Submitted:
16 August 2024
Posted:
20 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Histamine
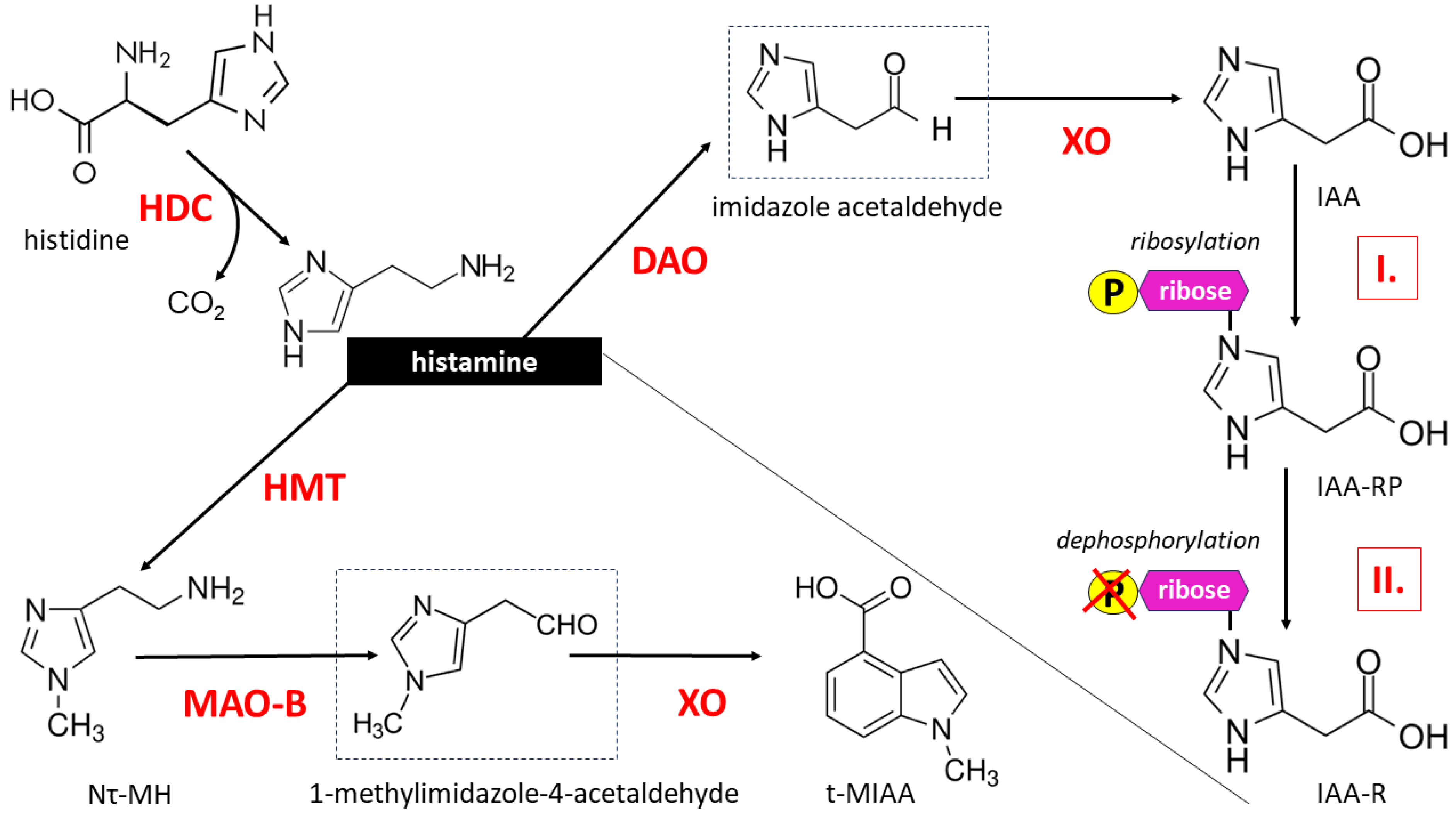
2.1. Histamine Biosynthesis and Metabolism
2.2. HA receptors
3. Cerebral HA and CNS Function
3.1. Importance of HA Content and Distribution in the Brain
3.2. Histaminergic System in the Human Brain
4. Histaminergic Dysfunction in the Developing and Adult CNS
4.1. The Role of HA and Neuroinflammation during the Development of the CNS
4.2. The Role of HA and Neuroinflammation in Neuropsychiatric (Neurodegenerative) Disorders
5. Brain HA Signaling as a Therapeutic Target in Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders
6. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
- 5-HT – serotonin
- 5-HTRs – serotonin receptors
- aa – amino acids
- AA – arachidonic acid
- AADE – arachidonic acid-derived eicosanoids
- AC – adenylyl cyclase
- ACh – acetylcholine
- AD – Alzheimer’s disease
- ADHD – attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
- AP-1 – activator protein 1
- APCs – antigen-presenting cells
- ARRB2 – arrestin beta-2, also known as beta-arrestin-2
- ASD – autism spectrum disorders
- BBB – blood-brain barrier
- bFGF – basic fibroblast growth factor
- cAMP – cyclic 3’,5’ adenosine monophosphate
- CBM – CBM signalosome complex = CARD11 (the caspase recruitment domain family member 11)—BCL10 (B cell CLL/lymphoma 10)—MALT1 (mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1) paracaspase,
- c-fos – protooncogene (human homolog of the retroviral oncogene v-fos)
- cGMP – cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- CNS – central nervous system
- CREB – cAMP-responsive element-binding protein
- CSF – cerebrospinal fluid
- DA – dopamine
- DAG – diacylglycerol
- DAO – diamine oxidase
- DCs – dendritic cells
- ECL cells – enterochromaffin-like cells
- ECs – endothelial cells
- eNOS – endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- ERS – endoplasmic reticulum stress
- GABA – γ-amino butyric acid
- GDP – guanosine diphosphate
- GLU – glutamate
- GTP – guanosine triphosphate
- GPCRs – G protein-coupled receptors, also known as the seven-(pass)-transmembrane (7TM) domain receptors
- H1R, H2R, H3R, H4R – four histamine receptors, respectively
- HA – histamine
- HD – Huntington's disease
- HDC – enzyme L-histidine decarboxylase
- HMT – histamine N-methyltransferase, also known as HNMT
- IAA – imidazole acetic acid
- IAA-RP – imidazole acetic acid ribotide
- ID – intellectual disability
- IFG – inferior frontal gyrus
- IFN-γ – interferon gamma
- IL-1β, IL-10, IL-12, IL-33 – interleukins: 1 beta, 10, 12 and 33, respectively
- IP3 – inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
- KD – dissociation constant
- LBs – Lewy bodies
- MAO-B – monoamine oxidase B
- MAPK – mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MCH – melanin-concentrating hormone
- MCs – mast cells
- MDD – major depressive disorder
- NA – norepinephrine
- NMD – neurodevelopmental motor disorders
- NSCs – neural stem cells
- NSD – narcolepsy spectrum disorder
- NF-κβ – nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- NK cells – natural killer cells
- NMDA – N-methyl-D-aspartate
- NO – nitric oxide
- NREM – non-rapid eye movement phase of sleep
- Nτ-MH – tele-methylhistamine
- OCPD – obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
- OCT3 – organic cation transporter 3
- PD – Parkinson’s disease
- PFC – prefrontal cortex
- PIP2 –phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
- PKA – protein kinase A
- PKC – protein kinase C
- PLA2 – phospholipase A2
- PLC – phospholipase C
- PLD – phospholipase D
- PMAT – plasma membrane monoamine transporter
- REM – rapid eye movement phase of sleep
- ROS – reactive oxygen species
- Schiz – schizophrenia
- SDAT – senile dementia of the Alzheimer's disease type
- SNP – single nucleotide polymorphism
- TGFβ – transforming growth factor beta
- Th1, Th2 – Type 1 T helper and type 2 T helper cells, respectively
- t-MIAA – tele-methylimidazole acetic acid
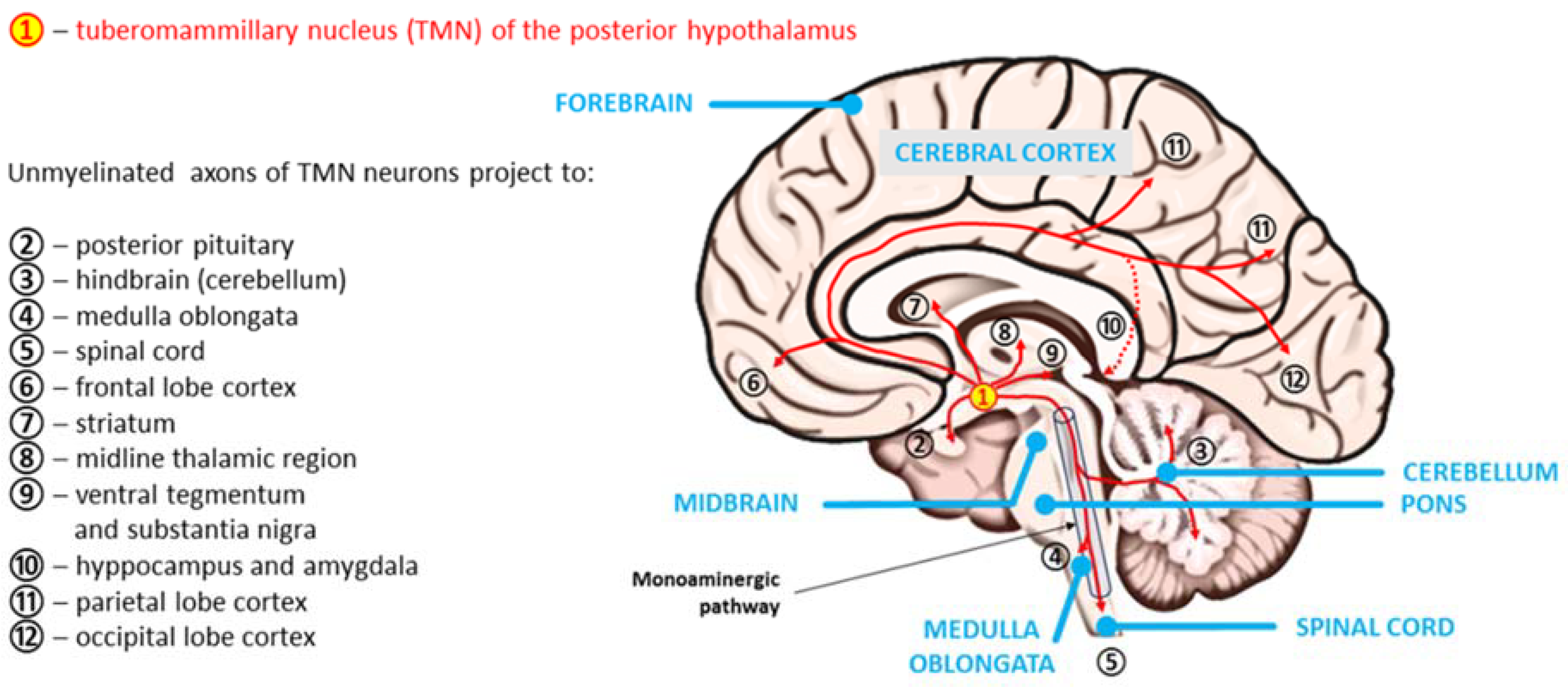
- TMN – tuberomammillary nucleus
- TNFα – tumor necrosis factor alpha
- TRAF6 – tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 6
- VEGF – vascular endothelial growth factor
- VMAT2 – vesicular monoamine transporter
- VSMCs – vascular smooth muscle cells
- XO – xanthine oxidase
References
- Tiligada E, Ennis M. Histamine pharmacology: from Sir Henry Dale to the 21st century. Br J Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, MK. Allergy, Histamine and Antihistamines. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017, 241, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashina K, Tsubosaka Y, Nakamura T, Omori K, Kobayashi K, Hori M, Ozaki H, Murata T. Histamine Induces Vascular Hyperpermeability by Increasing Blood Flow and Endothelial Barrier Disruption In Vivo. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0132367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikelis CM, Simaan M, Ando K, Fukuhara S, Sakurai A, Amornphimoltham P, Masedunskas A, Weigert R, Chavakis T, Adams RH, Offermanns S, Mochizuki N, Zheng Y, Gutkind JS. RhoA and ROCK mediate histamine-induced vascular leakage and anaphylactic shock. Nat Commun. 2015, 6, 6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmik R, Shaharyar MA, Sarkar A, Mandal A, Anand K, Shabana H, Mitra A, Karmakar S. Immunopathogenesis of urticaria: a clinical perspective on histamine and cytokine involvement. Inflamm Res. 2024, 73, 877–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sörbo J, Jakobsson A, Norrby K. Mast-cell histamine is angiogenic through receptors for histamine1 and histamine2. Int J Exp Pathol. 1994, 75, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk G, Pyzlak M, Klimkiewicz J, Smiertka W, Miedzińska-Maciejewska M, Szukiewicz D. Mast cells and histamine: do they influence placental vascular network and development in preeclampsia? Mediators Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 307189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Liu G, Wang X, Hong H, Li T, Li L, Wang H, Xie J, Li B, Li T, Lu D, Zhang Y, Zhao H, Yao C, Wen K, Li T, Chen J, Wu S, He K, Zhang WN, Zhao J, Wang N, Han Q, Xia Q, Qi J, Chen J, Zhou T, Man J, Zhang XM, Li AL, Pan X. Glioblastoma stem cell-specific histamine secretion drives pro-angiogenic tumor microenvironment remodeling. Cell Stem Cell. 2022, 29, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska S, Winiarska E, Globinska A, Jutel M. Histamine: A Mediator of Intestinal Disorders-A Review. Metabolites 2022, 12, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough LB. Histamine Actions in the Central Nervous System. In: Siegel GJ, Agranoff BW, Albers RW, et al., editors. Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular and Medical Aspects. 6th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1999. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK28245/.
- Scammell TE, Jackson AC, Franks NP, Wisden W, Dauvilliers Y. Histamine: neural circuits and new medications. Sleep 2019, 42, zsy183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigoni E, Fuller PM. The Role of the Central Histaminergic System in Behavioral State Control. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2022, 59, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough LB. Histaminergic Cells of the Central Nervous System: Anatomy and Morphology. In: Siegel GJ, Agranoff BW, Albers RW, et al., editors. Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular and Medical Aspects. 6th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1999. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK28098/.
- Blandina P, Munari L, Provensi G, Passani MB. Histamine neurons in the tuberomamillary nucleus: a whole center or distinct subpopulations? Front Syst Neurosci. 2012, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa T, Nakamura T, Yanai K. Histaminergic neurons in the tuberomammillary nucleus as a control centre for wakefulness. Br J Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 750–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough LB. Dynamics of Histamine in the Brain. In: Siegel GJ, Agranoff BW, Albers RW, et al., editors. Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular and Medical Aspects. 6th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1999. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK27916/.
- Maršavelski A, Mavri J, Vianello R, Stare J. Why Monoamine Oxidase B Preferably Metabolizes N-Methylhistamine over Histamine: Evidence from the Multiscale Simulation of the Rate-Limiting Step. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangam EB, Jemima EA, Singh H, Baig MS, Khan M, Mathias CB, Church MK, Saluja R. The Role of Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Mast Cell-Mediated Allergy and Inflammation: The Hunt for New Therapeutic Targets. Front Immunol. 2018, 9, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons ME, Ganellin CR. Histamine and its receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2006, 147 (Suppl 1), S127–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis WI, Kobilka BK. The Molecular Basis of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Activation. Annu Rev Biochem. 2018, 87, 897–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamato D, Thach L, Bernard R, Chan V, Zheng W, Kaur H, Brimble M, Osman N, Little PJ. Structure, Function, Pharmacology, and Therapeutic Potential of the G Protein, Gα/q,11. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2015, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfleger J, Gresham K, Koch WJ. G protein-coupled receptor kinases as therapeutic targets in the heart. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019, 16, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khouma A, Moeini MM, Plamondon J, Richard D, Caron A, Michael NJ. Histaminergic regulation of food intake. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023, 14, 1202089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Mir MI, Pollard H, Moreau J, Arrang JM, Ruat M, Traiffort E, Schwartz JC, Palacios JM. Three histamine receptors (H1, H2 and H3) visualized in the brain of human and non-human primates. Brain Res. 1990, 526, 322–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly WM, Shenton FC, Lethbridge N, Leurs R, Waldvogel HJ, Faull RL, Lees G, Chazot PL. The histamine H4 receptor is functionally expressed on neurons in the mammalian CNS. Br J Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeotti N, Sanna MD, Ghelardini C. Pleiotropic effect of histamine H4 receptor modulation in the central nervous system. Neuropharmacology 2013, 71, 141–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider EH, Seifert R. The histamine H4-receptor and the central and peripheral nervous system: A critical analysis of the literature. Neuropharmacology. 2016, 106, 116–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna MD, Ghelardini C, Thurmond RL, Masini E, Galeotti N. Behavioural phenotype of histamine H4 receptor knockout mice: Focus on central neuronal functions. Neuropharmacology. 2017, 114, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula, P. Histamine receptors, agonists, and antagonists in health and disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2021, 180, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula P, Chazot PL, Cowart M, Gutzmer R, Leurs R, Liu WL, Stark H, Thurmond RL, Haas HL. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCVIII. Histamine Receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2015, 67, 601–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Backer MD, Loonen I, Verhasselt P, Neefs JM, Luyten WH. Structure of the human histamine H1 receptor gene. Biochem J. 1998, 335 (Pt 3), 663–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit MJ, Hoffmann M, Timmerman H, Leurs R. Molecular properties and signalling pathways of the histamine H1 receptor. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999, 29, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert R, Strasser A, Schneider EH, Neumann D, Dove S, Buschauer A. Molecular and cellular analysis of human histamine receptor subtypes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013, 34, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad M, Söldner CA, Miao Y, Sticht H. Agonist Binding and G Protein Coupling in Histamine H2 Receptor: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishola AA, Joshi T, Abdulai SI, Tijjani H, Pundir H, Chandra S. Molecular basis for the repurposing of histamine H2-receptor antagonist to treat COVID-19. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022, 40, 5785–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höring C, Conrad M, Söldner CA, Wang J, Sticht H, Strasser A, Miao Y. Specific Engineered G Protein Coupling to Histamine Receptors Revealed from Cellular Assay Experiments and Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 10047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann P, Bönisch H, Oerters F, Brüss M. Structure of the human histamine H3 receptor gene (HRH3) and identification of naturally occurring variations. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2002, 109, 443–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai X, Ye L, Liao Y, Jin L, Ma Q, Lu B, Sun Y, Shi Y, Zhou N. Agonist-induced activation of histamine H3 receptor signals to extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 through PKC-, PLD-, and EGFR-dependent mechanisms. J Neurochem. 2016, 137, 200–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman SN, McNaught-Flores DA, Huppelschoten Y, da Costa Pereira D, Christopoulos A, Leurs R, Langmead CJ. Structural and Molecular Determinants for Isoform Bias at Human Histamine H3 Receptor Isoforms. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023, 14, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im D, Kishikawa JI, Shiimura Y, Hisano H, Ito A, Fujita-Fujiharu Y, Sugita Y, Noda T, Kato T, Asada H, Iwata S. Structural insights into the agonists binding and receptor selectivity of human histamine H4 receptor. Nat Commun. 2023, 14, 6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijmeijer S, de Graaf C, Leurs R, Vischer HF. Molecular pharmacology of histamine H4 receptors. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012, 17, 2089–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia R, Shi S, Xu Z, Vischer HF, Windhorst AD, Qian Y, Duan Y, Liang J, Chen K, Zhang A, Guo C, Leurs R, He Y. Structural basis of ligand recognition and design of antihistamines targeting histamine H4 receptor. Nat Commun. 2024, 15, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta P, Miszta P, Filipek S. Molecular Modeling of Histamine Receptors-Recent Advances in Drug Discovery. Molecules. 2021, 26, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers G, de Esch I, Leurs R. Molecular pharmacology of the four histamine receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010, 709, 11–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao M, Dekker ME, Leurs R, Vischer HF. Pharmacological characterization of seven human histamine H3 receptor isoforms. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024, 968, 176450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocking T, Bosma R, Rahman SN, Verweij EWE, McNaught-Flores DA, Vischer HF and Leurs R. Molecular Aspects of Histamine Receptors. In: Blandina P, Passani M. (eds) Histamine Receptors. The Receptors, 2016, vol 28. Humana, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Beyer L, Kabatas AS, Mommert S, Stark H, Werfel T, Gutzmer R, Schaper-Gerhardt K. Histamine Activates Human Eosinophils via H2R and H4R Predominantly in Atopic Dermatitis Patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 10294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatipoglu OF, Nishinaka T, Nishibori M, Watanabe M, Toyomura T, Mori S, Yaykasli KO, Wake H, Takahashi H. Histamine promotes angiogenesis through a histamine H1 receptor-PKC-VEGF-mediated pathway in human endothelial cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 2023, 151, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya-García AA, Pino-Ángeles A, Sánchez-Jiménez F, Urdiales JL, Medina MÁ. Histamine, Metabolic Remodelling and Angiogenesis: A Systems Level Approach. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um MY, Yoon M, Kim M, Jung J, Kim S, Kim DO, Cho S. Curcuminoids, a major turmeric component, have a sleep-enhancing effect by targeting the histamine H1 receptor. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12697–12706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan H, Silberstein SD. Histamine and Migraine. Headache. 2018, 58, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szukiewicz D, Pyzlak M, Stangret A, Rongies W, Maslinska D. Decrease in expression of histamine H2 receptors by human amniotic epithelial cells during differentiation into pancreatic beta-like cells. Inflamm Res. 2010, 59 Suppl 2, S205–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szukiewicz D, Szewczyk G, Mittal TK, Rongies W, Maslinski S. Involvement of histamine and histamine H2 receptors in nicotinamide-induced differentiation of human amniotic epithelial cells into insulin-producing cells. Inflamm Res. 2010, 59 Suppl 2, S209–11. [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa T, Hotta K, Ishihara K. Second-generation histamine H(2)-receptor antagonists with gastric mucosal defensive properties. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009, 9, 581–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumuham A, Nour MM, Veronese M, Onwordi EC, Rabiner EA, Howes OD. The histamine system and cognitive function: An in vivo H3 receptor PET imaging study in healthy volunteers and patients with schizophrenia. J Psychopharmacol. 2023, 37, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honkisz-Orzechowska E, Popiołek-Barczyk K, Linart Z, Filipek-Gorzała J, Rudnicka A, Siwek A, Werner T, Stark H, Chwastek J, Starowicz K, Kieć-Kononowicz K, Łażewska D. Anti-inflammatory effects of new human histamine H3 receptor ligands with flavonoid structure on BV-2 neuroinflammation. Inflamm Res. 2023, 72, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng L, Liu J, Chen Z. The Histaminergic System in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang XY, Peng SY, Shen LP, Zhuang QX, Li B, Xie ST, Li QX, Shi MR, Ma TY, Zhang Q, Wang JJ, Zhu JN. Targeting presynaptic H3 heteroreceptor in nucleus accumbens to improve anxiety and obsessive-compulsive-like behaviors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020, 117, 32155–32164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou Z, An Q, Zhang W, Li Y, Zhang Q, Yan H. Histamine and receptors in neuroinflammation: Their roles on neurodegenerative diseases. Behav Brain Res. 2024, 465, 114964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybowska-Kowalczyk A, Maslinska D, Wojciechowska M, Szukiewicz D, Wojtecka-Lukasik E, Paradowska A, Maldyk P, Maslinski S. Expression of histamine H4 receptor in human osteoarthritic synovial tissue. Inflamm Res. 2008, 57 Suppl 1, S63–4. [CrossRef]
- Schirmer B, Neumann D. The Function of the Histamine H4 Receptor in Inflammatory and Inflammation-Associated Diseases of the Gut. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver R, Silverman AJ, Vitković L, Lederhendler II. Mast cells in the brain: evidence and functional significance. Trends Neurosci. 1996, 19, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacabelos R, Yamatodani A, Niigawa H, Hariguchi S, Tada K, Nishimura T, Wada H, Brandeis L, Pearson J. Brain histamine in Alzheimer's disease. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1989, 11, 353–60. [Google Scholar]
- Passani MB, Panula P, Lin JS. Histamine in the brain. Front Syst Neurosci. 2014, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas HL, Sergeeva OA, Selbach O. Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol Rev. 2008, 88, 1183–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carthy E, Ellender T. Histamine, Neuroinflammation and Neurodevelopment: A Review. Front Neurosci. 2021, 15, 680214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardino, L. Histamine in the Crosstalk Between Innate Immune Cells and Neurons: Relevance for Brain Homeostasis and Disease. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2022, 59, 261–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han S, Márquez-Gómez R, Woodman M, Ellender T. Histaminergic Control of Corticostriatal Synaptic Plasticity during Early Postnatal Development. J Neurosci. 2020, 40, 6557–6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuutinen S, Panula P. Histamine in neurotransmission and brain diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010, 709, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula P, Sundvik M, Karlstedt K. Developmental roles of brain histamine. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 159–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez G, Velasco I, García-López G, Solís KH, Flores-Herrera H, Díaz NF, Molina-Hernández A. Histamine is required during neural stem cell proliferation to increase neuron differentiation. Neuroscience. 2012, 216, 10–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamanna J, Ferro M, Spadini S, Racchetti G, Malgaroli A. The Dysfunctional Mechanisms Throwing Tics: Structural and Functional Changes in Tourette Syndrome. Behav Sci (Basel). 2023, 13, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzà J, Gürsel DA, Schmitz-Koep B, Bremer B, Reinholz L, Berberich G, Koch K. Altered Cortico-Striatal Functional Connectivity During Resting State in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2019, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurkiewicz-Kwilecki IM, Nsonwah S. Changes in the regional brain histamine and histidine levels in postmortem brains of Alzheimer patients. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1989, 67, 75–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prell GD, Green JP, Kaufmann CA, Khandelwal JK, Morrishow AM, Kirch DG, Linnoila M, Wyatt RJ. Histamine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with chronic schizophrenia: their relationships to levels of other aminergic transmitters and ratings of symptoms. Schizophr Res. 1995, 14, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo TP, Matchett GA, Jadhav V, Martin RD, Jourdain A, Colohan A, Zhang JH, Tang J. Role of histamine in brain protection in surgical brain injury in mice. Brain Res. 2008, 1205, 100–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, N. Cerebral ischemia and brain histamine. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005, 50, 275–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obara I, Telezhkin V, Alrashdi I, Chazot PL. Histamine, histamine receptors, and neuropathic pain relief. Br J Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 580–599. [CrossRef]
- Fujita A, Bonnavion P, Wilson MH, Mickelsen LE, Bloit J, de Lecea L, Jackson AC. Hypothalamic Tuberomammillary Nucleus Neurons: Electrophysiological Diversity and Essential Role in Arousal Stability. J Neurosci. 2017, 37, 9574–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas H, Panula P. The role of histamine and the tuberomamillary nucleus in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003, 4, 121–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko PO, Gavrilov YV, Yamamoto M, Reddy H, Haybaeck J, Mignot E, Baumann CR, Scammell TE. Increase of histaminergic tuberomammillary neurons in narcolepsy. Ann Neurol. 2013, 74, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John J, Thannickal TC, McGregor R, Ramanathan L, Ohtsu H, Nishino S, Sakai N, Yamanaka A, Stone C, Cornford M, Siegel JM. Greatly increased numbers of histamine cells in human narcolepsy with cataplexy. Ann Neurol. 2013, 74, 786–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airaksinen MS, Paetau A, Paljärvi L, Reinikainen K, Riekkinen P, Suomalainen R, Panula P. Histamine neurons in human hypothalamus: anatomy in normal and Alzheimer diseased brains. Neuroscience 1991, 44, 465–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin W, Xu L, Zheng Y, An S, Zhao M, Hu W, Li M, Dong H, Li A, Li Y, Gong H, Pan G, Wang Y, Luo Q, Chen Z. Whole-brain mapping of histaminergic projections in mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023, 120, e2216231120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpati A, Neylan T, Grinberg LT. Histaminergic neurotransmission in aging and Alzheimer's disease: A review of therapeutic opportunities and gaps. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2023, 9, e12379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriwaki C, Chiba S, Wei H, Aosa T, Kitamura H, Ina K, Shibata H, Fujikura Y. Distribution of histaminergic neuronal cluster in the rat and mouse hypothalamus. J Chem Neuroanat. 2015, 68, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venner A, Mochizuki T, De Luca R, Anaclet C, Scammell TE, Saper CB, Arrigoni E, Fuller PM. Reassessing the Role of Histaminergic Tuberomammillary Neurons in Arousal Control. J Neurosci. 2019, 39, 8929–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas SD, Abdalla S, Eissa N, Akour A, Jha NK, Ojha S, Sadek B. Targeting Microglia in Neuroinflammation: H3 Receptor Antagonists as a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Autism Spectrum Disorder. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molderings GJ, Weissenborn G, Schlicker E, Likungu J, Göthert M. Inhibition of noradrenaline release from the sympathetic nerves of the human saphenous vein by presynaptic histamine H3 receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992, 346, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown RE, Haas HL. On the mechanism of histaminergic inhibition of glutamate release in the rat dentate gyrus. J Physiol. 1999, 515 (Pt 3), 777–86. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas HL, Panula P. Histamine receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2016, 106, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu J, Qu C, Lu X, Zhang S. Activation of microglia by histamine and substance P. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014, 34, 768–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta P, Miszta P, Rzodkiewicz P, Michalak O, Krzeczyński P, Filipek S. Enigmatic Histamine Receptor H4 for Potential Treatment of Multiple Inflammatory, Autoimmune, and Related Diseases. Life 2020, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John J, Wu MF, Boehmer LN, Siegel JM. Cataplexy-active neurons in the hypothalamus: implications for the role of histamine in sleep and waking behavior. Neuron. 2004, 42, 619–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provensi G, Costa A, Izquierdo I, Blandina P, Passani MB. Brain histamine modulates recognition memory: possible implications in major cognitive disorders. Br J Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura H, Shimizume R, Ikegaya Y. Histamine: A Key Neuromodulator of Memory Consolidation and Retrieval. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2022, 59, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa A, Ducourneau E, Curti L, Masi A, Mannaioni G, Hardt L, Biyong EF, Potier M, Blandina P, Trifilieff P, Provensi G, Ferreira G, Passani MB. Chemogenetic activation or inhibition of histaminergic neurons bidirectionally modulates recognition memory formation and retrieval in male and female mice. Sci Rep. 2024, 14, 11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabarean, IV. Histamine receptor signaling in energy homeostasis. Neuropharmacology. 2016, 106, 13–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata T, Yoshimatsu H, Kurokawa M. Hypothalamic neuronal histamine: implications of its homeostatic control of energy metabolism. Nutrition. 1997, 13, 403–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provensi G, Blandina P, Passani MB. The histaminergic system as a target for the prevention of obesity and metabolic syndrome. Neuropharmacology. 2016, 106, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu L, Lin W, Zheng Y, Wang Y, Chen Z. The Diverse Network of Brain Histamine in Feeding: Dissect its Functions in a Circuit-Specific Way. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024, 22, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael NJ, Zigman JM, Williams KW, Elmquist JK. Electrophysiological Properties of Genetically Identified Histaminergic Neurons. Neuroscience. 2020, 444, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno M. Metabotropic receptors mediate slow synaptic responses. In: The Synapse: Function, Plasticity, and Neurotrophism, Oxford, 1994; online edn, Oxford Academic, 22 Mar. 2012), pp. 68–82. [CrossRef]
- Hatton GI, Yang QZ. Synaptically released histamine increases dye coupling among vasopressinergic neurons of the supraoptic nucleus: mediation by H1 receptors and cyclic nucleotides. J Neurosci. 1996, 16, 123–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger SN, Baumberger B, Samaranayake S, Hersey M, Mena S, Bain I, Duncan W, Reed MC, Nijhout HF, Best J, Hashemi P. An In Vivo Definition of Brain Histamine Dynamics Reveals Critical Neuromodulatory Roles for This Elusive Messenger. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng Y, Fan L, Fang Z, Liu Z, Chen J, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Jiang L, Chen Z, Hu W. Postsynaptic histamine H3 receptors in ventral basal forebrain cholinergic neurons modulate contextual fear memory. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flik G, Folgering JH, Cremers TI, Westerink BH, Dremencov E. Interaction Between Brain Histamine and Serotonin, Norepinephrine, and Dopamine Systems: In Vivo Microdialysis and Electrophysiology Study. J Mol Neurosci. 2015, 56, 320–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada H, Inagaki N, Yamatodani A, Watanabe T. Is the histaminergic neuron system a regulatory center for whole-brain activity? Trends Neurosci. 1991, 14, 415–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimgampalle M, Chakravarthy H, Sharma S, Shree S, Bhat AR, Pradeepkiran JA, Devanathan V. Neurotransmitter systems in the etiology of major neurological disorders: Emerging insights and therapeutic implications. Ageing Res Rev. 2023, 89, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad AK, Akour A, Mahboob A, AbuRuz S, Sadek B. Role of Brain Modulators in Neurodevelopment: Focus on Autism Spectrum Disorder and Associated Comorbidities. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022, 15, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis SE, Cirincione AB, Jimenez-Torres AC, Zhu J. The Impact of Neurotransmitters on the Neurobiology of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 15340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu RI, Niculescu AG, Roza E, Vladâcenco O, Grumezescu AM, Teleanu DM. Neurotransmitters-Key Factors in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice SJ, Liu JL. Neurodevelopmental defects as a primer of neurodegeneration: lessons from spinal muscular atrophy and Huntington's disease. Neural Regen Res. 2023, 18, 1952–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman RA, O'Shea SA, Mehler MF, Chung WK. Neurogenetic disorders across the lifespan: from aberrant development to degeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022, 18, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schor NF, Bianchi DW. Neurodevelopmental Clues to Neurodegeneration. Pediatr Neurol. 2021, 123, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares J, Bou Diab Z, Nabha S, Fares Y. Neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus: history, regulation, and prospective roles. Int J Neurosci. 2019, 129, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott LC, Nigussie F. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian dentate gyrus. Anat Histol Embryol. 2020, 49, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva C, Barata-Antunes S, Santos T, Ferreiro E, Cristóvão AC, Serra-Almeida C, Ferreira R, Bernardino L. Histamine modulates hippocampal inflammation and neurogenesis in adult mice. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 8384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailaja K, Gopinath G. Ultrastructure of developing substantia nigra in humans. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1996, 14, 761–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottahedin A, Ardalan M, Chumak T, Riebe I, Ek J, Mallard C. Effect of Neuroinflammation on Synaptic Organization and Function in the Developing Brain: Implications for Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhala A, Yamatodani A, Panula P. Distribution of histamine-, 5-hydroxytryptamine-, and tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons and nerve fibers in developing rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1994, 347, 101–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvinen S, Panula P. Development of histamine-immunoreactive neurons in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1988, 276, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Hernández A, Díaz NF, Arias-Montaño JA. Histamine in brain development. J Neurochem. 2012, 122, 872–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil M, Ronda J, Weintraub M, Jain K, Silver R, Silverman AJ. Brain mast cell relationship to neurovasculature during development. Brain Res. 2007, 1171, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Hernández A, Velasco I. Histamine induces neural stem cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation by activation of distinct histamine receptors. J Neurochem. 2008, 106, 706–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao R, Chen Y, Cheng L, Fan L, Chen H, Wan Y, You Y, Zheng Y, Jiang L, Chen Z, Zhang X, Hu W. Histamine H1 Receptors in Neural Stem Cells Are Required for the Promotion of Neurogenesis Conferred by H3 Receptor Antagonism following Traumatic Brain Injury. Stem Cell Reports. 2019, 12, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson D, Krenger W. Interactions of mast cells with the nervous system--recent advances. Neurochem Res. 1992, 17, 939–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper SD, Facci L, Kee WJ, Strijbos PJ. Potentiation by histamine of synaptically mediated excitotoxicity in cultured hippocampal neurones: a possible role for mast cells. J Neurochem. 2001, 76, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong H, Zhang W, Zeng X, Hu G, Zhang H, He S, Zhang S. Histamine induces upregulated expression of histamine receptors and increases release of inflammatory mediators from microglia. Mol Neurobiol. 2014, 49, 1487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu J, Zhang X, Qian Q, Wang Y, Dong H, Li N, Qian Y, Jin W. Histamine upregulates the expression of histamine receptors and increases the neuroprotective effect of astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation. 2018, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang W, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Qu C, Zhou X, Zhang S. Histamine Induces Microglia Activation and the Release of Proinflammatory Mediators in Rat Brain Via H1R or H4R. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puttonen HAJ, Semenova S, Sundvik M, Panula P. Storage of neural histamine and histaminergic neurotransmission is VMAT2 dependent in the zebrafish. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai K, Tashiro M. The physiological and pathophysiological roles of neuronal histamine: an insight from human positron emission tomography studies. Pharmacol Ther. 2007, 113, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon TC, Befus AD, Kulka M. Mast cell mediators: their differential release and the secretory pathways involved. Front Immunol. 2014, 5, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranoglu Kilinc Y, Dilek M, Kilinc E, Torun IE, Saylan A, Erdogan Duzcu S. Capsaicin attenuates excitotoxic-induced neonatal brain injury and brain mast cell-mediated neuroinflammation in newborn rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2023, 376, 110450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti P, Ronconi G, Lauritano D, Mastrangelo F, Caraffa A, Gallenga CE, Frydas I, Kritas SK, Carinci F, Gaudelli F, Annicchiarico C, D'Ovidio C. Impact of TNF and IL-33 Cytokines on Mast Cells in Neuroinflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2024, 25, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti P, Lauritano D, Caraffa A, Gallenga CE, Kritas SK, Ronconi G, Martinotti S. Microglia and mast cells generate proinflammatory cytokines in the brain and worsen inflammatory state: Suppressor effect of IL-37. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020, 875, 173035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellenbroek, BA. Histamine H₃ receptors, the complex interaction with dopamine and its implications for addiction. Br J Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varaschin RK, Osterstock G, Ducrot C, Leino S, Bourque MJ, Prado MAM, Prado VF, Salminen O, Rannanpää Née Nuutinen S, Trudeau LE. Histamine H3 Receptors Decrease Dopamine Release in the Ventral Striatum by Reducing the Activity of Striatal Cholinergic Interneurons. Neuroscience. 2018, 376, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa T, Naganuma F, Iida T, Nakamura T, Harada R, Mohsen AS, Kasajima A, Sasano H, Yanai K. Molecular mechanism of histamine clearance by primary human astrocytes. Glia. 2013, 61, 905–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma F, Yoshikawa T. Organic Cation Transporters in Brain Histamine Clearance: Physiological and Psychiatric Implications. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021, 266, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung WS, Allen NJ, Eroglu C. Astrocytes Control Synapse Formation, Function, and Elimination. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015, 7, a020370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5 [5th ed., text revision (DSM-5-TR (TM))]. Washington: American Psychiatric Association. 2022. ISBN 978-0-89042-554-1.
- Gupta S, Kulhara P. What is schizophrenia: A neurodevelopmental or neurodegenerative disorder or a combination of both? A critical analysis. Indian J Psychiatry. 2010, 52, 21–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan L, Fronczek R, Lammers GJ, Swaab DF. The tuberomamillary nucleus in neuropsychiatric disorders. Handb Clin Neurol. 2021, 180, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan L, Bao AM, Swaab DF. The human histaminergic system in neuropsychiatric disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 167–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristino AS, Williams SM, Hawi Z, An JY, Bellgrove MA, Schwartz CE, Costa Lda F, Claudianos C. Neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders represent an interconnected molecular system. Mol Psychiatry. 2014, 19, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson OO, Walters GB, Ingason A, Johansson S, Zayats T, Athanasiu L, Sonderby IE, Gustafsson O, Nawaz MS, Jonsson GF, Jonsson L, Knappskog PM, Ingvarsdottir E, Davidsdottir K, Djurovic S, Knudsen GPS, Askeland RB, Haraldsdottir GS, Baldursson G, Magnusson P, Sigurdsson E, Gudbjartsson DF, Stefansson H, Andreassen OA, Haavik J, Reichborn-Kjennerud T, Stefansson K. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder shares copy number variant risk with schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 2019; 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruediger T, Bolz J. Neurotransmitters and the development of neuronal circuits. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007, 621, 104–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco B, Bonaccorso CM, Aloisi E, D'Antoni S, Catania MV. Neuro-Inflammatory Mechanisms in Developmental Disorders Associated with Intellectual Disability and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Neuro- Immune Perspective. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2016, 15, 448–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven WMA, Egger JIM, Janssen PKC, van Haeringen A. Adult male patient with severe intellectual disability caused by a homozygous mutation in the HNMT gene. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e235972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griswold AJ, Ma D, Cukier HN, Nations LD, Schmidt MA, Chung RH, Jaworski JM, Salyakina D, Konidari I, Whitehead PL, Wright HH, Abramson RK, Williams SM, Menon R, Martin ER, Haines JL, Gilbert JR, Cuccaro ML, Pericak-Vance MA. Evaluation of copy number variations reveals novel candidate genes in autism spectrum disorder-associated pathways. Hum Mol Genet. 2012, 21, 3513–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright C, Shin JH, Rajpurohit A, Deep-Soboslay A, Collado-Torres L, Brandon NJ, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Jaffe AE, Cross AJ, Weinberger DR. Altered expression of histamine signaling genes in autism spectrum disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 2017, 7, e1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa N, Sadeq A, Sasse A, Sadek B. Role of Neuroinflammation in Autism Spectrum Disorder and the Emergence of Brain Histaminergic System. Lessons Also for BPSD? Front Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abruzzo PM, Matté A, Bolotta A, Federti E, Ghezzo A, Guarnieri T, Marini M, Posar A, Siciliano A, De Franceschi L, Visconti P. Plasma peroxiredoxin changes and inflammatory cytokines support the involvement of neuro-inflammation and oxidative stress in Autism Spectrum Disorder. J Transl Med. 2019, 17, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco-Fontecilla, H. Is Histamine and Not Acetylcholine the Missing Link between ADHD and Allergies? Speer Allergic Tension Fatigue Syndrome Re-Visited. J Clin Med. 2023, 12, 5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa T, Nakamura T, Yanai K. Histamine N-Methyltransferase in the Brain. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco-Fontecilla H, Bella-Fernández M, Wang P, Martin-Moratinos M, Li C. Prevalence and Clinical Picture of Diamine Oxidase Gene Variants in Children and Adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Pilot Study. J Clin Med. 2024, 13, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan-Sencicek AG, Stillman AA, Ghosh AK, Bilguvar K, O'Roak BJ, Mason CE, Abbott T, Gupta A, King RA, Pauls DL, Tischfield JA, Heiman GA, Singer HS, Gilbert DL, Hoekstra PJ, Morgan TM, Loring E, Yasuno K, Fernandez T, Sanders S, Louvi A, Cho JH, Mane S, Colangelo CM, Biederer T, Lifton RP, Gunel M, State MW. L-histidine decarboxylase and Tourette's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2010, 362, 1901–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, C. The histidine decarboxylase model of tic pathophysiology: a new focus on the histamine H3 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldan LC, Williams KA, Gallezot JD, Pogorelov V, Rapanelli M, Crowley M, Anderson GM, Loring E, Gorczyca R, Billingslea E, Wasylink S, Panza KE, Ercan-Sencicek AG, Krusong K, Leventhal BL, Ohtsu H, Bloch MH, Hughes ZA, Krystal JH, Mayes L, de Araujo I, Ding YS, State MW, Pittenger C. Histidine decarboxylase deficiency causes tourette syndrome: parallel findings in humans and mice. Neuron 2014, 81, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu L, Zhang C, Zhong M, Che F, Guan C, Zheng X, Liu S. Role of histidine decarboxylase gene in the pathogenesis of Tourette syndrome. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhongling K, Yanhui C, Guofeng C, Yanyan L. Neuroinflammation in a Rat Model of Tourette Syndrome. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022, 16, 710116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Liu X, Chen L, Zhang X. The inflammatory injury in the striatal microglia-dopaminergic-neuron crosstalk involved in Tourette syndrome development. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1178113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, C. The role of the central histaminergic system on schizophrenia. Drug News Perspect. 2004, 17, 383–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrang, JM. Histamine and schizophrenia. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2007, 78, 247–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, A. Neuroinflammation in Schizophrenia: The Key Role of the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy CE, Walker AK, Weickert CS. Neuroinflammation in schizophrenia: the role of nuclear factor kappa B. Transl Psychiatry. 2021, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma Q, Jiang L, Chen H, An D, Ping Y, Wang Y, Dai H, Zhang X, Wang Y, Chen Z, Hu W. Histamine H2 receptor deficit in glutamatergic neurons contributes to the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023, 120, e2207003120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl T, Kaur G, Sehgal A, Bhardwaj S, Singh S, Buhas C, Judea-Pusta C, Uivarosan D, Munteanu MA, Bungau S. Multifaceted Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri PM, Banerjee A, Ghosal A, Layek B. Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Disorders: Current Knowledge and Therapeutic Implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2024, 25, 3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh K, Sethi P, Datta S, Chaudhary JS, Kumar S, Jain D, Gupta JK, Kumar S, Guru A, Panda SP. Advances in gene therapy approaches targeting neuro-inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2024, 98, 102321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong RA, Lantos PL, Cairns NJ. Overlap between neurodegenerative disorders. Neuropathology. 2005, 25, 111–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, RA. On the 'classification' of neurodegenerative disorders: discrete entities, overlap or continuum? Folia Neuropathol. 2012, 50, 201–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi F, Munitic I, Vidatic L, Papić E, Rački V, Nimac J, Jurak I, Novotni G, Rogelj B, Vuletic V, Liscic RM, Cannon JR, Buratti E, Mazzini L, Hecimovic S. Overlapping Neuroimmune Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Biomedicines. 2023, 11, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman FJ, Simkovic S, Pasinetti GM. Neuroimmune nexus of depression and dementia: Shared mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Br J Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 3558–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed RM, Devenney EM, Irish M, Ittner A, Naismith S, Ittner LM, Rohrer JD, Halliday GM, Eisen A, Hodges JR, Kiernan MC. Neuronal network disintegration: common pathways linking neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2016, 87, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakowsky A, Prasad AA, Peña-Ortega F, Lim SAO. Editorial: Neuronal network dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders. Front Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1151156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taslim S, Shadmani S, Saleem AR, Kumar A, Brahma F, Blank N, Bashir MA, Ansari D, Kumari K, Tanveer M, Varrassi G, Kumar S, Raj A. Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Bridging the Gap Between Neurology and Psychiatry. Cureus. 2024, 16, e51655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldossari AA, Assiri MA, Ansari MA, Nadeem A, Attia SM, Bakheet SA, Albekairi TH, Alomar HA, Al-Mazroua HA, Almanaa TN, Al-Hamamah MA, Alwetaid MY, Ahmad SF. Histamine H4 Receptor Antagonist Ameliorates the Progression of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis via Regulation of T-Cell Imbalance. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 15273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz KM, Pickett LA, Wright CL, Davis KT, Joshi A, McCarthy MM. Mast Cells in the Developing Brain Determine Adult Sexual Behavior. J Neurosci. 2018, 38, 8044–8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang W, Xiao D, Mao Q, Xia H. Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration development. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen JE, Veasey SC. Impact of sleep disturbances on neurodegeneration: Insight from studies in animal models. Neurobiol Dis. 2020, 139, 104820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailah, HG. Potential of Therapeutic Small Molecules in Apoptosis Regulation in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Updated Review. Molecules. 2022, 27, 7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabresi P, Mechelli A, Natale G, Volpicelli-Daley L, Di Lazzaro G, Ghiglieri V. Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies: from overt neurodegeneration back to early synaptic dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso-Escudero P, Parra A, Nassif M, Vidal RL. Outside in: Unraveling the Role of Neuroinflammation in the Progression of Parkinson's Disease. Front Neurol. 2018, 9, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, KA. Basic mechanisms of neurodegeneration: a critical update. J Cell Mol Med. 2010, 14, 457–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannoni F, Quintana FJ. The Role of Astrocytes in CNS Inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao F, Wang X, Wu H, Wu Q, Zhang J. Microglia and Neuroinflammation: Crucial Pathological Mechanisms in Traumatic Brain Injury-Induced Neurodegeneration. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 825086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio L, Viotti A, Martino G. Microglia in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration: From Understanding to Therapy. Front Neurosci. 2021, 15, 742065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan L, Swaab DF, Bao AM. Neuronal histaminergic system in aging and age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Exp Gerontol. 2013, 48, 603–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan L, Swaab DF. Changes in Histaminergic System in Neuropsychiatric Disorders and the Potential Treatment Consequences. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen TC, Gittis AH. Histamine and deep brain stimulation: the pharmacology of regularizing a brain. J Clin Invest. 2018, 128, 5201–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotemeyer A, McFleder RL, Wu J, Wischhusen J, Ip CW. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's Disease - Putative Pathomechanisms and Targets for Disease-Modification. Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 878771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan L, Liu CQ, Balesar R, Hofman MA, Bao AM, Swaab DF. Neuronal histamine production remains unaltered in Parkinson's disease despite the accumulation of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites in the tuberomamillary nucleus. Neurobiol Aging. 2012, 33, 1343–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla S, Eissa N, Jayaprakash P, Beiram R, Kuder KJ, Łażewska D, Kieć-Kononowicz K, Sadek B. The Potent and Selective Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist E169 Counteracts Cognitive Deficits and Mitigates Disturbances in the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway in MK801-Induced Amnesia in Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 12719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddafi F, Mirshafiey A. The neglected role of histamine in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2013, 28, 327–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Wamelen DJ, Shan L, Aziz NA, Anink JJ, Bao AM, Roos RA, Swaab DF. Functional increase of brain histaminergic signaling in Huntington's disease. Brain Pathol. 2011, 21, 419–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Delgado D, Puigdellívol M, Moreno E, Rodríguez-Ruiz M, Botta J, Gasperini P, Chiarlone A, Howell LA, Scarselli M, Casadó V, Cortés A, Ferré S, Guzmán M, Lluís C, Alberch J, Canela EI, Ginés S, McCormick PJ. Modulation of dopamine D1 receptors via histamine H3 receptors is a novel therapeutic target for Huntington's disease. Elife. 2020, 9, e51093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapanelli, M. The magnificent two: histamine and the H3 receptor as key modulators of striatal circuitry. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2017, 73, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia Q, Li S, Li XJ, Yin P. Neuroinflammation in Huntington's disease: From animal models to clinical therapeutics. Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 1088124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles-López QD, González-Espinosa C, Pérez-Severiano F. Mast cells and histamine are involved in the neuronal damage observed in a quinolinic acid-induced model of Huntington's disease. J Neurochem. 2022, 160, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersey M, Hashemi P, Reagan LP. Integrating the monoamine and cytokine hypotheses of depression: Is histamine the missing link? Eur J Neurosci. 2022, 55, 2895–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian H, Shu C, Xiao L, Wang G. Histamine and histamine receptors: Roles in major depressive disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2022, 13, 825591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar A, Dogra S, Sona C, Umrao D, Rashid M, Singh SK, Wahajuddin M, Yadav PN. Chronic histamine 3 receptor antagonism alleviates depression like conditions in mice via modulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and hypothalamus-pituitary adrenal axis. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019, 101, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhusaini M, Eissa N, Saad AK, Beiram R, Sadek B. Revisiting Preclinical Observations of Several Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonists/Inverse Agonists in Cognitive Impairment, Anxiety, Depression, and Sleep-Wake Cycle Disorder. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 861094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauvilliers Y, Delallée N, Jaussent I, Scholz S, Bayard S, Croyal M, Schwartz JC, Robert P. Normal cerebrospinal fluid histamine and tele-methylhistamine levels in hypersomnia conditions. Sleep. 2012, 35, 1359–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh P, Momtazmanesh S, Plazzi G, Rezaei N. Connecting the dots: An updated review of the role of autoimmunity in narcolepsy and emerging immunotherapeutic approaches. Sleep Med. 2024, 113, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan L, Dauvilliers Y, Siegel JM. Interactions of the histamine and hypocretin systems in CNS disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015, 11, 401–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barateau L, Krache A, Da Costa A, Lecendreux M, Debs R, Chenini S, Arlicot N, Vourc'h P, Evangelista E, Alonso M, Salabert AS, Silva S, Béziat S, Jaussent I, Mariano-Goulart D, Payoux P, Dauvilliers Y. Microglia Density and Its Association With Disease Duration, Severity, and Orexin Levels in Patients With Narcolepsy Type 1. Neurology. 2024, 102, e209326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passani MB, Blandina P. Histamine receptors in the CNS as targets for therapeutic intervention. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011, 32, 242–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronio D, Gonchoroski T, Castro K, Zanatta G, Gottfried C, Riesgo R. Histaminergic system in brain disorders: lessons from the translational approach and future perspectives. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2014, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang L, Wang Y, Chen Z. Central histaminergic signalling, neural excitability and epilepsy. Br J Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Rio R, Noubade R, Saligrama N, Wall EH, Krementsov DN, Poynter ME, Zachary JF, Thurmond RL, Teuscher C. Histamine H4 receptor optimizes T regulatory cell frequency and facilitates anti-inflammatory responses within the central nervous system. J Immunol. 2012, 188, 541–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman AC, Trias E, da Silva Chagas L, Trindade P, Dos Santos Pereira M, Refojo D, Hedin-Pereira C, Serfaty CA. Neuroimmune and Inflammatory Signals in Complex Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2018, 25, 246–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampeli E, Tiligada E. The role of histamine H4 receptor in immune and inflammatory disorders. Br J Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula P, Nuutinen S. The histaminergic network in the brain: basic organization and role in disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013, 14, 472–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundvik M, Panula P. Interactions of the orexin/hypocretin neurones and the histaminergic system. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2015, 213, 321–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou E, Zhang X, Dong B, Wang B, Zhu Y. Combination of H1 and H2 Histamine Receptor Antagonists: Current Knowledge and Perspectives of a Classic Treatment Strategy. Life (Basel). 2024, 14, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicker E, Kathmann M. Role of the Histamine H3 Receptor in the Central Nervous System. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017, 241, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerstein, TJ. Presynaptic receptors for dopamine, histamine, and serotonin. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008, 289–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellenbroek BA, Ghiabi B. The other side of the histamine H3 receptor. Trends Neurosci 2014, 37, 191–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwell V, Fasinu PS. Pitolisant and Other Histamine-3 Receptor Antagonists-An Update on Therapeutic Potentials and Clinical Prospects. Medicines (Basel). 2020, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek B, Saad A, Sadeq A, Jalal F, Stark H. Histamine H3 receptor as a potential target for cognitive symptoms in neuropsychiatric diseases. Behav Brain Res. 2016, 312, 415–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang Z, Chen J, Zheng Y, Chen Z. Targeting Histamine and Histamine Receptors for Memory Regulation: An Emotional Perspective. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024, 22, 1846–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghamari N, Zarei O, Arias-Montaño JA, Reiner D, Dastmalchi S, Stark H, Hamzeh-Mivehroud M. Histamine H3 receptor antagonists/inverse agonists: Where do they go? Pharmacol Ther. 2019, 200, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepańska K, Kuder KJ, Kieć-Kononowicz K. Dual-targeting Approach on Histamine H3 and Sigma-1 Receptor Ligands as Promising Pharmacological Tools in the Treatment of CNS-linked Disorders. Curr Med Chem. 2021, 28, 2974–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flik G. The histaminergic system and its interaction with relevant central neurotransmitter systems. [Thesis fully internal (DIV), University of Groningen]. University of Groningen 2022. [CrossRef]
- Adamu A, Li S, Gao F, Xue G. The role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases: current understanding and future therapeutic targets. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1347987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Molecular Characteristics and Biological Properties | H1R | H2R | H3R | H4R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromosomal location of the gene | 3p25.3 | 5q35.2 | 20q13.33 | 18q11.2 |
| Receptor proteins, molecular weight (MW) | 487 aa, 55.78 kDa | 358-359 aa, 40.1–44.5 kDa (2 isoforms) | 445 aa (full-length), 36.4–49 kDa (≥ 20 possible mRNA isoforms) | 390 aa, 34.5–44.5 kDa (2 isoforms) |
| Gene structure | No introns | No introns | Three introns | Two introns |
| Class of receptor | Rhodopsin-like GPCRs (metabotropic), seven transmembrane domain (7TM) receptors | |||
| Binding affinity | Low (2.5 x 10 –5 M) | Low (7.9 x 10 –6 M) | High (6.3 x 10 –9 M) | High (7.9 x 10 –9 M) |
| Coupling subunit of the G protein complex | Gαq/11 | Gαs | Gαi | Gαi |
| The equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) | ~ 10 μmol/L | ~ 30 μmol/L | ~ 10 nmol/L | ~ 20-40 nmol/L |
| Selective agonists | Histaprodiphen | Amthamine, Dimaprit, Impromidine | Imetit, Immepip, α-Methylhistamine | Imetit *, Immepip *, 4-methylhistamine, Clobenopropit (partial agonist) |
| Antagonists (incl. inverse agonists) | Mepyramine, Cetirizine, Chlorpheniramine, Clemastine, Diphenhydramine, Pyrilamine, Triploidine, | Cimetidine, Famotidine, Nizatidine, Ranitidine | Clobenpropit, Ciproxifan, Pitolisant, Thioperamide * | 2-aminopyrimidine Thioperamide, VUF-6002, JNJ-10191584, Toreforant (JNJ-38518168), JNJ-7777120, CZC-13788, PF-2988403, A-940894, A-987306 |
| Tissue distribution | Widespread expression in many cells and tissues, including smooth muscles (e.g., in the respiratory tract and vessels), vascular ECs cells, the heart, CNS, adrenal medulla | Widespread expression in various cells and tissues, such as gastric mucosa parietal cells, smooth mucle (e.g., airways, uterus, vessels), the heart, immune cells (e.g., B cells, T cells, DCs), CNS, skin, genitourinary system, endocrine and exocrine glands | High expression in the CNS (histaminergic neurons) and neuroendocrine tissues, including enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells in the gastric mucosa and adrenal cortex; to a lesser extent epression in the peripheral nervous system; low expression elsewhere | High expression in bone marrow, peripheral hematopoietic cells and immune cells, including MCs, DCs, T cells, NK cells, monocytes and eosinophils; low expression elsewhere |
| Transmitting intracellular signals/effector molecules (see also Figure 2.) | Mobilization of intracellular Ca 2+ levels: Gαq/11 activates PLC, which signals via DAG and PKC or IP3 to enhance Ca 2+ release from endoplasmic reticulum, activating eNOS to release NO; H1R can activate also PLA2, leading to the formation of AA and AADE. ↑ cGMP, cAMP accumulation (via Gβγ subunits), ↑ Ca 2+, ↑ NF-κβ, ↑ PLA2, ↑ PLD, ↑ AA, ↑ AADE |
Once AC activation is initiated by Gαs, subsequent signaling occurs via cAMP and PKA; Alternatively, via Gs, the H2R can activate PLC inducing DAG and IP3 pathways; Gαs promotes Ca2+, Na+ and Cl– chanel opening, changing the permeability of the cell membrane ↑ Ca 2+, ↑ c-fos , ↑ cAMP, ↑ PLC |
Activated Gαi inhibits AC and modulate MAPK activity via interaction with β-arrestin 2, the recruitment of which does not depend on the formation of an active G protein complex; Alternatively, activation of Gαi can inhibit K⁺ channels, Ca²⁺ channels, and the Na⁺/H⁺ transporter via arachidonic acid metabolites; ↓ cAMP, ↑ Ca 2+, ↑ MAPK and ↑ MAPK phosphorylation |
Recruitment of Gαi activates PLC and inhibits membrane-bound AC activity. As a result, Ca²⁺ is mobilized from intracellular stores, while cytosolic cAMP is diminished; Independently of G protein complex activation, β-arrestin 2 is recruited to the agonist-bound H4R, initiating MAPK cascade activation with subsequent receptor desensitization and internalization; ↓ cAMP, ↑ Ca 2+, ↑ MAPK and ↑ MAPK phosphorylation |
| Actions mediated | - Allergic disease: ↑ APCs capacity, degranulation of MCs and basophils (release of HA and other mediators), ↓ humoral immunity and ↑ Th1 priming, ↑ Th1, ↑ IFN-γ production, ↑ cellular adhesion molecule expression, and ↑ chemotaxis of eosinophils and neutrophils, ↑ vascular permeability, hypotension; - Smooth muscle contraction (airways, intestine, uterus) resulting in bronchoconstriction, vasodilation and uterine contraction, respectively; - Nociception (↑ pruritus, ↑ burning, ↑ pain); - Thermoregulation; - Regulation of the sleep-wake cycle, food intake, locomotion, emotions (aggressive behavior), memory and learning; - Negative dromotropic and negative atrial inotropic cardiac stimulation; - pro-angiogenic activity through H1R-PKC-VEGF-mediated pathway in EC. |
- Immune system: Suppression of immune cells (development of tolerance), including stimulation of suppressor T cells (Treg), ↓ neutrophil and basophil chemotaxis, ↓ neutrophil and basophil activation, ↓proliferation of lymphocytes, ↓ activity of NK cells; suppression of Th2 cells and cytokines; induction of IL-10 and suppression of IL-12 by DCs; ↑ humoral immunity; Indirect role in allergic response, autoimmunity, malignancy, and graft rejection; - Changes in H2R expression accompany the process of cell differentiation - ↑ Gastric acid secretion (↑ risk of gastric ulcer): - Inflammatory response: ↑ vascular permeability, vasodialtion (↑ risk of hypotension), flushing, headache; - Positive atrial chronotropic (↑ risk of tachycardia) and positive ventricular inotropic cardiac stimulation; - Bronchodilatation and ↑ mucus production (airways); - Uterus: relaxation. |
- Neurotransmission: Presynaptic autoreceptor function – inhibition of HA release (↓ histaminergic neurons activity), as well as presynaptic heteroreceptor activity in non-histaminergic neurons – inhibition of the release of DA, 5-HT, NA (↓ sympathetic tone), ACh, GABA and glutamate; - Sympathoinhibitory action, in vivo, leads to reduced vasoconstriction, thus may promote a vasodilatory effect; - Involvement in the pathophysiology of neuroinflammation through local neuron-MCs loops; proinflammatory effect through ↑ APCs activity; - Modulation of executive functions, involvement in cognitive impairment. |
- Immunomodulation: Involvement in DC activation and T cell differentiation; induction of proinflammatory AP-1 in Th2 cells and monocyte-derived DCs with simultaneous reduced production of the Th1-associated cytokine IL-12 and chemokine CXCL10 (IP10) in monocyte-derived DCs; modulation of eosinophil migration and selective recruitment of MCs leading to amplification of HA-mediated immune responses and subsequent chronic inflammation. |
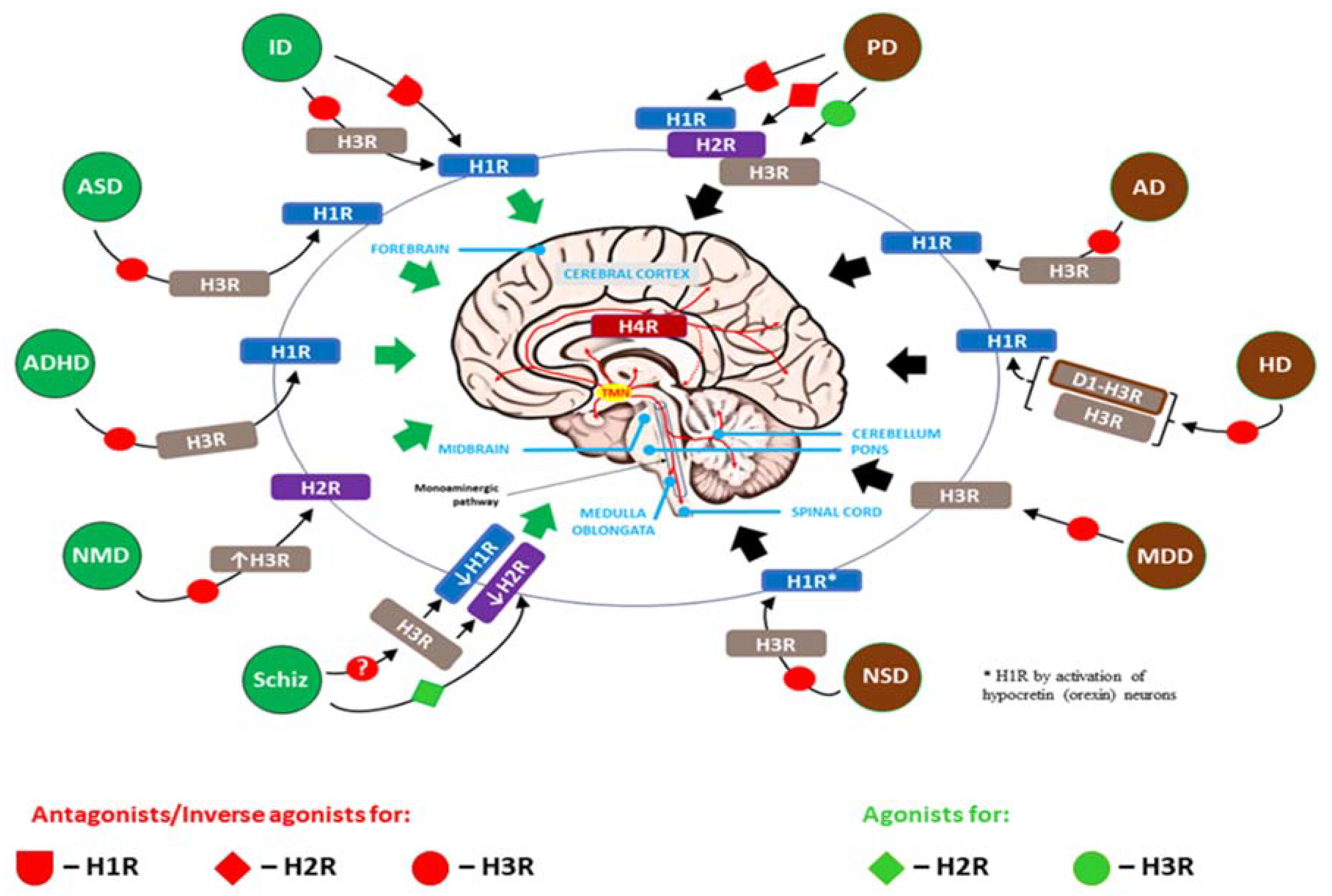
| Type/Name of disorder | HA level in the CNS (incl. controversies)/possible causes or accompanying circumstances | Major HA receptor involved* | Neuroinflammation (regardless of HA)/ typical clinical symptoms in brief | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intellectual disability (intellectual development disorder) | Increased, due to a homozygous mutation in the histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT) enzyme gene. HNMT is responsible for the degradation of intracellular HA. | H1R | Present / Previously called “mental retardation”; affected children start crawling, walking or talking later than other children and have trouble with learning (the main symptom is learning slowly), communicating, thinking rationally, making judgments, and planning | Di Marco et al., 2016 [150]; Verhoeven et al., 2020 [151] |
| Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) | Normal. This suggests that the response to HA is changed rather than its secretion or production in ASD. Different expression of the gene set of HNMT, H1R, H2R and H3R may explain the different effects of HS in ASD. | H1R, H3R | Present / Symptoms of this complex condition generally appear in the first 2 years of life and include persistent challenges with social communication (e.g., decreased sharing of interests with others, difficulty assessing emotions, lack of abstract thinking), restricted interests (inflexibility of behavior, extreme difficulty coping with change) and repetitive behavior (stereotypical movements such as hand flapping, rocking, spinning); the limitation of normal functioning due to these disorders shows significant differences between individuals with autism. | Di Marco et al., 2016 [150]; Verhoeven et al., 2020 [151]; Griswold et al., 2012 [152]; Wright et al., 2017 [153]; Eissa N et al., 2020 [154]; Abruzzo et al., 2019 [155] |
| Attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) | Increased, due to decreased activity of the diamine oxidase (DAO), the key enzyme responsible for extracellular HA degradation. Some single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) variants of the AOC1 gene associated with DAO deficiency or decreased DAO functionality may be involved in the pathomechanism of ADHD. The increase in brain HA may also result from SNP of the HNMT, encoding the main enzyme involved in intracellular metabolism of HA. It was demonstrated that the “T” allele at rs11558538 is associated with decreased HNMT activity. |
H1R, H3R | Present / Executive dysfunction that can be categorized into 2 types of behavioral problems: inattentiveness (difficulty concentrating and focusing) and hyperactivity and impulsiveness | Blasco-Fontecilla 2023 [156]; Yoshikawa et al., 2019 [157]; Blasco-Fontecilla et al., 2024 [158] |
| Neurodevelopmental motor disorders (e.g., Tourette’s syndrome) | Decreased, due to a rare nonsense mutation, HDC W317X, in the exon 9 of the L-histidine decarboxylase (HDC) gene. This hypomorphic mutation in the HDC gene is a rare but high penetrance genetic cause of TS. Subsequent deficiency of HA disrupts dopamine modulation of basal ganglia, because HA reduces dopamine levels in the stratum. | H2R and up-regulated H3R in the striatum | Present / Symptoms of motor disorders include tremors, jerks, twitches, spasms, contractions, or gait problems; these disorders can significantly limit intentional movements and cause an excess of involuntary movements, including tics (fast, repetitive muscle movements that result in sudden and difficult to control body jolts or sounds) | Ercan-Sencicek et al., 2010 [159]; Pittenger 2020 [160]; Baldan et al., [161]; Xu et al., 2022 [162]; Zhongling et al., 2022 [163]; Wang et al., 2023 [164] |
| Schizophrenia | Increased levels of N-tele-methylhistamine (Nτ-MH), a major brain metabolite of HA in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) | Reduced efficiency and/or decreased number of H1R binding sites, H2R (including deficit in glutamatergic neurons), H3R | Present, particularly in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (PFC) / A chronic mental health condition that causes a range of different psychological symptoms including reoccurring episodes of psychosis that are correlated with a general misperception of reality. The active form of schizophrenia is characterized by: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, trouble with thinking and lack of motivation. | Ito 2004 [165]; Arrang 2007 [166]; Vallée 2022 [167]; Murphy et al., 2021 [168]; Ma et al., 2023 [169] |
| Type/Name of disorder | HA level in the CNS (incl. controversies)/possible causes or accompanying circumstances | Major HA receptor involved* | Neuroinflammation (regardless of HA)/typical clinical symptoms in brief | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parkinson's disease (PD) | Unaltered or increased. Expression of HDC-mRNA in the TMN remains undisturbed and the enzymatic activity of HDC preserved within normal range. Moreover, the concentration of the main metabolite of HA, t-MeHA, remains unchanged in the CSF. However, abnormally high HA concentration in the basal ganglia of the brains of PD patients has been shown postmortem in other studies. |
H1R,H2R, H3R | Present / Motor symptoms include: tremor (particularly when at rest), slowness of movement (bradykinesia), rigidity (stiffness), posture and balance problems (frequent falls), involuntary movements (dyskinesia) and muscle spasms (dystonia), speech changes (weak, hoarse, nasal or monotonous voice, imprecise articulation, slow or fast speech, difficulty starting to speak, problems with accentuation or rhythm); non-motor symptoms include: anxiety and depression, stress, apathy, compulsive or impulsive behavior, dementia, changes in sleep | Cheng et al., 2021 [57]; Nuutinen and Panula, 2010 [69]; Shan et al., 2013 [191]; Shan and Swaab, 2022 [192]; Whalen and Gittis, 2018 [193]; Grotemeyer et al., [194] |
| Alzheimer's disease (AD) | Unaltered or decreased. Despite of the significant loss of histaminergic neurons in AD, expression of HDC-mRNA in the TMN remains unaltered. The decline in H1R binding may have a role in the cognitive deficits of patients with AD. Many studies have also demonstrated the involvement of H3R, whose loss of integrity and/or increased expression may locally reduce HA concentration in the CNS. |
H1R, H3R | Present / The typical and common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events; the symptoms of dementia develop gradually over many years and eventually become more severe; in the early stages of the disease, decline in non-memory aspects of cognition, such as finding the right word, trouble understanding visual images and spatial relationships, and impaired reasoning or judgment may be observed; in the advanced-stage Alzheimer’s, patients are diagnosed with severe impairment/loss of speaking ability, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues, including lack of response to stimuli from the environment; Alzheimer's disease is the most common type of dementia. | Zhou et al., 2024 [59]; Nuutinen and Panula, 2010 [69]; Shan et al., 2013 [191]; Shan and Swaab, 2022 [192]; Shan et al., 2012 [195]; Abdalla et al., 2023 [196]; Naddafi and Mirshafiey, 2013 [197] |
| Huntington's disease (HD) | Normal to increased. TMN volume and number of TMN neurons remain within the normal range, whereas the levels of HDC mRNA, HMT activity within the inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), H1R and H3R mRNA levels are increased. These findings indicate a functional increase in brain histaminergic signaling in HD that is linked to aberrant striatal function. | H3R, especially a hybrid dopamine-histamine receptor (D1R–H3R, heteromer), H1R | Present / Choreiform movements (jerking or writhing movements), psychiatric problems [depression, irritability/aggression, psychosis, executive dysfunction (e.g., obsessive-compulsive behaviors, apathy)], cognitive decline and dementia (the commonest genetic dementia with autosomal dominant inheritance). | van Wamelen et al., 2011 [198]; Moreno-Delgado et al., 2020 [199]; Rapanelli 2017 [200]; Jia Q et al., 2022 [201]; Angeles-López et al., 2022 [202] |
| Depression (also called major depressive disorder or clinical depression) | Decreased. A decrease in the HA level, especially related to the activation of H3R. Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) neurons express H3R through which HA directly inhibits release of MCH, an orexigenic peptide, with confirmed depressogenic effects. Moreover, other neural circuits may be influenced by lowered level of HA via H3R signaling, due to the crosstalk of HA-H3R signaling pathways with other depression-related neurotransmitters, such as 5-HT, DA and GLU. | H3R can interact with other depression-related transmitters (including 5-HT, DA, GLU, and MCH); thus, histamine may participate in the occurrence of depression through other neural circuits. | Present / A persistent feeling of sadness, tearfulness, emptiness or hopelessness with loss of interest or pleasure in most or all normal activities (e.g., sex, hobbies sports); angry outbursts, irritability or frustration, even over small matters; sleep disturbances (both insomnia or excessive sleepiness); weight loss or weight gain related to lack of appetite or overeating, respectively; loss of concentration, difficulty making decisions, slowness; feeling anxious, thinking about impending death or having suicidal thoughts; somatic ailments caused by a lower pain threshold. | Hersey et al., 2022 [203]; Qian et al., 2022 [204]; Kumar et al., 2019 [205]; Alhusaini et al., 2022 [206] |
| Narcolepsy [also called narcolepsy spectrum disorder (NSD)] | Increased together with the increase in the number of HA neurons in narcolepsy type 1 (narcolepsy with cataplexy) or unchanged to decreased, despite of increased number of HDC-positive neurons. In cases of elevated HA concentration, an ineffective compensatory mechanism in response to hypocretin (orexin) neurons may be suspected. |
H1R by activation of hypocretin (orexin) neurons | Present / A chronic sleep disorder characterized by sudden, excessive and uncontrollable daytime sleepiness, catalepsy (a sudden loss of control of muscle tension ranging from slight weakness to total collapse), sleep paralysis and hypnagogic (occurring immediately before falling asleep) hallucinations. | Cheng et al., 2021 [57]; Valko et al., 2013 [81]; John et al., 2013 [82]; Dauvilliers et al., 2012 [207]; Valizadeh P et al., 2024 [208]; Shan et al., 2015 [209]; Barateau et al., 2024 [210]; |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




