Introduction
Pancreatic β cells play an indispensable role in maintaining glucose homeostasis in the body1. These specialized cells, located in the islets of Langerhans within the pancreas, are the exclusive producers of insulin, a hormone crucial for the regulation of blood glucose levels. In fact insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by tissues and reduces glucose production by the liver and other organs, thereby lowering blood glucose concentrations1. Insulin is produced by β cells in its precursor form, namely preproinsulin2. Preproinsulin is cleaved in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to form proinsulin3,4, which is subsequently translocated to the Golgi apparatus (GA) where it is packaged into early secretory vesicles5,6. These immature vesicles undergo a series of maturation steps7–9 and are compartmentalized in the cytoplasm until the mobilization/release step stimulated by exposure to glucose or other secretagogues 10 . Indeed, dysregulation of insulin production and/or secretion by β cells is a hallmark of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes (T1D and T2D), chronic conditions characterized by persistent hyperglycemia11. β cells devote most of their total protein biosynthetic capacity to insulin production12–14 and can produce as much as 106 molecules of preproinsulin per minute following glucose stimulation12. Consequently, they possess a well-developed ER and are in turn highly susceptible to ER stress under conditions of increased insulin demand. Several studies report on the presence of ER stress in pancreatic islets from both diabetic mouse models and diabetic human subjects15,16 . In addition, significant ER stress has been observed in immortalized insulin-producing cells and human pancreatic islets exposed to pro-inflammatory cytokines17. By contrast, the role and extent of GA stress in the pathophysiology of insulin secretion are still largely unknown18. Interestingly, a recent bio-informatic study on publicly available datasets from human T1D and T2D islet models have evidenced that GA-associated genes are dysregulated in diabetes18. Similarly, exposure to lipotoxicity and glucolipotoxicity has been shown to induce alteration in the expression of Golgi structural proteins, GA glycosylation enzymes, and GA stress mediators in immortalized rat insulinoma cells19. Both ER and GA are highly dynamic structures that exhibit functional and morphological modifications in response to changes in cellular conditions such as developmental stage, intracellular signals, or pathological conditions20,21. Thus far, the structural properties of ER and GA under diabetes-mimicking conditions have been evaluated quite exclusively by means of Electron Microscopy (EM). Several studies reported morphological alterations of beta cell ER in diabetic mouse models22–26 and T2D subjects27,28. On the other hand, only a few studies have focused on imaging the morphological properties of the GA under diabetes-mimicking conditions. By using EM, Alcaron and coworkers observed an expansion of the GA in a mouse model of obesity-linked T2D26. More recently, Boyer and coworkers revealed significant morphological abnormalities in the GA of diabetic mice lacking leptin receptors, including shortened and swollen cisternae, fewer cisternae per Golgi stack, as well as partial vesiculation of the GA20.
In the present study, building on a recent report29, we couple the molecular specificity of antibody-based fluorescence optical microscopy with the super resolution power of the Airyscan microscopy to study the structural alterations of ER and GA in INS-1E cells exposed to pro-inflammatory cytokines. The results show significant morphological alterations of both the ER and GA structures. In detail, under exposure to IL-1β and IFN-γ for 24 hours, both organelles display vesicular fragmentation, with a marked reduction in the characteristic area and perimeter of the resulting structures, alongside an increase in their circularity, when compared to control cells. In addition, under the same conditions, we occasionally observed Organized Smooth ER (OSER) structures in cells, in which the ER forms stacked membranes by integrating preexisting branching ER 30,31. Overall, the ER and GA alterations complement the structural modifications we recently observed in microtubules and mitochondria together with the reduced number of insulin granules under cytokine exposure29, providing a comprehensive picture of the subcellular landscape of β cells in response to cytokine treatment.
Results and Discussion
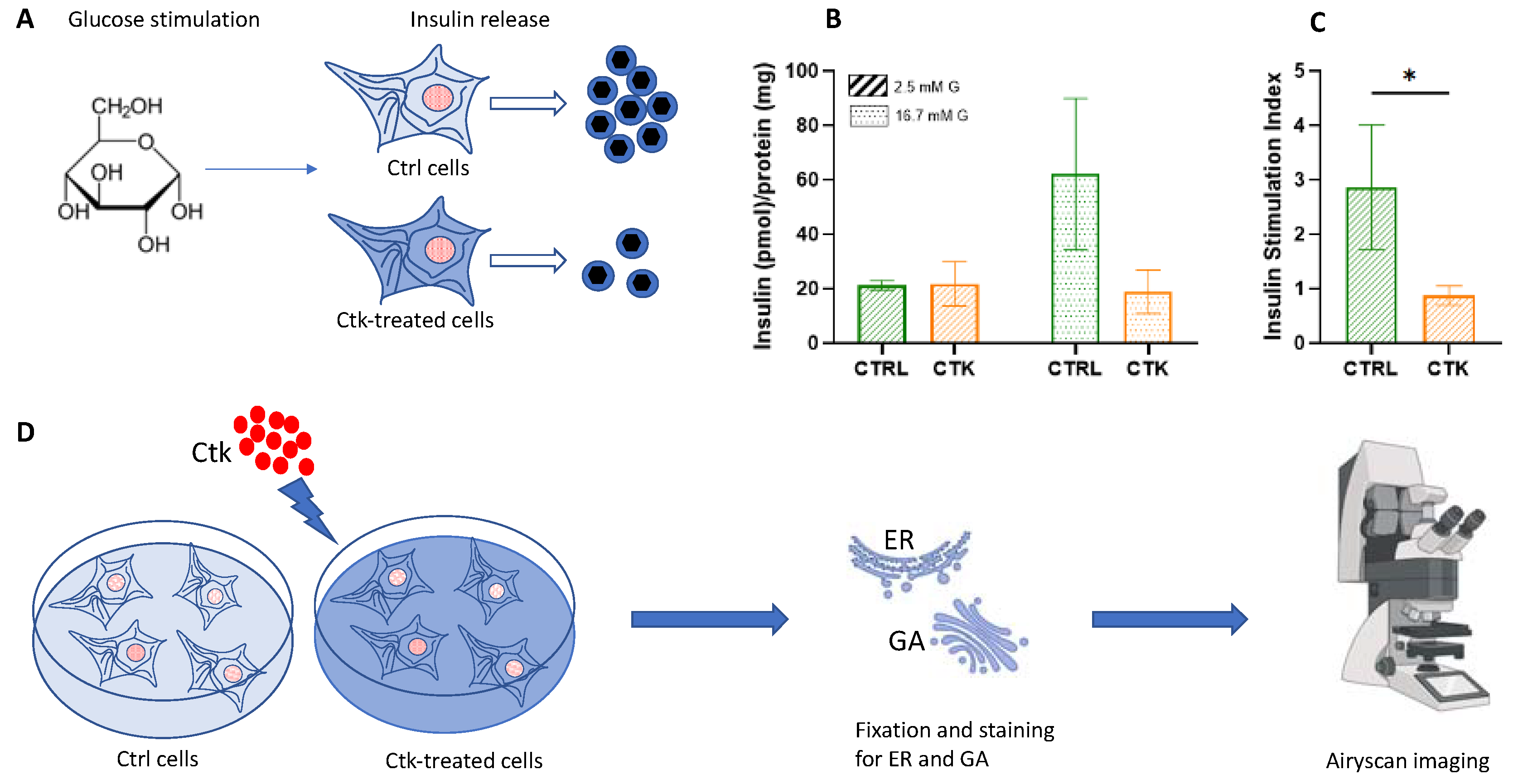
The upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines is considered a hallmark in the pathophysiology of diabetes32. To study the effect of pro-inflammatory cytokines on β-cells, we used Insulinoma 1E (INS-1E) cells. These cells exhibit many traits similar to primary β-cells, such as glucose-sensing capability, making them a widely accepted model for β-cells33. To verify the effectiveness of the cell system used, we evaluated INS-1E insulin secretory response to glucose stimulation in normal conditions and after 24 hours of cytokine treatment (
Figure 1A).
At 2.5 mM glucose, no significant differences in insulin secretion were observed between control and cytokine-treated cells. However, when exposed to a high glucose stimulus (16.7 mM), cytokine-treated cells displayed a markedly reduced insulin secretion capacity compared to control cells (
Figure 1B). Consequently, the insulin stimulation index was lower in cytokine-treated cells compared to control samples(
Figure 1C), in accordance with previous observations34,35. At this point, we conducted experiments to evaluate the possible alterations of the target cellular structures following cytokine treatment (
Figure 1D). After treating the INS-1E cells with cytokines for 24 hours, we fixed and stained them for the ER and GA to observe any structural changes. All the samples were imaged with an inverted Zeiss LSM 800 confocal microscope, equipped with an Airyscan detection unit to achieve super-resolution (see Methods for more details). To observe the ER, cells were immunostained with SERCA2 ATPase (Sarco-Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase) monoclonal antibody, and imaged using Airyscan microscopy. Subsequently, morphometric analysis of the ER was conducted by comparing cytokine-treated cells with control cells.
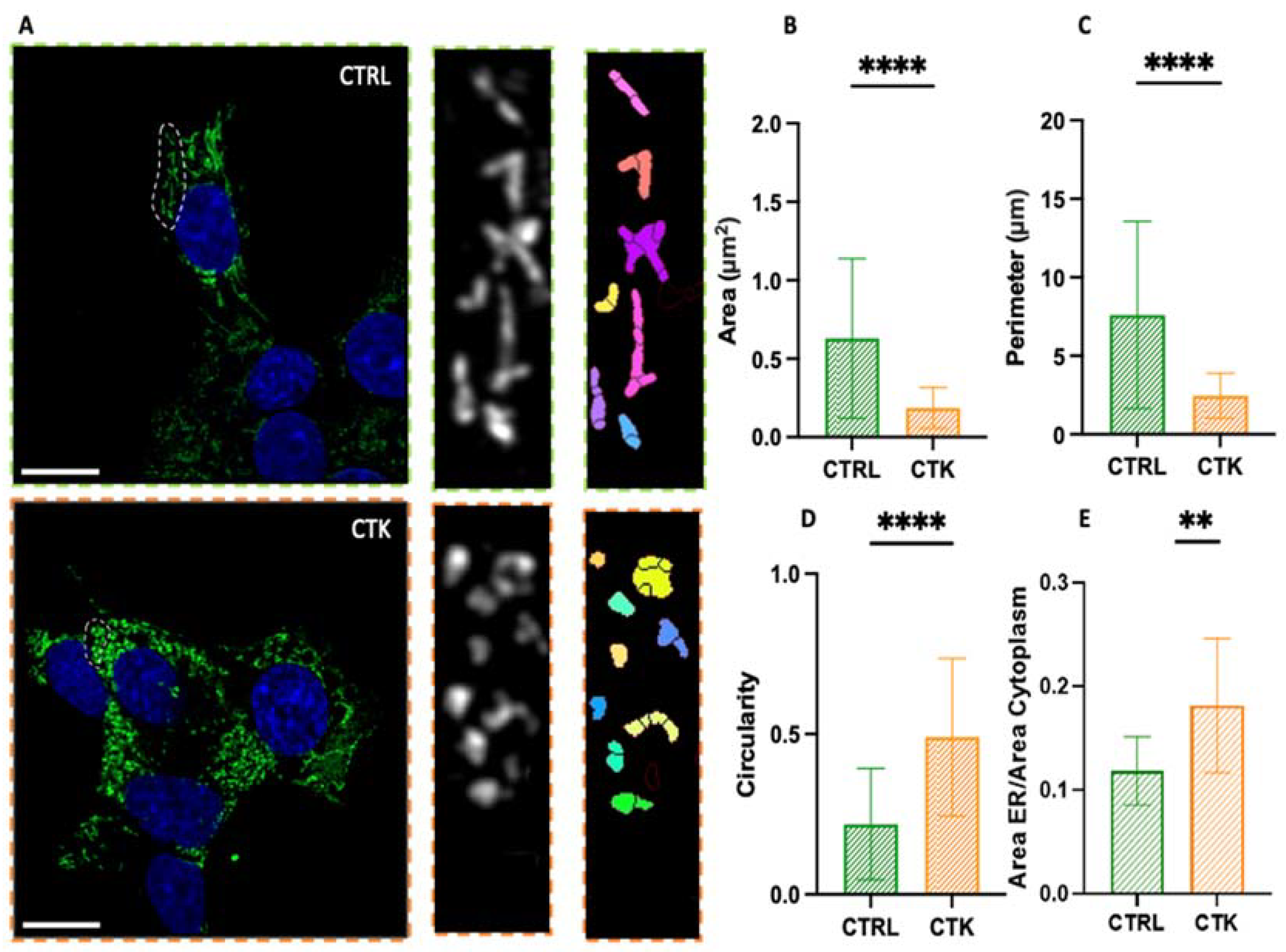
As shown in
Figure 2A, in control cells the ER has a structure composed of a set of membranous vesicles, more or less branched. On the contrary, cytokines-treated cells display an altered morphology characterized by extensive ER fragmentation, with the formation of more rounded and smaller structures, hereafter referred to also as ‘vesicles’ or ‘vesicle-like structures’. This observation is quantitatively evident in the analysis of parameters such as the area, perimeter, and circularity (
Figure 2B-D) of the ER structures: the typical area changed from 0.63 ± 0.51 µm2 in control cells to 0.19 ± 0.13 µm2 in cytokine-treated cells (i.e. ~70% reduction), the perimeter changed from 7.60 ± 5.95 µm in control cells to 2.45 ± 1.43 µm in cytokine-treated cells (i.e. ~70% reduction), the circularity changed from 0.22 ± 0.17 in control cells to 0.49 ± 0.24 in cytokine-treated cells (i.e. ~2-fold increase). The data thus show that this structure undergoes profound morphological changes upon exposure to pro-inflammatory cytokines and this might have consequences on insulin synthesis and then secretion. Additionally, in accordance with previous studies25–27, we found an increase in the total area occupied by the ER in the cell (
Figure 2E). Indeed, our immunofluorescence observations are in agreement with previous results obtained using electron microscopy27, showing that ER density volume was significantly increased in T2D β cells27. Worthy of mention, in cytokine-exposed cells we occasionally observed the presence of peculiar ER structures, known as organized smooth ER (i.e. OSER) (
Figure S1). The formation of OSER entails the integration of preexisting branching ER into stacked structures30,31. The function of OSER structures in cells is not fully understood, but they seem to retain proteins longer than branching ER. This may be due to their fewer connections, which might cause protein segregation and compartmentalization within the ER30. To our knowledge, while these structures have been observed previously in other cells and under pathological conditions30, this is the first documented occurrence in diabetes-mimicking conditions.
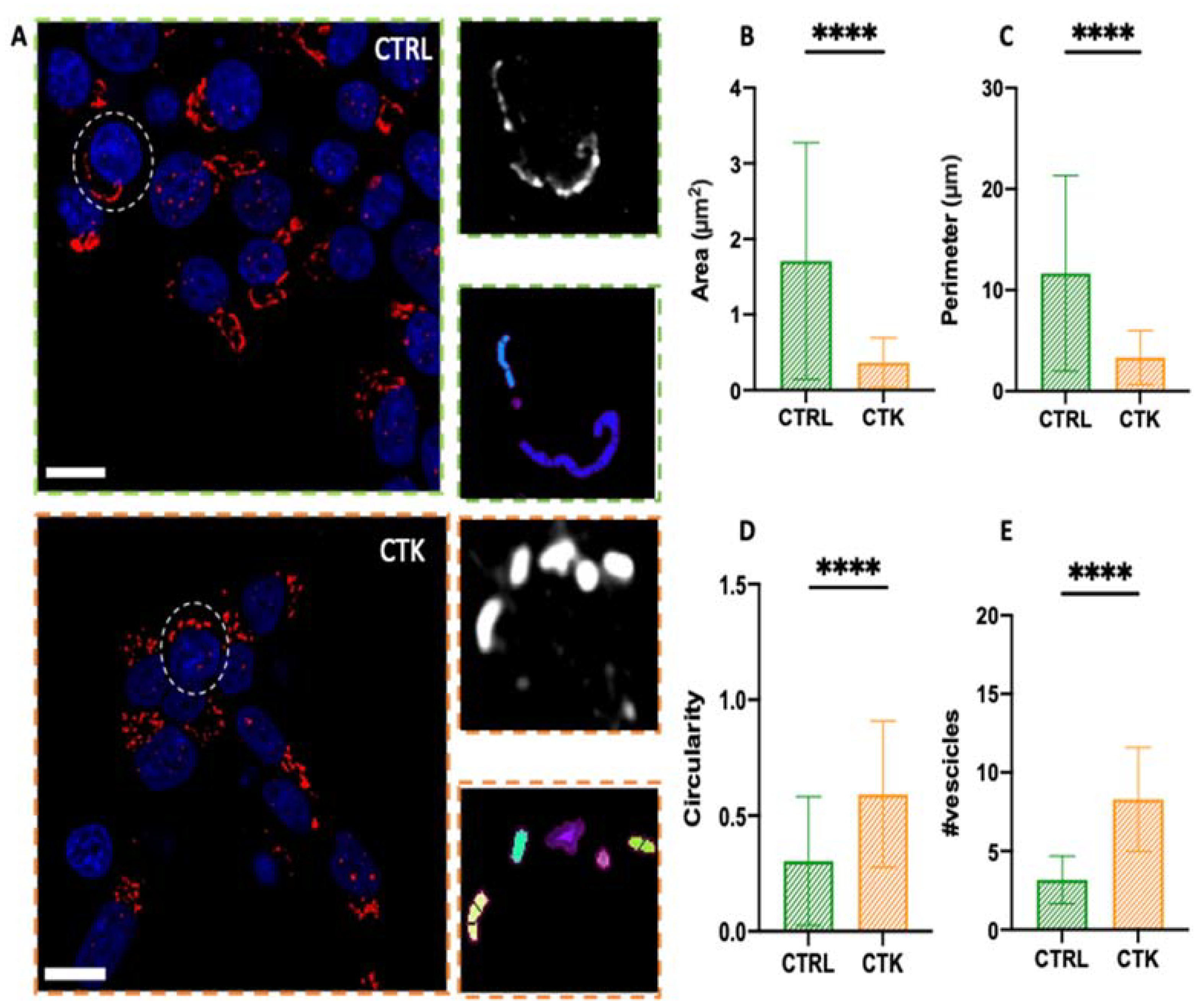
To study GA morphology following 24 hours of pro-inflammatory-cytokine treatment, INS-1E cells were fixed, immunostained with a GM130 antibody, and imaged using Airyscan microscopy. Similarly to what observed for the ER, INS-1E cells exposed to cytokines exhibited extensive fragmentation of the GA, with the formation of vesicle-like structures (
Figure 3A). Quantitatively, the area of the observed structures decreased from 1.71 ± 1.56 µm² in control cells to 0.36 ± 0.32 µm² in cytokine-treated cells (i.e. ~80% reduction%) (
Figure 3B), the perimeter decreased from 11.67 ± 9.68 µm in control cells to 3.33 ± 2.67 µm in cytokine-treated cells (i.e. ~70% reduction) (
Figure 3C), and structure circularity increased from 0.30 ± 0.28 in control cells to 0.59 ± 0.32 in cytokine-treated cells (i.e. ~2-fold increase) (
Figure 3D). Furthermore the fragmentation process caused an increase in the average number of vesicles present in each cell, from N~3 in control cells to N~8 in cytokine-treated cells (
Figure 3E), in accordance with previous ultrastructural analysis by Boyer and coworkers, performed using EM36.
Conclusions
To conclude, the cytokine-induced ER and GA alterations highlighted here complement the structural modifications of microtubules (i.e. extensive fragmentation) and mitochondria (i.e. increased circularity) and the altered number of insulin granules (i.e. reduced) recently observed by some of us under the same experimental conditions and by means of a similar optical-microscopy approach29. Taken together, these observations provide a comprehensive picture of the subcellular landscape of β cells in response to treatment with pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture. INS-1E cells (kindly provided by Prof. C. Wollheim, University of Geneva, Medical Center) were maintained in culture at 37°C, 5% CO2 in RPMI 1640 medium containing 11.1 mM D-glucose, supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 10 mM HEPES, 2 mM L-Glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin-streptomycin, 1 mM sodium-pyruvate, 50 μM tissue culture grade β-mercaptoethanol (all purchased from Gibco, ThermoFisher). INS1-E cells were plated at 70% confluency on 18 mm coverglass and grown for 48h. For each experiment carried out, a pair of samples was used: one control and one treated with cytokines (IL-1β 10 U/ml and IFN-γ 100 U/ml, diluted in 1 ml of complete medium RPMI) for 24h. For control samples, cells were washed and replaced with fresh complete medium. Cells used in this study resulted negative for the presence of mycoplasma contamination.
Insulin secretion. Insulin release in response to glucose (2.5 and 16.7 mmol/l) was assessed as previously reported37. Briefly, cells were washed twice with Krebs’ buffer containing 2.5 mmol/l glucose and pre-incubated with the same buffer for 45 min at 37°C. After another washing step, cells were incubated with Krebs’ buffer containing 2.5 mmol/l or 16.7 mmol/l glucose for 30 min at 37°C. Insulin was quantified on cell supernatant by High Range Rat Insulin ELISA kit (Mercodia AB, Uppsala, Sweden) and insulin release was normalized by protein content. Proteins were extracted with RIPA buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and quantified by Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The insulin stimulation index (ISI) was calculated as the ratio of insulin release at 16.7 mmol/l glucose over the release at 2.5 mmol/l glucose.
Immunostaining. Control and cytokine-treated cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in PBS for 30 min at RT and washed 3 times with PBS, 5 min each. After fixation, cells were permeabilized through 3 washing of 5 min each at RT with PBS+0.1% triton X-100 (PBST). Cells were then washed 3 times with PBS and blocked with 2% bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 30-45 min at RT. The samples were incubated with the following primary antibodies: anti-GM120 antibody for GA (ARG57583, Arigo Biolaboratories, Taiwan) diluted 1:100 in PBS + 0.1% Tween overnight at 4 °C; SERCA2 ATPase Monoclonal Antibody for ER (MA3-919, Invitrogen, USA) diluted 1:100 in PBS+0.1% Tween overnight at 37°C, in a humidified chamber. Then, after 1 wash with PBS+0.1% Tween and 2 washes with PBS of 5 min each at RT, the specimens were stained for 1h at RT with secondary antibodies: anti-Rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 ((IS-20015-1, Immunological Sciences, Italy) for GA and anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 (IS-20014-1, Immunological Sciences, Italy) for ER, diluted 1:100 in PBS + 0.1% tween, respectively. The stained samples were then washed 2 times with PBS, 10 min each, and then incubated with 1 μg/mL DAPI in PBS for 10 minutes. Specimens were mounted with Mowiol before imaging.
Fluorescence microscopy. Microscopic observation and photography were performed using an inverted Zeiss LSM 800 confocal microscope (Jena, Germany), equipped with an Airyscan detection unit. The acquisition was performed by illuminating the sample with a 405 and 488 laser using a 63×/NA 1.4 oil-immersion objective. DAPI and AlexaFluor 488 fluorescence were collected between 410-510 nm and 510-590 nm, respectively, with GaAsP detectors. The pinhole aperture was set at 1 Airy (53 μm). Detector gain and pixel dwell times were adjusted for each dataset keeping them at their lowest values in order to avoid saturation and bleaching effects. Imaging was performed using Airyscan microscopy (AM), that allows for simultaneous improvement in resolution and signal-to-noise without increasing the excitation power and acquisition time. AM offers fast and sensitive super-resolution confocal imaging which improves lateral resolution to 120 nm. Thus, it is filling the gap between classical confocal laser scanning microscopy and super-resolution Structured-illumination microscopy (SIM). Instead of employing a single photomultiplier detector (PMT) commonly found in traditional confocal microscopes, AM utilizes a specialized configuration of 32-channel gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP) detectors arranged in a hexagonal array. Each detection element within the GaAsP detector operates like a small pinhole, measuring 0.2 Airy units (AU) in size. The overall collection efficiency amounts to approximately 1.25 AU.
Data analysis. The morphology of the GA and ER was analyzed by selecting whole cells and specific regions within the cells, respectively. These selected images underwent processing using Fiji to enhance signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) through background subtraction and Gaussian filtering. Subsequently, MorphoLibJ plugin was employed for analysis by inputting "Object Image" and setting appropriate tolerance values for each Region of Interest (ROI). This process generated a binary image, which was then subjected to analysis using the MorphoLibJ "Analyze" tool to extract information on organelles’ area, perimeter, and circularity. To determine the ratio of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) area to cytoplasmic area, cells were selected by drawing a Region of Interest (ROI) around their perimeter in Fiji, and the total cell area was measured using "Analyze > Measure." The selected cells were processed to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio through background subtraction. A new ROI was then drawn around the nucleus to measure its area, which was subtracted from the total cell area to obtain the cytoplasmic area. To identify ER pixels within the ROI, the “Image > Adjust > Threshold” function was used, and after applying the threshold, a selection was created with “Edit > Selection > Create Selection”. To retain only the ER within the original ROI, “Edit > Clear Outside” was employed. The ER area within the original ROI was measured using "Analyze > Measure," and the ratio of ER area to cytoplasmic area was calculated.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
L.A.P. performed experiments, analyzed data, wrote the manuscript; V.D.L. performed experiments, wrote the manuscript; M.T. performed experiments; P.M. designed research, wrote the manuscript; F.C. provided funds, designed and supervised research, wrote the manuscript.
Data availability
Data will be made available upon request to the corresponding author, Francesco Cardarelli (francesco.cardarelli@sns.it).
Acknowledgments
This work has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement No 866127, project CAPTUR3D). PM and MT receive support from the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking under grant agreements No 115,797 (INNODIA) and 945,268 (INNODIA HARVEST). These Joint Undertakings receive support from the Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program and “EFPIA”, “JDRF” and “The Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust”.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Omar-Hmeadi, M. & Idevall-Hagren, O. Insulin granule biogenesis and exocytosis. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 78, 1957–1970 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Germanos, M., Gao, A., Taper, M., Yau, B. & Kebede, M. A. Inside the Insulin Secretory Granule. Metabolites 11, 515 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Davidson, H. W., Rhodes, C. J. & Hutton, J. C. Intraorganellar calcium and pH control proinsulin cleavage in the pancreatic β cell via two distinct site-specific endopeptidases. Nature 333, 93–96 (1988). [CrossRef]
- Smeekens, S. P. et al. Proinsulin processing by the subtilisin-related proprotein convertases furin, PC2, and PC3. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 89, 8822–8826 (1992). [CrossRef]
- Orci, L., Ravazzola, M. & Perrelet, A. (Pro)insulin associates with Golgi membranes of pancreatic B cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 81, 6743–6746 (1984). [CrossRef]
- Orci, L. et al. Nonconverted, amino acid analog-modified proinsulin stays in a Golgi-derived clathrin-coated membrane compartment. J Cell Biol 99, 2187–2192 (1984). [CrossRef]
- The structure of 2Zn pig insulin crystals at 1.5 Å resolution. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. B, Biological Sciences 319, 369–456 (1988). [CrossRef]
- Kuliawat, R., Klumperman, J., Ludwig, T. & Arvan, P. Differential Sorting of Lysosomal Enzymes Out of the Regulated Secretory Pathway in Pancreatic β-Cells. J Cell Biol 137, 595–608 (1997). [CrossRef]
- Orci, L. et al. Proteolytic maturation of insulin is a post-Golgi event which occurs in acidifying clathrin-coated secretory vesicles. Cell 49, 865–868 (1987). [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C. J. & Halban, P. A. Newly synthesized proinsulin/insulin and stored insulin are released from pancreatic B cells predominantly via a regulated, rather than a constitutive, pathway. J Cell Biol 105, 145–153 (1987). [CrossRef]
- Blair, M. Diabetes Mellitus Review. Urol Nurs 36, 27–36 (2016).
- Schuit, F. C., In’t Veld, P. A. & Pipeleers, D. G. Glucose stimulates proinsulin biosynthesis by a dose-dependent recruitment of pancreatic beta cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 85, 3865–3869 (1988). [CrossRef]
- Boland, B. B., Rhodes, C. J. & Grimsby, J. S. The dynamic plasticity of insulin production in β-cells. Mol Metab 6, 958–973 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. et al. Proinsulin misfolding and endoplasmic reticulum stress during the development and progression of diabetes☆. Mol Aspects Med 42, 105–118 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Eizirik, D. L., Cardozo, A. K. & Cnop, M. The Role for Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr Rev 29, 42–61 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Sahin, G. S., Lee, H. & Engin, F. An accomplice more than a mere victim: The impact of β-cell ER stress on type 1 diabetes pathogenesis. Mol Metab 54, 101365 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Brozzi, F. et al. Cytokines induce endoplasmic reticulum stress in human, rat and mouse beta cells via different mechanisms. Diabetologia 58, 2307–2316 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Bone, R. N. et al. A Computational Approach for Defining a Signature of β-Cell Golgi Stress in Diabetes. Diabetes 69, 2364–2376 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Başçıl Tütüncü, N. et al. Beta-Cell Golgi Stress Response to Lipotoxicity and Glucolipotoxicity: A Preliminary Study of a Potential Mechanism of Beta-Cell Failure in Posttransplant Diabetes and Intraportal Islet Transplant. Experimental and Clinical Transplantation 20, 585–594 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Kim, W. K., Choi, W., Deshar, B., Kang, S. & Kim, J. Golgi Stress Response: New Insights into the Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Targets of Human Diseases. Mol Cells 46, 191–199 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Almanza, A. et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling – from basic mechanisms to clinical applications. FEBS J 286, 241–278 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. et al. A mutation in the insulin 2 gene induces diabetes with severe pancreatic β-cell dysfunction in the Mody mouse. Journal of Clinical Investigation 103, 27–37 (1999). [CrossRef]
- Riggs, A. C. et al. Mice conditionally lacking the Wolfram gene in pancreatic islet beta cells exhibit diabetes as a result of enhanced endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Diabetologia 48, 2313–2321 (2005). [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, M. et al. Increased insulin demand promotes while pioglitazone prevents pancreatic beta cell apoptosis in Wfs1 knockout mice. Diabetologia 52, 653–663 (2009). [CrossRef]
- Scheuner, D. et al. Control of mRNA translation preserves endoplasmic reticulum function in beta cells and maintains glucose homeostasis. Nat Med 11, 757–764 (2005). [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, C. et al. Pancreatic β-Cell Adaptive Plasticity in Obesity Increases Insulin Production but Adversely Affects Secretory Function. Diabetes 65, 438–450 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, P. et al. The endoplasmic reticulum in pancreatic beta cells of type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetologia 50, 2486–2494 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Masini, M. et al. Ultrastructural morphometric analysis of insulin secretory granules in human type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 49, 247–252 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, L. A. et al. Unveiling nanoscale optical signatures of cytokine-induced β-cell dysfunction. Sci Rep 13, 13342 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Snapp, E. L. et al. Formation of stacked ER cisternae by low affinity protein interactions. J Cell Biol 163, 257–269 (2003). [CrossRef]
- Korkhov, V. M. & Zuber, B. Direct observation of molecular arrays in the organized smooth endoplasmic reticulum. BMC Cell Biol 10, 59 (2009). [CrossRef]
- Donath, M. Y., Dinarello, C. A. & Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Targeting innate immune mediators in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Immunol 19, 734–746 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Merglen, A. et al. Glucose Sensitivity and Metabolism-Secretion Coupling Studied during Two-Year Continuous Culture in INS-1E Insulinoma Cells. Endocrinology 145, 667–678 (2004). [CrossRef]
- Kiely, A., McClenaghan, N. H., Flatt, P. R. & Newsholme, P. Pro-inflammatory cytokines increase glucose, alanine and triacylglycerol utilization but inhibit insulin secretion in a clonal pancreatic β-cell line. Journal of Endocrinology 195, 113–123 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Tran, D. T. et al. Inflammatory Cytokines Rewire the Proinsulin Interaction Network in Human Islets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 107, 3100–3110 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Boyer, C. K., Bauchle, C. J., Zhang, J., Wang, Y. & Stephens, S. B. Synchronized proinsulin trafficking reveals delayed Golgi export accompanies β-cell secretory dysfunction in rodent models of hyperglycemia. Sci Rep 13, 5218 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Ciregia, F. et al. Palmitate-induced lipotoxicity alters acetylation of multiple proteins in clonal β cells and human pancreatic islets. Sci Rep 7, 13445 (2017). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).