1. Introduction
Cementitious materials are widely used in the construction industry because of their high compressive strength, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness. However, advancements in construction technology have revealed problems such as low tensile strength and limited functionality. To address these challenges, studies have focused on enhancing the performance of cementitious materials by incorporating nanomaterials [
1,
2,
3]. TiO
2 nanoparticles (TNPs) are widely used in various products such as ultraviolet protection materials, photocatalysts, self-cleaning glass, sunscreen, coatings, and inks, because of its high chemical stability and superhydrophilicity. The application of TNPs in construction materials has garnered considerable attention over the past 20 years because its effectiveness in adding novel functionalities and performance improvement [
4,
5]. In particular, TNPs have been predominantly used to enhance the mechanical properties of cementitious materials [
6,
7]. Cementitious materials are well-suited for incorporating TNPs because of their favorable binding characteristics and fine pore structures within the matrix, rendering them ideal for the development of functional construction products.
TNP can improve the mechanical characteristics of cementitious materials, such as compressive, tensile strengths [
8,
9]. Moreover, studies have revealed that TNP affects the early-age hydration characteristics of cementitious materials [
10,
11] and enhances performance aspects such as durability [
12] and photocatalytic functionality [
13,
14]. These improvements are typically attributed to the unique properties of TNP and the seeding and filling effects. TNP functions as a nucleation site, providing more surface area for the precipitation and growth of cement hydrates. This process accelerates early hydration, shortens the induction period, and increases the quantity of hydration products [
15,
16]. Furthermore, TNP can enhance strength by filling the pores between cement particles, densifying the microstructure [
17]. Unlike nano silica powder, which generates C–S–H gel by the pozzolanic reaction [
18], TNP is an inert material that is not reactive with cement. Nazari et al. investigated the effect of TNPs incorporation on the strength improvement of cementitious materials. Their findings indicated that adding 4% TNPs resulted in the most significant improvement in the compressive strength [
19,
20]. Rahim et al. found that the flexural and tensile strengths of cementitious materials using 4% TNPs enhanced by 42% and 34%, respectively, at 28 days of age [
21]. Li et al. studied the mechanical properties of cement mortar using various TNP sizes [
7]. Their findings indicated that the use of smaller TNPs considerably enhanced strength. Specifically, TNPs with an average particle size of 10 nm increased the strength by approximately 11% compared with those with an average particle size of 15 nm. This phenomenon occurred because the smaller TNPs provided more sites for nucleation, promoting cement hydration. Essawy et al. revealed that adding 5% TNPs by cement weight resulted in a compressive strength increase of approximately 5% [
22]. Limited studies have been conducted on the influence of TNPs on the initial hydration of cement and the intrinsic properties of hardening cement paste.
This study experimentally investigated the effects of TNPs on the hydration properties, microstructure, and compressive strength of cementitious materials. Cement paste and mortar specimens were prepared by varying TNPs incorporation rates (0%, 1%, 3%, 5%, and 10%) using the weight of cement as the primary variable. The effect on the hydration characteristics was assessed using setting time measurements and isothermal conduction calorimetry tests. Thermogravimetric (TG) analysis was performed to investigate the influence of TNPs on the degree of cement hydration. Mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) was performed to evaluate the effect on the microstructures.
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials
In this study, ordinary Portland cement (OPC) was used as the binder to fabricate cement composites incorporating TNPs. XRF analysis was used to perform the chemical oxide composition of the OPC (ZSX Primus II, Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan) as presented in
Table 1. The density and fineness of OPC are 3.13 and 3475 cm
2;/g, respectively. In this study, The TNP was a commercially available product, AEROXIDE P25, obtained from Company E in Germany, with a density of 4.59 g/cm
3 [
23]
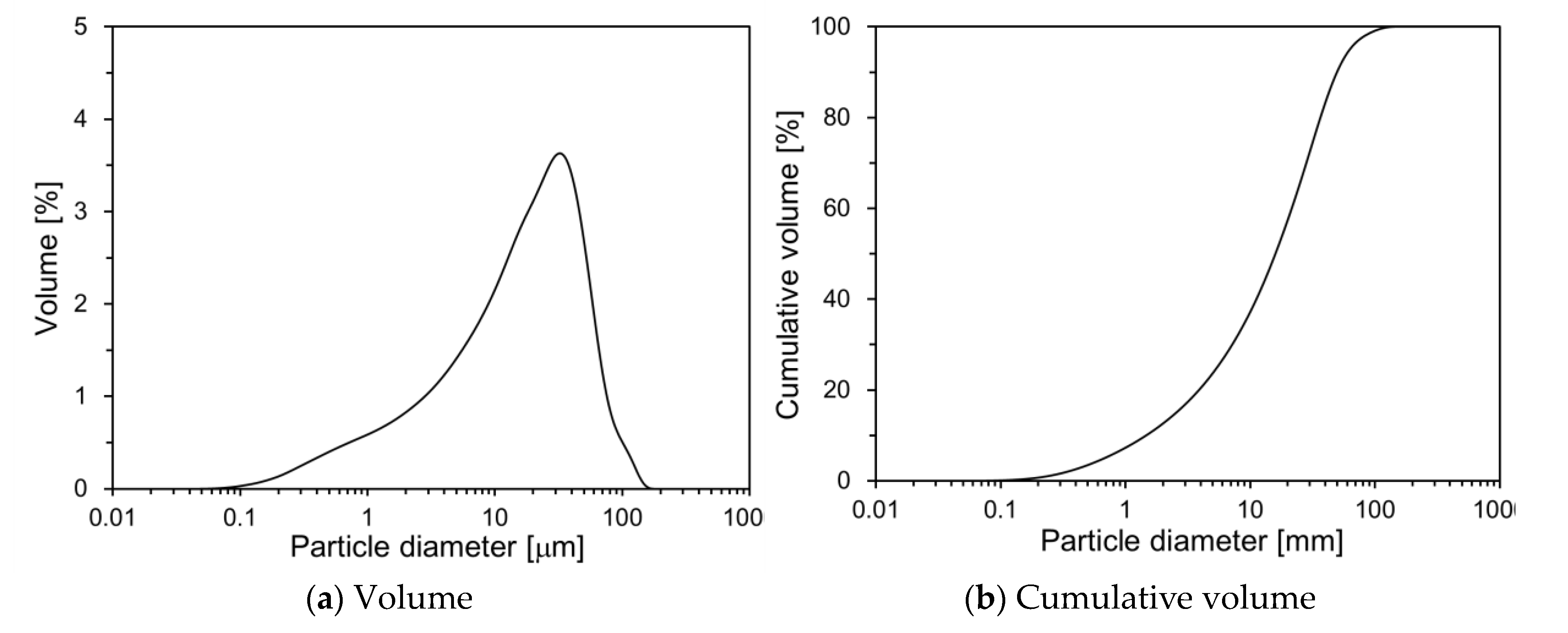
Figure 1 illustrates the particle size distribution (PSD) of OPC, measuring a LS 230 particle size analyzer (Beckman Coulter, California, US). As depicted in
Figure 2(a), the OPC particle sizes range from 0.1 to 150 µm, with an average particle size of 20.2 µm.
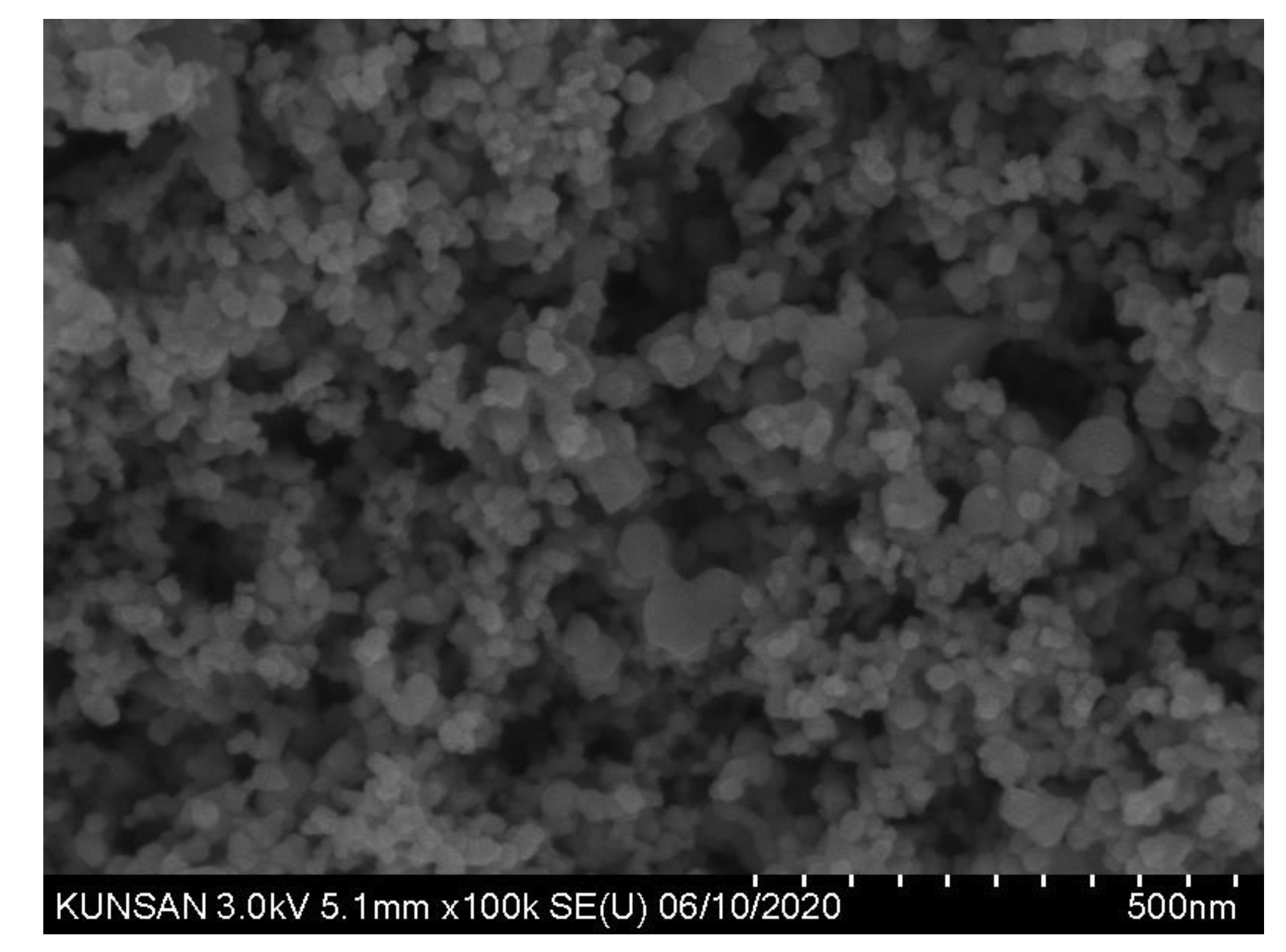
The TNPs, as depicted in
Figure 2, comprises nano-sized particles that agglomerate. Therefore, the PSD of TNP measured using the laser diffraction method can be inaccurate [
24]. Therefore, in this study, the PSD of P25 was determined based on the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images displayed in
Figure 2.
As presented in
Figure 2, P25 predominantly comprises small spherical particles with some larger angular particles.
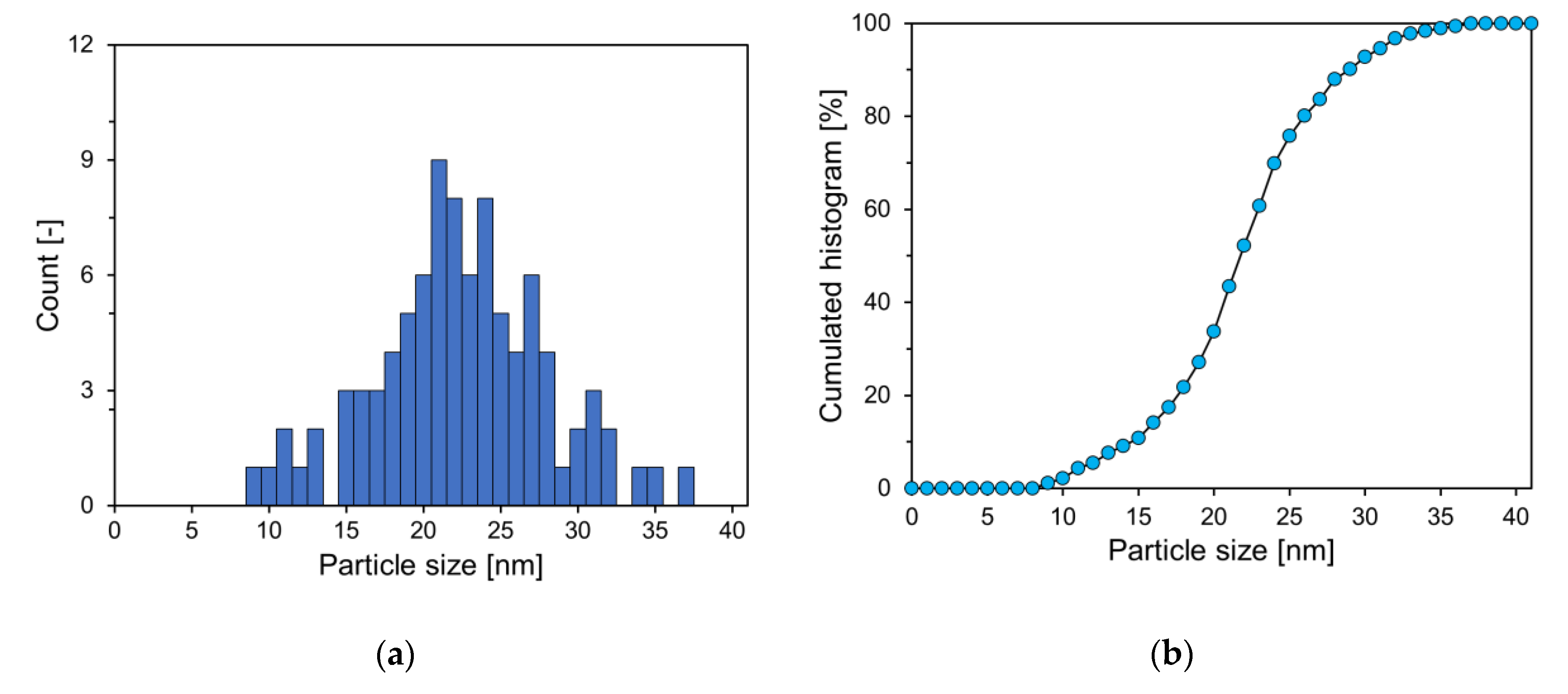
Figure 3 reveals the PSD estimated from SEM image analysis of P25. According to the graph in
Figure 3, the cumulative histogram of P25 exhibits an S-shape, with an average diameter of 22.6 nm.
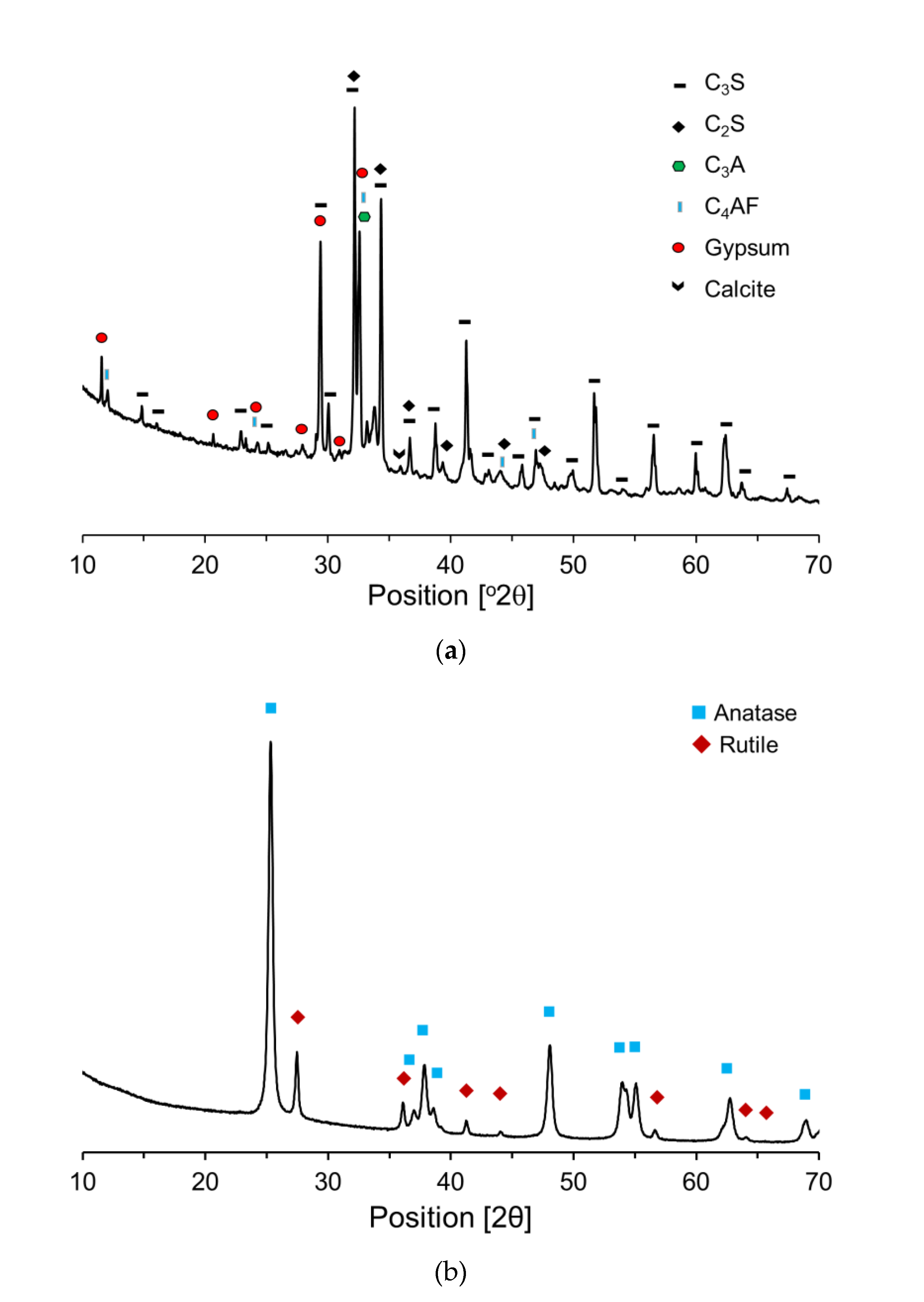
Figure 4 illustrates the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of OPC and P25. Based on these XRD patterns, the primary components of OPC and P25 were quantitatively determined using Rietveld refinement. From
Figure 4(a), the primary mineral components of the OPC were identified to be C
3S (58%), C
2S (16%), C
3A (7%), and C
4AF (10%). Additionally, the OPC contained gypsum and limestone powder, identified as 2.6% and 4.5%, respectively. As depicted in
Figure 4(b), the primary crystalline minerals of P25 were identified to be anatase and rutile, comprising 84.5% and 15.5%, respectively. Generally, anatase and rutile exist either as heterojunction phases or as individual nano-sized particles.
2.2. Mixture Proportions
In this study, cement paste and mortar specimens incorporating P25 were produced following the mixture proportions specified in
Table 2. Additionally, mortar specimens were fabricated to investigate the nitrogen oxide (NOx) removal performance. The primary variable in the study was the incorporation rate of P25, which was adjusted to 0%, 1%, 3%, 5%, and 10% of the cement weight. The water-to-cement ratio for the specimens was maintained at 0.5, and the cement-to-sand ratio was at 1:3. Standard sand (ISO 697) was used, and a polycarboxylate superplasticizer was added as a chemical admixture at 0.3% of the cement weight.
2.3. Test Methods
The morphology of P25 was analyzed using SEM images obtained using a Zeiss Sigma 500 scanning electron microscope (Zeiss, Baden-Württemberg, Germany). Mortars mixed according to
Table 2 were cast into molds (40 mm × 40 mm × 160 mm) and cured in a chamber with a temperature 20 ± 1°C and a relative humidity level above 90%) for one day before demolding. Subsequently, the specimens were demolded and cured in a constant temperature water bath until they reached the designated test ages (3, 7, 28, and 91 days). The compressive strengths of the mortar specimens were measured according to ISO 679. The setting times of paste specimens were measured in accordance with ISO 9597. XRD pattern analyses were conducted by a PANalytical X'Pert Pro MPD diffractometer (Malvern Panalytical Ltd, Malvern, United Kingdom). The diffractometer scan was performed with a 2θ range from 10° to 70° in a 0.04° step size.
To evaluate the effect of P25 incorporation on the cement hydration, the heat of hydration was analyzed using isothermal calorimetry with a TAM Air (TA instruments, New castle, US). The paste specimens were prepared for each variable, placed in glass vials, and continuously monitored for 72 h. TG analysis was conducted using SDT Q600 (TA instruments, New castle, US) to evaluate the effect of P25 on the degree of cement hydration. The temperature was increased at a constant rate of 10°C per min up to a maximum of 1000°C, and the weight changes were continuously measured. The experiment was conducted under a nitrogen atmosphere.
MIP was performed to investigate changes in the micropore structure due to P25 incorporation. The pore size of specimens was estimated by using an AutoPore IV 9500 (Micromeritics, Norcross, US). The paste specimens prepared for the MIP measurements were crushed into pieces approximately 1–2 mm in size. The sample for the MIP measurements was obtained from the middle part of the specimen. The crushed samples were vacuum-dried to halt hydration.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydration Characteristics
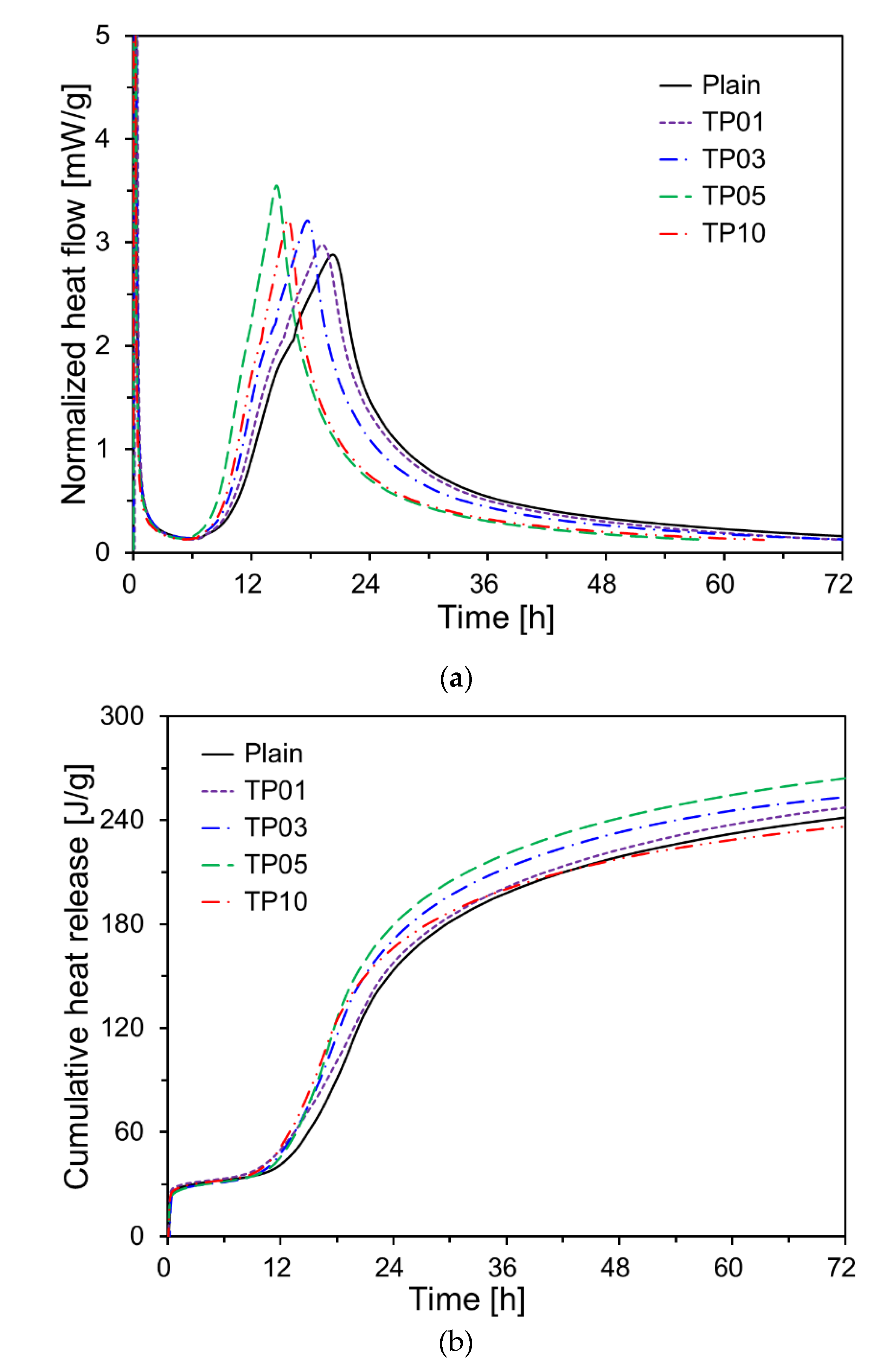
Figure 5 illustrates the results of heat of hydration of cement paste with 0%, 1%, 3%, 5%, and 10% of P25 by weight. As presented in Fig. 5(a), the second peak occurred earlier in all the samples with P25 than in Plain. When P25 was increased to 5% of the weight of cement, the second peak occurrence time decreased as the content of P25 increased, and the peak magnitude increased. This phenomenon indicates that the initial hydration of cement was accelerated by the presence of NTPs. The seeding effect of NTPs accelerated cement hydration, resulting in a reduction of the induction period [
16]. Additionally, the filling effect, in which TiO
2 particles fill the pores between cement particles, contributes to a denser microstructure. Similar effects have been reported for cement pastes incorporating nano silica powder [
25].
However, when 10% P25 by weight of cement was added (TP10), cement hydration was not promoted as effectively as in TP5; instead, it tended to be delayed. This is likely because of NTP agglomeration. In the cement paste, the agglomeration of NTPs involves individual nano-sized particles clustering to form larger aggregates. This phenomenon is driven by a combination of forces, including van der Waals forces, electrostatic interactions, and hydrophobic effects. The degree and nature of agglomeration depend on various factors, including the surface charge, particle size, concentration, pH of the medium, ionic strength, and the presence of surfactants or polymers. The agglomeration of TiO
2 particles negatively affects the homogeneity of the nanoparticle distribution, reducing the exposed surface area of NTPs and consequently decreasing its photocatalytic efficiency [
26]. Additionally, an uneven distribution of nanoparticles can negatively affect the mechanical properties and durability of concrete structures [
27].
Figure 5(b) presents the cumulative heat release curves for all specimens. During the first 42 h, the cumulative heat release of most samples containing P25 was higher than that of Plain. However, the 72-h cumulative heat release of TP10 was only 95% that of Plain. By contrast, the 72-h cumulative heat releases for TP1, TP3, and TP5 were 100.8%, 102.9%, and 107.2%, respectively, relative to that of Plain. The samples with P25 exhibited higher early hydration reactions than those of Plain after 10 h. Numerous studies have revealed that inert or reactive ultrafine particles can accelerate the cement hydration process [
28,
29,
30]. These particles can be used as nucleation sites for the hydration products of the cement, and the spaces between the particles can become densely filled with these nuclei and completely deformed early in the hydration process [
31,
32,
33].
3.2. Setting Time and Compressive Strength
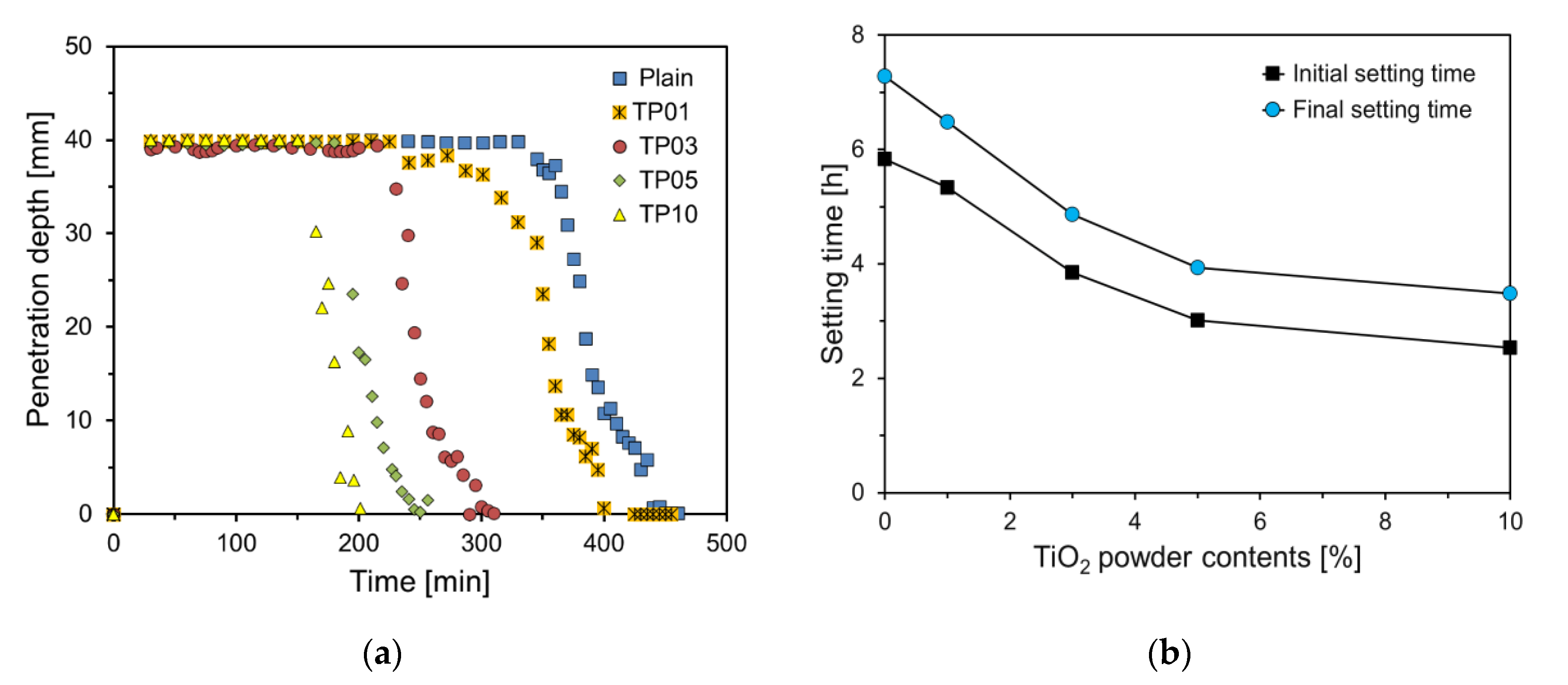
Figure 6(a) reveals the penetration depth of the vicat needle over time for cement pastes with varying amounts of P25. The graph indicates that as the amount of P25 increases, the penetration depth curves shift to the left. Materials with a high specific surface area, such as P25, have a greater capacity to adsorb water, resulting in the rapid consumption of free water within matrix. This accelerates the bridging of the gaps within the paste, thereby increasing its viscosity and promoting setting [
17].
Figure 6(b) depicts the graph of setting times in relation to the P25 content. The initial and final setting times for Plain were 5.83 and 7.28 h, respectively. The initial setting times for TP01, TP03, TP05, and TP10 were 91.4%, 66.0%, 51.7%, and 43.4%, respectively, of that of Plain. Up to a 5% incorporation rate of P25, the initial setting time decreased almost linearly and sharply with the increase in the P25 content, whereas at a 10% incorporation rate, the decrease was gradual. The final setting times for TP01, TP03, TP05, and TP10 were 6.48, 4.87, 3.93, and 3.48 h, respectively, exhibiting a similarly decreasing trend with the increase in the P25 content as observed for the initial setting times.
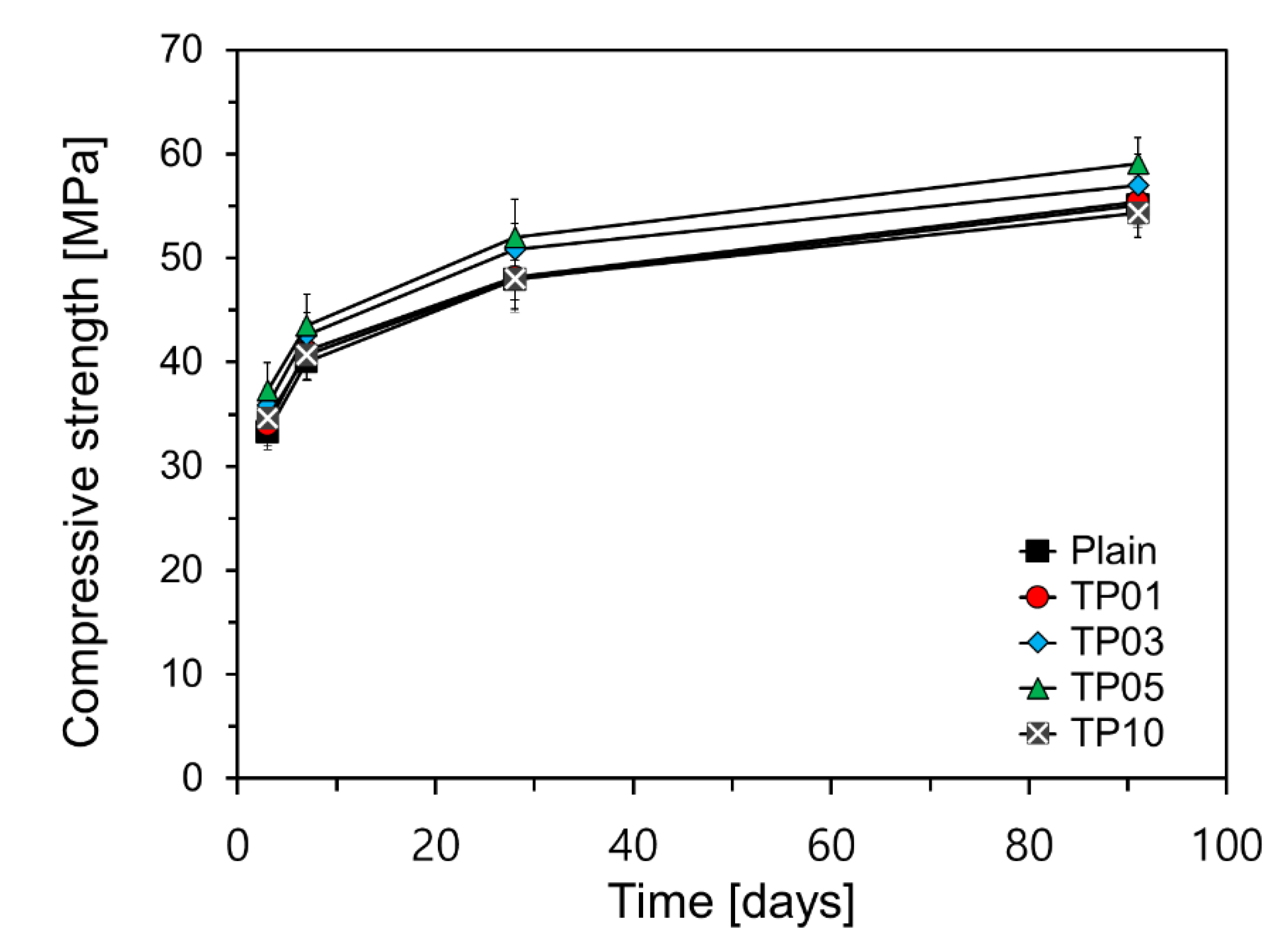
Figure 7 illustrates the graph of compressive strength for various variables over curing age. With a P25 content of up to 5%, a notable improvement in the compressive strength of the mortar specimens was observed. The enhancement in compressive strength could be attributed to the microfilling effect of NTPs. However, TP10, which contained 10% P25, revealed only a marginal increase in compressive strength up to 28 days, similar to TP01, when compared to Plain. By 91 days, the compressive strength of TP10 was 0.8 MPa lower than that of Plain.
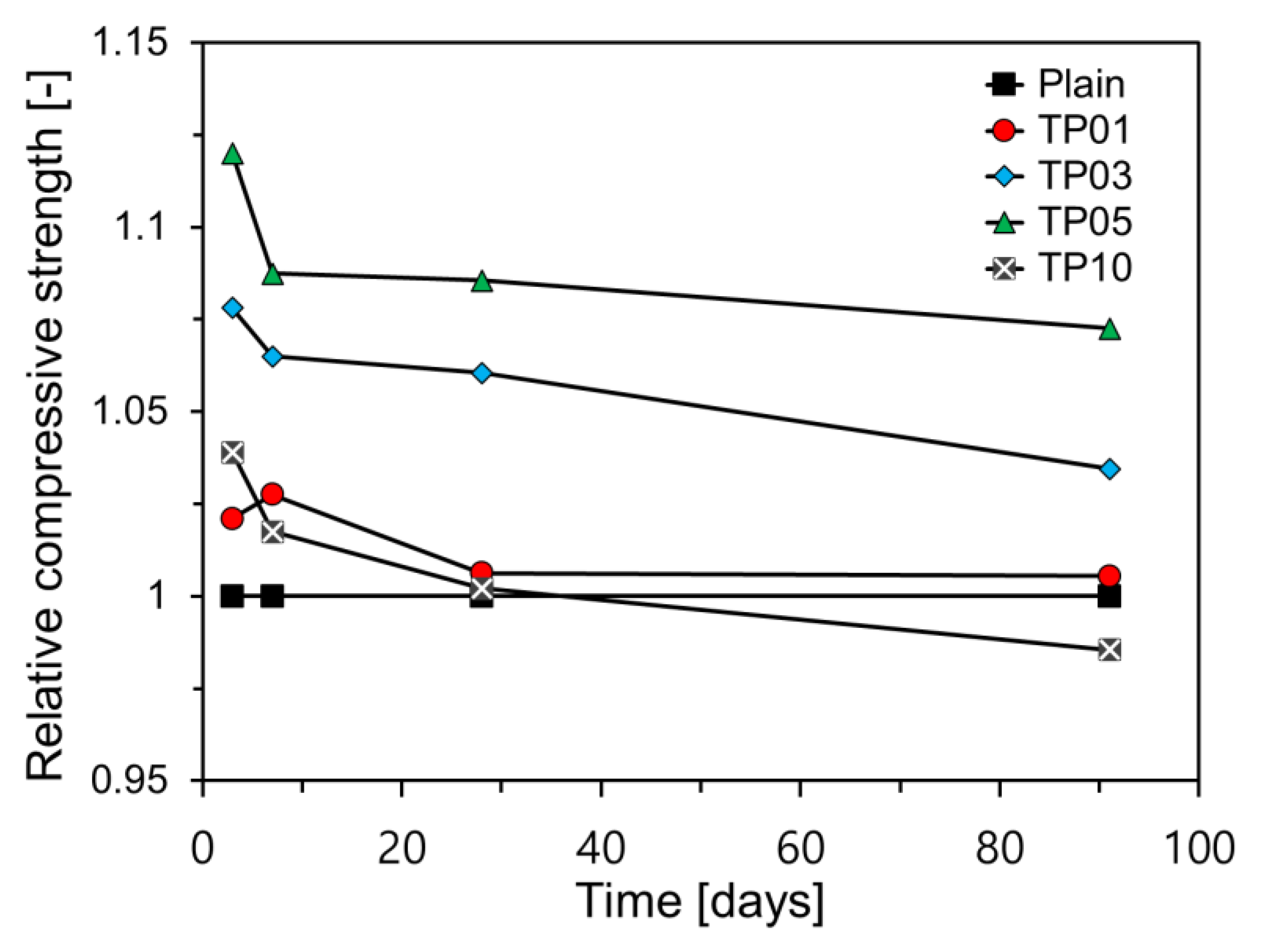
Figure 8 presents a comparison of the relative compressive strengths of the mortar specimens. In this study, relative compressive strength is defined as the ratio of a specimen’s compressive strength to that of Plain at a given age. The relative compressive strengths of all samples decreased as the age increased. With the exception of TP1, all the samples containing P25 exhibited the highest relative compressive strengths after three days. This strength sharply declined by day 7 and continued to gradually decrease until day 91. This pattern is attributed to the significant impact of NTPs on the early-age hydration of C3A and C3S, whereas their effect on the hydration of C2S, which has a slow reaction and influences long-term properties, is minimal [
17]
.
Studies have focused on the performance improvement of construction materials using nanomaterials, particularly nano silica powder, which exhibits excellent pozzolanic characteristics [
34]. Generally, nano silica powder accelerates the C
3S hydration in cement components, reducing the setting time [
35,
36,
37]. Furthermore, C
3S hydration has been reported to enhance the early-age strength of cementitious materials [
36,
37,
38]. During the cement hydration process, nano silica powder functions as a filler, providing additional nucleation sites, filling voids, and altering the microstructure.
In addition, because of its high surface reactivity, nano silica powder promotes pozzolanic reaction [
36,
38,
39]. NTP exhibit similar effects as nano silica powder in the cement hydration process. NTP enhances the early-age strengths and durability of cement matrices by filling both micropores and nanopores [
40,
41]. However, unlike nano silica, nano-TiO
2 particles are not pozzolanic.
3.3. Pore Structure
The pore size distributions of the paste specimens incorporating P25 were measured using MIP. The porosity measurements for both Plain and specimens with P25 are listed in
Table 3. P25 reduced the porosity of the cement paste. As the P25 content increased to 5% by weight of cement, the porosity decreased accordingly. However, when the P25 content reached 10%, porosity increased again and returned to a level similar to that of TP01.
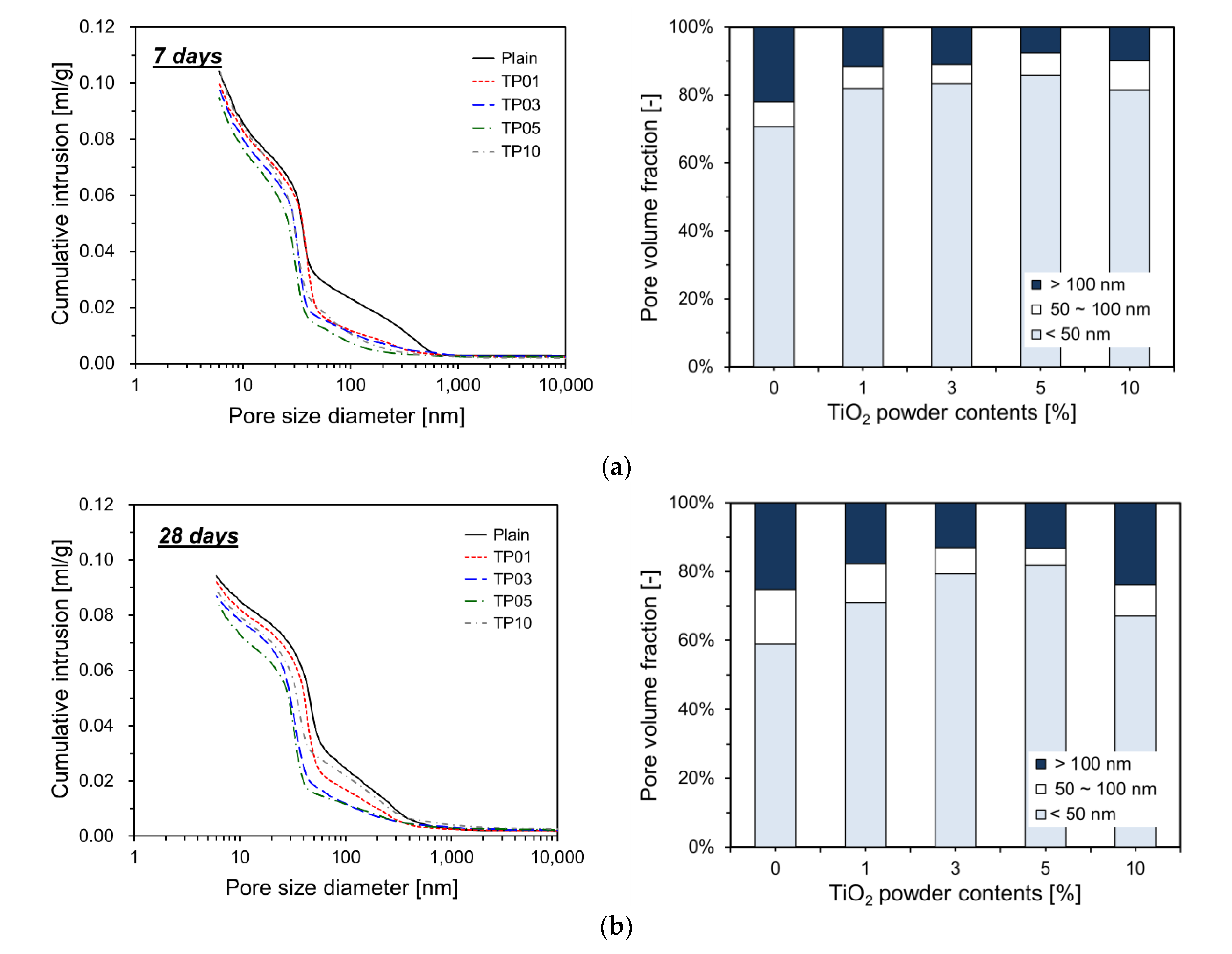
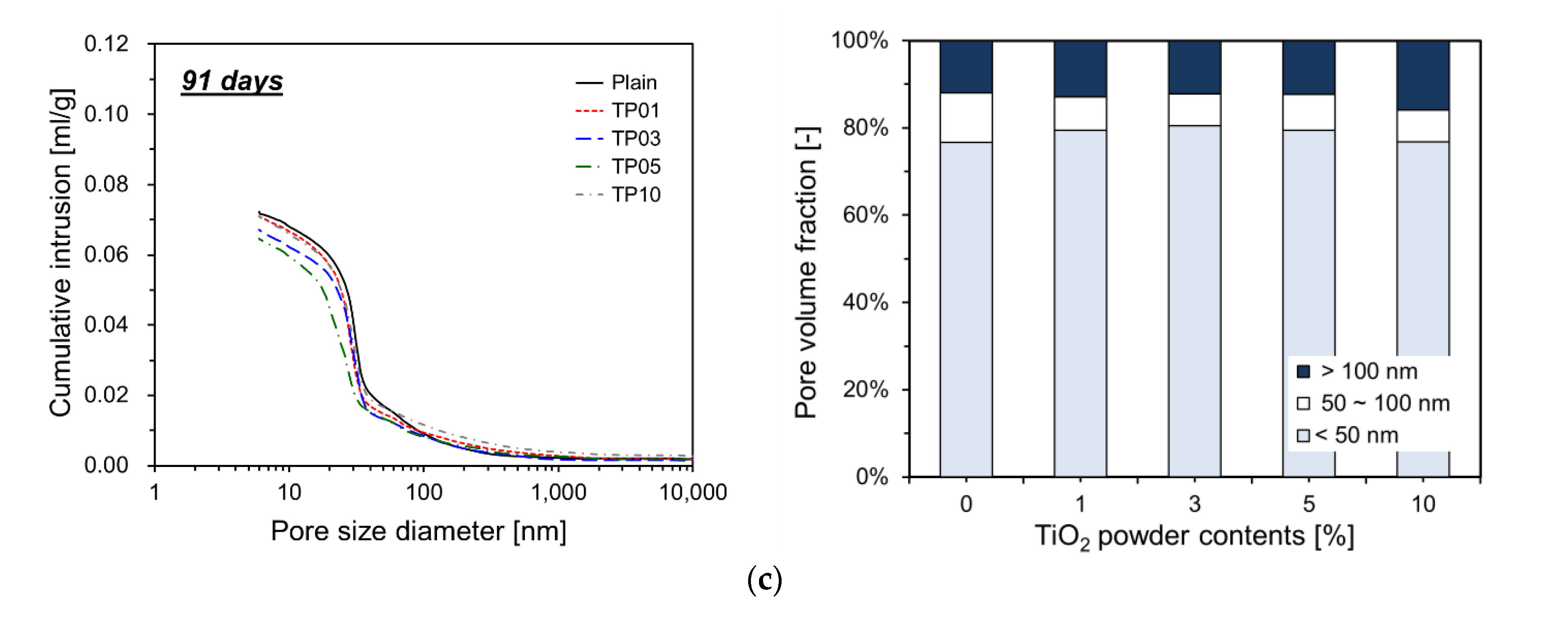
Figure 9 details the measurement results obtained by MIP. As presented in
Figure 9, the incorporation of P25 modifies the total pore volume of specimens. For all ages, the total pore volume of the specimens with P25 is lower than that of Plain. When P25 was added up to 5% by cement weight, the total pore volume decreased proportionally with the increase in the P25 content. This phenomenon implies that the NTPs function effectively as fillers in the pore spaces.
As the hydration reaction of the cement progresses, aggregates incorporating nanoparticles as nucleation sites expand and gradually occupy the surrounding pore spaces. These nucleation sites considerably accelerate the cement hydration reaction, resulting in hydration products that rapidly fill the pores and reduce the porosity. This effect is particularly pronounced at 7 and 28 days of curing but is less evident at 91 days. Fig. 9 illustrates that at 7 and 28 days, the specimens with P25 exhibit an increased proportion of capillary pores smaller than 50 nm within the total pore volume. This phenomenon implies that the NTPs function as nucleation sites, promoting the formation of additional hydration products that occupy the capillary pores, reducing their size [
17]. However, at 91 days, the influence of P25 incorporation on the pore volume fraction was less pronounced than that at earlier ages. This result could be attributed to the inert properties of the NTPs, which likely promoted the substantial formation of hydration products by day 28, resulting in filling of most capillary pores. Therefore, further growth of hydration products could have been restricted by the limited available space. For TP10, which included 10% P25, the pore volume increased compared with TP05, resulting in a pore distribution similar to TP01 because P25 particles tend to agglomerate easily in aqueous solutions. When a large quantity of P25 is added, agglomeration could hinder the particles from effectively serving as nucleation sites.
3.4. TG Analysis
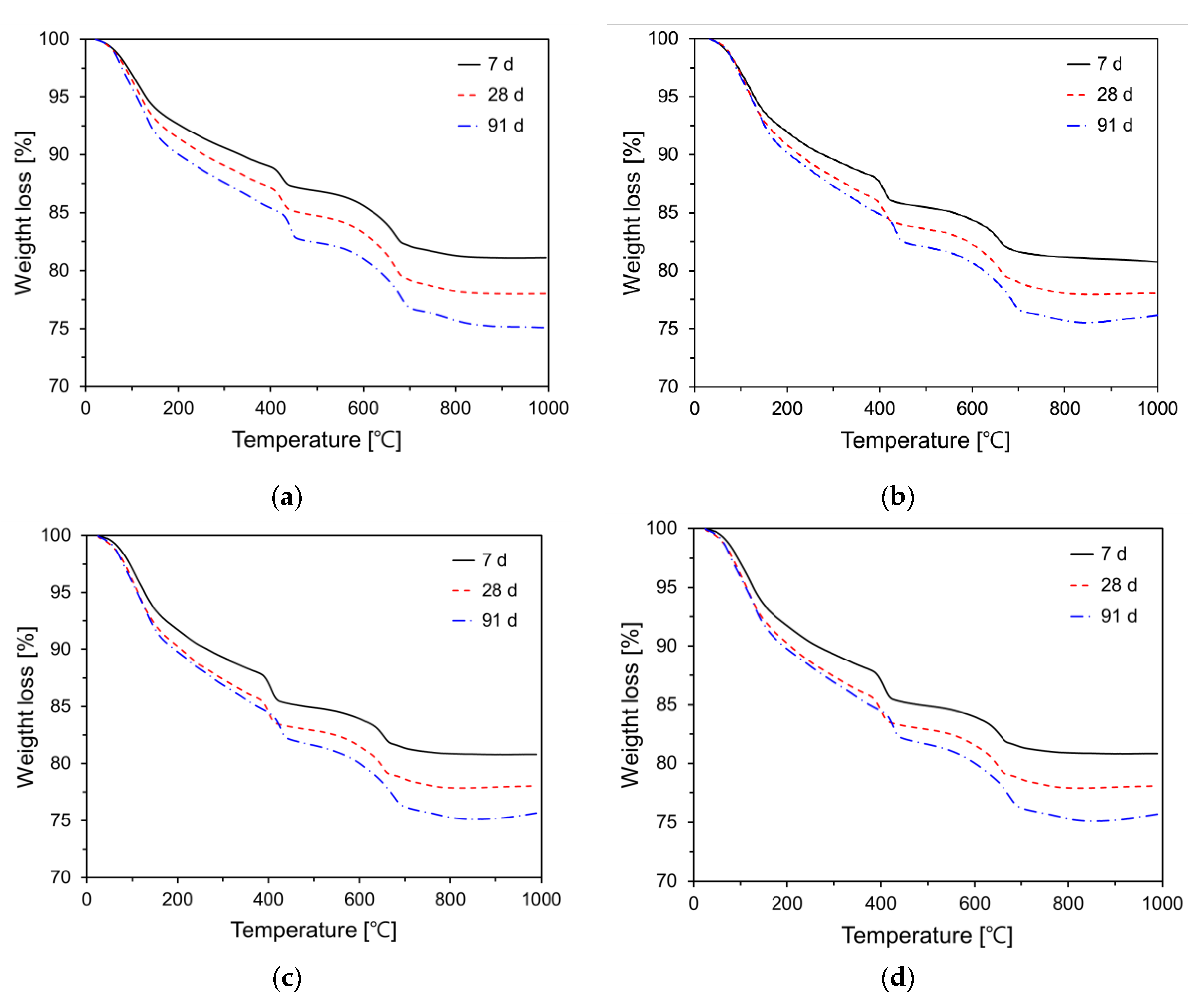
Figure 10 illustrates the TG analysis results for various P25 incorporation rates (0%, 3%, 5%, and 10%). When the cement paste specimens are exposed to elevated temperatures, weight loss occurs within a specific temperature range due to the dehydration, decomposition, and decarbonation of hydration products [
42,
43]. The TG graphs of all variables were similar in shape. This phenomenon indicates that the types of hydration products are similar. The TG curve of cement paste is typically delineated into the following regions: 40–200°C region, where dehydration of C–S–H gels, AFt, and AFm occurs (w
b1); 400–500°C region, where the decomposition of portlandite occurs (w
b2); and 500–750°C region, where the decarbonation of CaCO
3 occurs (w
b3) [
44,
45].
The content of chemically bound water (w
b) was determined from the relative weight loss observed in the three aforementioned temperature ranges, as expressed in Eq. (1). The coefficient 0.41 in Eq. (1) is derived from carbonated portlandite and used to estimate the content of chemically bound water [
46,
47]. The hydration degree of cement is defined as the ratio of w
b at a specific age to the maximum amount of w
b, as indicated in Eq. (2). The coefficient 0.24 in Eq. (2) denotes the maximum content of w
b required to fully hydrate cement 1 g, which generally falls within the range 0.23–0.25 g [
46,
47].
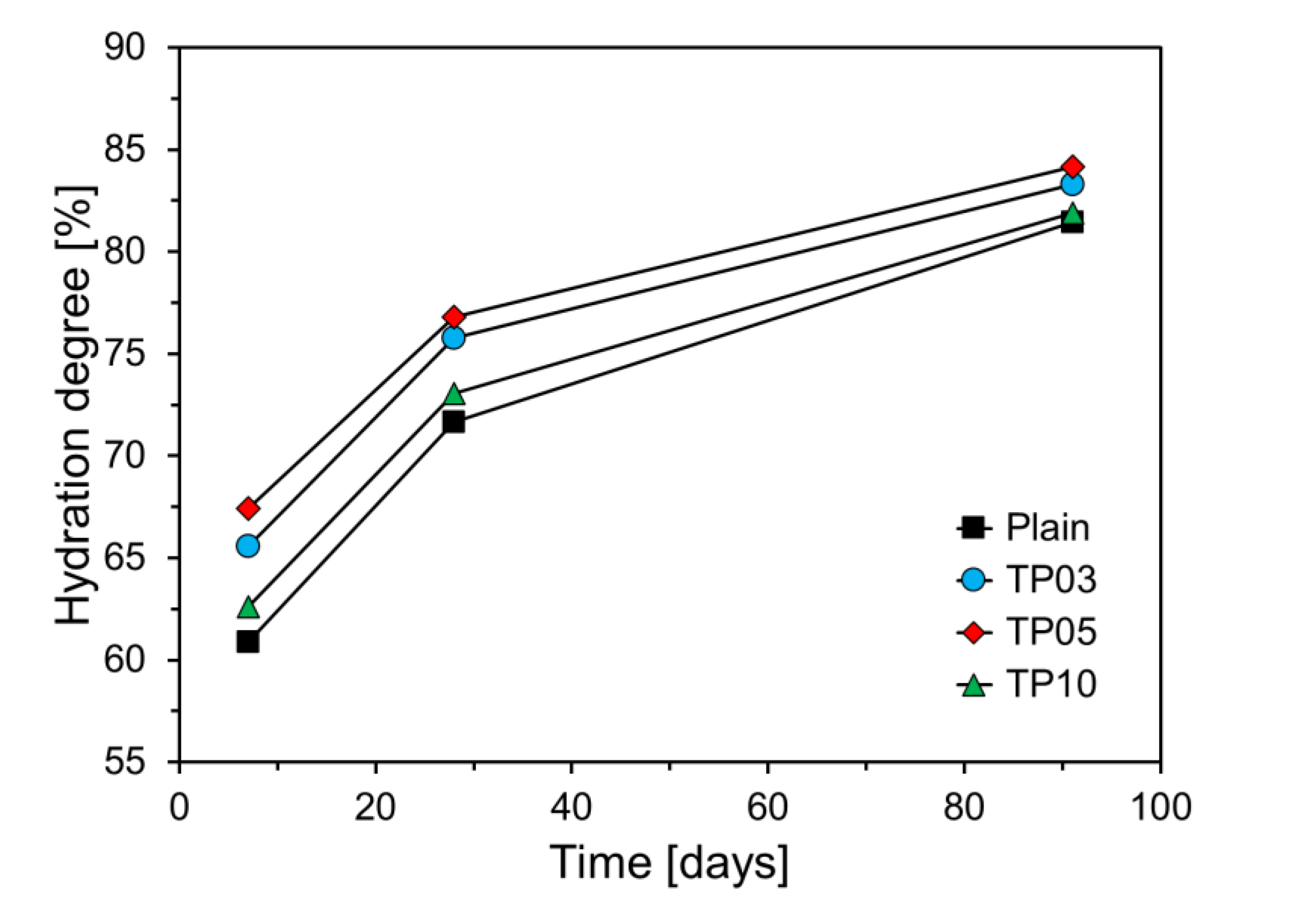
Figure 11 depicts the degree of cement hydration with respect to P25 incorporation. All variables revealed an increasing trend in the hydration degree as the curing age increased. Specimens with P25 exhibited a higher hydration degree than that of Plain, suggesting that P25 promotes C
3S hydration. This observation is consistent with the results of the heat of hydration and compressive strength. The specimen with 5% P25 by weight of cement (TP05) exhibited the highest hydration degree at all curing ages, notably showing approximately 6.6% higher hydration at 7 days compared with Plain. The hydration reaction in the specimens with P25 was markedly accelerated at early ages, with its influence diminishing at later ages. This phenomenon indicates that NTP substantially increased the content of w
b at early ages, thereby accelerating the formation and precipitation of hydrates and enhancing the degree of cement hydration.
4. Conclusions
Cementitious materials exhibit robust binding characteristics that can effectively immobilize nano-sized TiO2 particles within the matrix. This phenomenon enables the convenient integration of NTPs with cementitious materials without requiring additional processing steps. Furthermore, the porous structure of cement paste or mortar results in substantial advantages for the application of NTP. We conducted an experimental investigation into the effects of incorporating P25 on the hydration, microstructure, and compressive strength of cement. Incorporating P25 into cementitious materials promotes an early hydration reaction, shortening the induction period and reducing the setting time. Furthermore, P25 influences the mechanical properties of cementitious materials. The incorporation of P25 resulted in the modification of the capillary pores, leading to a decrease in the porosity of the cement paste. Additionally, the compressive strength exhibited an increasing trend at higher incorporation rates of P25.
The microstructural changes in the cement paste induced by incorporating P25 manifested at an early age, resulting in a pronounced enhancement in the early-age strength of the mortar specimens. The P25 particles effectively acted as fillers within the matrix, reducing void spaces. Furthermore, these particles were considered to be additional nucleation sites, thereby accelerating the cement hydration reaction. This acceleration resulted in the void filling with hydration products during the early stages, thereby improving the microstructure and mechanical properties. However, when a substantial amount of P25 was incorporated, the effect on the hydration reaction, microstructure, and compressive strength was not proportionally significant. This phenomenon is likely attributed to the propensity of P25 particles to agglomerate easily, impeding their effectiveness as nucleation sites during mixing.
Therefore, when developing novel functional construction materials using NTP, such as photocatalytic or self-cleaning products, carefully considering the influence of NTP on the hydration reactions of cementitious materials is crucial. Ensuring adequate dispersion of NTP within the matrix is essential for maximizing its functional benefits.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-C.C.; data curation, Y.-C.C.; formal analysis, Y.-C.C.; funding acquisition, Y.-C.C.; investigation, Y.-C.C.; methodology, Y.-C.C.; project administration, Y.-C.C.; supervision, Y.-C.C.; validation, Y.-C.C.; visualization, Y.-C.C.; writing—original draft, Y.-C.C.; writing—review & editing, Y.-C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (NRF-2020R1A2C2008926). This work was also supported by the Technology Innovation Program (RS-2023-00266009, Development of admixture and blended cement using unused inorganic resource) funded By the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy(MOTIE, Korea).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Su, Y. ; Hydration kinetics of cement-quicklime system at different temperatures. Thermochim. Acta. 2019, 673, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, K.; Gaylarde, C.C.; Shirakawa, M.A. Photocatalytic activity of ZnO and TiO2 ‘nanoparticles’ for use in cement mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tan, H.; He, X. Effects of nano-SiO2 on early strength and microstructure of steam-cured high volume fly ash cement system. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 194, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D. S.; Paul, S.C.; Anggraini, V.; Kong, S.Y.; Qureshi, T.S.; Rodriguez, C.R.; Liu, Q.; Šavija, B. Influence of SiO2, TiO2 and Fe2O3 nanoparticles on the properties of fly ash blended cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 119627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llano-Guerrero, E.A.; Gómez-Zamorano, L.Y.; Jiménez-Relinque, E. Effect of the addition of TiO2 nanoparticles in alkali-activated materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 245, 118370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Yan, C.J.; Luo, W.J.; Zhou, W. Effects of adding nano-TiO2 on compressive strength, drying shrinkage, carbonation and microstructure of fluidized bed fly ash based geopolymer paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.L.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Han. B.G. Investigating size effect of anatase phase nano-TiO2 on the property of cement-based composites. Mater. Res. Express. 2018, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S.; Yu, X.; Ou, J. Smart concretes and structures: a review. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 1303–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, J.; Yu, X.; Cui X, X.; Han, B. Comparison of compressive strength and electrical resistivity of cementitious composites with different nano- and micro-fillers. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018, 18, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.G.; Li, H.N.; Li, X.G.; Mei, J.P.; Lv, Y. Influence of nano-TiO2 on physical and hydration characteristics of fly ash-cement systems. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cheng, X.; Hou, P.; Ye, Z. Influences of nano-TiO2 on the properties of cement-based materials: hydration and drying shrinkage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 81, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, E.; Miyandehi, B.M.; Yang, J.; Yazdi, M.A. Single and combined effects of nano-SiO2, nano-Al2O3 and nano-TiO2 on the mechanical, rheological and durability properties of self-compacting mortar containing fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 84, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aïssa, A.H.; Puzenat, E.; Plassais, A.; Herrmann, J.M.; Haehnel, C.; Guillard, C. Characterization and photocatalytic performance in air of cementitious materials containing TiO2. Case study of formaldehyde removal. Appl. Catal. B. 2011, 107, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, A.; Allahverdi, A.; Hejazi, P. Effective dispersion of nano-TiO2 powder for enhancement of photocatalytic properties in cement mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 41, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reches, Y. Nanoparticles as concrete additives: review and perspectives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wang, E.; Hou, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Ye, J.; Qin, S. Characterization and mechanism of early hydration of calcium aluminate cement with anatase-TiO2 nanospheres additive. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 119922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kou, S.C.; Poon, C.S. ; Hydration and properties of nano-TiO2 blended cement composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.P.; Karade, S.R.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Yousuf, M.M.; Ahalawat, S. Beneficial role of nanosilica in cement based materials- a review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, A.; Riahi, S. TiO2 nanoparticles effects on physical, thermal and mechanical properties of self compacting concrete with ground granulated blast furnace slag as binder. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, A.; Riahi, S. The effects of TiO2 nanoparticles on flexural damage of self-compacting concrete. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2011, 20, 1049–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A.; Nair, R. Influence of nanomaterials in high strength concrete. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 974, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Essawy, A.A.; El, S.A. Physico-mechanical properties, potent adsorptive and photocatalytic efficacies of sulfate resisting cement blends containing micro silica and nano-TiO2. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.W.; Lee, J.W.; Park, B.; Choi, Y.C. Photocatalytic NOx degradation performance of TiO2-nanofiber-spray-coated foam composite according to saturated conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 358, 129414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F. Review of analytical studies on TiO2 nanoparticles and particle aggregation, coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, stabilization. Chemosphere. 2018, 212, 662–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Kawashima, S.; Wang, K.; Corr, D.J.; Qian, J.; Shah, S.P. Effects of colloidal nanosilica on rheological and mechanical properties of fly ash-cement mortar. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 35, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, F.; Pellutiè, L.; Sordello, F.; Minero, C.; Ortel, E.; Hodoroaba, V.D.; Maurino, V. Influence of agglomeration and aggregation on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B. 2017, 216, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, V.C. Multi-functional engineered cementitious composites (ECC). In Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC); Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 371–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutteridge, W.A.; Dalziel, J.A. Filler cement: the effect of the secondary component on the hydration of Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 1990, 20, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, A.M.; De Schutter, G.D. Cement hydration in the presence of high filler contents. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 2290–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, E.H.; Duval, R. Hydration heat kinetics of concrete with silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3388–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, E.M.; Young, J.F.; Damidot, D.A.; Jawed, I. Hydration of Portland cement. In Structure and Performance of Cements, Bensted, J., Barnes P., Eds.; Spon Press: London, UK, 2002; pp. 57–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.Y.; Kurtis, K.E. Influence of TiO2 nanoparticles on early C3S hydration. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 3399–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.J. A new approach to modeling the nucleation and growth kinetics of tricalcium silicate hydration. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 3282–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T. Preliminary study on the water permeability and microstructure of concrete incorporating nano-SiO2. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnström, J.; Martinelli, A.; Matic, A.; Börjesson, L.; Panas, I. Accelerating effects of colloidal nano-silica for beneficial calcium–silicate–hydrate formation in cement. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 392, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, D.; Chen, R. Influence of nano-SiO2 addition on properties of hardened cement paste as compared with silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senff, L.; Labrincha, J.A.; Ferreira, V.M.; Hotza, D.; Repette, W.L. Effect of nano-silica on rheology and fresh properties of cement pastes and mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2487–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G. Properties of high-volume fly ash concrete incorporating nano-SiO2. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.W.; Kim, C.H.; Tae, G.H.; Park, J.B. Characteristics of cement mortar with nano-SiO2 particles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.S.; Ferreira, V.M.; De Aguiar, J.L.B. Incorporation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mortars - influence of microstructure in the hardened state properties and photocatalytic activity. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 43, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaei, D.; Yang, S.; Berlouis, L.; Minto, J. Multiscale pore structure analysis of nano titanium dioxide cement mortar composite. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 22, 100779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Spiesz, P.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Effect of nano silica on the hydration and microstructure development of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) with a low binder amount. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, D.F. Application of sewage sludge ash and nano-SiO2 to manufacture tile as construction material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3312–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, I.; Hansen, W. Investigation of blended cement hydration by isothermal calorimetry and thermal analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo, S.M.; Moragues, A.; Gálvez, J.C.; Casati, M.J.; Reyes, E. The degree of hydration assessment of blended cement pastes by differential thermal and thermogravimetric analysis. Morphological evolution of the solid phases. Thermochim. Acta. 2014, 592, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tian, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Hou, G.; Shen, X. Studies on the size effects of nano-TiO2 on Portland cement hydration with different water to solid ratios. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 120390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Sun, J.; Hu, Y.; Xu, K.; Ma, S.; Shen, X. Research on cement hydration and hardening with different alkanolamines. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 141, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).