1. Introduction
Oral lichen planus (OLP) is a chronic inflammatory mucosal disease, and an apparent cause has not yet been identified [
1,
2,
3]. It is also known as one of the oral potentially malignant disorders [
4]. OLP forms reticulated or mottled white lesions on the oral mucosa as a result of abnormal keratinization of squamous epithelium. OLP sometimes presents with erythematous lesions due to thinning, erosions, and ulcerations of squamous epithelium. Patients with OLP often experience discomfort and contact pain during ingestion, which interferes with daily life [
5,
6]. OLP is refractory to treatment, and malignant transformation has been reported [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11].
Histopathologically, OLP often shows lymphocytic infiltration dominated in T-cells at the lamina propria of oral epithelium, basement membrane disruption, saw-tooth rete ridges, and hyperkeratinization of the epithelial cells [
1,
12,
13,
14,
15]. However, the mechanism of lymphocyte infiltration and activation in OLP, whether it is an autoimmune, allergic, or infectious disease, has not been elucidated [
16].
To date, there is no radical treatment for OLP, and it is treated by symptomatic treatment [
15]. Even if OLP is temporarily cured or improved by some treatments, many cases recur when the treatment is quit [
13]. Ideally, the causative factor of OLP should be eliminated with radical treatment, and the lesions should disappear completely. However, because we cannot remove the unknown causative factor, the treatment goal would be to maintain the lesion at least as a chronic inactive state by using symptomatic treatment [
17]. To achieve this goal, it is necessary to discover effective drugs with few adverse effects over long-term administration. Experimental models to validate pharmaceutical candidate drugs should be established for this purpose.
Cepharanthin
® is a medicinal product containing biscoclaurine alkaloid extracted from
Stephania cepharantha Hayata and composed mainly of cepharanthine (19.5-33.5%), isotetrandrine (25.0-39.0%), berbamine (7.0-16.5%) and cycreanine (6.5-16.5%) [
18]. Cepharanthine has been reported to inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway [
19], activate the 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway [
20], and inhibit the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway [
21]. Isotetrandrine and berbamine have been reported to inhibit the NF-κB pathway [
22,
23], and cycreanine inhibits the production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) [
24]. Based on these mechanisms, Cepharanthin
® is considered effective for the treatment of OLP in Japan and has been used for a long time clinically [
17,
25]. Cepharanthin
® has also been used to treat radiation-induced leukopenia, alopecia areata, pit viper bite, and exudative otitis media catarrh. Historically, it has also been used for tuberculosis, whooping cough, asthma, gastritis, and gastric ulcer in Japan [
20]. It has recently been reported to be effective against COVID-19 infection [
26].
As described above, although Cepharanthin
® has proven to be safe for long-term use and has long been used clinically as an effective treatment for OLP, its precise mechanism of action is unclear [
17,
25]. In this study, we used a newly established
in vitro OLP model to investigate the effects of Cepharanthin
® and its components on lymphocyte activation and the response of oral mucosal epithelial cells to inflammatory cytokines in order to clarify a mechanism of the action of Cepharanthin
®.
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Cepharanthine, Isotetrandrine, Berbamine, Cycreanine, and Cepharanthin® on the Activation of Human Acute T-Cell Leukemia Cell Line (Jurkat E6.1)
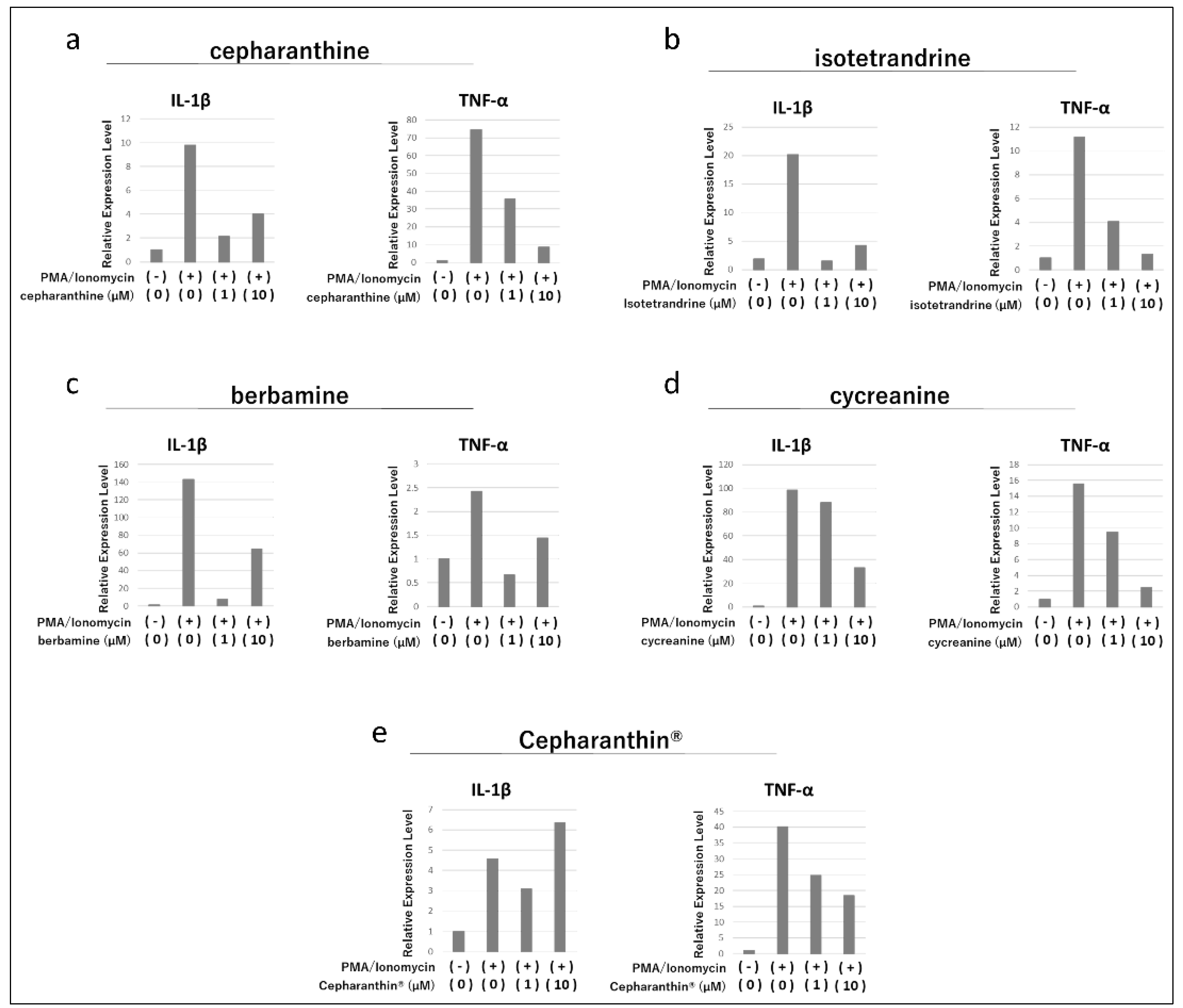
In Jurkat E6.1, treatment with Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)/Ionomycin increased the expression of IL-1β and TNF-α genes (
Figure 1a-e). Thereafter, cepharanthine, isotetrandrine, and berbamine markedly suppressed the increase in gene expression of IL-1β and TNF-α, but there was no clear concentration dependence (
Figure 1a-c). Cycreanine also mildly suppressed the increase in gene expression of IL-1β and TNF-α (
Figure 1d). On the other hand, Cepharanthin
®, a mixture of these components as a drug formulation, did not affect the increase in gene expression of IL-1β, but Cepharanthin
® at 1 µM and 10 µM slightly suppressed the increase in gene expression of TNF-α (
Figure 1e).
2.2. Effects of Cepharanthine, Isotetrandrine, Berbamine, Cycreanine, and Cepharanthin® on the Expression of Various Cytokine Genes Induced by Inflammatory Cytokine Stimulation in an Immortalized Human Oral Mucosa-Derived Epithelial Cell Line (hTERT-TIGKs)
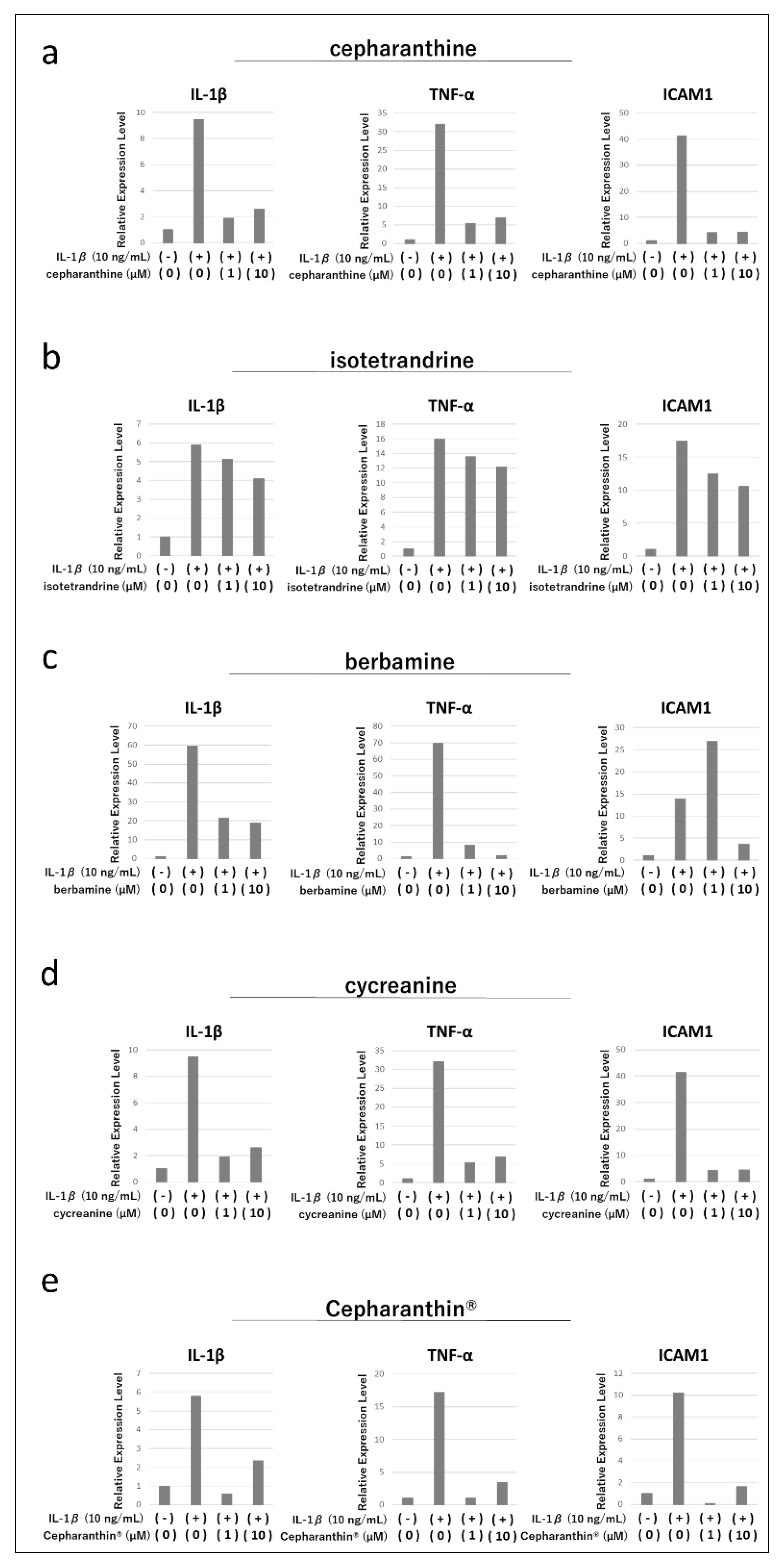
Treatment of hTERT-TIGKs with IL-1β increased gene expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, and ICAM1 (
Figure 2a-e). Thereafter, treatment with cepharanthine, berbamine, and cycreanine suppressed the increase in gene expression of IL-1β and TNF-α, but no clear concentration dependence was observed (
Figure 2a,c,d). Isotetrandrine treatment did not suppress the increase of IL-1β and TNF-α gene expression to any extent (
Figure 2b). Each drug showed different effects on ICAM1 gene expression, with cepharanthine and cycreanine strongly suppressing the increase of ICAM1 gene expression, isotetrandrine slightly suppressing it (
Figure 2a,b,d), and berbamine enhancing it at low concentrations, and suppressing it at high concentrations (
Figure 2c). In contrast, treatment with Cepharanthin
® suppressed the expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, and ICAM1 induced by IL-1β treatment, but the concentration dependence was not clear (
Figure 2e).
2.3. Effect of Cepharanthin® on Cytokine Gene Expression in hTERT-TIGKs in an In Vitro OLP Model
In an
in vitro OLP model, the expressions of IL-1β, TNF-α, ICAM1, and Involucrin (IVL) gene in hTERT-TIGKs were enhanced by activated T cells (PMA/Ionomycin-treated Jurkat E6.1) (
Figure 3). Cepharanthin
® markedly suppressed the enhanced IL-1β, TNF-α, and IVL gene expressions and mildly suppressed the ICAM1 gene expression (
Figure 3).
2.4. Effect of Cepharanthin® and/or Activated T Lymphocytes on the Proliferation of hTERT-TIGKs
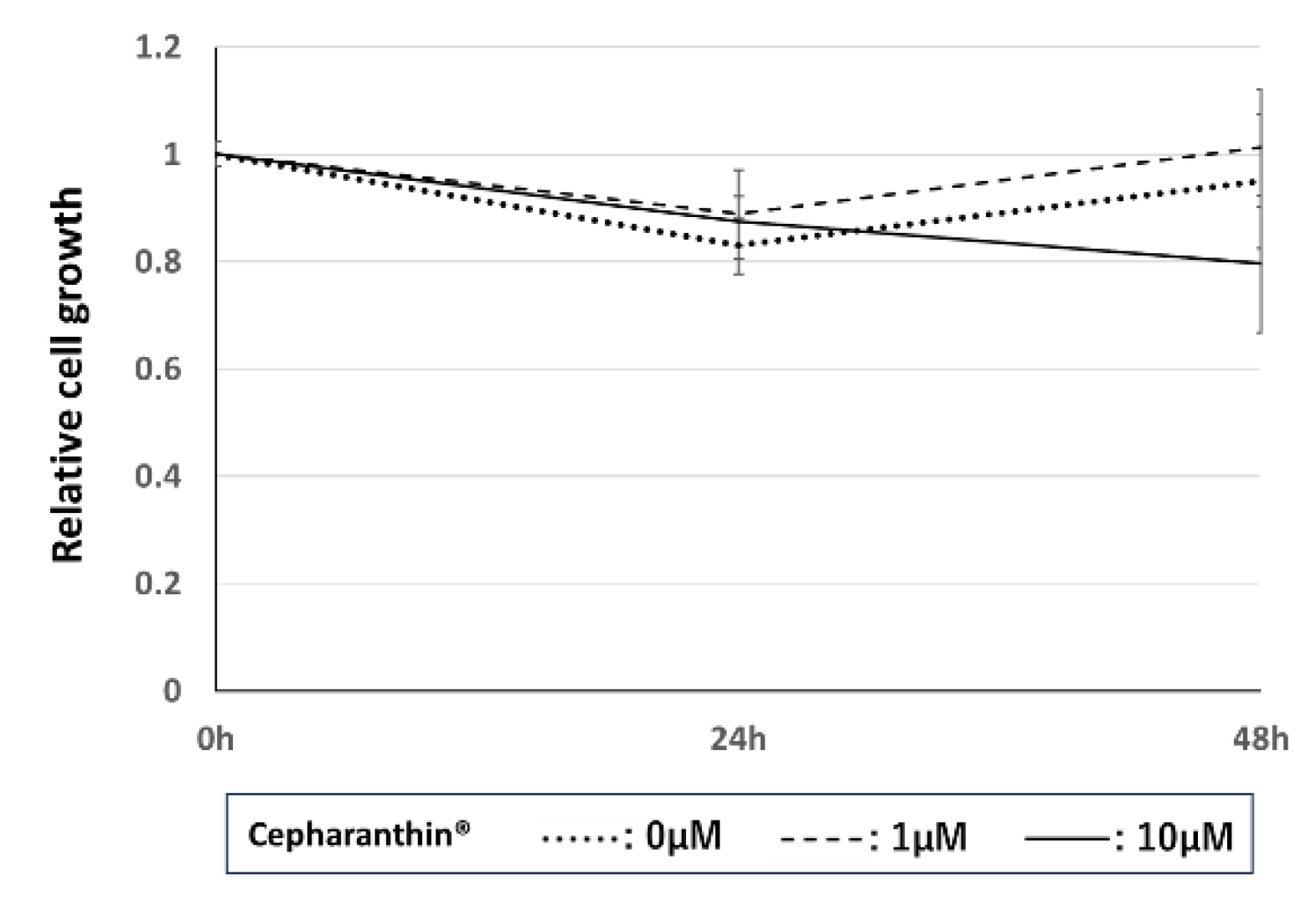
2.4.1. Effect of Cepharanthin® on the Proliferation of hTERT-TIGKs
We analyzed the cell number of hTERT-TIGKs at 24 h and 48 h after treatment with Cepharanthin
® at 0 µM, 1 µM, and 10 µM. Cepharanthin
® marginally affected the cell proliferation of hTERT-TIGKs at either 1 µM or 10 µM (
Figure 4).
2.4.2. Effect of Cephalanthin® on the Influence of Activated T Cells for the Proliferation of hTERT-TIGKs in an In Vitro OLP Model
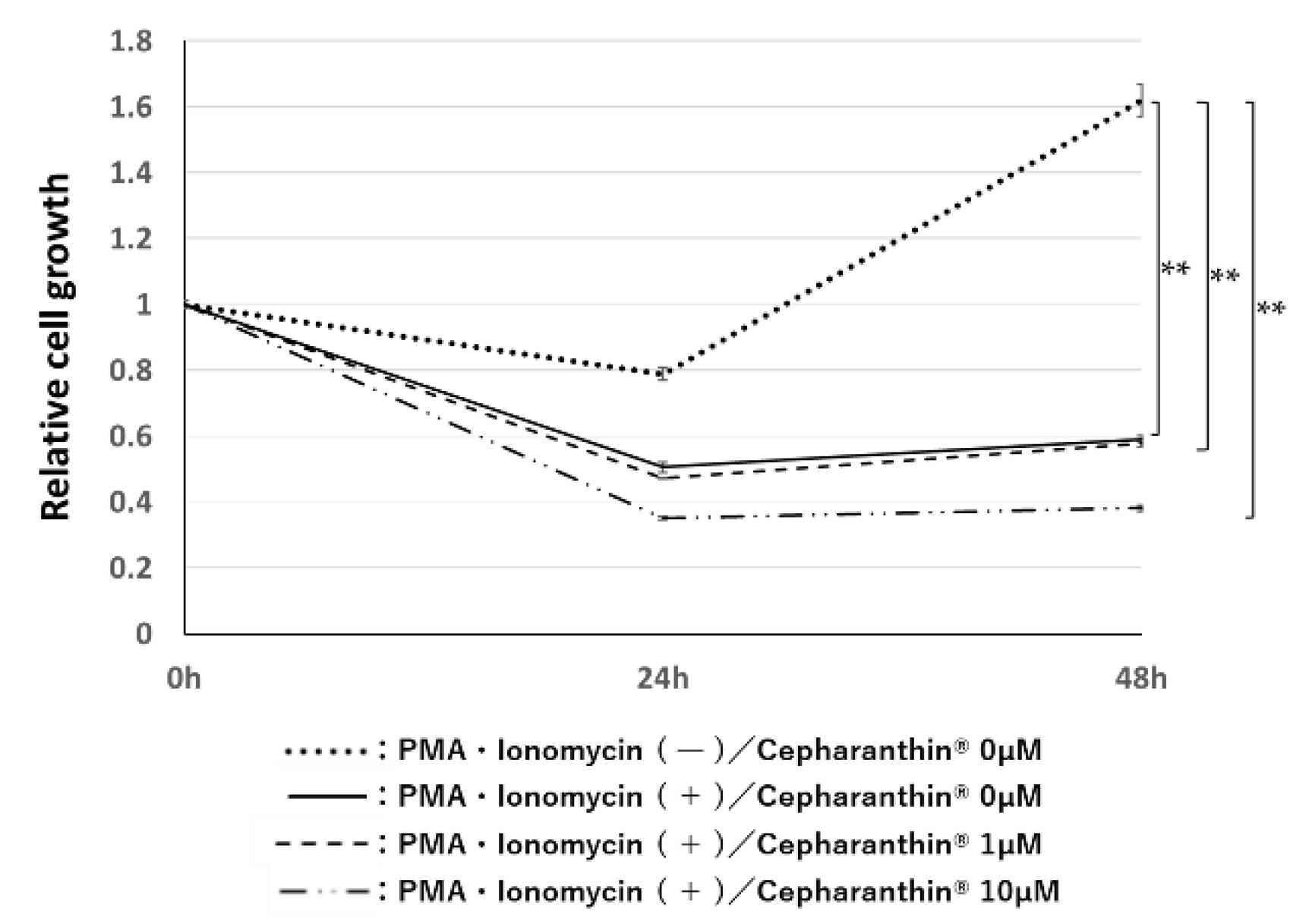
Activated T cells suppressed the proliferation of hTERT-TIGKs in non-contact co-culture. Cepharanthin
® had no significant effect on the inhibitory effect at either 1 µM or 10 µM concentration (
Figure 5).
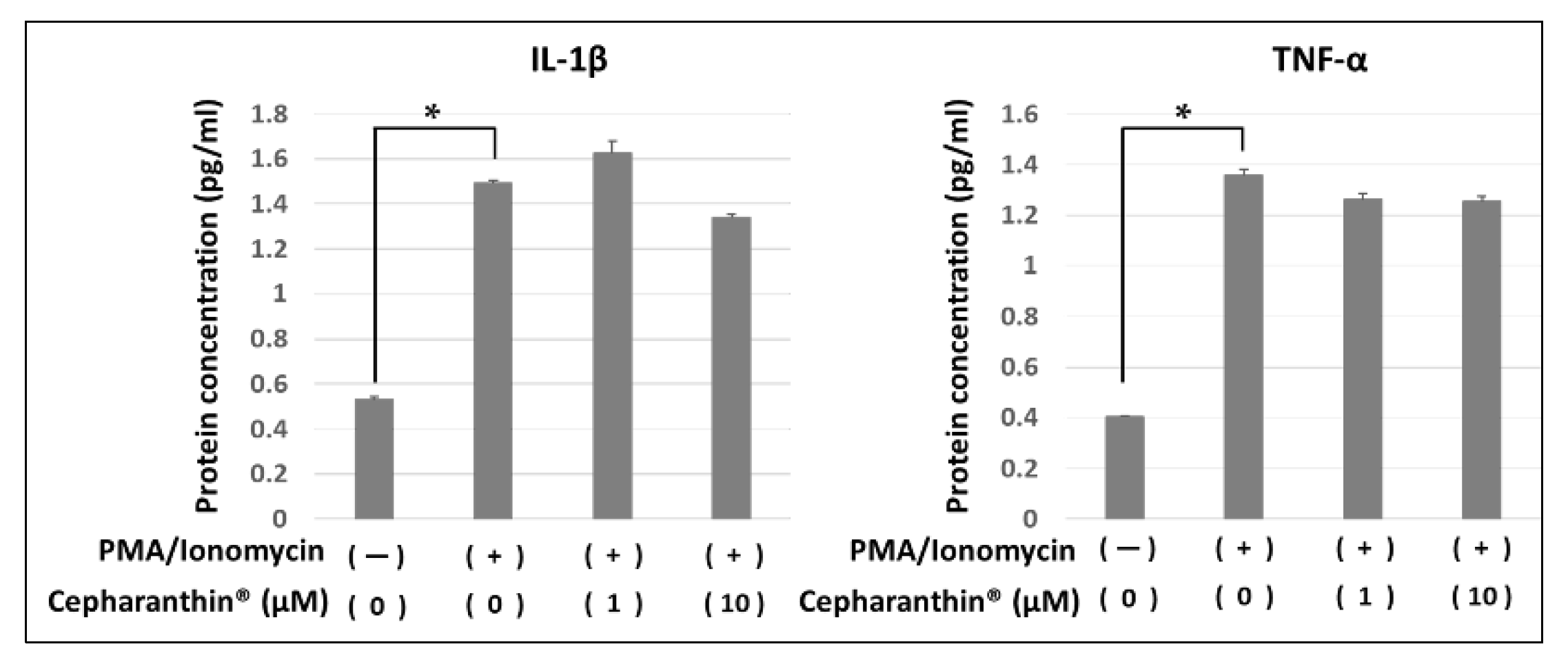
2.5. Effect of Cepharanthin® on the Production and the Accumulation of Inflammatory Factor Proteins from Activated T Cells and hTERT-TIGKs in an In Vitro OLP Model
The protein concentration of IL-β and TNF-α in the culture medium of non-contact co-culture of activated T cells and hTERT-TIGKs were examined by ELISA. Co-culture with activated T cells increased both cytokines, whereas Cepharanthin
® treatment had no apparent effect on the increased cytokines in this experimental condition (
Figure 6).
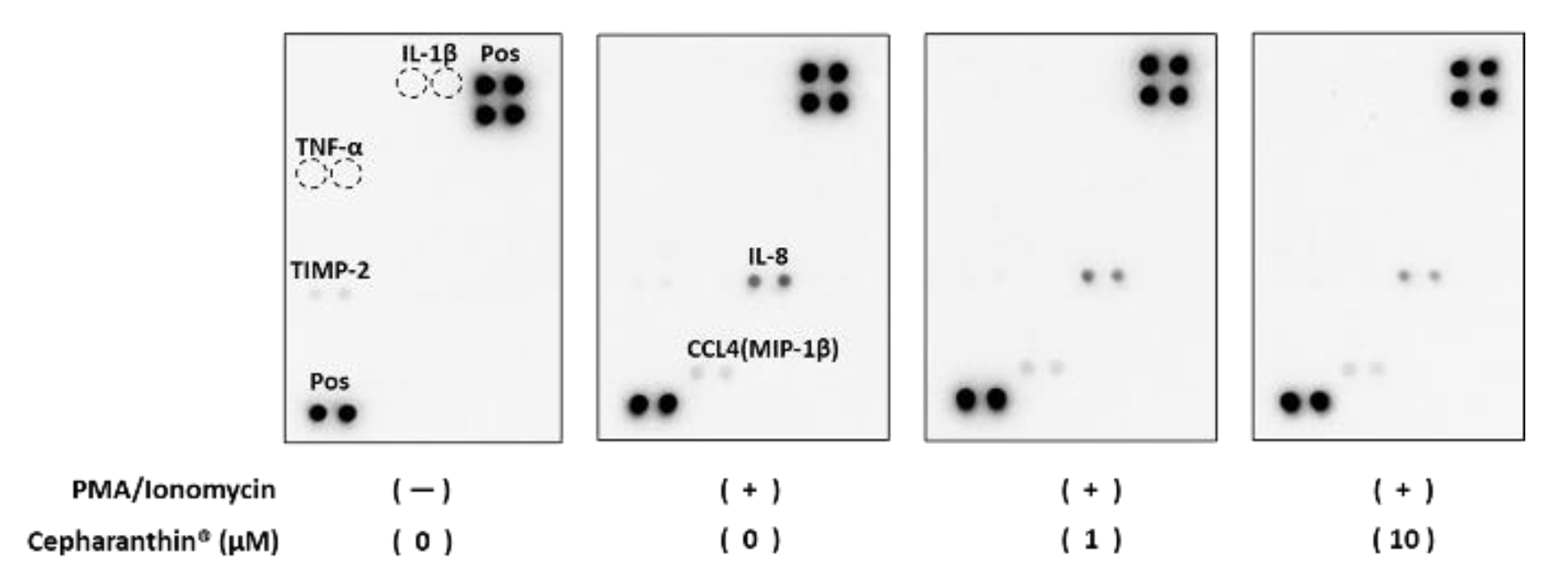
Some protein expressions (TIMP2, CCL4 (MIP-1β), and IL-8) were detectable by dot blotting. Inflammatory stimuli did not change TIMP2 expression, but its expression was abolished by Cepharanthin
® treatment (
Figure 7 and
Figure 8). On the other hand, CCL4 (MIP-1β) and IL-8 became detectable when co-cultured with activated T cells. Induced CCL4 (MIP-1β) protein production was reduced by Cepharanthin
® treatment at 10 µM. Induced production of IL-8 protein was also reduced by Cephalantin
® treatment at 1 µM and 10 µM (
Figure 7 and
Figure 8). Although 40 inflammatory factor proteins could be detectable on the blot used in this study, only 3 proteins from 40 were above the detection limit, and neither IL-1β nor TNF-α could be detectable in this dot blotting.
3. Discussion
This study clarified the effects of Cepharanthin® and its four major components on activated T cells or an immortalized human oral mucosa-derived epithelial cell line in vitro. Four alkaloids, the main components of Cepharanthin®, suppressed the expression of cytokine genes at various degrees in activated T cells. However, the effect of Cepharanthin®, a mixture of these components as a drug formulation, on the suppression of the induced expression of cytokine genes was limited. Cepharanthin® is a complex of many alkaloids other than the four components. The effect of Cepharanthin® as a drug formulation would be expressed as sum total of the effects of each component. On the other hand, Cepharanthin® and its four components suppressed the expression of various cytokine genes in hTERT-TIGKs when stimulated with IL-β. The effect was more apparent than the effect on activated T cells, suggesting that the action of Cepharanthin® in a clinical setting may be dominant on the epithelium.
In co-culture experiments in an in vitro OLP model, activated T cells increased the gene expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, ICAM1, and IVL in hTERT-TIGKs, while Cepharanthin® suppressed their gene expression. ICAM1 is a molecule involved in the adhesion process between T cells in the peripheral blood and vascular endothelial cells at the site of inflammation and in the infiltration process of T cells through blood vessels into the tissues. Increased expression of ICAM1 might cause OLP-specific T-cell-based lymphocytic infiltration at the lamina propria, and suppression of ICAM1 by Cepharanthin® might inhibit such infiltration. Suppression of epithelial proliferation by activated T cells could be consistent with changes in mucosal erythema of OLP caused by the thinning of the epithelial layer, which allows to show the underlying capillaries through the thinning epithelium. The increase of IVL represents the changes in white lesions due to hyperkeratosis in OLP. The suppression of cytokine-induced IVL expression by Cepharanthin® is consistent with the clinical effect of suppressing hyperkeratosis with Cepharanthin® in OLP.
In the reverse-transcription quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), we repeatedly conducted the experiments to obtain consistent results. As a pilot study, we examined the gene expression by stimulation at different concentrations of Cepharanthin® and its four components at different time points on each cell type. We determined the appropriate concentration and time points to detect the effect of the components. If data were collected independently for each experimental group (n=3), their means and standard deviations were calculated to examine whether there were significant differences among the groups. However, it was hard to show a significant difference because the Ct values of the internal control and the target molecule obtained in each well varied widely, and the ratio of these values increased the variation. In this experiment, we carried out independent experiments at least three times for each of these molecules and showed one of the representative results with similar results in Figures.
We examined whether the facts observed in the changes in gene expression could also be observed at the protein level. IL-1β and TNF-α in medium obtained from non-contact co-cultures of activated T cells and epithelial cells in an
in vitro OLP model were significantly increased. However, the suppressive effect of Cepharanthin
® was not apparent, which might be due to the limited effect of Cepharanthin
® on activated T cells. The cytokine concentration assessed in this experiment is the sum of proteins produced by both activated T cells and epithelial cells, which would be a limitation of the present model. The dot-blot experiments also detected the sum of proteins produced from activated T-cells and cytokine-stimulated epithelial cells. It was considered that CCL4 and IL-8 were mainly produced from activated T cells and decreased by Cepharanthin
® treatment. CCL4 is known to be a chemotactic factor for various immune cells, and suppression of its expression by Cepharanthin
® may be considered as one of the mechanisms for inhibiting the migration and aggregation of T lymphocytes. IL-8 is reported to be involved in the NF-κB pathway as well as IL-1β and TNF-α, suggesting that Cephalantin
® may have an anti-inflammatory effect on OLP by suppressing the NF-κB pathway, as also shown in previous reports [
27]. TIMP2 was detected in unstimulated controls and was not increased by stimulation of activated T cells, whereas its expression was abolished by Cepharanthin
® treatment. The association of MMPs and TIMPs with basement membrane disruption has been reported previously [
28,
29,
30]. The disruption is considered to occur when the balance of MMPs and TIMPs shifts to MMPs activation. In this experiment, we did not examine the production and activation of MMPs in both cell types, and it may not simply be interpreted as an increase in basement membrane disruption. It is necessary to investigate not only the expression of TIMPs but also the expression of MMPs and its balance with the expression and local activation to conclude the association of the MMPs and TIMPs in OLP pathogenesis.
The in vitro model established in this study could be a tool for elucidating the mechanisms of OLP pathogenesis and disease persistence. Although the mechanism involving the direct contact between T cells and epithelial cells cannot be analyzed, it is possible to examine gene expression specifically for each cell in the interaction by soluble factors.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
hTERT-TIGKs (ATCC, Virginia, USA) and Jurkat E6.1 (ATCC) are used in this study. hTERT-TIGKs are primary cultured human oral mucosa-derived epithelial cells immortalized with the human TERT gene [
31]. hTERT-TIGKs were cultured in a keratinocyte serum-free medium (KSFM: Thermo Fisher Scientific Japan, Tokyo, Japan) supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin solution. Jurkat E6.1 was cultured in RPMI-1640 (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corp, Osaka, Japan) supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin solution. In all experiments, cells were incubated at 37.0˚C in humidified air containing 5.0 % CO₂.
4.2. Effects of Cepharanthine, Isotetrandrine, Berbamine, Cycreanine, and Cepharanthin® on the Activation of Jurkat E6.1
As a model to confirm the effects of Cephalanthin® and its components on the activation of T lymphocytes, we activated Jurkat E6.1 with PMA (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and Ionomycin (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corp.). We examined the effects of cepharanthine, isotetrandrine, berbamine, cycreanine, and Cepharanthin® on the activated T cells. Jurkat E6.1 cells were cultured at 5.0×10⁶ cells/well in a 6-well plate and treated with 50 ng/ml of PMA, 2 µM of Ionomycin, and 1 µM and 10 µM of cepharanthine, isotetrandrine, berbamine, cycreanine, and Cepharanthin®, respectively. Cells were collected after 6 hours of incubation. The expression of IL-1β and TNF-α was examined by RT-qPCR. Cepharanthine, isotetrandrine, berbamine, cycreanine, and Cepharanthin® were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) at the concentration of 10 mM. Each drug was diluted to the final concentration of 1 µM and 10 µM in the culture medium and used in the experiments. The DMSO in each group was adjusted to a constant volume. Cepharanthine, isotetrandrine, berbamine, cycreanine, and Cepharanthin® were kindly provided by KAKEN SYOYAKU CO, LTD (Tokyo, Japan).
4.3. Effects of Cepharanthine, Isotetrandrine, Berbamine, Cycreanine, and Cepharanthin® on the Expression of Various Cytokine Genes Induced by Inflammatory Cytokine Stimulation in hTERT-TIGKs
We investigated the effects of Cepharanthin® and its components on the expression of various cytokine genes induced after stimulation in hTERT-TIGKs with inflammatory cytokines. hTERT-TIGKs cells were cultured at 1.0×10⁶ cells/well in a 6-well plate for 24 hours. Afterward, cells were treated with 10 ng/ml of IL-1β and 1 µM and 10 µM of cepharanthin, isotetrandrine, berbamine, cycreanine, and Cepharanthin®, respectively, and incubated for 1 hour. The expression status of IL-1β, ICAM1, and TNF-α was examined by RT-qPCR. Cepharanthine, isotetrandrine, berbamine, cycreanine, and Cepharanthin® were dissolved in DMSO, and the DMSO in each group was adjusted to a constant volume.
4.4. Effect of Cepharanthin® on Cytokine Gene Expression in hTERT-TIGKs in an In Vitro OLP Model
We established an in vitro OLP model that mimics the liquid factor-mediated reaction between the epithelium and infiltrating lymphocytes in OLP. Using THINCERT® (GREINER BIO-ONE, Baden-Württemberg, Germany), hTERT-TIGKs were cultured in the lower layer and activated Jurkat E6.1 were placed in the insert chamber and co-cultured without cell contact. Using this model, we confirmed the gene expression of inflammatory cytokines and epithelial cell differentiation marker in hTERT-TIGKs. We examined the effect of Cepharanthin®️ on these gene expressions. Jurkat E6.1 cells were treated with 50 ng/ml of PMA and 2 µM of Ionomycin in the insert chamber and incubated for 6 hours to activate Jurkat E6.1. Insert chambers containing activated T cells were placed on THINCERT®, where hTERT-TIGKs were cultured at 1.0 × 10⁶ cells/well in the lower layer. Then, co-culture continued for 1 hour. Cepharanthin® was added at concentrations of 1 µM and 10 µM, and the expression of IL-1β, ICAM1, TNF-α, and IVL in hTERT-TIGKs was investigated by RT-qPCR. Cepharanthin® was dissolved in DMSO, and the DMSO in each group was adjusted to a constant volume.
4.5. RT-qPCR
ISOGEN (Nippon Gene, Tokyo, JAPAN) was used to extract total RNA according to the manufacturer's protocol. cDNA was synthesized from the obtained RNA using ReverTra Ace® qPCR RT Master Mix (TOYOBO, OSAKA, JAPAN). qPCR was performed using the Thermal Cycler Dice® Real Time System II (Version 4.02, TAKARA BIO, Shiga, Japan). Independent experiments were carried out at least three times for each of these molecules, and one of the representative results with similar results is shown in Figures.
4.6. Effect of Cepharanthin® and/or Activated T Lymphocytes on the Proliferation of hTERT-TIGKs
4.6.1. Effect of Cepharanthin® on the Proliferation of hTERT-TIGKs
The effect of Cepharanthin® on the proliferation of hTERT-TIGKs was investigated. hTERT-TIGKs cultured at 1.0×10⁶ cells/well were treated with Cephalantin® at concentrations of 0 µM, 1 µM, and 10 µM, and the cell number was analyzed using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8; Dojindo, Tokyo, Japan) at 0h, 24h and 48h.
4.6.2. Effect of Cepharanthin® on the Influence of Activated T Cells on the Proliferation of hTERT-TIGKs in an In Vitro OLP Model
Jurkat E6.1 cells were treated with 50 ng/ml of PMA and 2 µM of Ionomycin in the insert chamber and incubated for 6 hours to activate Jurkat E6.1. Next, the insert chambers containing activated T cells were placed on THINCERT®, where hTERT-TIGKs were cultured at 1.0 × 10⁶ cells/well in the lower layer. Insert chambers containing non-activated T cells were set up as controls. Cepharanthin® was added at concentrations of 0 µM, 1 µM, and 10 µM, and the cell number was analyzed at 0h, 24h, and 48h.
4.7. Effect of Cepharanthin® on the Production and Accumulation of Inflammatory Factor Proteins from Activated T Cells and hTERT-TIGKs in an In Vitro OLP Model
We investigated the effect of Cephalantin® on the production and accumulation of inflammatory factor proteins produced from activated T lymphocytes and hTERT-TIGKs in an in vitro OLP model. Jurkat E6.1 cells were treated with 50 ng/ml of PMA and 2 µM of Ionomycin in the insert chamber and incubated for 6 hours to activate Jurkat E6.1. Next, the insert chambers containing activated T cells were placed on THINCERT®, where hTERT-TIGKs were cultured at 1.0 × 10⁶ cells/well in the lower layer. Insert chambers containing non-activated T cells were set up as controls. Cepharanthin® was added to each culture system at 1 µM and 10 µM concentrations, and the medium was collected after 24 hours. The protein amounts of IL-1 β and TNF-α in each medium were determined by ELISA (Human IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 ELISA Kit/Human TNF-alpha ELISA Kit, R&D Systems, Minnesota, USA).
Dot blotting was also performed using the Human Inflammation Antibody Array Membrane (Abcam, Cambridge, UK). Forty inflammatory factor proteins (Eotaxin, Eotaxin-2, GCSF, GM-CSF, ICAM-1, IFN-γ, I-309, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-6, IL-6sR, IL-7, IL-8, IL-10, IL-11, IL-12p40, IL-12p70, IL-13, IL-15, IL-16, IL-17, IP-10, MCP-1, MCP-2, M-CSF, MIG, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, MIP-1δ, RANTES, TGF-β1, TNF-α, TNF-β, sTNF-RI, sTNF-RII, PDGF-BB, TIMP-2) are detectable on this membrane. Dot blots were performed according to the provider's protocol, and chemiluminescence imaging was performed using a CCD camera, WSE-6100 LuminoGraph I (ATTO Corp, Tokyo, Japan). The images obtained were analyzed in Image J (National Institute of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, U.S.A.) [
32]. The region of interest was set to be a fixed area, and the integrated density within the region was calculated. The mean value of the integrated density of each spot was calculated.
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS ver. 29 (IBM SPSS, Inc., Tokyo, Japan). Tukey's method was used as a post-hoc analysis for proliferation experiments, and the student’s t-test was used for ELISA experiments. P-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study suggest that Cepharanthin®️ may exert its clinical effects on OLP by suppressing lymphocyte infiltration, thinning of the epithelial layer, and hyperkeratosis. The effects of Cepharanthin®️ might be expressed through two aspects: its effect of mildly suppressing the activation of T lymphocytes and strongly suppressing the response of epithelial cells to inflammatory stimuli.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama], T.W., and H.K.; methodology, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama].; validation, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama], Y.K. [Yoshiaki Kitsukawa], A.K., T.H. [Toshiki Hyodo], Y.K. [Yosuke Kunitomi], E.Y., T.H. [Tomonori Hasegawa], W.K., R.W., S.T., C.F., T.W., and H.K.; formal analysis, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama], and H.K.; investigation, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama].; resources, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama].; data curation, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama].; writing—original draft preparation, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama], and H.K.; writing—review and editing, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama], T.W., and H.K.; visualization, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama].; supervision, H.K.; project administration, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama].; funding acquisition, R.S., Y.K. [Yuske Komiyama], and E.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a Research Grant from Dokkyo Medical University (grant no. 1864,2153,2371) and JSPS KAKENHI grant numbers JP20K10123.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to KAKEN SYOYAKU CO, LTD for supplying cepharanthine, isotetrandrine, berbamine, cycreanine and Cepharanthine®.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sugerman P.B., Savage N.W., Walsh L.J., Zhao Z.Z., Zhou X.J., Khan A., Seymour G.J., Bigby M. The pathogenesis of oral lichen planus. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2002;13:350-365. doi: 10.1177/154411130201300405. [CrossRef]
- Lodi G., Scully C., Carrozzo M., Griths M., Sugerman P.B., Thongprasom K. Current controversies in oral lichen planus: Report of an international consensus meeting. Part 1. Viral infections and etiopathogenesis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;100:40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2004.06.077. [CrossRef]
- Deyhimi P,Arzhang E. Study of extrinsic apoptotic pathway in oral Lichen Planus using TNFR 1 and FasL immunohistochemical markers and TUNEL technique. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and Pathology. 2018;30:380-385.
- Deng S., Wang S., Shi X., Zhou H. Microenvironment in Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders: Multi-Dimensional Characteristics and Mechanisms of Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:8940. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168940. [CrossRef]
- Nosratzehi T. Oral lichen planus: an overview of potential risk factors, biomarkers and treatments. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP. 2018;19:1161-1167. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.5.1161. [CrossRef]
- Thongprasom K., Chaimusig M., Korkij W., Sererat T., Luangjarmekorn L., Rojwattanasirivej S. A randomized-controlled trial to compare topical cyclosporin with triamcinolone acetonide for the treatment of oral lichen planus. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36(3):142-146. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2007.00510.x. [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick S.G., Hirsch S.A., Gordon S.C. The malignant transformation of oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid lesions: a systematic review. J Am Dent Assoc. 2014;145:45-56. doi: 10.14219/jada.2013.10. [CrossRef]
- Georgakopoulou E.A., Troupis T.G., Troupis G., Gorgoulis V.G. Update of the cancer-associated molecular mechanisms in oral lichen planus, a disease with possible premalignant nature. J BUON. 2011;16:613-6.
- Giuliani M., Troiano G., Cordaro M., Corsalini M., Gioco G., Lo Muzio L., Pignatelli P., Lajolo C. Rate of malignant transformation of oral lichen planus: a systematic review. Oral Dis. 2019;25(3):693-709. doi: 10.1111/odi.12885. [CrossRef]
- Landini G, Mylonas P, Shah Z.I, Hamburger J. The reported rates of transformation of oral lichen planus. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and Pathology. 2014;26:213-220.
- Shirasuna K. Oral lichen planus: malignant potential and diagnosis. Oral Sci. Int. 2014;11:1-7. doi: 10.1016/S1348-8643(13)00030-X. [CrossRef]
- M. R. Roopashree., Rajesh V Gondhalekar., M. C. Shashikanth., Jiji George., S. H. Thippeswamy., Abhilasha Shukla. Pathogenesis of oral lichen planus - a review.J Oral Pathol Med. 2010;Nov;39(10):729-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2010.00946.x. [CrossRef]
- Scully C., Beyli M., Ferreiro M.C., Ficarra G., Gill Y., Griffiths M. Update on oral lichen planus: etiopathogenesis and management. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1998;9:86-122. doi: 10.1177/10454411980090010501. [CrossRef]
- Ismail S.B., Kumar S.K., Zain R.B. Oral lichen planus and lichenoid reactions: Etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, management and malignant transformation. J. Oral Sci. 2007;49:89-106. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.49.89. [CrossRef]
- Lodi G., Scully C., Carrozzo M., Griffiths M., Sugerman P.B., Thongprasom K. Current controversies in oral lichen planus: report of an international consensus meeting. Part 2. Clinical management and malignant transformation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;100:164-178. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2004.06.076. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2004.06.076. [CrossRef]
- El-Howati A, Thornhill MH, Colley HE, Murdoch C. Immune mechanisms in oral lichen planus. Oral Dis. 2023;29(4):1400-1415. doi: 10.1111/odi.14142. Epub 2022 Feb 8. [CrossRef]
- Kawamata H., Ito D., Tsushima F., Nakamura S., Kawano K., Sugawara Y., MoriyamaM., Iwabuchi H., Abiko Y., Maeda H., Sugita Y., Hasegawa H., Komiyama Y., Shiraishi R., Wakui T. Narrative Review and Task Force Consensus of Current Treatment Methods and Clinical Evaluation of the Outcome for Oral Lichen Planus. Journal of Japanese Society of Oral Medicine. 2023;29(2):21-35.
- Cepharanthin® ,KAKEN SYOYAKU CO, LTD. Available online: https://www.kakenshoyaku.com/product/cepharanthin.html (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Seubwai W., Vaeteewoottacharn K., Hiyoshi M., Suzu S., Puapairoj A., Wongkham C., Okada S., Wongkham S. Cepharanthine exerts antitumor activity on cholangiocarcinoma by inhibiting NF-kappaB. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:1590-1595. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01572.x. [CrossRef]
- Bailly C. Cepharanthine: an update of its mode of action, pharmacological properties and medical applications. Phytomedicine. 2019;62:152956. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152956. [CrossRef]
- Chen Z., Huang C., Yang Y.L., Ding Y., Ou-Yang H.Q., Zhang Y.Y., Xu M. Inhibition of the STAT3 signaling pathway is involved in the antitumor activity of cepharanthine in SaOS2 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012;33:101-108. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.164. [CrossRef]
- Xu W., Kusano J., Chen S., Yamamoto R., Matsuda H., Hara Y., Fujii Y., Hayashi S., Tanaka S., Sugiyama K., Yamada H., Hirano T. Absolute configuration of tetrandrine and isotetrandrine influences their anti-proliferation effects in human T cells via different regulation of NF-κB. Z. Fur Naturforschung. C J. Biosci. 2021;76:21-25. doi: 10.1515/znc-2020-0064. [CrossRef]
- Han C., Wang Z., Chen S., Li L., Xu Y., Kang W., Wei C., Ma H., Wang M., Jin X. Berbamine suppresses the progression of bladder cancer by Modulating the ROS/NF-kappaB axis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;8851763. doi: 10.1155/2021/8851763. [CrossRef]
- Kondo Y., Takano F., Hojo H. Suppression of lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatitis and tumor necrosis factor production by bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids in bacillus Calmette-Guerin-treated mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1993;46:1861-1863. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90594-m. [CrossRef]
- Sugawara Y, Jinbu Y, Sasano T, Kusama M, Mori Y, Kitagawa Y, Takahashi T, Sugiyama Y, Fukuda M, Kawamata H, Shibata T, Ueno T, Kishimoto H, Iida S, Nakamura N, Sugiura T. Retrospective study on clinical efficacy of Cepharanthine for oral Lichen Planus as determined by the multiple institutes collaborative project. J Jpn Oral Medicine 2016;22:59-67.
- Liu K., Hong B., Wang S., Lou F., You Y., Hu R., Shafqat A., Fan H., Tong Y. Pharmacological activity of cepharanthine. Molecules. 2023;28(13):5019. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135019. [CrossRef]
- Manna S.K., Ramesh G.T. Interleukin-8 induces nuclear transcription factor-kappaB through a TRAF6-dependent pathway. J. Boil. Chem. 2005;280(8):7010-7021. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410994200. [CrossRef]
- Kawamata H., Kawai K., Kameyama S., Johnson M.D., Stetler-Stevenson W.G., Oyasu R. Over-expression of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMP1 and TIMP2) suppresses extravasation of pulmonary metastasis of a rat bladder carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer. 1995;63:680-687. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910630513. [CrossRef]
- Kawamata H., Nakashiro K.i., Uchida D., Harada K., Yoshida H., Sato M. Possible contribution of active MMP2 to lymph-node metastasis and secreted cathepsin L to bone invasion of newly established human oral-squamous-cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer. 1997;70:120-127. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19970106)70:1<120::aid-ijc18>3.0.co;2-p.
- Sakai T., Furihata T., Kawamata H., Omotehara F., Shinagawa Y., Imura J., Kubota K., Terano A., Fujimori T. Molecular and genetic characterization of a non-metastatic human esophageal cancer cell line, T. Tn expressing non-functional mutated p53. Int. J. Oncol. 2002;21:547-552.
- Moffatt-Jauregui C.E., Robinson B., de Moya A.V., Brockman R.D., Roman A.V., Cash M.N., Culp D.J., Lamont R.J. Establishment and characterization of a telomerase immortalized human gingival epithelial cell line. Journal of Periodontal Research, 2013;48(6): 713-721. doi:10.1111/jre.12059. [CrossRef]
- Rasband W.S., ImageJ, U. S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA, http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/, 1997-2012.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).