1. Introduction
Subsurface drip irrigation (SDI) buried in the soil, in addition to integrating the existing surface drip irrigation technology that has achieved labor savings and automatic irrigation, provides the right amount of irrigation at the right time with outstanding advantages. SDI reduces the evaporation surface area, inhibits weed growth, reduces the risk of soil contamination and crop pests and diseases, extends the service life of the pipeline network without the need to replace the pipeline system every year, and other significant advantages. SDI is the existing irrigation technology with the greatest water–saving potential and is one of the most obvious ways to increase production and improve quality [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. In recent years, SDI has been widely studied in Northwest China [
5,
6], North China [
7,
8], and South China [
9], but the following problems exist: (1) To avoid soil tillage damage to SDI systems, it is necessary to bury the SDI systems below the soil tillage layer [
10]; additionally, the upward transport of soil moisture is less than the downward transport due to gravity [
11], which causes delayed crop emergence or nonemergence of seedlings, leading to reduced yields [
12,
13,
14]. (2) Compared with center pivot sprinklers, SDI systems must operate for more than 7 years to be economically competitive [
15], which implies a substantial increase in the risk of emitter clogging. The enhancement of emitter clogging resistance in SDI systems is critical.
In response to problem (1), Mo et al. [
16] proposed a variable flow emitter for SDI that automatically switches the operating phase according to the inlet pressure to achieve a step change in the outlet flow rate. A regular outlet flow rate of 1–2 L/h is provided during working stage I (regular flow water supply stage), which is used to supply water to the crop during most of its reproductive period. In work stage II (high–flow water–supply stage), by increasing the water–supply pressure, a stepwise increase in the water–output flow rate is realized, which promotes the upward movement of soil moisture, improves the soil moisture environment of the seed bed, and thus promotes seedling emergence. Gao et al. [
17] took a variable flow emitter as the research object to study its hydraulic performance response law (flow rate and flow index) to the parameters of the runner structure and determined the optimal combination of the runner structure corresponding to the outlet flow rate of 1.5 L/h at 0.1 MPa by using the traversal optimization algorithm. However, scholars have neglected the influence of a variable flow emitter runner structure on anti–clogging performance.
The hydraulic performance of the emitter determines the uniformity of water and fertilizer application in the whole drip irrigation system [
18,
19]. The flow rate (
q) and flow index (
x) are the two main hydraulic performance indices of the emitter, and a smaller
x corresponds to a lower sensitivity of the emitter effluent flow rate to the inlet pressure and a greater laying distance [
20,
21,
22]. Some scholars studying tooth–shaped runner emitters have reported that the runner width, number of cells, runner depth, and tooth height all have significant effects on
q [
23], that the
q of tooth–shaped emitters increases with increasing tooth turning angle and tooth spacing, that the tooth width has a greater effect on
q than does the bottom pitch of the tooth [
24,
25], and that
q is positively correlated with the tooth tip angle and the tooth tip covariance and negatively correlated with the cusp angle and cusp parameter [
26,
27]. Moreover, most scholars have used hydraulic performance tests and numerical simulations to investigate the primary and secondary order of the influence of the flow channel structural parameters on
x. For serrated runner emitters, the primary order is tooth spacing > tooth angle > tooth height > runner depth [
28]. The primary order of the structural parameters affecting
x changes when the structural parameter takes a different range of values, e.g., tooth base pitch > tooth height > tooth width[
29], runner depth > tooth height > tooth angle > tooth base pitch [
30]. For trapezoidal runner emitters, the primary order is runner width > number of runner cells > angle > runner depth [
31,
32]. For orthogonal labyrinth runners,
x is minimized when the intertooth angle is 70° [
27].
Reducing
q is an important way to increase the length of drip tape laying and reduce the investment in drip irrigation systems per unit area [
33,
34]. Most drip irrigation equipment manufacturers reduce
q only by reducing the depth of the flow path, but this drastically increases the risk of emitter clogging. According to the FAO, the probabilities of physical, chemical and biological clogging in the process of emitter clogging are 31%, 22% and 37%, respectively. Gilbert et al. [
35] reported that 55% of emitter clogging is caused by physical factors, with physical clogging caused by solid particles being the most common form [
36,
37]. Numerous scholars have adopted laser Doppler velocimetry (LDV), particle image velocimetry (PIV), particle tracking velocimetry (PTV), computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and other methods to visualize the operation of particles inside the emitter flow channel and to analyze the response laws of the water flow velocity, turbulent kinetic energy in the flow channel, turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate, and particle passage rate with the structural parameters of the emitter flow channel to increase the ability of the emitter to resist physical clogging. For rectangular and serrated runner emitters, some scholars have applied CFD two–phase flow numerical simulations and PIV technology to analyze the velocity vector, streamline distribution, and particle trajectory of the fluid, pointing out that the tip of the tooth is the most serious region of turbulent kinetic energy dissipation and that the low–speed vortex region at the sharp corners is the focus of the clogging location [
38,
39]. The clogging resistance of the emitters tends to decrease with increasing runner angle, and the emitters corresponding to a 60° angle were more resistant to clogging [
40]. Yu et al. [
41,
42] used a combination of CFD‒DEM coupled numerical simulation and LS–CWM laser particle sizer tests to analyze the movement of particles in a flow channel. They proposed that increasing the flow velocity in the low velocity zone of the flow channel and the eddy zone can strengthen the ability of water scouring and sand hostage, reduce the risk of solid particle deposition in the flow channel, and reduce the probability of clogging the emitter. The resistance of toothed runners to clogging was better than that of trapezoidal and triangular runners [
43]. For rectangular emitter runners, a runner with an internal tooth width × internal tooth height of 0.8 mm × 0.5 mm has the best clogging resistance [
44].
These studies focused on the hydraulic performance and anti–clogging performance of the emitter, and few studies have focused on the optimization of the emitter runner structure while comprehensively considering these two properties. Wang [
45] constructed a multiobjective optimization model of flow channel structural parameters for a bidirectional flow channel emitter with the optimization objectives of minimizing the steady flow index and maximizing the sediment particle passage rate and used an algorithm combining NSGA–II and a support vector machine to determine the distance between the diverter device and the sidewall, the tooth tip spacing from the retainer device, and the spacing between the retainer device and the sidewall at a rated flow rate of 3.0 L/h. Ensure an optimal combination of key structural parameters. Currently, the common intelligent optimization algorithms for mining the functional relationship between the objective function and each constraint parameter in optimization problems include the genetic algorithm (GA), particle swarm optimization algorithm (PSO), and ant colony algorithm (ACO) [
46,
47]. Compared with intelligent optimization algorithms, solving constrained optimization problems using the scipy.optimize.minimize function in Python is efficient and numerically stable and has been widely used in problems such as risk assessment in emergency decision–making for typhoon disasters [
48], benefit distribution in military supply chains[
49], and optimization of overhauling equipment in coal mining enterprises [
50], and this function is widely used and more suitable than other methods for addressing common optimization problems.
The flow rate of commonly used emitters in China is 1 ~ 2 L/h [
51,
52], and the difficulty of improving the anti–clogging performance of emitters gradually increases as
q decreases. In addition, for the new variable flow emitters, studying how to quickly determine the combination of flow channel structure parameters for scenarios such as better hydraulic performance, better clogging resistance, and better performance for a specific small flow rate is urgently needed. In this study, the variable flow emitter is taken as the research object, with the help of an orthogonal test to set up the tooth–shaped flow channel composed of different tooth heights (E), tooth spacings (B), tooth angles (A) and tooth depths (D). The sample is precision machined by CNC. The hydraulic and anticlogging performances of its working stage I are explored through numerical simulation and indoor tests. In addition, the evaluation indices of hydraulic and anticlogging performances are constructed with the structure. At the same time, a quantitative characterization mathematical model of hydraulic performance and anticlogging performance evaluation indices and structural parameters are constructed, and the optimized combination of structural parameters of the variable flow emitter flow channel under different scenarios is obtained by using the scipy.optimize.minimize function in Python.
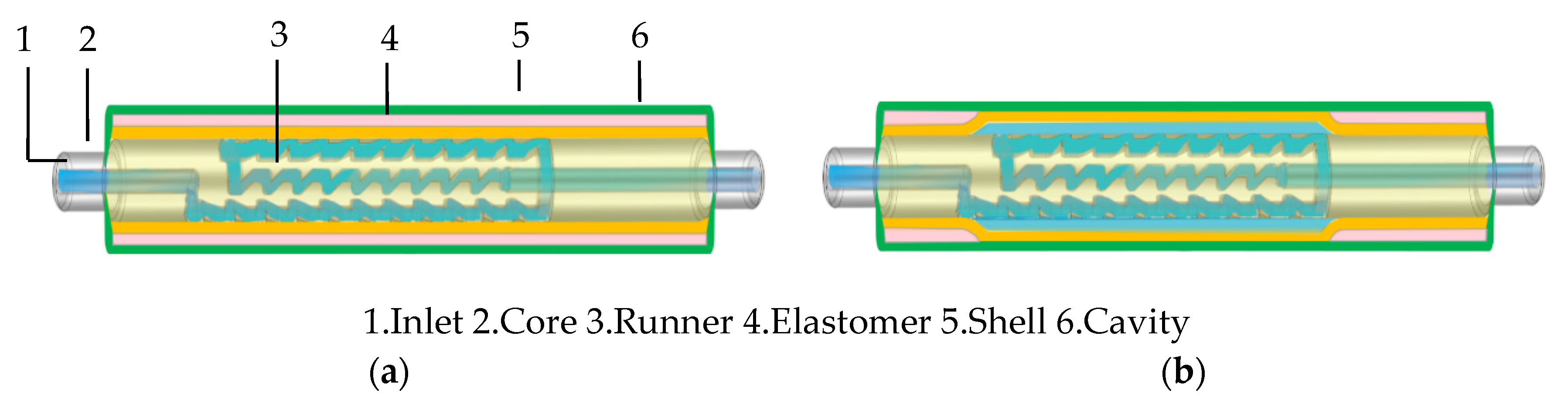
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the working principle of a variable flow emitter: (a) The regular flow water supply stage; (b) The high–flow water supply stage.
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the working principle of a variable flow emitter: (a) The regular flow water supply stage; (b) The high–flow water supply stage.
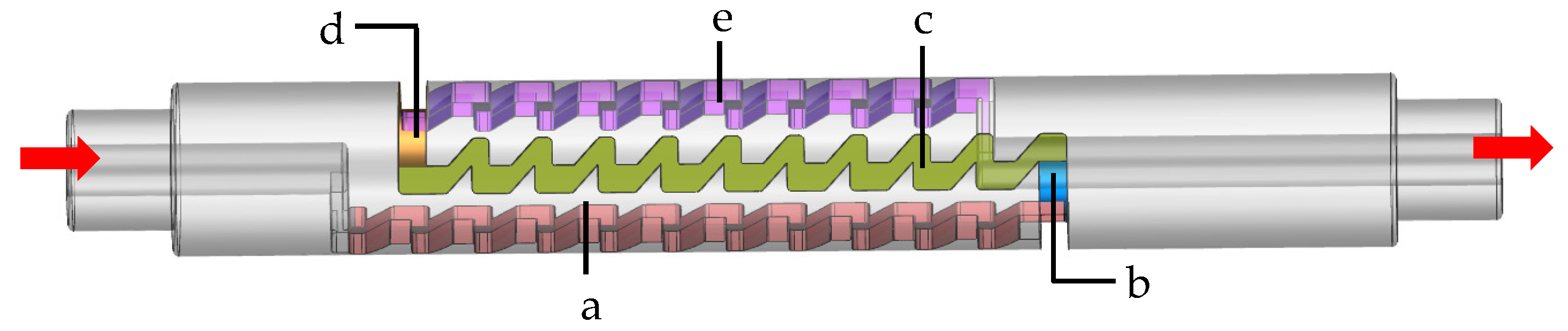
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the variable flow emitter runner structure.
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the variable flow emitter runner structure.
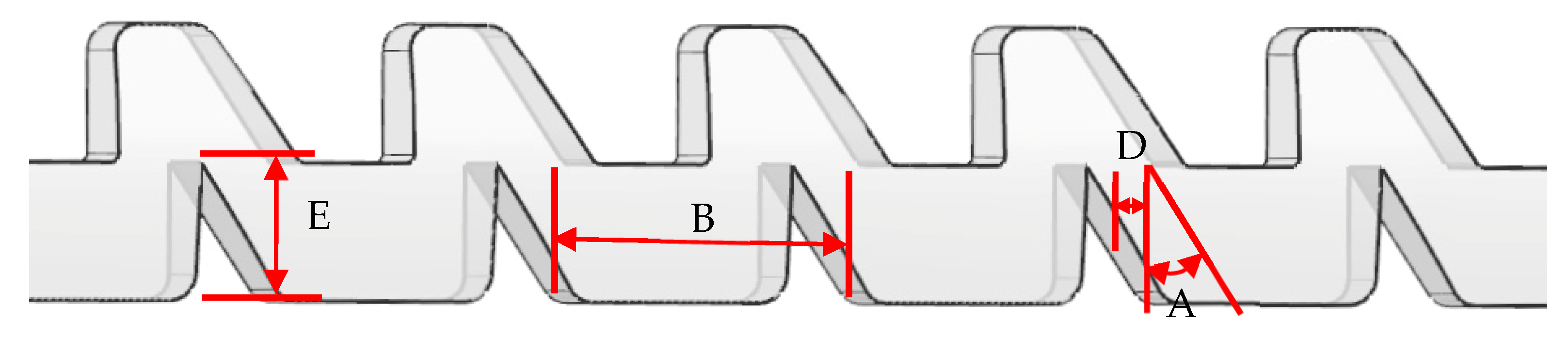
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the structural parameters of the toothed runner of the variable flow emitter.
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the structural parameters of the toothed runner of the variable flow emitter.
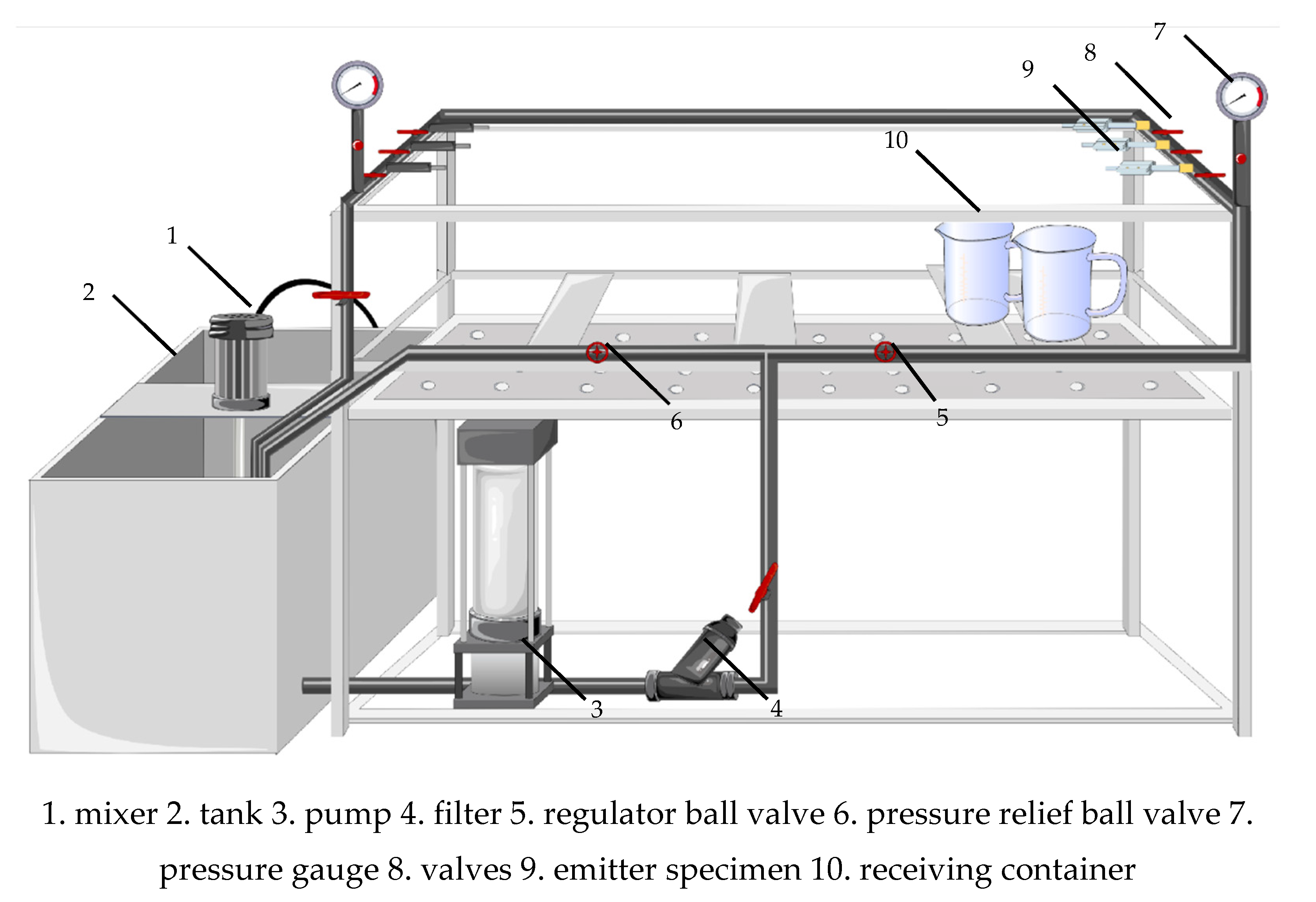
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the test platform of the emitter.
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the test platform of the emitter.
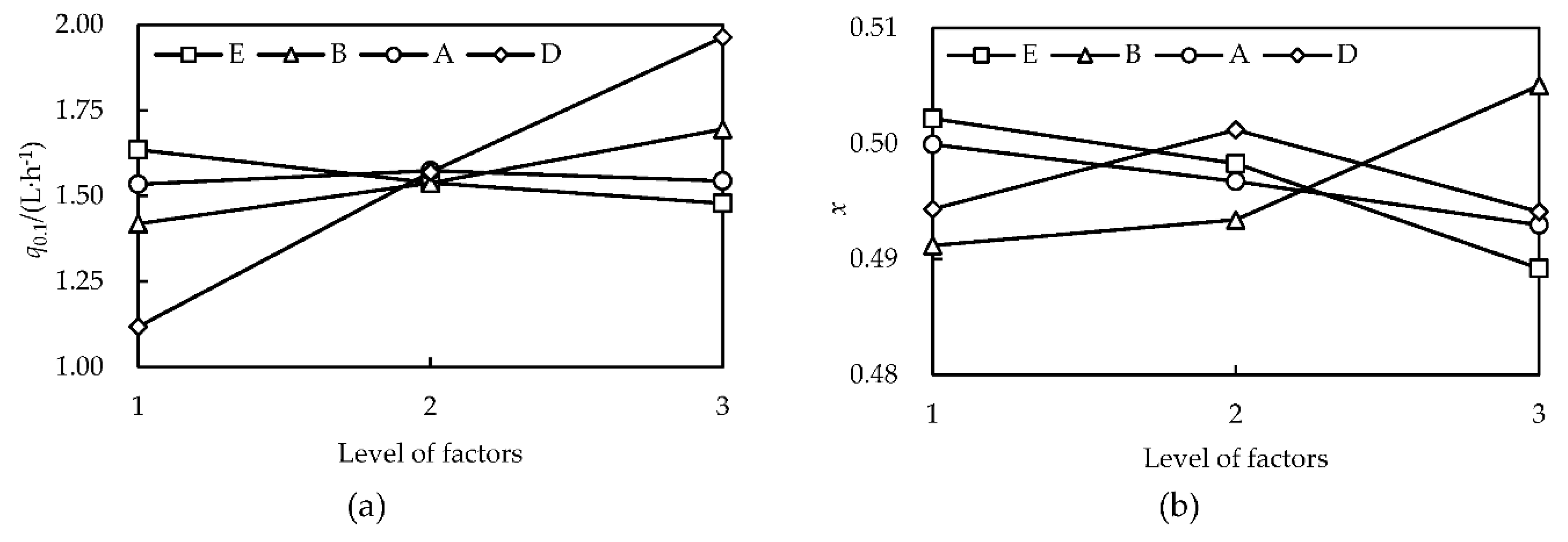
Figure 5.
Effects of different factor levels on q0.1 (a) and x (b).
Figure 5.
Effects of different factor levels on q0.1 (a) and x (b).
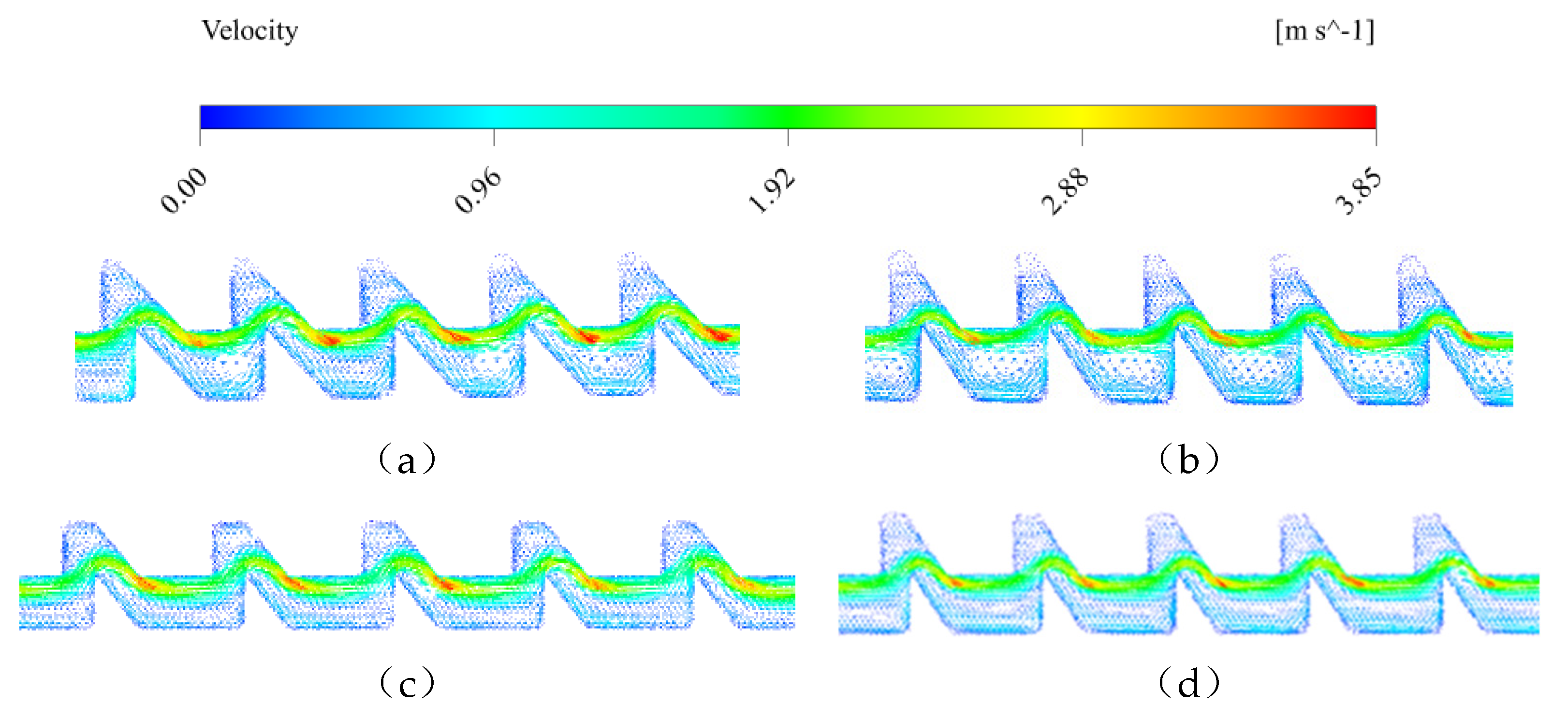
Figure 6.
Velocity vector distributions at the 1/2 position of runner a depth for 4# (a), 8# (b), 3# (c) and 6# emitters (d).
Figure 6.
Velocity vector distributions at the 1/2 position of runner a depth for 4# (a), 8# (b), 3# (c) and 6# emitters (d).
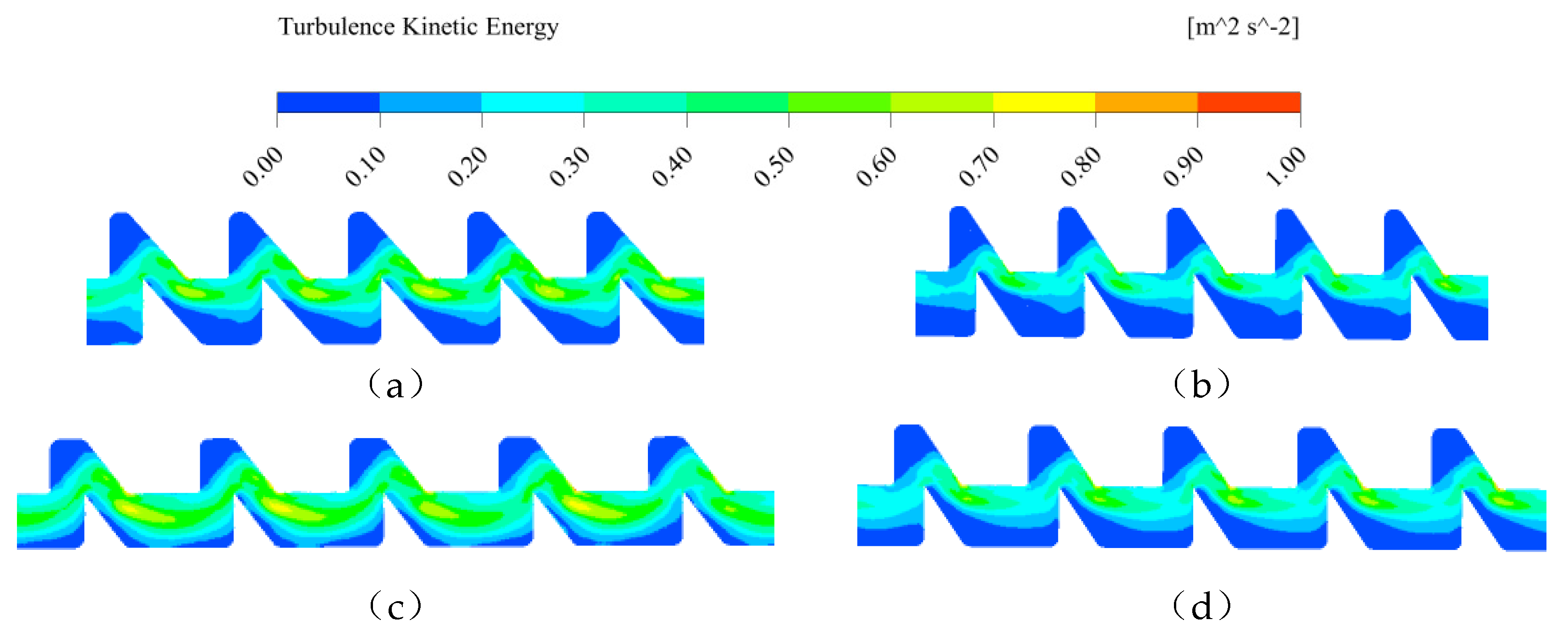
Figure 7.
Turbulent kinetic energy distributions at the 1/2 deep position of runner a for 4# (a), 8# (b), 3# (c) and 6# emitter (d).
Figure 7.
Turbulent kinetic energy distributions at the 1/2 deep position of runner a for 4# (a), 8# (b), 3# (c) and 6# emitter (d).
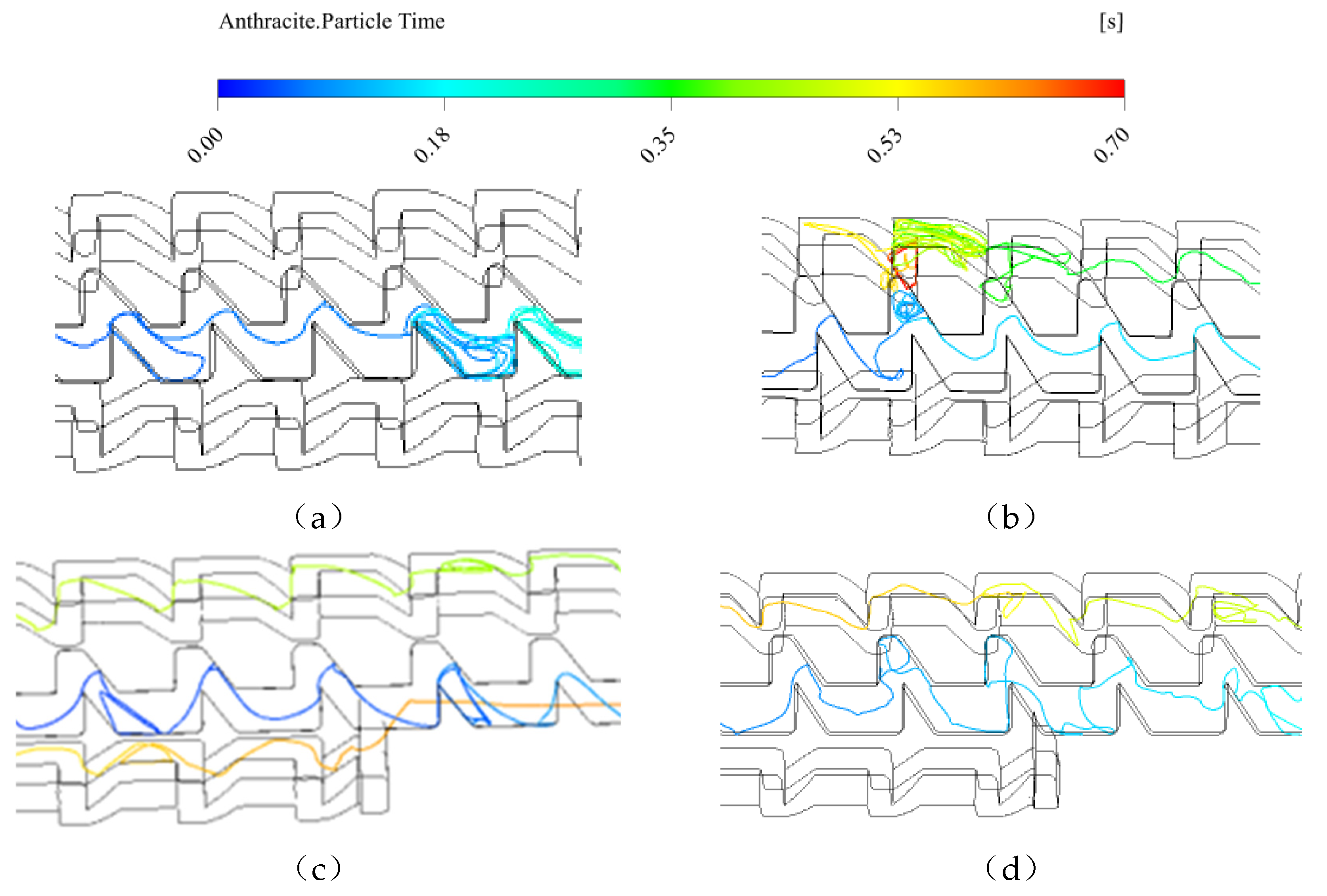
Figure 8.
Figure 8. Plots of individual particle trajectories versus retention times for the 4# (a), 8# (b), 3# (c) and 6# emitters (d) flow paths.
Figure 8.
Figure 8. Plots of individual particle trajectories versus retention times for the 4# (a), 8# (b), 3# (c) and 6# emitters (d) flow paths.
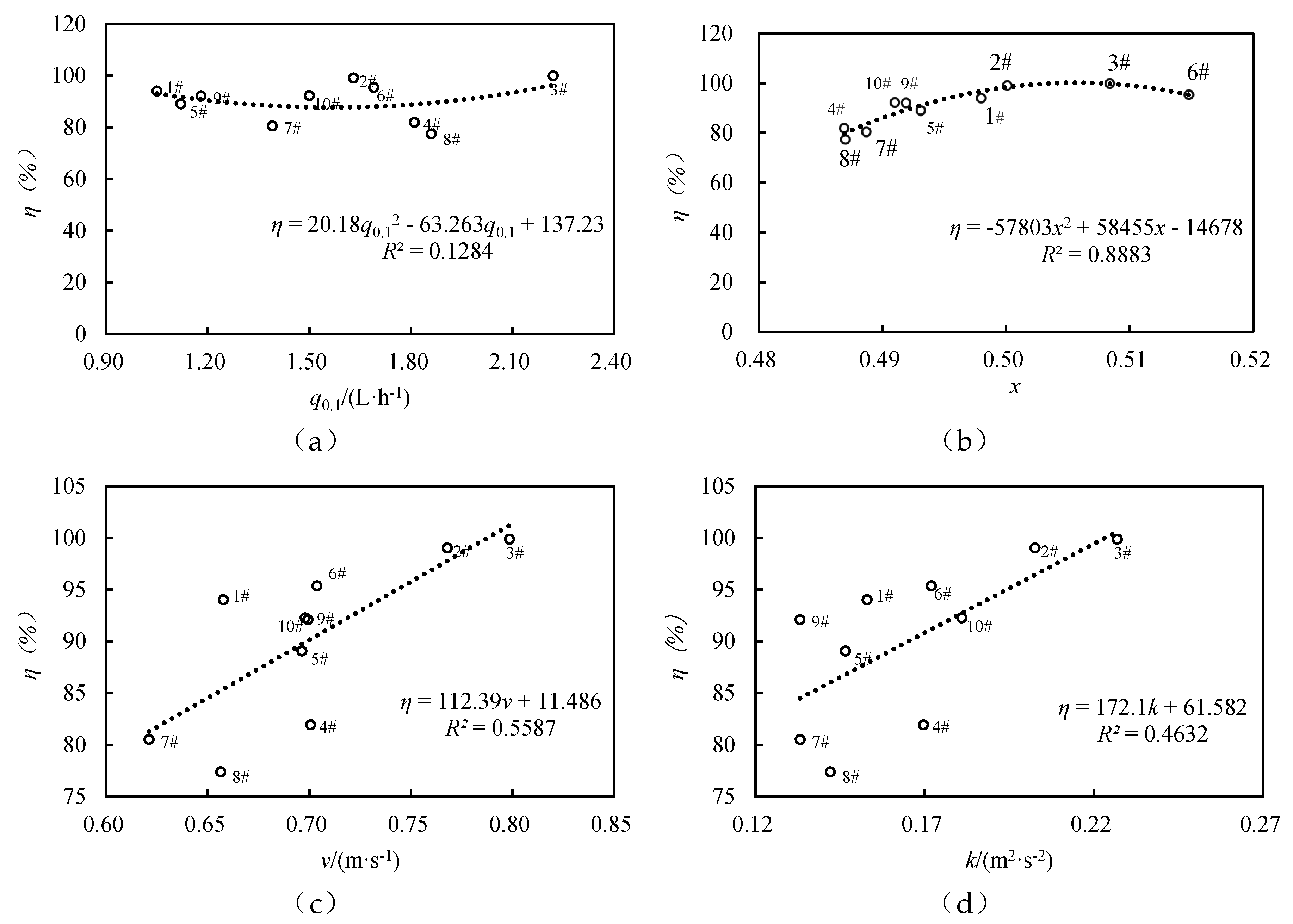
Figure 9.
Variation in η of the emitter with simulation results of q0.1 (a), x (b), v (c) and k (d).
Figure 9.
Variation in η of the emitter with simulation results of q0.1 (a), x (b), v (c) and k (d).
Table 1.
Experimental design.
Table 1.
Experimental design.
| Emitter serial number |
Experimental factors |
| E/mm |
B/mm |
A/° |
D/mm |
| 1 |
0.8 |
1.8 |
34 |
0.6 |
| 2 |
0.8 |
2.0 |
42 |
0.8 |
| 3 |
0.8 |
2.2 |
38 |
1.0 |
| 4 |
1.0 |
1.8 |
42 |
1.0 |
| 5 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
38 |
0.6 |
| 6 |
1.0 |
2.2 |
34 |
0.8 |
| 7 |
1.2 |
1.8 |
38 |
0.8 |
| 8 |
1.2 |
2.0 |
34 |
1.0 |
| 9 |
1.2 |
2.2 |
42 |
0.6 |
| 10 |
0.8 |
1.8 |
42 |
0.8 |
Table 2.
Measured (qm) and simulated (q) water flow rates out of 10# emitter.
Table 2.
Measured (qm) and simulated (q) water flow rates out of 10# emitter.
| Water flow rate from emitter |
H/MPa |
x |
| 0.04 |
0.06 |
0.08 |
0.10 |
0.12 |
0.15 |
|
qm/(L·h–1) |
1.02 |
1.24 |
1.47 |
1.64 |
1.84 |
2.07 |
0.515 |
|
q/(L·h–1) |
0.96 |
1.17 |
1.34 |
1.50 |
1.64 |
1.76 |
0.491 |
|
Relative Error/% |
5.88 |
5.65 |
8.84 |
8.54 |
10.87 |
14.98 |
4.66 |
|
nRMSE/% |
11.23 |
/ |
Table 3.
Simulation results of the emitter flow (q) and flow index (x).
Table 3.
Simulation results of the emitter flow (q) and flow index (x).
| Emitter serial number |
q/(L·h-1) |
x |
|
H=0.04 MPa |
H=0.06 MPa |
H=0.08 MPa |
H=0.10 MPa |
H=0.12 MPa |
H=0.15 MPa |
| 1 |
0.67 |
0.82 |
0.94 |
1.05 |
1.15 |
1.29 |
0.498 |
| 2 |
1.03 |
1.27 |
1.46 |
1.63 |
1.79 |
2.00 |
0.500 |
| 3 |
1.39 |
1.71 |
1.98 |
2.22 |
2.43 |
2.72 |
0.508 |
| 4 |
1.16 |
1.41 |
1.63 |
1.81 |
1.98 |
2.21 |
0.487 |
| 5 |
0.71 |
0.87 |
1.00 |
1.12 |
1.22 |
1.36 |
0.493 |
| 6 |
1.05 |
1.30 |
1.50 |
1.69 |
1.85 |
2.08 |
0.515 |
| 7 |
0.89 |
1.08 |
1.25 |
1.39 |
1.52 |
1.69 |
0.489 |
| 8 |
1.19 |
1.45 |
1.67 |
1.86 |
2.04 |
2.27 |
0.487 |
| 9 |
0.75 |
0.92 |
1.06 |
1.18 |
1.29 |
1.45 |
0.492 |
Table 4.
Polar analysis of the flow rate (q0.1) versus x for the emitter at 0.1 MPa.
Table 4.
Polar analysis of the flow rate (q0.1) versus x for the emitter at 0.1 MPa.
| Test indicators |
Structural parameters |
| E/mm |
B/mm |
A/° |
D/mm |
|
q0.1
|
q0.1 1
|
1.63 |
1.42 |
1.53 |
1.12 |
|
q0.1 2
|
1.54 |
1.54 |
1.57 |
1.57 |
|
q0.1 3
|
1.48 |
1.70 |
1.54 |
1.96 |
|
Rq
|
0.16 |
0.28 |
0.04 |
0.85 |
| x |
x1
|
0.5022 |
0.4912 |
0.4999 |
0.4943 |
|
x2
|
0.4983 |
0.4934 |
0.4967 |
0.5012 |
|
x3
|
0.4892 |
0.5050 |
0.4930 |
0.4941 |
|
Rx
|
0.0130 |
0.0138 |
0.0070 |
0.0071 |
Table 5.
Polar analysis of the particle passage rate (η) in the emitters.
Table 5.
Polar analysis of the particle passage rate (η) in the emitters.
| Test indicators |
Structural parameters |
| E/mm |
B/mm |
A/° |
D/mm |
|
ηi(%) |
η1(%) |
96.14 |
85.48 |
90.43 |
91.73 |
|
η2(%) |
90.29 |
88.49 |
88.31 |
93.14 |
|
η3(%) |
83.33 |
95.78 |
91.02 |
84.89 |
|
Rη(%) |
12.81 |
10.30 |
2.71 |
8.25 |
Table 8.
Preferred combinations of runner structure parameters.
Table 8.
Preferred combinations of runner structure parameters.
| Optimization solutions |
Emitter Specifications |
Runner structure parameters |
x |
η/% |
|
q0.1/(L·h–1) |
E/ mm |
B/ mm |
A/° |
D/mm |
| Min x
|
1.5 |
0.8 |
1.8 |
42 |
0.8 |
0.500 |
90.92 |
| 2.0 |
0.6 |
1.8 |
42 |
1.0 |
0.484 |
95.34 |
| Max η
|
1.5 |
0.6 |
2.0 |
42 |
0.7 |
0.529 |
98.80 |
| 2.0 |
0.7 |
2.2 |
36 |
0.9 |
0.533 |
96.62 |
| Min M
|
1.5 |
0.7 |
1.8 |
34 |
0.8 |
0.501 |
92.86 |
| 2.0 |
0.6 |
1.8 |
42 |
1.0 |
0.484 |
95.34 |