Submitted:
08 August 2024
Posted:
09 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
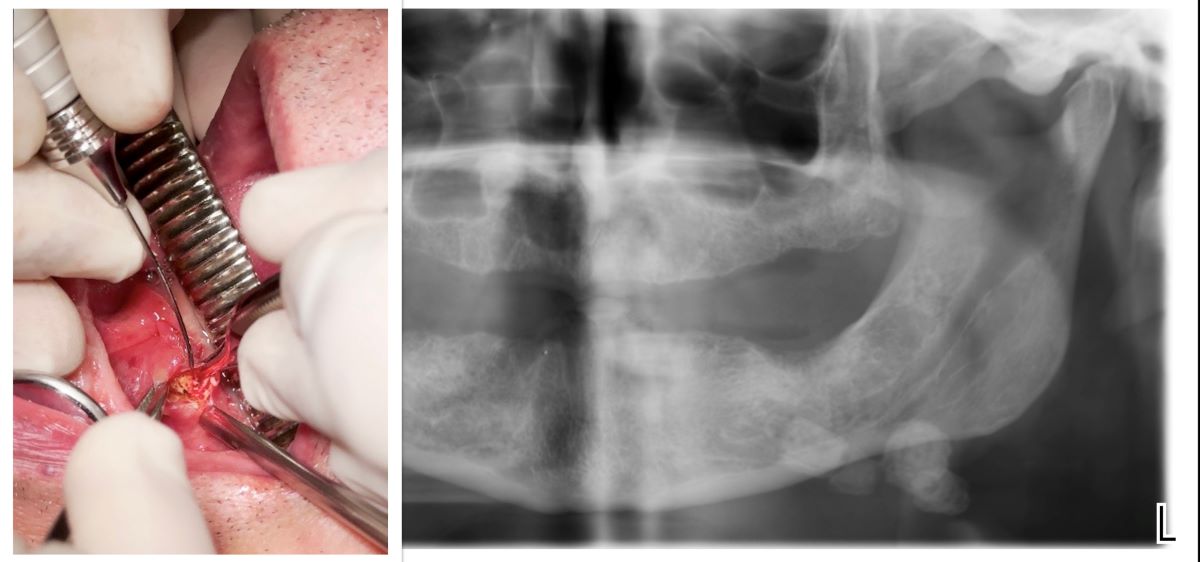
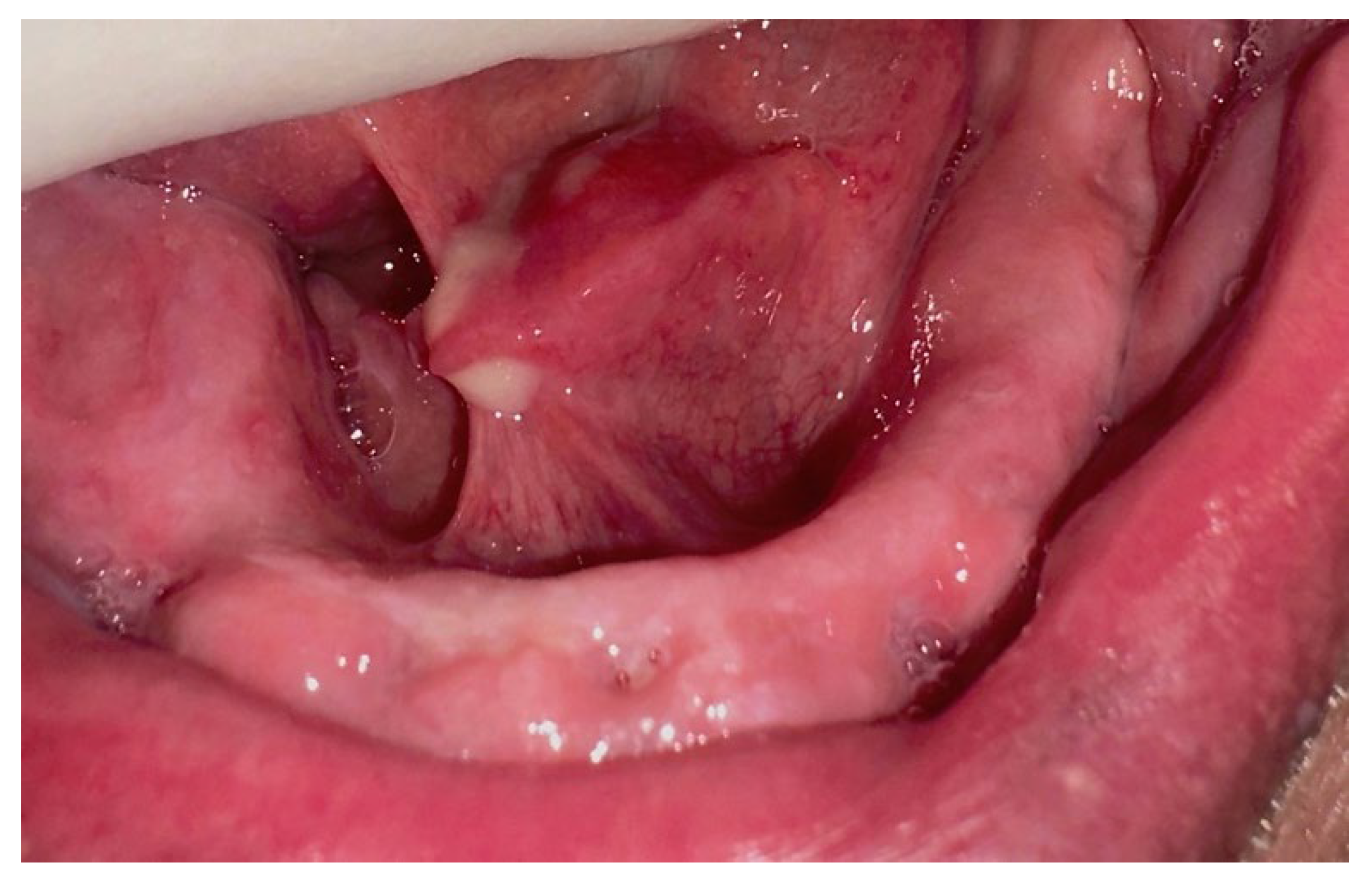
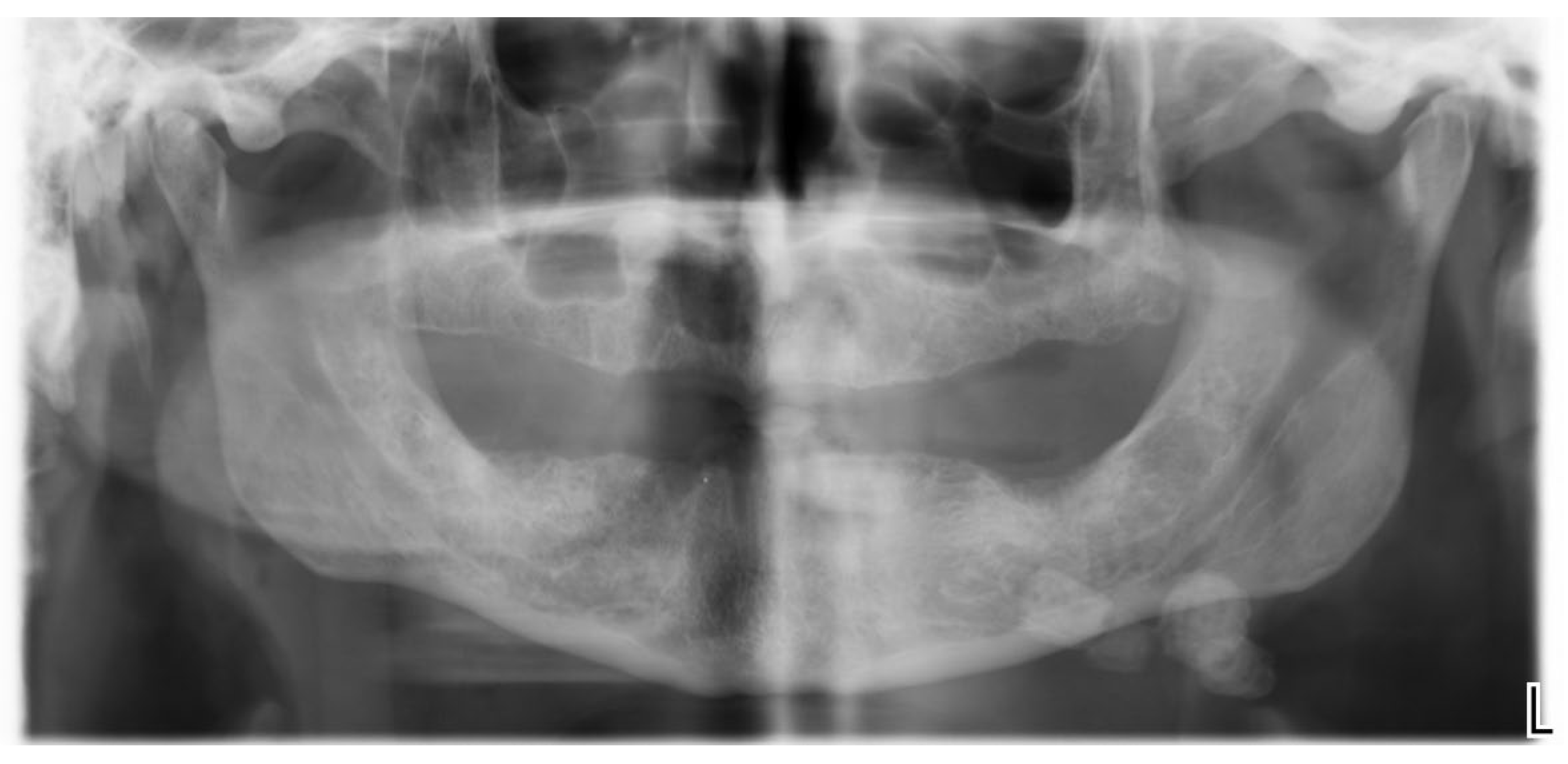
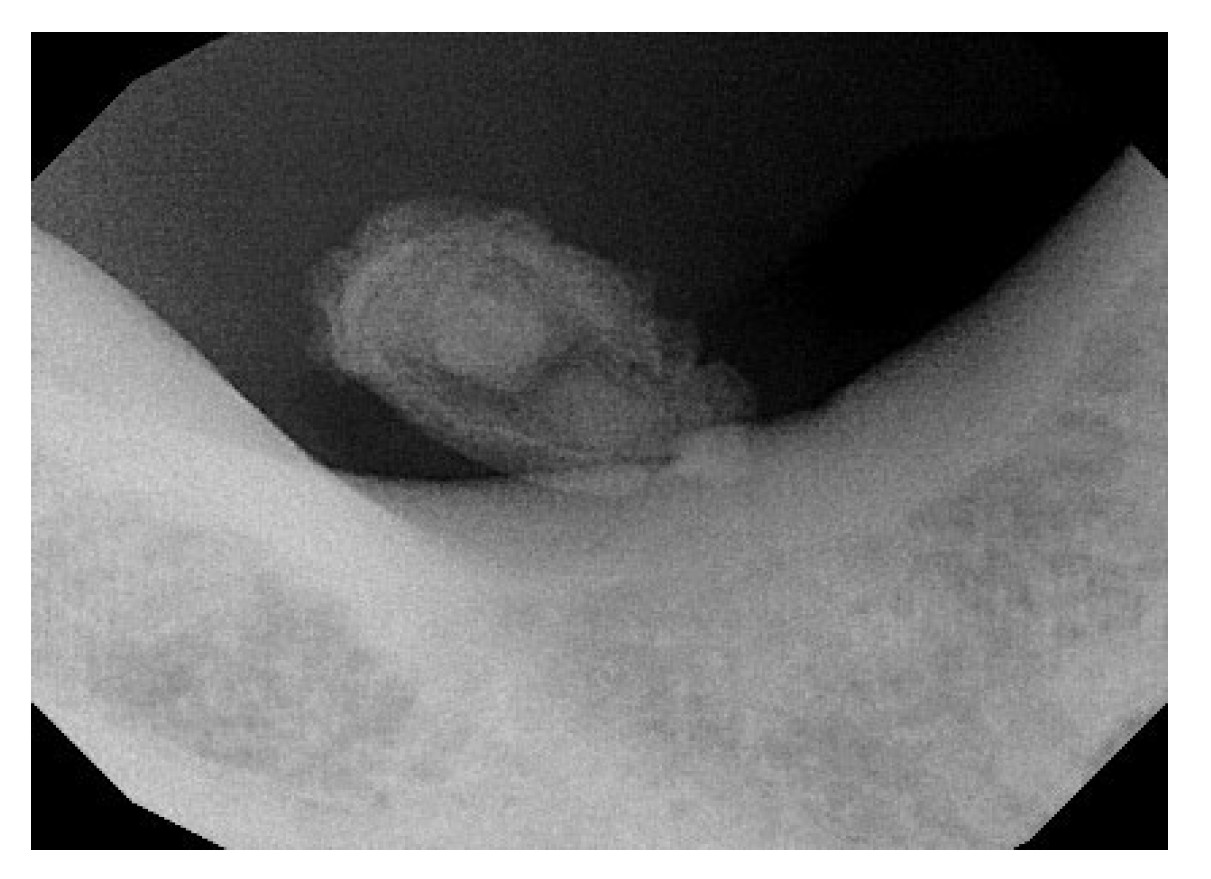
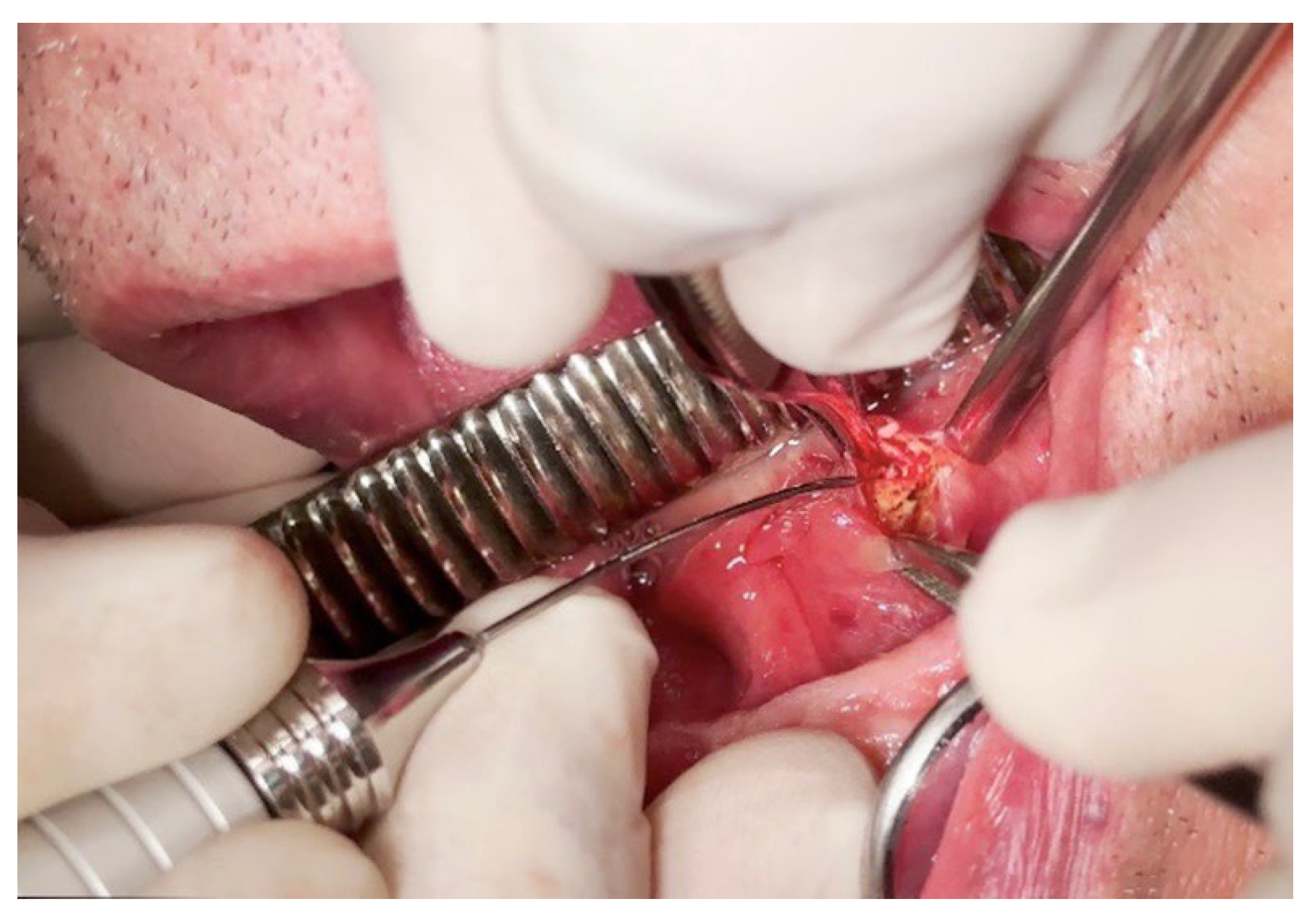
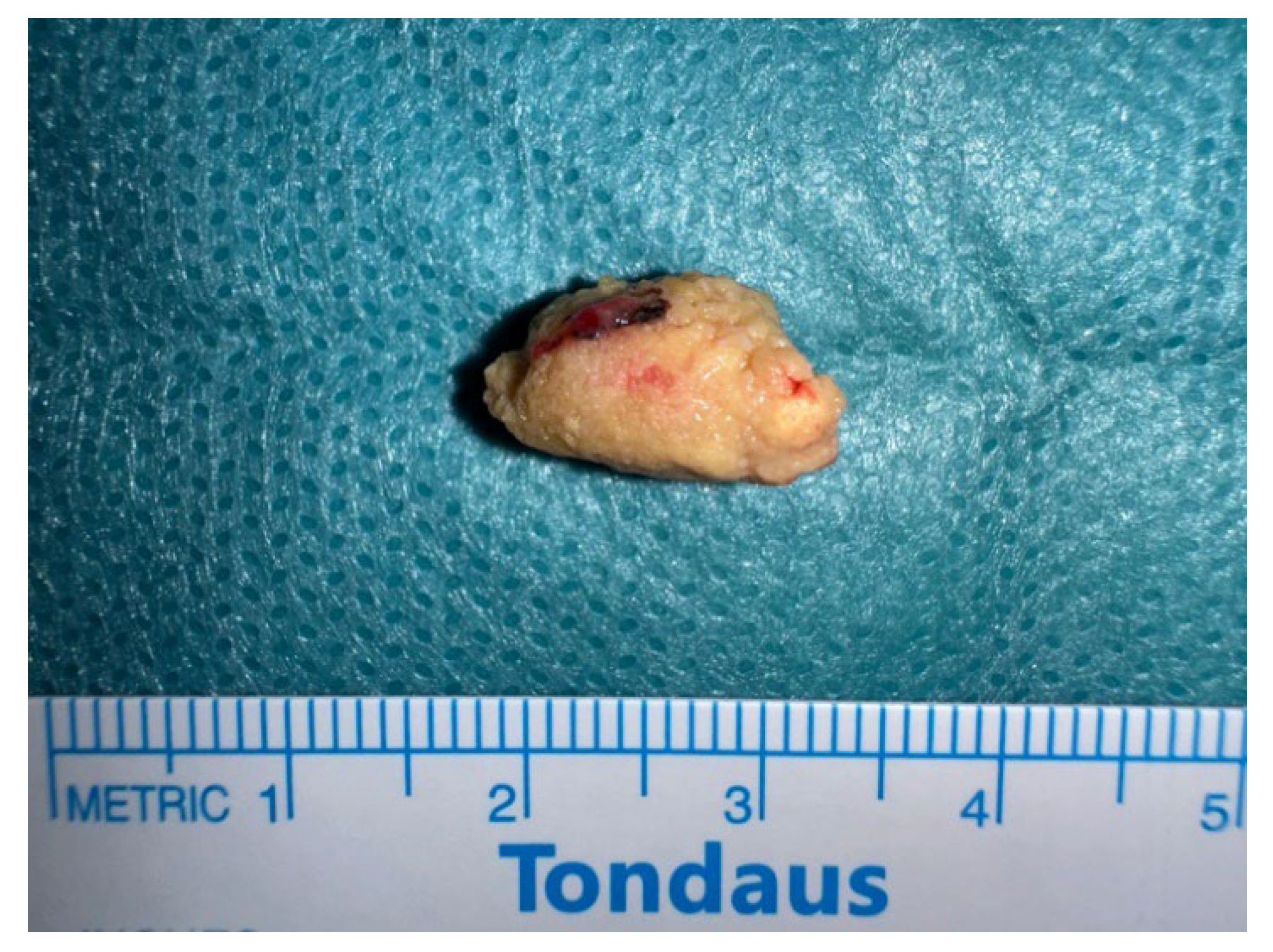
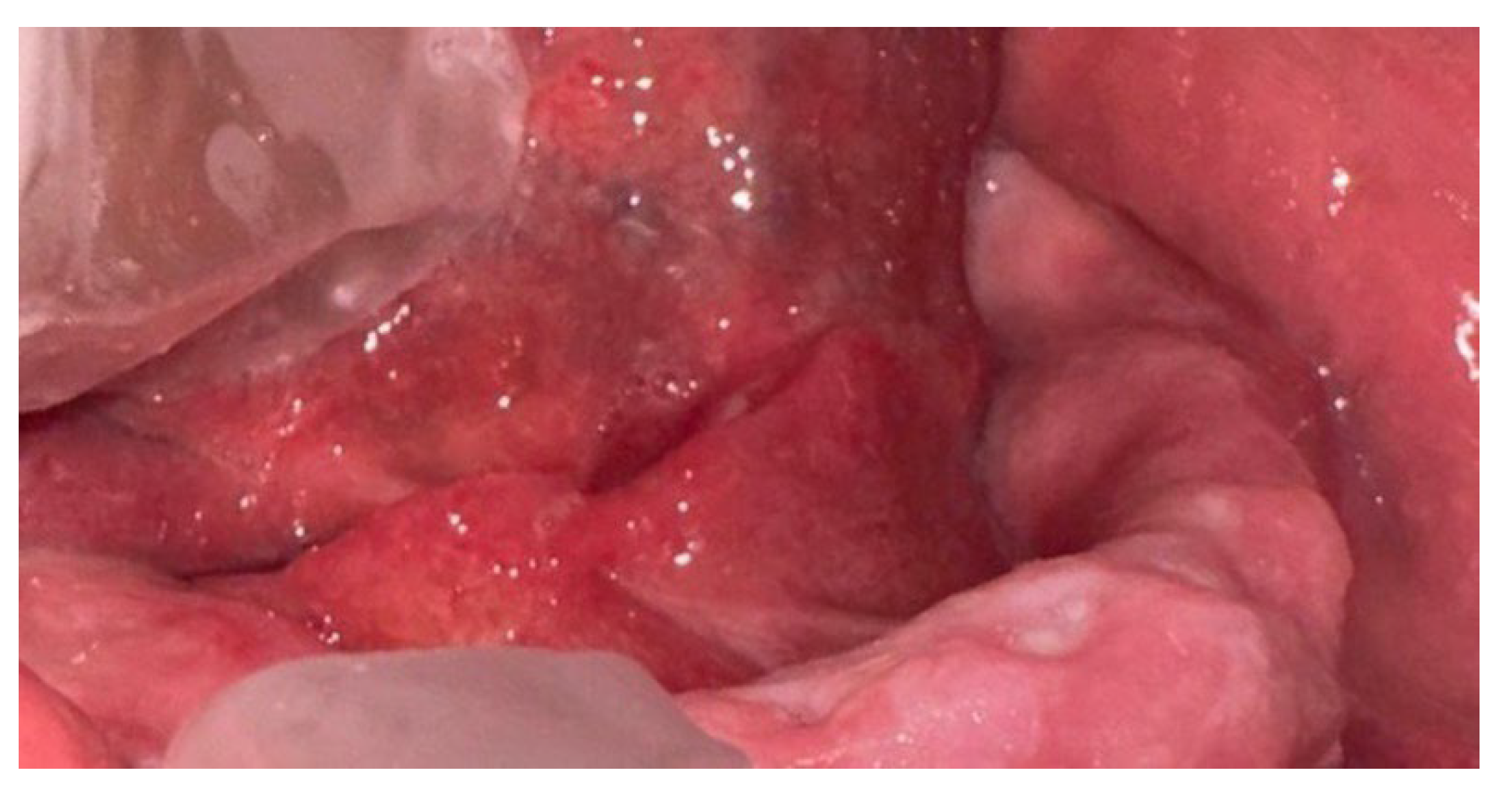
2.1. Case Report
2.2. Literature Review
3. Results
- Full text not available (n = 5);
- Clinica study on animals (n = 2).
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sánchez Barrueco A, Alcalá Rueda I, Ordoñez González C, Sobrino Guijarro B, Santillán Coello J, Tapia GD, Guerra Gutiérrez F, Campos González A, Brenna A, Cenjor Españo C, Villacampa Aubá JM. Transoral removal of submandibular hilar lithiasis: Results on the salivary duct system, glandular parenchyma, and quality-of-life recovery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Nov;280(11):5031-5037.
- Togni L, Mascitti M, Santarelli A, Contaldo M, Romano A, Serpico R, Rubini C. Unusual Conditions Impairing Saliva Secretion: Developmental Anomalies of Salivary Glands. Front Physiol. 2019 Jul 3;10:855. [CrossRef]
- Ungari C, Cicconetti A, Cerbelli E, Sulpasso A, Filiaci F. Giant submandibular sialolith: A case report. Clin Ter. 2022 May 25;173(3):217-221. [CrossRef]
- Romero NJ, Fuson A, Kieliszak CR, Joshi AS. Sonolocation during submandibular sialolithotomy. Laryngoscope. 2019 Dec;129(12):2716-2720. [CrossRef]
- Dabirmoghaddam P, Hosseinzadehnik R. Interventional sialendoscopy with endoscopic sialolith removal without fragmentation. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013 Apr;65(2):111-5. [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Martín D, García-Consuegra L, Junquera L, Rodríguez-Santamarta T, Olay S, Junquera-Olay S. Sialendoscopy approach in treating juvenile recurrent parotitis: A systematic review. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023 Aug 19;52(1):53. [CrossRef]
- Nofal A, El-Anwar MW, Al Shawadfy MA, Fouad YA. Drain-Less Submandibular Gland Excision With Preserved Facial Artery. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022 Dec 1:1455613221142735. [CrossRef]
- Witt RL, Iro H, Koch M, McGurk M, Nahlieli O, Zenk J. Minimally invasive options for salivary calculi. Laryngoscope. 2012 Jun;122(6):1306-11. [CrossRef]
- Capodiferro S, Maiorano E, Loiudice AM, Scarpelli F, Favia G. Oral laser surgical pathology: A preliminary study on the clinical advantages of diode laser and on the histopathological features of specimens evaluated by conventional and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Minerva Stomatol. 2008 Jan-Feb;57(1-2):1-6, 6-7.
- Capodiferro S, Maiorano E, Scarpelli F, Favia G. Fibrolipoma of the lip treated by diode laser surgery: A case report. J Med Case Rep. 2008 Sep 12;2:301. [CrossRef]
- Dell’Olio F, Baldassarre ME, Russo FG, Schettini F, Siciliani RA, Mezzapesa PP, Tempesta A, Laforgia N, Favia G, Li-mongelli L. Lingual laser frenotomy in newborns with ankyloglossia: A prospective cohort study. Ital J Pediatr. 2022 Sep 5;48(1):163. [CrossRef]
- Capodiferro S, Limongelli L, D’Agostino S, Tempesta A, Dolci M, Maiorano E, Favia G. Diode Laser Management of Primary Extranasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Presenting as Maxillary Epulis: Report of a Case and Literature Review. Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Jan 1;9(1):33. [CrossRef]
- da Costa Santos CM, de Mattos Pimenta CA, Nobre MR. The PICO strategy for the research question construction and evidence search. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2007 May-Jun;15(3):508-11. [CrossRef]
- Haas OL Jr, Scolari N, da Silva Meirelles L, Favoretto AX, de Oliveira RB. Sialolith removal in the submandibular region using surgical diode laser: Report of two cases and literature review. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018 Mar;22(1):105-111. [CrossRef]
- Mathew J, Pothanikat JJK, Vinod Kumar RB, Padikadan NO, Arakkal NJ. Extremely Large Submandibular Sialolith Removal - A Case Report. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2022 Jul-Dec;12(2):237-239. [CrossRef]
- Kılınç, Y. and Çetiner, S. (2014) Surgical Removal of a Giant Sialolith by Diode Laser. Open Journal of Stomatology, 4, 484-488. [CrossRef]
- Angiero F, Benedicenti S, Romanos GE, Crippa R (2008) Sialolithiasis of the submandibular salivary gland treated with the 810- to 830-nm diode laser. Photomed Laser Surg 26(6):517–521.
- Azaz B, Regev E, Casap N, Chicin R (1996) Sialolithectomy done with a CO2 laser: Clinical and scintigraphic results. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 54(6):685–688.
- Barak S, Horowitz I, Katz J, Kaplan I (1991) Experiences of the CO2 laser in the surgical treatment of intraoral salivary gland pa- thology. J Clin Laser Med Surg 9(4):295–299.
- Barak S, Katz J, Mintz S (1993) Use of the carbon dioxide laser to locate small sialoliths. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 51(4):379–381.
- Yang SW, Chen TA (2011) Transoral carbon dioxide laser sialolithectomy with topical anaesthesia. A simple, effective, and minimally invasive method. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 40(2):169– 172.
- Williams MF. Sialolithiasis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1999 Oct;32(5):819-34.
- Favia G, Capodiferro S, Turco M, Cortelazzi R. Lithiasis of minor salivary glands of the upper lip. Clinico-pathological report of a case with unusual presentation. Minerva Stomatol. 2004 Apr;53(4):179-83.
- Iro H, Dlugaiczyk J, Zenk J. Current concepts in diagnosis and treatment of sialolithiasis. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2006 Jan;67(1):24-8. [CrossRef]
- Hald J, Andreassen UK (1994) Submandibular gland excision: Short- and long-term complications. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 56(2):87–91.
- Sutter E, Giacomelli-Hiestand B, Rücker M, Valdec S. Der CO2-Laser und seine Anwendung in der Stomatologie [CO2 laser application in stomatology]. Swiss Dent J. 2019 Mar 11;129(3):214-215. German.
- Boj JR, Poirier C, Hernandez M, Espassa E, Espanya A. Case series: Laser treatments for soft tissue problems in children. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2011 Apr;12(2):113-7.
- Macrì M, D’Albis G, D’Albis V, Antonacci A, Abbinante A, Stefanelli R, Pegreffi F, Festa F. Periodontal Health and Its Relationship with Psychological Stress: A Cross-Sectional Study. J Clin Med. 2024 May 16;13(10):2942. [CrossRef]
- Tenore G, Palaia G, Mohsen A, Ambrogiano S, Gioia CRTD, Dominiak M, Romeo U. Could the super-pulsed CO2 laser be used for oral excisional biopsies? Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019 Nov;28(11):1513-1517.
- Sutter E, Giacomelli-Hiestand B, Rücker M, Valdec S. Der CO2-Laser und seine Anwendung in der Stomatologie [CO2 laser application in stomatology]. Swiss Dent J. 2019 Mar 11;129(3):214-215. German. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal M, Saokar A, Gopalkrishna P, Rajeshwari HR, Kumar S. Diode laser-assisted management of intraoral soft tissue overgrowth: A case series. Gen Dent. 2020 Jul-Aug;68(4):28-31.
- Romanos GE, Gutknecht N, Dieter S, Schwarz F, Crespi R, Sculean A. Laser wavelengths and oral implantology. Lasers Med Sci. 2009 Nov;24(6):961-70. [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Concepción D, Cano-Durán JA, Peña-Cardelles JF, Paredes-Rodríguez VM, González-Serrano J, López-Quiles J. The application of diode laser in the treatment of oral soft tissues lesions. A literature review. J Clin Exp Dent. 2017 Jul 1;9(7):e925-e928. [CrossRef]
- Al-Mohaya MA, Al-Malik AM. Excision of oral pyogenic granuloma in a diabetic patient with 940nm diode laser. Saudi Med J. 2016 Dec;37(12):1395-1400. [CrossRef]


| Focused Question |
What are the current uses of laser in sialolith removal? |
|---|---|
|
PICO criteria Population Intervention or Exposure Comparison Outcome |
Patients diagnosed with salivary gland stones (sialolithiasis). Electronic literature searches: #1 ((Laser [Mesh] OR (laser assisted) OR (laser treatment)) #2: ((Sialolith [Mesh] OR (Sialolith Removal) OR (Sialoadenectomy)) Traditional interventions or other non-laser techniques for stone removal. Effectiveness of the intervention (complete stone removal), healing times, recurrence rates, complications (bleeding, infection, tissue damage), post-operative pain, patient satisfaction. |
| Search Strategy |
|
|---|---|
|
Database search Electronic Journals |
PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science database Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Lasers in Medical Science, Journal of Clinical Laser Medicine & Surgery, Photomedicine and Laser Surgery, Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, Journal of Laser Applications |
|
Selection criteria Inclusion criteria Exclusion criteria |
Study Type: Randomized clinical trials, observational studies (cohort, case-control), case series, and case reports. Language: Studies published in English and other major languages. Publication Date: Studies published within the last 30 years. Full-Text Access: Studies for which the full text is available. Review articles, letter to editors Animal studies. Multiple publications on the same patient population. Full text not available/accessible. |
| A total of 8 full-text papers were included for data extraction after 2 more articles which respected the inclusion criteria were found through manual searching. [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21] All collected data from the analysis of the selected articles were compiled into a table for a comprehensive examination. (Table 3.) First Author (Year) Country |
Study Design | N° cases, Gender,age |
Sialolith locations | Laser type | Laser setting | Farmacological therapy | Complications |
Follow-up |
Outcome or Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haas OL H. et al. (2018) [14] | Case series | 2 cases, 1 M: 33 Y 1F: 93 Y |
Distal part of the submandibular duct and could be palpated intraorally. | Diode laser | 400-μm optical fiber emitting at a wavelength of 980 nm (infrared), 2.5 W output power, and in continuous pulse mode. | Amoxicillin (500mg) every 8h for 7 days and oral acetaminophen (750 mg) every 6h for 3 days | No intraoperative complications were reported | Evaluated on days 7,14, and 30 free surgery. | The diode laser is a safe, minimally invasive option for this procedure, offering enhanced coagulation, high-quality incisions, no bleeding, low nerve damage risk, and minimal comorbidities |
| Mathew J et al. (2022) [15] | Case report | 1 case, 1M: 50 Y |
Behind the lower right second permanent molar | Diode laser | 810 μm | - | Asymptomatic with undisturbed salivary flow | One year. | Newer treatment modalities offer effective alternatives to conventional surgical methods for sialoliths. |
| Kılınç et al. (2014) [16] | Case report | 1 cases, 1F: 57Y |
In the anterior part of the left side of the floor in the mouth. | Diode Laser | 810 nm of wavelength, 4.0 W of power, 0.5 ms continuous wave and 1000 Hz of frequency was selected. | Antibiotic: Amoxicillin clavulonate 1000 mg , every 12 h for 5 d. Rovamycine every 12 h for 5 d). Anti-inflammatory: 100 mgr flurbiprofen every 12 h for 3 d | No sign of infection was observed, and salivary flow was normal. | 10th days. | An 810-nm diode laser is a safe and effective technique, offering excellent cutting and coagulation with a low complication rate, making it suitable for this surgical procedure. |
| Angiero et al. (2008) [17] | Case series | 25 cases. | Wharton’s duct | Diode laser | Wavelength of 810-830nm ,2,5W CW with 5-10 sec irradiation time (energy density 12,5-25J,, flexible fibre 300-320 em | None of the patients required analgesic therapy | Postoperatively, three patients experienced odynophagia, impaired mouth opening, and submandibular swelling, which subsided in 2-3 days. | For up to 6 years. | It Is a valid alternative to traditional surgery |
| Azaz et al. (1996) [18] | Case series | 49 cases, 26 M ,23W: (15Y-18Y) |
Wharton’s duct :47 Stensen duct: 2 |
CO2 laser | 1020 8W CW | Four patients had antibiotics for 5 days | Four patients experienced discomfort | 7 days after for the follow up. And after one years. | Excellent results with no bleeding, minimal scarring, and little discomfort. Sialadenectomy should be considered for patients who suffer from recurrent symptoms. |
| Barak et al. (1991) [19] | Case series | 21 cases, 14M, 7W. |
Wharton’s duct: 10 patients.Submandibular/sublingual glands:8 patients.Stensen duct: 3 patients. | Co2 laser | 5W/10W in continuous mode | - | No complication | Three weeks. | Complete healing after three weeks |
| Barak et al. (1993) [20] | Case series | 6 cases, 2M (22-54 Y) 4W (19-32 Y) |
Wharton’s duct: 4 patients. Submandibular gland: 2 patients. |
Co2 laser | 10W in continuous mode | - | No complication. Postoperative Swelling in 2 patients (Hilus of submandibular gland) | 1 year. | Complete healing in 7 to 20 days |
| Yang et al. (2011) [21] | Case series | 19 cases, 12M, 7FW (8- 54 Y) |
In the posterior half of Wharton’s duct. | Co2 laser | 4-6W in continuous mode | - | One patient developed ranula formation after laser surgery | 1-3,5 years. | The results suggest that transoral CO2 laser sialolithectomy is a simple, safe, and low-complication procedure suitable for outpatient treatment. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




