1. Introduction
Sound sleep is crucial for maintaining health in humans. Sleep disturbances (acute) or sleep disorders (chronic) may predispose the individual to the development and progression of major illnesses, and neural changes such as depression and low mood [
1]. Sleep disruptions impact continuity, quality, and quantity of sleep and can lead to stress responsivity, somatic pain, reduced quality of life, emotional distress and mood disorders, and cognitive, memory, and performance deficits; over a prolonged period of time, these can contribute to medical issues such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, cardiovascular disease, weight-related issues, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and colorectal cancer [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6].
Insomnia, a chronic sleep disorder, is characterized by persistent difficulty encountered in either the induction or maintenance of sleep for at least one month [
7]. Recent evidence from the United States of America indicates that approximately 13% of older adults had frequent insomnia and 18.1% had poor-quality sleep [
8]. Moreover, according to the National Center for Health Statistics report for 2020, overall 14.5% of adults had trouble falling asleep and 17.8% of adults had trouble staying asleep [
9]. In the United Kingdom, around 34% of children (aged 7-16 years) and 64% of young people (aged 17-23 years) had a sleep problem three or more times over the previous seven nights [
10]. Prevalence of insomnia is also estimated by various studies conducted on Asian populations. A cross-sectional study from India reported a 33% of individuals having insomnia [
11].
The role of melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine, a chronobiotic hormone produced by the pineal gland) in sleep regulation and maintaining the sleep-wake cycle is well established. It primarily influences the body's internal circadian rhythm through interaction with the suprachiasmatic nucleus, which is the central circadian pacemaker, to align bodily functions with the light/dark cycle of the surrounding environment [
12]. Being considered a crucial endogenous synchronizer of the human biological clock, external melatonin is widely used in the management of insomnia and other sleep disorders, jet lag, and shift work normalization.
Several studies have reported varied pharmacokinetic profiles of melatonin. Following oral administration, melatonin is rapidly metabolized through the first-pass hepatic metabolic processes such as hydroxylation and conjugation and is eliminated from the body through urine [
13]. After oral administration, its time to reach C
max (T
max) has been reported to be approximately 50 min, while the elimination half-life (t
½) was about 45 min. The bioavailability of melatonin ranges from 9% to 33% following oral administration [
14]. Melatonin shows variations in its overall pharmacokinetic behavior in terms of absorption, metabolism, and elimination. Many factors such as age, caffeine consumption, smoking habits, oral contraceptive use, feeding patterns in lactating mothers, and coadministration of drugs have been reported to have an impact on melatonin pharmacokinetics [
15,
16,
17].
Despite being an effective ingredient for restoring a healthy sleeping cycle, melatonin’s short elimination half-life combined with a high degree of variability in pharmacokinetic parameters highlights the need for modified release formulations that offer continuous release of active compounds over a longer time period. Thus, novel sustained-release formulations of melatonin are required that can release a certain amount of the active compounds (up to 50%) immediately, thereby mimicking the endogenous melatonin profile, followed by a continuous and gradual release for a prolonged time to avoid the peak and trough effect, which normally occurs with exogenous products having immediate-release profile. Such sustained-release formulations are expected to provide elevated plasma melatonin levels for a longer duration of time, thus allowing it to exert its action for a longer duration and thus facilitating healthy sleep.
MelotimeTM, a nutraceutical supplement, was formulated as 5 mg sustained-release capsules of melatonin (Melatonin-SR, test product) to provide a uniform release and maintenance of melatonin levels in plasma during the sleep period of 8 h with a gradual tapering down effect without causing spillover of sleep during the waking hours. The present study aimed to compare the pharmacokinetic profile and the safety and tolerability of Melatonin-SR capsules with immediate-release 5 mg melatonin (Melatonin-IR, reference product) capsules after single-dose oral administration in healthy adults under fasting condition.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This was an open-label, balanced, randomized, single-dose, two-treatment, two-sequence, two-period, two-way cross-over, oral comparative pharmacokinetic study conducted in healthy adults under fasting condition at Spinos Life Science and Research Private Limited, Tamil Nadu, India, from Aug 28, 2022 to Sept 7, 2022.
2.2. Study Population Eligibility
Participants aged between 18 and 45 years with body mass index (BMI) ranging between 18.50 to 29.99 kg/m2; with no evidence of underlying disease during screening as documented by laboratory screening values (which were within normal limits as per the physician’s or principal investigator’s discretion); considered healthy based on the medical history, physical examination (including but not be limited to an evaluation of the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, respiratory, musculoskeletal and central nervous systems, gynecological examination and breast examination for women), vital sign assessments, 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) and chest x-ray; who were nonsmokers or ex-smokers (defined as one who completely stopped smoking for at least past three months of study initiation); and willing to comply with all the requirements of the study protocol and those instructed by the study personnel were included in this study. Participants having an allergy to melatonin, a history of any pre-existing disease (which might compromise the hemopoietic, gastrointestinal, renal, hepatic, cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, respiratory, central nervous system or any other body system), presence of diabetes mellitus, psychiatric disorders, renal or hepatic impairment, history of alcohol addiction or abuse, regular consumption of caffeine and xanthine products, or having used tobacco containing products for at least a day prior to study were excluded. Additional exclusion criteria included the use of any prescription medications/ any hormonal agent 14 days prior to study, use of any over the counter medicinal products 7 days prior to study, use of hormone replacement therapy 6 months prior to the study, donation of blood within 90 days prior to study, unusual diet, a positive result of a urine test for drug abuse, a positive test for alcohol, pregnant or breastfeeding women, or a history of difficulty in swallowing. Grapefruit and its juice and poppy-containing foods were restricted 48 h prior to and during the study period.
2.3. Study Procedure
After getting the informed consent from the participants, the screening evaluations were performed to determine the eligibility of participants within 21 days before the check-in period 1. The participants were housed at the clinical facility for at least 36.00 h pre-dose to 24.00 h post-dose for period 1 and period 2. Both the periods were separated by a 7-day washout period. The total study duration was 11 days.
The test product was Melatonin-SR capsules containing 5 mg melatonin (Nutriventia Limited, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India), and the reference product was Melatonin-IR capsules containing 5 mg melatonin (Huanggang Saikang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Huanggang City, Hubei, China). Both products were administered to the participants following a randomization schedule (using block randomization method with block size of 4) created using R software, version 4.0.4 (Auckland, New Zealand) (by an independent statistician). During each period, in the morning between 8:00 am to 8:14 am, the participants received Melatonin-SR or Melatonin-IR after overnight fasting of at least 10 h. As per the randomization schedule, the single oral dose of Melatonin-SR or Melatonin-IR was administered along with 240 mL of drinking water to the participants in an upright sitting position (under the supervision of the trained study personnel) and participants were instructed to remain in the same position for four hours post-dosing. Participants were not allowed to lie down during the restriction period. Thereafter, participants were allowed to move freely during the remaining part of the study. However, they were not allowed to be engaged in any kind of strenuous activity during the study period. Drinking water was allowed to be consumed ad libitum during the study period except for restricting for 1 h pre-dose and 1 h post-dose. Standardized meals were provided at -34.00, -24.00, -20.00, -16.00 and -12.00 h of each period pre-dose and at 4.00, 8.00, and 12.00 h after dosing. Standardized lighting conditions were maintained in the clinical phase unit to suppress the production of endogenous melatonin. This standardization included housing the participants in a windowless room on the dosing day and was maintained throughout the entire blood sampling period in both the treatment periods with all light readings between 500 to 600 Lux. Light levels were measured four times in a day on both the study periods (7:00 to 8:00 am, 12:00 noon to 1:00 pm, 5:00 to 6:00 pm and 11:00 pm to 12:00 midnight) using Luxmeter, horizontal plane at participants eye level [
18].
2.4. Bioanlytical Procedure
A total of 20 blood samples were collected from each participant at the following time points, 00.00 h (6 mL; pre-dose blood sample, within 60 minutes prior to dosing), 00.25, 00.50, 00.75, 01.00, 01.33, 01.67, 02.00, 02.33, 02.67, 03.00, 04.00, 05.00, 06.00, 07.00, 08.00, 10.00, 12.00, 14.00, and 24.00 h (5 mL, post-dose blood sample). All blood samples were collected in pre-labelled tubes filled with anticoagulant (dipotassium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid [K2EDTA]) and centrifuged at 3800 rpm for 10 min at 4°C (Centrifuge 5804 R) within 30 min of the collection of samples (at each collection time-point) to separate the plasma. The plasma samples were transferred to pre-labelled polypropylene tubes into two aliquots (approximately 1.2 mL in the first aliquot [Aliquot-1] and remaining plasma in the second aliquot [Aliquot-2]) and stored in a freezer at a temperature of -30±10°C for interim storage at the clinical site and then transferred to analytical site after the completion of clinical phase for bioanalytical study.
A sensitive and selective quantification method was used to quantify melatonin concentration in plasma by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy (UHPLC-MS/MS) in the bioanalytical facility of Spinos Life Science and Research Pvt. Ltd., Coimbatore, India. Plasma concentrations of melatonin over the concentration range 201.30 to 200629.90 pg/mL were estimated quantitatively using optimized and validated LC-MS/MS method. Melatonin D4 was used as an internal standard. The reference standards melatonin (99.34% purity) and melatonin D4 (99.45% purity) were purchased from Vivan Life Sciences, Mumbai, India. Prior to use, melatonin standard was stored at 2-8 °C, and melatonin D4 standard was stored at -20°C. Melatonin and melatonin D4 were selectively extracted from plasma sample by solid phase extraction technique. Melatonin and melatonin D4 were separated using Strata-X 33 μm (Phenomenex, Torrance, USA) Polymeric Reversed Phase cartridges. Chromatographic separation was achieved by reverse phase liquid chromatography on ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18 (4.6 mm x 100 mm, Agilent technologies, USA), 3.5 μm column maintained at 45°C. Internal standard was added to all the samples except blank and the samples were then further analyzed for melatonin concentration using API 4000 LC-MS/MS system (AB Sciex, USA) detector, LC30AD (Shimadzu, Japan) pump, SIL30AC (Shimadzu, Japan) autosampler, CTO20AC (Shimadzu, Japan) column oven, and analyst software version 1.6.2 (AB Sciex, USA) data acquisition system. Details of quantitative analysis of melatonin are provided in the
supplementary material.
2.4.1. Calibration Curve
Calibration curves of melatonin were constructed by spiking standard solutions in human blank plasma samples to obtain nine calibration standards at 201.60, 504.20, 4400.00, 8747.50, 17495.00, 34990.10, 69980.20, 139960.30, and 199943.30 pg/mL. Calibration curves were analyzed individually using a least square-weighted linear regression (1/X2) and regression values (r2) were >0.98. Using an optimized method, the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) observed for melatonin in human plasma was 201.30 pg/mL.
2.4.2. Bioanalytical Method Validation
The International Council for Harmonisation Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysis M10 (ICH M10) and the Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry by the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) were followed for the development of validation protocol of bioanalytical method [
19,
20]. Optimized method was validated for specificity, selectivity, sensitivity, precision, accuracy, and recovery and all the parameters were within the acceptance criteria.
2.5. Pharmacokinetic Evaluations
Primary pharmacokinetic parameters including Cmax, area under curve from time 0 to the last quantifiable time-point (AUC0-t), and area under curve from time 0 to infinity (AUC0-∞) and secondary pharmacokinetic parameters including Tmax, elimination rate constant (Kel), t½, and AUC_%Extrap_obs were determined for both products.
2.6. Safety Assessment
Safety assessment was measured by assessing the number of adverse events (AEs) reported for Melatonin-SR and Melatonin-IR. The participants were closely observed by study personnel for any AEs and serious adverse events (SAEs) during and after the completion of the study. The AEs were categorized based on their severity as mild, moderate, or severe.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics (arithmetic mean, geometric mean, standard deviation [SD], coefficient of variation [CV], minimum, median, and maximum) for all parameters were calculated. The sample size for this study was determined referring to the guidelines of Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) which recommend including a minimum of 16 subjects in the bioavailability studies. The 90% confidence interval (CI) and the ratio of geometric least square means for the mean concentrations of melatonin present in both products was calculated for log-transformed parameters (Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-∞). The log-transformed pharmacokinetic parameters were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) test followed by Dunnett’s test (student’s t-test) to determine the statistical significance between two products at a significance level of 5%. A P-value < 0.05 was considered significant. Statistical analysis was performed using a non-compartmental model of SAS® software (SAS Institute Inc., USA) on Windows, version 9.4.
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Details
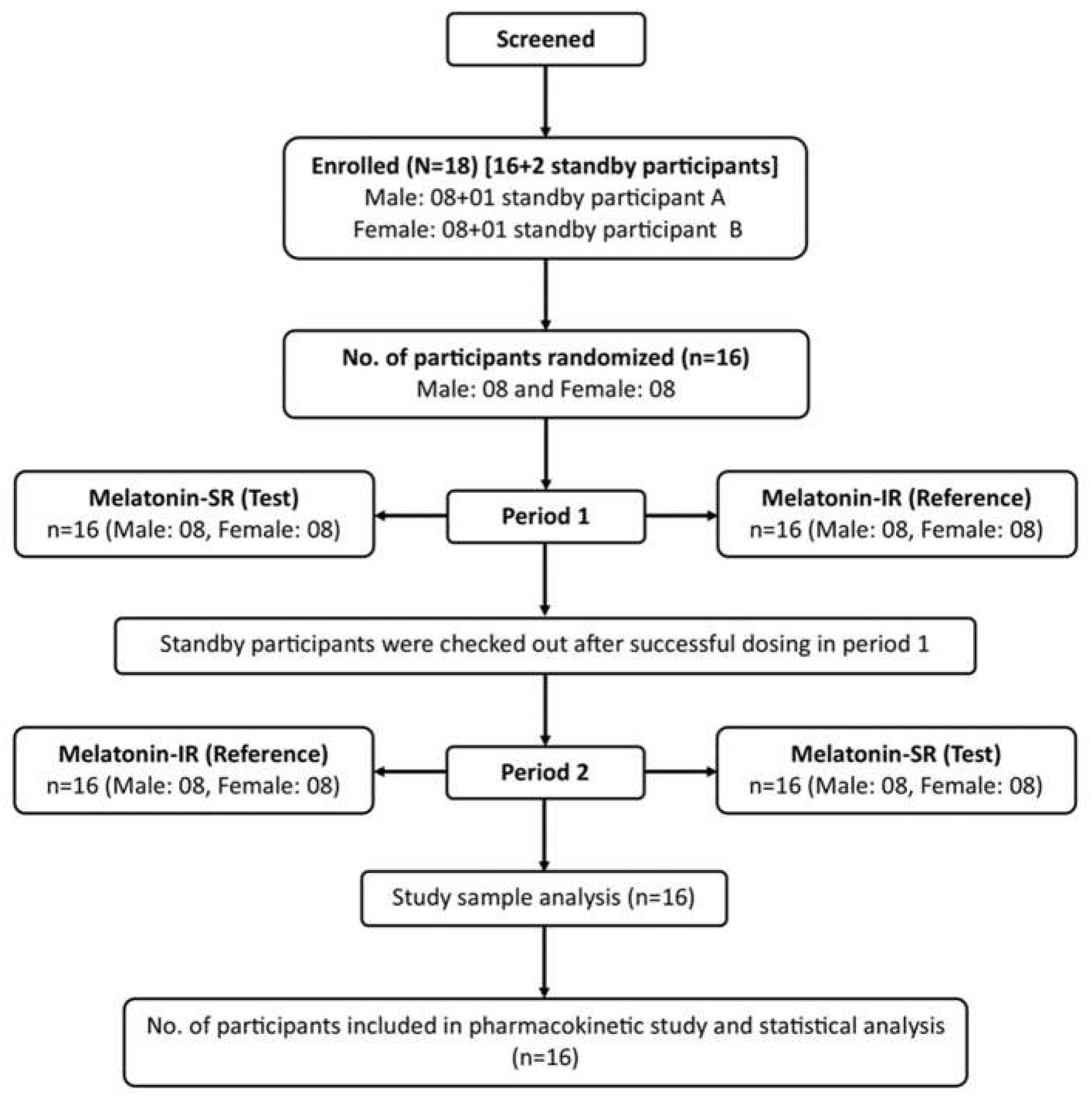
Sixteen healthy participants (eight men and eight women) who met all the eligibility criteria were enrolled in the study (
Figure 1). All the participants successfully completed the study and were administered Melatonin-SR and Melatonin-IR in both the study periods. Demographic details of study participants are summarized in
Table 1. The mean (SD) age and mean (SD) BMI of the participants was 33.25 (4.45) years and 25.48 (3.46) kg/m
2, respectively (
Table 1).
3.2. Pharmacokinetic parameters
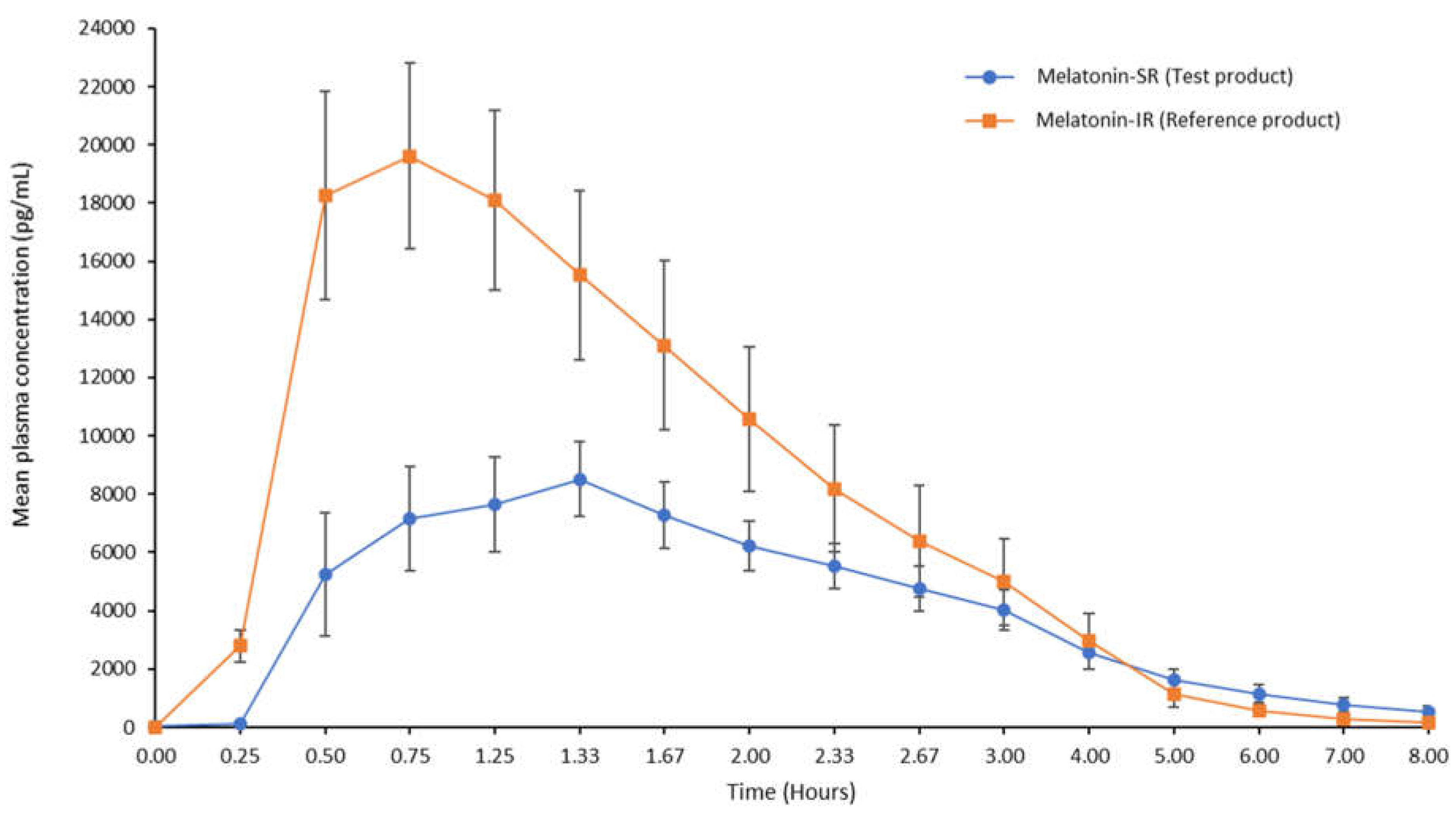
Following oral administration, the mean (SD) C
max of the test product (Melatonin-SR) was lower (11446.87 [7804.98] pg/mL) as compared to reference product (Melatonin-IR) (22786.30 [13772.70] pg/mL) (
Table 2).
Analysis of secondary pharmacokinetic parameters is summarized in
Table 3. The test product reported a higher mean T
max as compared to the reference product (1.26 [0.59] h vs. 0.87 [0.42] h). The mean (SD) t
1/2 of the reference product (1.01 [0.68] h) was lower compared to the test product (5.10 [4.38] h) (
Table 3).
Clear differences in the release profiles of both the melatonin products were observed. In the initial phase (0-4 h), plasma concentration of melatonin in the test product was lower as compared to that in the reference product. However, in the delayed phase (4-8 h), plasma concentration of melatonin in the test product was higher as compared to that in the reference product (1.39- to 3.14-fold increase) for all time points until 8 h (
Figure 2).
3.3. Safety Assessment
One AE of a single episode of vomiting was reported in one female participant during the study in period 1, at around 5 h after administration of the reference product (Melatonin-IR). This AE was mild and was considered as possibly related to the product. The participant had normal vitals, general and systematic examinations. The participant was followed-up for vital signs and physical and general clinical examinations until the next day. All the parameters were normal throughout the observation period, and the AE was considered resolved by the principal investigator. No other AEs or SAEs were reported by any other participants.
4. Discussion
The present study evaluated the pharmacokinetic profile of Melatonin-SR versus Melatonin-IR in healthy adults under the fasting condition. The key observations of this pharmacokinetic study were lower Cmax, higher Tmax, and five-fold prolonged half-life of melatonin in the test product compared to that in the reference product. These results indicate the sustained-release pharmacokinetic profile of the test product Melatonin-SR.
Various publications have reported the pharmacokinetic profile of melatonin [
7,
14,
16,
18,
21,
22,
23,
24]. A phase 3, randomized, cross-over study conducted on 12 healthy subjects under fasting condition showed a mean C
max of 5766 pg/mL, mean T
max of 60.3 min, and mean t
1/2 of 65.0 min following 4 mg oral administration of melatonin [
22]. In the present study, the test product Melatonin-SR showed higher C
max, prolonged T
max, and longer t
1/2 as compared to these results. A pharmacokinetic profile of melatonin reported by Gooneratne et al. (2012) was similar to the present study. It was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study which included 27 patients with insomnia who received 4 mg oral sustained-release product of melatonin and reported a T
max of 1.5 h, mean elimination half-life of 2.1 h, and mean C
max of 3999 (700) pg/mL [
21]. Further, in the present study, the sustained-release profile of the test product was evident by the higher plasma concentration in the delayed phase from 4 to 8 h as compared to the reference product. This may have implications in minimizing the dosing frequency of melatonin in participants with sleeping disorders [
22,
24].
The role of melatonin in the induction and maintenance of sleep is well documented. Patients with insomnia and other sleep disorders lack N-acetyltransferase; this enzyme is involved in the conversion of melatonin into the hypnotic derivative of melatonin, which helps induce and maintain sleep [
25]. Melatonin plasma concentration ranges from 80 to 120 pg/mL in adults during nighttime, which is necessary to maintain sound sleep in humans [
13]. In our study, the mean plasma concentration of melatonin following test product administration was maintained above the normal range in healthy adults. This indicated that the melatonin released through the test product remained in plasma for longer duration, which can help induce and maintain sound sleep for long hours in healthy adults. This can also be beneficial for adults with an abnormal sleep cycle, who are on shift work, and for those who are badly affected by jet lag.
Delayed sleep-wake phase disorder is considered as the most common of the circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders, which is an increasingly recognized and diagnosed group of sleep disorders. These disorders are primarily caused by external factors like jet lag or shift work. Melatonin formulations are widely used in these cases but not without limitations like quick clearance, low plasma concentration, shorter half-life, and shorter T
max [
26]. Consequently, these patients often face high pill burden to manage their symptoms. In our study, test product showed prolonged T
max, longer half-life, and maintained a high level of plasma concentration for 8 h compared to reference product, which in turn can help in minimizing dosing frequency in these sleep disorders. In the Melatonin-IR group, we observed a decline in the plasma levels of melatonin after 0.75 h; however, in the melatonin-SR group, this decline was observed at later time point, i.e. after 1.33 h, which gradually continued up to 8 h. Although, this decrease in melatonin levels was observed in both groups, the rate at which melatonin levels declined in the Melatonin-SR group was slower than that of Melatonin-IR group. In particular, in the delayed phase, i.e., after 4 h till 8 h, the plasma levels of melatonin in the Melatonin-SR group were 1.39- to 3.41-fold higher than the Melatonin-IR group. These observations indicate that the SR formulation provides a steady and slow release of melatonin throughout the 8-hour sleep period. Additionally, this gradual decline in plasma melatonin levels in the body would further help maintain consistent sleep throughout the night without compromising morning alertness [
27]. Given the limitations of exogenous melatonin in IR formulations, such as short elimination half-life, which can disrupt sleep, the SR formulation offers a superior alternative. With its extended half-life, and continuous, gradual release of melatonin over a longer duration, the SR formulation would be effective in facilitating a peaceful and longer sleep while maintaining a balanced sleep-wake cycle [
13,
14,
26].
In our study, one participant reported an AE following the administration of the reference product; it was of mild severity, short-lived, and resolved on its own. Therefore, both the products were considered as well tolerated and safe for oral administration. Safety results of an open-label, two-way, crossover, randomized study, comparing continuous release and absorption melatonin (melatonin-CRA) (5 mg) vs. melatonin-IR (5 mg), reported treatment emergent AEs (including emesis, stomach cramps, nausea, and irritability) in patients who received melatonin-IR and no AEs in the melatonin-CRA group. These results are in line with the present study [
18]. Furthermore, Foley and Steel in their systematic review (included 50 clinical studies) documented AEs associated with melatonin oral administration. The most common AEs were related to fatigue, mood, or psychomotor and neurocognitive performance which were generally short-lived and associated with day-time dosing [
28].
Limitations of this study include a small sample size of 16 healthy participants and a single dose study. However, large-scale studies with multiple doses administered over multiple days or weeks on a larger participant pool from varied demographic backgrounds can help obtain a more real-world pharmacokinetic profile of the newly developed Melatonin-SR capsules.
5. Conclusions
Melatonin-SR capsules, on a single oral dose administration, elevated plasma melatonin levels and sustained them over an extended period (up to 8 h) as compared to immediate release product. Melatonin-SR was safe and well-tolerated. Thus, Melatonin-SR may be considered as a promising nutraceutical supplement for promoting and maintaining healthy sleep patterns, especially for adults grappling with erratic sleep cycles.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, Quantitative analysis of melatonin by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.T. and R.S.; Formal analysis and data curation, R.A. and S.T; Investigation, R.A.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, S.T.; Writing—Review & Editing, all authors; Visualization, R.S.; Supervision, S.T. and R.A.; Project Administration, S.T.; Funding acquisition, R.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Nutriventia Limited, India.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study protocol and other documents were reviewed and duly approved by the Research Ethics Committee (REC), on Aug 5, 2022 (vide registration number ECRl841lndtlTN/2013/RR-19). This study was registered with the Clinical Trial Registry of India (Registration No. CTRI/2022/08/044837). The study was conducted at Spinos Life Science and Research Private Limited, Tamil Nadu, India, in accordance with all applicable international and Indian guidelines (National Ethical Guidelines For Biomedical and Health Research Involving Human Participants, Indian Council on Medical Research [ICMR] [2017], International Conference on Harmonization [ICH] [Step 5] Guidance on Good Clinical Practice, New Drugs and Clinical Trials Rules 2019 G.S.R. 227[E] dated 19 March 2019, Good Laboratory Practice, Good Clinical Practices for Clinical Research in India guidelines, Good Clinical Laboratory Practice [GCLP], and Declaration of Helsinki [Fortaleza, October 2013]).
Informed Consent Statement
The written informed consent was obtained from each participant prior to initiation of the clinical study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used for this study will be available from the corresponding author on a reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Niraj Vyas, PhD, and Dr. Disha Dayal, PhD, of Iwana Consultancy Solutions, for providing medical writing support for this manuscript, which was funded by Nutriventia Limited.
Conflicts of Interest
Ms. Rajat Shah and Dr. Shefali Thanawala are employees of Nutriventia Limited. Ms. Rajat Shah also has ownership interests. Ms. R. Abiraamasundari is an employee of SpinoS Life Science Research and Private Limited and received consulting fees from Nutriventia Limited. The authors do not have any other conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Irwin, M.R. Why sleep is important for health: a psychoneuroimmunology perspective. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2015, 66, 43–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, S.M.; Videnovic, A. Chronic sleep disturbance and neural injury: Links to neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Sci. Sleep. 2016, 8, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, T.; Choe, J.; Awab, A.; Wagener, T.L.; Orr, W.C. Sleep, immunity and inflammation in gastrointestinal disorders. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 9231–9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.W.; Jeong, J.H.; Hong, S.C. The impact of sleep and circadian disturbance on hormones and metabolism. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 591729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medic, G.; Wille, M.; Hemels, M.E. Short- and long-term health consequences of sleep disruption. Nat. Sci. Sleep. 2017, 9, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasali, E.; Leproult, R.; Ehrmann, D.A.; Van, Cauter, E. Slow-wave sleep and the risk of type 2 diabetes in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, A.G.; Ford, I.; Crawford, G.; Mcconnachie, A.; Nir, T.; Laudon, M.; and Zisapel, N. Nightly treatment of primary insomnia with prolonged release melatonin for 6 months: A randomized placebo-controlled trial on age and endogenous melatonin as predictors of efficacy and safety. BMC. Med. 2010, 8, 51. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1741-7015/8/51.
- Gordon, N.P.; Yao, J.H.; Brickner, L.A.; Lo, J.C. Prevalence of sleep-related problems and risks in a community-dwelling older adult population: A cross-sectional survey-based study. BMC. Public Health. 2022, 22, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjaye-Gbewonyo D.; Ng A.E.; Black L.I. Sleep difficulties in adults: United States, 2020 Key findings data from the national health interview survey. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/index.htm. Accessed on 5 September 2023.
- National Health Service report. Part of mental health of children and young people surveys, Mental health of children and young people in England 2022 - wave 3 follow up to the 2017 survey, England, Published on 29 Nov 2022 Available from: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/mental-health-of-children-and-young-people-in-england/2022-follow-up-to-the-2017-survey/part-2-sleep-loneliness-and-health-behaviours Accessed on 10 October 2023.
- Bhaskar, S.; Hemavathy, D.; Prasad, S. Prevalence of chronic insomnia in adult patients and its correlation with medical comorbidities. J. Family Med. Prim. Care. 2016, 5, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinali, D.P.; Pévet, P. Basic aspects of melatonin action. Sleep Med. Rev. 1998, 2, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordjman, S.; Chokron, S.; Delorme, R.; Charrier, A.; Bellissant, E.; Jaafari, N.; Fougerou, C. Melatonin: Pharmacology, functions and therapeutic benefits. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpsøe, N.G.; Andersen, L.P.H.; Gögenur, I.; Rosenberg, J. Clinical pharmacokinetics of melatonin: a systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 71, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Härtter, S.; Nordmark, A.; Rose, D.M.; Bertilsson, L.; Tybring, G.; Laine, K. Effects of caffeine intake on the pharmacokinetics of melatonin, a probe drug for CYP1A2 activity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 56(6), 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilli, J.; Korhonen, T.; Turpeinen, M.; Hokkanen, J.; Mattila, S.; Laine, K. The effect of oral contraceptives on the pharmacokinetics of melatonin in healthy subjects with CYP1A2 g.-163C> A Polymorphism. J. Clin. Pharmacol 2008, 48, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursing, C.; von Bahr, C.; Brismar, K.; Röjdmark, S. Influence of cigarette smoking on melatonin levels in man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 61, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiden, D.J.; Shah, S.M. A randomized, crossover, pharmacokinetics evaluation of a novel continuous release and absorption melatonin formulation. Prim. Care Companion CNS. Disord. 2019, 21, 19m02450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry USFDA 2018. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Bioanalytical-Method-Validation-Guidance-for-Industry.pdf. Accessed on 12 July 2024.
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use: Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysis M10 (ICH M10) (Adopted on 24 May 2022). Available from: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/M10_Guideline_Step4_2022_0524.pdf. Accessed on 12 July 2024.
- Gooneratne, N.S.; Edwards, A.Y.Z.; Zhou, C.; Cuellar, N.; Grandner, M.A.; Barrett, J.S. Melatonin pharmacokinetics following two different oral surge-sustained release doses in older adults. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demuro, R.L.; Nafziger, A.N.; Blask, D.E.; Menhinick, A.M.; Bertino, J.S. The absolute bioavailability of oral melatonin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 40, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandolfi, J.V.; Bernardo, A.P.A.Di.; Chanes, D.A.V.; Martin, D.F.; Joles, V.B.; Amendola, C.P.; Sanches, L.C.; Ciorlia, G.L.; Lobo, S.M. The effects of melatonin supplementation on sleep quality and assessment of the serum melatonin in ICU patients: A randomized controlled trial. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48(12), e1286–e1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román, Martinez, M.; García, Aguilar, E.; Martin, Vílchez, S.; González, García, J.; Luquero-Bueno, S.; Camargo-Mamani, P.; Mejia-Abril, G.; García-Castro, L.; de Miguel-Cáceres, A.; Saz-Leal, P.; Abad-Santos, F.; Nieto, Magro, C.; Ochoa, Mazarro, D. Bioavailability of Oniria®, a melatonin prolonged-release formulation, versus immediate-release melatonin in healthy volunteers. Drugs R.D. 2022, 22, 235–243. [CrossRef]
- Fourtillan, J.B. Role of melatonin in the induction and maintenance of sleep. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2002, 4, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, A.D. Delayed sleep-wake phase disorder. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S103–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, N.F.; Badr, M.S.; Belenky, G.; Bliwise, D.L.; Buxton, O.M.; Buysse, D.; Dinges, D.F.; Gangwisch, J.; Grandner, M.A.; Kushida, C.; Malhotra, R.K.; Martin, J.L.; Patel, S.R.; Quan, S.F.; Tasali, E. Recommended amount of sleep for a healthy adult: A joint consensus statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and Sleep Research Society. Sleep. 2015, 38, 843–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, H.M.; Steel, A.E. Adverse events associated with oral administration of melatonin: A critical systematic review of clinical evidence. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 42, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).