1. Introduction
Dextro-transposition of the great arteries (D-TGA) is a critical congenital heart defect that affects a significant number of newborns, with a prevalence of 1 to 47 cases per 10,000 births. In this condition, the pulmonary artery and the aorta are switched, but the atrioventricular concordance is maintained [
1,
2]. This results in a lethal hemodynamic pattern where both systemic and pulmonary circulations run in parallel, causing severe hypoxemia in the brain and vital organs, deep acidemia, and low cardiac output. Survival crucially depends on mixing oxygenated and deoxygenated blood through the atrial septal defect (ASD or persistent foramen ovale - FO), ventricular septal defect (VSD), or patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). The spontaneous closure or restriction of these defects at birth significantly increases the risk of severe cyanosis and acute cardiorespiratory deterioration [
3]. Dextro-transposition of the great arteries can be classified as simple if the ventricular septum is intact or complex if it is accompanied by other congenital heart defects, such as ventricular septal defect (VSD), left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, or coarctation of the aorta.
The clinical presentation of D-TGA depends on the mixing of blood through additional communications, resulting in cyanosis that is unresponsive to oxygen supplementation, isolated tachypnea, and occasionally a cardiac murmur associated with PDA or ASD/VSD. This condition can be accurately diagnosed through either a prenatal or postnatal echocardiogram [
4].
The arterial switch is the gold-standard surgical approach for treating D-TGA. After birth, immediate management includes ensuring blood mixes between the systemic and pulmonary circulations. Prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) is administered intravenously to maintain a patent ductus arteriosus. If PGE1 treatment is ineffective and the newborn is unstable, or if the ASD/PFO is restricted, it is crucial to perform Raskind atrial balloon septostomy (BAS), ideally within the first 24 hours of life [
5,
6].
The cardiac anomalies in D-TGA may alter cerebral blood flow (CBF) and oxygenation even before birth, leading to ischemic and hypoxic cerebral injuries and long-term neurodevelopmental impairments [
7]. Preoperative medications required to maintain PDA and BAS for atrial blood mixing can also contribute to these complications [
8]. After birth, preoperative/intraoperative and post-surgery brain monitoring can detect alteration in CBF and oxygenation, enabling interventions to enhance neurological outcomes [
9].
Arterial spin-labeled perfusion magnetic resonance imaging (ASL-pMRI) and optical diffuse correlation spectroscopy allow for accurate determination of CBF after birth. However, its accessibility in neonatal units or during the preoperative period is often limited by patient hemodynamic instability [
10,
11,
12,
13]. Instead, cerebral Doppler ultrasound (CDU) is a noninvasive bedside tool used to evaluate CBF intermittently and provides a real-time overview of cerebral perfusion. It assesses the blood flow velocity in the cerebral arteries during both systole and diastole and helps estimate resistance to cerebral blood flow [
14,
15]. Assessing blood flow velocity in the diastole can indicate the degree of ductal steal phenomenon. If a retrograde diastolic flow is present, it means an early need for surgical correction [
4].
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a method used to measure the trend of cerebral regional tissue oxygen saturation (crSO
2) and cerebral fractional tissue extraction (cFTOE). This helps in assessing preoperative cerebral hypoxia by indirectly measuring the balance of cerebral oxygen consumption and supply [
10]. NIRS values provide information about perfusion and oxygenation status.
Limited data exists regarding the impact of pre-surgical interventions on cerebral oxygenation and hemodynamics in neonates with D-TGA, using noninvasive NIRS technology and cerebral Doppler investigation. This study aims to investigate the early effects of preoperative interventions at 24 hours of life on the cerebral hemodynamics and oxygenation of neonates diagnosed with D-TGA. The evaluation data of infants who received PGE1 treatment alone, those with BAS, and age-matched controls were compared in dynamics.
2. Materials and Methods
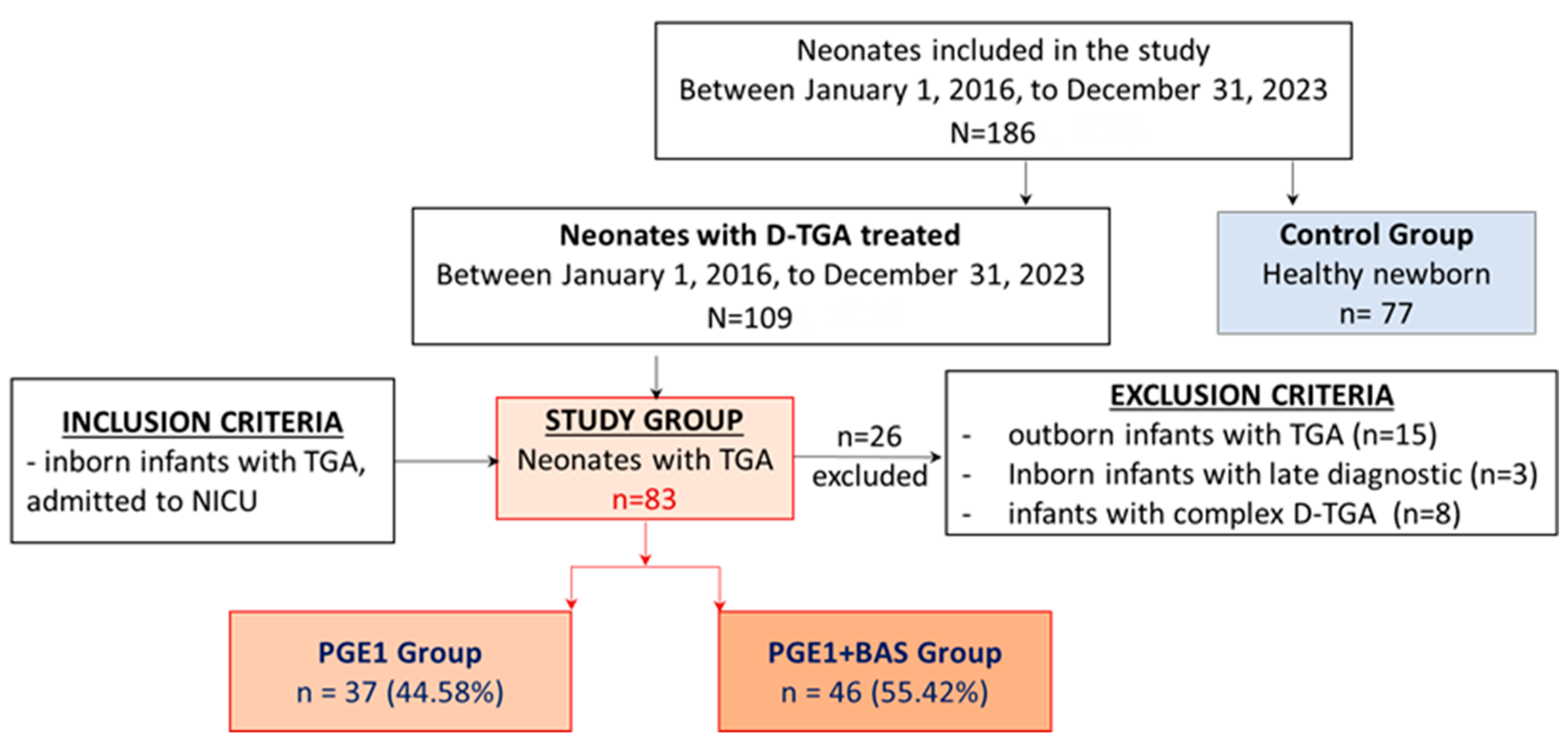
This retrospective case-control study was conducted at a tertiary perinatal center (Târgu Mureș County Emergency Clinical Hospital, Romania) with onsite pediatric cardiology and neonatal cardiac surgery from January 1, 2016, to December 31, 2023. We aimed to identify the changes in CBF and cerebral oxygenation after the initiation of preoperative PGE1 treatment to maintain patency of ductus arteriosus and BAS, respectively. The study was approved by the hospital’s ethics board committee (Nr.35518/27.11.2019). Written consent of the mother was obtained for this study.
Study groups
Inclusion criteria: inborn neonates diagnosed pre/postnatally with D-TGA with intact ventricular septum (IVS-TGA) and D-TGA with ventricular septal defect (VSD-TGA).
Exclusion criteria: inborn neonates with complex D-TGA or with late diagnosis (after 24 hours of life) and D-TGA newborns transferred to our center after 24 hours of life.
Newborns with D-TGA undergoing heart surgery for the arterial switch were divided into two groups: the PGE1 group and the PGE1+BAS group. The control group included healthy full-term newborns who were recruited from the low-risk obstetrics department (
Figure 1).
D-TGA Management and Study Intervention
As per the unit protocol, the management of D-TGA involves initiating continuous intravenous PGE1 treatment at a starting dose of 0.03–0.05 micrograms per kilogram per minute to achieve peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) of 80-85%. In cases where SpO2 does not improve, and other left-to-right shunts that facilitate blood mixing for oxygenation are insufficient, the pediatric cardiologist may indicate performing BAS as soon as possible after starting PGE1 infusion. Arterial switch surgery is routinely performed at our institution for patients with D-TGA aged 7 to 16 days. PGE1 doses are meticulously adjusted based on hemodynamic stability, SpO2 levels, and serial echocardiographic assessments.
Data Collection
The demographic data collected from clinical records for study groups include gender, gestational age (GA), birth weight (BW), head circumference (HC), antenatal care, antenatal diagnosis, intrauterine transfer, mode of delivery, Apgar scores (at 1 and 5 minutes), days between birth and arterial switch operation, and pre-and post-surgery deaths.
The clinical and ultrasound data collected include blood pressure (BP) measurement, pre-ductal oxygen saturation (SpO2), cerebral regional oxygen saturation (crSO2), cerebral fractional tissue extraction (cFTOE), FiO2, and arterial blood gases (pO2, HCO3, lactate, hemoglobin level), cardiac and head ultrasounds. For D-TGA groups, we noted the presence of tachypnea, cyanosis, cardiac murmur, need for mechanical ventilation and inotropes, and PGE 1 doses.
The outcome variables included the change in pre-ductal SpO2, crSO2, cFTOE, blood gases, FiO2, and BP at 24 hours of life after each intervention (PGE1 treatment/BAS). We noted the changes in the ACA velocities and RI at 24 hours after delivery in all groups, and we assessed the size of the ASD after the BAS procedure in the D-TGA group who underwent septostomy.
Timing of patient evaluation
For the clinical and ultrasound evaluation of the patients and comparison purposes, we defined three specific time points: 1. for all study groups, the first assessment took place within the first 2 hours after birth; 2. for the group that required septostomy, the second assessment occurred just before BAS procedure; 3. The third assessment was conducted 24 hours after birth for all study groups (
Table 1).
Cardiac Ultrasounds
An echocardiogram, performed by a pediatric cardiologist, was used to evaluate the overall cardiac function, anatomy, and type of D-TGA (TGA-IVS or TGA-VSD). In the study, every newborn with D-TGA received an echocardiogram within two hours after delivery before starting PGE1 treatment. Subsequent echocardiograms were performed at 24 hours of life in the PGE1 group. Additionally, an echocardiogram was conducted before septostomy and at 24 hours of life in the PGE1+BAS group, measuring ASD size (mm), ASD gradient, and PDA size (mm) post-BAS procedure. As per the unit protocol, we defined an ASD/FOP as restrictive if the size is less than 4 mm and the gradient is more than 5 mmHg.
Cerebral Ultrasounds
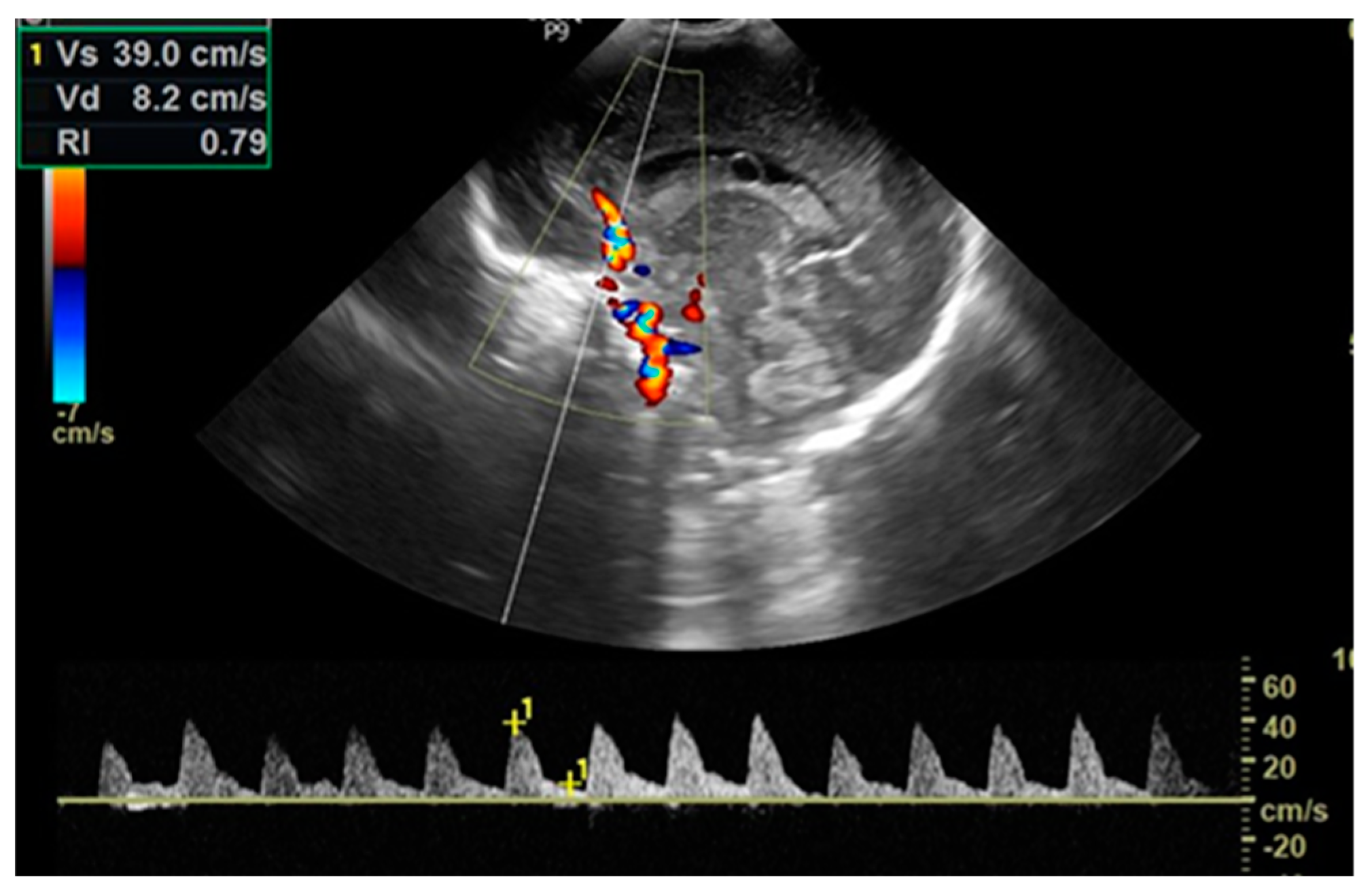
The cerebral ultrasound was performed using the LOGIQ e9 ultrasound machine in coronal and sagittal planes by trained neonatologists with a 7.5-12 MHz transducer. After scanning for structural abnormalities, a Doppler investigation was conducted by placing a pulsed Doppler sample volume gate at the level of the anterior cerebral artery (ACA), positioned anterior to the genu of the
corpus callosum in the sagittal view, with the insonation angle close to 0. The ACA flow velocities were assessed by measuring peak systolic velocity (PSV in cm/s) and end-diastolic velocity (EDV in cm/s) and then automatically calculating the resistive index (RI/Pourcelot index) (
Figure 2). Cerebral ultrasounds were performed for every newborn in the D-TGA and control groups within two hours after delivery and again at 24 hours of life. Newborns with BAS also underwent another cerebral ultrasound examination before septostomy.
SpO2 Measurement
In our practice, we continuously monitor SpO2 in both the right upper limb (pre-ductal) and lower limb (post-ductal) using pulse oximetry. The SpO2 values were measured using Nellcor (Medtronic) sensors. For this study, we used pre-ducal SpO2 for comparison, which reflects the level of oxygenation reaching the brain.
crSO2 and cFTOE Measurement
We utilized an INVOS 5100C near-infrared spectrometer (NIRS) for continuous monitoring of cerebral oxygenation (crSO2). Neonatal NIRS sensors were positioned on the infants’ foreheads, and cerebral fractional tissue oxygen extraction (cFTOE) was determined using the formula (SpO2—crSO2)/SpO2.
Blood Pressure Measurement
Noninvasive blood pressure (BP) measurements were taken using the oscillometric method with a properly sized cuff on the right upper arm. BP values were recorded at specific time points. We measured blood pressure (systolic, diastolic, mean arterial pressure (MAP)).
Blood Gases Measurement
The capillary blood sample was taken from the heel and analyzed with the same blood gas analyzer. pH, partial pressure of oxygen (pO2), and lactate were recorded and analyzed.
Statistical Analyses
The statistical processing of the analyzed variables was performed in SPSS v.29 (IBM Ireland Product Distribution Limited, IBM House, Shelbourne Road, Balls-bridge, Dublin, Ireland) and the STATA 16 software (StataCorp LLC, 4905 Lakeway Drive, College Station, TX, USA). The descriptive presentation of the analyzed parameters and comparison tests were applied according to the type of variables. Continuous variables were reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD) in the case of normal distributions or median (interquartile range – IQR) when the variable was not normally distributed. The verification of the normal distribution was carried out with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. At the same time, the homogeneity of the variables was checked by applying the Levene test (the Levene Homogeneity of Variance Test). To compare the corresponding parameters, the Kruskal-Wallis H Test was applied, specifically for comparisons between three or more series of values and the post-hoc analysis or Student’s t-test. Depending on the characteristics of the variables, the Mann-Whitney U Test was applied where appropriate.
The qualitative variables have been presented as absolute frequency (n) and relative frequency (%). The comparison of qualitative variables was performed by applying the non-parametric Pearson Chi-square test. The level of significance calculated in the tests applied in the analysis (p-value) was considered significant for values lower than the reference value p = 0.05.
3. Results
We have identified 109 patients who were diagnosed with D-TGA and received treatment in our NICU. We excluded 26 patients: eight complex D-TGA cases, three inborn D-TGA cases with late diagnosis, and 15 outborn D-TGA cases. Therefore, 83 out of 109 participants were enrolled in the study and received initial PGE1 treatment, of which 46 underwent BAS. The control group consisted of 77 healthy newborns matched for gestational age (
Figure 1).
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
In our study, we found no significant differences in GA, BW, or antenatal care between the groups. Additionally, there were no substantial variances in prenatal diagnosis, in-utero transfer, mode of delivery, Apgar scores, age at surgery, and pre-and post-surgery mortality between the two groups with D-TGA. Conversely, the head circumference was significantly smaller in the PGE1+BAS group compared to the control group (33.8 ± 1.3 cm vs. 34.5 ± 1 cm, p = 0.0151) (
Table 2).
The Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes were similar between the D-TGA groups but significantly lower than those in the control group. Furthermore, we observed a higher rate of neonatal deaths in the PGE1+BAS group compared to the PGE1 group (17.4% vs. 2.7%, p=0.0240).
3.2. Clinical Characteristics, Interventions, and Heart Ultrasound Evaluation
We analyzed both study groups with D-TGA based on the clinical characteristics, interventions (PGE1 treatment and BAS procedure), and heart ultrasound evaluation. The clinical variables such as tachypnea, cyanosis, cardiac murmur, and the need for mechanical ventilation and inotropes did not show significant differences between the D-TGA groups. Although the initial doses of PGE1 (μg/kg/min) were almost similar, at 24 hours of life, the doses were significantly lower in the PGE1+BAS group compared with the PGE1 group (0.031 ± 0.015 vs. 0.040 ± 0.016; p = 0.0136). In the PGE1+BAS group, the mean time to BAS was 8.71 ± 5.05 hours after delivery. After septostomy, the size of ASD/FOP increased from a median of 3 mm to 4.65 mm in the PGE1+BAS group. No deaths occurred because of the BAS procedure, and no early complications related to the procedure were recorded. The results are presented in
Table 3.
Regarding the characteristics of the PDA, such as size and direction of blood flow, we did not find any significant differences between the D-TGA groups. However, we noticed variations in left-to-right shunts that facilitate blood mixing for oxygenation. Thus, at birth, the group requiring septostomy had a significantly smaller median size of ASD/PFO (median 3 mm vs. 4.8 mm; p<0.001) and a significantly higher ASD gradient (8.7 mmHg vs. 5 mmHg; p < 0.001). In the PGE1+BAS group, the VSD size (0.63 ± 1.99 mm vs. 1.57 ± 2.59 mm; p = 0.0393) was observed to be smaller compared to the PGE1 group.
3.3. Effect of PGE1 and BAS on Peripheric and Cerebral Oxygenation
Within 2 hours of life, before initiation of PGE1 infusion, the median of pre-ductal SpO2 was significantly lower in the group treated with PGE1 and BAS compared to the group treated with PGE1 alone (median value 72% vs. 80%; p = 0.00012), while both D-TGA groups had lower pre-ductal SpO2 than the control group (median value 99%). Conversely, at 24 hours of life, the median of pre-ductal SpO2 was significantly higher in the PGE1+BAS group than in the PGE1 group (median value 84.5% vs. 82%; p = 0.00003), but it was still lower than in the control group (99%).
Patients requiring septostomy had significantly lower median crSO2 before initiating medical treatment, as compared to those receiving only PGE1 treatment (median value 43% vs. 47%; p = 0.0412). Both D-TGA study groups had significantly lower median crSO2 values than the control group (median value 83%; p < 0.001). At 24 hours after birth, crSO2 increased in both D-TGA groups. The values were similar but still significantly lower than those in the control group (median value 50% and 51% vs. 87%; p < 0.001).
The median cFTOE values in the PGE1 (median value 0.38 vs. 0.16; p < 0.001) and PGE1+BAS (median value 0.39 vs. 0.16; p < 0.001) groups were higher than those in the control group, both before initiation of PGE1 treatment and at 24 hours of life (median value 0.38 vs. 0.11; p < 0.001) (
Table 4).
Before starting PGE1 treatment, both D-TGA groups had significantly higher oxygen demand compared to the control group (30% and 40% vs. 21%, p < 0.0001), while median pO2 levels were lower in PGE1+BAS group than PGE1 group (median 26 mmHg vs. 31 mmHg; p = 0.0431). At 24 hours after birth, after PGE1 treatment initiation/after BAS, the requirement for oxygen decreased significantly in both groups with D-TGA. Still, it remained higher than in the control group (p < 0.0001). The median pO2 values were similar in the D-TGA groups but significantly lower compared to the control group (median 56 mmHg; p < 0.001).
Regarding blood pressure, we observed a lower mean arterial pressure (MAP) in the PGE1 group compared to the PGE1+BAS group (43.73 mmHg vs. 49.3 mmHg; p = 0.0012) before PGE1 initiation. However, this difference no longer existed at 24 hours of life. Mean systolic blood pressure was significantly lower in the PGE1 group compared to the PGE1+BAS group (65.41 mmHg vs. 69.78 mmHg; p = 0.0147) and in the control group (65.41 mmHg vs. 73.10 mmHg; p = 0.00003) 24 hours after birth. Mean diastolic blood pressure was also lower in the PGE1 group compared to both the PGE1+BAS group (29.70 mmHg vs. 33.67 mmHg; p = 0.0140) and the control group (29.70 mmHg vs. 36.96 mmHg; p = 0.00004) within two hours after delivery. At 24 hours of life, the mean diastolic blood pressure was similar in the two D-TGA groups but significantly lower compared to the control group.
3.4. Effect of PGE1 and BAS
Before starting PGE1 infusion, the mean RI was similar in both D-TGA groups, with no significant difference compared to the control group. Instead, at 24 hours after birth, newborns with D-TGA exhibited significantly higher mean RI compared to the control group (0.769 and 0.764 vs. 0.681; p = 0.00002), due to the significant decrease of EDV in the D-TGA groups (
Table 4).
3.5. Comparison of Cerebral/Peripheric Oxygenation and Cerebral Velocities between Groups
Table 5.
Comparison of cerebral/peripheric oxygenation and cerebral velocities between groups
Table 5.
Comparison of cerebral/peripheric oxygenation and cerebral velocities between groups
| Clinical variables |
PGE1 Groupn=37 |
PGE1, BAS+Group
n=46 |
| |
2h of life |
24 hours of life
(after PGE) |
p-value |
2h of life |
before BAS |
24 hours of life
(after BAS) |
p-value |
| crSO2 § |
47 (41 – 55) |
50 (47 – 54) |
0.00029* |
43 (39 – 47) |
42 (39 – 46) |
51 (48 – 59) |
<0.0001* |
| cFTOE § |
0.38
(0.34 – 0.4) |
0.38
(0.33 – 0.43) |
0.1717* |
0.39
(0.33 – 0.45) |
0.45
(0.35 – 0.48) |
0.38
(0.31 – 0.42) |
0.0002* |
| SpO2 preductal § |
80 (75 – 83) |
82 (80 – 85) |
0.0053* |
72 (65 – 78) |
77 (72 – 80) |
84.5 (83 – 87) |
<0.0001* |
| RI § |
0.718 (0.054) |
0.769 (0.036) |
0.000002* |
0.708 (0.054) |
0.759 (0.046) |
0.764 (0.041) |
0.00002* |
| PSV § |
39.75 (7.41) |
38.99 (5.29) |
0.2512 |
37.666 (7.82) |
40.41 (8.92) |
39.72 (6.53) |
0.49415 |
| EDV § |
10.71 (1.61) |
8.74 (1.31) |
< 0.0001* |
10.86 (2.54) |
9.27 (1.91) |
9.16 (2.00) |
0.00004* |
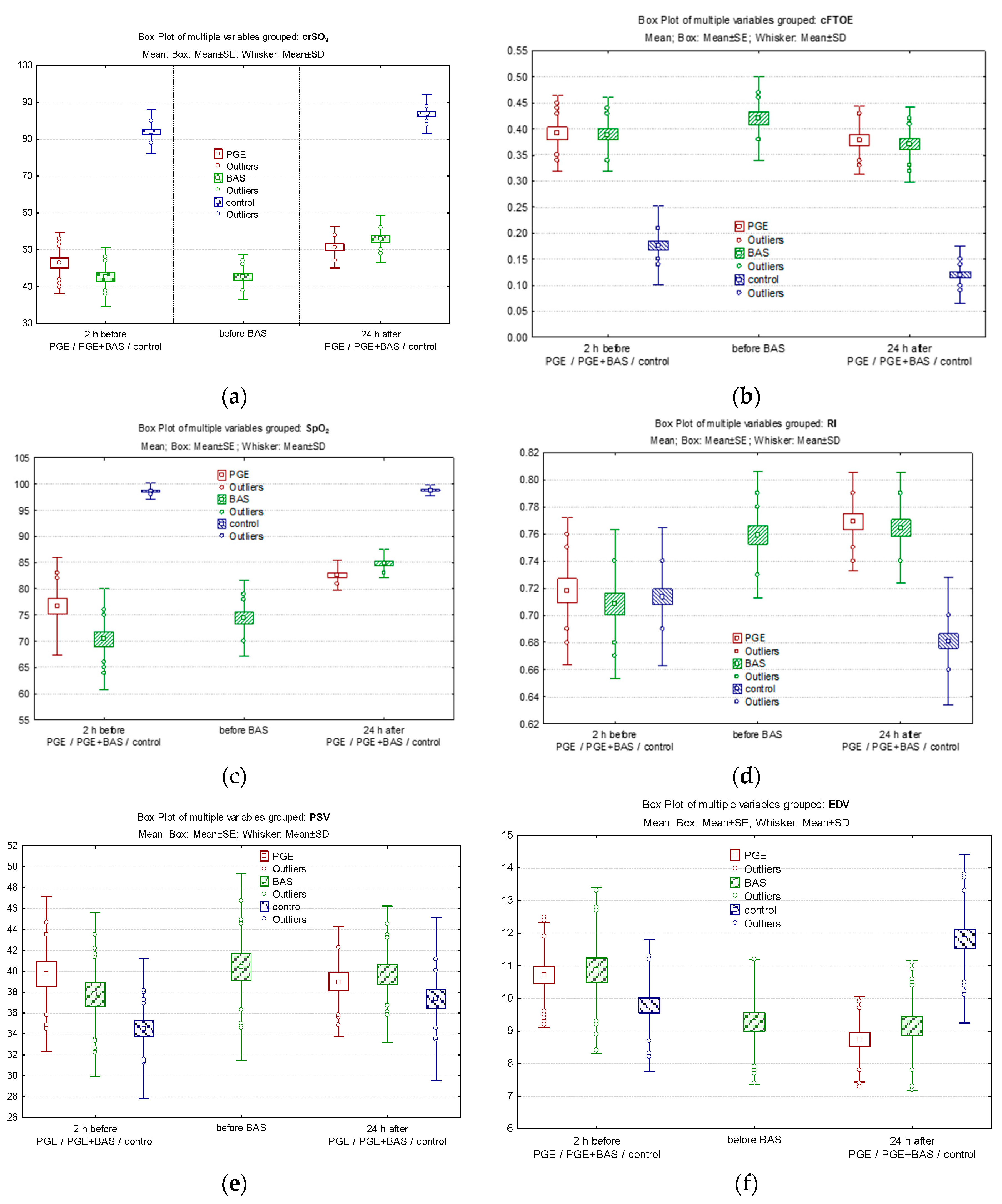
In the PGE1 group, following PGE1 treatment, crSO
2 improved from a median of 47% before PGE1 to 50% at 24 hours of life (
Figure 2a), while cFTOE remained constant and did not change significantly (
Figure 2b). SpO
2 significantly improved from a median of 80% before PGE1 to 82% at 24 hours of life (
Figure 2c). The RI significantly increased 24 hours after delivery (0.769 ± 0.036 vs. 0.718 ± 0.054; p = 0.000002) (
Figure 2d) due to decreased EDV (8.74 ± 1.31 vs. 10.71 ± 1.61; p < 0.0001) following PGE1 treatment (
Figure 2e), while SV remained unchanged (
Figure 2f).
In the PGE1+BAS group, crSO
2 decreased from a median of 43% before the initiation of PGE1 treatment to 42% before the BAS procedure and then increased to 51% at 24 hours of life following septostomy (
Figure 2a). cFTOE increased before septostomy and decreased significantly at 24 hours (
Figure 2b). Pre-ductal SpO
2 significantly improved, rising from a median of 72% before PGE1 to 77% before BAS and reaching 84.5% at 24 hours of life (p < 0.0001) (
Figure 2c). Doppler parameters in ACA followed the same trend as in the PGE1 group. This involved an increase in the RI (0.708 ± 0.054 vs. 0.759 ± 0.046 vs. 0.764 ± 0.041; p=0.00002), a decrease in end-diastolic velocity (10.86 ± 2.54 vs. 9.27 ± 1.91 vs. 9.16 ± 2.00; p = 0.00004) and maintenance of PSV within the same limits at the three specific time points of evaluation (
Figure 2d, 2e, 2f).
4. Discussion
This study aimed to assess the impact of PGE1 treatment and BAS on cerebral and peripheric oxygenation and blood flow velocities 24 hours after birth, as both interventions affect cerebral hemodynamics. In our study, 70.3% of patients with D-TGA who received PGE1 treatment and 63.04% of patients who were treated with both PGE1, and BAS were prenatally diagnosed and confirmed postnatally. This detection rate is consistent with findings from other studies, which typically range between 50% and 80% [
16,
17]. All patients were born at our center, with over 50% transferred in utero, enabling early management and preventing severe hypoxemia and hemodynamic compromise during postnatal transfer, especially in patients with inadequate intracardiac blood mixing. A study conducted by Thomas et al. revealed that infants born at a tertiary care center had a shorter median time to BAS (4 hours vs. 14.1 hours, p < 0.0001) compared to those requiring transport. Shorter time to BAS was correlated with reduced NICU and hospital stays (r = 0.21, p = 0.046, and r = 0.24, p = 0.02, respectively), but it had no impact on mortality [
16]. Veal and collab. found no significant differences in outcomes between infants delivered in tertiary centers and those transferred in by a specialized team [
18].
In this study, the mean age at the arterial switch was 14 ± 10.1 days in the PGE1 group and 14.1±6.6 days in the PGE1+ BAS group, respectively, higher than reported in an extensive study of 1,772 D-TGA patients conducted by Dorobantu et all (9.5 days (IQR: 6.5-14.5)) [
19]. The timing of surgery in the first few hours of life [
20] is still a subject of debate, while current guidelines recommend surgery in the first week of life [
21].
Newborns with D-TGA usually experience delayed closure of the ductus arteriosus for a few days due to inadequate constriction stimulation caused by low partial pressure of oxygen [
22,
23]. Therefore, PGE1 infusion is the standard of care in newborns with D-TGA. The goal of PGE1 treatment is to enhance hemodynamic status and oxygenation, protecting the brain from the adverse effects of hypoxemia until the arterial switch intervention [
4,
24]. PGE1 functions by interacting with specific G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) on the surface of target cells, notably the EP receptors (EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4) [
25,
26]. The binding of PGE1 to these receptors stimulates intracellular signaling cascades, including the adenylate cyclase pathway, which increases cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels [
26,
27]. Elevated cAMP functions as a secondary messenger, activating protein kinase A (PKA). PKA, in turn, phosphorylates many target proteins, causing smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation [
28]. The vasodilator action is crucial for keeping the ductus arteriosus open to allow proper mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood Furthermore, PGE1 has been proven to inhibit platelet aggregation and have anti-inflammatory characteristics, which adds to its therapeutic effectiveness in neonates with D-TGA [
29]. PGE1 reduces the chances of severe hypoxemia and cardiac instability in diagnosed neonates by ensuring proper blood flow and oxygen delivery. In our study, all 83 D-TGA patients were treated with PGE1 within the first two hours after birth at the mean initial dose between 0.042 and 0.05 μg/kg/min. The PGE1 infusion was adjusted based on echocardiographic assessments, peripheral oxygen saturations, and clinical signs to administer the lowest effective dose, considering its dose-dependent side effects [
4]. High doses may lead to increased pulmonary circulation and worsened breathing, requiring oxygen therapy and respiratory support [
30].
However, adequate interatrial communication is essential for mixing oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, and septostomy is necessary when communication is restrictive [
31]. Thus, ensuring the stabilization of neonates with D-TGA before surgery significantly enhances the postoperative outcomes. The BAS procedure, as recommended by a pediatric cardiologist following an echocardiographic evaluation, was performed in 55.42% of cases. The BAS rate was higher than reported in a recent study (27.7%) [
32]. In 8 cases (17.39%), BAS was indicated even before birth by measuring the FO size and flap motility [
33,
34]. The procedure was performed at the NICU bedside in 47% of cases and the neonatal cardiac surgery unit in 53% of cases, about 8.71 hours after birth on average. Umbilical venous access was utilized in 73% of cases, while femoral access was used in 27% of cases. All patients undergoing BAS were sedated, intubated, and mechanically ventilated during the procedure. In our study, in all infants, we maintained PGE1 infusion at the lowest effective dose until the day of surgery (14.1±6.6 days) following the BAS procedure. There are controversies regarding the discontinuation of PGE1 treatment once adequate mixing has been achieved at the atrial level. Thus, some studies have shown that approximately 33-50% of infants have PGE1 restarted due to the risk of rebound hypoxemia after discontinuation [
35,
36].
Cerebral Oxygenation
Many studies have defined reference ranges for crSO2 and cFTOE during the first few days after birth [
37,
38]. In full-term infants, crSO
2 rapidly increases from 44% at 3 minutes after birth to between 70% and 80% at 15 minutes and then stabilizes. At the same time, cFTOE decreases from a median of 0.33 (0.11-0.70) at 2 minutes to 0.18 (0.07-0.34) at 15 minutes after birth [
37].
In our study, treatment with PGE1 significantly increased crSO
2 from 47% to 50% in the PGE1 group at 24 hours of life. Additionally, there was an increase in SpO
2 and pre-ductal pO
2, while the cFTOE remained constantly elevated, likely due to increased oxygen demand. However, these values remained below those of healthy newborns. The PGE1 treatment alone did not have the expected effect on SpO
2, pre-ductal pO
2, and crSO
2 in the D-TGA group with restrictive ASD/FO. Performing BAS significantly increased these parameters due to improved mixing at the atrial level and a 12.5% rise in SpO
2, reflected mainly in the increase in crSO
2 at 51%. Basically, at 24 hours of life, following BAS, the SpO
2, pre-ductal pO
2, crSO
2, and cFTOE values reached levels like those of the group that received PGE1 alone. In a previous study, the mean crSO
2 values were found to be 56.3 ± 11.3% [
39]. Another study reported median values of 48% at 2 hours after BAS and 64% at 24 hours after BAS [
40] in newborns with D-TGA. However, it’s worth noting that the timing of measurement in these studies differed from the timing in our study.
CrSO
2 depends on the level of oxygen delivery and brain oxygen consumption, reflecting the balance between cerebral oxygen supply and demand [
41]. Oxygen delivery is closely related to SpO
2, cerebral blood flow, and hemoglobin level. However, in our study, the low crSO
2 value appears unlikely to be caused by a decrease in hemoglobin concentration, especially since the values at birth were within normal limits. Due to the anatomical and functional characteristics of the malformation, infants with D-TGA typically have SpO
2 levels less than 85% and crSO
2 in the low 50% range [
42]. A reassuring SpO
2 level between 80-85% obtained after PGE1 treatment and/or BAS at 24 hours of life was associated with low crSO
2, indicating low cerebral oxygen delivery or increased oxygen demands due to hypoxia. Low crSO
2 values suggest cerebral hypoxic hypoxia, while high FTOE values suggest cerebral ischemic hypoxia, both indicating low oxygen availability to cerebral tissue. Prolonged cerebral hypoxia can lead to increased central nervous system injury, either before or after birth, particularly affecting the white matter. In our study, we did not find any cerebral lesions, but we observed that the head circumference was significantly smaller in the PGE1+BAS group compared to the control group (33.8±1.3 cm vs. 34.5±1 cm, p=0.0151). The study conducted by Licht found that newborns with D-TGA had a delay in brain development of approximately one month and a mean head circumference one standard deviation below the expected value for their age [
43]. However, surgical intervention must be performed at the optimal time to prevent future neurological complications.
Cerebral Blood Flow
Adequate postnatal cerebral blood flow, which is closely related to cardiac output and cerebral vascular resistance, is essential for the delivery of oxygen to brain tissue. Newborns with D-TGA have altered cerebral hemodynamics compared to healthy newborns. Healthy newborns experience increased cerebral blood flow within the first few weeks of life, marked by elevated flow velocities in cerebral arteries, likely caused by the closure of the arterial duct [
15].
Bedside Doppler ultrasound measurements instantly provide imaging for monitoring brain perfusion, as continuous information about cerebral blood flow is lacking. Our center performs dynamic Doppler assessments, including after adjusting PGE1 doses. Our study revealed that PGE1 treatment resulted in a significant increase in the RI from birth to 24 hours after delivery in the group treated with PGE1 alone due to a decrease in EDV, while PSV remained unchanged. The increase in RI was even more pronounced in the group that underwent septostomy, both before and after the procedure, respectively, at 24 hours after delivery. We consider that cerebral perfusion is diminished due to the ductus arteriosus maintained open by PGE1 treatment. The phenomenon of ductal stealing in the case of a large patent ductus arteriosus may alter cerebral hemodynamics.
The existing literature offers limited information on pre-surgery Doppler measurements of the cerebral arteries in newborns with D-TGA. Mir et al. monitored 38 patients with congenital heart disease using cerebral Doppler ultrasound. They found increased PSV, decreased end EDV (β = -5.75 cm/s, 95% CI -8.38 to -3.12, p < 0.001), and a significant increase in the resistive index of the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) (β = 0.16, 95% CI 0.10 – 0.22, p < 0.001). There was no retrograde diastolic flow in the ACA [
44]. In a prospective study of pediatric patients undergoing congenital heart surgery, ultrasound RI of the major cranial vessels was measured prior to surgery, immediately post-operatively, and prior to discharge. There were no significant correlations between the RI and neurodevelopmental outcomes [
45].
This study has limitations due to its retrospective nature and the limited number of cases. We investigated changes in cerebral oxygenation and hemodynamics during the transition period of newborns with D-TGA based on emergency management. Larger sample sizes, provided by multicenter studies, would be more valuable. More information is needed on the impact of abnormal blood flow associated with congenital heart defects. This may help to identify the optimal timing for surgical correction and to optimize neurodevelopmental outcomes.
5. Conclusions
PGE1 treatment and atrial septostomy are lifesaving interventions that may improve cerebral perfusion and oxygenation in newborns with D-TGA during their transition to extrauterine life. Our findings underscore the potential of these interventions to improve pre-surgery outcomes for these patients, providing reassurance and confidence in their efficacy. Close monitoring of cerebral velocities using Doppler ultrasound and cerebral oxygen saturation with NIRS is essential for better management before surgical correction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C. and M.M.; methodology, M.C., M.M., M.L.O. and A.C.P.; software, M.S., L.M.S., D.V.G. and E.M.; validation, M.C., M.M. and M.L.O; formal analysis, M.M., A.C.P. and D.V.G.; investigation, M.C., M.S., L.M.S., E.M.; resources, M.C., M.L.O. and M.M.; data curation, A.C.P., D.V.G. and E.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C. and M.M.; writing—review and editing, M.C., M.M., M.L.O. and A.C.P.; visualization, A.C.P., M.S., L.M.S., D.V.G and E.M.; supervision, M.C. and M.M.; project administration, M.C. and M.M.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Sciences and Technology „George Emil Palade of Târgu Mureș, grant number 10126/3 17.12.2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Sciences and Technology „George Emil Palade of Târgu Mureș, 10126/3 17.12.2020.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cohen MS, Eidem BW, Cetta F, Fogel MA, Frommelt PC, Ganame J, Han BK, Kimball TR, Johnson RK, Mertens L, Paridon SM, Powell AJ, Lopez L. Multimodality Imaging Guidelines of Patients with Transposition of the Great Arteries: A Report from the American Society of Echocardiography Developed in Collaboration with the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance and the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2016 Jul;29(7):571-621. [CrossRef]
- Bakker MK, Bergman JEH, Krikov S, Amar E, Cocchi G, Cragan J, de Walle HEK, Gatt M, Groisman B, Liu S, Nembhard WN, Pierini A, Rissmann A, Chidambarathanu S, Sipek A Jr, Szabova E, Tagliabue G, Tucker D, Mastroiacovo P, Botto LD. Prenatal diagnosis and prevalence of critical congenital heart defects: An international retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2019 Jul 2;9(7):e028139. [CrossRef]
- Talemal L, Donofrio MT. Hemodynamic consequences of a restrictive ductus arteriosus and foramen ovale in fetal transposition of the great arteries. Journal of Neonatal-perinatal Medicine. 2016 Sep;9(3):317-320. [CrossRef]
- Séguéla PE, Roubertie F, Kreitmann B, Mauriat P, Tafer N, Jalal Z, Thambo JB. Transposition of the great arteries: Rationale for tailored preoperative management. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2017 Feb;110(2):124-134. [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk I, Walter A, Menzel T, Weber EC, Wendt S, Sreeram N, Gembruch U, Berg C, Abel JS. D-Transposition of the great arteries with restrictive foramen ovale in the fetus: The dilemma of predicting the need for postnatal urgent balloon atrial septostomy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024 Apr;309(4):1353-1367. [CrossRef]
- Villafañe J, Lantin-Hermoso MR, Bhatt AB, Tweddell JS, Geva T, Nathan M, Elliott MJ, Vetter VL, Paridon SM, Kochilas L, Jenkins KJ, Beekman RH 3rd, Wernovsky G, Towbin JA; American College of Cardiology’s Adult Congenital and Pediatric Cardiology Council. D-transposition of the great arteries: The current era of the arterial switch operation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Aug 5;64(5):498-511. [CrossRef]
- Kelly CJ, Arulkumaran S, Tristão Pereira C, Cordero-Grande L, Hughes EJ, Teixeira RPAG, Steinweg JK, Victor S, Pushparajah K, Hajnal JV, Simpson J, Edwards AD, Rutherford MA, Counsell SJ. Neuroimaging findings in newborns with congenital heart disease prior to surgery: An observational study. Arch Dis Child. 2019 Nov;104(11):1042-1048. [CrossRef]
- Chen H, Yan Y, Li C, Zheng X, Wang G, Jin Z, Shi G, He X, Tong X, Chen H, Zhu Z. Inattention and hyperactivity in children and adolescents with repaired D-transposition of the great arteries: Prevalence, perioperative risk factors, and clinical outcomes. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 20;9:937311. [CrossRef]
- El-Dib M, Soul JS. Monitoring and management of brain hemodynamics and oxygenation. Handb Clin Neurol. 2019;162:295-314. [CrossRef]
- Licht DJ, Wang J, Silvestre DW, Nicolson SC, Montenegro LM, Wernovsky G; et al. Preoperative cerebral blood flow is diminished in neonates with severe congenital heart defects. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2004; 128: 841–849. [CrossRef]
- Durduran T, Zhou C, Buckley EM, Kim MN, Yu G, Choe R; et al. Optical measurement of cerebral hemodynamics and oxygen metabolism in neonates with congenital heart defects. J Biomed Opt 2010; 15: 037004. [CrossRef]
- Goff DA, Buckley EM, Durduran T, Wang J, Licht DJ. Noninvasive cerebral perfusion imaging in high-risk neonates. Semin Perinatol. 2010 Feb;34(1):46-56. [CrossRef]
- Jain V, Buckley EM, Licht DJ; et al. Cerebral Oxygen Metabolism in Neonates with Congenital Heart Disease Quantified by MRI and Optics. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 2014;34(3):380-388. [CrossRef]
- Jarmund AH, Pedersen SA, Torp H, Dudink J, Nyrnes SA. A Scoping Review of Cerebral Doppler Arterial Waveforms in Infants. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2023 Apr;49(4):919-936. [CrossRef]
- De Silvestro AA, Kellenberger CJ, Gosteli M. et al. Postnatal cerebral hemodynamics in infants with severe congenital heart disease: A scoping review. Pediatr Res. 2023;94:931–943. [CrossRef]
- Thomas C, Yu S, Lowery R, Zampi JD. Timing of Balloon Atrial Septostomy in Patients with d-TGA and Association with Birth Location and Patient Outcomes. Pediatr Cardiol. 2023 Aug;44(6):1333-1341. Epub 2022 Dec 24. PMID: 36565310. [CrossRef]
- Nagata H, Glick L, Lougheed J, Grattan M, Mondal T, Thakur V, Schwartz SM, Jaeggi E. Prenatal Diagnosis of Transposition of the Great Arteries Reduces Postnatal Mortality: A Population-Based Study. Can J Cardiol. 2020 Oct;36(10):1592-1597. Epub 2020 Jan 20. PMID: 32622839. [CrossRef]
- Veal C, Hunt R, Tume LN. Do infants with transposition of the great arteries born outside a specialist centre have different outcomes? Cardiol Young. 2019 Aug;29(8):1030-1035. [CrossRef]
- Dorobantu DM, Espuny Pujol F, Kostolny M, Brown KL, Franklin RC, Crowe S, Pagel C, Stoica SC. Arterial Switch for Transposition of the Great Arteries: Treatment Timing, Late Outcomes, and Risk Factors. JACC Adv. 2023 Jul 19;2(5):100407. [CrossRef]
- Nevvazhay T, Chernogrivov A, Biryukov E, Biktasheva L, Karchevskaya K, Sulejmanov S, Kalinicheva J, Artemiev N. Arterial switch in the first hours of life: No need for Rashkind septostomy? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012 Sep;42(3):520-3. [CrossRef]
- Sarris GE, Balmer C, Bonou P; et al. Clinical guidelines for the management of patients with transposition of the great arteries with intact ventricular septum: The Task Force on Transposition of the Great Arteries of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) and the Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Cardiology in the Young. 2017;27(3):530-569. [CrossRef]
- Gournay V. The ductus arteriosus: Physiology, regulation, and functional and congenital anomalies. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2011 Nov;104(11):578-85. [CrossRef]
- Wheeler CR, Sen S, Levy PT. The ductus arteriosus in neonates with critical congenital heart disease. J Perinatol. 2022 Dec;42(12):1708-1713. [CrossRef]
- Akkinapally S, Hundalani SG, Kulkarni M, Fernandes CJ, Cabrera AG, Shivanna B, Pammi M. Prostaglandin E1 for maintaining ductal patency in neonates with ductal-dependent cardiac lesions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 27;2(2):CD011417. [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Roh, K.; Cho, E.; Park, D.; Whang, W.; Jung, E. Isookanin Inhibits PGE2-Mediated Angiogenesis by Inducing Cell Arrest through Inhibiting the Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and CREB in HMEC-1 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6466. [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.-T.; Sun, W.-Y.; Li, X.-R.; Sun, J.-C.; Du, J.-J.; Wei, W. Emerging Roles of G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1366. [CrossRef]
- Gumułka, P.; Tarsa, M.; Dąbrowska, M.; Starek, M. Quantification of Grapiprant and Its Stability Testing under Changing Environmental Conditions. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2821. [CrossRef]
- Socha, M.W.; Flis, W.; Pietrus, M.; Wartęga, M. Results of Induction of Labor with Prostaglandins E1 and E2 (The RIPE Study): A Real-World Data Analysis of Obstetrical Effectiveness and Clinical Outcomes of Pharmacological Induction of Labor with Vaginal Inserts. Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 16, 982. [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Lin, X.; Meng, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Yang, J.; et al. A Novel Small Molecular Prostaglandin Receptor EP4 Antagonist, L001, Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis. Molecules 2022, 27, 1209. [CrossRef]
- Singh Y, Tissot C. Echocardiographic Evaluation of Transitional Circulation for the Neonatologists. Front Pediatr. 2018 May 15;6:140. [CrossRef]
- Al-Kassmy J, Navarro-Castellanos I, Barlatay FG, Miró J, Dahdah N. Balloon Atrial Septostomy: Does the Balloon Size Matter? CJC Pediatr Congenit Heart Dis. 2022 Oct 28;1(6):253-259. [CrossRef]
- Hamzah M, Othman HF, Peluso AM, Sammour I, Aly H. Prevalence and Outcomes of Balloon Atrial Septostomy in Neonates With Transposition of Great Arteries. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2020 Apr;21(4):324-331. [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk I, Walter A, Menzel T, Weber EC, Wendt S, Sreeram N, Gembruch U, Berg C, Abel JS. D-Transposition of the great arteries with restrictive foramen ovale in the fetus: The dilemma of predicting the need for postnatal urgent balloon atrial septostomy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024 Apr;309(4):1353-1367. [CrossRef]
- Della Gatta AN, Contro E, Lenzi J, Balducci A, Gargiulo G, Bodnar T, Palleri D, Bonetti S, Hasan T, Donti A, Ragni L, Angeli E, Bartolacelli Y, Larcher L, Pilu G, Perolo A. Prenatal sonography of the foramen ovale predicts urgent balloon atrial septostomy in neonates with complete transposition of the great arteries. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2021 Sep;3(5):100379. [CrossRef]
- Finan E, Mak W, Bismilla Z, McNamara PJ. Early discontinuation of intravenous prostaglandin E1 after balloon atrial septostomy is associated with an increased risk of rebound hypoxemia. J Perinatol. 2008 May;28(5):341-6. [CrossRef]
- Gilg S, Acosta S, Loomba RS, Rizk C, Stapleton GE, Faraoni D, Savorgnan F. Association between balloon atrial septostomy and prostaglandin E1 therapy until repair of transposition of the great arteries in neonates. Pediatr Investig. 2024 Apr 8;8(2):135-138. [CrossRef]
- Pichler G, Binder C, Avian A, Beckenbach E, Schmölzer GM, Urlesberger B. Reference ranges for regional cerebral tissue oxygen saturation and fractional oxygen extraction in neonates during immediate transition after birth. J Pediatr. 2013 Dec;163(6):1558-63. [CrossRef]
- Urlesberger B, Grossauer K, Pocivalnik M, Avian A, Muller W, Pichler G: Regional oxygen saturation of the brain and peripheral tissue during birth transition of term infants. J Pediatr 2010;157:740-744. [CrossRef]
- Kim MJ, Baek JS, Kim JA, Cha SG, Yu JJ. Cerebral and Somatic Oxygen Saturation in Neonates with Congenital Heart Disease before Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(11):2455. [CrossRef]
- Kurth CD, Steven JL, Montenegro LM, Watzman HM, Gaynor JW, Spray TL, Nicolson SC. Cerebral oxygen saturation before congenital heart surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001 Jul;72(1):187-92. [CrossRef]
- Lim JM, Kingdom T, Saini B, Chau V, Post M, Blaser S, Macgowan C, Miller SP, Seed M. Cerebral oxygen delivery is reduced in newborns with congenital heart disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 Oct;152(4):1095-103. [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj UD, Evangelou IE, Donofrio MT, Vezina LG, McCarter R, du Plessis AJ, Limperopoulos C. Impaired Global and Regional Cerebral Perfusion in Newborns with Complex Congenital Heart Disease. J Pediatr. 2015 Nov;167(5):1018-24. [CrossRef]
- Licht DJ, Shera DM, Clancy RR, Wernovsky G, Montenegro LM, Nicolson SC, Zimmerman RA, Spray TL, Gaynor JW, Vossough A. Brain maturation is delayed in infants with complex congenital heart defects. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009 Mar;137(3):529-36; discussion 536-7. [CrossRef]
- Mir M, Moore SS, Wutthigate P, Simoneau J, Villegas Martinez D, Shemie SD, Brossard-Racine M, Dancea A, Bertolizio G, Altit G. Newborns with a Congenital Heart Defect and Diastolic Steal Have an Altered Cerebral Arterial Doppler Profile. J Pediatr. 2023 Jun;257:113369. [CrossRef]
- Jenks CL, Hernandez A, Stavinoha PL, Morris MC, Tian F, Liu H, Garg P, Forbess JM, Koch J. Elevated cranial ultrasound resistive indices are associated with improved neurodevelopmental outcomes one year after pediatric cardiac surgery: A single center pilot study. Heart Lung. 2017 Jul-Aug;46(4):251-257. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).