pharmacovigilance standard criteria and Clinical Severity Classification used in an Italian region. The study revealed a low agreement of only 58% (Cohen’s Kappa=0.17). To address this issue, the Green Channel, a specialized service for pre-vaccination counseling established in 1993 by the Veneto Region Public Health Authority, regularly re-evaluates reports of serious adverse event based on clinical severity criteria [
29]. The re-classification of clinical severity of AEFIs performed by experts plays a crucial role in improving public communication, providing accurate information about real serious risks, enhancing transparency, and contributing to the promotion of vaccinations [
19].
In our study, the clinical evaluation of seriousness resulted in 50 confirmed serious cases, among which 31 had events at least potentially associated with vaccination, corresponding to an incidence of approximately 7 severe AEFI per 100,000 doses. These reports describe events known within the risk profile of the suspected vaccines. Furthermore, no fatal cases have been reported, and no sequelae have been found in the follow-up when available. The high number of collected reports, which underwent clinical review and severity assessment, increased the relevance of retrieved results, confirming the favorable risk profile of pediatric vaccinations.
In terms of sex distribution, a similar proportion of SMSs were sent to both the male and female population (51% versus 49%). However, when considering SMS reporting AEFI, male children showed a slightly higher significant risk of AEFIs compared to females (with an increase between 3 and 9%). Moreover, male children showed a higher risk for serious events (approximately 30%), although this difference was not statistically significant. According to literature data, adult women have twice the risk of experiencing Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) compared to men, as well as a higher risk of hospitalization for ADRs [
30]. However, a different trend has been observed in the paediatric population where male children seem to have a higher risk for serious or fatal events [
31]. Furthermore, an analysis of ADRs reports in the NPN on relationship between age and sex among children indicates that males experience more adverse drug reactions episodes before the age of 2 years [
32].
Our data are consistent with the available evidence. The retrieved higher risk for serious events in the male population appears to be particularly high for MMRV-induced febrile convulsions, with 73% of cases (among a limited number of 11 cases retrieved). Despite this difference is not statistically significant, the limited number of serious cases retrieved suggests the need for more extensive studies to better explore any disparities. Regarding the type of serious AEFIs retrieved, the majority of reported cases were specifically associated with febrile seizures. As expected, according to the literature, most of these cases followed MMRV vaccinations [
33,
34] Despite being rare, febrile seizures are well-known events after MMRV vaccination; however, the literature shows wide variability in their rate of occurrence, likely depending on several factors such as the methodology implemented for data collection, the duration of follow-up, the definition of the relationship with vaccinations, etc.
A recent systematic review estimated the incidence of febrile seizures after MMRV vaccination to be approximately 96 cases per 100,000 children during the second week post-vaccination, roughly three times higher than the rate found in our active surveillance project (32.3 per 100,000 doses) [
35]. When comparing studies with age cohorts (i.e., under 2 years old) and follow-up periods similar to our study (i.e., within 21 days), the incident rates were nearly twice as high as ours: 58 per 100,000 doses occurring between 7-10 days after MMRV vaccination in a retrospective cohort study of a cohort aged 12-23 months, and 70 per 100,000 doses occurring between 5-12 days after MMRV in another retrospective cohort study of a cohort aged 12-60 months [
36,
37]. A systematic review and meta-analysis found the incidence rate in children aged 10–24 months ranging between 62 to 96 per 100,000 calculated for four retrospective cohort studies during the second week after vaccination. The same study found an incidence between 93 and 129 per 100,000 doses considering children aged 12-23 months 7-10 days after vaccination [
38].
The observed discrepancy in febrile seizures rates between our project and those reported in the literature is probably due to the type of our study which focuses on spontaneous reporting, even though stimulated. Febrile seizures are actually well-known reactions that generally do not results in serious consequences and resolve without any residual effects, as also observed in our data [
39].
The literature demonstrates that the incidence of febrile seizures in the general paediatric population is significantly higher than the rate associated with vaccination (e.g., 4000 cases per 1,000,000 children) [
35]. According to available data, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlights the crucial role of vaccines in preventing a greater number of febrile seizures cases by protecting children against diseases known to induce fever and febrile seizures (e.g., measles, mumps, rubella, chickenpox, influenza, pneumococcal infections, etc.) [
40].
The observed rate of thrombocytopenia following the MMRV vaccine is consistent with data found in the literature. A recent Cochrane systematic review on the safety profile of all vaccines containing measles, rubella, mumps, and varicella strains in individuals under 12 years of age shows an incidence of Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) of 1 case per 40,000 administered MMR doses compared to our result of 1 case of Thrombocytopenia per 34,008 after MMRV vaccination [
41]. Cases of ITP following natural infection are higher (i.e., 5 cases per 100.000 individuals), thus confirming the favorable risk-benefit profile of vaccination.
Likewise, the retrieved rate of intussusception following the rotavirus vaccine (i.e., 3.17 per 100.000 doses) aligns with the available evidence. Based on CDC data, the risk within a week following the first or second dose is estimated to vary from 1 in 20,000 to 1 in 100.000 vaccinated infants who receive the rotavirus vaccine in the US [
42]. The background rate in Italy is estimated to be much higher, with 20 cases per 100.000 doses [
43]. Two recent meta-analyses, one involving randomized controlled trials (with 104,647 participants receiving the vaccine and 95,947 receiving a placebo) and the other involving observational studies (with more than 4,500,000 participants receiving the first dose), examined the association between the rotavirus vaccine and intussusception [
44,
45]. The analyses found no associations in RCT and respectively a 3.7 increased risk for cohort studies and an 8.45 for case-control studies. An interrupted time series even demonstrated a decrease in intussusception incidence during the post-vaccine period compared to the pre-vaccine period [
46]. Our data support the evidence that intussusception following rotavirus vaccine is a rare event that does not affect the risk-benefit ratio, which remains in favour of vaccination [
47].
In conclusion, the results from our active surveillance project, based on a large pediatric population, confirm the favourable risk profile for childhood vaccines.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, U.M.; formal analysis, L.A.G., G.Z. and U.M.; investigation, L.A.G., A.C., C.D.S., L.F., E.G., G.G., X.H., M.L., O.L., A.M.P.M , P.M.T., V.M., M.C.M., C.P., A.M.P., P.R., M.R., F.S., E.S., C.S.3; C.S.8; and M.T.; data curation, U.M., and L.A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, L.A.G. and F.M.; writing—review and editing, L.A.G., F.M., U.M., G.Z., A.C., C.D.S., L.F., E.G., G.G., X.H., M.L., O.L., A.M.P.M , P.M.T., V.M., M.C.M., C.P., A.M.P., P.R., M.R., F.S., E.S., C.S.3; C.S.8; and M.T. ; visualization, L.A.G. and F.M.; supervision, U.M.; project administration, U.M. and L.A.G.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.