1. Introduction
In response to the evolving demands of modern industries driven by societal progress and technological advancements, material requirements have become increasingly stringent [
1,
2]. Materials are now expected to exhibit not only high strength and hardness but also significant toughness and plasticity. As a result, traditional single-material systems are increasingly inadequate to meet these comprehensive demands. This has spurred urgent research and development into materials that combine superior mechanical properties with exceptional performance[
3]. Steel, a traditional metal with a diverse range of types and properties, offers substantial opportunities for designing and applying metal matrix composites (MMCs)[
4,
5,
6,
7]. Its versatility makes steel an ideal matrix material for ceramic-reinforced metal matrix composites (CMMCs), a field that has garnered considerable research interest both domestically and internationally[
8,
9,
10].
Historical research on steel-based composites has primarily concentrated on carbide-reinforced and boride-reinforced systems [
11,
12]. A significant focus has been on the in-situ self-generation techniques for fabricating ceramic-reinforced steel matrix composites [
13]. These methods aim to incorporate high-hardness particles to produce composites with enhanced overall strength and stiffness. This approach leverages the inherent mechanical advantages of ceramics while capitalizing on the toughness and workability of steel, providing a promising pathway for advanced material applications in demanding environments [
14,
15].
Increasing the content of ceramic reinforcements is a key strategy to improve the hardness and wear resistance of steel matrix composites. However, the reinforcement phase cannot be increased indefinitely due to constraints imposed by fabrication techniques and material compatibility. Some scholars have employed the hot isostatic pressing (HIP) method to produce TiC-reinforced composites. By incorporating SiC into a stainless steel matrix, they have created composites suitable for high-performance applications such as valve seats and mechanical seals [
16]. These materials, when subjected to oil or inert gas quenching, achieve hardness levels exceeding HRC65 and exhibit excellent transverse rupture strength. This makes them suitable for tools and components that must withstand high bending and tensile stresses, while also offering superior machinability and thermal shock resistance. Similarly, using the powder metallurgy method, scholars have prepared metal matrix composites with ceramic content exceeding 20%. These composites are embedded in high-alloy steel to fabricate molds, which have demonstrated a lifespan 5-10 times longer than molds made from ledeburitic chromium steel [
17]. This remarkable durability underscores the benefits of incorporating high-volume ceramic reinforcements. Many findings reveal that the TiC-steel combination offers the best interfacial bonding among various reinforcements [
18]. While the addition of ceramic reinforcements significantly improves wear resistance, it also reduces tensile strength, ductility, and impact toughness. These observations highlight the inherent trade-offs involved in optimizing the composition and microstructure of advanced composites to meet specific application requirements.
Various fabrication methods for ceramic-reinforced steel matrix composites have been explored, including spray deposition, powder metallurgy, in-situ reaction, and casting techniques [
19]. Each method presents distinct advantages and challenges. Spray deposition allows for precise control over the reinforcement volume fraction and maintains good interfacial stability between the reinforcement and matrix. However, its high production costs, complex processes, and the need for specialized equipment limit its large-scale application. Powder metallurgy can produce composites with strong matrix-reinforcement bonding but involves complex equipment and processes, resulting in high production costs. Additionally, the tendency for reinforcement particles to agglomerate can lead to non-uniform material properties.
The in-situ reaction method is advantageous due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, producing a clean interface with strong bonding between the reinforcement and matrix. However, this method is constrained by a lengthy processing cycle and a limited range of possible reinforcement systems, making it difficult to produce composites with large reinforcement particles [
20]. Casting techniques, while not ideal for composites with small, high-volume fraction ceramic reinforcements due to challenges in achieving uniform distribution, remain a practical choice for industrial-scale production. Casting is favored for its simplicity, low cost, and widespread applicability, particularly for composites with moderate to low reinforcement content [
21,
22].
To address the challenges of brittleness and low ductility in steel matrix composites, employing steels with excellent plastic deformation capabilities as the matrix material is a viable strategy. Twinning Induced Plasticity (TWIP) steel, a newly developed material, offers a remarkable combination of high strength and ductility [
23,
24]. Composed primarily of Fe with 15-30% Mn, TWIP steel features a stable austenitic structure. Under applied external loads, TWIP steel undergoes a mechanical twinning mechanism induced by strain, resulting in significant uniform elongation without necking. This unique behavior imparts exceptional mechanical properties, including elongation rates ranging from 30% to 95% and tensile strengths of 600 to 1924 MPa [
25,
26]. Furthermore, TWIP steel’s ability to absorb impact energy exceeds that of conventional high-strength steels by more than twice, making it an ideal matrix material to mitigate the brittleness of ceramic reinforcements.
Incorporating large-scale ceramic elements, such as rods, plates, or blocks, can further enhance the ceramic reinforcement content. These larger ceramic reinforcements possess extremely high strength and hardness. Combining TWIP steel as the matrix with such centimeter-scale ceramic reinforcements is anticipated to result in composites exhibiting a synergistic combination of properties: the high hardness and strength of the ceramics coupled with the high ductility and toughness of the TWIP steel matrix [
27,
28]. This innovative composite structure could represent a significant advancement in the field of metal matrix composites, offering a unique blend of superior mechanical characteristics.
Based on these insights, this study aims to investigate the feasibility of fabricating large-sized ceramic-reinforced TWIP steel matrix composites using conventional liquid casting techniques. The research will assess the influence of various ceramic reinforcement shapes and sizes on the composite’s overall properties and structural integrity. By analyzing the impact of different reinforcement geometries, the study seeks to provide valuable technical support and empirical data for the design and development of novel ceramic particle-reinforced steel matrix composites. This research endeavors to bridge gaps in current materials science and demonstrate that traditional casting methods can be effectively adapted to produce advanced composites with enhanced mechanical properties, thereby contributing to the broader field of metal matrix composites.
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Experimental Materials
To investigate the feasibility of fabricating large-sized ceramic-reinforced TWIP steel matrix composites using liquid casting techniques, this study selected four types of ceramic reinforcements: block, particulate, plate, and rod shapes. The specific dimensions of these ceramic reinforcements are detailed in
Table 1. The chosen ceramics were selected for their diverse geometries and sizes, allowing a comprehensive assessment of their effects on the composite’s properties.
For the matrix material, a high-toughness TWIP steel was designed with a composition optimized for enhancing the composite’s mechanical performance. The chemical composition of the TWIP steel matrix, as presented in
Table 2, includes carbon (C), silicon (Si), and manganese (Mn) as the primary alloying elements, with strict control of sulfur (S) and phosphorus (P) impurities to maintain high material purity and prevent deleterious effects on mechanical properties. The high manganese content is particularly crucial for stabilizing the austenitic phase and promoting the twinning-induced plasticity effect, which is central to achieving the desired combination of high strength and ductility in the composite material.
The TWIP steel matrix was specifically designed to leverage the mechanical twinning mechanism under strain, a characteristic that imparts excellent ductility and high strain hardening rates. This is essential for counterbalancing the brittleness typically associated with ceramic reinforcements, thereby achieving a composite with an optimal balance of hardness, strength, and toughness. The low levels of sulfur and phosphorus are critical to preventing the formation of brittle phases that could compromise the composite’s performance, especially under dynamic loading conditions.
By utilizing these materials and carefully controlling their compositions and dimensions, this study aims to explore the interaction between the TWIP steel matrix and the ceramic reinforcements. The goal is to develop a composite material that not only exhibits the superior hardness and wear resistance characteristic of ceramics but also maintains the high ductility and toughness of TWIP steel. This combination is expected to open new avenues for the application of these composites in demanding industrial environments where both high mechanical performance and durability are required.
2.2. Preparation of Casting Molds
In this study, the lost foam casting process was employed to fabricate large-sized ceramic-reinforced TWIP steel matrix composites. The procedure involved several key steps to ensure the successful integration of ceramic reinforcements within the TWIP steel matrix.
The process began with cutting a foam block into the desired shape, corresponding to the TWIP steel matrix model, serving as a placeholder for the subsequent metal casting. Ceramic reinforcements of various geometries—blocks, particles, plates, and rods—were strategically positioned and bonded with the foam pattern, ensuring correct alignment and intended positions in the final composite structure. The foam pattern, now combined with the ceramic reinforcements, was coated with a refractory material to prevent the molten metal from reacting with the foam, maintain the mold shape during casting, and enhance the surface finish of the final product. This coating was dried at 45°C, a process repeated 2-3 times to achieve sufficient thickness and strength. The fully coated and dried foam pattern was then embedded in a casting sand box, forming the final mold for the casting process. The sand box provided structural support during the casting and helped maintain the shape of the composite.
The overall process is illustrated in
Figure 1, depicting the sequential steps involved in preparing the large-sized ceramic-reinforced TWIP steel matrix composite.
The raw materials used for melting the TWIP steel matrix included pure iron, medium carbon ferromanganese, and Q235 steel. The chemical composition of these materials is detailed in
Table 3.
The TWIP steel matrix material was melted using a 100 kg medium-frequency induction furnace. The lost foam casting process was conducted under vacuum conditions to improve the metal’s filling ability, ensuring a dense and homogeneous microstructure in the resulting composite material. During the melting process, pure iron and Q235 steel were first fully melted, followed by the addition of medium carbon ferromanganese. This sequence ensures that the ferromanganese melts completely and integrates well into the steel matrix. A covering agent was added after the complete melting of the ferromanganese to prevent oxidation and loss of manganese. The melt was then held at temperature for 10 minutes before casting, ensuring the molten metal was homogenized. The pouring temperature was carefully controlled, with the molten metal being poured at a temperature no lower than 1540°C to guarantee optimal flow and filling characteristics. This meticulous preparation of the casting molds and careful control of the casting process parameters were essential for producing high-quality composites with uniform distribution of ceramic reinforcements, achieving the desired balance of mechanical properties.
2.3. Analysis of Composite Effects
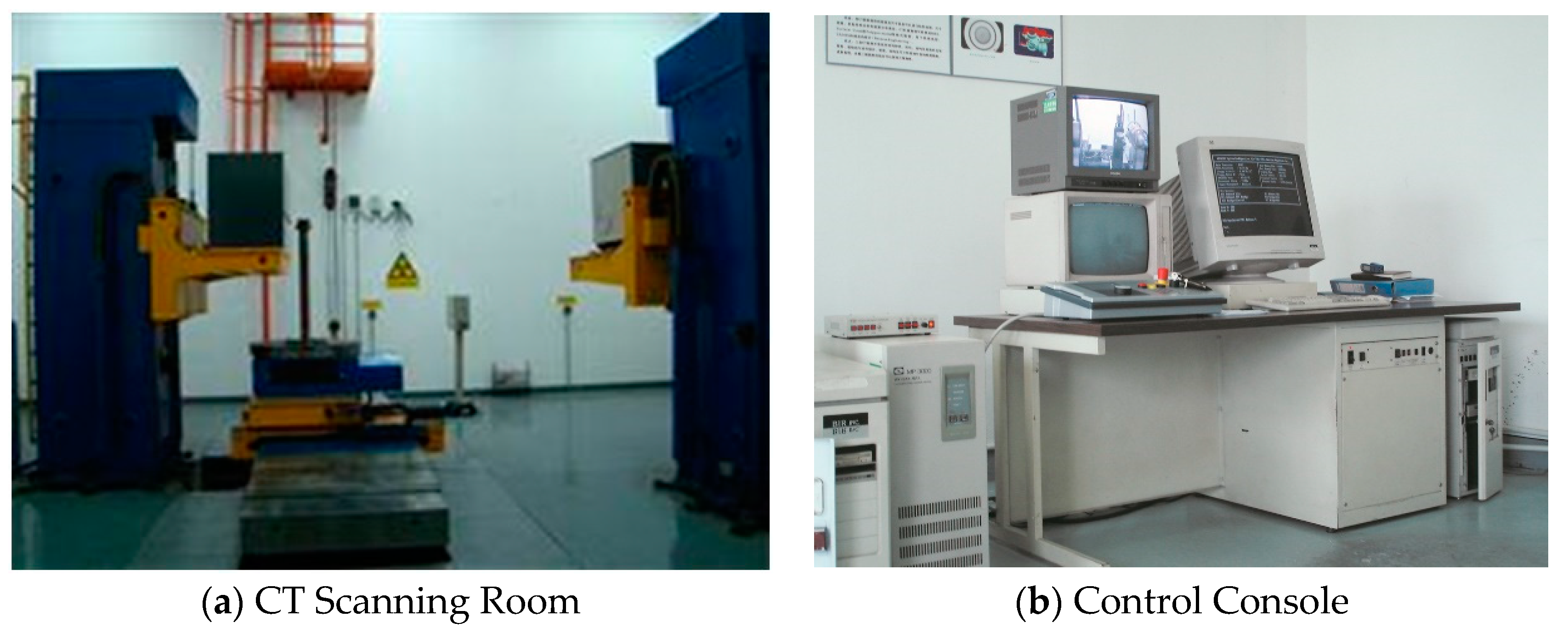
To evaluate the effectiveness of the composite fabrication and assess the quality of the resulting large-sized ceramic-reinforced TWIP steel matrix composites, a high-performance industrial computed tomography (CT) system supplied by Granpect Company Limited (Beijing, China) was employed. This non-destructive testing method provided detailed tomographic images of the composite samples, allowing for an in-depth analysis of the integration between the ceramic reinforcements and the TWIP steel matrix. It also facilitated the identification of any defects formed during the composite preparation process, such as voids, cracks, or improper bonding.
The setup involved positioning the X-ray source and detector at precise distances from the sample: the source was 2.75 meters away, while the detector was positioned 3.4 meters from the source. This configuration optimized the resolution and accuracy of the CT imaging, ensuring that even subtle details in the composite structure could be captured and analyzed. The experimental setup is illustrated in
Figure 2.
For further microstructural analysis, the composite samples were subjected to mechanical processing and wire-cutting to prepare specimens for scanning electron microscopy. A Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) analysis was performed using a JEOL JSM-7800F microscope (Akishima, Japan), offering high-resolution imaging of the composite’s microstructure with a specific emphasis on the interface between the large-sized ceramic reinforcements and the TWIP steel matrix. This analysis was crucial for understanding the bonding characteristics at the microscopic level, including the integrity and continuity of the interface, the presence of any interfacial phases, and the overall distribution of the reinforcement within the matrix.
The combination of CT imaging and SEM analysis provided a comprehensive understanding of the composite’s internal structure and the quality of the ceramic-matrix bonding. The insights gained from these observations contribute to optimizing the fabrication process, ensuring the production of high-performance composites with minimal defects and superior structural integrity.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication of Ceramic-Reinforced TWIP Steel Matrix Composites
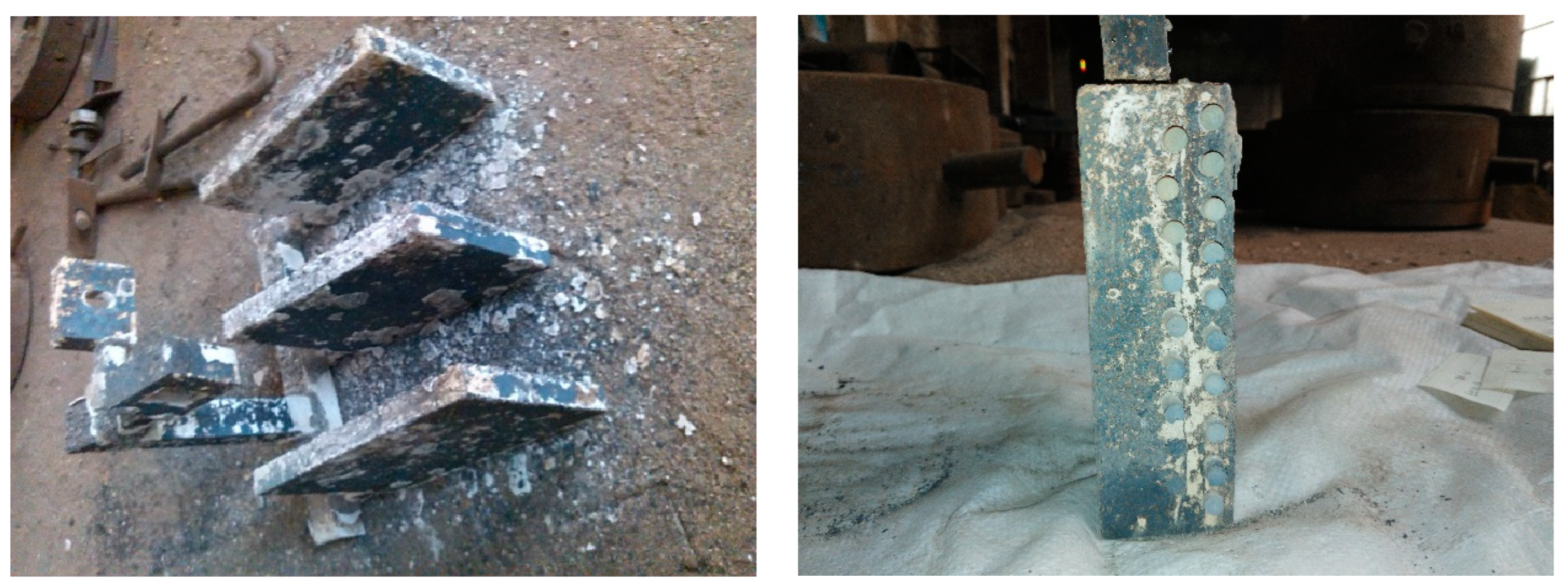
To determine the optimal size and shape of ceramic reinforcements for TWIP steel matrix composites, we utilized various configurations: large block ceramics (115×40×25 mm), thin plate ceramics with significant sectional differences (40×40×5 mm), uniformly cross-sectioned rod ceramics (φ5×95 mm), and spherical ceramic particles (φ10×10 mm). The fabrication process employed a lost foam casting technique, with foam patterns used as the mold for the liquid steel. This method successfully produced large-sized ceramic-reinforced TWIP steel matrix composites, with samples shown in
Figure 3.
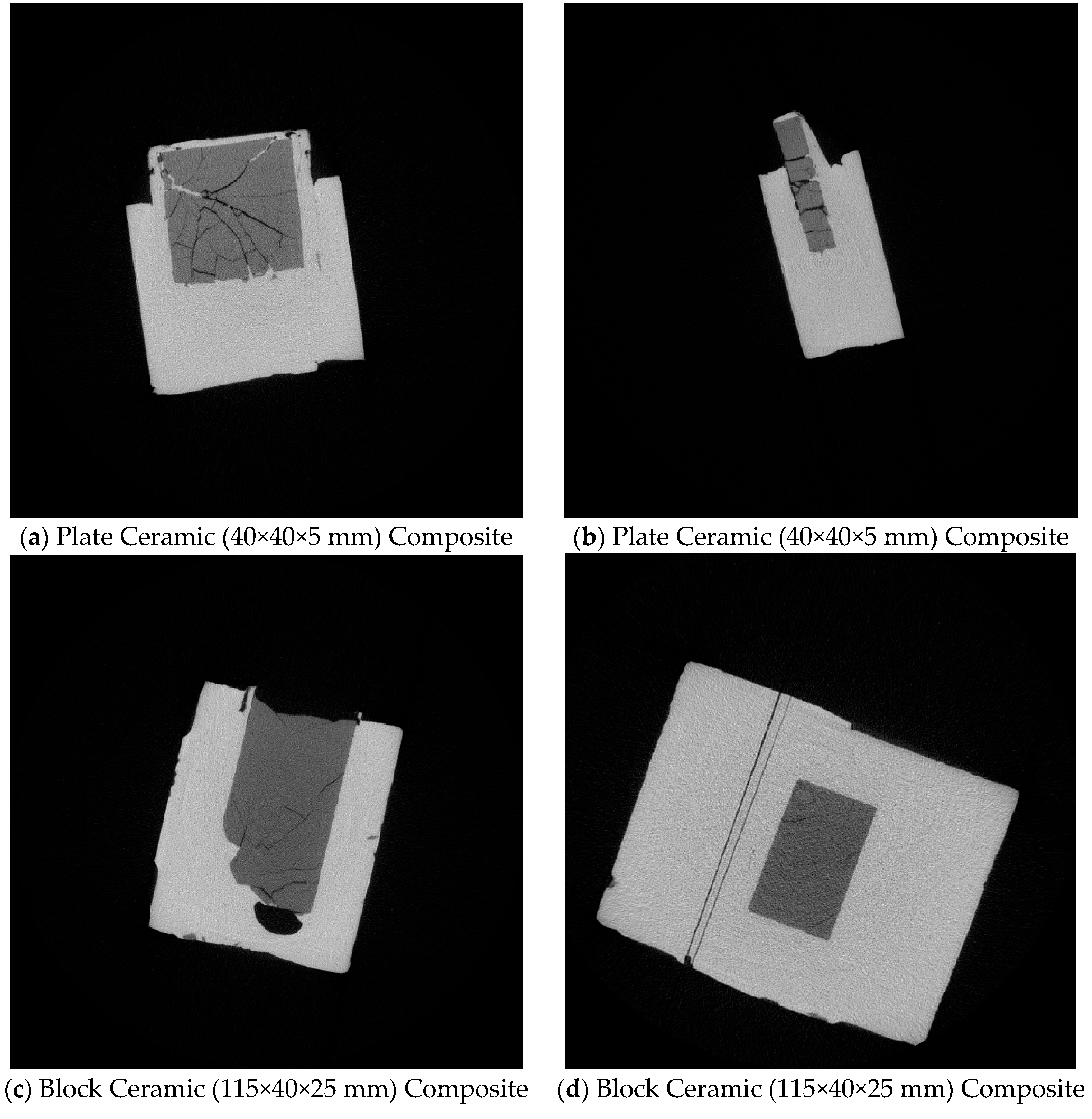
To analyze the effectiveness of the bonding between different ceramic shapes and the TWIP steel matrix, industrial CT was employed for non-destructive testing. The results for plate and block ceramics are illustrated in
Figure 4.
Figure 4 presents the industrial CT scan results in different orientations. It is evident that large block ceramics (115×40×25 mm) and thin plate ceramics (40×40×5 mm) experienced significant cracking during casting. These cracks compromised the integrity of the ceramic reinforcements, as seen in
Figure 4a,b, rendering them ineffective in strengthening the matrix. The fragmented ceramics not only failed to enhance the matrix but also potentially degraded its properties. Furthermore, as shown in
Figure 4c, substantial voids formed at the interface between the large ceramics and the matrix during the casting process, preventing a strong bond. This suggests that large block and thin plate ceramics are prone to cracking and porosity formation during the composite fabrication process, making them unsuitable as reinforcements for large-sized TWIP steel matrix composites.
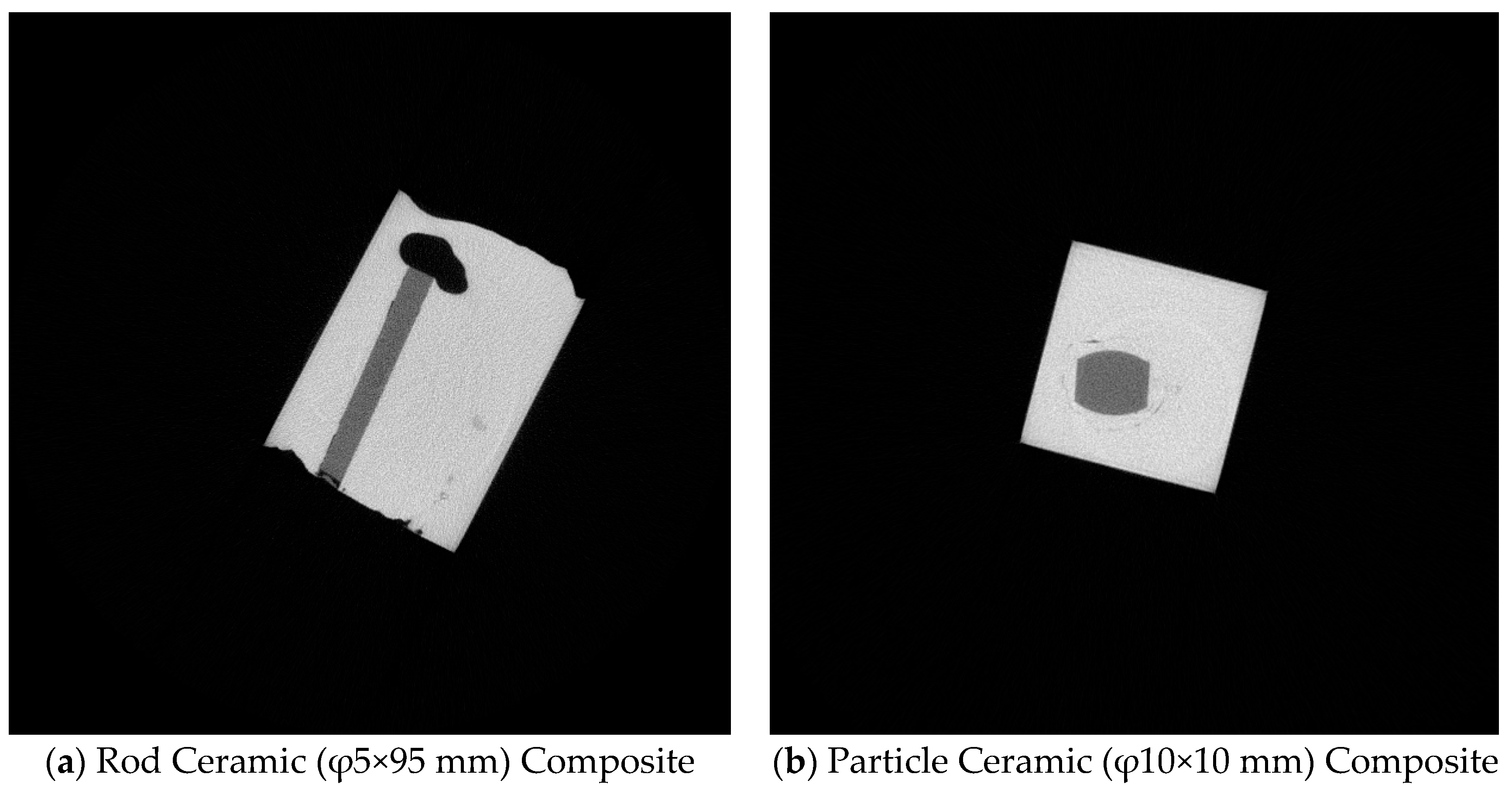
In contrast, the results for rod ceramics (φ5×95 mm) and ceramic particles (φ10×10 mm) are shown in
Figure 5.
Figure 5 demonstrates that when uniformly cross-sectioned rod ceramics (φ5×95 mm) and ceramic particles (φ10×10 mm) were used, no visible cracks or fragmentation occurred. The ceramic reinforcements maintained their integrity, and there was a good bonding between the ceramics and the TWIP steel matrix. The interface quality was significantly better compared to that of block and plate ceramics. This indicates that rod and particle ceramics, with their symmetrical cross-sections, can form a strong and cohesive bond with the TWIP steel matrix, making them suitable for the fabrication of large-sized ceramic-reinforced TWIP steel matrix composites.
These observations underline the importance of selecting appropriately shaped and sized ceramic reinforcements to ensure the structural integrity and mechanical performance of the resulting composites. The study confirms that rod and particle ceramics are optimal for achieving a robust composite with TWIP steel, offering a promising approach for advanced material applications requiring a balance of strength and toughness.
3.2. Interfacial Morphology Analysis of Large-Sized Ceramic-Reinforced TWIP Steel Matrix Composites
To investigate the interfacial bonding and microstructural characteristics of the ceramic particles with the TWIP steel matrix, samples of φ10×10 mm ceramic particle-reinforced TWIP steel composites were sectioned and examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results are shown in
Figure 6.
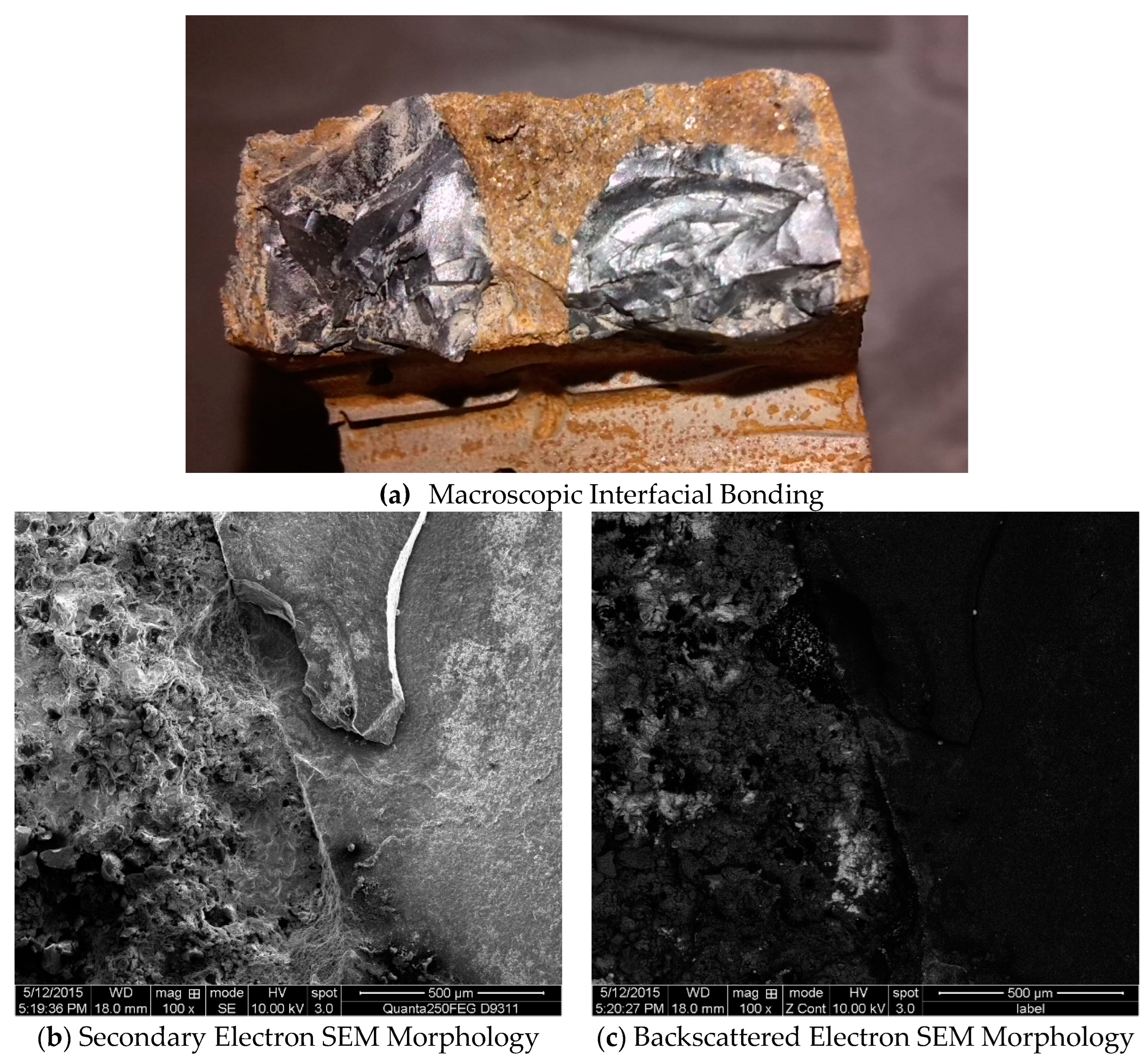
In
Figure 6a, the macroscopic observation reveals that the ceramic particles are tightly embedded in the surrounding TWIP matrix, indicating a robust macroscopic bond. The SEM images further support this observation. As seen in
Figure 6b, the secondary electron SEM morphology shows a well-defined and intimate bonding between the ceramic reinforcement and the TWIP steel matrix at the microscopic level. The tight integration of the ceramics with the metal matrix suggests a strong interfacial bond, essential for effective load transfer and composite performance. Notably, the cracks observed in the right side of the ceramic particle in
Figure 6b are attributed to the sample preparation process and not the casting process, indicating the robustness of the interface under the actual manufacturing conditions. The backscattered electron SEM morphology in
Figure 6c provides additional insight into the compositional differences at the interface. This image clearly delineates the ceramic particles and the TWIP steel matrix, showing a distinct interface region where the two phases interact.
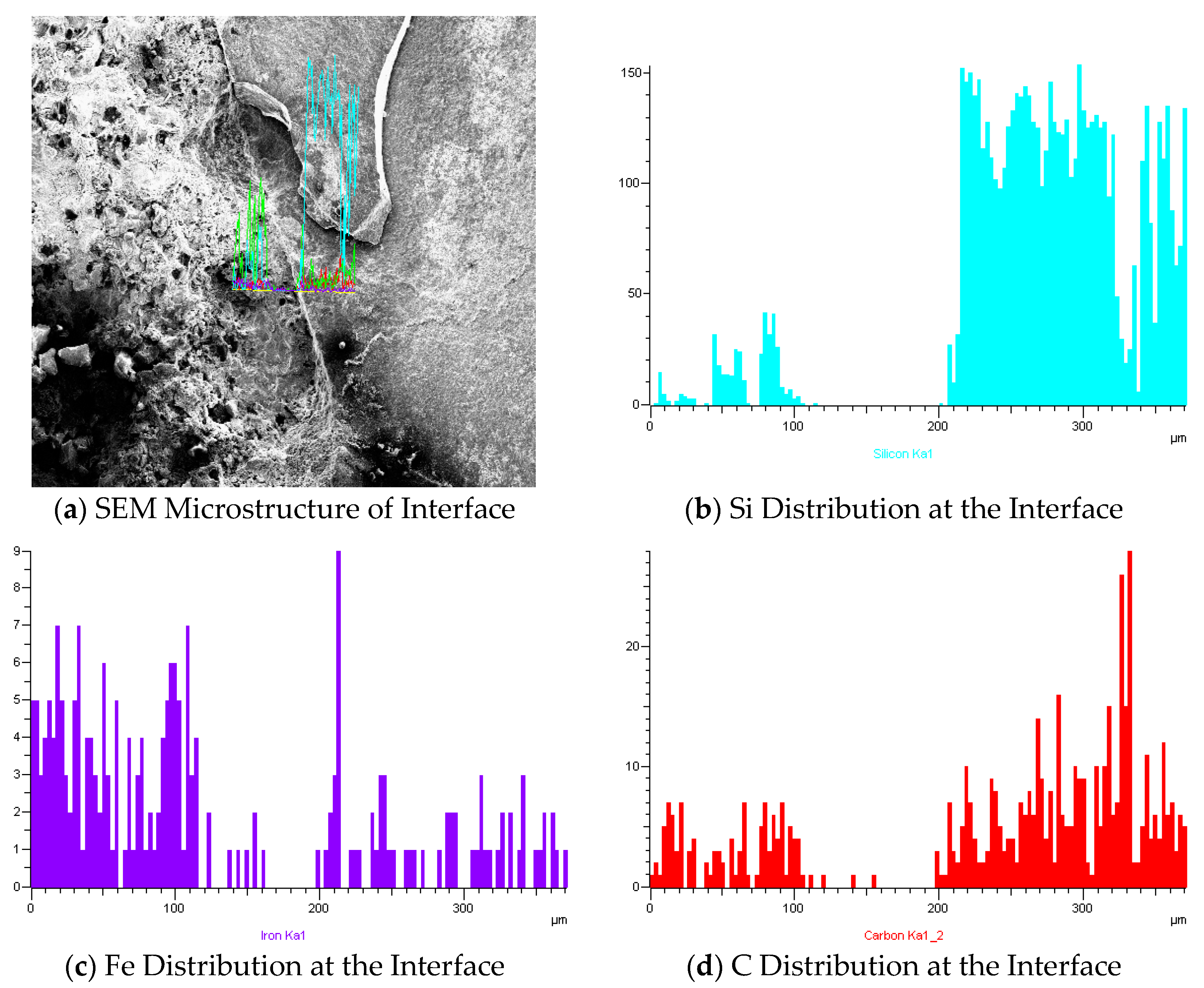
To further understand the compositional characteristics at the interface, elemental line scans were performed across the ceramic and matrix phases. The results are presented in
Figure 7.
The elemental line scans in
Figure 7 reveal a distinct transition zone where the ceramic particles and the TWIP steel matrix meet. The distributions of Fe, C, and Si across the interface indicate some degree of elemental diffusion, suggesting the formation of a transitional layer. This diffusion can enhance the interfacial bonding strength and contribute to a smoother stress transfer between the ceramic and metallic phases. The presence of a transitional layer, characterized by gradual changes in elemental composition, further confirms the good microstructural compatibility and bonding at the interface.
The SEM and elemental analysis indicate that the φ10×10 mm ceramic particles form a strong and cohesive interface with the TWIP steel matrix. This is crucial for achieving the desired mechanical properties in the composite, such as improved strength and toughness. The study demonstrates that the selected ceramic particles can effectively reinforce the TWIP steel matrix, making them suitable for applications requiring advanced material performance.
3.3. Analysis of the Composite Process for Large-Sized Ceramics with TWIP Matrix
The analysis of the composite process indicates that ceramics with more uniform cross-sectional dimensions, such as rod-shaped and spherical ceramics, are more suitable as reinforcement materials for TWIP steel matrix composites. In contrast, large block-shaped and plate-like ceramics, which exhibit significant differences in cross-sectional dimensions, are prone to fragmentation and cracking, hindering their effective integration with the TWIP steel matrix. This behavior is closely related to the casting performance of the matrix and the stress state of the ceramic reinforcement during the casting process.
One critical factor affecting the composite process is the temperature gradient between the molten steel and the ceramic reinforcement. When molten steel comes into contact with the ceramic, a significant temperature drop occurs due to the high thermal conductivity of the ceramics. This temperature change can significantly influence the formation and quality of the composite material. For smaller-sized ceramics, such as φ10×10 mm cylindrical ceramics and φ5×95 mm rod-shaped ceramics, the molten steel’s temperature drop is relatively small upon contact. The subsequent heat transfer from the molten steel maintains sufficient fluidity and feeding capacity, ensuring a good bond between the ceramic and the matrix material. In contrast, larger ceramics experience a rapid temperature drop upon contact with the molten steel, leading to localized solidification. Despite subsequent heat conduction from the molten steel, the rapid temperature decrease impedes the fluidity and feeding of the molten steel, making defect formation more likely. Therefore, from the perspective of the effect of ceramics on the molten steel’s fluidity and feeding capacity, smaller-sized ceramics such as φ10×10 mm cylindrical and φ5×95 mm rod-shaped ceramics are the optimal choices.
During the casting process, ceramic reinforcements are subjected to various stresses, including thermal stress, shrinkage stress from the molten steel, and internal stress. The magnitude of these stresses depends on the ceramic’s surface area. Ceramics with larger differences in cross-sectional dimensions experience uneven force distribution, increasing the likelihood of cracking under unbalanced external forces. When the ceramic reinforcements are φ5×95 mm rods or φ10×10 mm cylinders, the uniformity in cross-sectional shape ensures that the molten metal almost instantly and uniformly envelops the ceramic particles during pouring. Consequently, the ceramics experience uniform stress, preventing crack formation and maintaining the integrity of the ceramic reinforcement.
In essence, the findings underscore the critical importance of selecting ceramic reinforcement materials with uniform cross-sectional dimensions to achieve a stable and defect-free composite process. The φ10×10 mm cylindrical and φ5×95 mm rod-shaped ceramics demonstrate superior compatibility with the TWIP steel matrix, making them ideal candidates for the production of large-sized ceramic-reinforced TWIP steel matrix composites. This selection not only ensures good interfacial bonding but also minimizes the risk of defects, thereby enhancing the composite material’s overall mechanical properties.
4. Conclusion
In this study, we have successfully demonstrated the feasibility of producing large-sized ceramic-reinforced TWIP steel matrix composites using the lost foam casting technique. The research investigated various ceramic shapes and sizes, including blocky, flaky, rod-like, and granular forms, to determine their suitability as reinforcement materials. Key findings and insights from this study are as follows:
1. It was observed that blocky (115×40×25 mm) and flaky (40×40×5 mm) ceramic reinforcements experienced significant cracking and fragmentation during the casting process. These defects compromised the integrity of the composite and diminished the reinforcement’s effectiveness. In contrast, rod-like (φ5×95 mm) and granular (φ10×10 mm) ceramics demonstrated superior compatibility with the TWIP steel matrix. They maintained their structural integrity, resulting in a robust and cohesive composite material.
2. The SEM and CT analyses revealed that rod-like and granular ceramics formed favorable interfacial bonding with the TWIP matrix. The microstructural examination indicated that the ceramic particles were well-embedded within the matrix, with minimal interfacial defects.
3. Smaller, more uniformly shaped ceramics, such as rods and granules, allowed for better heat dissipation and reduced thermal stress. This led to fewer defects and better overall material properties. The findings underscore the importance of controlling ceramic size and shape to minimize thermal and mechanical stresses during casting.
4. Based on the comprehensive analysis, rod-like and granular ceramics emerged as the optimal choices for reinforcing large-sized TWIP steel matrix composites. They demonstrated structural integrity and excellent compatibility with the TWIP steel matrix, establishing their suitability as reinforcements.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S.; methodology, G.S.; investigation, G.S.; software, Q.W.; data curation, Q.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge financial support from the Kunlun Talent Project of Qinghai Province (2023-QLGKLYCZX-032).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Lee, H., Lee, S. & Ryu, S. Advancements and Challenges of Micromechanics-based Homogenization for the Short Fiber Reinforced Composites. Multiscale Sci. Eng. 5, 133–146 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Alhmoudi, A., Sheikh-Ahmad, J., Almaskari, F. et al. Joining of polymer to metal using material extrusion additive manufacturing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 129, 3303–3319 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Sethi, D., Acharya, U., Kumar, S. et al. Effect of Reinforcement Particles on Friction Stir Welded Joints with Scarf Configuration: an Approach to Achieve High Strength Joints. Silicon 14, 6847–6860 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Khammatova, E.A., Gainutdinov, R.F., Klimova, N.S. et al. Use of Plasma Treatment to Increase the Seam Strength of Protective Clothing Made of Composite Material. Fibre Chem 54, 218–221 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, R., Padmanabham, K.C.A., Chandrasekhar, G.L. et al. Synthesis and Characteristics of Heat Treated Al6061-Zirconium Dioxide Metal Matrix Composites. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D 104, 795–804 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Kalita, K., Kumar, V. & Chakraborty, S. A novel MOALO-MODA ensemble approach for multi-objective optimization of machining parameters for metal matrix composites. Multiscale and Multidiscip. Model. Exp. and Des. 6, 179–197 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.R., Vaidya, A.M., Meshram, P.D. et al. Machining behavior investigation of aluminium metal matrix composite reinforced with TiC particulates. Int J Interact Des Manuf 18, 2911–2925 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Hwang, JI., Kim, S.H., Heo, YU. et al. Tempering Behavior of TiC-Reinforced SKD11 Steel Matrix Composite. Met. Mater. Int. 24, 644–651 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H., Kim, D.H., Hwang, KC. et al. Heat treatment response of TiC-reinforced steel matrix composite. Met. Mater. Int. 22, 935–941 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Chen, Ph., Li, Yb., Li, Rq. et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties, and wear resistance of VCp-reinforced Fe-matrix composites treated by Q&P process. Int J Miner Metall Mater 25, 1060–1069 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y., Han, L., Jiang, Y. et al. Effects of Ni60WC25 powder content on the microstructure and wear properties of WCp reinforced surface metal matrix composites. Trans Indian Inst Met 71, 2415–2422 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Kračun, A., Jenko, D., Godec, M. et al. Nanoparticles Reinforcement for the Improved Strength and High-Temperature Wear Resistance of Mn-Cr Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 49, 5683–5694 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.M.N., Nair, F. Fabrication and Microscale Characterization of Iron Matrix Composite Wires Reinforced by in situ Synthesized Iron Boride Phases. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 3909–3930 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M., Chandan, G.K. & Kanchan, B.K. Development of SiC Ceramic Reinforced Composite Interlayer Cladding with AISI304 Stainless Steel Wire on Low Carbon Steel Substrate Using TIG Cladding Process. Silicon 15, 7733–7743 (2023).
- Karthick, S., Elanchezhian, C., Ramnath, B.V. et al. Effect of brown rice husk α-Si3N4 on Ni–P composite coating of austenitic AISI 316L steel: Taguchi grey relational approach. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 13, 12999–13008 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.S.S., Prasad, K. & Patnaik, L. Effect of SiC and TiC Reinforcements on the Mechanical Properties of ZrB2- SiC- TiC Hybrid Composite Fabricated Through Spark Plasma Sintering. Silicon 15, 3339–3351 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Aghajani, S., Pouyafar, V., Meshkabadi, R. et al. Mechanical characterization of high volume fraction Al7075-Al2O3 composite fabricated by semisolid powder processing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 125, 2569–2580 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z., Shao, W., He, C. et al. Microstructure and wear resistance of in situ TiC-reinforced low-chromium iron-based hardfacing alloys. Weld World 68, 605–620 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Lakshmikanth, B., Jesudas, T. Influence of Stainless Steel Short Fibres as Reinforcements in Enhancing the Performance of Aluminium 7075 Alloy Matrix Composites. Trans Indian Inst Met 77, 495–501 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Shavnev, A.A., Kurbatkina, E.I., Nyafkin, A.N. et al. Fabrication Technologies of a Dispersion-Reinforced Metallic Composite Material Based on an Aluminum Alloy—Review. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 14, 76–80 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Dong, Ts., Liu, Jh., Fang, Q. et al. High strength bimetallic composite material fabricated by electroslag casting and characteristics of its composite interface. China Foundry 13, 389–395 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Binesh, F., Zamani, J. & Ghiasvand, M. Ordered Structure Composite Metal Foams Produced by Casting. Inter Metalcast 12, 89–96 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.S., Song, H., Jo, M.C. et al. Novel 1.5 GPa-strength with 50%-ductility by transformation-induced plasticity of non-recrystallized austenite in duplex steels. Sci Rep 7, 1255 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Wang, YN., Yang, J., Wang, RZ. et al. Effects of Non-metallic Inclusions on Hot Ductility of High Manganese TWIP Steels Containing Different Aluminum Contents. Metall Mater Trans B 47, 1697–1712 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Lapovok, R., Berner, A., Bisht, A. et al. Strain-induced solid-state coating of TWIP steel sheets with zinc. J Mater Sci 59, 5538–5557 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Lv, W., Gu, Y., Huang, Y. et al. An Experimental Investigation on Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Asymmetric Warm-Rolled Fe-27Mn-3Si-4Al TWIP Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 6704–6716 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z., Wang, S., Zhou, Y. et al. Influence of aging treatment on mechanical properties and wear resistance of medium manganese steel reinforced with Ti(C,N) particles. Friction 11, 2059–2072 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Vidilli, A.L., Coury, F.G., Gonzalez, G. et al. Tailoring the Microstructure and Properties of Reinforced FeMnAlC Composites by In-Situ TiB2–TiC–M2B Formation. Metall Mater Trans A 55, 101–117 (2024). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).