1. Introduction
The introduction of polymeric materials, specifically polypropylene, to the market in 1951 [
1], represented a pivotal advancement in the field of materials science and engineering. These polymers have since become integral across a diverse array of industrial applications like automotive, medical, construction, electronics and consumer goods [
2,
3,
4]. The preference for polymeric materials, particularly polypropylene, is based on their outstanding mechanical properties, intrinsic resistance to aging, capability to maintain dimensional stability throughout their lifecycle, superior resistance to crack initiation or propagation, and their suitability for high-volume manufacturing processes such as extrusion and injection molding [
5,
6,
7].
Effective design process of designing and validating component made of polymers in industries requires the usage of simulation methods, including the Finite Element Method [
8]. To make this possible, it is necessary to accurately represent the behavior of plastics under the different loading regimes and to relative them in the numerical material model [
9,
10,
11]. In addition to the commonly known nonlinear behavior of thermoplastics, influence of strain rate, temperature, stress state and loading type [
12,
13,
14,
15], the critical phenomena is the influence of hydrostatic pressure on the yield stress, plastic flow, the destruction criterion [
16,
17,
18]. Studies conducted in the past have clearly demonstrated the occurrence of different elastoplastic properties for loads of different characteristics resulting from tests ranging from compression, through shear, to tension [
19,
20,
21,
22].
One of the widely used constitutive model capable to reproduce the plastic behavior is the linear Drucker-Prager criterion, which makes the transition of the material to the plastic range, i.e. the value of the yield stress, dependent on the value of hydrostatic pressure. Thanks to this, it is possible to distinguish the behavior of polymers under different load conditions, including fact that for most of thermoplastics the yield strength for compression is higher than for tension [
23,
24,
25,
26]. The method originally comes from soil research but it has found wide application for plastics, composites and metals [
27,
28,
29,
30].
This article focuses on the use of the Arcana machine which is widely used when the only possible form of material samples are flat plates of a defined thickness [
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36]. It is necessary to properly cut the plates to obtain a multiaxial state of tension using an appropriate fillet radius at the necking point. An additional verification is a uniaxial compression test with extend criteria to compression state. The obtained material model is finally tested in the Abaqus numerical software to confirm the compliance of the obtained parameters for the Drucker-Prager model and the numerical simulations carried out using it with the actual behavior of polypropylene samples.
2. Material Behavior
Stress tensor (
) according to the matrix form from Equation 1 could be explain using hydrostatic (mean) (
) stress tensor responsible for volumetric change and deviatoric stress tensor (
) cause body shape deviation.
where Kronecker Delta function is defined by:
Dilatation state defined by pressure (
) could be drawn using stress tensor first invariant (
):
Equivalent stress called von Mises (
) is defined by second invariant of deviator state (
):
Thirst invariant of deviator state (
) needed to explain Drucker-Prager criterion could by defined by:
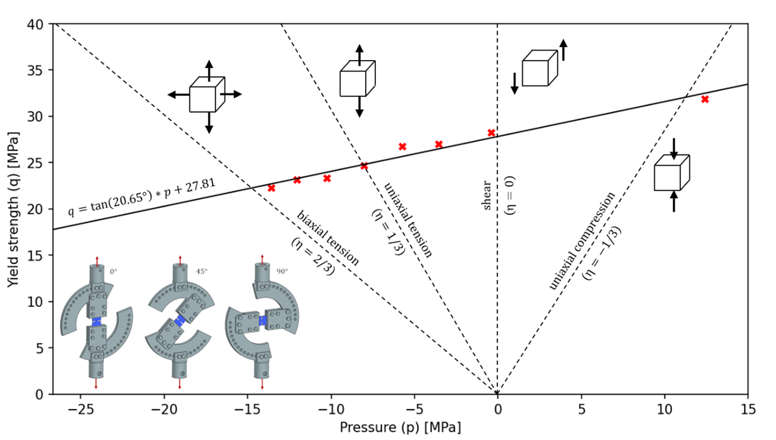
The linear Drucker–Prager criterion commonly used for polymers can be represented in the meridian plane by the yield surface using deviatoric stress factor (
) as a function of hydrostatic pressure (
) as in
Figure 1, where the parameters defining its location are the friction angle (
) and material cohesion (
) according to Equation 8:
where deviatoric stress factor (
) could be defined by Equation 9:
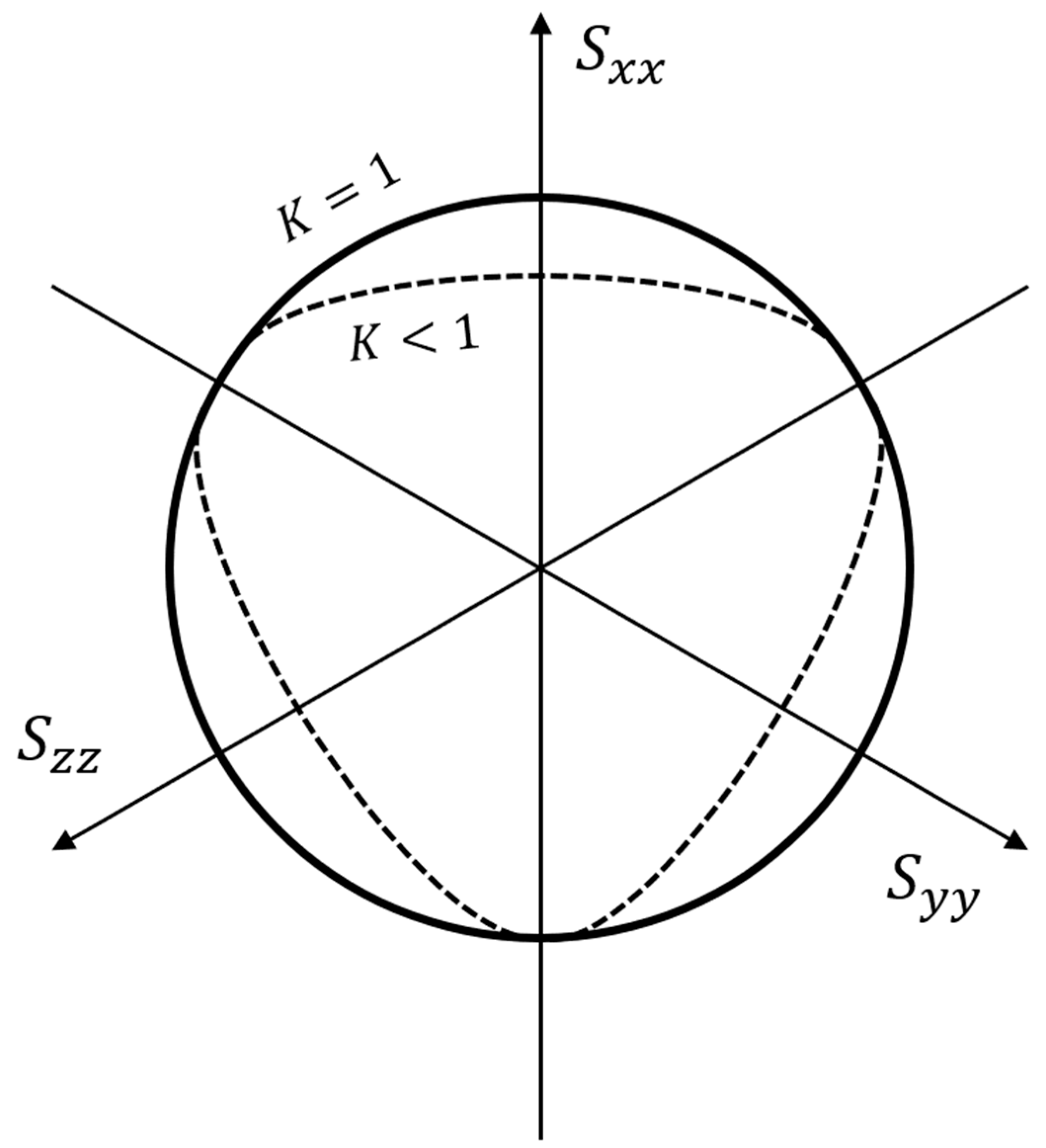
using ratio of yield stress for triaxial tension and compression (
), what could be described on deviatoric plane in
Figure 2. Based on the research on Polypropylene [
22] and due to the limited scope of possible tests on the Arcana machine, a K factor of 1 was assumed. Due to this
on
Figure 1.
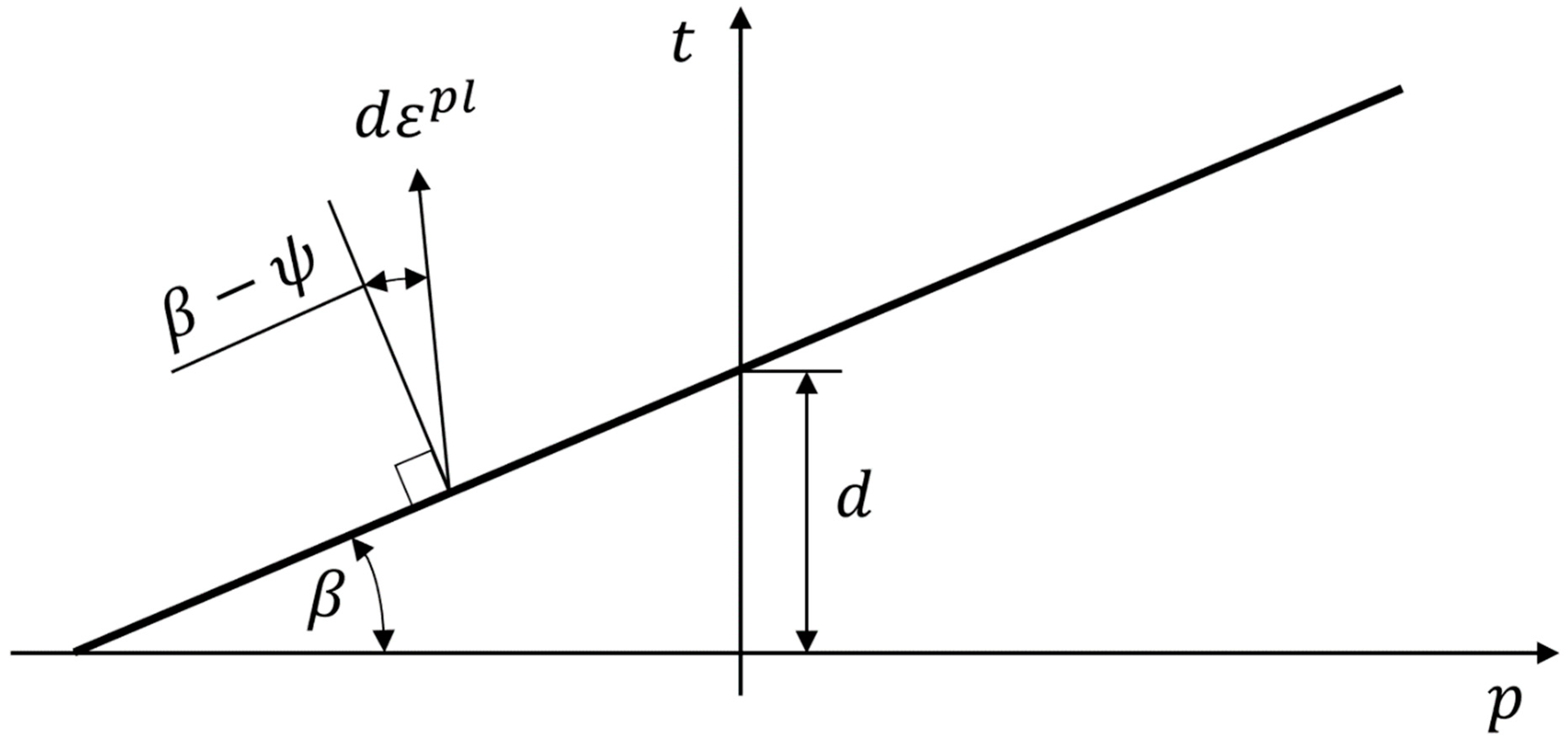
Plastic flow direction (
) for polymer could be defined in Equation 10 by dilatation angle (
) using Poison ration (
) [
37,
38].
In Equation 8:
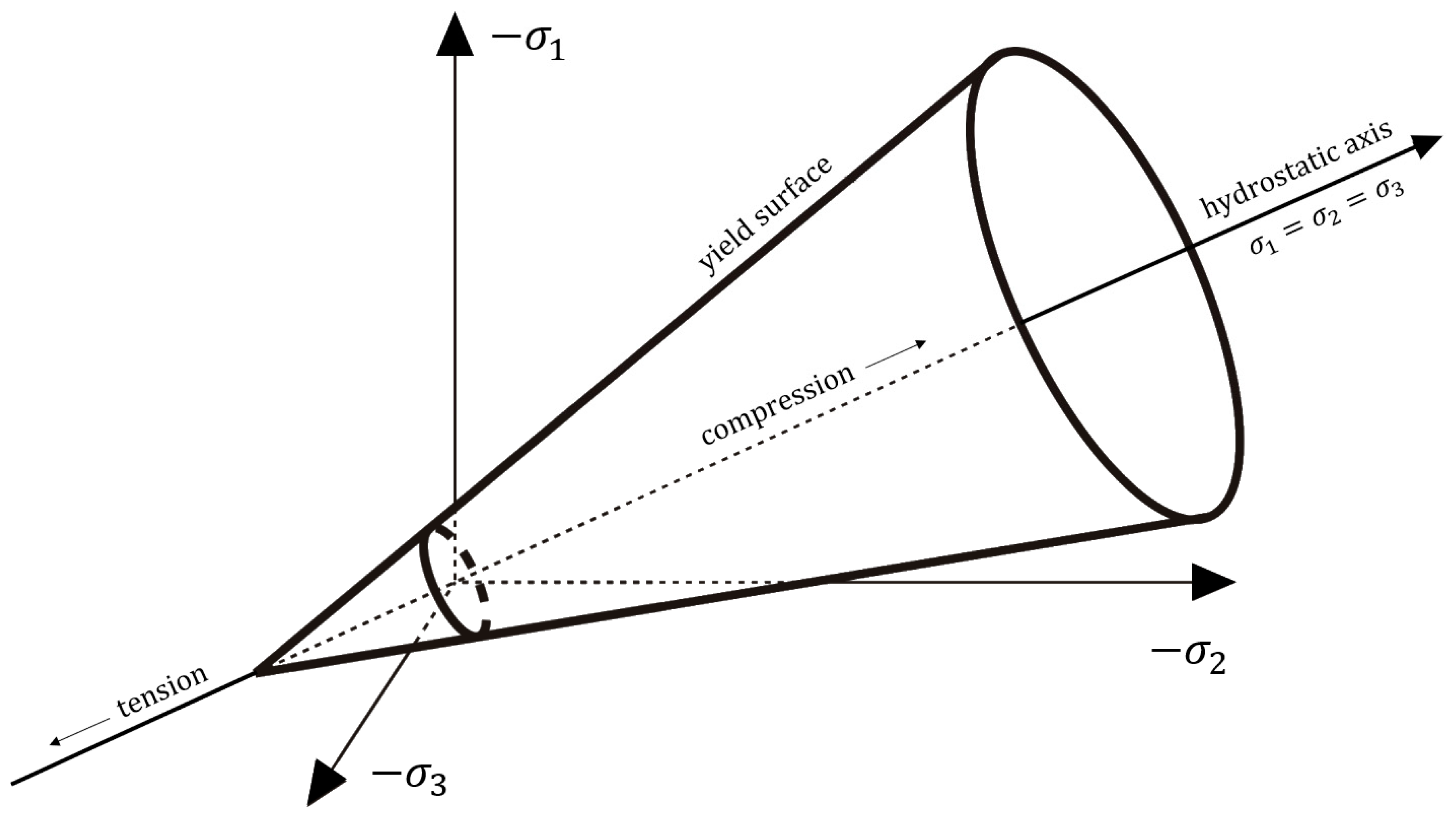
Drucker-Prager yield surface in the reverse principal axes is a cone around hydrostatic axis with a circular cross section for K factor equal to 1 as on
Figure 3.
To clearly determine the loading state of the material, the triaxiality (
) parameter (Equation 12) should be used, the basic values of which are given in
Table 1.
3. Material, Samples and Experimental Techniques
The following tests were performed for thermoplastic Sabic 83MF10 material, universal polypropylene polymer provided by Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (SABIC) and the basic parameters of which are presented in
Table 2. Dilatation angle was calculated based on Equation 2.
Due to the fact that despite the lack of reinforcing inclusions in the material such as fibers, noticeable anisotropy of properties is possible [
41,
42], it was decided to cut samples from the plate far away from the injection points. This allowed to obtain a quasi-random arrangement of molecules.
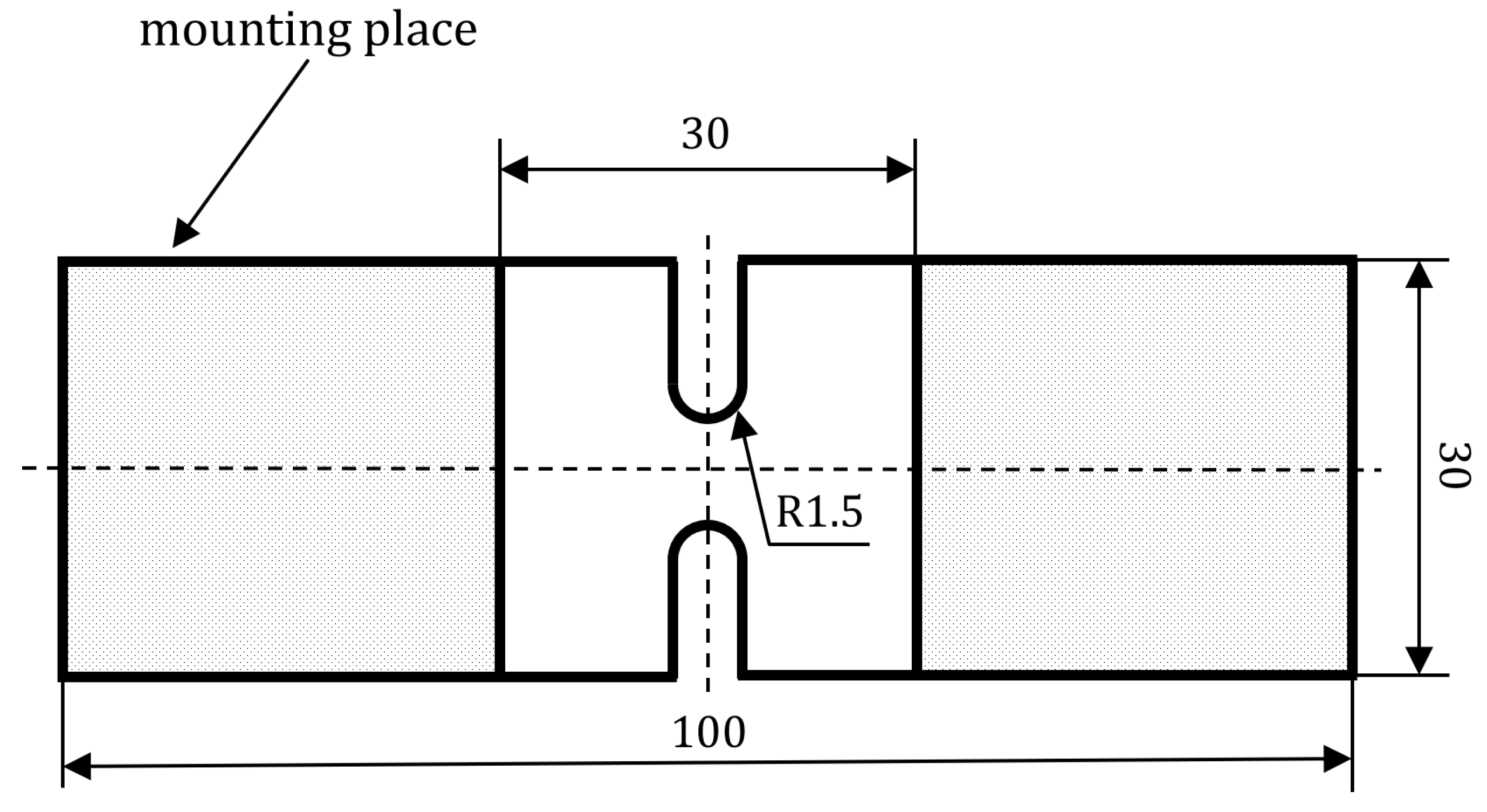
Tension and shear samples subjected to analysis on a Zwick type universal testing machine with Arcana handle was obtained in the form of flat plates received in injection molding process, with a thickness of
. The samples were machine cut with the radius of
and dimensions described on
Figure 4.
The sample for uniaxial compression tests is a single cylinder with a diameter of cut from the previously mentioned plates.
To achieve wide range of triaxiality
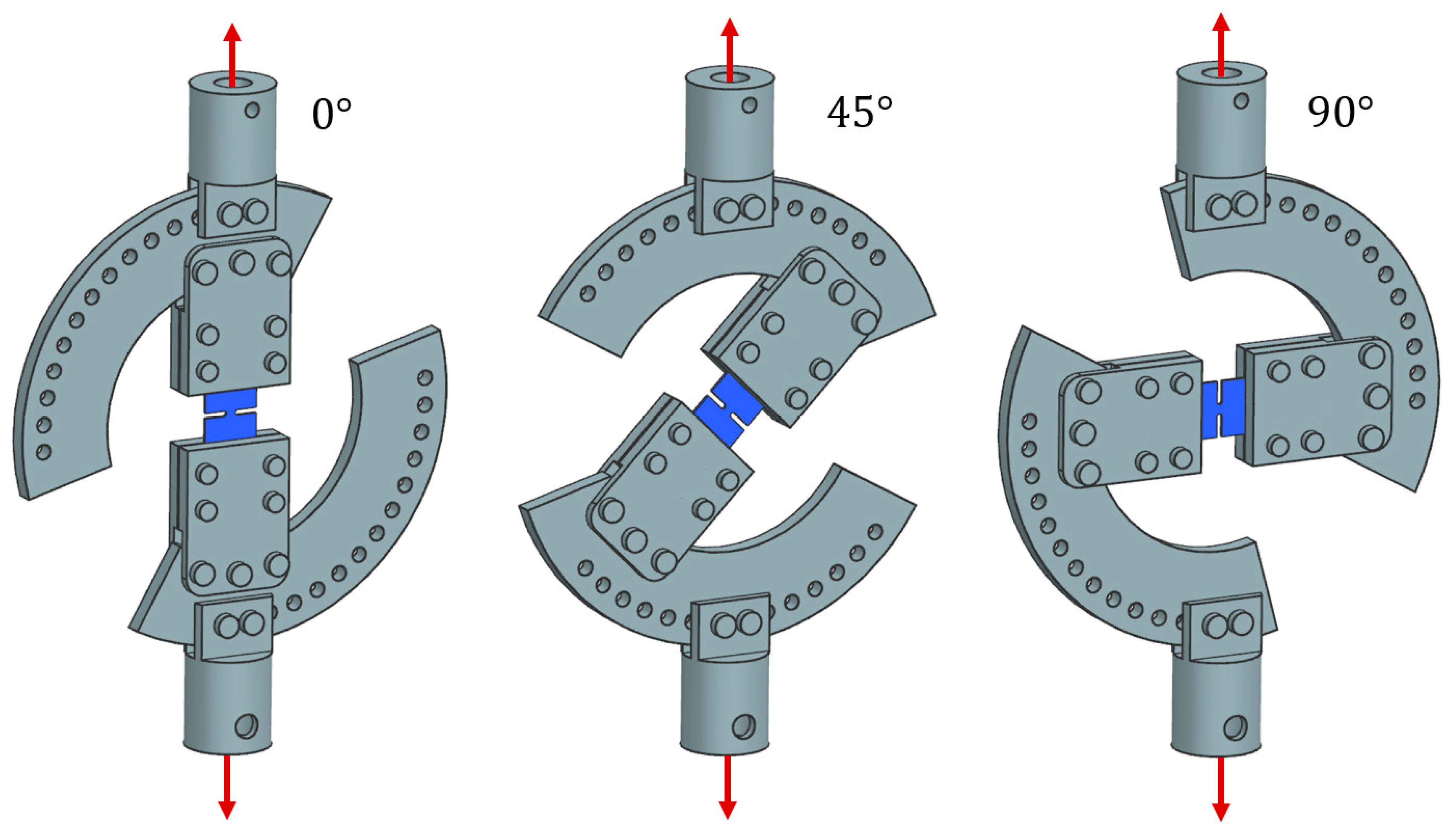
and according to it different load type in stated between tension and shear, the Arcana machine was used (
Figure 5). This type of holder allows to stretch samples at angles from 0 to 90 degrees. It consists of a pair of holders that secure it to the testing machine, two semicircular discs with holes that allow for mounting at 7.5 degrees and holders that grip the tested sample directly. The entire structure is made of aluminum alloy 7075 (Fortal), ensuring high rigidity of the structure.
All test on Arcana machine were performed with constant head travel speed of
which allows to achieve strain rate (
) between
and
during the tests. Due to the selected machine speed it was possible to avoid, on the one hand, the influence of material hardening at high strain rates described e.g. by Cowper-Symonds model [
39,
40] and, on the other hand, the effect of polymer relaxation [
43,
44].
4. Experimental Data Processing and Results
The linear Drucker-Prager criterion was chosen for further calibration due to the impossibility of obtaining results for triaxial tension on flat samples with undercut.
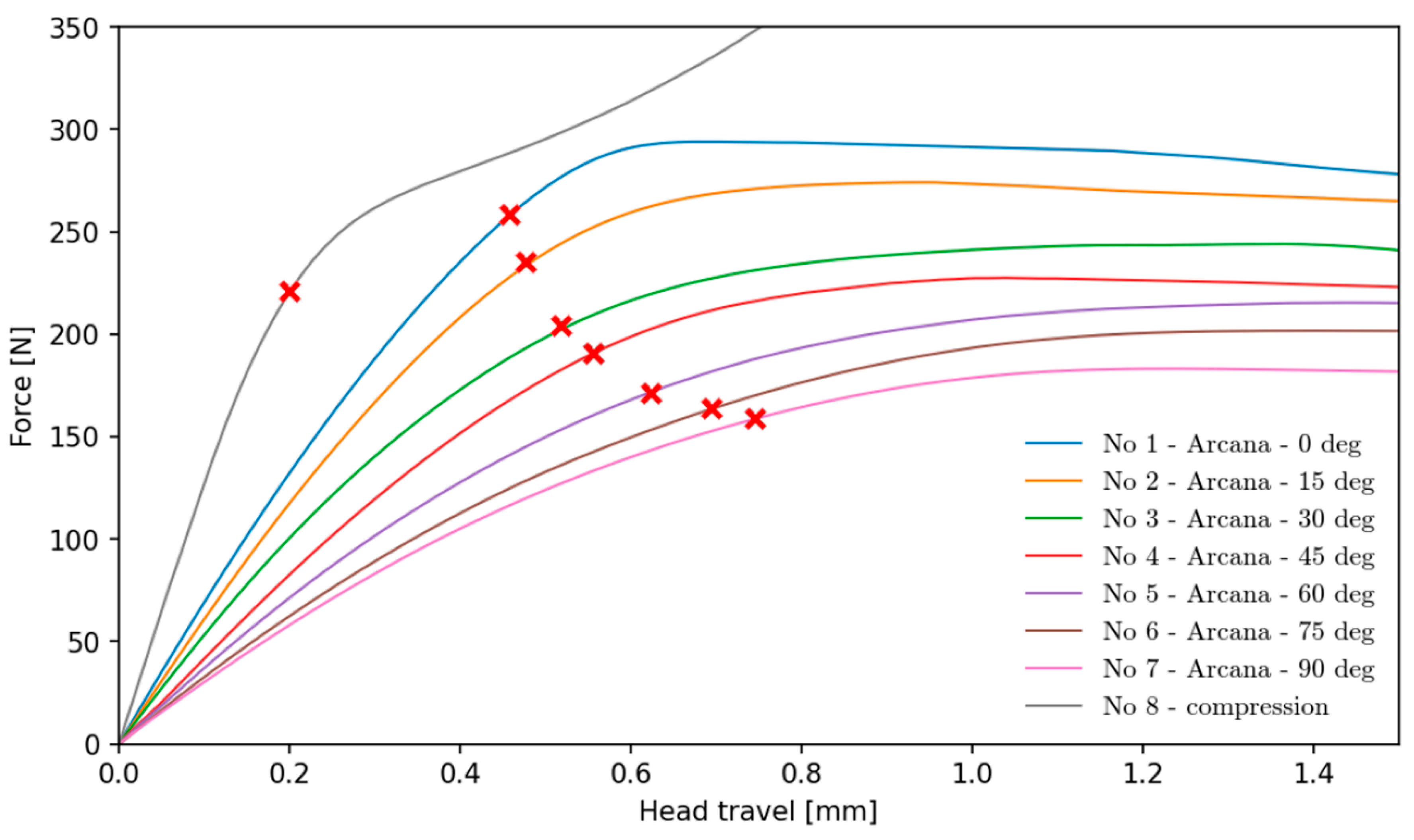
Figure 6 shows the results of tension (and shear) tests on the Arcana machine and the result of the compression test of a cylindrical sample. For each variant, three tests were performed, and two extreme cases (max and min values) in terms of yield strength were rejected from further evaluation.
The following tests were performed to determine the yield strength, which according to ISO 527-1 defines yielding as the first deviation in true stress-strain curve from pure elastic response due to the lack of a distinct yield strength. Force (
) and displacement (
) were measure using Zwick embedded cross-head sensor. The values of triaxiality (
), pressure (
) and equivalent von Mises stress (
) were determined from FEM simulations representing the behavior of the samples based on the calibration of the material curve with the load case as a average value for whole cross section in the critical most strained surface. All results needed for further evaluation were described below in
Table 3.
The larger the angle on the Arcana machine, the lower the yield strength seems to be. This does not reflect the actual parameters, due to the complex stress state, different for each sample. The decreasing apparent stiffness of the sample with increasing angle results from the transition from pure tension to pure shear, where instead of Young's modulus (
), the basic parameter defining elasticity is the Kirchhoff’s (
) modulus, which calculated according to Equation 13 is 2.8 times lower.
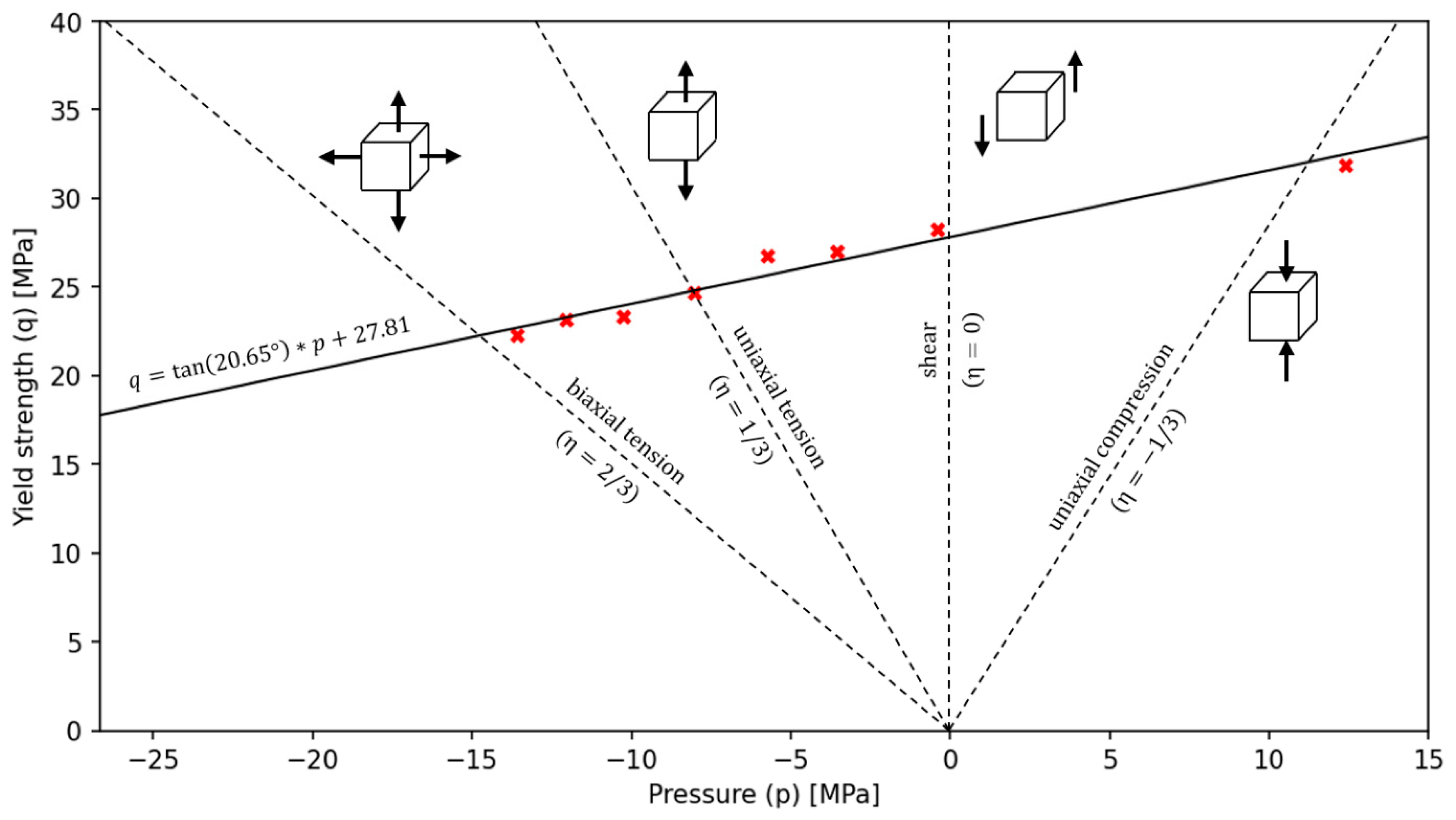
All the result in x relationship were described as a linear function of Drucker-Prager yield criteria in
Figure 7. The regression line was obtained using solver which has the objective function with scope to minimize the
error value.
As can be seen in the above graph, the results obtained for the Arcana machine correspond to the values from pure shear (
) to biaxial tension (
), which was possible thanks to the proposed undercuts on flat samples. The disc compressed on the strength machine obtained a result slightly lower (
) than for uniaxial compression due to its relatively small thickness and the friction occurring in the test between the upper and lower external surfaces of the sample and the contact linings of the testing machine. Final values for linear Drucker-Prager criteria were described in
Table 4.
All points achieved an average
error value of
, which suggests a very good fit to the linear relationship. An extension of the proposed linear criterion can be the tension cut-off, which determines the limiting value of the tensile pressure (
), beyond which plastic deformation occurs, regardless of the value of von Mises stress (
) [
45].
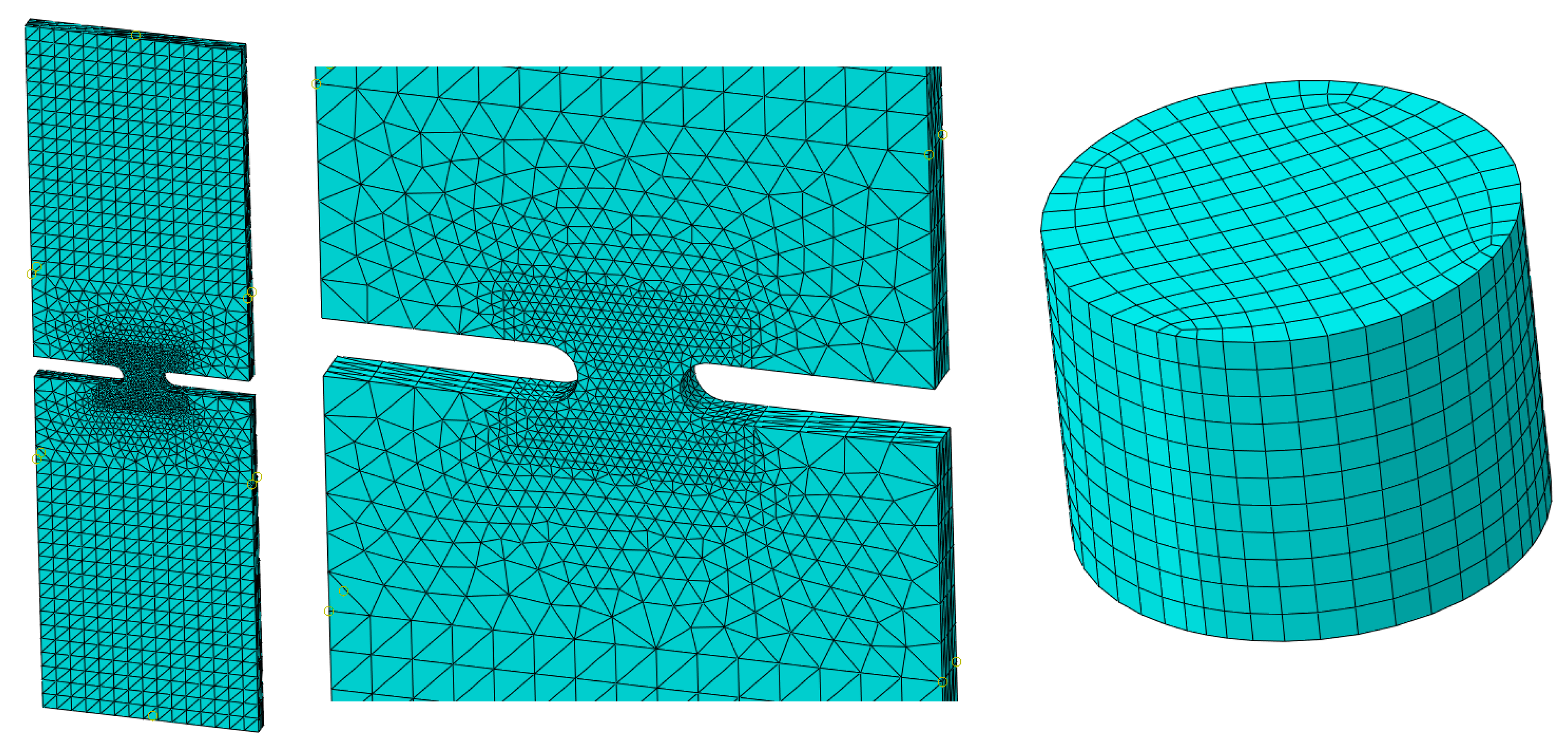
In order to confirm the correct validation of the Drucker-Prager model, simulations were performed on previously tested samples and the calculation results in Abaqus were compared to the values obtained on the strength test bench. Implicit simulations were used using Abaqus Standard solver. The discretized models used in the simulations (shown in
Figure 8) for Arcana and compression have respectively 16263 C3D10, 10-node quadratic tetrahedron elements with characteristic size of
in critical space and 2200 C3D20, 20-node quadratic hexahedral elements with
for whole geometry.
The finite element simulation was performed in a way that was designed to reproduce the actual test conditions as precisely as possible. For the samples tested on the Arcana machine, the model was completely fixed on the lower side in the locations indicated as mounting place in
Figure 4. On the other side, a displacement was imposed in the vertical direction. The Arcana machine itself was not included in the simulation due to the stiffness of the entire structure made of aluminum that was several orders of magnitude higher. For the disc compressed on both sides, contact surfaces were simulated with a friction coefficient of
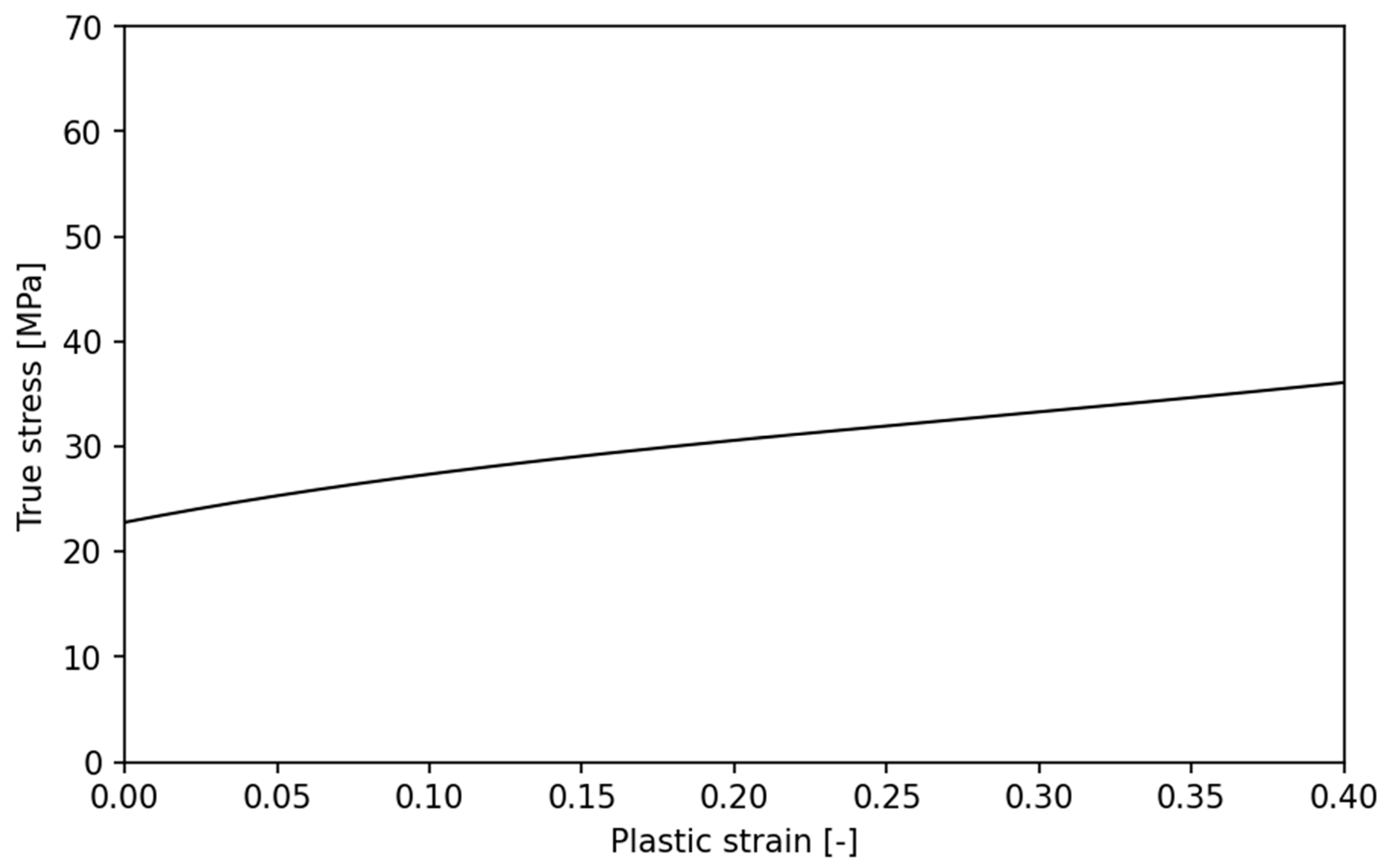
, of which only one, the upper surface, moves towards the lower fixed plane. In order to follow the simulation progress above the yield point, the yield curve shown in
Figure 9 was determined using numerical calibration from sample no 1 (Arcana – 0deg) test curve.
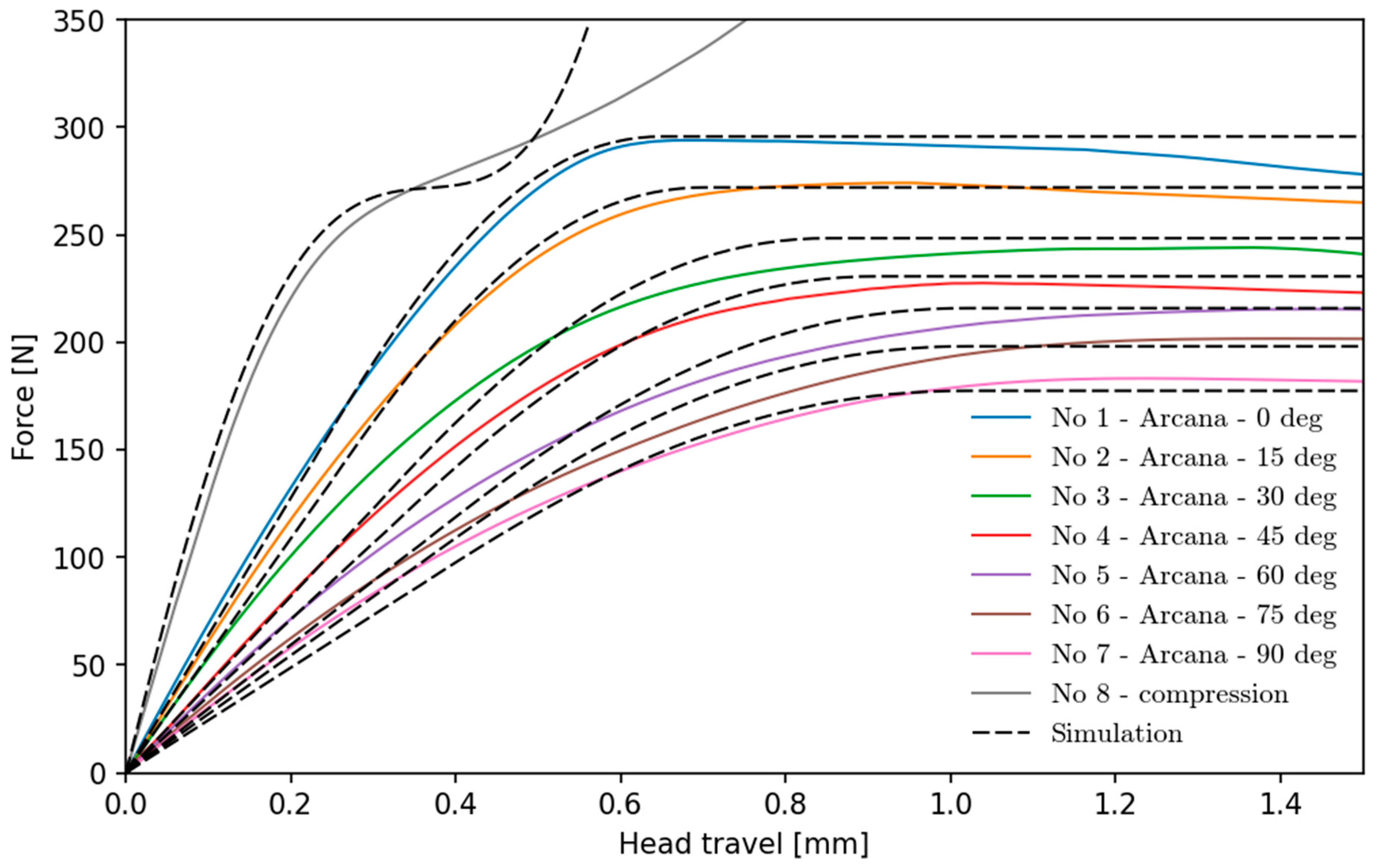
The hardening behavior was determined for range from 0 to 0.4 of plastic strain and implemented in Abaqus numerical software in tabular form with 17 points. Based on the above data, a comparison (on
Figure 10) between previous laboratory results and the numerical simulation results was made for all proposed samples.
As shown in the above graph, the simulation result shows the moment of yielding with a satisfactory result. The moment of appearance of the first plasticized finite elements and the transition of the entire critical cross-section into the plastic range are clearly visible. Due to the determination of the plasticity curve used for simulation based on sample no. 1, the simulation course outside the elastic range is best shown. For models with an angle of setting above 30°, the laboratory results are characterized by a less clear moment of yielding compared to the simulation results. This may result from the settings in the Abaqus program, which do not take into account the possibility of small angular movements of the samples at the place of attachment, which can occur during tests on the Arcana machine. For the compressed sample, the moment of yielding is shown satisfactorily in the numerical model, however, a comparison of the course in the plastic range shows clearly that the yield curve differs significantly from that obtained from the tensile sample. The anisotropic nature of the elastic range is noticeable, which is demonstrated by the fact that for Arcana machine settings close to 90° introducing a shear state in the sample, the Young Modulus () values are nearly 10% lower than those originally used in the simulation.
5. Conclusions and Areas for Further Research
The comprehensive study of Drucker-Prager presented in this article has shown a noticeable and significant linear dependence of the yield strength on the material state and, consequently, an unequivocal effect of pressure on the criterion under study. The proposed approach using a specially manufactured Arcana machine with samples with special undercuts allows for the representation of the state from pure shear to biaxial tension, which is not possible using standard samples. The supplementation and extension of the studies to the scope of uniaxial compression is a compression test performed on a slender disc. The obtained results uniformly achieve a linear character of variation.
All previously laboratory tested samples were numerically simulated, which allowed us to confirm the ability of the Drucker-Prager criterion implemented in the Abaqus program to properly reflect the moment of plasticization of samples. Due to the demonstrated variable course of the plasticization curve for different material loading states (Triaxiality), it seems advisable to take this phenomenon into account in future studies. At the moment, there are no ready-made solutions. Due to the stiffening of the numerical model of the sample mounting points in the holder, a small deviation occurred for the elastic range in samples with a machine inclination angle >15°.
Further research should focus on the longer range of Triaxiality, above 2-axis stretching and determining the so-called tension cut-off, which defines the pressure at which the material immediately plasticizes. A certain simplification of this phenomenon may be an attempt to calibrate the exponent or hyperbolic model, which indirectly takes into account the mentioned phenomenon.
Acknowledgments
The article was created as part of the 6th edition of the program of the Minister of Education and Science entitled “Implementation doctorate” Agreement No. DWD/6/0399/2022.
References
- Stinson, Stephen (1987). "Discoverers of Polypropylene Share Prize". Chemical & Engineering News. 65 (10): 30. [CrossRef]
- Fried, J. R. (2014). Polymer Science and Technology (Illustrated ed.). Prentice Hall. ISBN 0137039557, 9780137039555.
- Young, R. J., & Lovell, P. A. (2011). Introduction to Polymers (3rd ed.). CRC Press. [CrossRef]
- Vasile, C., & Pascu, M. (2005). Practical Guide to Polyethylene. Smithers Rapra Technology. ISBN 978-1859574935.
- Maddah, H. A. (2016). Polypropylene as a Promising Plastic: A Review. American Journal of Polymer Science, 6(1), 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M. T., Shahid, M. A., Mahmud, N., Habib, A., Rana, M. M., Khan, S. A., & Hossain, M. D. (2024). Research and application of polypropylene: A review. Nano, 19(2). [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J., & Bárány, T. (2019). Polypropylene Handbook: Morphology, Blends and Composites. SpringerLink. [CrossRef]
- Maier, C., & Calafut, T. (1998). Applications. In C. Maier & T. Calafut (Eds.), Polypropylene (pp. 87-107). William Andrew Publishing. ISBN: 9781884207587.
- Johri, N., Agarwal, G., Mishra, R. K., & Thakur, H. C. (2022). FEM analysis of polymeric hybrid composites. Materials Today: Proceedings, 57(Part 2), 383-390. [CrossRef]
- Du, S., Hamdi, M., & Sue, H.-J. (2020). Experimental and FEM analysis of mar behavior on amorphous polymers. Wear, 444-445, 203155. [CrossRef]
- Gariya, N., Prasad, B., & Kumar, P. (2020). FEM based analysis of soft polymer composites with crack. Materials Today: Proceedings, 28(Part 4), 2426-2430. [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, G., Zaïri, F., Naït-Abdelaziz, M., & Gloaguen, J. M. (2010). Modelling large deformation behaviour under loading–unloading of semicrystalline polymers: Application to a high density polyethylene. International Journal of Plasticity, 26(3), 329-347. [CrossRef]
- Laiarinandrasana, L., Besson, J., Lafarge, M., & Hochstetter, G. (2009). Temperature dependent mechanical behaviour of PVDF: Experiments and numerical modelling. International Journal of Plasticity, 25(7), 1301-1324. [CrossRef]
- Arruda, E. M., Boyce, M. C., & Jayachandran, R. (1995). Effects of strain rate, temperature and thermomechanical coupling on the finite strain deformation of glassy polymers. Mechanics of Materials, 19(2-3), 193-212. [CrossRef]
- Chou, S. C., Robertson, K. D., & Rainey, J. H. (1973). The effect of strain rate and heat developed during deformation on the stress-strain curve of plastics - Temperature rise developed during deformation can have significant effects on the stress-strain relationship. Four hard plastics are tested at various strain rates, and temperature changes are measured during deformation of the specimen. Experimental Mechanics, 13(10), 422-432. [CrossRef]
- Alves, M., & Jones, N. (1999). Influence of hydrostatic stress on failure of axisymmetric notched specimens. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 47(3), 643-667. [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Hameed, H., Messager, T., Ayoub, G., Zaïri, F., Naït-Abdelaziz, M., Qu, Z., & Zaïri, F. (2014). A two-phase hyperelastic-viscoplastic constitutive model for semi-crystalline polymers: Application to polyethylene materials with a variable range of crystal fractions. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 37, 323-332. [CrossRef]
- Hong, K., & Strobl, G. (2008). Characterizing and modeling the tensile deformation of polyethylene: The temperature and crystallinity dependences. Polymer Science - Series A, 50(5), 483-493. [CrossRef]
- Hachour, K., Zaïri, F., Naït-Abdelaziz, M., Gloaguen, J. M., Aberkane, M., & Lefebvre, J. M. (2014). Experiments and modeling of high-crystalline polyethylene yielding under different stress states. International Journal of Plasticity, 54, 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, R., Gaertner, R., Brunet, M., Chazeau, L., Vidal-Sallé, E., & Gauthier, C. (2011). Modeling of the mechanical behavior of amorphous glassy polymer based on the quasi-point defect theory—Part II: 3D formulation and finite element modeling of polycarbonate. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 46(3), 507-518. [CrossRef]
- Olsson, R. (2011). A survey of test methods for multiaxial and out-of-plane strength of composite laminates. Composites Science and Technology, 71(6), 773-783. [CrossRef]
- Manaia, J. P., Pires, F. A., & de Jesus, A. M. P. (2019). Elastoplastic and fracture behaviour of semi-crystalline polymers under multiaxial stress states. Frattura ed Integrità Strutturale, 13(47), 82-103. [CrossRef]
- Pae, K. D., & Bhateja, S. K. (1975). The Effects of Hydrostatic Pressure on the Mechanical Behavior of Polymers. Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part C, 13(1), 1–75. [CrossRef]
- Olufsen, S., Clausen, A. H., & Hopperstad, O. S. (2019). Influence of stress triaxiality and strain rate on stress-strain behaviour and dilation of mineral-filled PVC. Polymer Testing, 75, 350-357. [CrossRef]
- Pae, K. D., & Bhateja, S. K. (1975). The Effects of Hydrostatic Pressure on the Mechanical Behavior of Polymers. Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part C, 13(1), 1–75. [CrossRef]
- Ward, I. M. (1971). Review: The yield behaviour of polymers. Journal of Materials Science, 6(11), 1397-1417. [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D. C., & Prager, W. (1952). Soil mechanics and plastic analysis for limit design. Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 10(2), 157–165. [CrossRef]
- Pulungan, D., Lubineau, G., Yudhanto, A., Yaldiz, R., & Schijve, W. (2017). Identifying design parameters controlling damage behaviors of continuous fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites using micromechanics as a virtual testing tool. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 117, 177-190. [CrossRef]
- Naya, F., González, C., Lopes, C. S., Van der Veen, S., & Pons, F. (2017). Computational micromechanics of the transverse and shear behavior of unidirectional fiber reinforced polymers including environmental effects. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 92, 146-157. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J., Wan, L., Ismail, Y., Hou, P., Ye, J., & Yang, D. (2021). Micromechanical analysis of UD CFRP composite lamina under multiaxial loading with different loading paths. Composite Structures, 269, 114024.
- Popelar, C., Liechti, K. A Distortion-Modified Free Volume Theory for Nonlinear Viscoelastic Behavior. Mech Time-Depend Mater 7, 89–141 (2003). [CrossRef]
- Hao, P., Ud Din, I., & Panier, S. (2019). Development of Modified Arcan Fixture for biaxial loading response of fiber-reinforced composites. Polymer Testing, 80, 106148. [CrossRef]
- Cognard, J. Y., Sohier, L., & Davies, P. (2011). A modified Arcan test to analyze the behavior of composites and their assemblies under out-of-plane loadings. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 42(1), 111-121. [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.C., Liechti, K.M. An evaluation of the arcan specimen for determining the shear moduli of fiber-reinforced composites. Experimental Mechanics 37, 460–468 (1997). [CrossRef]
- Arcan, M., Hashin, Z., & Voloshin, A. (1978). A method to produce uniform plane-stress states with applications to fiber-reinforced materials - A specially designed specimen yields material properties under pure shear or uniform plane-stress conditions. Experimental Mechanics, 18(4), 141-146. [CrossRef]
- Voloshin, A., & Arcan, M. (1980). Pure shear moduli of unidirectional fibre-reinforced materials (FRM). Fibre Science and Technology, 13(2), 125-134. [CrossRef]
- Morelle, X.P., Chevalier, J., Bailly, C. et al. Mechanical characterization and modeling of the deformation and failure of the highly crosslinked RTM6 epoxy resin. Mech Time-Depend Mater 21, 419–454 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Quino, G., Gargiuli, J., Pimenta, S., Hamerton, I., Robinson, P., & Trask, R. S. (2023). Experimental characterisation of the dilation angle of polymers. Polymer Testing, 125, 108137. [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.-m.; Huang, G.-y.; Feng, S.-s.; McShane, G.J.; Stronge, W.J. Static and Dynamic Properties of Semi-Crystalline Polyethylene. Polymers 2016, 8, 77. [CrossRef]
- Marangoni, A. L., & Massaroppi, E.. (2017). Cowper-Symonds parameters estimation for ABS material using design of experiments with finite element simulation. Polímeros, 27(3), 220–224. [CrossRef]
- Schrauwen, B. A. G., van Breemen, L. C. A., Spoelstra, A. B., Govaert, L. E., Peters, G. W. M., & Meijer, H. E. H. (2004). Structure, deformation, and failure of flow-oriented semicrystalline polymers. Macromolecules, 37(23), 8618-8633. [CrossRef]
- Katti, S. S., & Schultz, M. (1982). The microstructure of injection-molded semicrystalline polymers: A review. Polymer Engineering & Science, 22(16), 1001-1017. [CrossRef]
- Swallowe, G.M. (1999). Relaxations in Polymers. In: Swallowe, G.M. (eds) Mechanical Properties and Testing of Polymers. Polymer Science and Technology Series, vol 3. Springer, Dordrecht. [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, C., Cavaille, J. Y., & Perez, J. (1989). Mechanical relaxations in polypropylene: A new experimental and theoretical approach. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics, 27(11), 2171-2184. [CrossRef]
- Krabbenhoft, K., Karim, M. R., Lyamin, A. V., & Sloan, S. W. (2012). Associated computational plasticity schemes for nonassociated frictional materials. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 90(9), 1089–1117. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).