1. Introduction
The Chinese Baijiu industry is rooted in traditional brewing practices. However, with modern technological advancements and scientific research, Baijiu production methods have continually evolved and improved Ye et al., (2021). Xiaoqu Baijiu has a rich history and is distinguished by its crisp and pure aroma, mellow and balanced flavor, and invigorating aftertaste (Yan et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2023). Xiaoqu Baijiu does, however, have several drawbacks, including a thin body, a narrow range of flavors, high concentrations of fusel alcohols, and low levels of ethyl acetate (Huang et al., 2024). Studies have shown that incorporating Rhizopus fuqu can increase the lactic acid ethyl ester content in Jiang-flavor Baijiu (Yi et al., 2019). Enhanced fermentation using aroma-producing functional microbes in fuqu has elevated the concentrations of acids, alcohols, and esters in fermented grains (Wang et al., 2017). This indicates that incorporating functional microbes into fuqu for fortified fermentation is a successful strategy. Wickerhamomyces demonstrates excellent stability and fermentation efficiency, offering promising potential for streamlining fermentation procedures and boosting the flavor of fermented beverages (Choi et al., 2024; Zhao and Gao, 2024). Currently, Wickerhamomyces is extensively utilized in the fermentation industry. Employing Wickerhamomyces in Chinese Te-flavor Baijiu brewing markedly augmented the ethyl esters content (Liu et al., 2022). Using Saccharomyces and Wickerhamomyces in the fermentation of rice wine significantly increased the quantities of flavor compounds, including phenylethyl alcohol, isobutanol, and hexanol (Chen et al., 2021). mixed culture with Wickerhamomyces could Improve flavor metabolism of Saccharomyces in Chinese Baijiu making (Zha et al., 2018). Overall, Wickerhamomyces contributes positively to enhancing the flavor of alcoholic beverages. Nevertheless, its use in Xiaoqu Baijiu brewing is not well understood. Further research is needed to determine if incorporating it in fuqu as a medium can enhance the quality of Xiaoqu Baijiu.
Our study hypothesizes that Wickerhamomyces could potentially enhance the flavor of Xiaoqu Baijiu by examining the correlation between the fungal community structure of Xiaoqu and ester compounds. By incorporating Wickerhamomyces into the fermentation of Xiaoqu using fuqu as the medium, we aimed to investigate the effects of this fortified fermentation on both the fermentation environment and alcohol yield. The effects of fortified fermentation on the flavor compounds of Xiaoqu Baijiu were examined using gas chromatography. Additionally, high-throughput sequencing technology was employed to analyze how fortified fermentation disrupted the fungal community structure in fermented grains. Furthermore, PICRUSt2 marker gene sequences were utilized to predict the types and abundances of enzymes associated with distinct compounds.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fermentation of Xiaoqu Baijiu
The fermentation substrate used was commercially available Japonica sorghum along with its husk. Three types of Xiaoqu (XQ1, XQ2, XQ3) were purchased from the local markets and their microbial communities were analyzed. A simulation experiment was conducted based on the brewing process of Xiaoqu Baijiu. The sorghum was soaked in boiling water for 24 h. It was then cooked twice and pasteurized to ensure that the moisture content of the cooked grain was above 50%. Once the grains had cooled, 5% (5 g/100 g) of steamed husk was added, and Xiaoqu was added for saccharification 24 h later. The saccharified sorghum was fermented using a mixed distillation method for 7 days. This process was carried out in a 5-L fermentation tank. Following the completion of fermentation, the fermented grains were distilled to obtain Baijiu samples. Each experimental group consisted of 3 replicates.
2.2. Production of Wickerhamomyces fuqu (WF)
Wickerhamomyces was procured from the Liquor Brewing Biotechnology and Application Key Laboratory, Sichuan Province. Square stainless steel boxes were utilized as the container, adhering to the traditional fuqu production technique. 100 grams of bran was weighed and water was added to achieve a moisture content of 55%. The mixture was sealed with four layers of gauze and sterilized at 121 °C for 20 mins. In an aseptic centrifuge tube, 4 mL of seed liquid was collected and centrifuged at 500 rpm, and the supernatant was discarded. The cells were then rinsed with 4 mL of sterile water inoculated into the sterilized bran. After thorough mixing and covering with gauze, it was cultivated in an incubator at 30°C for 36 h. Upon the completion of cultivation, it was dried in an oven at 30°C and stored for future use.
2.3. Preparation for Intensive Fermentation
In the experimental group (QH), sorghum underwent soaking, cooking, and cooling before the addition of WF (0.6%, 0.1 g/100 g) and XQ2 (0.6%, 0.6 g/100 g). In the control group (DZ), only XQ2 (0.6%) was added. This fermentation process was identical to that described in section 2.1. Cooked sorghum (ZL), saccharified fermented grains (TH), and fermented grains collected on days 1, 3, 5, and 7 were subjected to analysis. After thorough mixing, the samples were stored at -20°C for further analysis.
2.4. Detection of Physicochemical Indicators of Fermented Grains
The moisture content was assessed using the gravimetric method. The acidity of the fermented grains was measured through acid-base titration. Quantification of reducing sugars and starch was carried out using Fehling’s reagent method, following the procedure outlined by Ren (Ren et al., 2024).
2.5. Detection of Flavor Substances in Xiaoqu Baijiu
The headspace vial was placed in a water bath set at 50°C for 20 mins to achieve thermal equilibrium. Subsequently, a 50/30 DVB/CAR/PDMS extraction head was inserted for a 30-minute adsorption period. Once adsorption was complete, the extraction head was promptly inserted into the GC-MS inlet for desorption over 5 mins. Chromatographic analysis was conducted using a DB-Wax capillary column (60 m x 0.25 mm, 0.25 µm). The chromatographic and mass spectrometric conditions followed those detailed in the literature and internal standards such as ethyl valerate, 2-octanol, and 2-ethylbutyric acid were employed (Tong et al., 2023). Each volatile component was quantified by comparing its ratio to a corresponding internal standard, applying a correction factor of 1. Aromatic compounds were initially identified by comparing their mass spectra to the NIST17.L standard mass spectra, ensuring a similarity threshold above 75% for preliminary identification. Further verification was conducted using standard flavor substances. Compounds with a S/N ratio exceeding 10 were chosen for analysis of flavor data.
The flavor compounds in Baijiu samples were quantified using hydrogen flame gas chromatography (GC-FID) (Agilent 8890). 1 mL of Baijiu sample was carefully pipetted into a sample bottle and analyzed using the external standard method. The chromatographic column used was LZP-950.2 (50 m×0.32 mm×1 µm), with a split ratio of 40:1. The injection volume was 0.4 µL and the inlet temperature was set at 230 ℃. The temperature program was as follows: starting at 60 ℃ for 3 mins, increasing at a rate of 3 ℃/mins to 90 ℃ and holding for 5 mins, further increasing at 3 ℃/mins to 140 ℃ and holding for 2 mins, then increasing at 3 ℃/minute to 150 ℃ and holding for 5 mins, finally increasing at 3 ℃/minute to 220 ℃ and maintain this temperature for 15 mins. High-purity nitrogen was used as the carrier gas.
2.6. Calculation of Odor Activity Value (OAV)
The Odor Activity Value (OAV) for each flavor component was measured using the aroma intensity method. A higher OAV signifies that the flavor component has a stronger aroma intensity in Baijiu, thereby exerting a greater influence on the overall aroma profile of the beverage. The calculation formula is as follows:
where xi is the concentration of the flavor component in g/L and OTi is the odor threshold value of the flavor component in μg/L.
2.7. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
10 g of samples were weighed and mixed with 25 mL of sterilized and cooled 0.1 mol/L PBS buffer, along with sterile glass beads. The mixture was vortexed for 30 mins and then washed thrice with PBS buffer. The supernatant was collected by centrifugation (300 g, 5 mins) and all supernatants were combined to obtain the precipitate, which was then washed thrice with PBS (9000 g, 3 mins). DNA extraction was carried out using the phenol-chloroform method. The density and quality of the extracted DNA were assessed using a NanoDrop ND-2000 spectrophotometer (Illumina, USA) and 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. For fungal amplification, primers ITS1F (5’-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3’) and ITS4R (5’-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3’) were used. PCR was conducted in triplicate with a 20 μL mixture using a MyCycler Thermal (Bio-Rad, USA), following the method described by Liu (Liu et al., 2021). Subsequent library preparation for next-generation sequencing and high-throughput sequencing was carried out at Shanghai Majorbio Biopharm Technology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China).
Quality control and assembly of the raw sequenced data were performed using Trimmomatic software (
https://cloud.majorbio.com/) and FLASH software (
https://cloud.majorbio.com/), respectively. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were clustered based on 97% similarity, with single sequence removal and chimera removal conducted using UPARSE software (version 7.1
http://drive5.com/uparse/). Each sequence was taxonomically annotated using the RDP classifier and compared with the database.
2.8. Statistical analysis
Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) was employed for significant difference analysis. Origin software analyzed changes in physicochemical indicators and microorganisms in fermented grains. R software was used to create heat maps for visualization and conduct redundancy analysis. Using the KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) database and the PICRUSt tool, online functional prediction was conducted based on OTU classification. ASV sequences were aligned with reference sequences and placed into a reference tree to infer gene families' copy numbers and predict gene content. This data was integrated with MinPath to determine gene family abundance in each sample. The gene family information was then compared with the KEGG database to obtain functional information and abundance data, which was used to create metabolic pathways and bubble charts based on enzyme abundance.
3. Results
3.1. Aroma Activity Values of Xiaoqu Baijiu Esters
The OAV of ester compounds was calculated based on previous studies (Chen et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021). The OAV values for ester compounds in Xiaoqu Baijiu are presented in
Table 1. Ethyl esters were the predominant esters found in Baijiu. The flavor compounds with OAV > 1 included ethyl acetate, ethyl isovalerate, ethyl caproate, ethyl caprylate, ethyl decanoate, ethyl phenylacetate, isoamyl acetate, and ethyl cetostearyl acetate. Despite the relatively low concentrations of ethyl isovalerate and ethyl caprylate, their OAV exceeded 1, denoting that they significantly contributed to the aroma profile of Baijiu, exemplifying the characteristic of ‘small amount and large aroma.
3.2. The Correlation between Fungal Community and Esters in Xiaoqu Baijiu
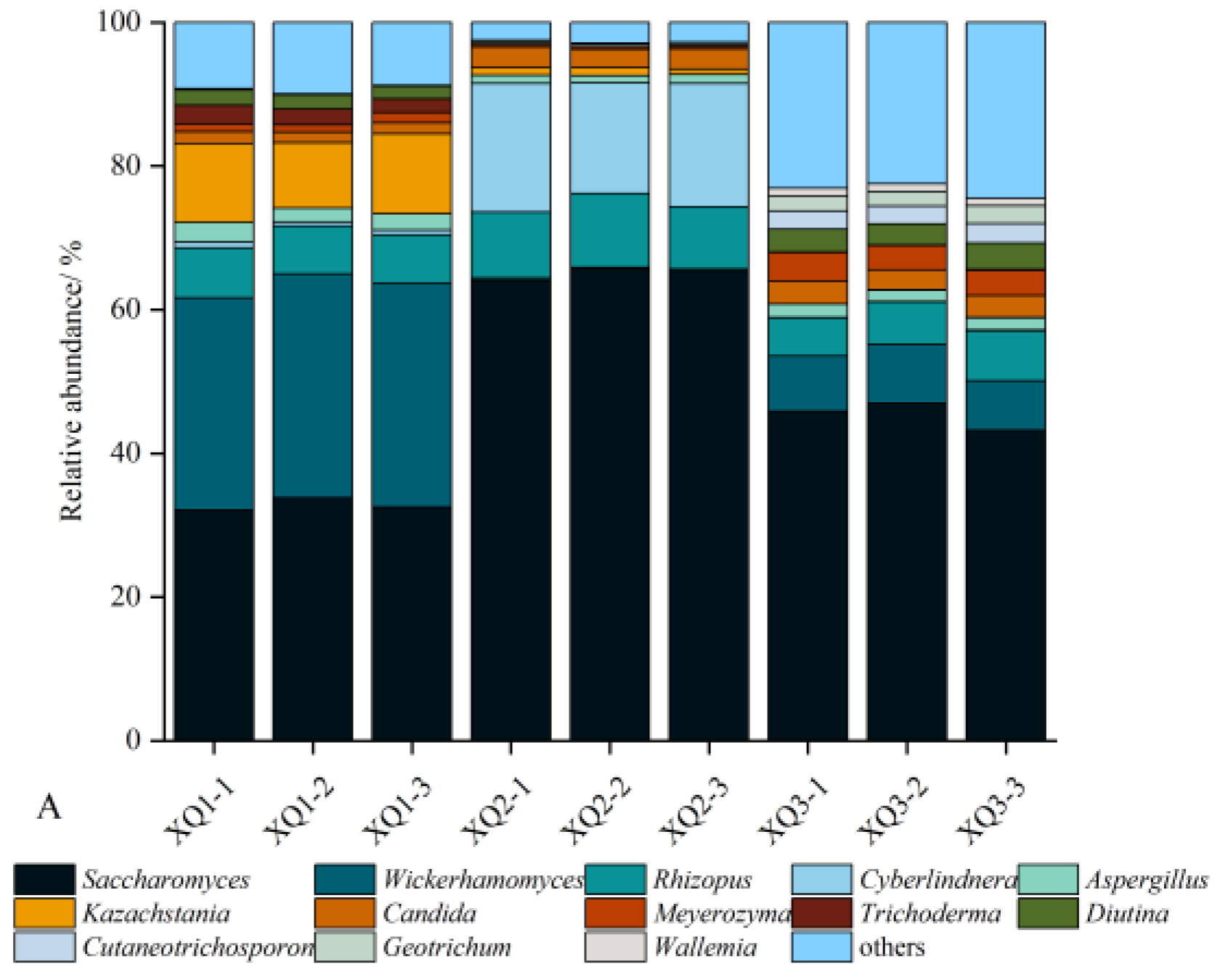
The predominant fungus in Xiaoqu was yeast, which served as the primary source of ethanol during Baijiu fermentation. Ester-producing yeasts also played a crucial role in the fermentation process of Baijiu. As illustrated in
Figure 1-A,
Saccharomyces,
Rhizopus,
Aspergillus, and
Candida were the common dominant fungal genera (relative abundance > 1 %) across the three types of Xiaoqu.
Cyberlindnera was the dominant fungal genus unique to XQ2, contributing to the metabolism of acetate and ethyl esters, thereby increasing the concentration of flavor-active esters (Meersman et al., 2016).
Trichoderma was the main genus specific to XQ1, with secondary metabolites including phenolic compounds, ketones, and terpenoids (Bai et al., 2023).
Wickerhamomyces had the highest relative abundance in XQ1, producing various glycosidases such as β-D-glucosidase, β-D-xylosidase, α-L-rhamnosidase, etc.
Wickerhamomyces contributed to aroma, ester, and alcohol production, significantly enhancing Baijiu’s sensory quality, and making it a crucial functional microorganism in the fermentation process (Shimizu et al., 2020).
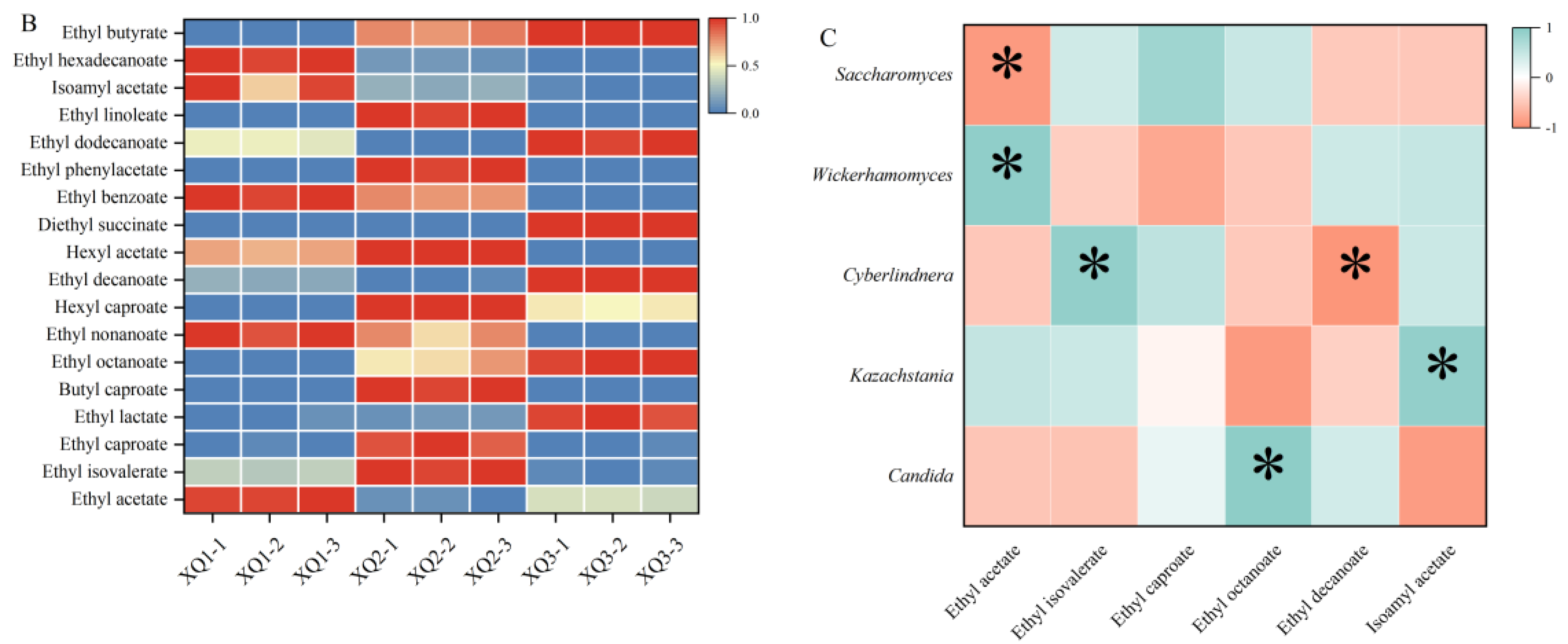
Figure 1-B presents significant differences in the composition and content of ester compounds across different Xiaoqu Baijiu samples. The correlation between six ester compounds with OAV greater than 1 and five dominant fungi was analyzed. As shown in
Figure 1-C, there was a notable correlation between these fungi and ester compounds. Ethyl acetate displayed a significant negative correlation with
Saccharomyces and a significant positive correlation with
Wickerhamomyces.
Cyberlindnera was significantly positively correlated with ethyl isovalerate and significantly negatively correlated with ethyl decanoate. Additionally, ethyl caprylate and isoamyl acetate showed significant positive correlations with
Candida and
Kazachstania, respectively.
Therefore, the presence of fungi in Xiaoqu could influence the metabolism of ester compounds during the fermentation process of Xiaoqu Baijiu. Ethyl acetate represented the primary flavor substance in Xiaoqu Baijiu. Modulating the ethyl acetate content could potentially alter the overall quality of baijiu, with a notable positive correlation observed between this compound and Wickerhamomyces. Enhancing the fermentation process with Wickerhamomyces in Xiaoqu might thus enhance the flavor profile of Xiaoqu Baijiu.
3.3. Effects of WF Intensive Fermentation on Physicochemical Indicators and Baijiu Yield
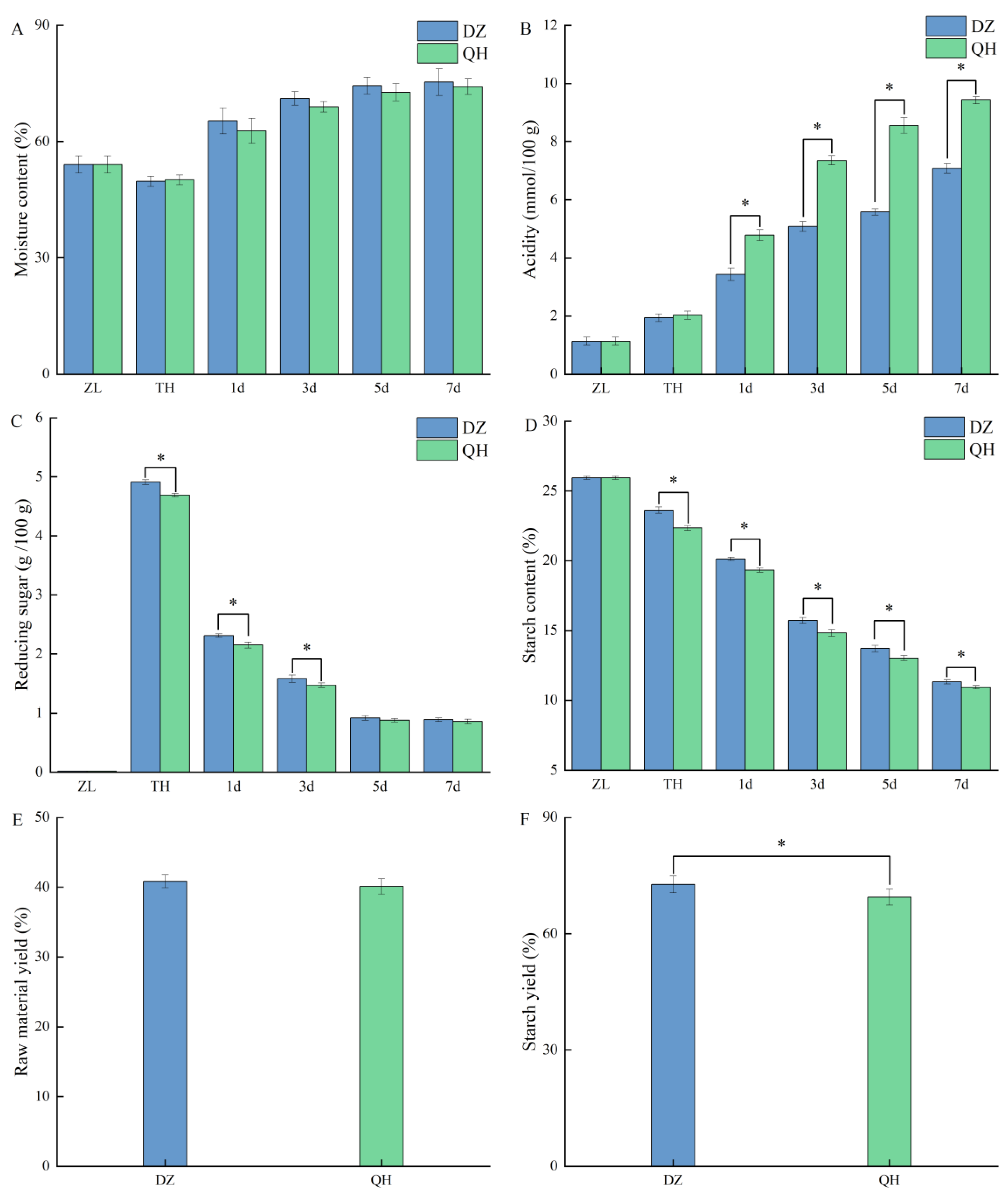
As depicted in
Figure 2-A, the moisture content of cooked sorghum was 54.08%. During open saccharification, the moisture content of the control group decreased by 4.36%, while that of the test group decreased by 3.96%. Throughout the fermentation process, the moisture content of fermented grains showed a general increase. There were no significant differences in moisture content between the control and experimental groups at corresponding fermentation stages (
P > 0.05). The acidity levels showed a tendency to rise with the advancement of fermentation (
Figure 2-B). There were no significant differences observed between the control and experimental groups in the acidity of fermented grains following cooking and saccharification. The acidity of fermented grains in the experimental group after 1 d was significantly elevated compared to the control group (
P < 0.05), suggesting that
Wickerhamomyces metabolized and generated acids during fermentation, thereby increasing the overall acidity of the fermented grains. In
Figure 2-C, it is evident that the highest levels of reducing sugars occurred at the conclusion of saccharification. Throughout the time points of TH, 1 d, and 3 d, the control group consistently exhibited significantly greater amounts of reducing sugars compared to the experimental group (P < 0.05). The starch content exhibited a decline over the fermentation period. However, at TH, 1 d, 3 d, 5 d, and 7 d, the experimental group consistently showed significantly lower starch content compared to the control group (
P < 0.05) (
Figure 2-D). Although there was no significant difference in the raw material liquor yield rate between the control and the experimental group (
P > 0.05), the starch liquor yield rate in the experimental group was significantly lower than that in the control group (
P < 0.05).
Previous research indicated that Wickerhamomyces exhibited greater acid-producing capabilities compared to Saccharomyces. The observed increase in acidity of the fermented grains in the test group could be attributed to the metabolic activity of Wickerhamomyces (Lin et al., 2022). Changes in the concentration of reducing sugars in the fermented grains partly reflected the balanced and coordinated interaction between saccharification and fermentation rates (Xue et al., 2023). At the end of saccharification, the hydrolysis of starch by amylase resulted in a peak in reducing sugars. At this stage, the yeast population was low, and reducing sugars remained high. As fermentation progressed, the yeast and other microorganisms proliferated, utilizing reducing sugars as a carbon source. The levels of reducing sugar decreased quickly and eventually reached a stable state. During the initial 3 days, which are crucial for Xiaoqu Baijiu fermentation, the reducing sugar content in the fermented grains of the test group was significantly lower than that of the control group at both 1d and 3d. Despite this, the raw material yield between the control and experimental groups did not show significant differences. This suggests that intensive WF fermentation increased the conversion rate of ethanol without impacting its overall yield. The starch content served as the foundation for alcoholic fermentation, ensuring that the rates of saccharification and fermentation remained balanced to support the normal progression of fermentation in grains. Microorganisms aside from Saccharomyces can generate biological enzymes during the brewing process. They utilize fermentation substrates to produce aroma compounds such as esters and higher alcohols, enhancing flavor complexity and thereby elevating the quality of Baijiu (Jiang et al., 2020). Variations in starch conversion yield in liquor may stem from Wickerhamomyces metabolism and its interaction with other microorganisms during fermentation, leading to the conversion of starch into diverse flavor compounds.
3.4. Effect of WF Intensive Fermentation on Flavor Substances of Xiaoqu Baijiu
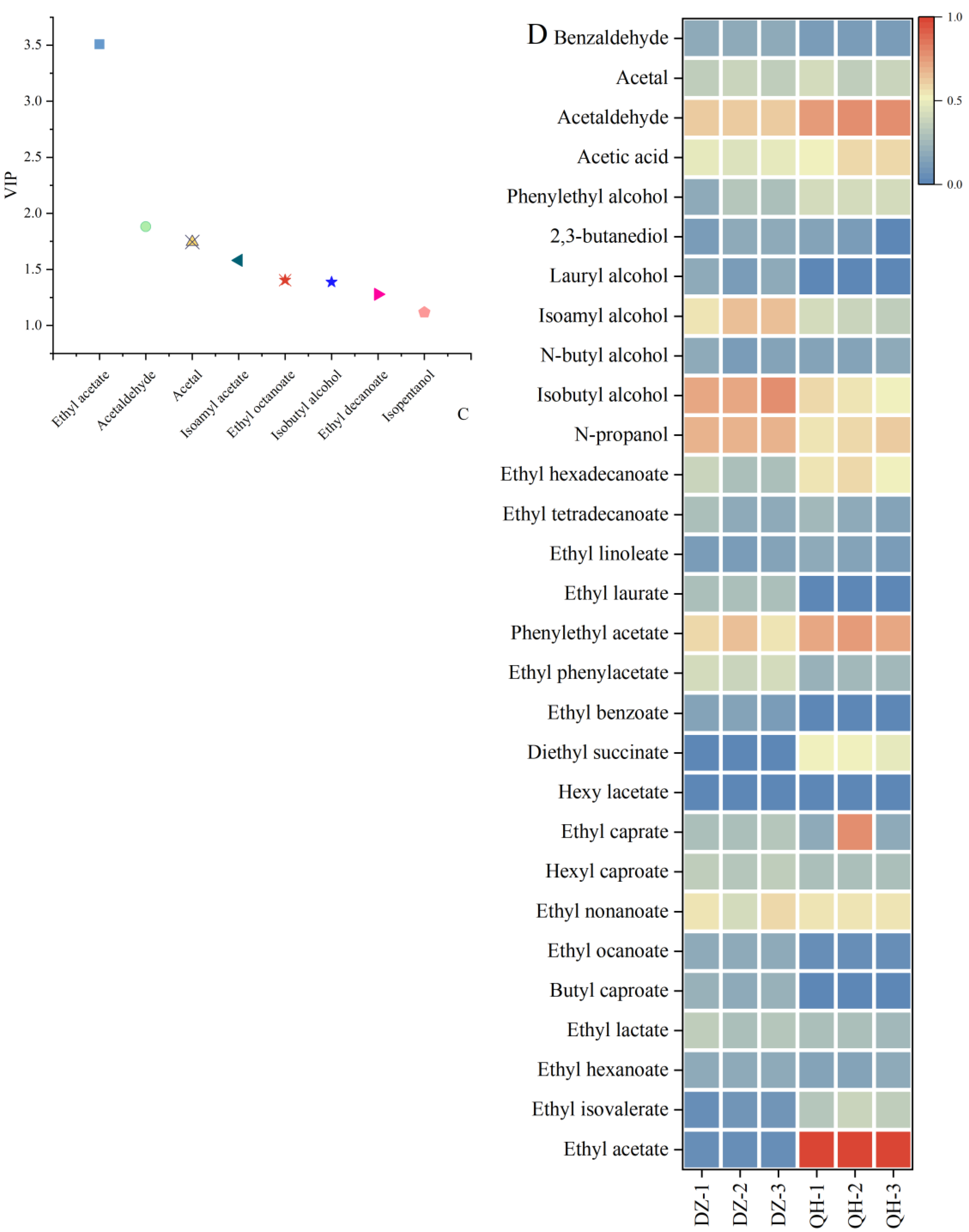
GC-MS was employed to analyze the volatile flavor compounds in Baijiu.
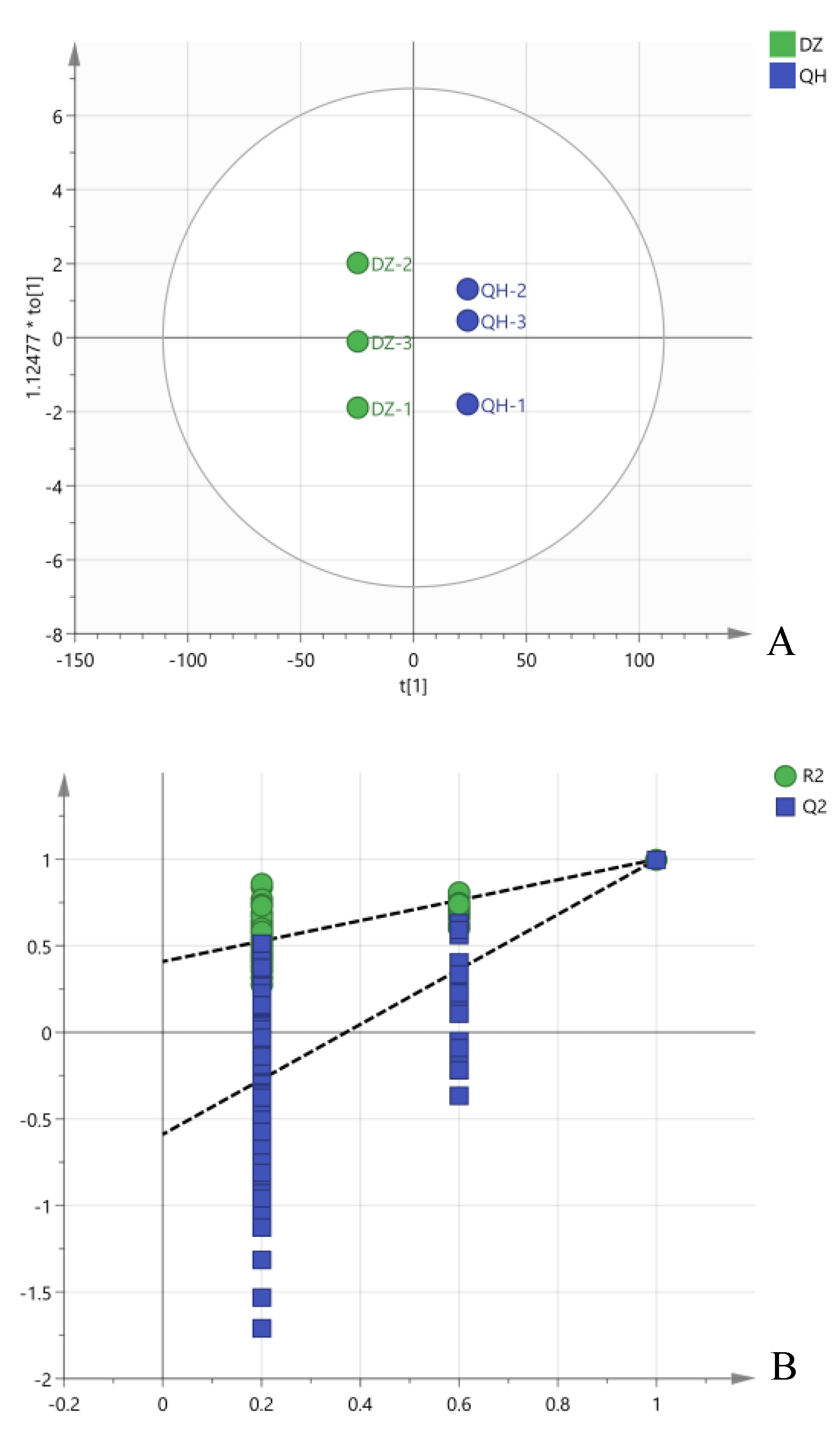
Figure 3-A illustrates the distinct separation of Baijiu samples from the control and test groups on the PLS-DA score plot, with the control group positioned on the left and the test group on the right. The quality of the model fit was evaluated using a permutation test (n = 200), yielding
R2Y = 0.48 and
Q2Y = -0.59 (
Figure 3-B). The negative
Q2Y value suggests a good fit of the model. Based on the variable importance in projection (VIP) values (> 1), eight volatile compounds were identified as markers, comprising four esters (ethyl acetate, isoamyl acetate, ethyl caprylate, ethyl decanoate), two aldehydes (acetaldehyde, acetal), and two alcohols (isobutanol, isoamyl alcohol) (
Figure 3-C).
The data was normalized to visualize the concentration of volatile compounds in the samples (
Figure 3-D). Importantly, the experimental group showed significantly higher levels of ethyl acetate compared to the control group. Ethyl acetate was identified as the primary contributor in the discriminant model and is a key aromatic component of Xiaoqu Baijiu, influencing its quality and character. Based on these findings, we tentatively concluded that WF-intensive fermentation has positively influenced the quality of Xiaoqu Baijiu.
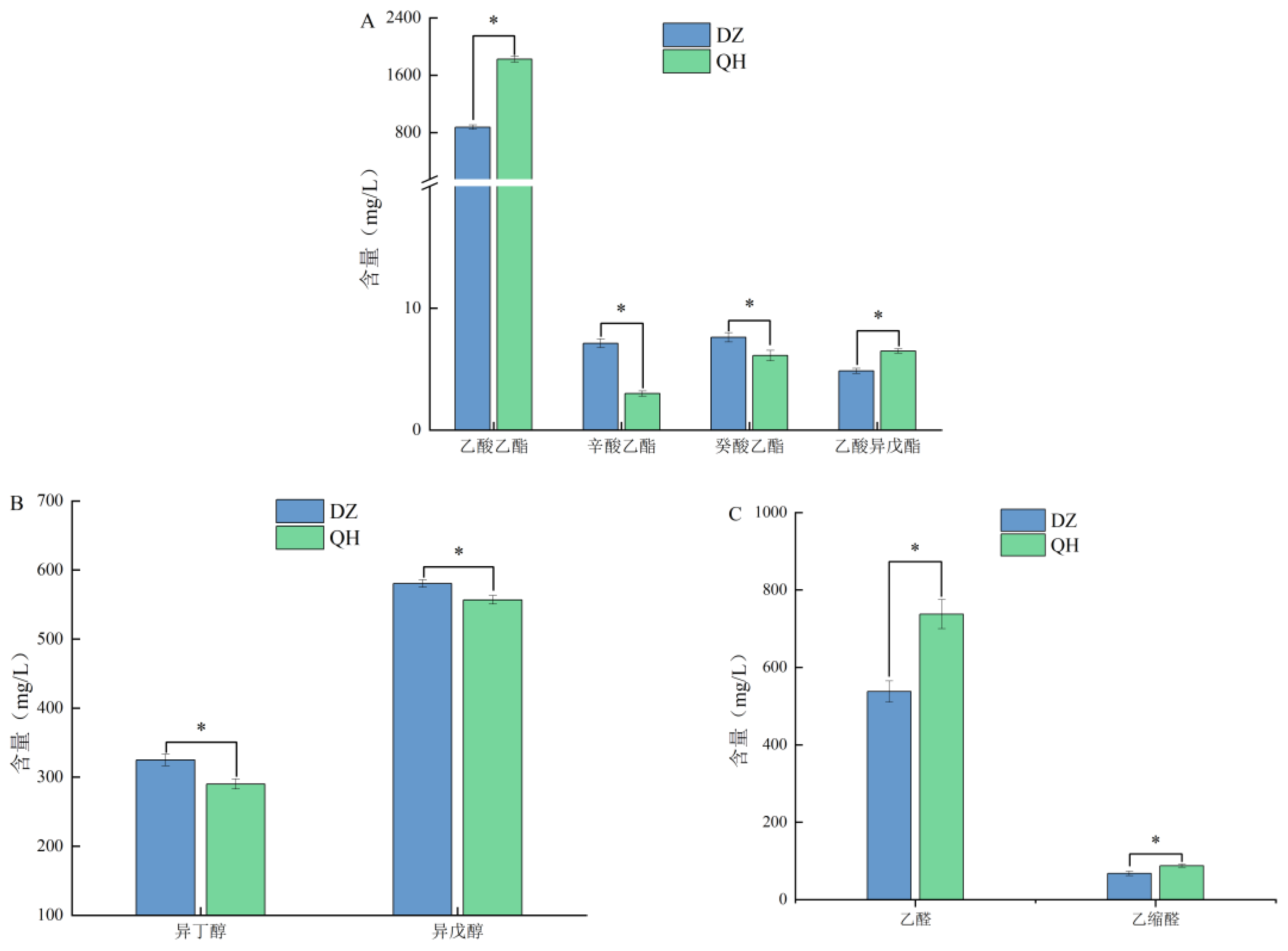
3.5. Differences in Volatile Flavor Compounds
The flavor compounds identified as having significant VIP values were quantitatively analyzed using GC. The test group exhibited significantly higher levels of ethyl acetate and isoamyl acetate compared to the control group (P < 0.05). Specifically, the concentration of ethyl acetate in the test group was elevated by 949.94 mg/L compared to the control group. Ethyl acetate and isoamyl acetate levels in the test group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.05=, with ethyl acetate showing a 2.09-fold increase compared to the control group. Ethyl acetate, a key aroma compound in Xiaoqu Baijiu, contributes distinct pineapple and apple notes to the beverage (Wang et al., 2020). The concentration of isoamyl acetate in Xiaoqu Baijiu was lower, yet due to its lower aroma threshold, it imparted a robust fruity aroma to Xiaoqu Baijiu. In the test group, isoamyl acetate increased by 1.63 mg/L, contributing a distinct banana flavor to the beverage. Conversely, the levels of ethyl caprylate and ethyl decanoate decreased compared to the control group. Esters constituted the primary aromatic compounds in Xiaoqu Baijiu, and their formation depended on the physicochemical properties of fermented grains and the fermentation environment. During ethanol fermentation, esters such as fatty acid ethyl esters were synthesized from acetyl coenzyme A and ethanol with the aid of esterase catalysis, while acetate was synthesized from acetyl coenzyme A and higher alcohols (Liu et al., 2023).
In addition to esters, alcohols also contributed significantly to the aroma profile of Xiaoqu Baijiu, with suitable alcohols enhancing its overall harmony. As illustrated in
Figure 4-B, the experimental group showed significantly lower levels of isobutanol and isoamyl alcohol compared to the control group (
P < 0.05), with reductions of 34.81 mg/L and 23.62 mg/L, respectively. Meanwhile, the levels of acetaldehyde and acetal in the experimental group were significantly higher compared to those in the control group (
P < 0.05). Acetaldehyde contributes to the aging process and aroma development in Baijiu, and an optimal acetaldehyde content is considered a favorable aroma component (Wang et al., 2021). Acetaldehyde can also condense with ethanol to produce acetal, which imparts a light fragrance and enhances the flavor profile of Baijiu.
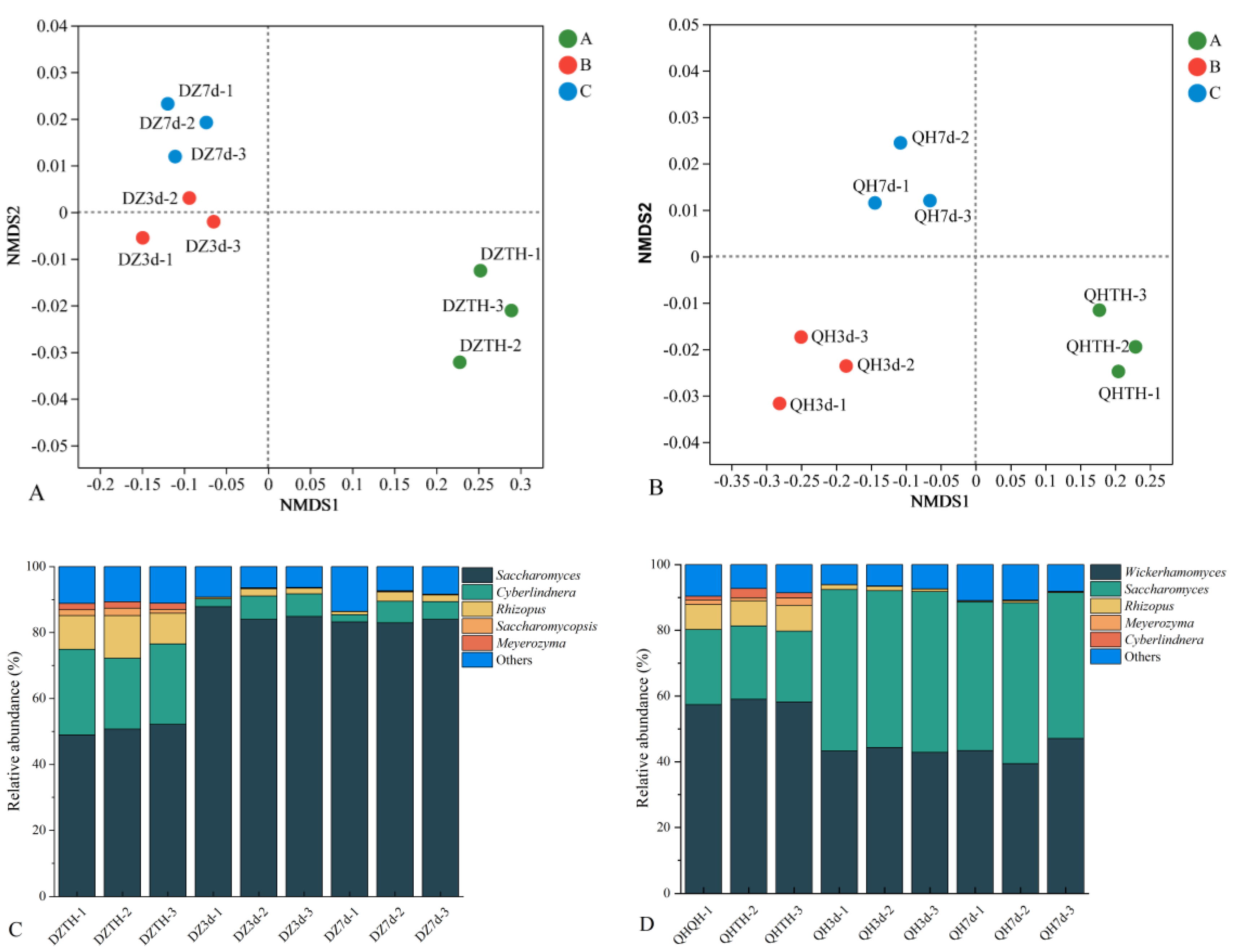
3.6. Alterations in the Composition of Fungal Communities in Fermented Grains during the Fermentation Process
Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis using the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity matrix at the genus level was conducted to assess variations in microbial community composition in fermented grains. Significant differences in fungal communities were observed over the course of fermentation (
Figure 3A and B). Specifically, at days 3 and 7 of fermentation, samples from the experimental group exhibited greater spatial separation from each other, indicating that intensive WF fermentation influenced the succession of fungal community structure. Bar charts were constructed to visually track changes in fungal community structure in fermented grains (Figures 3C and D). In the fermented grains of the control group, five prominent fungi (with relative abundance >1%) were identified namely
Saccharomyces,
Cyberlindnera,
Rhizopus,
Saccharomymycopsis, and
Meyerozyma. Following saccharification,
Cyberlindnera,
Rhizopus,
Saccharomymycopsis, and
Meyerozyma exhibited the highest relative abundances. However, their levels gradually declined throughout fermentation due to changes in the environment of the fermented grains.
Saccharomyces, initially at its lowest relative abundance post-saccharification, peaked at day 3 with an average relative abundance of 90.67 %. Subsequently, its relative abundance decreased by day 7, showing a pattern of initial increase followed by a decline over the fermentation period.
Five primary fungi were identified in the fermented grains of the test group, namely Wickerhamomyces, Saccharomyces, Rhizopus, Meyerozyma, and Cyberlindnera. Following saccharification, Saccharomyces, Cyberlindnera, Rhizopus, and Meyerozyma remained dominant in both the test and control groups, while Wickerhamomyces replaced Saccharomymycopsis as a dominant fungus in the test group. Wickerhamomyces exhibited the highest relative abundance immediately after saccharification, gradually declining throughout fermentation. Saccharomyces exhibited an initial increase followed by a decrease, mirroring the trend observed in the control group. Rhizopus, Meyerozyma, and Cyberlindnera maintained lower abundances compared to the control group throughout fermentation. These findings indicate that intensive WF fermentation altered the fungal community structure of the fermented grains.
3.7. Metabolic Analysis of the Different Flavor Compounds
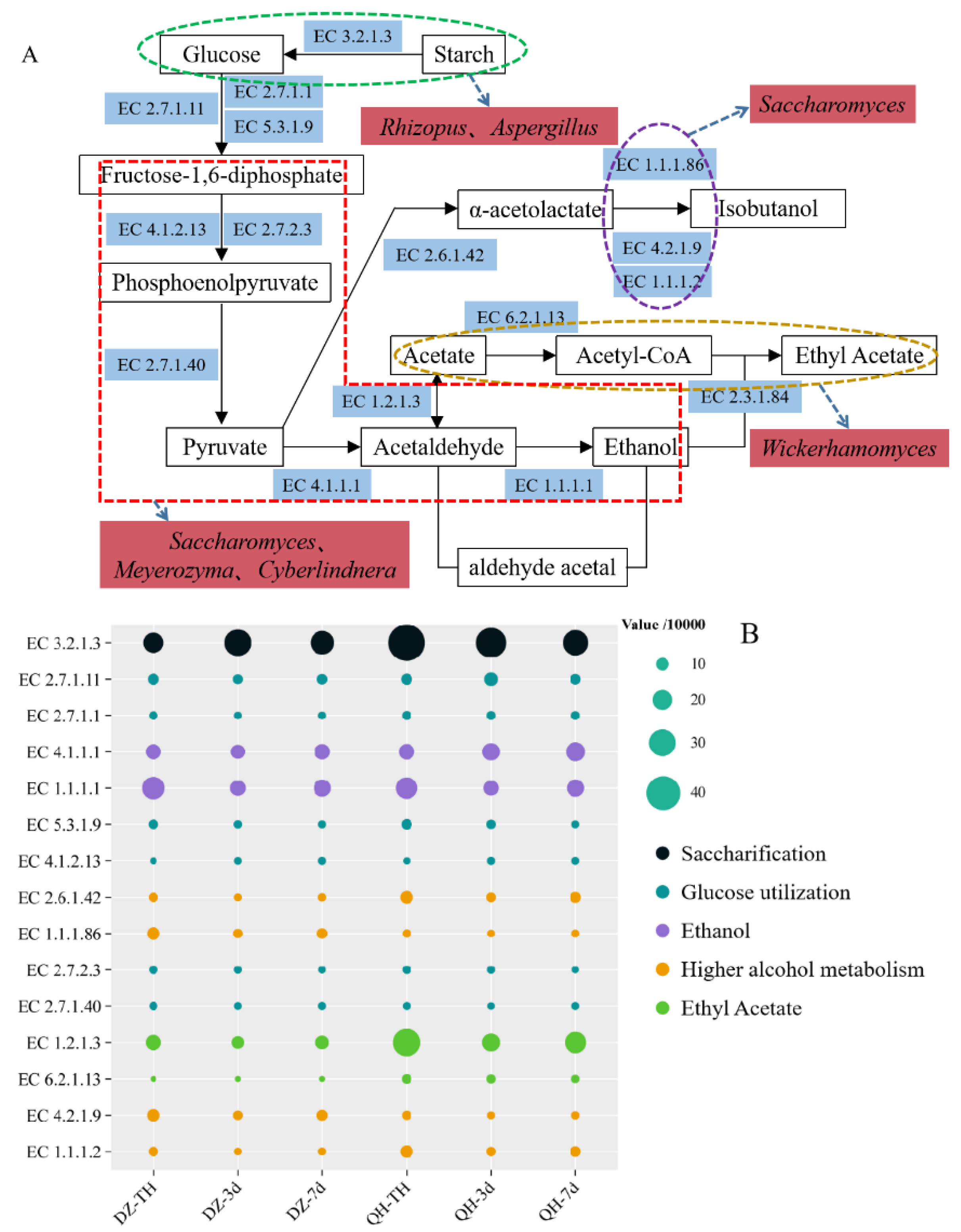
A metabolic map was constructed based on the annotated fungal species found in fermented grains, the KEGG database, and the significant differences in flavor compounds between the control and experimental groups (
Figure 6-A). The primary metabolic pathways involving the fungi in the fermented grains included saccharification, glycolysis, ethanol synthesis, higher alcohols synthesis, and ethyl acetate synthesis. Additionally, gene sequences were tagged with PICRUSt to predict the functional enzyme abundance in both the control and test groups, and a bubble map was created (
Figure 6-B). The relative abundance of EC3.2.1.3 (amyloglucosidase) was significantly higher (
P < 0.05) in the test group at TH, 3d, and 7d compared to the control group. This enzyme hydrolyzed various sugar-containing compounds in both endo- and exo-cut manners, breaking down starch into sugars usable by microorganisms. Consequently, the residual starch content in the experimental group was significantly lower than in the control group after fermentation (
P < 0.05), likely due to the increased expression of EC3.2.1.3. The key enzymes involved in glycolytic metabolism included EC2.7.1.1 (hexokinase), EC2.7.1.11 (6-phosphofructokinase), EC5.3.1.9 (glucose-6-phosphate isomerase), EC4.1.2.13 (fructose-bisphosphate aldolase), EC2.7.2.3 (phosphoglycerate kinase), and EC2.7.1.40 (pyruvate kinase). The relative abundance of these enzymes showed no notable difference between the control and experimental groups. EC4.1.1.1 (pyruvate kinase) and EC1.1.1.1 (alcohol dehydrogenase), which are critical for ethanol synthesis, also exhibited no significant difference in relative abundance between the two groups. This lack of difference in the abundance of pyruvate kinase and alcohol dehydrogenase likely explains why the Baijiu yield did not significantly differ between the control and experimental groups.
It is widely accepted that during fermentation, yeasts utilize glucose to metabolize ethanol and acetic acid via the glycolysis pathway, and subsequently generate ethyl acetate through the action of esterase (Zhang et al., 2020). Yeast enzymes, both intracellular and extracellular, have the capability to catalyze esterification. Additionally, yeasts can produce esters through the reverse reaction of esterase during esterification (Yoshimoto and Bogaki, 2023). Numerous studies have indicated that an increase in acetyl coenzyme A content enhances ethyl acetate synthesis. The key enzymes for acetyl coenzyme A synthesis are EC1.2.1.3 (aldehyde dehydrogenase) and EC6.2.1.13 (acetyl coenzyme A synthetase), and the relative abundance of these enzymes was significantly higher in the test group compared to the control group (P < 0.05).
4. Discussion
In this study, Wickerhamomyces was effectively utilized in the brewing of Xiaoqu Baijiu using fuqu as the medium. This approach enhanced the acidity of the fermented grains, improved the starch utilization rate, increased the ethyl acetate content, reduced the higher alcohol content, and overall improved the quality of Xiaoqu Baijiu to some extent. Notably, the acidity of the fermented grains increased. The acids in the fermented grains are mainly organic, including acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, lactic acid, amino acids, and higher fatty acids produced during fermentation (Qian et al., 2021; Xue et al., 2021). The metabolism of these organic acids chiefly involves the glycolysis pathway and the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), with acetic acid being a metabolite of Wickerhamomyces and a precursor for ethyl acetate synthesis. The synthesis of ethyl acetate in Wickerhamomyces is facilitated by alcohol acyltransferase (Fan et al., 2019). Studies have shown that introducing ester-producing functional bacteria into Maotai-flavor liquor significantly increases the acidity of fermented grains (Yang et al., 2023). Therefore, it is likely that Wickerhamomyces enhances ethyl acetate synthesis by regulating the acidity of the fermented grains. Additionally, this enhanced fermentation alters the fungal community composition in the fermented grains, with Wickerhamomyces replacing the dominant fungus Saccharomymycopsis in the control group. This is attributed to the significant competitive edge of Wickerhamomyces in the fermentation environment, characterized by its strong adaptability to low pH and high ethanol concentrations (Li et al., 2022; Ren et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2020). This adaptability allows it to quickly dominate the fermentation process. By competing for resources and occupying space, Wickerhamomyces further suppresses the reproduction of other yeasts. In the early stages of fermentation, this yeast rapidly proliferates, occupies most of the space in the fermentation system, and consumes a substantial amount of nutrients, such as glucose and amino acids, thereby depriving other yeasts of the resources needed for growth and metabolism (Ciani and Ferraro, 1998). By the end of fermentation, Wickerhamomyces increases ethyl acetate content and decreases the levels of higher alcohols. Ethyl acetate, an important ester compound, imparts Baijiu with a fresh fruity aroma and pleasant taste. During yeast metabolism, ethyl acetate is largely formed through the action of acetyltransferase, catalyzing acetyl coenzyme A and ethanol. Holt S highlighted that the expression levels of acetyltransferase genes (such as ATF1 and ATF2) directly influence ethyl acetate production (Holt et al., 2018). Cordente AG suggested that yeast metabolic pathways, including those regulating fatty acid synthesis, significantly affect ester production (Cordente et al., 2019). The synthesis of higher alcohols in yeast mainly involves nitrogen source metabolism and the amino acid metabolic pathways. According to Chen and Puyo M, the expression of genes like BAT2, encoding branched-chain amino acid transaminase, plays a vital role in higher alcohols production. They noted that inhibiting the expression of this gene significantly reduces higher alcohols yield (Chen and Fink, 2006; Puyo et al., 2024). The expression of genes in microorganisms is intricately linked to environmental factors and microbial interactions, which collectively influence the production and functional outcomes of their metabolites. This research offers insights into enhancing the quality of Xiaoqu Bajiu through augmented fermentation with Wickerhamomyces. However, further exploration is needed into the interactions between yeast and other microorganisms in fermented grains.
5. Conclusion
This study confirmed that Wickerhamomyces plays a critical role in enhancing the fermentation process of Xiaoqu Baijiu. Enhanced fermentation led to increased acidity in the fermented grains, improved starch utilization, and altered the fungal community composition during fermentation. Additionally, Wickerhamomyces-enhanced fermentation resulted in higher levels of ethyl acetate and decreased levels of higher alcohols. These findings indicate that Wickerhamomyces contributes positively to enhancing the flavor profile of Xiaoqu Bajiu. Overall, the results of this study hold promise for enhancing the aroma of Baijiu.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support by Sichuan Science and Technology Innovation and Entrepreneurship Seedling Project (Project NO.2023JDRC0116).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bai, B.,Liu C.,Zhang C.,He X.,Wang H.,Peng W., & Zheng C. (2023). Trichoderma species from plant and soil: An excellent resource for biosynthesis of terpenoids with versatile bioactivities. Journal of Advanced Research, 49, 81-102. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H., & Fink G. R. (2006). Feedback control of morphogenesis in fungi by aromatic alcohols. Genes & Development, 20, 1150-1161. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.,Li D.,Ren L.,Song S.,Ma X., & Rong Y. (2021). Effects of simultaneous and sequential cofermentation of Wickerhamomyces anomalus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on physicochemical and flavor properties of rice wine. Food Science & Nutrition, 9, 71-86. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.,Tang J.,Fan S.,Zhang J.,Chen S.,Liu Y.,Yang Q., & Xu Y. (2021). Comparison of Potent Odorants in Traditional and Modern Types of Chinese Xiaoqu Liquor (Baijiu) Based on Odor Activity Values and Multivariate Analyses. Foods, 10. [CrossRef]
- Choi, K. T.,Lee S. H.,Kim Y. J.,Choi J. S., & Lee S. B. (2024). Improvement of volatile aromatic compound levels and sensory quality of distilled soju derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Wickerhamomyces anomalus co-fermentation. Food Chemistry: X, 22, 101368. [CrossRef]
- Ciani, M., & Ferraro L. (1998). Combined use of immobilized Candida stellata cells and Saccharomyces cerevisiae to improve the quality of wines. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 85, 247–254. [CrossRef]
- Cordente, A. G.,Schmidt S.,Beltran G.,Torija M. J., & Curtin C. D. (2019). Harnessing yeast metabolism of aromatic amino acids for fermented beverage bioflavouring and bioproduction. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 103, 4325-4336. [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.,Teng C.,Xu D.,Fu Z.,Minhazul K.,Wu Q.,Liu P.,Yang R., & Li X. (2019). Enhanced production of ethyl acetate using co-culture of Wickerhamomyces anomalus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 128, 564-570. [CrossRef]
- Holt, S.,Trindade de Carvalho B.,Foulquie-Moreno M. R., & Thevelein J. M. (2018). Polygenic Analysis in Absence of Major Effector ATF1 Unveils Novel Components in Yeast Flavor Ester Biosynthesis. Mbio, 9. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.,Liu Y.,He Z.,Mao Y.,Wu H.,Tian L.,Xiang S.,Long L.,Li Y., & Guan T. (2024). Environmental temperature variations drive the changes of microbial communities to affect Baijiu flavor quality: Case study of Qingxiangxing Baijiu. Food Bioscience, 59. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.,Lu Y., & Liu S. Q. (2020). Effects of Different Yeasts on Physicochemical and Oenological Properties of Red Dragon Fruit Wine Fermented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Torulaspora delbrueckii and Lachancea thermotolerans. Microorganisms, 8. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.,Long H.,Jiang G.,Yu Z.,Huang M.,Zou S.,Guan T.,Zhao Y., & Liu X. (2022). Protective effects of thiamine on Wickerhamomyces anomalus against ethanol stress. Front Microbiol, 13, 1057284. [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.,Tang J.,Yang Q.,Su Z.,Zhu L.,Li Q.,Jiang W.,Zhang L.,Liu Y., & Chen S. (2022). Microbial succession and its effect on key aroma components during light-aroma-type Xiaoqu Baijiu brewing process. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 38, 166. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.,Huang L., & Lian J. (2023). Alcohol acyltransferases for the biosynthesis of esters. Biotechnology for Biofuels and Bioproducts, 16, 93. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.,Tan G.,Chen Q.,Dong W.,Chen P.,Cai K.,Hu Y.,Zhang W.,Peng N.,Liang Y., & Zhao S. (2021). Detection of viable and total fungal community in zaopei of Chinese strong-flavor baijiu using PMA combined with qPCR and HTS based on ITS2 region. BMC Microbiol, 21, 274. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.,Chen Y.,Fu G.,Chen Y.,Wan Y.,Deng M.,Cai W., & Li M. (2022). Improvement of the flavor of major ethyl ester compounds during Chinese Te-flavor Baijiu brewing by Wickerhamomyces anomalus. Food Bioscience, 50. [CrossRef]
- Meersman, E.,Steensels J.,Struyf N.,Paulus T.,Saels V.,Mathawan M.,Allegaert L.,Vrancken G., & Verstrepen K. J. (2016). Tuning Chocolate Flavor through Development of Thermotolerant Saccharomyces cerevisiae Starter Cultures with Increased Acetate Ester Production. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 82, 732-746. [CrossRef]
- Puyo, M.,Scalabrino L.,Romanet R.,Simonin S.,Klein G.,Alexandre H., & Tourdot-Marechal R. (2024). Competition for Nitrogen Resources: An Explanation of the Effects of a Bioprotective Strain Metschnikowia pulcherrima on the Growth of Hanseniaspora Genus in Oenology. Foods, 13. [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.,Lu Z. M.,Chai L. J.,Zhang X. J.,Li Q.,Wang S. T.,Shen C. H.,Shi J. S., & Xu Z. H. (2021). Cooperation within the microbial consortia of fermented grains and pit mud drives organic acid synthesis in strong-flavor Baijiu production. Food Research International, 147, 110449. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.,Chen Q.,Tang T., & Huang Z. (2024). Unraveling the Water Source and Formation Process of Huangshui in Solid-State Fermentation. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.,Xie J.,Tang T., & Huang Z. (2024). Short-Chain Carboxylates Facilitate the Counting of Yeasts in Sub-High Temperature Daqu. Pol J Microbiol, 73, 167-176. [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.,Konno Y., & Tomita Y. (2020). Wickerhamomyces psychrolipolyticus f.a., sp. nov., a novel yeast species producing two kinds of lipases with activity at different temperatures. International Journal of Systematic And Evolutionary Microbiology, 70, 1158-1165. [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.,Wang S.,Yang Y.,Huang Z.,Li Y.,Huang D.,Luo H., & Zhao L. (2023). Insights into the Dynamic Succession of Microbial Community and Related Factors of Vanillin Content Change Based by High-Throughput Sequencing and Daqu Quality Drivers. Foods, 12. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.,Zhu L.,Zheng F.,Zhang F.,Shen C.,Gao X.,Sun B.,Huang M.,Li H., & Chen F. (2021). Determination and comparison of flavor (retronasal) threshold values of 19 flavor compounds in Baijiu. Journal of Food Science, 86, 2061-2074. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.,Wu Q.,Jiang X.,Wang Z.,Tang J., & Xu Y. (2017). Bacillus licheniformis affects the microbial community and metabolic profile in the spontaneous fermentation of Daqu starter for Chinese liquor making. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 250, 59-67. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.,Fan G.,Li X.,Fu Z.,Liang X., & Sun B. (2020). Application of Wickerhamomyces anomalus in Simulated Solid-State Fermentation for Baijiu Production: Changes of Microbial Community Structure and Flavor Metabolism. Front Microbiol, 11, 598758. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.,Wei J.,Wang Y.,Zhu T.,Huang M.,Wu J.,Xu Y.,Zhang J., & Wang B. (2021). A new method to predict the content changes of aroma compounds during the aging process of Niulanshan Baijiu using the GM (1,1) gray model. Flavour and Fragrance Journal, 37, 5-19. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.,Xizhen Sun 2,and Y. L., & Hong Yang 1. (2020). Characterization of Key Aroma Compounds in Xiaoqu Liquor and Their Contributions to the Sensory Flavor. Beverages, 6. [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.,Zhang J.,Wang T.,Bai B.,Hou Z.,Cheng J.,Bo T., & Fan S. (2023). Reveal the microbial communities and functional prediction during the fermentation of Fen-flavor Baijiu via metagenome combining amplicon sequencing. Annals of Microbiology, 73. [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.,Tang F.,Cai W.,Zhao X.,Song W.,Zhong J.,Liu Z.,Guo Z., & Shan C. (2021). Bacterial Diversity, Organic Acid, and Flavor Analysis of Dacha and Ercha Fermented Grains of Fen Flavor Baijiu. Front Microbiol, 12, 769290. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.,Zhang K.,Zou W., & Hou Y. (2021). Three main flavour types of Chinese Baijiu: characteristics, research, and perspectives. Journal of the Institute of Brewing, 127, 317-326. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.,Zeng S.,Zhou M.,Li Y.,Jiang Z.,Cheng P., & Zhang C. (2023). Comprehensive genomic and metabolomic analysis revealed the physiological characteristics and pickle like odor compounds metabolic pathways of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ZZ7 isolated from fermented grains of Maotai-flavor baijiu. Front Microbiol, 14, 1295393. [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.,Wang J.,Shi J.,Du J.,Zhou Y.,Huang M., & Sun B. (2021). Automatic and Intelligent Technologies of Solid-State Fermentation Process of Baijiu Production: Applications, Challenges, and Prospects. Foods, 10. [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.,Jin Y.,Xiao Y.,Chen L.,Tan L.,Du A.,He K.,Liu D.,Luo H.,Fang Y., & Zhao H. (2019). Unraveling the Contribution of High Temperature Stage to Jiang-Flavor Daqu, a Liquor Starter for Production of Chinese Jiang-Flavor Baijiu, With Special Reference to Metatranscriptomics. Front Microbiol, 10, 472. [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, H., & Bogaki T. (2023). Mechanisms of production and control of acetate esters in yeasts. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 136, 261-269. [CrossRef]
- Zha, M.,Sun B.,Wu Y.,Yin S., & Wang C. (2018). Improving flavor metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by mixed culture with Wickerhamomyces anomalus for Chinese Baijiu making. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 126, 189-195. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.,Guo F.,Yan W.,Dong W.,Zhou J.,Zhang W.,Xin F., & Jiang M. (2020). Perspectives for the microbial production of ethyl acetate. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 104, 7239-7245. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J., & Gao Z. (2024). Dynamic changes in microbial communities and flavor during different fermentation stages of proso millet Baijiu, a new product from Shanxi light-flavored Baijiu. Front Microbiol, 15, 1333466. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.,Liang F.,Wu Y.,Ban S.,Huang H.,Xu Y.,Wang X., & Wu Q. (2023). Unraveling multifunction of low-temperature Daqu in simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of Chinese light aroma type liquor. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 397, 110202. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).