1. Introduction
In the face of escalating climate change concerns and the urgent need for sustainable practices, the intersection of technology and sustainability has become a critical focus across various sectors, including healthcare logistics [
1,
2]. The transportation of medical samples between laboratories, a vital part of healthcare infrastructure, is currently reliant on traditional methods, which contribute significantly to carbon emissions and environmental degradation [
3,
4,
5]. This pressing issue necessitates a reevaluation and optimization of transportation methods within the healthcare sector [
6,
7,
8].
The transportation of medical samples plays a pivotal role in the healthcare ecosystem, serving as the conduit through which crucial diagnostic information is conveyed between laboratories and healthcare facilities [
9,
10]. Swift and reliable sample delivery is not only essential for ensuring timely patient care but also for minimizing preanalytical errors that may arise from sample degradation or mishandling during transit [
11,
12]. Indeed, studies have shown that prolonged transport times and inadequate handling protocols can significantly impact the integrity of medical samples, leading to erroneous test results and potential clinical misinterpretations [
13].
In light of these considerations, the ecological implications of sample transportation methods take on added significance, as the quest for sustainability in healthcare logistics intersects with the imperative of maintaining sample quality and integrity. Traditional transportation modalities, such as combustion cars, have long been the default choice for sample transport, despite their well-documented environmental footprint [
14,
15]. However, the advent of alternative technologies, including drones and electric vehicles, presents an opportunity to reimagine and optimize sample transport in a manner that prioritizes both environmental sustainability and sample integrity.
This study investigates into the multifaceted challenges and opportunities inherent in medical sample transportation, with a keen focus on the ecological impact, efficiency, and sample integrity considerations associated with different transportation modalities. By evaluating key parameters such as CO2 emissions, transport distances, and delivery times, the research endeavors to provide empirical evidence for the establishment of sustainable practices in healthcare logistics.
Operating within the mountainous landscape of two central European countries, the Principality of Liechtenstein and Switzerland, this study aims to capture the complexities of sample transportation across diverse terrains, weather conditions, and logistical challenges. Through a combination of field experiments and data analysis, the research aims to elucidate the trade-offs and synergies between environmental sustainability, operational efficiency, and sample integrity in healthcare logistics.
In addition to its environmental implications, the choice of transportation modality also holds implications for patient care and clinical outcomes. Furthermore, efficient sample transport can enhance healthcare accessibility, particularly in remote or underserved areas where timely diagnostic information is critical for guiding patient management decisions.
Against the backdrop of mounting environmental concerns and evolving healthcare needs, this study endeavors to contribute to the ongoing discourse on sustainable healthcare logistics aimed at fostering a greener, more resilient healthcare system.
2. Materials and Methods
Study Design: This research employed a comprehensive study design to evaluate and compare the environmental impact and efficiency of medical sample transportation methods. The study was conducted in two central European countries, the Principality of Liechtenstein and Switzerland, encompassing diverse terrains and weather conditions.
Sample Transportation Routes: Authorized aerial and road routes were utilized for transporting medical samples between laboratories in the two countries. These routes were selected to mimic real-world scenarios and to capture the complexities of sample transportation across varying geographical landscapes.
Transportation Modalities: A range of transportation modalities was evaluated, including eight types of combustion cars, two types of electric cars, and one drone model. The drone model was selected for its maximal efficiency since it is based on glider technology (hybrid drone, Jedsy.ch) which can transition into a hoovering mode while landing. Each modality was assessed for its environmental impact, efficiency, and suitability for medical sample transportation.
Detailed Specifications of Transportation Modalities
Combustion Cars: Mercedes Vito (2020), Renault Kangoo (2022), Peugeot 2008 (2021), 208 (2020), 308 (2023), VW Polo (2019), Citroen C3 (2022), Skoda Fabia (2019).
Electric Cars: Specific models include Tesla Model 3 (2021) and Nissan Leaf (2020).
Drone: Hybrid drone from Jedsy.ch with glider technology for maximal efficiency, transitioning to a hover mode for landing. (
Table 1)
Aircraft: Operations are performed using the Jedsy Glider. The aircraft configuration features ADS-B IN transceiver, FLARM and Remote ID broadcast. Each aircraft used has a serial number compliant with ANSI/CTA-2063-A-2019, Small Unmanned Aerial Systems Serial Numbers, 2019, according to Article 40(4) of Regulation (EU) 2019/945. Jedsy’s manufacturer code is 1883, assigned by the International Civil Aviation Organization.
Table 1.
Technical data of the drone used:.
Table 1.
Technical data of the drone used:.
| Aircraft type |
Unmanned electric aircraft, capable of vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) and fixed-wing flight. x |
| Dimensions |
35 x 290 x 240 cm [H x W x L] |
| Weight |
18 Kg empty incl. batteries |
| 21 Kg max. gross take-off weight (MGTOW) |
| Propulsion |
Hovering motors: 8x 150Kv motors with 22inch propellers (IP 45 rating) |
| Cruising motors: 2x 360Kv motors with 12inch propellers |
| Avionics |
1x 64 Bit ARM 6 Cores, 6 MB L2 + 4 MB L3, 8 GB RAM, 128-Bit-LPDDR4x 59,7 GB/s |
| 1x 32 Bit ARM, 480MHz, 2MB memory, 512KB RAM |
| 1x 32 Bit ARM, 24MHz, 8KB SRAM (3x Accelerometers/Gyros, 2x Barometers, 2x airspeed sensors, 1x GPS Module) |
| 1x 32 Bit ARM, 480MHz, 2MB memory, 512KB RAM |
| 1x 32 Bit ARM, 72MHz, 64KB SRAM (2x Accelerometers/Gyros, 2x Barometers, 1x GPS Module) |
| Awareness systems |
1x downward-facing awareness systems |
| 2x forward-facing awareness systems |
| 1x LiDAR ground altimeter: downward facing for long range |
| Awareness radios |
1x ADS-B In |
| 1x FLARM in and out |
| 1x remote ID, compliant with FAR Part 89 |
| Connectivity (CON2) |
3x LTE SIM cards slots for three different providers |
| Flight modes |
Multicopter mode and Fixed wing mode |
| Cruise Speed |
59 KIAS (30m/s) |
| Stall Speed (MGTOW) in Fixed Wing mode |
33 KIAS (17m/s) |
| Max Density Altitude |
2438m |
| Max Endurance |
118 minutes |
| Max Wind |
29 KTS (15m/s) |
| Max Precipitation |
Light to moderate |
| Operating time |
DayNight (under dev) |
| Operating temperature |
-20° to 50° C |
| Range |
max 120km, 2min hovering, 3kg payload, 5m/s of head wind, ideal cruising speed, 200m AMSL, no altitude changes or curves, 10% reserve |
| Weather limitations |
suitable for operation in coastal and offshore climate |
| no operation during heavy rain, icing conditions, hail, and thunderstorms |
| Noise Emissions |
While cruising at 60m above ground level: 58dB |
| Delivery methods |
Mailbox docking on balcony or window (under development) |
| Ground landing |
| Customer Privacy |
The video transmitted to the pilot for landing is blurred at the source |
| The recorded flight data is deleted and overwritten after every flight |
Data Collection: Data collection was conducted under various weather conditions, distances, and terrains, as well as different traffic conditions, to ensure the robustness and reliability of the findings in different real-life circumstances. Energy consumption data were meticulously recorded for each transportation modality, and CO2 footprint was calculated according to established methodologies endorsed by the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN). Data on consumption and CO2 footprint of combustion cars were collected using car monitoring data from a period over nine months with over 1′632′500 km driven by 54 cars and eight models (Mercedes Vito (2020), Renault Kangoo (2022), Peugeot 2008 (2021), 208 (2020), 308 (2023), VW Polo (2019), Citroen C3 (2022), Skoda Fabia (2019)). To assess the ecological impact of the electric cars, data was generated by driving transportation routes between laboratories with a total of over 15′300 km over a period of 6 months. The consumption of the electric Car (Tesla Model 3 (2023) and X (2021)) was also monitored by internal consumption monitoring from the car.
Routes: The routes for this experiment were choosen, so a high varriability of different alditudes and terrains could be achieved. Here is to say that implementation and CO2 consumption varries highly between different rountes and is therefore highly individual for every region and country.
Table 2.
Routes travelled in flat terrain.
Table 2.
Routes travelled in flat terrain.
| Name of Route |
Start and Destination |
Start and Destination (GPS) |
| Route 1 |
Buchs SG – Vaduz |
47.166668, 9.466664 - 47.134787, 9.513150 |
| Route 2 |
Zürich Tiefenbrunnen – Zürich Oerlikon |
47.351448, 8.559639 - 47.406385, 8.542571 |
| Route 3 |
Meilen – Zürich |
47.272483, 8.652122 - 47.351448, 8.559639 |
| Route 4 |
Meilen – Rapperswil |
47.272483, 8.652122 - 47.220530, 8.843807 |
| Route 5 |
Chur – Grüsch |
46.856858, 9.517722 - 46.977926, 9.644353 |
| Route 6 |
Buchs SG – Mels |
47.166668, 9.466664 - 47.036573, 9.436659 |
| Route 7 |
Glarus – Walenstadt |
47.036125, 9.065019 - 47.118043, 9.310155 |
| Route 8 |
Buchs SG – Chur |
47.166668, 9.466664 - 46.856858, 9.517722 |
| Route 9 |
Buchs SG – Stephanshorn SG |
47.166668, 9.466664 - 47.446111, 9.410633 |
Table 3.
Routes travelled in mountainous terrain.
Table 3.
Routes travelled in mountainous terrain.
| Name of Route |
Start and Destination |
Start and Destination (GPS) |
| Route 1 |
Buchs SG – Gaflei |
47.166668, 9.466664 - 47.142344, 9.544172 |
| Route 2 |
Meilen – Oetwil am See |
47.272483, 8.652122 - 47.267415, 8.728000 |
| Route 3 |
Lugano - Bidogno |
46.023625, 8.961412 - 46.081164, 8.999985 |
| Route 4 |
Buchs SG - Wildhaus |
47.166668, 9.466664 - 47.202323, 9.349811 |
| Route 5 |
Buchs SG - Malbun |
47.166668, 9.466664 - 47.103642, 9.607433 |
| Route 6 |
Chur - Arosa |
46.856858, 9.517722 - 46.784364, 9.683340 |
| Route 7 |
Saas-Fee - Visp |
46.110250, 7.931477 - 46.297230, 7.874027 |
| Route 8 |
Albula - Bonaduz |
46.663515, 9.575630 - 46.808014, 9.403732 |
| Route 9 |
Davos - Landquart |
46.797116, 9.825824 - 46.961172, 9.566139 |
Comparative and statistical Analyses: Comparative analyses were conducted to quantify the environmental impact of each transportation method. Key parameters such as CO2 emissions, transport distances, and delivery times were analyzed to provide insights into the relative sustainability and efficiency of the transportation modalities. The program MedCalc was used to perform the statistical test for significance (paired T-Test) and to visualize the data with box plots. The visualization apart from the box plots was done with Microsoft excel. For the calculation of the CO2 emission from Cars a 2640 g/L emission was assumed (EPA, United States Environmental Protection Agency). For the CO2 emission from electricity used both by cars and drones the estimated CO2 emission per kilo Watt hour (kWh) was 29.8g (BAG, Federal Office of the Environment FOEN).
Quality Assurance: Rigorous quality assurance measures were implemented throughout the study to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data collected. Standard operating procedures (SOPs) were followed for sample collection, transportation, and analysis, and stringent quality control protocols were employed to minimize potential sources of bias and error.
Ethical Considerations: Ethical considerations were carefully addressed throughout the study to ensure the protection of patient confidentiality and compliance with relevant regulations and guidelines governing medical sample transportation and research involving human subjects. No patient samples were flown by drone, since in this study only compared the ecological impact, and efficiency of drones and different cars.
Table 4.
Flight geography.
Table 4.
Flight geography.
| cruising |
Horizontally |
35m on each side of the Flight Path.
This accounts for inaccuracy of the navigation due to GPS imprecision or meteorological
conditions and allows the aircraft to safely maneuver within the margins of error. |
| cruising |
Vertically |
20m above the Flight Path -> 120m AGL |
| hovering |
Horizontally |
10m on each side of the flight path.
This accounts for the low speed of the aircraft. |
| hovering |
Vertically |
10m above the Flight Path -> 40m AGL
This accounts for the low speed of the aircraft. |
Table 5.
Contingency Volume.
Table 5.
Contingency Volume.
| cruising |
Horizontally |
35m on each side of the Flight Geography.
This conservatively allows the aircraft to automatically initiate the Flight Geography
contingency procedure to stop and hover from a cruise speed of 30m/s (approx. 26m),
considering a positioning inaccuracy of 4m and an extra margin of 5m. |
| cruising |
Vertically |
20m above the Flight Geography -> 150m AGL
assuming 1s of reaction time at 45 deg pitch up at 20m/s + 4m of GPS error |
| hovering |
Horizontally |
10m on each side of the Flight Geography.
This accounts for the low speed of the aircraft. |
| hovering |
Vertically |
10m above the Flight Geography -> 50m AGL
This accounts for the low speed of the aircraft and the flight mode. |
Functionality
The RPIC activates the FTS using a mobile phone app (segregated from the GCS).
The app sends the activation command through the mobile network to the FTS comms module installed on the aircraft (segregated from the C2 link and using a different network provider).
The FTS comms module activates the FTS device.
Once activated, the FTS reroutes the motor and servo inputs to be controlled by the auxiliary Flight Controller which is pre-programmed to:
- 4.
Stabilize and stop the aircraft in Hovering mode as quickly as possible (approx. 4G deceleration)
- 5.
Navigate to the horizontal GPS location where the FTS was triggered in Hovering mode at slow speed (5m/s),
- 6.
Turn into the wind using the weathervane function to let the Cruising motor help in countering the wind more efficiently,
- 7.
Slowly descend at 3m/s or less until touchdown,
- 8.
Disarm the aircraft.
The RPIC can disable the FTS at any time using the same FTS segregated trigger and regain full control of the aircraft (this is done only in case of inadvertent activation).
System Architecture
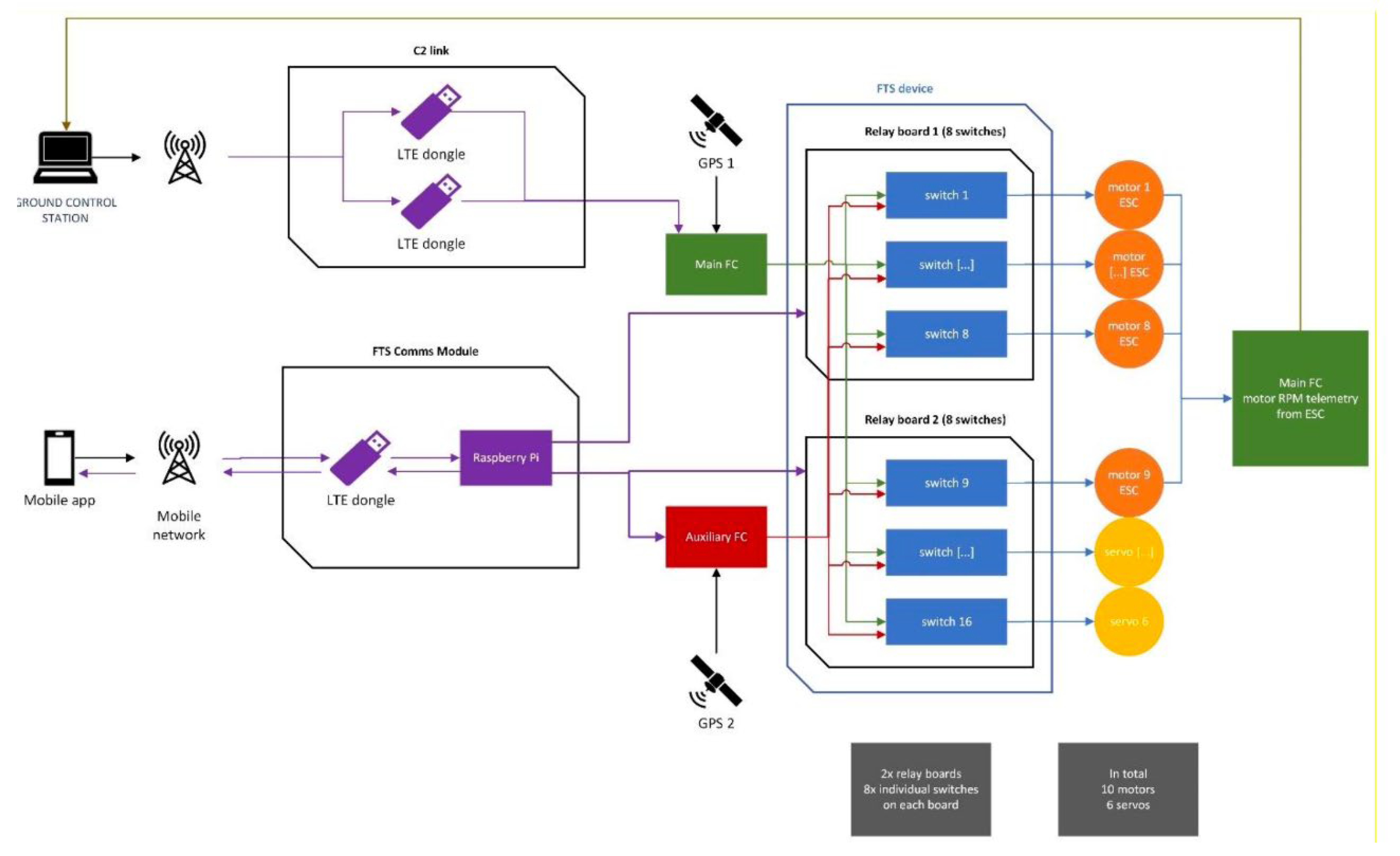
Figure 1.
Functional diagram.
Figure 1.
Functional diagram.
The FTS Comms module features an LTE dongle, to provide connectivity to the mobile network, and a Raspberry Pi, used to manage the connection to the mobile app trigger and send the activation command to the FTS device and the auxiliary FC. The Raspberry Pi transmits its status back to the mobile app, so that the connection to the FTS can be constantly monitored during operations. The main FC has access to all the sensors of the aircraft except for the GPS module 2. The auxiliary FC has access only to the GPS module 2 and its own built-in sensors (IMUs and barometer), all completely segregated from the sensors used by the main FC during normal operations. The FTS device is comprised of 16 switches on two relay boards. Each switch controls one motor or servo command line. Each switch input comes from either the Main or the Auxiliary Flight Controller, determining which of the FCs has command over the motors and the servos: in normal operations the Main FC has control, when the FTS is engaged the Auxiliary FC has control. The motors’ ESC output their telemetry data to the Main FC: their RPM individual values are displayed on the RPIC interface of the Ground Control Station. This functionality is used to verify the functionality of the FTS during the pre-flight checks.
Hardware details
FTS Device - Relay modules (2x)
Product link:
Technical data:
Relay switching current: approx. 8x60mA
Operating voltage: 3.3V to 5V
8x relay (switching power DC: max. 30V / 10A AC: max. 250V / 10A)
Relay with 3 contacts (change switch)
Direct control with microcontroller via digital output
Header pin for control RM 2.54mm
8x 3 screw terminals each for connecting the load
8x status LED for displaying the relay status
4x mounting holes 3mm
Size: 138 x 50 x 19mm
Weight: 105g
FTS Comms module – LTE Dongle
ZTE MF833V USB modem
Product link:
FTS Comms module – Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi Zero WH
Product link:
Technical data:
BCM 2835 SOC @ 1GHz
512MB RAM
On-board wireless LAN - 2.4 GHz 802.11 b / g / n (BCM43438)
On-board Bluetooth 4.1 + HS Low-energy (BLE) (BCM43438)
micro SD slot
mini HDMI type C connection
1x micro-B USB for data
1x micro-B USB for power supply
CSI Camera Connector (requires a separately available adapter cable)
Equipped 40-pin GPIO connector
Compatible with available pHAT / HAT add-on boards
Dimensions: 65 x 30 x 5mm
Auxiliary FC
Holybro Pixhawk 6C
Product link:
Processors & Sensors
FMU Processor: STM32H743
32 Bit Arm® Cortex®-M7, 480MHz, 2MB memory, 1MB SRAM
IO Processor: STM32F103
32 Bit Arm® Cortex®-M3, 72MHz, 64KB SRAM
On-board sensors
Accel/Gyro: ICM-42688-P
Accel/Gyro: BMI055
Mag: IST8310
Barometer: MS5611
Mechanical data
Dimensions: 84.8 * 44 * 12.4 mm
Weight (Plastic Case): 34.6g
Other
Operating temperature: -40 ~ 85°c
Platform:
NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX KI System-on-Modul, NVIDIA®
reComputer J202 - Carrier Board for Jetson Xavier NX/Nano/TX2 NX
3. Results
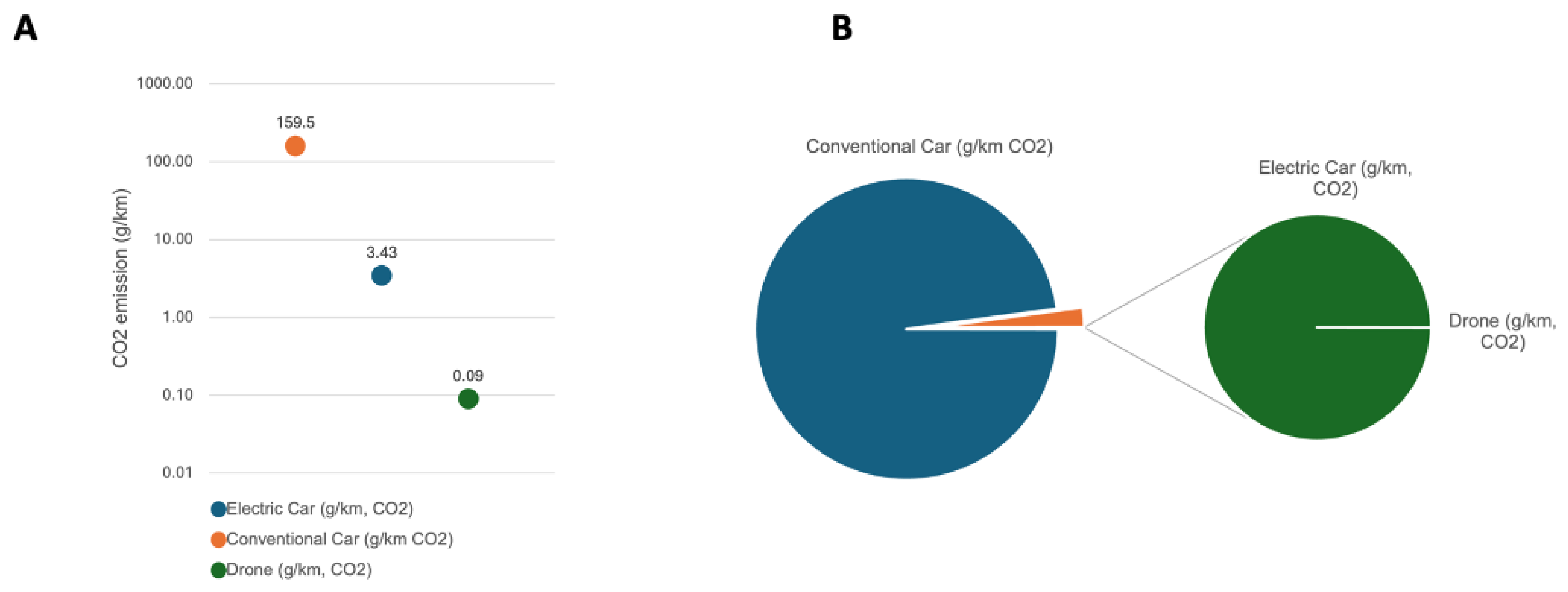
The analysis of CO2 emissions revealed distinct patterns among the transportation modalities. Combustion cars exhibited the highest average CO2 release, emitting approximately 159.5 grams per kilometer (g/km). In contrast, electric cars emitted significantly less CO2, with an average of 3.43g/km, representing a mere 2.15% of the emissions of combustion cars. Drones emerged as the most environmentally friendly option, displaying the lowest CO2 emissions per kilometer at an average of 0.09g/km. This equates to only 0.07% of the emissions of combustion cars and 2.6% of the emissions of electric cars (
Figure 2A & B).
Figure 2.
(A) CO2 emission of combustion cars, electric cars and drones per km travelled on logarithmic scaling. (B): Ratio of CO2 emission from the different transportation vehicles.
Figure 2.
(A) CO2 emission of combustion cars, electric cars and drones per km travelled on logarithmic scaling. (B): Ratio of CO2 emission from the different transportation vehicles.
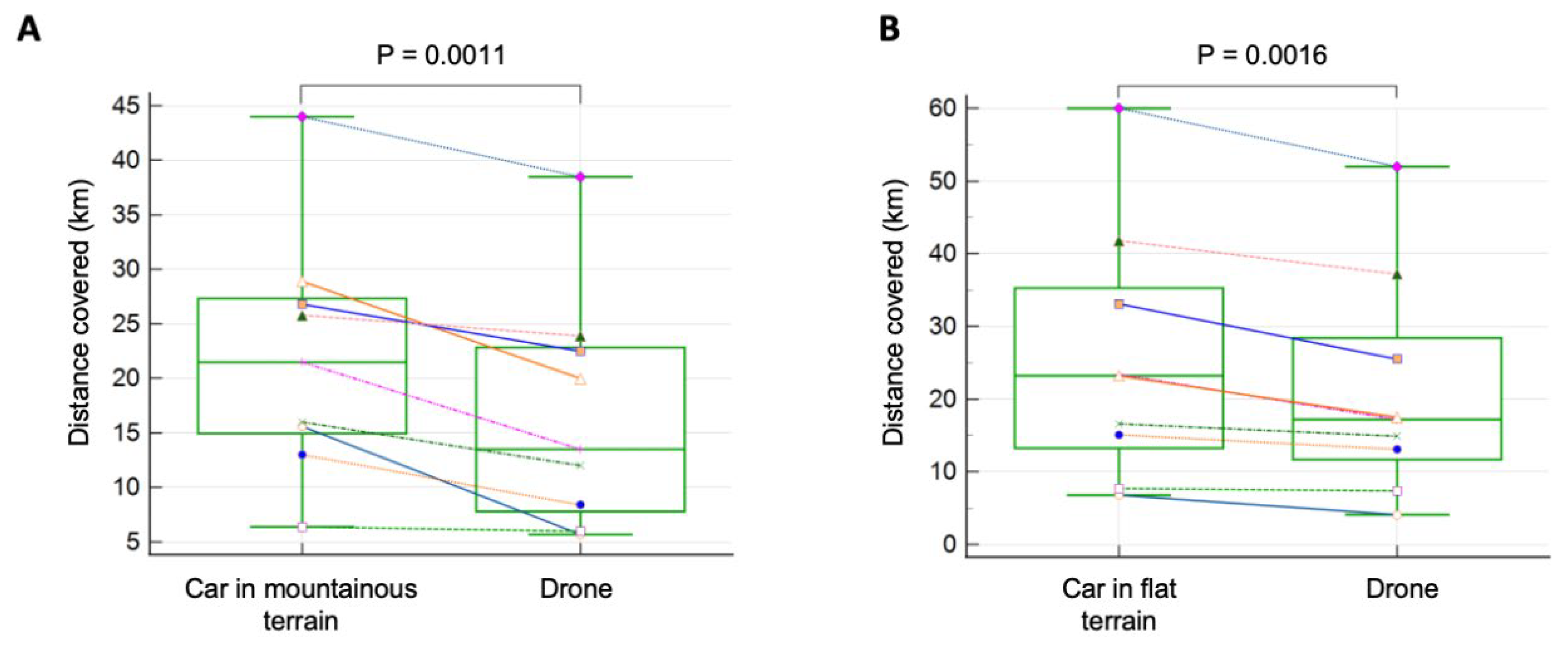
Regarding transport distances, drones exhibited notable efficiency advantages compared to combustion cars and electric cars. On flat terrain, drones could follow a path that was on average 17% shorter than the path taken by cars (P = 0.0016) (
Figure 3B). In mountainous terrain, drones showed an even larger relative reduction of 24% (mean) in transport distances compared to cars (P = 0.0011) (
Figure 3A). These findings highlight the potential of drones to optimize sample transportation routes and minimize environmental impact.
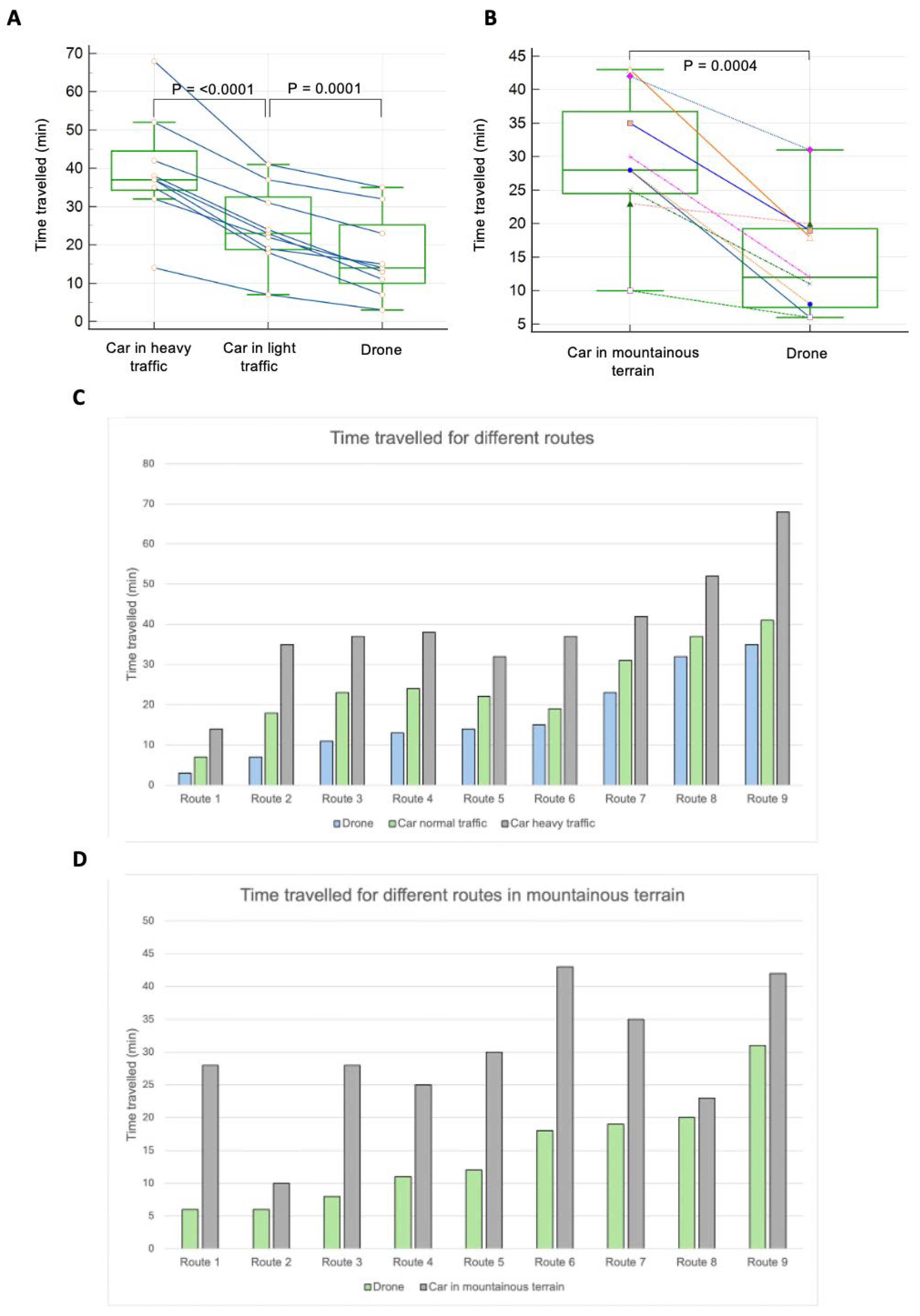
Furthermore, the analysis of delivery times underscored the efficiency gains associated with drone transport. Drones demonstrated faster delivery times compared to combustion cars and electric cars, with relative time savings ranging from 13% to 80% per delivery on 18 different routes tested. Time saved by the drone on flat terrain compared to a car in light traffic was on average 31% (P = 0.0001) and for a car in heavy traffic 57% (P = <0.0001) (
Figure 4A & C). The time saved by the drone over a car in heavy traffic over the nine routes tested ranged from 80% to 45.2%, and for a car in light traffic from 61.1% to 13.5%. Furthermore, a significant time benefit was shown when nine routes in mountainous terrain were compared. The drone was on average 50% faster (P = 0.0004), with a range over the nine routes from 78.6% to 13% quicker delivery (
Figure 4B & D).
4. Discussion
The findings of this study provide valuable insights into the environmental impact and efficiency of different transportation modalities for medical sample transport.
Environmental Impact: The analysis of CO
2 emissions in our study reveals a compelling narrative of the environmental advantages offered by alternative transportation modalities, notably drones [
16,
17,
18]. The stark contrast between the CO
2 emissions per kilometer of drones, combustion cars, and electric cars emphasizes the transformative potential of drone technology in mitigating environmental degradation and advancing sustainability efforts.
Drones emerge as clear frontrunners in terms of environmental impact, exhibiting significantly lower CO
2 emissions compared to traditional combustion cars and electric cars. This disparity underscores the critical role that technological innovation can play in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and curbing the adverse effects of climate change [
19].
The adoption of drone technology in medical sample transportation holds immense promise for reducing the healthcare sector’s carbon footprint and contributing to carbon footprint reduction efforts on a broader scale. By facilitating the transition towards cleaner and more sustainable transportation, drones have the potential to revolutionize not only healthcare logistics but also the broader transportation landscape. Furthermore, the adoption of drone technology in medical sample transportation aligns with the objectives outlined in international agreements such as the Paris Agreement [
20], which seek to limit global temperature rise and mitigate the impacts of climate change. If implemented in a laboratory which operates on a national scale with 54 cars active and over 2′176′000 km driven in one year, which results CO
2 emission of over 426 metric tons, drones can reduce this footprint significantly by only taking over a relatively small number of routes which are the most inefficient in terms of terrain or traffic.
Moreover, the environmental benefits of drone technology extend beyond CO
2 emissions reduction. Drones have the potential to minimize air pollution and habitat disruption associated with conventional transportation methods, further enhancing their environmental credentials [
21].
Efficiency Gains: The efficiency gains observed in our study underscore the transformative potential of drone-based transportation in revolutionizing healthcare logistics. Drones emerge as game-changers, offering unparalleled advantages in terms of transport distances, delivery times, and overall operational efficiency compared to conventional combustion cars and electric cars. This applies not only to routes in difficult terrain, such as mountain routes or routes with poor road conditions, but also to traffic congestion.
One of the most striking findings of our study is the significant reduction in transport distances achieved through drone-based transportation. Drones demonstrated a remarkable ability to navigate complex terrains, including mountainous regions, with relative ease, resulting in transport distances that were on average 24% shorter compared to traditional transportation modalities. This reduction in transport distances is particularly noteworthy as it not only minimizes the time required for sample delivery but also optimizes route efficiency, further reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
Moreover, the delivery times achieved by drones surpass those of conventional transportation methods by a substantial margin. In scenarios characterized by heavy traffic conditions, drones delivered samples up to 80% faster than cars, showcasing their ability to bypass congestion and navigate urban environments with agility and precision. This remarkable efficiency advantage translates into significant time savings for healthcare logistics operations, enabling faster sample processing, diagnosis, and treatment, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes [
22,
23,
24,
25].
The efficiency gains offered by drone-based transportation have far-reaching implications for healthcare logistics operations. By streamlining sample transport processes and minimizing delivery times, drones enhance the overall effectiveness and responsiveness of healthcare systems, particularly in time-sensitive scenarios such as emergency medical situations and critical diagnostic tests. Furthermore, the efficiency advantages of drones translate into tangible benefits for healthcare providers, including cost savings, improved resource allocation, and enhanced service quality [
26,
27].
Practical Implications: The practical implications of our study are far-reaching, offering healthcare organizations invaluable insights into the adoption of drone technology for sample transport management. By demonstrating the environmental and operational benefits of drones, our findings empower healthcare decision-makers to embrace sustainable and efficient transportation modalities that prioritize both environmental stewardship and operational effectiveness.
One of the foremost practical implications of our study lies in the informed decision-making afforded to healthcare organizations regarding transportation modalities. By highlighting the superior environmental performance and operational efficiency of drones compared to conventional combustion cars and electric cars, our findings enable healthcare administrators to make strategic investments in drone technology. This informed decision-making process is crucial for healthcare organizations seeking to align their transportation practices with sustainability goals and regulatory requirements, ultimately contributing to a greener and more socially responsible healthcare sector. The efficiency gains achieved through drone-based transportation translate into reduced operational costs, as fewer resources are expended on fuel, maintenance, and labor associated with conventional transportation methods [
28,
29,
30].
Moreover, the adoption of drone technology has the potential to address healthcare accessibility challenges in remote or underserved areas where traditional transportation methods may be impractical or inefficient [
7,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35]. By overcoming geographical barriers and delivering medical samples swiftly and efficiently, drones enable healthcare organizations to extend their reach and provide essential healthcare services to populations in need. This enhanced healthcare accessibility not only improves health outcomes for underserved communities but also contributes to the overall resilience and inclusivity of the healthcare system.
Limitations and Future Directions: Acknowledging the limitations of our study is crucial for contextualizing the findings and guiding future research efforts aimed at addressing remaining challenges and advancing the field of medical sample transportation. While our study provides valuable insights into the environmental and operational aspects of drone-based transportation, several limitations should be acknowledged to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
In practice, the deployment of drones for medical sample transportation may encounter additional challenges such as airspace regulations, weather conditions which are not as pronounced in central Europe, and logistical constraints. Future research should aim to bridge this gap between controlled experiments and real-world scenarios by conducting field trials in diverse geographical settings and under varying operational conditions.
Moreover, scalability represents a significant challenge that warrants further investigation. While our study demonstrates the feasibility and effectiveness of drone-based transportation for medical samples within the scope of our experiments, scaling up such operations to accommodate larger volumes of samples and broader geographical coverage presents logistical and operational challenges. Future research should explore strategies for scaling drone-based transportation systems, including fleet management, route optimization, and infrastructure development, to ensure the practicality and sustainability of widespread implementation.
Additionally, regulatory considerations represent a critical aspect that must be addressed to facilitate the integration of drones into existing transportation infrastructure. While our study operated within the confines of authorized routes and regulatory frameworks, navigating the complex landscape of aviation regulations, privacy laws, and safety standards poses significant challenges for real-world implementation. Future research should engage stakeholders, policymakers, and regulatory authorities to develop clear and comprehensive guidelines for the safe and responsible deployment of drones in healthcare logistics.
Furthermore, assessing the long-term environmental impact and cost-effectiveness of drone-based transportation represents an important area for future research. While our study provides insights into the immediate environmental benefits and efficiency gains associated with drones, understanding the sustainability of drone operations over extended periods and under different operational scenarios is essential for informed decision-making. Future studies should employ life cycle assessments and cost-benefit analyses to evaluate the environmental, economic, and social implications of adopting drone technology in healthcare logistics.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study provides compelling evidence of the transformative potential of drone technology in revolutionizing medical sample transportation practices. Through a comprehensive analysis of key parameters such as CO2 emissions, transport distances, and delivery efficiency, we have demonstrated the significant environmental and operational benefits offered by drones compared to conventional transportation modalities.
Moreover, our study highlights the efficiency gains afforded by drones in terms of transport distances and delivery efficiency. Drones demonstrate a remarkable ability to navigate diverse terrains and bypass traffic congestion, resulting in shorter transport distances and faster delivery times compared to traditional transportation methods. These efficiency gains translate into tangible benefits for healthcare logistics operations, including cost savings, improved sample integrity, and enhanced patient care outcomes.
The findings of our study underscore the transformative impact of technology on healthcare delivery and logistics management. By embracing drone technology, healthcare organizations can optimize their transportation practices, reduce their environmental footprint, and enhance the overall efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare services. The integration of drones into existing transportation systems represents a paradigm shift in healthcare logistics, offering a sustainable and innovative solution to the challenges faced by traditional transportation modalities.
Furthermore, our study emphasizes the importance of prioritizing environmental sustainability in healthcare logistics operations. As the global community grapples with the urgent need to address climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the adoption of drone technology presents a tangible pathway towards achieving these goals within the healthcare sector. By investing in sustainable transportation solutions such as drones, healthcare organizations can demonstrate leadership in environmental stewardship and contribute to building a greener and more resilient healthcare system for future generations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S, L.R and M.R.; methodology, N.S, L.R.; formal analysis, N:S.; resources, L.R and M.R; data curation, N.S and F.L.; writing—original draft preparation, N.S.; writing—review and editing, N.S, L.R, F.L and M.R.; visualization, N.S.; supervision, L.R.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We would like to extend our deepest gratitude to all those who contributed to this research. Our heartfelt thanks to the laboratory personnel and transportation service providers in the Principality of Liechtenstein and Switzerland for their invaluable support and cooperation during the data collection phase. Special thanks to Lorenz Risch, and Martin Risch for their unwavering guidance and expertise. We are also grateful to the environmental experts and stakeholders who participated in our workshops, offering their insights and helping us prioritize the criteria for evaluating transportation modalities. Their contributions were crucial in shaping the direction and scope of this study. Our appreciation goes to the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN) for providing the established methodologies and tools necessary for the accurate calculation of CO2 footprints. The technical and logistical support received from various institutions and organizations has been instrumental in the successful completion of this research. Lastly, we thank our families and friends for their constant encouragement and understanding throughout this journey. Without their support, this work would not have been possible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
References
- Angelov, S.; Jimenez, C.K.; Wall, V.; O'Croínin, D. An assessment of sustainable transport infrastructure in a national healthcare system. Surg. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berniak-Woźny, J.; Rataj, M. Towards Green and Sustainable Healthcare: A Literature Review and Research Agenda for Green Leadership in the Healthcare Sector. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2023, 20, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawthorne, D.; Wynsberghe, A.R.-V. From HealthDrone to FrugalDrone: Value-Sensitive Design of a Blood Sample Transportation Drone. 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Technology and Society (ISTAS). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, USADATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1–7.
- Lenzen, M.; Malik, A.; Li, M.; Fry, J.; Weisz, H.; Pichler, P.-P.; Chaves, L.S.M.; Capon, A.; Pencheon, D. The environmental footprint of health care: a global assessment. Lancet Planet. Heal. 2020, 4, e271–e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckelman, M.J.; Sherman, J. Environmental Impacts of the U.S. Health Care System and Effects on Public Health. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0157014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshta, N.; Devi, Y.; Chauhan, C. Evaluating Barriers to the Adoption of Delivery Drones in Rural Healthcare Supply Chains: Preparing the Healthcare System for the Future. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2022, 71, 13096–13108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, Sumit, et al. “Implementation of drone based delivery of medical supplies in North-East India: experiences, challenges and adopted strategies.” Frontiers in Public Health 11 (2023): 1128886.
- Magnusson, Sofia, and Pauline Pettersson Hagerfors. “Drone deliveries of medical goods in urban healthcare.” (2019).
- Nybo, Mads, et al. “Sample transportation–an overview.” Diagnosis 6.1 (2019): 39-43.
- Tripathi, Anju, et al. “Collection, storage, and transportation of samples for offsite analysis.” Handbook on Biological Warfare Preparedness. Academic Press, 2020. 133-149.
- Plebani, Mario. “Quality indicators to detect pre-analytical errors in laboratory testing.” The Clinical Biochemist Reviews 33.3 (2012): 85.
- Romero, A.; Cobos, A.; López-León, A.; Ortega, G.; Muñoz, M. Preanalytical mistakes in samples from primary care patients. cclm 2009, 47, 1549–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almatrafi, Alya Aali. “Preanalytical errors: a major issue in medical laboratory.” Acta Sci Med Sci 3.2 (2019): 93-5.
- Šimenc, M. Overview and comparative analysis of emission calculators for inland shipping. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2015, 10, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadimetov, Yusufjan, Dmitriy Ayrapetov, and Вotir Ergashev. “Transport, ecology and health.” Transport 8.4 (2021).
- Goodchild, A.; Toy, J. Delivery by drone: An evaluation of unmanned aerial vehicle technology in reducing CO2 emissions in the delivery service industry. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 61, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidzadeh, E.; Molana, S.M.H.; Soltani, R.; Hafezalkotob, A. Assessing the sustainability of using drone technology for last-mile delivery in a blood supply chain. J. Model. Manag. 2021, 16, 1376–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, S.; Suh, K. A Comparative Analysis of the Environmental Benefits of Drone-Based Delivery Services in Urban and Rural Areas. Sustainability 2018, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.A.; Patrikar, J.; Oliveira, N.L.; Matthews, H.S.; Scherer, S.; Samaras, C. Drone flight data reveal energy and greenhouse gas emissions savings for very small package delivery. Patterns 2022, 3, 100569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agreement, Paris. “Paris agreement.” report of the conference of the parties to the United Nations framework convention on climate change (21st session, 2015: Paris). Retrived December. Vol. 4. No. 2017. Getzville, NY, USA: HeinOnline, 2015.
- Kuczewska, H.; Bartoszewski, B.; Ekiert-Radecka, M. REDUCTION OF AIR POLLUTION AND SOLVING THE PROBLEM OF EFFECTIVE DELIVERY OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS WITH AUTONOMOUS DRONE DELIVERY. 22nd SGEM International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference 2022. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, AustriaDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Peck Palmer, Octavia M., et al. “Recognition of the prehospital preanalytical phase: collaborative efforts between laboratory medicine and emergency medicine to ensure quality testing.” Clinical Chemistry 66.8 (2020): 998-1005.
- Lippi, G.; von Meyer, A.; Cadamuro, J.; Simundic, A.-M.; Null, N. PREDICT: a checklist for preventing preanalytical diagnostic errors in clinical trials. cclm 2019, 58, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakirca, G. The Evaluation of Error Types and Turnaround Time of Preanalytical Phase in Biochemistry and Hematology Laboratories. Iran. J. Pathol. 2018, 13, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morias, Christopher, Greg Palmer, and Abishek Santhakumar. “Pre-analytical errors and their prevention in an emergency department setting.” Australian Journal of Medical Science 44.2 (2023): 46-61.
- Garg, Vipul, et al. “Drones in last-mile delivery: A systematic review on Efficiency, Accessibility, and Sustainability.” Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment 123 (2023): 103831.
- Li, X.; Tupayachi, J.; Sharmin, A.; Ferguson, M.M. Drone-Aided Delivery Methods, Challenge, and the Future: A Methodological Review. Drones 2023, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudbury, Adrienne Welch, and E. Bruce Hutchinson. “A cost analysis of amazon prime air (drone delivery).” Journal for Economic Educators 16.1 (2016): 1-12.
- Lee, Jaihyun. “Optimization of a modular drone delivery system.” 2017 annual IEEE international systems conference (SysCon). IEEE, 2017.
- Shen, Y.; Xu, X.; Zou, B.; Wang, H. Operating policies in multi-warehouse drone delivery systems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 59, 2140–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lim, G.J.; Cho, J.; Côté, M.J. Drone-Aided Healthcare Services for Patients with Chronic Diseases in Rural Areas. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2017, 88, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaaba, A.A.; Ayamga, M. Intricacies of medical drones in healthcare delivery: Implications for Africa. Technol. Soc. 2021, 66, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, G.M.; Isarinade, T.D.M.; Emmanuel, K.M.; Olatunji, D.M.; Aderinto, N.M. Exploring the transformative role of drone technology in advancing healthcare delivery in Africa; a perspective. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 5279–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haula, K.; Agbozo, E. A systematic review on unmanned aerial vehicles in Sub-Saharan Africa: A socio-technical perspective. Technol. Soc. 2020, 63, 101357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, Vanita, and Nalin Luthra. “Medical assistance using drones for remote areas.” Proceedings of International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Applications: ICAIA 2020. Springer Singapore, 2021.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).