1. Introduction
Rapid urbanisation escalates the human population in urban areas. It is projected that 68% of the population will reside in urban areas [
1], driving an unprecedented surge in construction and demolition (C&D) activities and waste generation. Moreover, the by-products of C&D waste engender substantial environmental issues such as global warming and land degradation and impose a significant strain on natural resources [
2], whereby 33% of greenhouse gases (GHG) emissions and over 40% of global energy consumption can be attributed to C&D activities [
2]. Despite these challenges, the potential of C&DW management to mitigate environmental impacts through recycling and reuse remains untapped, with a marked propensity for materials to be directed towards landfills [
3]. Therefore, promoting C&DW recycling and reuse proved to be imperative and effective in alleviating excessive carbon emissions and resource exploitation from a life cycle-thinking perspective by substituting virgin materials with salvaged products [
4,
5]. However, The current research landscape has predominantly pivoted towards the environmental aspect of waste management [
5] by appraising the performance of waste management alternatives merely based on the environmental indicators [
3], where the multifaceted trade-offs between economic, environmental, and social pillars of sustainability are often overlooked. Furthermore, stakeholders with different initiatives and knowledge backgrounds are collaborating on the C&D planning, including government policymakers, private sector developers, project managers, demolition contractors, site engineers, environmental consultants, and local communities that attend to various responsibilities and conflicting priorities, which inevitably increases the uncertainty and divergence in the decision-making process [
6]. Thus, maintaining the rapid pace of economic development without compromising the living environment for future generations calls for both technological innovation and policy enhancement to support sustainable C&D activities.
In the construction sector, BIM, as a digital embodiment of buildings, capitalises on parametric modelling and cooperative working methodology to create, maintain, update and exchange diversified information relevant to building properties, including geometric dimensions, materials characteristics, and other customisable parameters [
7,
8,
9]. [
10] analyse the potential applications of BIM in prevalent sustainability assessment tools like LEED, BREEAM, Green Star, and SBTool. Nevertheless, several persistent issues, such as the lack of data interoperability, LCA database, waste management and sustainability-related IFC properties [
11], hinder the development of a coherent BIM-based sustainability assessment workflow.
Prior studies typically concentrated on the environmental and economic implications of DWM [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16], where a consensus has been reached as off-site recycling being deemed the most environmentally sound DWM strategy, except the environmental performance and economic feasibility of recycling is inversely proportional to the transportation distance [
17,
18,
19,
20]. Nevertheless, the impact assessment results produced by LCA and Life Cycle Costing (LCC) are represented in different units and cannot intuitively construct the decision by dictating the overall sustainability of DWM scenarios [
21]. To this end, MCDA methods serve as decision-aiding tools to assess the trade-offs between conflicting criteria and their relative importance to the sustainability goal of DWM [
22]. As such, the LCA/LCC results subject to quantitative analysis are converted into a commensurable sustainability score against different DWM alternatives [
23]. Although it is impractical to simultaneously incorporate all the impact categories, waste streams, and DWM alternatives into the sustainability assessment framework, the objective is to develop a framework based on predefined objectives, scope, definite criteria, and scenarios, along with proper decision-making mechanism, for implementing the sustainability assessment in real-world building demolition projects.
The current research gap lies in the fragmented approach to C&DW management, which often overlooks the balance between environmental viability and economic and social impacts. This study aims to bridge this gap by proposing a novel BIM-based decision-aiding framework that combines LCA and MCDA to appraise the sustainability of various DWM scenarios on a BIM platform. For demonstration purposes, this paper adopts a virtual pilot demolition project for a case study demonstration and the list of suitable sustainability indicators identified by [
2], where the indicator selection and weighting considered experienced local practitioners’ inputs and preferences and executed based on a modified Delphi-AHP method.
This research aims to address the gap in facilitating intuitive, actionable decision-making for sustainability-oriented DWM planning by presenting a BIM-based decision-aiding framework that is augmented by integrating LCSA and hybrid MCDA methods into a BIM environment. To this end, the novelty of this study is evidenced by the development of a BIM-based sustainability assessment workflow that provides intuitive decision guidance for DWM planning via 3D visualisation of carbon-intensive components and DWM scenario ranking based on a composite sustainability index. More specifically, this framework not only efficiently assesses the accumulated environmental, social, and economic impacts associated with different DWM scenarios but also visualises the predicted impacts (e.g., carbon emission) on various building components. Furthermore, this study hybridises the decision-making mechanisms of two different MCDA techniques (i.e., AHP and TOPSIS) to derive the optimal DWM scheme by assessing the trade-offs between environmental and economic criteria. Equipping with BIM’s parametric modelling and 3D visualisation features, this DWM planning framework empowers sustainable selective dismantling design by automatically locating building components with extraordinary, embodied carbon and recycling value. In this vein, the sustainability scores and colour-coded 3D BIM model derived from the DWM framework using the hybrid MCDA and colour gradient algorithms serve as design guidance for architects, engineers and other stakeholders to harvest decarbonising building design and carbon-neutral demolition in future.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Sustainability Assessment Methodologies at the Building’s End-of-Life (EoL) Stage
LCA is universally perceived as a comprehensive assessment methodology complying with the ISO 14040 standard that assesses various impacts across different phases of buildings from a life cycle thinking perspective [
6]. Whereas LCC prominently focuses on the economic feasibility of a project by predicting the whole life cycle cost through acquisition to end-of-life [
11]. Combining LCA with LCC captures a broader spectrum of sustainability impacts, providing a multi-dimensional perspective often missing in conventional LCA [
24]. Furthermore, the evaluation of societal indicators has become more prevalent, led by the maturation of the social life cycle assessment (SLCA) methodology, in which the impact assessment related to human toxicity has been constantly accentuated [
25]. In light of this, conducting a comprehensive LCSA calls for the integration of all three assessment methodologies.
Recent advancements have seen LCA’s application in DWM gaining substantial momentum, especially as the construction sector grapples with sustainability challenges. Despite the potential, there remain significant methodological hurdles owing to the wide-ranging incommensurable indicators [
26] and the lack of recycling data in the Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) and commercial LCA databases for EoL analysis [
27]. The robustness of LCC assessment hinges on the availability and preciseness of economic data, which is often kept confidential. Data availability is the bottleneck for conducting SLCA, where the data collection requires constant site visits and surveys to gather information from the practitioners and local residents [
28]. Plus, [
13] stated that a standardised, consistent SLCA method is lacking, which further underpins the importance of developing quantitative social indicators.
Extending the LCSA application in the DWM domain calls for redefining the assessment framework that goes beyond the system boundary, where inventory and impact assessment have far-reaching implications on resource recovery and waste recycling [
12]. Adopting LCSA in DWM practices is progressively gaining traction, with scholars proposing new frameworks to overcome data gaps, especially in the social and economic domains [
29].
Recent studies predominately focused on estimating Global Warming Potential (GWP) arising from demolition activities and how waste recycling can mitigate carbon emissions by providing benefits beyond the “cradle to grave” boundary [
3,
15,
30,
31,
32]. Apart from that, waste-to-energy conversion is another prominent topic intensively investigated by academia [
33,
34,
35]. Several studies established multi-criteria sustainability assessment frameworks to assess the trade-offs between multi-dimensional indicators [
15,
16,
29,
36,
37]. Quantifying multi-dimensional impacts produced by various building materials at their EoL phase requires powerful data management capacity, necessitating the linkage between LCSA databases and BIM material libraries and integration of DWM-related properties into the BIM environment [
11,
13,
38].
2.2. BIM-Enable Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment
BIM, founded on parametric modelling, allows for seamless geometric, functional, semantic, and topographic data integration, extraction, and exchange between parametric objects and external data sources that are compliant with the IFC sharing format [
39]. The convergence of BIM with LCSA is opening new avenues for more detailed and accurate sustainability assessments in DWM, capitalising on the data processing and management capacity of BIM [
13], wherein BIM serves as a centralised data repository that enables automated quantity take-off, dynamic real-time scenario assessment, intuitive LCSA results 3D visualisation, facilitating the LCSA process and stakeholder communication for more efficient decision-making[
40].Efforts are directed towards enhancing interoperability between BIM tools and LCA, SLCA and LCC databases to streamline the sustainability assessment process [
8,
41]. Recent efforts towards the integration of BIM and LCSA have typically been formalised via three different routes: (1) extracting the bill of quantities (BoQ) from the BIM and organising the data within an Excel template before importing the quantities data into professional LCA software [
42]; (2) creating an automatic linkage between the bill of material quantities and relevant LCSA information based on custom-built material IDs, which is founded on linking the BIM model with an external database containing essential LCSA properties and information required for conducting impact assessment [
43]; (3) Integrating LCSA parameters into the IFC properties to conduct the sustainability assessment within the BIM platform [
44]. The first route is hindered by the lack of data interoperability among different platforms, restraining the integrity and efficiency of information exchange.
The second approach hinges on establishing a permanent bidirectional link between the BIM model and the LCI database to facilitate the calculation and visualisation of the environmental impacts arising from the construction material’s life cycle [
43,
45]. The appropriate classification of BIM objects and data mapping is crucial for developing the portals to receive the information transferring between the BIM and external databases [
11].
Adopting the second route can reduce the license and training costs of operating proprietary LCA software compared to the first approach. However, the external databases’ lack of flexibility and comprehensiveness hampers the practicability and reliability of the second approach. Another challenge lies in the precise classification of data, including mapping various building materials. In light of this, creating LCSA databases embodying product-specific information conforming to the BIM environment ontologically and semantically is the key to data interoperability [
39]. Moreover, maintaining a dynamic and permanent bidirectional link between BIM and other tools requires validation mechanisms to ensure data integrity, the enrichment of IFC properties to improve data interoperability, and the prevention of unauthorised access to sensitive data [
46]. In response to this challenge, utilising official Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for encrypted, interoperable data exchange between BIM and different systems enables real-time synchronisation, automated data validation, and secure communication [
47].
The conspicuous advantage offered by the third approach is that the BIM contains all the necessary information, and the LCSA analysis is performed within the BIM platform. Therefore, there is no need for data manipulation or exchange across different tools, avoiding information loss and interoperability issues. On the flip side, data extraction, mapping, and integration are highly susceptible to manual mistakes [
48]. Compared to two previous methods that require re-exporting material information and re-connecting it to external databases for synchronising the LCIA results [
49], the third approach fulfils the full potential of BIM as a multidisciplinary data management platform where any modifications on the building’s elements or LCA data can be automatically reflected on the impact assessment results, thus transforming a segregated BIM-based LCA workflow into an interactive BIM-based sustainability assessment of design alternatives. [
14] stated that the developed integration method could not adapt smoothly to other contexts due to the lack of explicit data structure. Thus, for conducting a comprehensive LCA analysis, 26 mandatory properties and 111 optional properties are required, which calls for the development of an information delivery manual and a model view definition (IDM/MVD) to facilitate the sustainability information exchange among different software tools, thus empowering the broader adoption of BIM-based LCA on various BIM platforms.
Despite the inherent data interoperability challenges associated with BIM-based sustainability assessment, several studies have explored the feasibility of BIM as the centralised data hub to facilitate the LCA and LCC of the refurbishment strategies of existing dwellings [
50], progressive low-carbon design of infrastructure projects [
32], and the multi-objective optimisation of building’s embodied and operational impacts at early architectural design stage [
51]. However, previous studies failed to automate the BIM-enable LCSA process as the existing commercial databases lack data (e.g., recycling) beyond the conventional system boundary and only provide generic environmental profiles of materials incompatible with the regional context.
2.3. Coupling LCSA with MCDA to Improve the Decision-Making
The interpretation of the assessment results is a pivotal step for designers and stakeholders to make informed decisions, where the trade-off between various conflicting criteria needs to be deliberated with the aid of MCDA methods. Typically, the integration of MCDA and LCSA comes in two forms: (1) LCSA adds environmental, economic, and social indicators to the MCDA process, and (2) utilising MCDA to interpret LCSA results by weighing and aggregating multiple indicators with different unit types into a single index score [
22]. The downside of this integration is that adopting MCDA means introducing more subjectivity and uncertainty to the decision-making process, wherein a broad range of information needs to be collected and analysed [
52]. Previous studies show that combining LCA and MCDA methods can significantly improve the basic understanding of the sustainability implications of various construction materials on different LCA impact categories [
22]. [
53] proposed a hybrid fuzzy decision-aiding model that enables the translation of linguistic variables into fuzzy numbers to evaluate the performance of C&DWM alternatives against sustainable development criteria. Similarly, [
54] developed a Fuzzy decision support pipeline to select the most suitable concrete waste management strategy aligning with Thailand’s pursuit of the circular economy construction industry.
Despite the ascending trend of outranking MCDA methods in sustainable built environment studies, the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) remains the most recurrent approach for assessment result interpretation to facilitate sustainability-oriented decision-making [
22], where the relative weights of a set of criteria are obtained by pairwise comparisons considering their relative significance to achieving the overall objective of a decision-making problem [
55] The prominent advantage of AHP lies in its ability to decompose complex problem into relative simple elements within a hierarchical structure, in which quantitative measurable and qualitative subjective indicators can be compared pair-wisely, irrespective of other options, thus substantially simplifying the weighing process [
56]. Moreover, Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) is a scenario ranking technique that prioritises the best alternative based on its geometric distance from the ideal solution [
57]. The method adopts the Euclidean distance measure to define the Positive Ideal Solution (PIS) and the Negative Ideal Solution (NIS). Notably, the weights assigned to assessment criteria have a significant influence on the ideal solution and alternative ranking [
58]. Several studies have validated the applicability of integrating AHP and TOPSIS in solving multi-criteria outranking decision-making problems in the C&DWM field, including DWM scenario outranking [
59,
60], construction material supplier selection [
61], and sustainable materials alternatives [
62,
63]. Therefore, a hybrid MCDA method, AHP-TOPSIS, was adopted in this study to calculate the weights of assessment criteria and performance scores of alternatives sequentially. To that end, the Dynamo visual scripting method aligns with the requirements of BIM-LCSA-MCDA consolidation, which has been proven to be effective in facilitating the integration of multiple data sources for early design stage LCA analysis [
40,
43,
64], and MCDA functions for appraising the sustainability performance building component design [
65] and construction solutions [
66,
67].
3. Results
3.1. Goal and Scope Definition
It is necessary to identify the goal and scope of the analysis clearly and accurately, including functional unit, system boundary, target audience, assumptions, and limitations [
68]. According to EN15798 standards, a building’s life cycle encompasses A: Production and construction phase, B: Use phase, C: EoL phase, and D: Benefits and loads beyond the system [
27]. The scope of this study only covers the environmental and economic implications of building materials at their EoL phase (C1-C4), where the building is demolished, and the DW materials are disposed of at landfills. Moreover, the benefits of potentially reutilising and recycling DW materials (Phase D) are also incorporated into the LCA. The functional unit is m3 of DW materials.
It is assumed that the building would be imploded at the EoL stage. Hence, the input and output associated with DW sorting and collection procedures should be added to the inventory analysis. The system boundary is defined as the impacts associated with the DWM procedures, from building demolition to waste processing, transportation, and final disposal and recovery. The same system boundary is adopted during the environmental, economic, and social analyses so that the harmonisation of the three approaches occurs satisfactorily.
3.2. Criteria and Alternatives Description
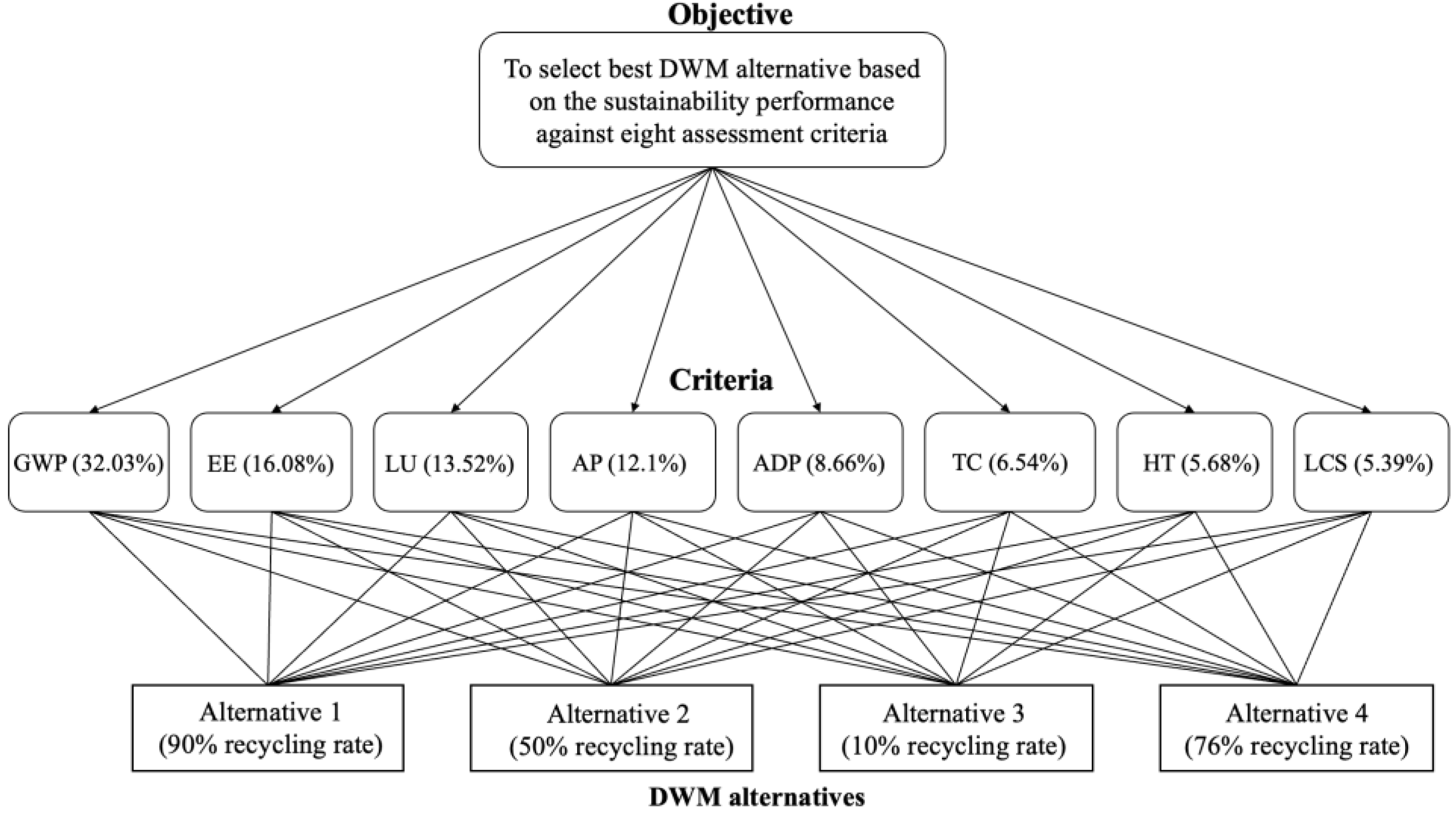
The assessment considered eight assessment criteria (sustainability indicators), namely, ‘Global Warming Potential (GWP)’, ‘Energy Efficiency (EE)’, ‘Land Use (LU)’, ‘Acidification Potential (AP)’, ‘Abiotic Depletion Potential (ADP)’, ‘Total Cost (TC)’, ‘Human Toxicity (HT)’, and ‘Landfill Cost Saving (LCS)’ in order of their relative importance. The procedures and results of identifying and weighing sustainability indicators can be found in the author’s prior study [
37]. The AHP hierarchy diagram demonstrating the relationships between the decision-making objective, sustainability indicators, and DWM alternatives is depicted in
Figure 1 below.
For validation purposes, this case study compares the sustainability performance of four prevalent DWM practices during the life cycle of DWM defined in the earlier section. When setting the basic project parameters, the transportation distance between the site and the landfill is identical to the distance between the site and the recycling facility, which is set as 50 kilometres. Further, the recycling gate fee is charged at 5 Australian dollars per ton, while the landfill levy is 3 Australian dollars per ton, applied to all kinds of waste streams. Additionally, the transportation unit cost, fuel and energy consumption rate of vehicles and machinery are referred to the Ecoinvent database. The relevant parameters and data for the inventory analysis are stored in the external custom database and linked to the BIM model via Dynamo scripts.
The four DWM alternatives are only differentiated by their respective target recycling rate, where Alternative 1 represents the prevalent DWM practice among European countries, Alternative 2 denotes the baseline scenario, Alternative 3 represents the landfilled-dominant DWM strategy in China, and Alternative 4 reflects the current average recycling rate of DW in Australia. As demonstrated in Figure 4, the recycling rates corresponding to DWM Alternatives 1 to 4 are 90%, 50%, 10%, and 76%, respectively.
3.3. Life Cycle Inventory Analysis and Impact Assessment
After detailing the recycling rate, landfill levy, recycling unit cost, transportation distance to each terminal, and the work efficiency of waste processing equipment, four DWM alternatives differentiated by the overall recycling rate were formulated. The inventory analyses were conducted within the Dynamo visual programming platform, and the results were exported into an eToolLCD-compatible spreadsheet template for subsequent LCIA.
The LCIA results derived from the eToolLCD platform are displayed in
Table 1. It can be observed that external walls are the main contributor to the impact categories, including GWP, EE, AP, and ADP in all DWM scenarios. Accompanied by partition walls and other structural components composed of masonry or concrete materials, those elements are responsible for the dominant portion of the carbon emissions, energy consumption, and other environmental footprints, as highlighted by prior inventory analyses. These findings echoed the colour pattern of building components displayed on the 3D BIM model, where the contour of the building enclosed by infilled frame was automatically rendered in red since the concrete columns and infill masonry walls are the main contributors to carbon emissions. The results are consistent with previous research [
15,
53,
69] that underscore the GHG reduction potential of recycling and reusing concrete and masonry materials, in which a significant portion of embodied carbon can be conveyed to a new life cycle of building components constituting salvaged materials.
3.4. Results Interpretation Using the AHP-TOPSIS Method
The LCIA results exported from the online LCA tool were linked to a preassembled spreadsheet embedded with TOPSIS functions. The calculation process of sustainability scores for different DWM alternatives is depicted in
Table 2 below. Alternative 1 obtained the highest sustainability score (91.63), followed by Alternative 4 (89.54) and Alternative 3 (76.07). In comparison, Alternative 3 reflects the status quo of China’s DWM, achieving the lowest score at 8.37. Overall, it is predictable that the sustainability scores of DWM schemes are ascending with their target recycling rate in the hypothesised context, where the discrepancy between the transportation distance from the demolition site to recycling plants and landfills is within a reasonable range. Additionally, the divergence in the landfill levy and recycling unit cost is diminutive. However, it is worth noting that the relationship between the sustainability score and recycling rate is not linear, where the growth curve of sustainability scores progressively gets flattened, suggesting that initial efforts by increasing the recycling rate yield significant sustainability benefits before the improvement discernibly diminishes when reaching a certain threshold. With that in mind, achieving the optimal sustainability outcome calls for the calibration of the most fitting recycling rate by incorporating more scenarios to develop a nonlinear time-series forecast model [
70,
71]. As such, the decision-maker can quickly identify the optimal solution and the worst-case scenario at the DWM planning stage by efficiently interpreting the LCA results into scenario ranking with the BIM-embedded hybrid MCDA function.
4. Discussion
4.1. Benefits and Limitations of the Study
The developed framework demonstrates that the sustainability assessment of DWM alternatives can be performed automatically within a BIM-based environment, where the potential environmental, economic, and societal impacts throughout the life cycle of a building demolition project can be simulated and visualised on a BIM model. Moreover, a hybrid MCDA approach was integrated into the framework to prioritise the optimal DWM alternative based on the interpreted results of streamlined sustainability analysis.
Nevertheless, several limitations reside in this BIM-based sustainability assessment approach. Firstly, a limited range of DW materials was considered in this study, which means the shared parameters were only inserted into the properties of concrete, aluminium, steel, bricks, glass, wood, and gypsum. As such, only BIM elements (e.g., partition walls, windows, structural components) constituted by those materials are considered in the sustainability assessment. To enhance the applicability of this framework in real-world demolition projects, the users must manually insert the customised parameters into other BIM objects’ properties for a more complex building structure with MEP components and a diverse range of materials. Secondly, the framework adopts eight sustainability indicators identified in the author’s previous research [
37], wherein the environmental impact categories (indicators) are predominately derived from the CML-IA methodology, and the economic indicators are assessed based on the original models. The justification for the choice of assessment criteria and methods is needed to validate the decision-making for DWM alternatives evaluation and ranking. Lastly, the lack of EPDs covering the environmental impacts generated from the material’s EoL phase hinders the development of the customised database, thus affecting the accuracy and reliability of the sustainability assessment by adopting generic LCA data. Considering the circumstances, this research limits the scope of the assessment by only considering the principal building components and materials in the pilot study, in which the environmental profiles of those materials are well documented in etoolLCD databases. Nevertheless, time-consuming user interventions and data collection are required to conduct a comprehensive and robust sustainability assessment in real-world settings because the project-specific data and detailed characteristics of DWM scenarios, waste materials, and procedures are lacking due to the limited EPDs and regional material databases. In the scenario analysis, only four DWM scenarios differentiated by a sole variable (i.e., target recycling rate) were appraised. The more in-depth schematic design hinges on the fine-tuning of the target target recycling rate corresponding to the optimal sustainability performance. Moreover, sensitivity analysis is desired once additional design parameters are introduced into the equation (e.g., transportation distance), and criteria weighting varies under different contexts.
4.2. Contribution to Knowledge
Unlike existing tools that establish a linkage between geometric information and the material composition of building elements with external LCA databases, the developed sustainability assessment approach incorporates relevant parameters into the BIM object’s properties, making the newly added parameters the receivers of LCA values derived from the external database. In this way, a permanent link is created between the BIM elements and material LCA profiles for data exchange within the Dynamo platform. The stakeholders can perform the sustainability assessment without replicating the data mapping procedure or being confined to a specific LCA tool. Another contribution of this study is that it advocates the establishment of a national benchmarking system for demolition projects by developing tailor-made BIM libraries for DWM. In summary, the developed framework aids real-world DWM practices with its abilities to (1) identify and improve the recycling rate of high embodied carbon building components via 3D dismantling coordination; (2) utilise hybrid MCDA methods to efficiently prioritise the most sustainability-sound waste management scheme; and (3) improve stakeholders’ awareness towards sustainability-oriented demolition planning and willingness to adopt the LCSA into the project tender prerequisites.
4.3. Future Recommendations
In real-world circumstances, multidisciplinary stakeholders with diverse duties and conflicting priorities will be engaging in the decision-making process, introducing more complexities in communication, schematic design, and feasibility analysis. That said, it is essential to incorporate diverse perspectives by engaging stakeholders from different parties of interest to reconstruct real-life demolition project scenarios, where the priorities (criteria weighting) of the sustainability assessment shall be more aligned with the local practitioner’s perspectives. To this end, the simulated results can be more effectively applied to real-world DWM practices.
The applicability of this assessment framework to different local contexts should be investigated in future to increase the adaptability of this method. Alternatively, a Revit add-in is desired to allow users to adjust the assessment criteria and weighting based on their judgment. Expanding the scope of assessment requires the enrichment of EPDs of different building materials, especially for estimating the environmental implications at their end-of-life stage and beyond (e.g., waste recycling). To that end, industry and academia collaboration should encourage and standardise more rigorous data collection protocols and detailed documentation of recycling practices to enhance the comprehensiveness and quality of EPDs. It is of mutual benefit to embed EPDs into BIM material libraries to improve the richness of the data repository and streamline the assessment workflow. Furthermore, the current BIM-based sustainability assessment framework should evolve into a decision-aiding tool for calibrating the most fitting recycling rate by coupling MCDA with gradient descent optimisation [
72,
73] and other nonlinear forecasting techniques [
74,
75].
5. Materials and Methods
The objective of this study herein is to develop a BIM-based sustainability assessment approach to facilitate the decision-making for DWM alternative selection, wherein established methodologies like LCA, LCC, and Social-LCA are combined to support a comprehensive assessment of sustainability implications that cover the three pillars of sustainability (environmental, economic, and societal)As such, an streamlined workflow was proposed for linking the BIM elements with relevant databases, performing inventory analysis on the visual programming platform, and interpreting assessment results using MCDA techniques.
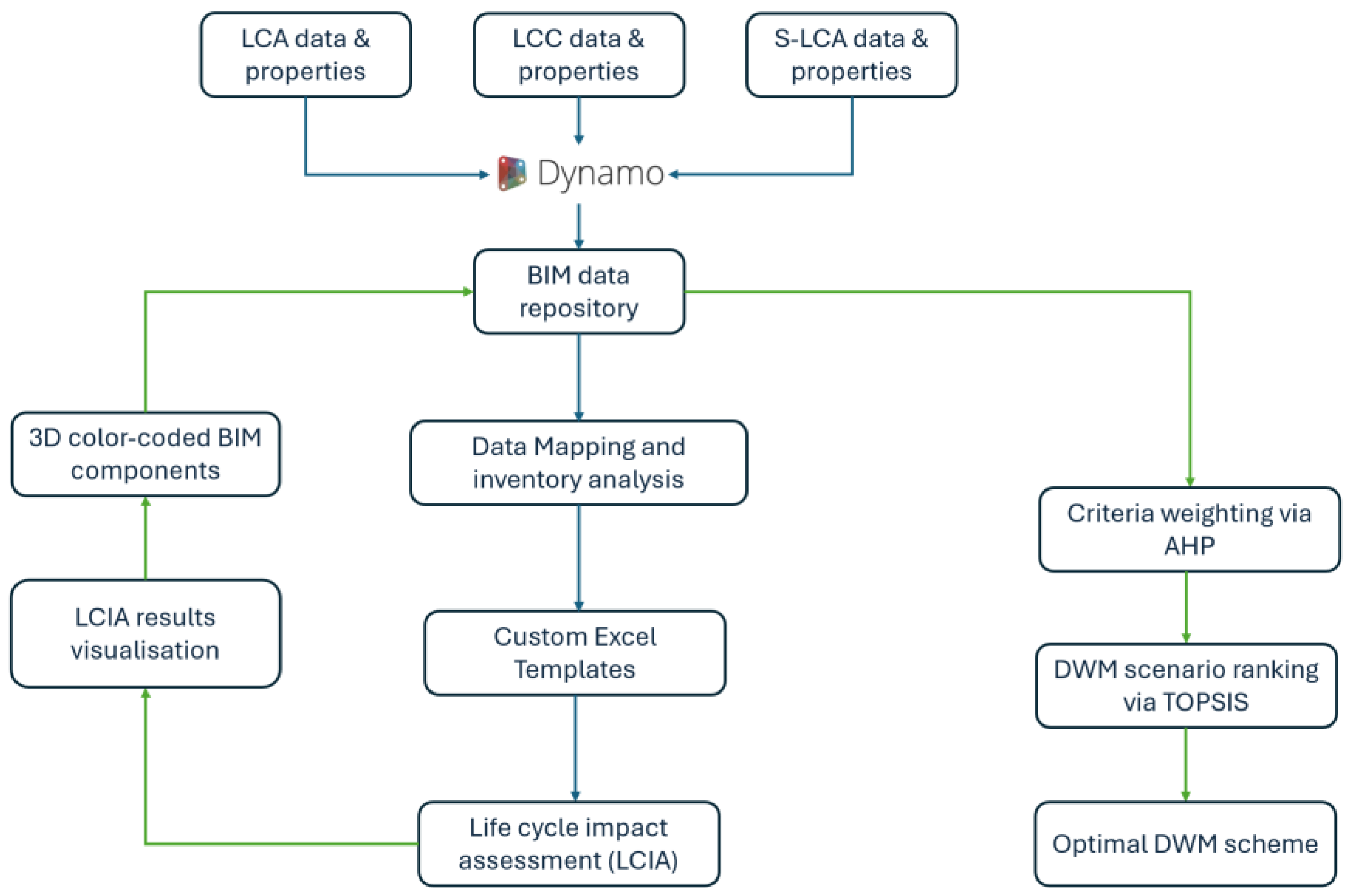
Figure 2 elucidates the methodology flowchart, where the sustainability assessment process, elements, inputs and outputs of the system are outlined.
The workflow was formalised as a BIM-based sustainability assessment framework encompasses the following components: (1) data identification and structuring, (2) data integration, (3) BIM-based inventory analysis, (4) eToolLCD impact assessment, and (5) DWM scenario ranking via MCDA.
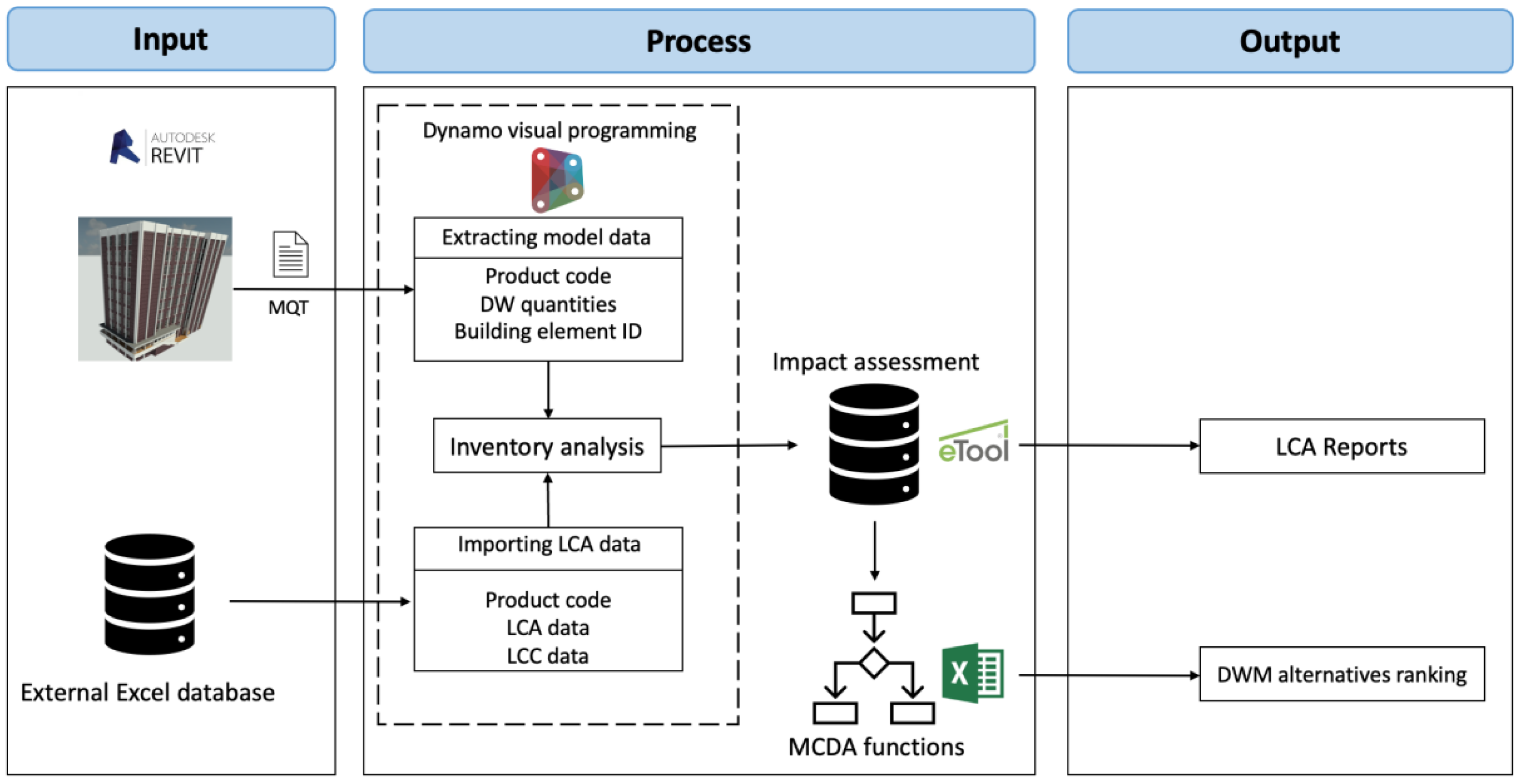
Figure 3 depicts the process of the BIM-based decision-aiding approach at the DWM planning phase.
As can be seen from the above graph, the identification of data required for inventory analysis is the prerequisite step for data structuring. Once the required data is obtained and structured, the external Excel database can be developed and linked to the material information extracted from the BIM model accordingly. The process stage includes data integration, LCIA, and MCDA. First, a unique material ID was assigned to each material in the BIM library and the developed Excel database. As such, the automated link was established between the BIM model and the external database. Collectively, the inputs of BIM-based inventory analysis were integrated into the Dynamo visual programming platform, where the emissions associated with the life cycle of different DW materials under various DWM scenarios were calculated using custom Dynamo visual scripts. Secondly, the inventory analysis results were exported to an online LCA tool (i.e., eToolLCD) for detailed LCIA. Subsequently, the impact assessment results were interpreted by the MCDA functions embedded in an Excel spreadsheet to obtain the best DWM alternative with the highest sustainability score.
The following subsections comprise two parts. The first part illustrates the workflow of establishing the connections between BIM and LCA software by extending the IFC properties and linking the BIM libraries with the LCA database. As such, it realises BIM-based sustainability assessment by leveraging BIM as a centralised data management platform to quantify the emissions and costs arising from DWM activities at the building’s EoL stage and export the inventory analysis results to professional LCA software for detailed impact assessment. The second part describes the integration process of LCA and MCDA methods to facilitate the decision-making for prioritising sustainability-oriented DWM alternatives (ranking DWM alternatives based on respective sustainability scores calculated by MCDA methods). Finally, this developed approach was exemplified by using a real-life demolition project.
5.1. Identification of Required LCA Parameters and Data for Developing the External Database
The current IFC4 schema does not contain adequate IFC properties to store essential LCA, LCC, and SLCA data in the BIM objects and materials [
11]. In light of this, the development of a custom LCSA-DWM database starts with identifying the relevant data and parameters for conducting the BIM-based LCSA based on the components of the sustainability assessment.
Table 1 presents the indicators and assessment methods adopted in the sustainability assessment, where the indicators and respective weights are consistent with a prior study investigating the essential sustainability indicators and their relative importance against the sustainability goal [
37]. As can be seen from
Table 3, a total of eight sustainability indicators from three dimensions of sustainability and corresponding assessment methods should be integrated into the BIM-based assessment framework.
5.2. Developing an Integrated Workflow for Implementing DWM Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment in the BIM-Based Environment
Data incompatibility issues in current LCA practices occur during the inventory and impact assessment stages when the data needs to be transferred across different platforms [
64]. The benefits stemming from adopting BIM technology as the centralised data repository to accommodate LCA-related information into BIM objects’ properties substantially streamline the multiformity data transactions. Therefore, the range of parameters covered by the BIM-based MQT process can be extended to streamline the life cycle inventory analysis of building materials. To this end, data derived from the BIM model and the custom LCA database should be integrated via a dynamic link to develop an automated method for conducting the BIM-based LCA. In view of this, Dynamo is an open-source visual programming extension designed for Autodesk Revit, which allows Revit users to manipulate the data, create various parameters as data carriers, and establish connections between the Revit platform and LCA software and databases. Moreover, Dynamo scripting can automate the calculation processes of the life cycle inventory analysis and impact assessment and colour-coding of the BIM elements to display the LCA results [
76].
The following subsections illustrate using dynamo scripts to establish the bidirectional link between the BIM model and the custom database, which encompasses three main procedures: data extraction, data integration and calculation, and result visualisation [
77].
The first step is to create LCA-related IFC properties as new parameters at the material, element, and project level, wherein the data regarding the project profile and sustainability indicators required for the inventory analysis and impact assessment should be added. It is crucial to adopt a more concise and manageable set of indicators without compromising the comprehensiveness of the sustainability assessment. With that in mind, eight indicators (see
Table 1) identified and weighted by [
37] in their prior Delphi-AHP investigation were deemed the most representative and intuitive assessment criteria for demonstrating the sustainability assessment and decision-making workflow in a consistent manner.
Those assessment criteria are included in the shared parameters of BIM objects, including materials, ceilings, doors, floors, roofs, walls, windows, beams, columns, foundations, and stairs. To this end, Dynamo visual programming replaces conventional programming languages like C#. It allows the programmer to depict the workflow and relationships between different modules by connecting pre-set nodes into a logical sequence [
48]. It is worth mentioning that this study does not concern the availability and collection of the primary LCA data, such as the carbon emission factor of a specific material. The environmental profiles of building components and materials were obtained from the etoolLCD database and EPDs for practicability consideration.
The next step is to enable the newly added parameters as the recipients of data derived from the external database, where the LCA data can be imported into the Dynamo platform and integrated with the material information to calculate the environmental and economic outputs produced from various building materials and relevant DWM activities. Linking the LCA data with related parameters of BIM objects is done by matching the same nomenclature for the component’s name in the spreadsheet and BIM family types. In this case, Dynamo visual programming not only creates the essential parameters onto the IFC model but also establishes the routes for importing the LCA data into the designated parameters [
48]. It is a prerequisite to identify the BIM elements based on customised classification codes prior to data integration. The classification schemes adopted in this study are a dynamic and unified classification system developed by NBS that covers all sectors and partners with industry-leading firms like Arup and AECOM. After implementing the NBS classification scheme, the classification codes are loaded into Autodesk Revit as “Assembly Code”, a built-in parameter for Revit families with UniFormat classification.
Performing data-intensive inventory analysis within the BIM environment requires data mapping to match the LCA values with BIM elements based on the assembly codes assigned to designated building components. The DW material quantities can be extracted from the parametric model and assembled in a spreadsheet using the material take-off function. Afterwards, LCA values derived from the external database are linked to corresponding elements or materials in the spreadsheet by matching the respective classification codes. To conduct an inventory analysis as a part of LCA for DWM, related BIM properties incorporated into the BIM objects as shared parameters should include the sustainability indicators, material density, the transportation distance to each destination, waste conversion factor, carbon emission factor, and predefined waste management scenarios as parts of the missing parameters required for the analysis. Then, the LCIA results by each sustainability indicator will be exported to a pre-formatted spreadsheet template and linked with the etoolLCD to perform LCIA, where the components created in the BIM model were automatically matched with the templates provided by the etoolLCD. However, for BIM components with material composition different from the original etoolLCD templates, we manually create the template on the etoolLCD platform and match it with the corresponding Revit families. However, the automation level of the template matching hinges on the richness of the etoolLCD template database and the standardised Revit object naming. At last, the LCA profile of each component will be created individually and then aggregated into the LCSA results of the whole building under different EoL DWM scenarios.
After the inventory analysis and LCIA, the results need to be translated into intuitive information to facilitate the decision-making for DWM alternative selection. As stated in the CML-IA method, the classification and characterisation of different impact categories are compulsory, whereas normalisation, grouping, and weighting are optional [
63]. Therefore, AHP and TOPSIS are combined as a hybrid MCDA approach to facilitate decision-making by calculating the sustainability scores of DWM alternatives. TOPSIS functions are embedded into a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet, where the LCIA results are interpreted and converted into respective sustainability scores of DWM alternatives to indicate their overall performance under various correlated or conflicting criteria. The relative weights of sustainability indicators are applied according to the AHP results derived from [
37]. Moreover, the linkage between the sustainability assessment results and the MCDA functions was established via Dynamo visual programming, where the preassembled Excel spreadsheet received the sustainability performance of the whole building model under various EoL DWM scenarios. As such, the sustainability score corresponding to each DWM scenario can be automatically calculated within the spreadsheet and exported as a comprehensive report.
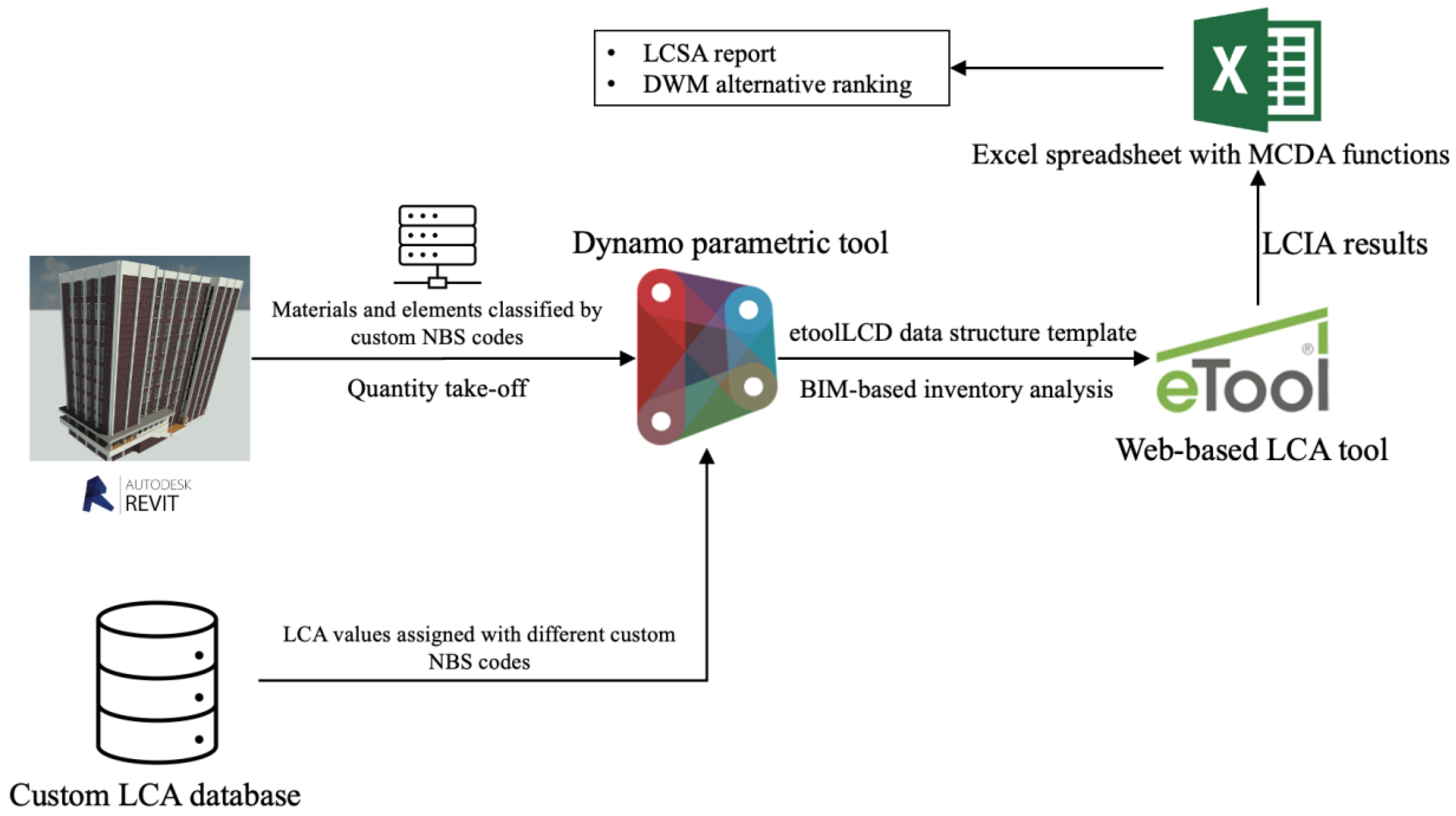
Figure 4 illustrates the correlations between each component within the BIM-based decision-aiding framework and the data exchange between various platforms.
5.3. Development of the BIM-Based Decision-Aiding Framework Using the Dynamo Visual Scripting
The actualisation of BIM-based decision-aiding for sustainable DWM encompasses three main stages, including (1) data extraction, (2) data integration and calculation, and (3) result interpretation. The following elucidates the development process of the BIM-based decision-aiding framework that integrates LCA and MCDA into a BIM-based environment.
Firstly, the data should be extracted from the BIM model, which includes material volume, types, and assembly codes of BIM elements and materials. To that end, a series of nodes and Python scripts were connected to import the essential data from the BIM model into the Dynamo parametric programming platform. Similarly, LCA data and related project information such as the recycling rate, the transportation distance to each waste treatment facility, the carbon emission factors of different materials and energy sources, and the unit cost of each DWM procedure were imported into the Dynamo environment from the external custom database. After exporting the essential data from the BIM model and external database, two data sources were integrated based on the NBS classification codes assigned to the BIM components and respective LCA values.
Subsequently, the LCIA was executed in the etoolLCD platform, and the impact results were written back to a preassembled Excel spreadsheet with TOPSIS functions. Thus, the performance scores of different DWM alternatives against eight sustainability indicators were normalised, weighted, and aggregated into sustainability scores to obtain the best alternative. Moreover, auxiliary Dynamo scripts were developed aimed to assist designers in identifying the top contributors to different environmental impacts (e.g., GWP) by visualising the contribution of an element to a specific impact category, where LCIA results of the BIM element were written back to its properties and displayed in a colour-override 3D view. Lastly, the graphical representation of sustainability assessment results was provided as bar graphs showing the performance of various DWM alternatives and the contribution from each primary waste stream to different impact categories.
5.4. Case Study Validation
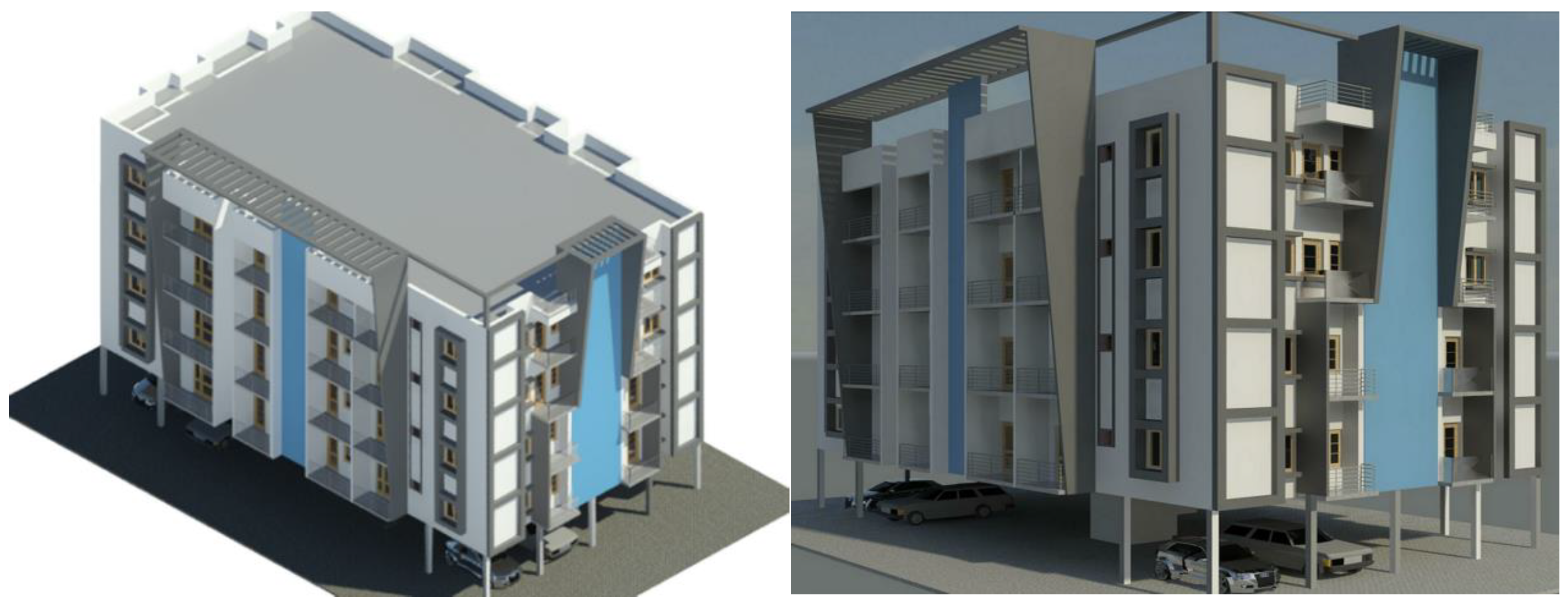
The applicability of the proposed framework was verified in a case study of a conceptual four-storey concrete frame residential apartment created in Autodesk Revit. The BIM elements representing the components within the building are categorised into external walls, structural slabs, structural columns, structural beams, structural roofs, and partition walls. The material composition of those elements includes timber, steel, aluminium, steel, masonry, and glass. After assigning the corresponding material and thickness to each component’s layer, the total volume (m3) of each type of material is accumulated in a spreadsheet by performing the BIM-based material quantity take-off (MQT) function. Subsequently, the building’s total gross floor area (m2) was obtained via MQT after defining the boundary and function of each zone in the plan view. The data derived from the BIM model was mapped and linked to the respective LCA values extracted from the external database via Dynamo scripts presented earlier. The embodied impacts of DW streams and building element classes under different DWM scenarios are calculated in Dynamo. The 3D rendering view of the BIM model is depicted in
Figure 5.
6. Conclusions
With the aim of enhancing the sustainability performance of DWM by selecting the optimal DWM alternative, this paper proposes a sustainability assessment framework that combines the BIM-based sustainability assessment with hybrid MCDA methods to prioritise the optimal DWM alternative from a life cycle sustainability perspective. Previous studies have yet to develop a workflow that simultaneously evaluates the sustainability performance of various EoL scenarios and facilitates decision-making during DWM planning. Thus, this study improves the sustainability awareness among stakeholders and the efficiency of DWM execution by showcasing the multifaceted benefits of sustainability-oriented DWM planning. By integrating parametric modelling, this approach is easily adaptable to other regions with different emphases on sustainability by adopting suitable indicators and enriching relevant IFC properties, BIM libraries, and LCA databases considering the local context. More specifically, by adopting this BIM-based framework, the project manager can decide the most effective on-site material processing option, adopt the least carbon-intensive demolition scheme with the aid of 3D coordinated selective demolition, and derive the relatively preferable DMW plan according to the predefined project’s priorities and settings. Furthermore, the case study demonstrates the applicability of the developed framework in the actual design process. The results reveal that Alternative 1, with a 90% recycling rate, achieves the best sustainability outcome out of the four DWM scenarios being assessed. It is worth noting that the growing trend of sustainability score stalls as the recycling rate exceeds the ‘business as usual’ threshold at 76% because the divergence in sustainability score is minimal between Alternatives 1 and 4, indicating a nonlinear relationship between recycling rate and sustainability performance. Future studies should couple MCDA methods with gradient descent optimisation algorithms or nonlinear forecasting techniques to obtain the most fitting target recycling rate in a specific predefined project setting.
Overall, this study tackles the challenges of adopting BIM-based DWM sustainability assessment caused by the data interoperability issues, where a successful integration pathway of BIM, LCA tools, and MCDA methods has been paved. Moreover, it sheds light on (1) employing AI techniques for automated data mapping, thus reducing the time and effort on error-prone manual data mapping, and (2) promoting the development of OpenBIM standards to extend the applicability of BIM in other domains, fostering a more efficient collaboration across different industries via standardised data exchange protocols.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Dongchen Han.; methodology, Dongchen Han.; software, Dongchen Han.; validation, Dongchen Han.; formal analysis, Dongchen Han.; investigation, Dongchen Han.; resources, Dongchen Han, Abbas Rajabifard.; data curation, Dongchen Han.; writing—original draft preparation, Dongchen Han.; writing—review and editing, Dongchen Han, Abbas Rajabifard.; visualization, Dongchen Han.; supervision, Abbas Rajabifard.; project administration, Abbas Rajabifard.; funding acquisition, Dongchen Han, Abbas Rajabifard. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript”.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/
Supplementary Materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The researchers acknowledge the support provided by the Centre for Spatial Data Infrastructures and Land Administration, the University of Melbourne.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Klein, T.; Anderegg, W.R.L. A Vast Increase in Heat Exposure in the 21st Century Is Driven by Global Warming and Urban Population Growth. Sustain Cities Soc 2021, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Kalantari, M.; Rajabifard, A. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Australia: A Research Agenda. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shi, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, S. A BIM-Based Construction and Demolition Waste Information Management System for Greenhouse Gas Quantification and Reduction. J Clean Prod 2019, 229, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovea, M.D.; Powell, J.C. Developments in Life Cycle Assessment Applied to Evaluate the Environmental Performance of Construction and Demolition Wastes. Waste Management 2016. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisellini, P.; Ripa, M.; Ulgiati, S. Exploring Environmental and Economic Costs and Benefits of a Circular Economy Approach to the Construction and Demolition Sector. A Literature Review. J Clean Prod 2018, 178, 618–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llatas, C.; Soust-Verdaguer, B.; Passer, A. Implementing Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment during Design Stages in Building Information Modelling: From Systematic Literature Review to a Methodological Approach. Build Environ 2020, 182, 107164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Paasch, J.M.; Paulsson, J.; Tarandi, V.; Harrie, L. A BIM-Based Approach to Design a Lifecycle 3D Property Formation Process: A Swedish Case Study. Land use policy 2023, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, M.V.A.P.M.; da Costa, B.B.F.; Najjar, M.; Figueiredo, K. V.; de Mendonça, M.B.; Haddad, A.N. Sustainability Assessment of a Low-Income Building: A BIM-LCSA-FAHP-Based Analysis. Buildings 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichter, E.; Richter, V.; Frisch, J.; van Treeck, C. Automatic Generation of Second Level Space Boundary Geometry from IFC Models. In Proceedings of the Building Simulation Conference Proceedings; International Building Performance Simulation Association; 2022; pp. 1083–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, J.P.; Bragança, L.; Mateus, R. A Systematic Review of the Role of BIM in Building Sustainability Assessment Methods. Applied Sciences (Switzerland) 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Costa, A.A.; Silvestre, J.D.; Pyl, L. Integration of LCA and LCC Analysis within a BIM-Based Environment. Autom Constr 2019, 103, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maria, A.; Eyckmans, J.; Van Acker, K. Downcycling versus Recycling of Construction and Demolition Waste: Combining LCA and LCC to Support Sustainable Policy Making. Waste Management 2018, 75, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soust-Verdaguer, B.; Bernardino Galeana, I.; Llatas, C.; Montes, M. V.; Hoxha, E.; Passer, A. How to Conduct Consistent Environmental, Economic, and Social Assessment during the Building Design Process. A BIM-Based Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment Method. Journal of Building Engineering 2022, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Aguiar Costa, A.; Silvestre, J.D.; Pyl, L. Development of a BIM-Based Environmental and Economic Life Cycle Assessment Tool. J Clean Prod 2020, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X. Economic and Environmental Assessment of Carbon Emissions from Demolition Waste Based on LCA and LCC. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, S.; Garbarino, E.; Cerreta, M.; Tonini, D. Sustainability Assessment of Construction and Demolition Waste Management Applied to an Italian Case. Waste Management 2021, 128, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussat, N.; Dujet, C.; Méhu, J. Choosing a Sustainable Demolition Waste Management Strategy Using Multicriteria Decision Analysis. Waste Management 2009, 29, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gálvez-Martos, J.L.; Styles, D.; Schoenberger, H.; Zeschmar-Lahl, B. Construction and Demolition Waste Best Management Practice in Europe. Resour Conserv Recycl 2018, 136, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, X.; Lenihan, H.; O’Regan, B. A Model for Assessing the Economic Viability of Construction and Demolition Waste Recycling - The Case of Ireland. Resour Conserv Recycl 2006, 46, 302–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Xiao, J.; Tam, V.W.Y. A Closed-Loop Life Cycle Assessment of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Utilization in China. Waste Management 2016, 56, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invidiata, A.; Lavagna, M.; Ghisi, E. Selecting Design Strategies Using Multi-Criteria Decision Making to Improve the Sustainability of Buildings. Build Environ 2018, 139, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanghelini, G.M.; Cherubini, E.; Soares, S.R. How Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) Is Aiding Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) in Results Interpretation. J Clean Prod 2018, 172, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Ma, J.; Ahmad, N.; Ullah, Z.; Ahmed, R.I. Uptake and Adoption of Sustainable Energy Technologies: Prioritizing Strategies to Overcome Barriers in the Construction Industry by Using an Integrated AHP-TOPSIS Approach. Adv Sustain Syst 2021, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, M.; Bemani, A.; Erfani, M.; Yarami, N.; Siyahati, G. Integration of LCSA and GIS-Based MCDM for Sustainable Landfill Site Selection: A Case Study. Environ Monit Assess 2023, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvidsson, R.; Hildenbrand, J.; Baumann, H.; Islam, K.M.N.; Parsmo, R. A Method for Human Health Impact Assessment in Social LCA: Lessons from Three Case Studies. International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment 2018, 23, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthin, A.; Traverso, M.; Crawford, R.H. Assessing the Social Life Cycle Impacts of Circular Economy. J Clean Prod 2023, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, C.; Du, X. Life Cycle Assessment of Building Demolition Waste Based on Building Information Modeling. Resour Conserv Recycl 2022, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qian, S. Evaluation of Social Life-Cycle Performance of Buildings: Theoretical Framework and Impact Assessment Approach. J Clean Prod 2019, 213, 792–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llatas, C.; Angulo Fornos, R.; Bizcocho, N.; Cortés Albalá, I.; Falcón Ganfornina, R.; Galeana, I.; Garcia-Martinez, A.; Gómez De Cózar, J.C.; López Alonso, S.; Meda, P.; et al. Towards a Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment Method for the Quantification and Reduction of Impacts of Buildings Life Cycle. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 2019, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Li, J.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, D. A BIM-LCA Approach for Estimating the Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Large-Scale Public Buildings: A Case Study. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Cui, C.; Skitmore, M. BIM-Based Approach for the Integrated Assessment of Life Cycle Carbon Emission Intensity and Life Cycle Costs. Build Environ 2022, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Zheng, B.; Chi, H.L.; Hsu, S.C. Automated and Continuous BIM-Based Life Cycle Carbon Assessment for Infrastructure Design Projects. Resour Conserv Recycl 2023, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayanti, B.; Songok, J.; Helo, P. Multi-Objective Optimization to Improve Energy, Economic and, Environmental Life Cycle Assessment in Waste-to-Energy Plant. Waste Management 2021, 127, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milutinović, B.; Stefanović, G.; Đekić, P.S.; Mijailović, I.; Tomić, M. Environmental Assessment of Waste Management Scenarios with Energy Recovery Using Life Cycle Assessment and Multi-Criteria Analysis. Energy 2017, 137, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, D.; Laishram, B. Energy Analysis of High-Rise Residential Buildings under Demolition Using Controlled Explosion: An Indian Case Study. J Clean Prod 2023, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taelman, S.; Sanjuan-Delmás, D.; Tonini, D.; Dewulf, J. An Operational Framework for Sustainability Assessment Including Local to Global Impacts: Focus on Waste Management Systems. Resources, Conservation and Recycling: X 2019, 2, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Kalantari, M.; Rajabifard, A. Identifying and Prioritizing Sustainability Indicators for China’s Assessing Demolition Waste Management Using Modified Delphi–Analytic Hierarchy Process Method. Waste Management and Research 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llatas, C.; Bizcocho, N.; Soust-Verdaguer, B.; Montes, M. V.; Quiñones, R. An LCA-Based Model for Assessing Prevention versus Non-Prevention of Construction Waste in Buildings. Waste Management 2021, 126, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrecht, T.P.; Röck, M.; Hoxha, E.; Passer, A. BIM and LCA Integration: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LLatas, C.; Soust-Verdaguer, B.; Hollberg, A.; Palumbo, E.; Quiñones, R. BIM-Based LCSA Application in Early Design Stages Using IFC. Autom Constr 2022, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boje, C.; Hahn Menacho, Á.J.; Marvuglia, A.; Benetto, E.; Kubicki, S.; Schaubroeck, T.; Navarrete Gutiérrez, T. A Framework Using BIM and Digital Twins in Facilitating LCSA for Buildings. Journal of Building Engineering 2023, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.S.; Cho, K. BIM Application to Select Appropriate Design Alternative with Consideration of LCA and LCCA. Math Probl Eng 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, M.; Hollberg, A.; Habert, G.; Passer, A. LCA and BIM: Visualization of Environmental Potentials in Building Construction at Early Design Stages. Build Environ 2018, 140, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Costa, A.A.; Silvestre, J.D.; Vandenbergh, T.; Pyl, L. BIM-Based Life Cycle Assessment and Life Cycle Costing of an Office Building in Western Europe. Build Environ 2020, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eldik, M.A.; Vahdatikhaki, F.; dos Santos, J.M.O.; Visser, M.; Doree, A. BIM-Based Environmental Impact Assessment for Infrastructure Design Projects. Autom Constr 2020, 120, 103379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.; Zhou, Y.; Illankoon, C.; Le, K.N. A Critical Review on BIM and LCA Integration Using the ISO 14040 Framework. Build Environ 2022, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhou, X.; Huang, L.; Sandanayake, M.; Yap, P.S. Recent Technological Advancements in BIM and LCA Integration for Sustainable Construction: A Review. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, C.; Pereira, L.M.; Fabricio, M.M. Life Cycle Assessment and Environmental-Based Choices at the Early Design Stages: An Application Using Building Information Modelling. Architectural Engineering and Design Management 2018, 14, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, M.; Wojtasiewicz, M.; Martínez-Rocamora, A.; Solís-Guzmán, J.; Alba-Rodríguez, M.D. BIM-LCA Integration for the Environmental Impact Assessment of the Urbanization Process. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauletbek, A.; Zhou, P. BIM-Based LCA as a Comprehensive Method for the Refurbishment of Existing Dwellings Considering Environmental Compatibility, Energy Efficiency, and Profitability: A Case Study in China. Journal of Building Engineering 2022, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tam, V.W.; Le, K.N. Developing a Multi-Objective Optimization Model for Improving Building’s Environmental Performance over the Whole Design Process. Build Environ 2023, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, B.G.; Kroeze, C.; Jawjit, W. Assessing Environmental Performance by Combining Life Cycle Assessment, Multi-Criteria Analysis and Environmental Performance Indicators. J Clean Prod 2007, 15, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali-Zarch, M.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Dehghan-Sanej, K.; Kaboli, A. Prioritizing the Effective Strategies for Construction and Demolition Waste Management Using Fuzzy IDOCRIW and WASPAS Methods. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management 2022, 29, 1109–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonkanit, P.; Suthiluck, K. Developing a Decision-Making Support System for a Smart Construction and Demolition Waste Transition to a Circular Economy. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, K.; Gavanas, N.; Pyrgidis, C.; Pitsiava-Latinopoulou, M. Identifying and Prioritizing Sustainable Urban Mobility Barriers through a Modified Delphi-Ahp Approach. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2021, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gompf, K.; Traverso, M.; Hetterich, J. Using Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) to Introduce Weights to Social Life Cycle Assessment of Mobility Services. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2021, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.; Chen, T. Green Supplier Selection Using an AHP-Entropy-TOPSIS Framework. Supply Chain Management 2015, 20, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Wu, G.; Ji, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Gao, T. Evaluation of Provincial Carbon Neutrality Capacity of China Based on Combined Weight and Improved Topsis Model. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2021, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, B.G.; Yetilmezsoy, K. A Hybrid Fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS Approach for Implementation of Smart Sustainable Waste Management Strategies. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Kalantari, M.; Rajabifard, A. The Development of an Integrated BIM-Based Visual Demolition Waste Management Planning System for Sustainability-Oriented Decision-Making. J Environ Manage 2024, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Sabbah, M. AHP-TOPSIS Social Sustainability Approach for Selecting Supplier in Construction Supply Chain. Cleaner Environmental Systems 2021, 2, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Qureshi, M.N.; Mallick, J.; Ben Kahla, N. Selection of Sustainable Supplementary Concrete Materials Using OSM-AHP-TOPSIS Approach. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, K.; Pierott, R.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Haddad, A. Sustainable Material Choice for Construction Projects: A Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment Framework Based on BIM and Fuzzy-AHP. Build Environ 2021, 196, 107805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamari, A.; Kotula, B.M.; Schultz, C.P.L. A BIM-Based LCA Tool for Sustainable Building Design during the Early Design Stage. Smart and Sustainable Built Environment 2022, 11, 217–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, A.; Jalaei, F.; Khanzadi, M.; Banihashemi, S. BIM-Integrated TOPSIS-Fuzzy Framework to Optimize Selection of Sustainable Building Components. International Journal of Construction Management 2022, 22, 1240–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.P.; Villaschi, F.S.; Bragança, L. Assessing Life Cycle Environmental and Economic Impacts of Building Construction Solutions with BIM. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Duan, T.; Li, Z.; Xiahou, X.; Zeng, N.; Li, Q. Development Path of Construction Industry Internet Platform: An AHP–TOPSIS Integrated Approach. Buildings 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollberg, A.; Genova, G.; Habert, G. Evaluation of BIM-Based LCA Results for Building Design. Autom Constr 2020, 109, 102972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, M.; Hollberg, A.; Habert, G.; Passer, A. LCA and BIM: Integrated Assessment and Visualization of Building Elements’ Embodied Impacts for Design Guidance in Early Stages. Procedia CIRP 2018, 69, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, K.; AzariJafari, H. Challenges and Opportunities for Integrating BIM and LCA: Methodological Choices and Framework Development. Sustain Cities Soc 2021, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshand, A.; Khanlari, K.; Abbasianjahromi, H.; Zoghi, M. Construction and Demolition Waste Management: Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process Approach. Waste Management and Research 2020, 38, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, M.; Uçar, E. Carbon Footprint Forecasting Using Time Series Data Mining Methods: The Case of Turkey. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Saifoddin, A.; Shirmohammadi, R.; Aslani, A. Forecasting of CO2 Emissions in Iran Based on Time Series and Regression Analysis. Energy Reports 2019, 5, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Maity, S.R.; Dey, S.; Dutta, S. Modeling and Combined Application of MOEA/D and TOPSIS to Optimize WEDM Performances of A286 Superalloy. Soft comput 2021, 25, 14697–14713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, G.P.; Das, S. Hesitant T-Spherical Fuzzy Linear Regression Model Based Decision Making Approach Using Gradient Descent Method. Eng Appl Artif Intell 2023, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. An Automated Project Carbon Planning, Monitoring and Forecasting System Integrating Building Information Model and Earned Value Method. J Clean Prod 2023, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Akbarnezhad, A.; Arashpour, M. A Neural Network Approach to Predicting the Net Costs Associated with BIM Adoption. Autom Constr 2020, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).