1. Introduction
Congenital heart defects affecting a single ventricle are often marked by underdevelopment or absence of one ventricular chamber, necessitating complex surgeries. The three-stage Fontan procedure has become crucial in establishing functional circulation for these patients. Enhanced perioperative management and reduced arrhythmias have improved survival rates and outcomes, with the Fontan patient population projected to double in the next two decades (1-3). Despite this, the 30-year survival rate remains around 85%, indicating room for improvement (3, 4).
Postoperative challenges include limited exercise capacity, affecting quality of life (5, 6). The unique haemodynamic of Fontan circulation limits cardiac output during physical activity, reducing exercise tolerance (7). This, coupled with low pulmonary vascular resistance, leads to exercise intolerance and a sedentary lifestyle, raising cardiovascular risk and impairing psychosocial well-being (5, 6). Exercise training programs could address these challenges, with initial studies showing that physical activity improves fitness, endurance, and mental health without adverse effects (10-12). However, practical implementation remains limited, and adherence to exercise guidelines is often inadequate.
This review and meta-analysis evaluated the safety, efficacy, and best exercise approaches for Fontan patients. By critically appraising existing research, this study aims to create a framework for integrating exercise training into postoperative management, ultimately improving long-term outcomes and quality of life in this growing patient group.
2. Materials and Methods
Search strategy
In collaboration with librarians from Nova Medical School, we devised a search strategy using terms and synonyms related to Fontan circulation and cardiac rehabilitation (CR) (detailed in the Supplementary Material). On August 24, 2023, we conducted a comprehensive search across PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library, filtering for articles in English, French, Portuguese, and Spanish published between 1970 and August 2023. Any relevant articles published after that date were manually included in the search results.
Eligibility Criteria:
This systematic review examined the effects of CR in patients with Fontan circulation. To be included, studies had to meet the following criteria:
Population: Patients diagnosed with univentricular hearts and Fontan-type circulation.
Intervention: CR programs involving exercise training, lifestyle counselling, or medication management.
Outcomes: Reported effects of cardiac rehabilitation, such as mortality, quality of life, exercise tolerance, cardiac function, and hospital readmissions. Only primary research articles were considered, particularly Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs).
Exclusion criteria included: A) Studies lacking univentricular heart patients or those that did not separately analyse this group. B) studies focused solely on surgical or pharmacological treatments without a CR component. C) Studies without clear outcome measures for the efficacy of CR. D) Articles unavailable in full text through PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, or Cochrane Library. E) Systematic reviews, meta-analyses, case reports, editorials, and commentaries were excluded.
Data extraction
Searches from PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library were consolidated in Rayyan QCRI for deduplication and initial screening. Two researchers independently assessed articles, resolving discrepancies through consensus. Titles, abstracts, and full texts were screened against predefined criteria to exclude irrelevant studies. Manually identified relevant studies outside the initial search were included. Data extraction focused on study characteristics and the impact of cardiac rehabilitation on Fontan patients, and it was conducted from the final selection of articles.
Quality assessment
Bias assessment used the Cochrane Collaboration’s Risk of Bias Tool 2 for RCTs (13) and the STROBE checklist for cohort studies (14). The Risk of Bias Tool 2 evaluated five domains, classifying each as low risk, some concerns, or high risk. The STROBE checklist, covering 22 items across study design elements, deemed studies sufficiently reported if over 70% of criteria were met (15).
Statistical analyses
A meta-analysis was conducted using OpenMeta[Analyst] to evaluate the impact of exercise training programs on exercise capacity (peak VO2 and peak workload) in Fontan patients. Other outcomes were presented descriptively due to limited reporting. Normally distributed continuous variables are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD), while non-normally distributed data are presented as medians with interquartile ranges. Categorical variables are provided as percentages and counts.
All data were sourced directly from published papers. Given the clinical variability between studies, a random-effects model was used. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I² statistic. Subgroup analyses explored the type and location of the intervention (home-based vs. supervised).
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Review
3.1.1. Study Selection
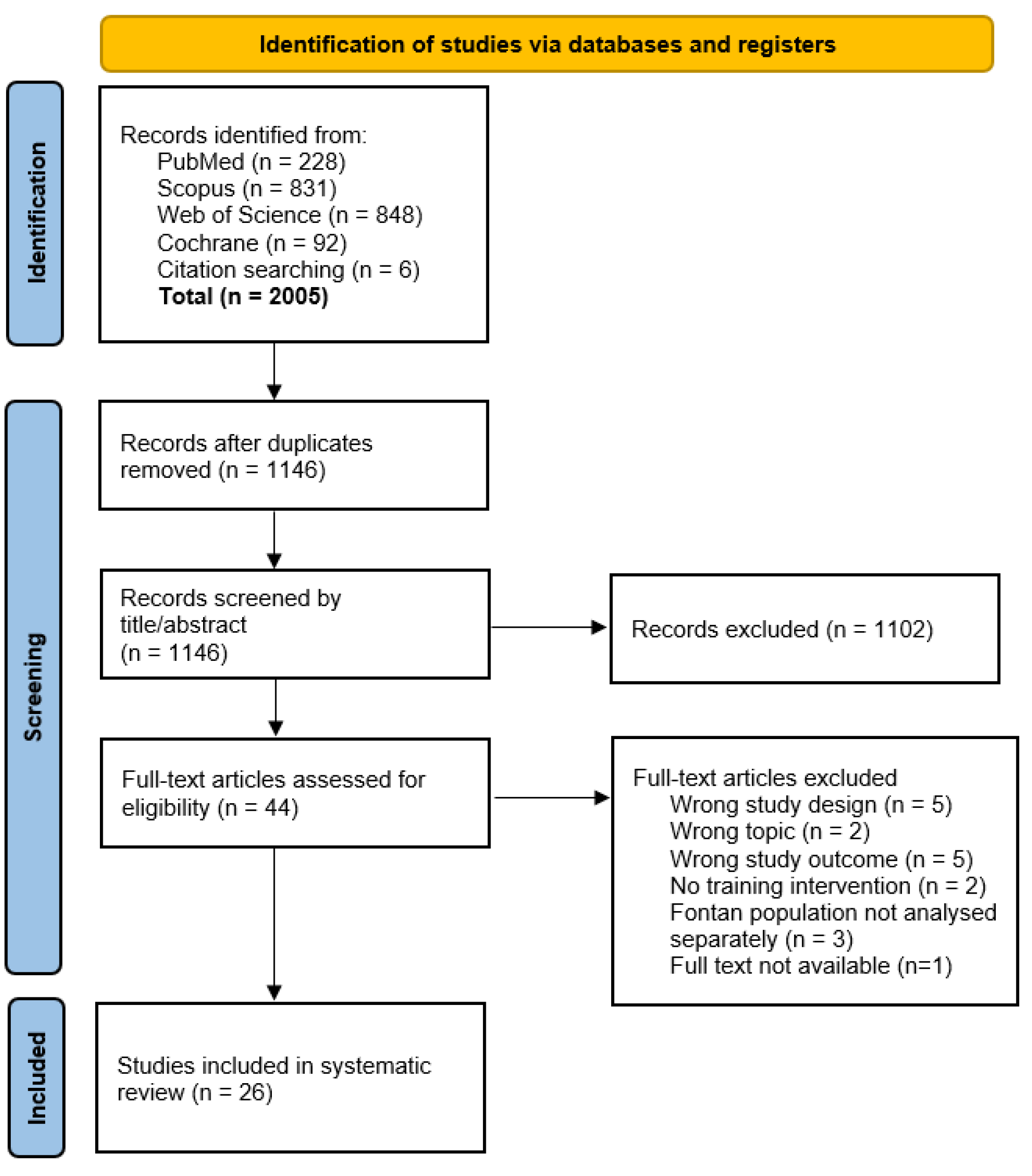
After removing duplicates, 1,140 articles were identified, and six additional articles were found through a manual search. Of 44 articles screened in full, 26 (16-41) met the inclusion criteria.
Figure 1 details the selection process and exclusion criteria.
3.1.2. Study and Intervention Characteristics
Among the 26 studies (7 RCTs, 19 cohort studies), there were 22 distinct cohorts. Some studies examined the same cohorts while measuring different outcomes. Sample sizes ranged from 5 to 61 patients, with follow-ups lasting 4 weeks to 24 months. Interventions included:
Aerobic Exercise Training (AET): 18 studies
Resistance Training: 11 studies
Inspiratory Muscle Training (IMT): 6 studies
Rehabilitation programs were either hospital-based (12) or home-based (14), with weekly frequencies ranging from daily to once per week. Program durations varied from 4 to 12 months (see
Supplementary Table S1 for details).
3.1.3. Patient Characteristics
428 Fontan patients actively participated in CR programs across the included studies. The control groups were stratified into Fontan patients (n=98) and healthy matched controls (n=32). Ages ranged from 7 to 45 years, including both children and adults. Both genders were evenly represented, and patient characteristics like dominant ventricle and age at Fontan completion varied widely (see
Supplementary Table S2).
3.1.4. Quality Assessment
According to the Cochrane tool, all RCTs showed a low risk of bias, while cohort studies met the STROBE checklist criteria (>70%).
Supplementary Tables S3 and S4 provide more details.
3.2. Study Observations
3.2.1. Exercise Capacity
Peak oxygen uptake (VO2) was the primary measure used to evaluate the impact of CR on Fontan patients. Most studies used cardiopulmonary exercise testing to measure peak VO2, except for Jacobsen et al. (2016), who used a shuttle run test.
Across the 22 cohorts reviewed, 12 studies reported no significant changes in peak VO2 after, C.R.; while 11 observed notable improvements. Turquetto et al.'s study showed a 23% increase (from 27.0 to 33.3 mL/kg/min, p=0.012) following AET and a 9% rise (from 26.6 to 29.1 mL/kg/min, p=0.008) after IMT.
Four studies using the six-minute walk test (6 MWT) also found significant improvements. Sutherland et al. reported the largest gain, with a 48-meter increase (from 521m ± 101 to 569m ± 81, p < 0.005) following an 8-week combined AET and resistance training program.
3.2.2. Peak Workload
Six of the 13 studies reviewed showed no significant changes in peak workload, measured during cardiopulmonary exercise testing. However, seven studies observed significant improvements, primarily in aerobic and/or resistance training. Scheffers et al. reported the most notable increase, an 18% rise in peak workload after high-weight leg resistance training combined with a high-protein diet. Only one study focused solely on IMT.
3.2.3. VE/VCO2 Slope
Of 13 studies assessing the VE/VCO2 slope, 10 reported no significant change, while three documented enhancements. Two of these, by Wittekind and Pykkönen, combined AET with resistance training. Third, Laohachai focused on IMT.
3.2.4. Activity Levels
Four of the seven studies that measured activity levels used accelerometers. Duppen, Jacobsen, and Scheffers found no significant activity increase, but Longmuir reported a notable rise in moderate-to-vigorous activity by 36±31 minutes weekly (p=0.04) at 24 months. The other three studies, which relied on self-reports, showed mixed results. Hedlund and Pyykkönen observed increased activity, but Hedlund noted a decline at the 1-year post-training mark.
3.2.5. Cardiac Output
Three of the eight studies assessing cardiac output using MRI or echocardiography reported significant increases following CR. Laohachai found a 0.3 L/min improvement in resting output after IMT (p = 0.03). Scheffers et al. reported increased single-ventricle stroke volume (43 to 46 ml/beat/m^2, p = 0.014). At the same time, Cordina et al. found higher stroke volumes at rest and during exercise in a trained Fontan group compared to a detraining period, with significant increases at rest (77.8 ± 10.3 vs 66.7 ± 9.3 ml, p = 0.01) and during exercise.
3.2.6. Cardiac Biomarkers
Three studies examined the effect of training on cardiac biomarkers. Duppen and Scheffers found no significant changes in biomarkers after, C.R.; while Perrone et al. observed a substantial reduction in NT-proBNP levels (from 96.3 ± 6.7 to 62.5 ± 46.1, p < 0.001).
3.2.7. Lung Function
Nine studies examined the impact of CR on lung function. Seven (excluding Hedlund and Brassard) implemented IMT as a component of CR. Notably, the study conducted by Brassard introduced AET and resistance training as part of CR. However, this was unique because it did not demonstrate a statistically significant increase in lung function following, C.R.; setting it apart from other studies.
3.2.8. Lower Limb Muscle Function
Four studies (Avitabile, Pyykkönen, Brassard, and Scheffers) evaluated lower limb muscle function following, C.R.; incorporating strength and resistance training. Scheffers et al.'s study, unique in its focus on high-weight resistance training and a high-protein diet, was the only study to report significant improvements in leg muscle strength. Other studies lacking this dietary component showed no notable enhancement in lower-limb muscle function.
3.2.9. Quality of Life
Seven of the ten studies on Fontan patients' quality of life after CR showed improvements. Six studies assessed quality of life via patient and parent reports. Jacobsen et al. noted improved parent-reported quality of life at 12 weeks and 6 months, but patient-reported measures declined at 6 months. Three studies, including Dirks et al., found no improvement in quality of life post-CR.
3.2.10. Adverse Events
Of the 20 studies reviewed, six did not report adverse events, and 14 reported no adverse events related to CR. Overall, CR appears generally safe, with few adverse events.
3.3. Meta-Analysis
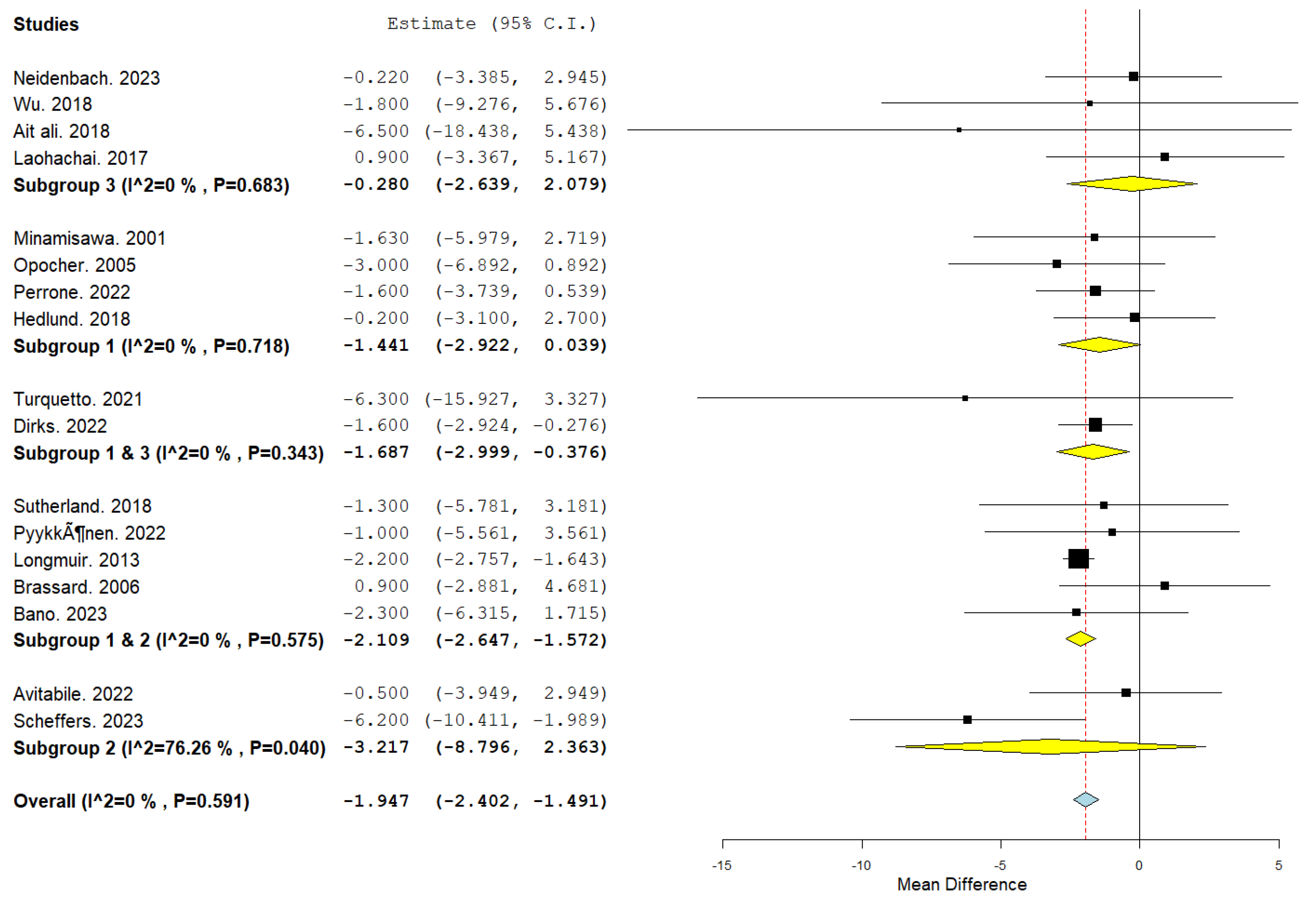
Our meta-analysis evaluated the differential impact of various CR interventions, including AET, resistance training, and IMT, on patients after the Fontan procedure. The analysis used a continuous random-effects model with the mean difference as the primary metric.
3.3.1. Effectiveness of Intervention Types
The effectiveness of CR interventions was assessed by evaluating improvement in exercise capacity, measured by peak VO2. The overall pooled effect indicated a significant improvement, with a mean difference of -1.947 (95% confidence interval [CI]: -2.402 to -1.491; p < 0.001), suggesting that rehabilitation benefits this patient population.
Subgroup Analyses
Subgroup analyses were performed to assess the efficacy of the different interventions.
IMT: This subgroup did not demonstrate a significant effect, with a mean difference of -0.280 (95% CI: -2.639–2.079; p = 0.816).
AET: AET alone approached statistical significance, with a mean difference of -1.441 (95% CI: -2.922–0.039; p = 0.056), suggesting a potential benefit of AET in improving outcomes.
Combined AET and Resistance Training: The combination of AET and resistance training provided a significant mean difference of -2.109 (95% CI: -2.647 to -1.572; p < 0.001), indicating the robust effect of this hybrid intervention.
Combined AET and IMT: The addition of IMT to AET also yielded a favourable outcome, with a mean difference of -1.687 (95% CI: -2.999 to -0.376; p=0.012).
Resistance Training Alone: Resistance training alone did not reach significance, with a mean difference of -3.217 (95% CI: -8.798 to 2.363; p = 0.259).
These findings suggest that, while individual interventions may offer some benefits, the combination of AET with either resistance training or IMT appears more effective for patients following the Fontan procedure (
Figure 2).
Subgroup analyses regarding rehabilitation setting (home-based, supervised, or a hybrid of both) showed only a significant improvement in peak VO2 with Home-Based rehabilitation (
Figure 3).
Heterogeneity and Consistency Across Studies
The consistency of the results across the included studies was evaluated using the I² statistic. In our meta-analysis, an I² value of 0% was observed (p = 0.591), indicating no evidence of heterogeneity and suggesting that the variations in the study estimates are compatible with what would be expected by random chance alone. This enhances the reliability of the overall effect estimates, as it implies that the observed treatment effects are consistent across different interventions and study populations within the included literature.
3.3.2. Effect of Cardiac Rehabilitation on Peak Work
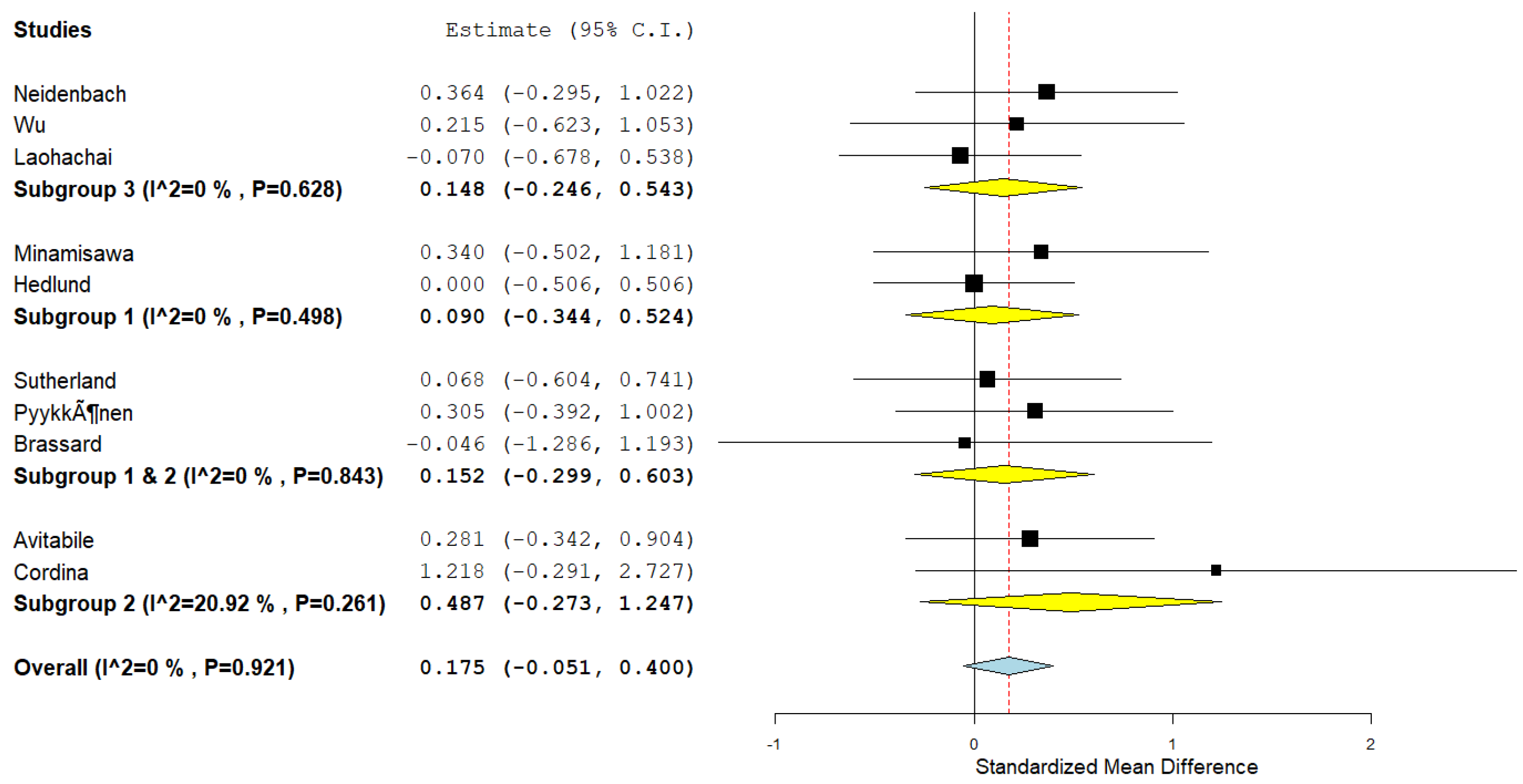
We further investigated the influence of various CR interventions on Peak Work capacity, expressed as standardised mean difference (SMD) to accommodate the different scales used in the studies.
The overall effect size for all interventions combined was modest and not statistically significant, with an SMD of 0.175 (95% CI: -0.051–0.400; p = 0.128), suggesting a small and uncertain effect of CR on peak work capacity (
Figure 4).
Subgroup Analyses
The impact of different interventions on peak work yielded the following results:
IMT: No significant change (SMD: 0.148; 95% CI: -0.246 to 0.543; p = 0.461).
AET: No significant improvement (SMD: 0.090; 95% CI: -0.344 to 0.524; p = 0.684).
Combined AET and Resistance Training: No significant effect (SMD: 0.152; 95% CI: -0.299 to 0.603; p = 0.509).
Resistance Training Alone: A non-significant trend toward improvement (SMD: 0.487; 95% CI: -0.273 to 1.247; p = 0.209).
The I² statistic was 0% (p = 0.920), indicating no observed heterogeneity and consistent study results. The lack of statistically significant changes across interventions suggests that the type of CR program may not significantly affect peak work capacity in Fontan patients.
Figure 4.
Forest plot demonstrating the effect of cardiac rehabilitation interventions by evaluating the parameter peak work, regarding intervention type, using a continuous random-effects model. The overall pooled effect did not show a significant improvement in peak work after participating in a cardiac rehabilitation intervention (p=0.0128). Subgroup analysis investigated the effect of different types of cardiac rehabilitation interventions. Subgroup 1, Aerobic exercise training. Subgroup 2, Resistance training. Subgroup 3, Inspiratory muscle training.
Figure 4.
Forest plot demonstrating the effect of cardiac rehabilitation interventions by evaluating the parameter peak work, regarding intervention type, using a continuous random-effects model. The overall pooled effect did not show a significant improvement in peak work after participating in a cardiac rehabilitation intervention (p=0.0128). Subgroup analysis investigated the effect of different types of cardiac rehabilitation interventions. Subgroup 1, Aerobic exercise training. Subgroup 2, Resistance training. Subgroup 3, Inspiratory muscle training.
4. Discussion
Fontan Procedure and Postoperative Challenges
The Fontan procedure is critical in treating single-ventricle congenital heart defects, improving outcomes and increasing survival rates. However, with a 30-year survival rate of about 85%, challenges remain, particularly with exercise capacity and quality of life. While exercise training programs promise to enhance physical fitness and psychosocial outcomes for Fontan patients, low adherence to guidelines limits their impact.
This systematic review and meta-analysis sought to clarify the safety, efficacy, and best practices of exercise training programs for Fontan patients, aiming to create an evidence-based framework for postoperative management.
Safety
All studies validated CR to be safe. It needs to be taken into account that in most of the studies, Fontan patients with worse clinical conditions were excluded (e.g. heart failure patients, patients with exercise restrictions, low exercise capacity or frequent symptomatic arrhythmias). This raises the question of whether exercise training is also safe for these patients. Patients with lower baseline values might benefit more from the CR. Thus, it feels contradictory to exclude patients with worse clinical conditions. For this group of Fontan patients, exercise training programs might be needed and might provide a lot of improvement.
Impact of Exercise Training on Fontan Patients
Exercise training offers significant potential for improving various health outcomes in Fontan patients. In particular, AET has been shown to enhance exercise capacity, with a notable study revealing a 23% increase in peak VO2. Resistance training and IMT also boosted exercise capacity, though not all studies reported significant improvements. These interventions have demonstrated that targeted exercise regimens can help address exercise performance challenges in this patient group.
Cardiac biomarkers also responded to exercise training, as some studies reported significant reductions in NT-proBNP levels, suggesting improved cardiac function and potentially better clinical outcomes. However, the variability in findings across different studies indicates that further investigation is needed to understand the relationship between exercise and cardiac biomarkers fully.
Lung function and lower-limb muscle strength were positively affected by exercise training, with high-weight resistance training, especially when combined with a high-protein diet, resulting in considerable gains in muscle strength. While one study did not significantly improve lung function, others showed notable enhancements, emphasising the importance of structured training programs.
The effects on quality of life were more varied. Some studies found improvements, particularly in assessments reported by parents, while others observed no significant changes. This discrepancy underscores the complex interplay between physical and psychosocial factors influencing quality of life. It reinforces the need for a holistic approach that considers physiological and psychological aspects to improve patient well-being.
Efficacy of Different Cardiac Rehabilitation Interventions
Our meta-analysis provides essential insights into the efficacy of different CR interventions for Fontan patients. The overall pooled effect indicated significant benefits, particularly with specific combinations. AET paired with resistance training or IMT showed promising results, suggesting a synergistic effect that can comprehensively improve exercise capacity and cardiac health.
Subgroup analysis revealed more nuanced findings. While IMT alone did not show significant effects, its combination with AET yielded favourable outcomes, emphasising the value of a multifaceted exercise approach. AET nearly reached statistical significance, highlighting its importance in CR programs for Fontan patients. However, resistance training alone did not significantly improve outcomes, suggesting it is best used alongside other modalities for maximum effectiveness. These findings underscore the importance of integrating multiple exercise types to deliver optimal results for this unique patient group.
Synergetic effect of different training modalities
As previously stated, the meta-analysis found that combining different training modalities yields better outcomes due to a synergistic effect. The reduced exercise capacity and cardiac health in Fontan patients result from complex interactions among various factors. Addressing the problem at multiple levels logically leads to more significant improvements.
The Fontan circulation lacks a sub-pulmonary pump, causing venous blood to drain directly into the lungs and limiting hemodynamics. This restricts cardiac augmentation during exercise, reduces exercise capacity (7, 8). As a result, Fontan patients often lead a sedentary lifestyle, worsening their muscle atrophy (5) and further reducing exercise capacity (42), creating a downward spiral. Tackling this issue on multiple fronts is essential.
AET can improve overall cardiorespiratory capacity, enabling more physical activity (20, 24). Resistance training helps increase muscle mass, making activity easier while potentially enhancing non-pulsative venous flow. This, in turn, boosts systemic preload, cardiac output, and exercise capacity (28, 36, 43). IMT can also improve pulmonary blood flow by strengthening the thoracic pump (27).
Therefore, combining different training modalities targets multiple aspects of the Fontan circulation, potentially leading to a synergistic effect that produces the most favourable outcomes for these patients.
Limitations and Future Perspectives
Most studies had small cohorts, and only 7 of the 26 were RCTs. The heterogeneity in study design, patient characteristics, and excluding patients in more severe conditions requires cautious interpretation.
Long-term efficacy remains unclear, necessitating more extended follow-up studies. Further research is needed to determine optimal CR parameters, understand the long-term health outcomes, and uncover the mechanisms behind exercise training benefits. This will help refine and optimise CR for this group. Moreover, studies are needed to assess the safety and efficacy of exercise training in Fontan patients with severe conditions.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, exercise training can improve exercise capacity, cardiac biomarkers, lung function, and muscle strength in Fontan patients, potentially leading to a better quality of life. Further research should refine exercise protocols, assess long-term effects, and clarify underlying mechanisms to enhance these patients' outcomes and quality of life.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Ana Félix and Sérgio Laranjo; Data curation, Luna de Ven and Ana Félix; Methodology, Luna de Ven and Sérgio Laranjo; Supervision, Fatima Pinto and Sérgio Laranjo; Writing – original draft, Luna de Ven; Writing – review & editing, Ana Félix, Jorge Dias, Fatima Pinto and Sérgio Laranjo.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Unidade Local de Saúde São José (Ethics Committee approval number 974/2020). Ethical approval was obtained prior to the commencement of the study, ensuring that all procedures adhered to the ethical standards set forth in the Declaration..
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study. As the study involved the analysis of previously collected medical records and did not require direct interaction with patients, obtaining individual consent was deemed impractical and unnecessary. Additionally, all data were anonymised prior to analysis to protect patient confidentiality, in compliance with institutional guidelines and data protection regulations..
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the reported results in this study are not publicly available due to privacy and ethical restrictions. The study involved patient medical records, and the data were anonymised to protect patient confidentiality in accordance with institutional guidelines. Access to the data is restricted and may be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request, subject to approval by the Institutional Review Board and in compliance with applicable data protection regulations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kverneland, L.S.; Kramer, P.; Ovroutski, S. Five decades of the Fontan operation: A systematic review of international reports on outcomes after univentricular palliation. Congenital heart disease. 2018, 13, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, C.; Dalziel, K.; Nunn, R.; Du Plessis, K.; Shi, W.Y.; Celermajer D; et al. The Fontan epidemic: Population projections from the Australia and New Zealand Fontan registry. International journal of cardiology. 2016, 219, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rychik, J.; Atz, A.M.; Celermajer, D.S.; Deal, B.J.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Gewillig MH; et al. Evaluation and management of the child and adult with Fontan circulation: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019, 140, e234–e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, T.E.; Allen, K.Y.; Glatz, A.C.; Rogers, L.S.; Ravishankar, C.; Rychik J; et al. Long-term survival after the Fontan operation: Twenty years of experience at a single center. The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. 2017, 154, 243–253.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffers, L.E.; Berg LEv, Ismailova, G. ; Dulfer, K.; Takkenberg, J.J.; Helbing WA. Physical exercise training in patients with a Fontan circulation: A systematic review. European journal of preventive cardiology. 2021, 28, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrindle, B.W.; Williams, R.V.; Mital, S.; Clark, B.J.; Russell, J.L.; Klein G; et al. Physical activity levels in children and adolescents are reduced after the Fontan procedure, independent of exercise capacity, and are associated with lower perceived general health. Archives of disease in childhood. 2007, 92, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.J.; Avitabile, C.M.; McBride, M.G.; Paridon, S.M. Exercise capacity in the Fontan circulation. Cardiology in the Young. 2013, 23, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewillig, M. The fontan circulation. Heart. 2005, 91, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Ven, J.P.; van den Bosch, E.; Bogers, A.J.; Helbing, WA. State of the art of the Fontan strategy for treatment of univentricular heart disease. F1000Research. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, N.; Jones, B.; d’Udekem, Y. Should we recommend exercise after the Fontan procedure? Heart, Lung and Circulation. 2015, 24, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longmuir, P.E.; Brothers, J.A.; De Ferranti, S.D.; Hayman, L.L.; Van Hare, G.F.; Matherne GP; et al. Promotion of physical activity for children and adults with congenital heart disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013, 127, 2147–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmuir, P.E. Importance of Physical Activity and Exercise in Paediatric Fontan Patients. CJC Pediatric and Congenital Heart Disease. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne JAC, Savović, J. ; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron I; et al. RoB 2, a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, JP. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2007, 335, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, N.; Salehi, A.; Molavi Vardanjani, H.; Marzban, M.; Behbood, A. Using STROBE checklist to assess the reporting quality of observational studies affiliated with Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, and its correlates: A scientometric study from Iran. Scientometrics. 2020, 122, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidenbach, R.; Freilinger, S.; Stöcker, F.; Ewert, P.; Nagdyman, N.; Oberhoffer-Fritz R; et al. Clinical aspects and targeted inspiratory muscle training in children and adolescents with Fontan circulation: A randomized controlled trial. Cardiovascular diagnosis and therapy. 2023, 13, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamisawa, S.; Nakazawa, M.; Momma, K.; Imai, Y.; Satomi, G. Effect of aerobic training on exercise performance in patients after the Fontan operation. The American journal of cardiology. 2001, 88, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opocher, F.; Varnier, M.; Sanders, S.P.; Tosoni, A.; Zaccaria, M.; Stellin G; et al. Effects of aerobic exercise training in children after the Fontan operation. The American journal of cardiology. 2005, 95, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, C.; Müller, J.; Oberhoffer, R.; Ewert, P.; Hager, A. Inspiratory muscle training did not improve exercise capacity and lung function in adult patients with Fontan circulation: A randomized controlled trial. International journal of cardiology. 2020, 305, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turquetto ALR, Dos Santos, M. R.; Agostinho, D.R.; Sayegh ALC, de Souza, F.R.; Amato LP; et al. Aerobic exercise and inspiratory muscle training increase functional capacity in patients with univentricular physiology after Fontan operation: A randomized controlled trial. Int J Cardiol. 2021, 330, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulfer, K.; Duppen, N.; Kuipers, I.M.; Schokking, M.; van Domburg, R.T.; Verhulst FC; et al. Aerobic exercise influences quality of life of children and youngsters with congenital heart disease: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of adolescent health. 2014, 55, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duppen, N.; Kapusta, L.; de Rijke, Y.B.; Snoeren, M.; Kuipers, I.M.; Koopman LP; et al. The effect of exercise training on cardiac remodelling in children and young adults with corrected tetralogy of Fallot or Fontan circulation: A randomized controlled trial. International journal of cardiology. 2015, 179, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duppen, N.; Etnel, J.R.; Spaans, L.; Takken, T.; van den Berg-Emons, R.J.; Boersma E; et al. Does exercise training improve cardiopulmonary fitness and daily physical activity in children and young adults with corrected tetralogy of Fallot or Fontan circulation? A randomized controlled trial. American heart journal. 2015, 170, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, N.; Jones, B.; Westcamp Aguero, S.; Melchiori, T.; du Plessis, K.; Konstantinov IE; et al. Home- and hospital-based exercise training programme after Fontan surgery. Cardiol Young. 2018, 28, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, R.M.; Ginde, S.; Mussatto, K.; Neubauer, J.; Earing, M.; Danduran, M. Can a Home-based Cardiac Physical Activity Program Improve the Physical Function Quality of Life in Children with F ontan Circulation? Congenital heart disease. 2016, 11, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, R.; Danduran, M.; Mussatto, K.; Hill, G.D.; Ginde, S. Can a home-based cardiac physical activity program improve and sustain quality of life and exercise capacity in children with Fontan circulation? Progress in Pediatric Cardiology. 2018, 50, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirks, S.; Kramer, P.; Schleiger, A.; Speck, H.M.; Wolfarth, B.; Thouet T; et al. Home-Based Long-Term Physical Endurance and Inspiratory Muscle Training for Children and Adults With Fontan Circulation-Initial Results From a Prospective Study. Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine. 2021, 8, 784648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avitabile, C.M.; McBride, M.G.; Zhang, X.; Ampah, S.; Goldstein, B.H.; Alsaied T; et al. Peak Work Rate Increases With Lower Extremity-Focused Exercise Training in Adolescents With Fontan Circulation. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2022, 11, e027464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, M.A.; Pomiato, E.; Palmieri, R.; Di Già, G.; Piemonte, F.; Porzio O; et al. The Effects of Exercise Training on Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing and Cardiac Biomarkers in Adult Patients with Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome and Fontan Circulation. Journal of cardiovascular development and disease. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyykkönen, H.; Rahkonen, O.; Ratia, N.; Lähteenmäki, S.; Tikkanen, H.; Piirilä P; et al. Exercise Prescription Enhances Maximal Oxygen Uptake and Anaerobic Threshold in Young Single Ventricle Patients with Fontan Circulation. Pediatric cardiology. 2022, 43, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.M.; Opotowsky, A.R.; Denhoff, E.R.; Gongwer, R.; Gurvitz, M.Z.; Landzberg MJ; et al. A Pilot Study of Inspiratory Muscle Training to Improve Exercise Capacity in Patients with Fontan Physiology. Seminars in thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. 2018, 30, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, E.R.; Lundell, B.; Söderström, L.; Sjöberg, G. Can endurance training improve physical capacity and quality of life in young Fontan patients? Cardiol Young. 2018, 28, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedlund, E.R.; Ljungberg, H.; Söderström, L.; Lundell, B.; Sjöberg, G. Impaired lung function in children and adolescents with Fontan circulation may improve after endurance training. Cardiol Young. 2018, 28, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittekind, S.; Mays, W.; Gerdes, Y.; Knecht, S.; Hambrook, J.; Border W; et al. A Novel Mechanism for Improved Exercise Performance in Pediatric Fontan Patients After Cardiac Rehabilitation. Pediatric cardiology. 2018, 39, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ait Ali, L.; Pingitore, A.; Piaggi, P.; Brucini, F.; Passera, M.; Marotta M; et al. Respiratory Training Late After Fontan Intervention: Impact on Cardiorespiratory Performance. Pediatric cardiology. 2018, 39, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordina, R.L.; O'Meagher, S.; Karmali, A.; Rae, C.L.; Liess, C.; Kemp GJ; et al. Resistance training improves cardiac output, exercise capacity and tolerance to positive airway pressure in Fontan physiology. International journal of cardiology. 2013, 168, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmuir, P.E.; Tyrrell, P.N.; Corey, M.; Faulkner, G.; Russell, J.L.; McCrindle, B.W. Home-based rehabilitation enhances daily physical activity and motor skill in children who have undergone the Fontan procedure. Pediatric cardiology. 2013, 34, 1130–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, P.; Poirier, P.; Martin, J.; Noël, M.; Nadreau, E.; Houde C; et al. Impact of exercise training on muscle function and ergoreflex in Fontan patients: A pilot study. Int J Cardiol. 2006, 107, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffers, L.E.; Helbing, W.A.; Pereira, T.; Utens, E.; Dulfer, K. ; Hirsch A; et al. Leg-focused high-weight resistance training improves ventricular stroke volume, exercise capacity and strength in young patients with a Fontan circulation. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bano, M.; Hussain, T.; Samels, M.R.; Butts, R.J.; Kirk, R.; Levine, B.D. Cardiovascular remodelling in response to exercise training in patients after the Fontan procedure: A pilot study. Cardiol Young. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laohachai, K.; Winlaw, D.; Selvadurai, H.; Gnanappa, G.K.; d'Udekem, Y.; Celermajer D; et al. Inspiratory Muscle Training Is Associated With Improved Inspiratory Muscle Strength, Resting Cardiac Output, and the Ventilatory Efficiency of Exercise in Patients With a Fontan Circulation. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selamet Tierney, E.S.; Palaniappan, L.; Leonard, M.; Long, J.; Myers, J.; Dávila T; et al. Design and rationale of re-energize fontan: Randomized exercise intervention designed to maximize fitness in fontan patients. Am Heart J. 2023, 259, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordina, R.; Celermajer, D.S.; d’Udekem, Y. Lower limb exercise generates pulsatile flow into the pulmonary vascular bed in the setting of the Fontan circulation. Cardiology in the Young. 2018, 28, 732–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).