1. Introduction
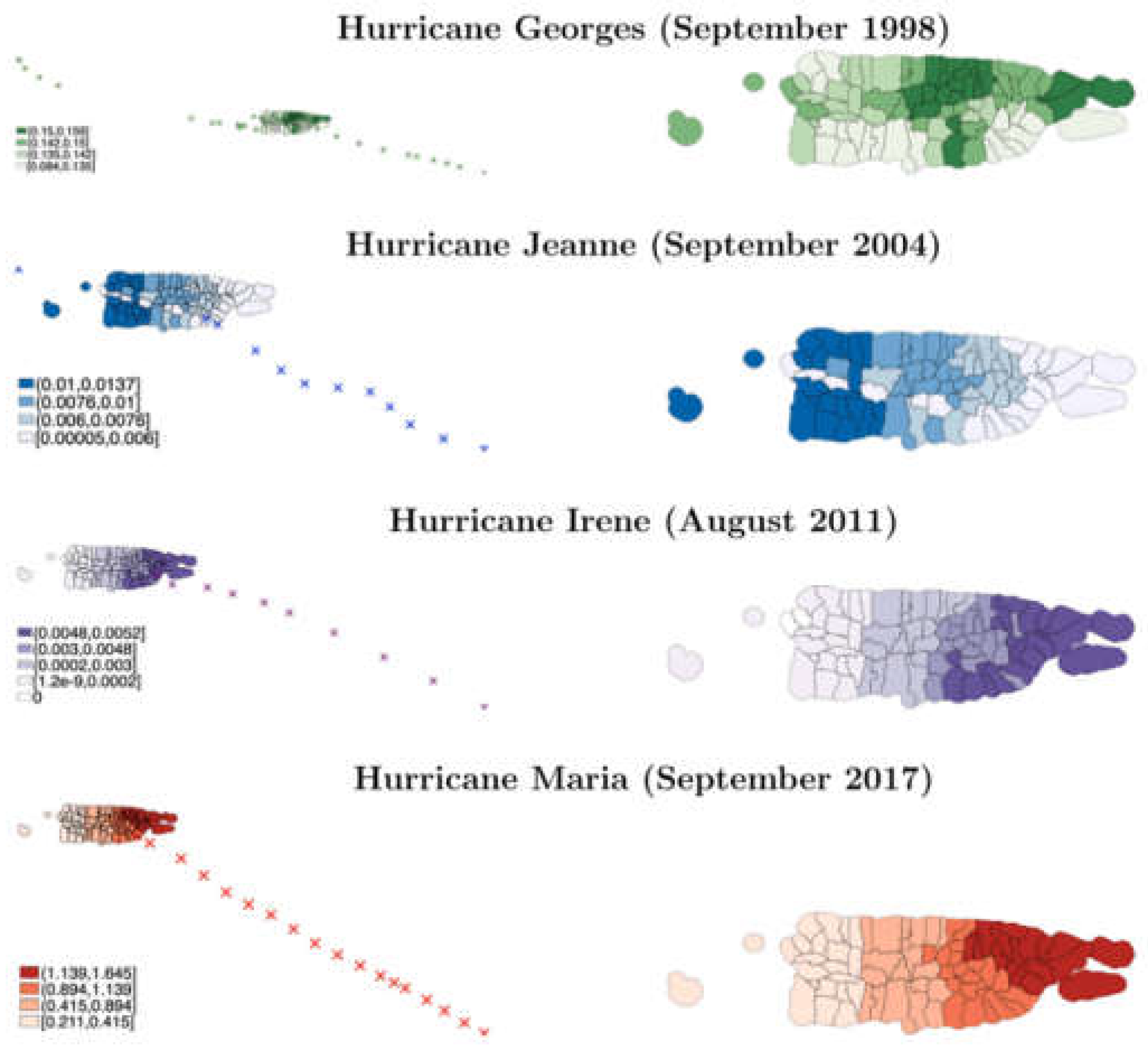
Puerto Rico, an island in the Caribbean, is susceptible to natural disasters, particularly hurricanes and tropical storms [
1] (see
Figure 1). The geographic and climatic conditions of the region contribute to frequent and severe weather events, which have significant impacts on the island’s infrastructure and economy [
1]. The island's location in the Atlantic hurricane belt means it is regularly exposed to storms that can cause widespread devastation. This vulnerability was starkly illustrated in September 2017, when Hurricane Maria, a Category 4 hurricane, struck Puerto Rico [
2]. The hurricane caused catastrophic damage, with sustained winds of 155 mph and heavy rainfall leading to flooding and landslides. The impact was profound, leaving millions without power and disrupting essential services for months [
2].
Hurricane Maria's destruction extended beyond immediate physical damage to the island's infrastructure. The hurricane resulted in an almost complete collapse of Puerto Rico's power grid, highlighting the fragility and inefficiency of its centralized energy system [
3]. The aftermath of Maria exposed the critical need for resilient and sustainable energy solutions. Over 80% of the transmission and distribution system was damaged, leading to prolonged outages that affected hospitals, water supply systems, and communications. The slow recovery process underscored the limitations of relying on a centralized grid system, which proved highly vulnerable to extreme weather events [
3].
In this context, the implementation of decentralized and renewable energy systems, such as those based on biomass, becomes essential for enhancing the island’s resilience against future disasters. Biomass energy, derived from organic materials such as agricultural residues, woody biomass, and other organic waste, offers a renewable and potentially self-sustaining source of power that can be crucial in post-disaster scenarios [
4]. Unlike fossil fuels, biomass is renewable and can be locally sourced, reducing dependence on external supplies and enhancing energy security [
4].
Biomass energy systems can be rapidly deployed and are versatile in their applications. They can provide both electricity and thermal energy, making them highly suitable for emergency situations [
5]. These systems can convert readily available organic waste into valuable energy, thus also addressing waste management issues. By integrating biomass energy into Puerto Rico’s energy mix, the island can enhance its capacity to respond to and recover from natural disasters while promoting sustainable development. The benefits include not only energy security and resilience but also economic and environmental gains [
6]. Using biomass reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, and the development of biomass projects can create local jobs and stimulate the economy [
5,
6].
The potential for biomass energy in Puerto Rico is significant given the island's abundant organic resources [
7]. Agricultural residues, such as sugarcane bagasse, and urban waste can be utilized to generate energy. For instance, the implementation of biomass-fueled microgrids can provide reliable power to critical infrastructure and communities, reducing the vulnerability of these areas during and after a disaster [
7,
8]. Moreover, the production of biochar as a byproduct of biomass energy can improve soil health and agricultural productivity, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient agricultural sector [
8].
The primary objective of this review is to examine the role of biomass energy in disaster recovery, using Puerto Rico as a case study. This paper will explore how biomass conversion technologies can be utilized to provide emergency energy solutions in the wake of natural disasters. By analyzing the specific experiences and initiatives undertaken in Puerto Rico following Hurricane Maria, we aim to highlight the potential of biomass energy to contribute to the island’s resilience and long-term sustainability.
Additionally, this review will:
Provide an overview of the different biomass conversion technologies applicable in post-disaster scenarios.
Assess the implementation and effectiveness of biomass energy systems in Puerto Rico post-Hurricane Maria.
Evaluate the broader impacts of biomass energy on community resilience, economic recovery, and environmental sustainability.
By addressing these objectives, this paper aims to contribute to the understanding of biomass energy’s role in disaster recovery and to provide insights that can inform policy and practice in other regions facing similar challenges.
2. Background
2.1. Impact of Hurricane Maria
In September 2017, Hurricane Maria made landfall in Puerto Rico as a Category 4 hurricane, causing unprecedented destruction across the island. With sustained winds of 155 mph and torrential rainfall, Maria resulted in catastrophic damage to infrastructure, housing, and natural landscapes. The hurricane triggered widespread flooding and landslides, exacerbating the destruction of roads, bridges, and power lines. An estimated 80% of the island's crop value was lost, severely impacting the agricultural sector [
9,
10].
The most significant and long-lasting consequence of Hurricane Maria was the complete collapse of Puerto Rico’s energy infrastructure. The hurricane knocked out power to nearly 3.4 million residents, plunging the entire island into darkness [
10]. The island’s aging and fragile power grid, already weakened by inadequate maintenance and previous storms, was ill-prepared to withstand such a severe natural disaster. The destruction of the transmission and distribution networks meant that restoring power was a monumental challenge, leading to some areas being without electricity for up to 11 months [
9].
The extensive damage to the energy infrastructure not only hindered immediate recovery efforts but also had severe implications for healthcare, water supply, and communication systems [
9,
10,
11]. Hospitals were forced to operate on limited generator power, impacting the delivery of critical medical services. Water treatment facilities and pumping stations were incapacitated, leading to a scarcity of clean drinking water. The loss of communication networks further complicated coordination and relief efforts, leaving many communities isolated and in dire need of assistance [
11].
2.2. Pre-Hurricane Energy Sources and Infrastructure
Before Hurricane Maria, Puerto Rico's energy landscape was dominated by a centralized power grid heavily reliant on fossil fuels. The Puerto Rico Electric Power Authority (PREPA), the sole provider of electricity on the island, primarily used imported oil, coal, and natural gas for power generation [
12]. Approximately 98% of the island’s electricity was derived from these non-renewable sources, with only about 2% coming from renewable resources like solar and wind [
12].
PREPA’s infrastructure was notably outdated and poorly maintained, contributing to its inefficiency and vulnerability. The centralized grid system, with its dependence on long transmission lines, was prone to failures, particularly during extreme weather events [
12,
13]. The high reliance on imported fossil fuels also made the energy system expensive and subject to the volatility of global fuel prices, adding economic strain to the island’s energy sector [
13]. The limited adoption of renewable energy technologies before the hurricane reflected both policy and infrastructural barriers that hindered the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
2.3. Post-Hurricane Energy Restoration Efforts
The aftermath of Hurricane Maria brought about extensive efforts to restore and improve Puerto Rico's energy infrastructure. Initial recovery efforts were led by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) [
14]. These efforts focused on restoring basic power services through temporary repairs and the deployment of generators. Despite these immediate actions, the restoration process was slow and challenged by logistical difficulties, bureaucratic delays, and the sheer scale of the destruction [
14,
15].
One of the most significant lessons from Hurricane Maria was the vulnerability of Puerto Rico’s centralized power grid. In response, there has been a substantial push towards decentralizing the energy system to enhance resilience and reliability. Decentralized energy systems, such as microgrids, have been proposed and implemented in various areas. Microgrids can operate independently of the main grid and provide localized energy solutions, making them particularly valuable in post-disaster scenarios [
16].
Renewable energy projects have also seen expansion in the wake of the hurricane. Solar and wind energy installations have been prioritized to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and to create a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure [
17]. Additionally, there is growing interest in leveraging biomass energy as a viable alternative. Biomass energy, which uses organic materials like agricultural residues and woody biomass, offers a renewable and locally sourced energy option. It can contribute to both energy generation and waste management, addressing multiple challenges simultaneously [
18].
The integration of renewable energy sources into Puerto Rico’s energy mix aims to build a more robust and resilient infrastructure capable of withstanding future natural disasters. By diversifying energy sources and incorporating advanced technologies, Puerto Rico is working towards a more sustainable and secure energy future.
3. Biomass Conversion Technologies
3.1. Overview of Biomass as an Energy Source
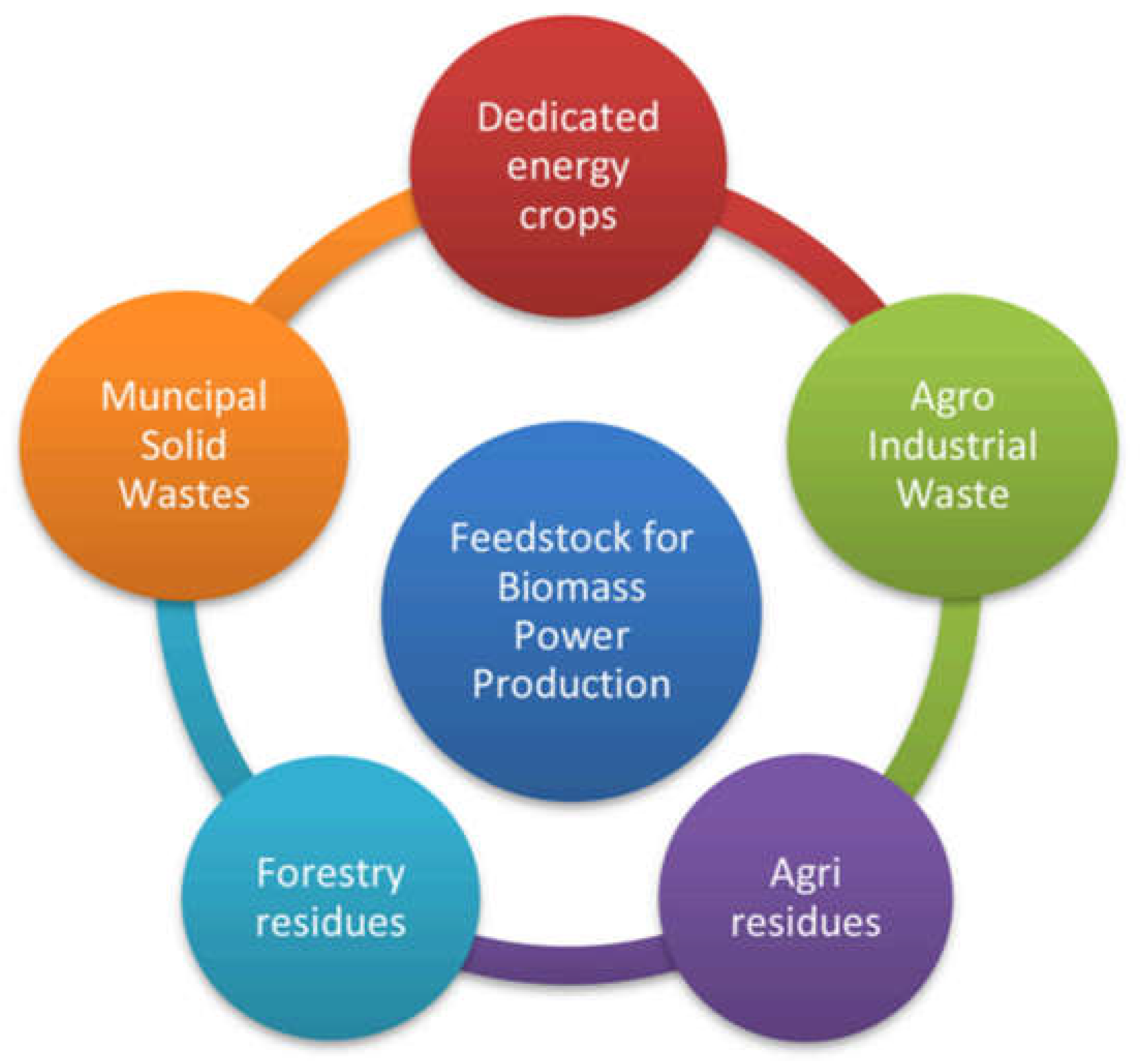
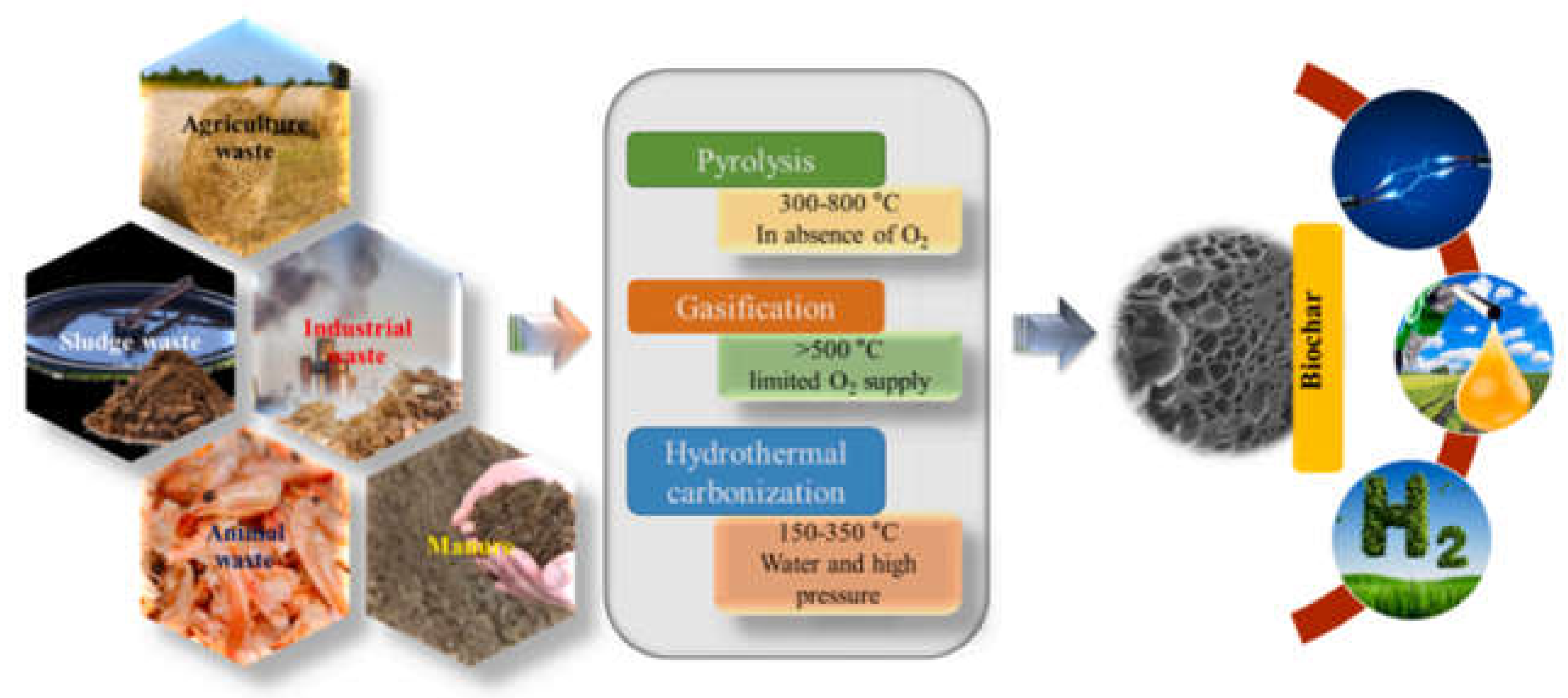
Biomass refers to organic materials that are used as a source of energy. These materials include a wide range of biological matter, which can be categorized into three main types: woody biomass, agricultural residues, and municipal solid waste (MSW) [
19,
20] (see
Figure 2).
Woody biomass includes wood chips, sawdust, forest residues, and dedicated energy crops like willow and poplar [
21]. This category is a significant source of biomass due to its high energy content and availability from forestry operations and wood processing industries. The energy density of woody biomass makes it an efficient fuel source, and its availability from sustainable forestry practices ensures a continuous supply [
21].
Woody biomass is derived from various sources including logging residues, thinnings, and mill residues. Energy crops like willow and poplar are specifically grown for energy purposes, contributing to a sustainable supply. Woody biomass is characterized by its high lignocellulosic content, which provides substantial calorific value when used for energy production [
21].
Agricultural residues are by-products of agricultural activities, such as crop residues (e.g., corn stover, wheat straw) and animal manure [
22]. These residues are abundantly available and can be used for energy production without affecting the food supply. Utilizing agricultural residues helps in managing waste and improving overall agricultural sustainability [
22].
Crop residues include the non-edible parts of crops, such as stalks, leaves, and husks. Animal manure, another form of agricultural residue, can be processed through anaerobic digestion to produce biogas [
22]. The use of agricultural residues for energy not only provides a renewable energy source but also helps in reducing waste and greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural activities [
22].
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) includes organic components of household and industrial waste, such as food waste, paper, and yard clippings [
23]. MSW offers the dual benefit of waste management and energy production. By converting MSW into energy, municipalities can reduce landfill use and generate renewable energy [
23].
The organic fraction of MSW, which includes biodegradable materials, can be converted into energy through processes like anaerobic digestion and incineration. This conversion not only helps in managing urban waste but also reduces methane emissions from landfills, contributing to climate change mitigation [
23].
Biomass energy, derived from renewable organic materials, offers several advantages, including sustainability, carbon neutrality, and versatility in energy production. It plays a significant role in waste reduction by utilizing waste materials, and its use supports local economies through job creation in collection and transport [
23]. However, challenges such as the logistical difficulties of biomass collection and transportation, lower energy efficiency compared to fossil fuels, and potential competition with food crops for land use present significant obstacles. Additionally, the environmental impact of biomass production requires careful management to avoid issues like deforestation and biodiversity loss.
Table 1 shows a summary of the advantages and challenges of biomass energy.
3.2. Conversion Technologies
Direct combustion is the simplest and most common method of biomass conversion [
24]. It involves burning biomass in the presence of oxygen to produce heat, which can be used directly for heating or to generate electricity via steam turbines. The heat generated from combustion can also be utilized in combined heat and power (CHP) systems, which enhance overall energy efficiency by simultaneously generating electricity and useful thermal energy [
24]
This process is straightforward and well-established, making it a widely used method for energy production from biomass. One of the primary advantages of direct combustion is its flexibility, as it can utilize a wide variety of biomass types, including wood, agricultural residues, and waste materials. This versatility allows it to be applied in different contexts, ranging from small-scale residential heating to large-scale industrial power generation, thus offering scalability in deployment [
24].
However, direct combustion has certain limitations. The process can produce pollutants such as particulate matter (PM), carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which may have adverse environmental and health effects [
25]. To mitigate these impacts, modern combustion systems often incorporate emission control technologies. Despite these advancements, direct combustion generally exhibits lower energy efficiency compared to other biomass conversion methods, such as gasification or anaerobic digestion. The efficiency can, however, be improved by utilizing advanced combustion technologies and integrating CHP systems, which optimize energy utilization by capturing and using both heat and power generated during combustion [
25].
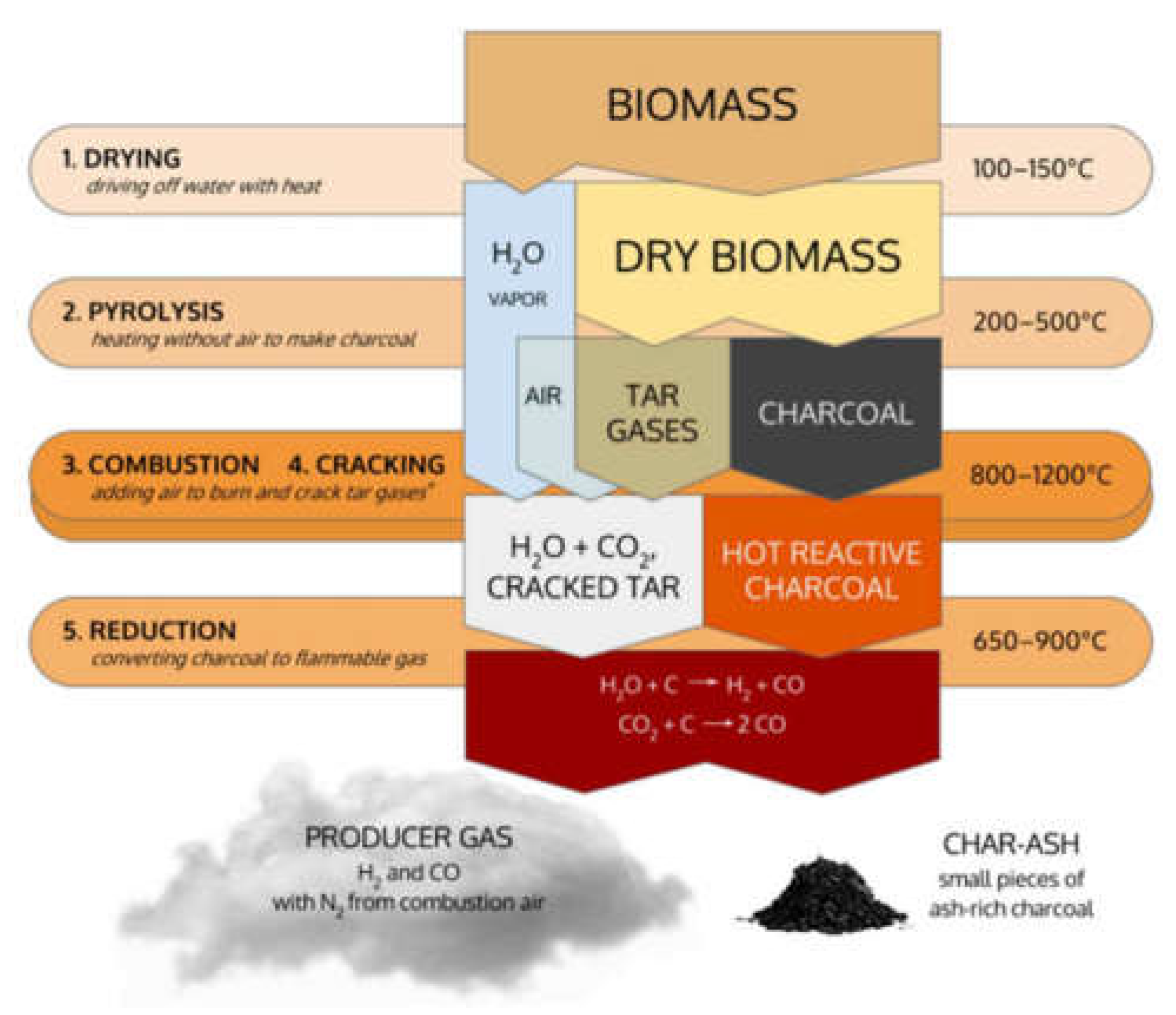
Gasification converts biomass into syngas (a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H
2), and methane (CH
4) by reacting it with a controlled amount of oxygen and/or steam at high temperatures (typically 700-1,200°C) [
26]. The syngas produced can then be used for electricity generation, as a fuel for internal combustion engines, or as a feedstock for producing chemicals and biofuels (see
Figure 3). Gasification can achieve higher efficiency and lower emissions compared to direct combustion [
26].
Gasification projects in Puerto Rico have shown promise in utilizing agricultural residues and urban waste for energy production. For instance, the University of Puerto Rico has conducted studies on gasification of sugarcane bagasse and other residues, demonstrating its feasibility and benefits in local energy systems [
27]. These projects have highlighted the potential of gasification to enhance energy security and sustainability on the island by converting local biomass resources into valuable energy products [
27].
Anaerobic digestion involves the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas (mainly methane (CH
4) and carbon dioxide (CO
2) and digestate (a nutrient-rich residue) [
28]. Biogas can be used for heating, electricity generation, or as a vehicle fuel, while the digestate can be applied as a fertilizer. The process typically occurs in a sealed vessel (digester) where the conditions are controlled to optimize microbial activity [
28].
Anaerobic digestion is particularly suitable for managing livestock manure and food waste in Puerto Rico, helping to reduce waste and generate renewable energy. Projects focusing on community-scale digesters have been proposed to support local energy needs and agricultural practices [
29]. These systems can provide a reliable source of energy for rural areas and contribute to sustainable waste management and soil fertility improvement through the use of digestate as fertilizer [
29].
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass in the absence of oxygen, producing bio-oil, syngas, and biochar [
30]. The process operates at temperatures between 300-700°C. Bio-oil can be refined into liquid fuels, syngas can be used for energy generation, and biochar can be used as a soil amendment to enhance soil properties and carbon sequestration [
30].
Pyrolysis is beneficial in post-disaster scenarios due to its ability to process various types of biomass waste into valuable products [
31]. The biochar produced can improve soil fertility, aiding in agricultural recovery, while bio-oil and syngas provide alternative energy sources for communities. Pyrolysis systems can be designed for small-scale, decentralized applications, making them suitable for rural and disaster-affected areas where centralized infrastructure may be compromised [
31].
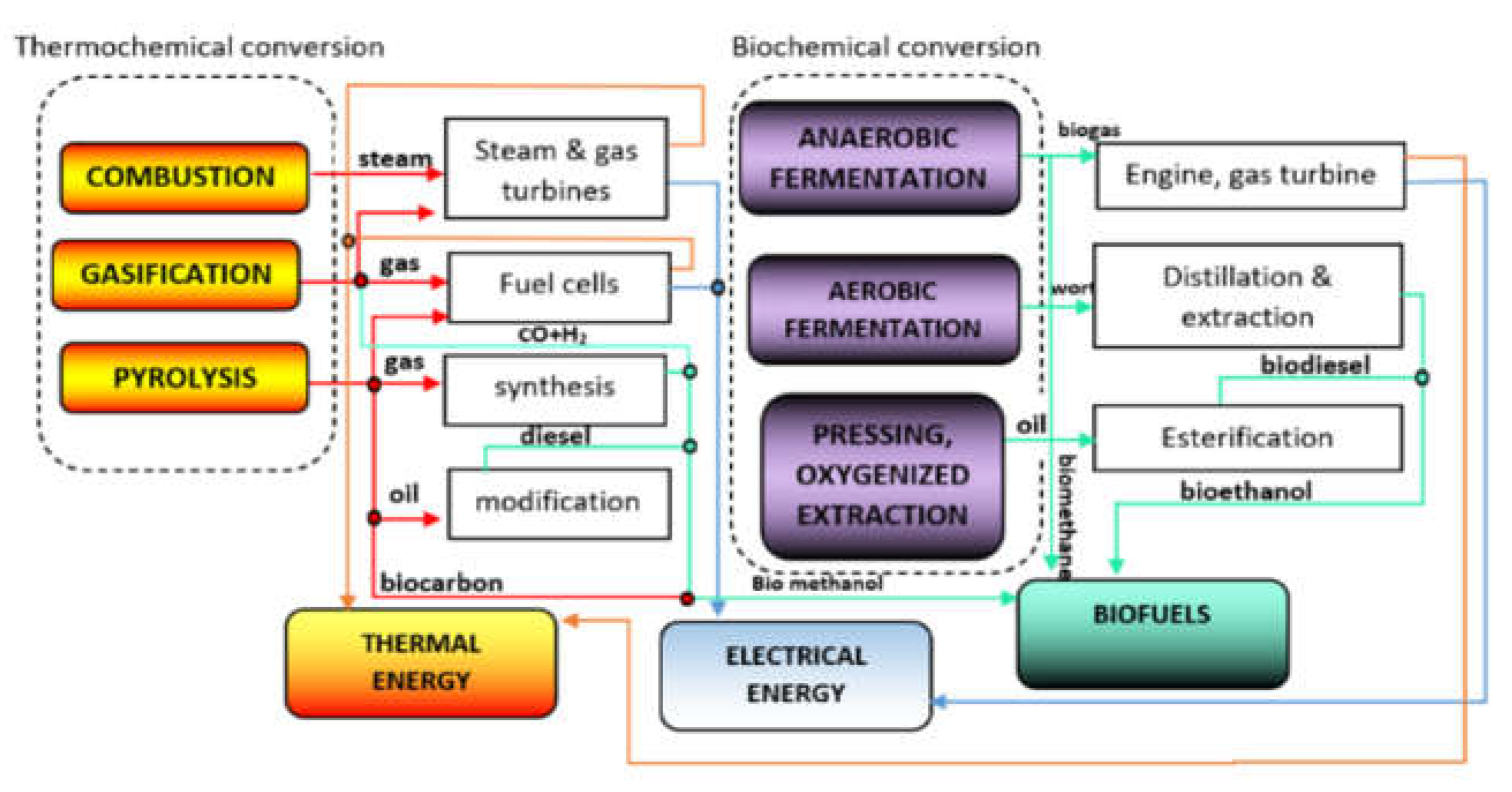
Figure 4 shows an overview of the thermochemical and biochemical conversion processes for energy and biofuel production.
4. Emergency Energy Solutions
4.1. Immediate Post-Disaster Needs
Natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods, often lead to significant disruptions in energy supply, leaving affected regions without power for extended periods. The immediate aftermath of a disaster is characterized by critical energy demands for various essential services, which are vital for both immediate response and long-term recovery efforts: a) Hospitals and clinics require uninterrupted power for the operation of medical equipment, lighting, and refrigeration of medicines and vaccines. Power outages in healthcare facilities can lead to life-threatening situations for patients relying on electrical medical devices and can compromise the storage of essential medicines [
32]. After Hurricane Maria, many hospitals in Puerto Rico struggled to maintain critical services due to prolonged power outages [
33]. b) Reliable energy is essential for maintaining communication networks, including cell towers, emergency response coordination systems, and public information dissemination channels. Effective communication is crucial for coordinating rescue operations, providing updates to the public, and managing relief efforts [
33]. The failure of communication systems can lead to chaos and hinder effective disaster response. c) Energy is needed for the operation of water treatment plants, sewage systems, and water distribution networks. Power outages can result in the failure of these systems, leading to a lack of clean drinking water and proper sanitation, which can cause outbreaks of waterborne diseases [
33]. After Hurricane Maria, many areas in Puerto Rico faced water shortages and sanitation issues, exacerbating the public health crisis [
34]. d) Shelters and relief centers require power for heating, cooling, cooking, lighting, and other essential services to support displaced populations. Providing a safe and comfortable environment in shelters is crucial for the well-being of disaster survivors. Reliable power in these centers ensures that they can operate efficiently and provide the necessary support to affected individuals [
34].
Biomass energy can play a crucial role in meeting these immediate post-disaster energy needs. Biomass systems can be rapidly deployed and utilize locally available organic materials, such as agricultural residues, wood, and organic waste, to generate electricity and heat [
35]. This not only provides a renewable energy source but also aids in waste management, which is often a significant challenge post-disaster. For instance, after Hurricane Maria, the use of wood debris from the storm for biomass energy helped in both generating power and clearing debris.
4.2. Microgrids and Distributed Energy Systems
Microgrids are localized energy systems that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid [
36]. They integrate various distributed energy resources (DERs) such as solar panels, wind turbines, and biomass generators to provide reliable power. Microgrids enhance energy resilience by maintaining power supply during grid outages and can be tailored to meet the specific needs of communities [
36]. By incorporating renewable energy sources and storage systems, microgrids can offer a sustainable and resilient energy solution.
Puerto Rico has seen the implementation of biomass-powered microgrids, especially in the aftermath of Hurricane Maria. These microgrids utilize locally sourced biomass to generate power, thus reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels and enhancing energy security. Notable examples include:
Casa Pueblo: A community-based initiative in Adjuntas, Casa Pueblo has implemented a hybrid solar-biomass microgrid that provides power to critical infrastructure, including a radio station and community center. The system uses biomass gasification to produce syngas, which is then used for electricity generation. This microgrid has been crucial in maintaining community services and enhancing local resilience [
37].
Fajardo Sports Complex: Arensis, an international provider of distributed energy systems, installed a biomass conversion system at the Sports Complex in Fajardo. This microgrid converts woody biomass and hurricane debris into electricity, providing power to the facility, which served as a refugee shelter and distribution center during the disaster. The project demonstrated the potential of biomass energy to provide immediate and reliable power in disaster scenarios [
38].
4.3. Case Study: Arensis Biomass Conversion System
Arensis, an international provider of distributed energy systems, launched a biomass conversion initiative in Fajardo, Puerto Rico, in response to the devastation caused by Hurricane Maria. The project aimed to provide immediate relief by generating electricity from woody biomass and hurricane debris, addressing the urgent need for power in a region where the centralized power grid had been severely damaged [
38]. The system was strategically installed at the Sports Complex in Fajardo, which served as a shelter and distribution center during the disaster, supporting numerous displaced residents and relief operations.
The biomass conversion system implemented by Arensis utilizes advanced gasification technology to convert woody biomass into syngas, a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane, which is then used to generate electricity [
39]. The system includes a debris processor to handle the biomass feedstock and a gasifier to convert the processed biomass into syngas. Each unit of the system can generate 50 kilowatts (kW) of electricity and 120 kW of thermal energy. Its modular design allows for the deployment and stacking of multiple units to scale up the power output, making it adaptable to the needs of larger facilities or multiple smaller sites. This scalability is particularly beneficial in disaster scenarios where energy demands can vary significantly.
The entire biomass conversion system is housed in a 20-foot shipping container, providing a compact and mobile design that allows for rapid deployment and ease of transport, ideal for disaster response situations. These containerized units can be quickly relocated as needed, offering flexible and adaptable energy solutions [
40]. The system's immediate impact was evident as it provided reliable power to the Fajardo Sports Complex, enabling it to function as a critical relief center. This deployment demonstrated the feasibility and effectiveness of biomass energy in disaster response, supporting essential services such as lighting, heating, cooling, and medical equipment operation, thereby significantly improving living conditions for displaced residents and the efficiency of relief efforts.
The Arensis system's use of locally available biomass reduced dependence on imported fuels, which are often scarce and expensive in post-disaster scenarios [
40]. The project also contributed to waste management efforts by converting hurricane debris into valuable energy, showcasing the dual benefits of energy production and waste reduction. This initiative underscored the potential of biomass energy to enhance community resilience and sustainability, with the use of renewable biomass minimizing the carbon footprint and supporting long-term environmental goals.
The success of the Fajardo project set a precedent for scaling up biomass microgrid solutions across Puerto Rico and other disaster-prone regions. The modular and scalable design of the Arensis system facilitates its replication in various settings, from small communities to larger urban areas. Future projects can build on the lessons learned from the Fajardo initiative, such as the importance of local biomass resource assessment, community involvement in planning and operation, and the integration of biomass systems with other renewable energy sources for optimal resilience.
5. Community Impacts
5.1. Economic Benefits
Biomass energy projects can play a vital role in stimulating local economies by creating jobs at various stages, from biomass collection and processing to system installation and maintenance [
41]. These projects provide employment opportunities in both rural and urban areas, thereby enhancing economic activity and stability. In Puerto Rico, the implementation of biomass energy systems has resulted in new job opportunities in sectors such as forestry, agriculture, and engineering. Direct employment is created within the biomass energy sector, including positions in feedstock supply, operation of biomass conversion facilities, and maintenance of energy systems [
41]. For instance, the harvesting and processing of biomass feedstock involves labor-intensive activities, providing jobs for local workers.
Additionally, indirect employment opportunities arise in supporting industries such as equipment manufacturing, transportation, and construction, which benefit from the increased demand for services and products related to biomass energy systems [
42]. Biomass projects can also stimulate local economies by creating new markets for agricultural and forestry residues, thereby increasing the income of farmers and forest owners. The establishment of biomass facilities can lead to the development of local supply chains and encourage investment in related sectors. In Puerto Rico, the use of agricultural residues for energy production has provided additional revenue streams for farmers, contributing to rural economic development [
40].
In the long term, biomass energy projects contribute to economic resilience by diversifying the energy mix and reducing reliance on imported fuels. This diversification protects local economies from global fuel price volatility and enhances energy security. The development of local biomass resources ensures a sustainable and reliable energy supply, fostering economic stability and growth. In Puerto Rico, the integration of biomass energy into the energy portfolio could reduce the island's vulnerability to external energy market fluctuations and promoted energy independence.
5.2. Environmental Impacts
Biomass energy systems play a crucial role in reducing waste and greenhouse gas emissions. By converting organic waste into energy, these projects help divert waste from landfills, thereby reducing methane emissions that result from waste decomposition [
43]. Furthermore, the combustion and gasification processes in biomass energy systems produce lower levels of sulfur dioxide (SO
2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) compared to traditional fossil fuels [
43]. This makes biomass energy a cleaner alternative. Effective waste management is another significant benefit, as biomass energy systems utilize agricultural residues, forest residues, and urban organic waste, thereby reducing landfill use. For instance, in Puerto Rico, biomass energy projects have made use of hurricane debris and agricultural waste, aiding in waste reduction efforts.
Additionally, biomass energy systems can contribute to emission reductions. When managed sustainably, these systems can achieve net-zero carbon emissions, as the CO
2 released during combustion is balanced by the CO
2 absorbed during the growth of the biomass feedstock [
44]. This characteristic of carbon neutrality makes biomass energy a viable option for climate change mitigation. Advanced biomass technologies also include emission control systems, which help minimize the release of harmful pollutants, thereby enhancing the environmental benefits of these systems [
44].
Another important aspect of biomass energy systems is the production of biochar, a byproduct of biomass pyrolysis [
45] (see
Figure 5). Biochar can be used as a soil amendment to enhance soil health and fertility. It improves soil structure, increases water retention, and provides a habitat for beneficial soil microbes [
45]. Additionally, biochar sequesters carbon in the soil, contributing to long-term carbon storage and climate change mitigation. The application of biochar to soils has been shown to improve soil fertility by increasing nutrient availability and enhancing microbial activity, which can lead to higher crop yields and improved agricultural productivity. Moreover, biochar's stable carbon structure allows it to persist in the soil for extended periods, effectively sequestering carbon and reducing atmospheric CO
2 levels, thereby contributing to efforts to combat climate change [
45].
5.3. Social and Health Impacts
Improved access to reliable and sustainable energy through biomass projects can significantly enhance the quality of life for local communities. A stable energy supply supports essential services such as healthcare, education, and communication, which in turn contribute to overall well-being and development [
46]. For instance, in Puerto Rico, biomass energy systems have provided stable power to critical facilities, thereby improving living conditions and bolstering community resilience. In healthcare, reliable energy access ensures that medical facilities can operate efficiently, offering continuous medical services and maintaining the functionality of critical equipment [
46]. In the educational sector, a stable energy supply allows institutions to provide uninterrupted services, creating a better learning environment. Additionally, improved energy access strengthens communication infrastructure, enhancing connectivity and coordination during emergencies and daily activities [
46].
While biomass energy can offer numerous health benefits, it also presents potential concerns. On the positive side, replacing traditional biomass cooking methods with modern biomass energy systems can significantly reduce indoor air pollution, which is a major health risk in many developing regions [
47]. This transition can lead to a decrease in respiratory diseases and an overall improvement in public health. However, biomass combustion can still produce pollutants such as particulate matter (PM), which may have adverse health effects if not properly managed. To mitigate these concerns, it is crucial to implement advanced emission control technologies and promote the use of clean biomass technologies. These measures can help control emissions from biomass combustion, reducing the release of harmful pollutants and ensuring the health benefits of modern biomass systems [
47].
5.4. Community Engagement
Involving local communities in biomass projects is crucial for their success. Active participation and engagement ensure that these projects are tailored to the specific needs and conditions of the community, leading to greater acceptance and sustainability [
48]. When communities are involved in the planning, implementation, and operation of biomass projects, it not only helps in creating solutions that are practical and effective but also builds local capacity and empowers residents. This engagement fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, which is essential for the long-term success of the projects.
Community involvement helps design biomass projects that address specific local challenges and preferences. By engaging the community, the projects can be adapted to meet the unique needs of the area, ensuring they are both practical and effective. Furthermore, involving local residents builds their skills and capacity, empowering them to manage and sustain the projects independently. This empowerment contributes to the long-term sustainability and success of the initiatives.
A notable example of successful community engagement in Puerto Rico is the Casa Pueblo initiative in Adjuntas, as mentioned before. This grassroots organization implemented a hybrid solar-biomass microgrid to power critical community infrastructure. Local residents were involved in every stage of the project, from planning to operation, ensuring that the system met the community's needs and priorities. Casa Pueblo’s approach has been widely recognized for its effectiveness in fostering community resilience and sustainable development. Additionally, various biomass projects in Puerto Rico have conducted workshops and training sessions for local residents. These initiatives have provided the community with the skills and knowledge needed to operate and maintain the energy systems, building local expertise and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the projects. By empowering community members to take active roles in managing and sustaining biomass energy systems, these programs have enhanced local capacity and resilience.
6. Policy and Governance
6.1. Regulatory Framework
Puerto Rico has been actively pursuing renewable energy strategies to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels and improve energy resilience. The regulatory framework supporting biomass energy includes several key policies and initiatives. The Puerto Rico Energy Public Policy Act (Act 17-2019) is a comprehensive energy reform law that aims to transform Puerto Rico’s energy sector by promoting the adoption of renewable energy sources, including biomass [
49]. It sets a target of achieving 100% renewable energy by 2050 and mandates the integration of diverse renewable energy sources into the island’s energy mix. The act also includes provisions for modernizing the energy infrastructure, increasing energy efficiency, and promoting distributed generation systems such as microgrids [
49].
The Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) requires electricity providers to obtain a certain percentage of their power from renewable sources. Biomass is recognized as a qualifying renewable resource under this standard, encouraging utilities to invest in biomass energy projects [
50]. The RPS in Puerto Rico is designed to incrementally increase the share of renewables, providing a structured pathway toward achieving the 100% renewable target set by Act 17-2019. Various financial incentives, such as tax credits, grants, and low-interest loans, are available to support the development of renewable energy projects, including biomass. These incentives are designed to reduce capital costs and make biomass projects more economically viable [
50]. The Puerto Rico Green Energy Incentives Program offers specific benefits to renewable energy projects, helping to lower barriers to entry for biomass energy developers.
Despite the supportive policies, several regulatory challenges and barriers hinder the widespread adoption of biomass energy in Puerto Rico. Obtaining the necessary permits for biomass energy projects can be a lengthy and complicated process. Developers often face bureaucratic delays and inconsistencies in regulatory requirements, which can deter investment. The need for multiple approvals from different agencies can create bottlenecks and increase project timelines. Additionally, strict land use and environmental regulations can limit the availability of suitable sites for biomass facilities [
51]. Ensuring compliance with environmental standards adds to the complexity and cost of project development, as concerns about deforestation, biodiversity loss, and soil degradation require careful site selection and sustainable practices.
Infrastructure limitations also pose a significant challenge. The existing infrastructure may not be adequately equipped to integrate biomass energy systems. Upgrading grid infrastructure to accommodate distributed generation sources, such as biomass, requires significant investment [
52]. The lack of modernized grid infrastructure can impede the efficient integration of biomass energy into the national grid [
53]. Furthermore, the lack of a stable and predictable market for biomass energy can create uncertainty for investors and project developers. Fluctuations in feedstock availability and prices, as well as competition from other renewable sources, can affect the financial viability of biomass projects. A comprehensive strategy to stabilize the market and ensure consistent feedstock supply is necessary to attract investment.
6.2. Recommendations for Policy Makers
To promote the adoption of biomass energy in Puerto Rico and overcome existing barriers, policymakers should consider several key changes. First, streamlining and expediting the permitting process for biomass projects can significantly reduce delays and lower development costs. Establishing clear guidelines and timelines for permit approvals would provide greater certainty for project developers. Additionally, creating a one-stop-shop for permits could streamline the process and reduce bureaucratic obstacles. Enhancing financial incentives, such as tax credits, grants, and subsidies, would make biomass projects more attractive to investors. Providing additional support for research and development could also foster innovation in biomass technologies, while expanded incentives would help mitigate financial risks and lower the upfront costs associated with these projects.
Developing reliable and sustainable biomass feedstock supply chains is essential to ensure a steady supply of raw materials for biomass facilities [
54]. Encouraging partnerships between the agricultural, forestry, and energy sectors can facilitate feedstock production and logistics. Furthermore, developing infrastructure for efficient collection, processing, and transportation of biomass feedstock is crucial [
54]. Establishing long-term power purchase agreements (PPAs) for biomass energy would provide financial stability and predictability for project developers. These contracts would help secure financing and ensure a stable revenue stream, offering investors the confidence needed to invest in biomass energy projects.
Integrating biomass energy into disaster recovery plans is another critical strategy for enhancing energy resilience and sustainability after natural disasters. Policymakers should recognize biomass energy as a vital component of emergency energy plans, developing protocols for the rapid deployment of biomass systems to provide immediate power during disaster recovery. Emergency energy plans should include detailed guidelines for mobilizing biomass resources and setting up temporary biomass power units. Investing in mobile biomass energy units that can be quickly transported to disaster-affected areas is also essential. These units can utilize locally available biomass feedstock, such as hurricane debris, to generate power and support relief efforts. Designed for quick setup and operation, mobile units provide a flexible and adaptable energy solution during emergencies.
Encouraging community-based biomass projects can enhance local energy resilience by engaging communities in the planning and implementation of biomass systems. This involvement ensures that projects meet local needs and priorities, providing localized energy solutions that strengthen overall community resilience to disasters. Promoting collaboration and training is also vital, fostering partnerships between government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private sector partners to develop and implement biomass energy solutions. Offering training and capacity-building programs can equip local communities with the necessary skills to operate and maintain biomass systems, leveraging resources and expertise for the success and sustainability of these projects.
7. Technological Innovations
The field of biomass energy is advancing rapidly, with innovative technologies being developed to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and broaden the range of usable biomass feedstocks [
55]. One key emerging technology is advanced gasification. Innovations in this area, such as plasma gasification and supercritical water gasification, are increasing the conversion efficiency of biomass into syngas [
56]. Plasma gasification utilizes electrically generated plasma to gasify biomass at extremely high temperatures, resulting in cleaner syngas with fewer impurities [
56]. In contrast, supercritical water gasification processes wet biomass in water under supercritical conditions, enabling efficient conversion without requiring biomass drying [
56].
Second-generation biofuels, derived from non-food biomass sources like agricultural residues and waste materials, are gaining popularity due to their potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fossil fuels [
57]. Technologies like cellulosic ethanol production, which transforms lignocellulosic biomass into ethanol, and advanced fermentation processes are enhancing the feasibility and scalability of these biofuels [
57]. These second-generation biofuels offer a sustainable alternative without competing with food production.
Algae-based biomass is another promising area of research. Algae can be cultivated in various environments, including wastewater, and can produce more biofuel per acre than traditional crops [
58]. Optimized algae cultivation systems, such as photobioreactors and open pond systems, are being developed for large-scale production. Additionally, algae can sequester carbon dioxide, contributing to efforts to reduce greenhouse gases [
58]. Research is focused on improving algal strains, optimizing cultivation conditions, and developing cost-effective harvesting and processing techniques.
Technologies that convert biomass into hydrogen are also being explored as part of the transition to a hydrogen economy [
59]. Methods like steam reforming of bio-oil and biogas offer renewable pathways to hydrogen production. Steam reforming involves reacting bio-oil or biogas with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide [
59]. Another promising approach is biomass gasification followed by a water-gas shift reaction and hydrogen separation. Efforts are underway to refine these technologies to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and integrate them with existing energy infrastructure.
Puerto Rico stands to benefit from these technological advancements by incorporating them into its biomass energy strategy. One potential application is the development of waste-to-energy facilities. Advanced gasification and anaerobic digestion technologies can convert municipal solid waste and agricultural residues into electricity and heat, addressing waste management challenges while providing renewable energy [
60]. These facilities can enhance waste management sustainability and generate local energy, integrating waste collection, sorting, and conversion processes for maximum efficiency.
Establishing biofuel production plants in Puerto Rico could also reduce dependence on imported fuels and improve energy security. These plants could use local feedstocks, such as sugarcane bagasse and corn stover, to produce ethanol and other biofuels, stimulating the local economy and creating jobs [
61]. Microalgae cultivation, leveraging coastal and wastewater resources, offers another sustainable biomass source for biofuel production and carbon sequestration [
62]. Puerto Rico's favorable climate and coastal resources are well-suited for large-scale algal biomass production, which could integrate into the existing fuel supply chain while contributing to wastewater treatment and carbon capture.
Finally, implementing biomass-to-hydrogen technologies could support Puerto Rico's shift towards a hydrogen economy, providing a clean energy carrier for various applications, including transportation and industrial processes. Biomass-derived hydrogen could be utilized in fuel cells for clean electricity generation or as a fuel for hydrogen-powered vehicles, diversifying Puerto Rico's energy portfolio and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
7.1. Scaling Up and Replicability
There are significant opportunities to expand biomass projects in Puerto Rico and replicate successful models in other regions. One key area for growth is in developing comprehensive feedstock supply chains by engaging local agricultural and forestry sectors [
63]. This involves setting up systems for collecting agricultural residues, forest residues, and organic waste from urban areas. By establishing robust infrastructure for the collection, processing, and storage of biomass, these projects can stabilize feedstock availability, reduce supply chain disruptions, and lower costs. Collaborative efforts with local farmers and foresters can provide them with additional revenue streams, fostering economic development.
Creating integrated energy systems that combine biomass with other renewable sources, such as solar and wind, can also enhance energy reliability and resilience [
64]. These hybrid systems can ensure continuous power supply, even during grid outages. For instance, solar panels and wind turbines can generate electricity during favorable weather conditions, while biomass systems can provide backup power when solar or wind energy is insufficient. The integration of battery storage with these hybrid systems can further guarantee a stable and reliable energy supply, supporting critical infrastructure and enhancing disaster preparedness.
Promoting community-based biomass projects is another avenue to explore. These projects can foster local engagement and ownership, which enhances the sustainability and impact of biomass energy initiatives. Community projects can be specifically designed to meet local needs, ensuring that the benefits of biomass energy directly reach residents. Examples include small-scale biomass plants supplying energy to local communities, agricultural cooperatives converting farm waste into energy, and educational programs raising awareness about biomass energy benefits. Involving local communities in the planning and implementation processes can build trust and ensure the long-term success of these initiatives.
The successful deployment of biomass energy systems in Puerto Rico can serve as a model for other disaster-prone regions. One replicable strategy is the development of mobile biomass units that can be quickly deployed in disaster-affected areas. These units can process locally available biomass, such as debris from hurricanes or agricultural waste, into electricity and heat. The mobility of these units makes them ideal for rapid deployment in emergency situations, providing power to critical facilities when the main grid is down.
Building partnerships with local governments, non-profits, and private sector entities is crucial for tailoring biomass projects to regional needs and conditions. These partnerships can help mobilize resources, secure funding, and ensure regulatory compliance [
65]. Collaborative efforts can also enhance the scalability and replicability of biomass projects by leveraging the expertise and capabilities of different stakeholders. For instance, partnerships with universities can drive research and innovation, while collaborations with non-profits can support community engagement and educational efforts.
Finally, capacity building through training and technical assistance is essential for the successful operation and maintenance of biomass systems, ensuring their long-term sustainability. Training programs can equip local residents with the necessary skills to operate biomass conversion technologies, manage feedstock supply chains, and maintain energy systems. These initiatives can also promote local entrepreneurship, encouraging the development of small businesses that support the biomass energy sector. Ensuring that local communities have the knowledge and resources to sustain biomass projects is crucial for their long-term success and resilience.
7.2. Ongoing Research and Development
Ongoing research in biomass energy is focused on enhancing conversion efficiencies, expanding the range of feedstock options, and reducing environmental impacts [
66]. Key areas of investigation include advanced biochemical conversion processes, such as enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation [
67]. Enzymatic hydrolysis involves breaking down complex carbohydrates in biomass into simple sugars using specific enzymes, which are then fermented by microorganisms to produce bioethanol and other valuable chemicals [
67]. Current research aims to improve enzyme efficiency, reduce costs, and increase the yield of fermentable sugars.
Another area of focus is the development of new thermochemical conversion technologies, including pyrolysis and hydrothermal liquefaction [
68,
69]. Pyrolysis thermally decomposes biomass in the absence of oxygen to produce bio-oil, biochar, and syngas [
68]. Hydrothermal liquefaction, on the other hand, processes wet biomass into bio-oil under high pressure and temperature, making it possible to handle biomass with high moisture content without the need for drying [
69].
Genetic engineering of biomass crops, such as switchgrass and miscanthus, is also a significant research area [
70]. Genetic modifications aim to enhance biomass yield, improve resistance to pests and diseases, and increase the ability of these crops to grow in marginal soils [
70]. This research can lead to the development of more robust and high-yielding energy crops, making biomass energy more sustainable and cost-effective.
There are several areas that require further study to advance the field of biomass energy and fully realize its potential. One of these areas is sustainability assessments, which involves conducting comprehensive life cycle assessments to evaluate the environmental, economic, and social impacts of biomass energy systems [
71] (see
Figure 6). These assessments help identify best practices and mitigate potential negative effects by considering the entire process, from feedstock production to energy generation, including emissions, resource use, and socio-economic impacts.
Integrated waste management is another area needing further exploration [
72]. Research into integrating biomass energy with waste management systems can optimize resource use and reduce waste generation. This integration supports the development of circular economy models, where waste products are reused and recycled, thus minimizing environmental impact [
72]. For example, combining anaerobic digestion with wastewater treatment can produce biogas while treating organic waste.
Lastly, studying the resilience and adaptability of biomass energy systems in the face of climate change and natural disasters is critical [
73]. This research can inform the design of robust and flexible energy systems capable of withstanding extreme conditions. Developing biomass systems resilient to supply chain disruptions, weather extremes, and other challenges is essential for ensuring a reliable energy supply during emergencies.
8. Conclusions
The role of biomass in post-disaster energy solutions is multifaceted and crucial for enhancing resilience in regions prone to natural disasters. Biomass energy provides several benefits, making it an effective option for disaster recovery and long-term energy sustainability. Firstly, biomass energy systems can be quickly deployed to meet immediate post-disaster needs, providing essential power for healthcare facilities, communication systems, water and sanitation infrastructure, and shelters. These systems leverage locally available organic materials, reducing the dependence on imported fuels and aiding in waste management.
Secondly, biomass-powered microgrids and distributed energy systems enhance energy resilience by decentralizing power generation. They can operate independently of the main grid, ensuring a continuous power supply during emergencies. Examples such as the Casa Pueblo initiative and the Arensis biomass conversion system in Puerto Rico highlight the effectiveness of these solutions. Thirdly, technological innovations in biomass energy, including advanced gasification, second-generation biofuels, algae-based biomass, and biomass-to-hydrogen conversion, are increasing efficiency and expanding the range of feedstocks. These innovations hold significant promise for regions like Puerto Rico, seeking sustainable energy solutions.
Fourthly, there are opportunities for scaling up and replicating biomass projects by developing comprehensive feedstock supply chains, creating integrated energy systems, and promoting community-based projects. The success of biomass systems in Puerto Rico can serve as a model for other disaster-prone areas. Finally, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving conversion efficiencies, expanding feedstock options, and minimizing environmental impacts. Key research areas include biochemical conversion processes, thermochemical conversion technologies, and genetic engineering of biomass crops. Further studies are necessary in areas like sustainability assessments, integrated waste management, and system resilience.
The potential of biomass energy to enhance resilience in Puerto Rico is substantial. It not only offers a renewable and sustainable source of power but also supports local economies, reduces waste, and enhances environmental sustainability. By integrating biomass into energy strategies, Puerto Rico can build a more resilient and self-sufficient energy infrastructure capable of withstanding future disasters.
Policymakers should continue to support and enhance regulations that promote biomass energy. Streamlining permitting processes, enhancing financial incentives, and developing long-term contracts can encourage investment and innovation in this sector. Additionally, active community engagement is vital to ensure that biomass projects meet regional needs and preferences, fostering a sense of ownership among residents and enhancing project sustainability. Continued investment in research and innovation is crucial for advancing biomass technologies and addressing existing challenges. Collaboration between academia, industry, and government can drive innovation and bring new solutions to market. By taking these steps, stakeholders and policymakers can fully harness the potential of biomass energy, contributing to a more resilient and sustainable future for Puerto Rico and beyond.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained in the article and are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Barattieri, A.; Borda, P.; Brugnoli, A.; Pelli, M.; Tschopp, J. The Short-Run, Dynamic Employment Effects of Natural Disasters: New Insights from Puerto Rico. Ecological Economics 2023, 205, 107693. [CrossRef]
- Rivera, F.I. Puerto Rico’s Population before and after Hurricane Maria. Popul Environ 2020, 42, 1–3. [CrossRef]
- Kishore, N.; Marqués, D.; Mahmud, A.; Kiang, M.V.; Rodriguez, I.; Fuller, A.; Ebner, P.; Sorensen, C.; Racy, F.; Lemery, J.; et al. Mortality in Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria. N Engl J Med 2018, 379, 162–170. [CrossRef]
- Antar, M.; Lyu, D.; Nazari, M.; Shah, A.; Zhou, X.; Smith, D.L. Biomass for a Sustainable Bioeconomy: An Overview of World Biomass Production and Utilization. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2021, 139, 110691. [CrossRef]
- Falcone, P.M.; Sica, E. Assessing the Opportunities and Challenges of Green Finance in Italy: An Analysis of the Biomass Production Sector. Sustainability 2019, 11, 517. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. Engineering Abiotic Stress Response in Plants for Biomass Production. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2018, 293, 5035–5043. [CrossRef]
- Martinuzzi, S.; Cook, B.D.; Helmer, E.H.; Keller, M.; Locke, D.H.; Marcano-Vega, H.; Uriarte, M.; Morton, D.C. Patterns and Controls on Island-wide Aboveground Biomass Accumulation in Second-growth Forests of Puerto Rico. Biotropica 2022, 54, 1146–1159. [CrossRef]
- Yaffar, D.; Norby, R.J. A Historical and Comparative Review of 50 Years of Root Data Collection in Puerto Rico. Biotropica 2020, 52, 563–576. [CrossRef]
- Cortés, J. Puerto Rico: Hurricane Maria and the Promise of Disposability. Capitalism Nature Socialism 2018, 29, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Kwasinski, A.; Andrade, F.; Castro-Sitiriche, M.J.; O’Neill-Carrillo, E. Hurricane Maria Effects on Puerto Rico Electric Power Infrastructure. IEEE Power Energy Technol. Syst. J. 2019, 6, 85–94. [CrossRef]
- Santos-Burgoa, C.; Sandberg, J.; Suárez, E.; Goldman-Hawes, A.; Zeger, S.; Garcia-Meza, A.; Pérez, C.M.; Estrada-Merly, N.; Colón-Ramos, U.; Nazario, C.M.; et al. Differential and Persistent Risk of Excess Mortality from Hurricane Maria in Puerto Rico: A Time-Series Analysis. The Lancet Planetary Health 2018, 2, e478–e488. [CrossRef]
- Simpson, N.P. Accommodating Landscape-Scale Shocks: Lessons on Transition from Cape Town and Puerto Rico. Geoforum 2019, 102, 226–229. [CrossRef]
- De Onís, C.M. Fueling and Delinking from Energy Coloniality in Puerto Rico. Journal of Applied Communication Research 2018, 46, 535–560. [CrossRef]
- Engelman, A.; Guzzardo, M.T.; Antolin Muñiz, M.; Arenas, L.; Gomez, A. Assessing the Emergency Response Role of Community-Based Organizations (CBOs) Serving People with Disabilities and Older Adults in Puerto Rico Post-Hurricane María and during the COVID-19 Pandemic. IJERPH 2022, 19, 2156. [CrossRef]
- Pullen, L.C. Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria. American Journal of Transplantation 2018, 18, 283–284. [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.H.; Fangzong, W.; Kalwar, B.A.; Iqbal, S. A Review on Microgrids’ Challenges & Perspectives. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 166502–166517. [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.; Naeth, M.A.; Jennings, P.D.; Gamal El-Din, M. Perspectives on Environmental Impacts and a Land Reclamation Strategy for Solar and Wind Energy Systems. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 718, 134602. [CrossRef]
- Tun, M.M.; Juchelkova, D.; Win, M.M.; Thu, A.M.; Puchor, T. Biomass Energy: An Overview of Biomass Sources, Energy Potential, and Management in Southeast Asian Countries. Resources 2019, 8, 81. [CrossRef]
- Saghir, M.; Zafar, S.; Tahir, A.; Ouadi, M.; Siddique, B.; Hornung, A. Unlocking the Potential of Biomass Energy in Pakistan. Front. Energy Res. 2019, 7, 24. [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, N.A.; Chai, Y.H.; Yusup, S. Biomass Energy in Malaysia: Current Scenario, Policies, and Implementation Challenges. Bioenerg. Res. 2022, 15, 1371–1386. [CrossRef]
- Pang, S. Advances in Thermochemical Conversion of Woody Biomass to Energy, Fuels and Chemicals. Biotechnology Advances 2019, 37, 589–597. [CrossRef]
- Koul, B.; Yakoob, M.; Shah, M.P. Agricultural Waste Management Strategies for Environmental Sustainability. Environmental Research 2022, 206, 112285. [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Shahbeig, H.; Popat, K.; Patel, Z.; Vyas, S.; Shah, A.V.; Barceló, D.; Hao Ngo, H.; Sonne, C.; Shiung Lam, S.; et al. Sustainable Management of Municipal Solid Waste through Waste-to-Energy Technologies. Bioresource Technology 2022, 355, 127247. [CrossRef]
- Sivabalan, K.; Hassan, S.; Ya, H.; Pasupuleti, J. A Review on the Characteristic of Biomass and Classification of Bioenergy through Direct Combustion and Gasification as an Alternative Power Supply. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2021, 1831, 012033. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gan, C.; Zhou, J.; Novakovic, V. Performance Analysis of Biomass Direct Combustion Heating and Centralized Biogas Supply System for Rural Districts in China. Energy Conversion and Management 2023, 278, 116730. [CrossRef]
- Safarian, S.; Unnþórsson, R.; Richter, C. A Review of Biomass Gasification Modelling. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2019, 110, 378–391. [CrossRef]
- Laboy-Nieves, E. Energy Recovery from Scrap Tires: A Sustainable Option for Small Islands like Puerto Rico. Sustainability 2014, 6, 3105–3121. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Silva, E.L.; Varesche, M.B.A. Hydrothermal Processing of Biomass for Anaerobic Digestion – A Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2018, 98, 108–124. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Nuñez, J.R.; Castillo Baltazar, O.S. Anaerobic Digestion Technology for Management of Organic Wastes: Latin American Context. In Biogas Production; Balagurusamy, N., Chandel, A.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 39–55 ISBN 978-3-030-58826-7.
- Dhyani, V.; Bhaskar, T. Pyrolysis of Biomass. In Biofuels: Alternative Feedstocks and Conversion Processes for the Production of Liquid and Gaseous Biofuels; Elsevier, 2019; pp. 217–244 ISBN 978-0-12-816856-1.
- Ighalo, J.O.; Iwuchukwu, F.U.; Eyankware, O.E.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Olotu, K.; Bright, O.C.; Igwegbe, C.A. Flash Pyrolysis of Biomass: A Review of Recent Advances. Clean Techn Environ Policy 2022, 24, 2349–2363. [CrossRef]
- Olatomiwa, L.; Blanchard, R.; Mekhilef, S.; Akinyele, D. Hybrid Renewable Energy Supply for Rural Healthcare Facilities: An Approach to Quality Healthcare Delivery. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments 2018, 30, 121–138. [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.R.; Voyles, C.; Williams, K.D.; Smith, E.; Chilton, M. Colonial Neglect and the Right to Health in Puerto Rico After Hurricane Maria. Am J Public Health 2020, 110, 1512–1518. [CrossRef]
- Joshipura, K.J.; Martínez-Lozano, M.; Ríos-Jiménez, P.I.; Camacho-Monclova, D.M.; Noboa-Ramos, C.; Alvarado-González, G.A.; Lowe, S.R. Preparedness, Hurricanes Irma and Maria, and Impact on Health in Puerto Rico. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2022, 67, 102657. [CrossRef]
- Gital, Y.; Bilgen, B. Resilient Strategies for Managing Supply and Facility Disruptions in a Biomass Supply Chain. Applied Energy 2024, 372, 123808. [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.A.P.; Madureira, A.G.; Moreira, C. A View of Microgrids. In Advances in Energy Systems; Lund, P.D., Byrne, J., Haas, R., Flynn, D., Eds.; Wiley, 2019; pp. 149–166 ISBN 978-1-119-50828-1.
- Massol Gonz�lez, A. Casa Pueblo: A Puerto Rican Model of Self-Governance; Lever Press: Ann Arbor, MI, 2022; ISBN 978-1-64315-034-5.
- Wallsgrove, R.; Woo, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Akiba, L. The Emerging Potential of Microgrids in the Transition to 100% Renewable Energy Systems. Energies 2021, 14, 1687. [CrossRef]
- Jeffers, R.; Baca, M.; Wachtel, A.; DeRosa, S.; Staid, A.; Fogleman, W.; Outkin, A.; Currie, F. Analysis of Microgrid Locations Benefitting Community Resilience for Puerto Rico; 2018; p. SAND--2018-11145, 1530167, 669609;
- Doukas, H.; Spiliotis, E.; Jafari, M.A.; Giarola, S.; Nikas, A. Low-Cost Emissions Cuts in Container Shipping: Thinking inside the Box. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment 2021, 94, 102815. [CrossRef]
- Drożdż, W.; Bilan, Y.; Rabe, M.; Streimikiene, D.; Pilecki, B. Optimizing Biomass Energy Production at the Municipal Level to Move to Low-Carbon Energy. Sustainable Cities and Society 2022, 76, 103417. [CrossRef]
- Hung, N.T. Effect of Economic Indicators, Biomass Energy on Human Development in China. Energy & Environment 2022, 33, 829–852. [CrossRef]
- Sri Shalini S.; Palanivelu K.; Ramachandran A.; Raghavan, V. Biochar from Biomass Waste as a Renewable Carbon Material for Climate Change Mitigation in Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions—a Review. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2021, 11, 2247–2267. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Nielsen, C.P.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Yanga, H.; Chen, H. Hybrid Life-Cycle Assessment for Energy Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions of a Typical Biomass Gasification Power Plant in China. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 205, 661–671. [CrossRef]
- Kant Bhatia, S.; Palai, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Kant Bhatia, R.; Kumar Patel, A.; Kumar Thakur, V.; Yang, Y.-H. Trends in Renewable Energy Production Employing Biomass-Based Biochar. Bioresource Technology 2021, 340, 125644. [CrossRef]
- Tezer, Ö.; Karabağ, N.; Öngen, A.; Çolpan, C.Ö.; Ayol, A. Biomass Gasification for Sustainable Energy Production: A Review. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 15419–15433. [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M. Possibility of Utilizing Agriculture Biomass as a Renewable and Sustainable Future Energy Source. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08905. [CrossRef]
- Cavalaglio, G.; Cotana, F.; Nicolini, A.; Coccia, V.; Petrozzi, A.; Formica, A.; Bertini, A. Characterization of Various Biomass Feedstock Suitable for Small-Scale Energy Plants as Preliminary Activity of Biocheaper Project. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6678. [CrossRef]
- Baggu, M.; Burton, R.; Blair, N.; Sengupta, M.; Harris, T.; Barrows, C.; Sky, H.; Gevorgian, V.; Keen, J.; Smith, E.; et al. Puerto Rico Grid Resilience and Transitions to 100% Renewable Energy Study (PR100) (Summary Report); 2024; p. NREL/TP--6A20-88615, 2301688, MainId:89394;
- Kim, J.E.; Tang, T. Preventing Early Lock-in with Technology-Specific Policy Designs: The Renewable Portfolio Standards and Diversity in Renewable Energy Technologies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2020, 123, 109738. [CrossRef]
- Jayarathna, L.; Kent, G.; O’Hara, I.; Hobson, P. A Geographical Information System Based Framework to Identify Optimal Location and Size of Biomass Energy Plants Using Single or Multiple Biomass Types. Applied Energy 2020, 275, 115398. [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, S.G.; Sequeira, T.; Santos, M.; Mendes, L. Biomass-Related Sustainability: A Review of the Literature and Interpretive Structural Modeling. Energy 2019, 171, 1107–1125. [CrossRef]
- Oyekale, J.; Petrollese, M.; Tola, V.; Cau, G. Impacts of Renewable Energy Resources on Effectiveness of Grid-Integrated Systems: Succinct Review of Current Challenges and Potential Solution Strategies. Energies 2020, 13, 4856. [CrossRef]
- Umakanth, A.V.; Datta, A.; Reddy, B.S.; Bardhan, S. Biomass Feedstocks for Advanced Biofuels: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management. In Advanced Biofuel Technologies; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 39–72 ISBN 978-0-323-88427-3.
- Uddin, M.N.; Techato, K.; Taweekun, J.; Rahman, M.M.; Rasul, M.G.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Ashrafur, S.M. An Overview of Recent Developments in Biomass Pyrolysis Technologies. Energies 2018, 11, 3115. [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.; Akram, S.; Liaqat, Z.; Mushtaq, M. Thermal/Photocatalytic Conversion of Sewage Sludge and Biomass to Energy. In Sewage and Biomass from Wastewater to Energy; Inamuddin, Altalhi, T., Luqman, M., Kapuku, J., Eds.; Wiley, 2024; pp. 1–41 ISBN 978-1-394-20431-1.
- Hirani, A.H.; Javed, N.; Asif, M.; Basu, S.K.; Kumar, A. A Review on First- and Second-Generation Biofuel Productions. In Biofuels: Greenhouse Gas Mitigation and Global Warming; Kumar, A., Ogita, S., Yau, Y.-Y., Eds.; Springer India: New Delhi, 2018; pp. 141–154 ISBN 978-81-322-3761-7.
- Rahman, A.; Agrawal, S.; Nawaz, T.; Pan, S.; Selvaratnam, T. A Review of Algae-Based Produced Water Treatment for Biomass and Biofuel Production. Water 2020, 12, 2351. [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.B.; Singh, A.; Bhatnagar, A. A Review on Biomass Based Hydrogen Production Technologies. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 1461–1480. [CrossRef]
- Obileke, K.; Makaka, G.; Nwokolo, N. Recent Advancements in Anaerobic Digestion and Gasification Technology. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 5597. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dien, B.S.; Rausch, K.D.; Tumbleson, M.E.; Singh, V. Improving Ethanol Yields with Deacetylated and Two-Stage Pretreated Corn Stover and Sugarcane Bagasse by Blending Commercial Xylose-Fermenting and Wild Type Saccharomyces Yeast. Bioresource Technology 2019, 282, 103–109. [CrossRef]
- Efroymson, R.A.; Jager, H.I.; Mandal, S.; Parish, E.S.; Mathews, T.J. Better Management Practices for Environmentally Sustainable Production of Microalgae and Algal Biofuels. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 289, 125150. [CrossRef]
- Panoutsou, C.; Singh, A. A Value Chain Approach to Improve Biomass Policy Formation. GCB Bioenergy 2020, 12, 464–475. [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Pham, V.V.; Nguyen, X.P. Integrating Renewable Sources into Energy System for Smart City as a Sagacious Strategy towards Clean and Sustainable Process. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 305, 127161. [CrossRef]
- Horstink, L.; Wittmayer, J.M.; Ng, K.; Luz, G.P.; Marín-González, E.; Gährs, S.; Campos, I.; Holstenkamp, L.; Oxenaar, S.; Brown, D. Collective Renewable Energy Prosumers and the Promises of the Energy Union: Taking Stock. Energies 2020, 13, 421. [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.; Bridgwater, T.; Lea-Langton, A.; Ross, A.; Watson, I. Biomass Conversion Technologies. In Greenhouse Gases Balances of Bioenergy Systems; Elsevier, 2018; pp. 107–139 ISBN 978-0-08-101036-5.
- Saini, J.K.; Himanshu, .; Hemansi, .; Kaur, A.; Mathur, A. Strategies to Enhance Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Biorefinery Applications: A Review. Bioresource Technology 2022, 360, 127517. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Y.; Fan, X.; Tu, R.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, C.C.; et al. Applications of Catalysts in Thermochemical Conversion of Biomass (Pyrolysis, Hydrothermal Liquefaction and Gasification): A Critical Review. Renewable Energy 2022, 196, 462–481. [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Okolie, J.A.; Nanda, S.; Dalai, A.K. A Review of Biomass Resources and Thermochemical Conversion Technologies. Chem Eng & Technol 2022, 45, 791–799. [CrossRef]
- Brandon, A.G.; Scheller, H.V. Engineering of Bioenergy Crops: Dominant Genetic Approaches to Improve Polysaccharide Properties and Composition in Biomass. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 282. [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, I.; Von Cossel, M.; Winkler, B.; Bauerle, A.; Gaudet, N.; Kiesel, A.; Lewin, E.; Magenau, E.; Marting Vidaurre, N.A.; Müller, B.; et al. An Adapted Indicator Framework for Evaluating the Potential Contribution of Bioeconomy Approaches to Agricultural Systems Resilience. Advanced Sustainable Systems 2024, 8, 2300518. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Tester, J.W. Sustainable Management of Unavoidable Biomass Wastes. Green Energy and Resources 2023, 1, 100005. [CrossRef]
- De Paulo Gewehr, L.L.; Deggau, A.B.; Da Silva Neiva, S.; De Andrade Guerra, J.B.S.O. Resilience in the Context of Climate Change. In Sustainable Cities and Communities; Leal Filho, W., Marisa Azul, A., Brandli, L., Gökçin Özuyar, P., Wall, T., Eds.; Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 528–539 ISBN 978-3-319-95716-6.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).