1. Introduction
Among landslides, those involving the shallow soil (up to 2-3 m of depth) are most frequently induced by rainfall and are highly dangerous as no premonitory signs are present over territories. The landslide occurrence is the final step of a chain of processes that start from the rainfall infiltration and lead to the slope collapse. Therefore, a tool including process quantification is necessary to get prepared against potential landslides hazards.
Over time, different techniques have been employed to predict shallow landslides occurrences in response to rainfall. The use of physical-mathematical models, especially after the spread of computers, has gained large consensus among engineers and the scientific community, not only for applications at local or slope scale, but also at larger extensions.
To detect landslide events, two main approaches are recognized: physically-based modeling and statistical modeling. PBDMs belong to the first category, and are also referred to as process-based models. Statistical approaches are further named “data-driven models” as they use data on past landslide events. Although they represent interesting techniques for large scale hazard assessments, they highly depend on the resolution of past landslides inventories, which in most cases are not very consistent, thus leading to high levels of uncertainty propagation. Moreover, under climate change conditions, data-driven approaches have to be undertaken carefully since new, extreme climatic conditions may not be represented by past data.
Physically-based distributed models (PBDMs) have been widely used to accurately quantify landslides-related processes at different geographic scales in recent years [
1]. Whether the aim is to design emergency plans to warn people or informing policy makers about consequences of extreme climatic events, PBDMs represent valid tools as they can detect landslide occurrences in advance.
On the other hand, physically-based models start from the quantification of individual processes, helping to design mitigation measures thanks to the possibility of assessing single aspects’ contribution to the overall stability. When dealing with future landslide prediction and climate change impacts on slope stability, this modeling approach is considerable noteworthy, especially when vegetation presence is considered [
2].
PBDMs can be used to back-analyze real landslides to derive the required soil parameters as well. These models can be highly sensitive to the input parameters variability. However, their use for both small scale and large scale applications is approved as they can maintain a low computational effort. To avoid errors in assigning unknown soil parameters, some physical models comprise probabilistic treatments of input uncertainty or are coupled with other approaches to get probability maps of failure as outputs.
When developing new models for shallow landslide detection, decisions upon which processes to consider must be taken. Normally, PBDMs for shallow landslide prediction are composed by a hydrological module interfaced with a geotechnical module, typically based on the estimation of the slope safety factor through the limit equilibrium method. The hydrological processes involved in landslides initiation are many and including all of them in a single model can make it impossible to be practically used over large areas in reasonable computational times. Because of this complexity, in the majority of the existing models, when considering hydrological aspects in detail, the mechanical aspects are considered in simplified ways, and vice-versa. The simplified approach based on the infinite slope scheme (ISS) is adopted in the majority of PBDMs for shallow landslides . In this approach, the assumption of a planar failure geometry is consistent with shape, size, and failure mechanisms of rainfall-induced shallow landslides.
In recent years, models including antecedent hydrological information have raised importance in landslide hazard assessment [
3], and including vegetation-related processes has become a central issue in shallow landslides prediction. This is because canopies and roots modify, both hydrologically and mechanically, the stability condition of slopes [
4,
5,
6]. Moreover, the rooted portion of soil has peculiar characteristics and its behavior, together with a proper consideration of unsaturated soil mechanics, should be taken into account in shallow landslides prediction. In fact, the interest in nature based solutions (NBSs) and bioengineering techniques has raised importance in preventing landslides over territories, not only because of environmental purposes but also because of economic aspects [
7,
8,
9]. Thus, assessing quantitatively the role of vegetation on slope stability is of importance, although a comprehensive methodology is still lacking.
In this work, a narrative review about the main physically-based distributed models developed over time is presented, highlighting which aspects or techniques were used and introduced over time by the different models. The review is restricted to the models that adopt the infinite slope scheme and are based on the limit equilibrium method. The aim is drawing a chronological memory of rainfall-induced shallow landslides modeling, also to address new research efforts in directions that were not yet explored. The paper is organized as follows. In the second section, a brief discussion about shallow landslides modeling methods is presented, stretching some conceptual aspects about hydrology and plants’ contribution. The third section focuses on models considered relevant to the aim of the review, including only models that don’t use any kind of probabilistic approach. This choice is meant to be helpful for researchers, in order to classify rainfall-induced physically-based models for shallow landslides in two different groups: “purely” physically-based distributed deterministic models (PBDDMs), i.e. the specific topic of this review, and hybrid forms. At the end, a conclusive section considers aspects that still have to be properly explored in PBDDMs. Some suggestions are also provided.
2. Shallow Landslides Modeling Methods
As already mentioned, the majority of the existing PBDDMs for rainfall-induced shallow landslides prediction are composed by two interfaced modules: one computes the hydrology, the other computes the slope stability.
The most observed mechanism for shallow landslides activation is the formation of nil or positive pore water pressure because of soil saturation. Saturated lenses develop in response to rainfall events because of infiltration and seepage processes and they can trigger landslides when enlarged enough. Water can accumulate in the soil because of the presence of an impermeable or a low-permeability layer, either during the capillary uprising process or the vertical downward seepage [
10].
Because of these observations, the first slope stability models were developed based on saturated soil conditions [
11], mainly considering the pore water pressure as a function of depth [
12]. Under saturation conditions, soil properties and hydrological parameters can be assumed as constant and the role of matric suction (i.e negative pore water pressure) is absent. Real meteorological conditions can even be ignored in models based on saturated soil mechanics, otherwise real rainfall amounts are considered as contributing to the uprising of an existing ground water table.
Some limitations of these simplified approaches have been recognized and practical applications related to slope stability problems also involve unsaturated soil mechanics [
13]. In particular, as shallow landslides have been observed to occur even under negative pore water pressure, i.e. when the soil is in partially saturated condition [
14,
15], it is important to consider the evolution in time of water pressure and unsaturated soil mechanics in PBDDMs.
The unsaturated soil mechanics is normally based on non-linear soil properties functions, including the constitutive relationship between soil water content and soil suction (also defined as water potential, or hydraulic head), namely the Soil Water Retention Curve (SWRC, or Soil Water Characteristic Curve, SWCC), and the one which relates soil suction or soil water content to soil hydraulic conductivity, namely the Hydraulic Conductivity Function (HCF) [
16,
17]. The relationships are unique for a certain pore size distribution of soil and are empirically defined. However, because of hysteretic behavior, these properties follow different patterns during the year, namely during wetting or drying phases [
18]. Moreover, the presence of vegetation may change the pore size distribution because of root growth, thus leading to an evolution of the SWRC and of the soil permeability during time with respect to SWRC or HCF of a bare soil [
19].
When considering unsaturated conditions, transient or stationary input rainfall can be considered for the hydrological balance computation, and water movements can be assessed through a transient analysis. The most used approach to get transient values of soil water content is the use of partial differential equations, in particular, numerical solutions of Richards’ equation for unsaturated seepage process [
20,
21], at different spatial domains (i.e. 1-D, 2-D or 3-D). This approach allows to consider different hydrological processes into a single balance equation, although in 3-D domain its computation can be consuming, both in terms of energy and time.
When dealing with rainfall-induced landslide hydrology, several processes should be quantified. In any case, the major water input is represented by rainfall infiltration, which enters the soil matrix and undergoes gradient and gravity-driven movements. Then, subsurface flows and redistribution processes take place.
When a numerical problem is involved, it is essential to define boundary conditions, that is defining how the considered physical system acts at the borders of its spatial and temporal domains. This allows the problem to be consistent with the physical reality.
As already mentioned, defining the antecedent condition of soil moisture prior to rainfall is fundamental to correctly simulate water movements during a precipitation event. The global soil water balance equation should be solved for a certain period to assess a consistent soil moisture condition prior to the analysis in the period of interest.
In this sense, as a key hydrological process, plant growth and evapotranspiration activity should not be neglected [
22]. In fact, vegetation alters the soil water content through different mechanisms, including the absorption of water over the rooted portion of the soil, the modification of SWRCs and parameters such as the saturated hydraulic conductivity, canopies rainfall interception, and the creation of preferential flow patterns through roots and stems. This latter aspect is very difficult to be considered simultaneously with matrix flow equations, out if the model allows to consider two different domains at the same time [
23]. Although preferential flow paths have different nature and originate in different ways (i.e., desiccation cracks, voids left by decaying roots etc), any of them is replicable by models only if approaches such as dual-permeability (or double porosity) are adopted [
24,
25].
Notwithstanding the effectiveness of Richards’ equation in soil water balance computation, this approach may not be the most efficient in specific cases. For example, when a landslide is triggered because of a wetting front depth propagation, the hydrological mechanisms can be approximated through simplified approaches for infiltration (e.g. [
26,
27]).
For what concerns geotechnical modules of PBDDMs, the most simplified and used approach for slope stability is the computation of a Factor of Safety (FoS). This approach is based on the limit equilibrium method and considers the relation between stabilizing and destabilizing actions on a slope. When the FoS is equal to 1, the slope is in a critical equilibrium state; as the FoS drops below 1, the entire slope is estimated as unstable.
Several methods to compute the FoS exist [
28]. In a general sense, the FoS is computed over one or more potential failure surfaces, to detect under which conditions and/or at which depth the whole slope becomes unstable. PBDDMs should adopt an automatic procedure for analyzing different slip surfaces, especially when the soil strength and pressure profiles differ along with depth.
Since shallow landslides are normally translational and their length/depth ratio is generally low, the infinite slope method (ISM), which assumes a ground-parallel planar failure surface, represents the most used approach, although it has some limitations [
29]. Among others, Lu and Godt developed an equation for FoS that allows the classic saturated soil mechanics theory based on the effective stress concept to be easily extended also to the unsaturated regime [
30]. However, models that aim to simulate rotational movement also exist as well as models that can approximate the landslide runout [
31].
It is known that vegetation contributes to soil reinforcement in different ways [
9]. For what concerns plant roots, it is known that the rooting system can extend the soil shear strength either through water absorption and mechanical reinforcement, normally quantified as an additional cohesive term extending the soil cohesion. More in detail, the mechanical improvement of soil shear strength through the root network tensile strength and its interaction with soil and bedrock. Both large and fine roots contribute to the global reinforcement exerted. The overall root cohesion can be derived through different methods, namely the Wu and Waldron model (WWM), the Fiber Bundle Model (FBM) and the Root Bundle Model (RBM) [
4]. The root reinforcement can be either basal or lateral when exerted, respectively, at the base of a failure plane or on the lateral sides of the landslide body. Nevertheless, in soil conditions near saturation it is not totally clear if these effects are present or not [
32].
PBDDMs can be applied at slope scale (small scale) or territorial scale (large scale). In the first case, it may be possible to carry on field campaigns to get specific soil hydraulic and geotechnical parameters. In the second case, especially when the analyzed area is larger than a single slope or a small catchment, field works can become very expensive and assigning reliable soil parameters can be challenging. It is possible to refer to literature data for similar cases or, if models are capable to be provided with, some parameters uncertainty treatment should be also involved [
33]. For models that do not involve probabilistic approaches, parameters values based on texture or pedotransfer functions are also normally involved if field campaign data are not available.
3. Models
SHALSTAB [
34] is one of the first published PBDMs, in 1994. It computes slope stability for cohesionless soils over an infinite slope under a steady-state flow condition and it is intended to be used with ESRI-ArcGIS. It was one of the first GIS-based PBDDMs. By assuming a steady saturated flow, the model is able to calculate the rainfall amount that is necessary to trigger a landslide over a specified area, using a contour-based Digital Elevation Model (DEM) methodology. Its output is an estimation of the critical saturated soil height, computed through an hydrological model called TOPOG [
35]. The model neglects the effects of the degree of saturation in the vadose zone. Because of its structure and mathematical formulations, SHALSTAB is not suitable for forecasting the timing of landslide triggering.
In 1995 the dSLAM model was published [
36]. The model aim was quantifying the slope instability in steep and forested areas. With dSLAM, mechanical root reinforcement models were introduced in shallow landslides PBDDMs, while hydraulic vegetation effects were ignored. The model was designed for translational slide overlying a lithic contact. dSLAM is a contour-based model and does not account for rainfall spatial distribution.
In 1998 the SHETRAN model was extended with a shallow landslide erosion and sediment yield component [
37]. It is a basin scale model that considers spatial variability of rainfall input and hydrological responses. It considers snowmelt as a triggering factor as well. The model computes the impact on sediment yields at the basin outlet. Two levels of resolution are comprised: first, a spatial assessment of shallow landslide susceptibility is carried out and a critical soil saturation condition is obtained; subsequently, a time-varying simulation based on the hydrological grid-based physical SHE model [
38] is conducted at a coarser resolution; thus the model can be computationally sustainable for basin-scale simulations. The SHE model comprises evapotranspiration activity and canopies interception.
In 2000, Iverson published its model intending to assess the effects of transient rainfall on timing, rates and locations of landslides [
39]. The hydrology is computed considering the soil infiltration capacity equal to the saturated hydraulic conductivity, in order to derive analytical values of pressure head, assuming a pre-existing steady-state pore pressure. The aim of the model is deriving rainfall thresholds for shallow landslides triggering, corresponding to the peak-value of pore pressure, by deriving transient pore pressure distributions that sum to the pre-existing one. Although a simplified transient analysis is included, Iverson’s model is better suitable for shallow landslides related to short duration rainfall (approximately, from 1 h to 70 h), as the model neglects lateral water transmission [
40].
TRIGRS [
41] is a grid-based PBDDM that aims at locating timing and size of landslides. At the time, most of the landslide prediction models were producing only susceptibility maps, not involving a complete transient and distributed analysis. In its first version, TRIGRS solves on a pixel-by-pixel basis the one-dimensional vertical version of Richards equation, assuming differentiated bare soil areas characterized by a unique homogeneous isotropic layer. The safety factor is computed in the infinite slope general framework. In general, TRIGRS is the most used PBDDM for shallow landslides at regional scale, even if no graphical interface is provided. Its use is linked to a Geographical Information System (GIS), where input data can be prepared and outputs can be visualized. Many versions of TRIGRS have been developed over time, including the vegetation effect, the condition of unsaturated regime, a parallelized version, and so on. TRIGRS provides the minimum Factor of Safety (FoS) calculated at selected time steps of a rainstorm, the pore water pressures, and the depth of minimum FoS at a certain time step. The soil is described by a SWRC. The unique consideration of 1-D water movements, although accurate under certain conditions, is not appropriate when complex topography is present over a large area. Moreover, the input DEM spatial resolution seems to strongly influence the results [
42].
In the same year 2008, the SLIP model was developed [
43]. It is a PBDDM that adopts a simplified hydrological approach to simulate soil water balance, assuming that the saturated portion of soil becomes larger with increasing rainfall. The soil consequently desaturates through a percolation process. To be quickly applied to large areas with low computational effort, the model avoids the need of being provided with complex hydrological formulation and approximates a transient seepage computation. In its recent versions, the SLIP model also included a simplified approach for accounting plants interception and roots cohesion [
44]. SLIP represents a valid example of a simplified although effective solution for Early Warning Systems over large areas, that is an urgent need due to climate change.
In 2011, the SUSHI model by Capparelli e Versace was published [
45]. It describes water movements in a bi-dimensional domain, allowing the consideration of an irregular soil stratigraphy and different soil parameters. A 2-D Richards’ equation is involved in the model, following the assumption of isotropic soil, through the adoption of a specific capillarity coefficient called C(Ψ). This coefficient represents the rate at which water is absorbed or released because of pressure head changes in the soil. A fully implicit method and the finite difference method are employed in the SUSHI model. Evapotranspiration is accounted for, by adopting a uniform root distribution and, deriving a sink transpiration term. The vegetation is modeled considering a fixed Leaf Area Index value (LAI) throughout the year.
Arnone et al. [
46] published in 2011 a model called tRIBS-Landslide, then modified to include vegetation as well in 2013 [
47] and in 2016 [
48], turning the model into tRIBS-VEGGIE-Landslide. Their methodology is based on a Triangular Irregular Network (TIN) mesh and accounts for post-failure movement by considering certain angles as thresholds for determining if the landslide body will move up to a run-out distance. Landslide movement is assumed to follow the same flow directions evaluated by tRIBS hydrological component (the deepest descend), which is based on a transient computation of infiltration and redistribution processes. The basin morphology can be modified by landslides material, with consequent impact on most of the simulated processes. For what concerns vegetation, the model version of 2016 considers a root density distribution with depth through a Root Bundle Model, the evapotranspiration estimated through the resistivity formulation based on daily LAI that must be provided as mean annual variation. The model has not been validated in a real case study.
In 2014, Milledge et al. pointed out that the existing models were highly computationally demanding such that not practically applicable across landscapes [
49]. The proposed model, called MD-STAB, simulates lateral resistances acting on landslide margins using earth pressure theory and lateral root distribution, which is modeled as an exponential function of soil depth, in a three-dimensional limit equilibrium force balance. This assumption allows the model to consider roots that cross laterally the shearing surfaces. The possibility of considering forces that act on the lateral sides of rigid blocks contradicts the infinite slope assumption, for which the inter-slice interactions are ignored. This model was extended, including derivation of root reinforcement from field measured forest stand characteristics [
50]. The model ignores infiltration, soil suction and capillary rises and the groundwater level is steady and parallel to the slope surface.
In 2017, SOSlope was published by Cohen and Schwarz [
51]. The model focuses on the effect of roots and soil strength on slope stability in forests. The hydrological aspects are considered through a simplified and empirical dual-porosity model. Through this approach, SOSlope can approximate the water dynamics in both the soil matrix and the preferential flow domains. The model is suitable for assessing fundamental aspects such as the role of forest structure (e.g., tree size, tree spacing), root distribution, and root mechanical properties on the triggering mechanisms of shallow landslides. SOSlope considers both lateral and basal root reinforcement. The model is particularly suitable for highly-detailed forest management purposes and outputs can be used in GIS environments.
Lizàrraga and Buscarnera in 2018 developed a model that uses suction-dependent plasticity and limit equilibrium theories to derive slope factor of safety in unsaturated soils [
52]. Their model considers mechanical aspects usually not included in other models, such as suction-hardening and liquefaction potential. The aim is to simultaneously quantify the susceptibility to frictional failure and wetting-induced liquefaction in shallow slopes, in order to incorporate these considerations in regional-scale landslide hazard mapping [
53], coupled with a transient hydrology computation based on Richards’ equation. Laboratory data are used to determine input parameters. The model application points out the strong interplay between infiltration mechanisms (i.e., slow or fast) and the mode and depth of slope instability. Vegetation effects are neglected.
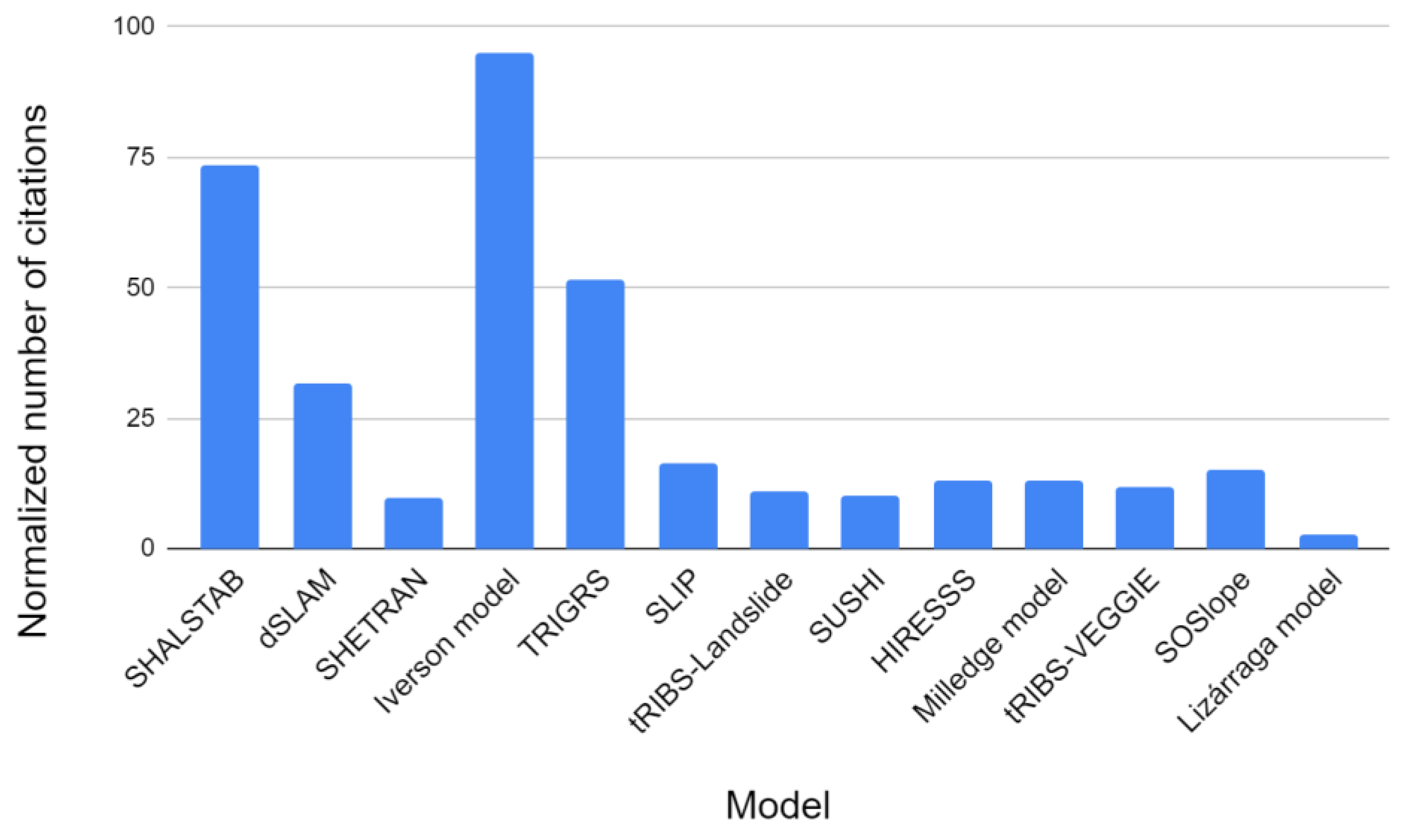
In
Figure 1 the normalized number of citations of the different models considered are represented. It can be seen that the most cited models are the Iverson model, SHALSTAB and TRIGRS. Out of them, only the dSLAM model has a normalized citation number higher than 25. These four models can thus be considered as milestones of PBDDMs knowledge and development over time.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Based on publishing date, several models were briefly described in this narrative review trying to draw a comprehensive timeline of physically-based deterministic models for shallow landslides.
By analyzing the literature, purely deterministic approaches appear to have recently become less explored than they were in the last decades. However, it appears clear that the attention given to the stabilizing effects of vegetation has grown over years, as testified by the arising complexity involved when trying to assess these effects in a consistent way. Big challenges are still open about this topic, since most of the root reinforcement models are based on variables and parameters not easily derivable such as root architecture or root diameters. Most of the root reinforcement models have a strong empirical basis not easily applicable at large scale, particularly when different kinds of plant species cohabit [
54]. New paradigms and expedients should be explored for roots’ effect quantification over large areas, and purely deterministic models can help in this task, as the processes and the related parameters can be quantified and studied singularly in a specific way. An example is provided by [
55], where root-induced modifications of soil hydraulic properties (namely, the saturated hydraulic conductivity and the Soil Water Retention Curve) are included in a physically-based model. From this point of view, involving vegetation as a dynamic variable, for example accounting for growing in time and space of roots and canopy, based on real meteorological data (i.e., models based on heat accumulation of plants and thermal growth thresholds [
56]), worth to be tested at different spatial scales. More studies such as those based on remote sensing, linking canopies development with root architectures, rooting depth and root spatial extensions, could help in applying root development models over large areas and vegetation growth can be more easily derived [
57].
An important aspect that constitutes a strong point since the first PBDMs were published, is the interoperability with GIS environments. This aspect can help decision makers to cross different sources of information about territories. As it is difficult to have a unique, comprehensive PBDDM for all the processes that should be accounted for in landslide hazard assessment, overlaying different models outputs or different spatial information can provide more insights on a large scale. In fact, it should not be overlooked that PBDDMs pretend to give a single, specific output based on single, selected input parameters that may not represent the reality, especially when large periods are considered. Comparing different sources of information through pre- or post-processing techniques and procedures may help raise the reliability of landslide risk assessment analyses, maintaining an acceptable operational time.
In distributed models, sensitivity analysis to different DEM (or mesh) spatial resolutions should be included. It is known that accuracy changes according to the spatial resolution considered, either when computing hydrology or stability, especially when this latter is based on an infinite slope method. This aspect appears not properly considered when new models are developed, although the problem is crucial for a proper application of the model itself. In fact, spatial discretization of the domain can lead to different results [
58].
Although rarely discussed when new models are developed, an important aspect for practical applications is the required running time of the different algorithms. This problem is crucial especially if the model should be used in early warning systems for civil protection purposes.
It is worth remembering that a very important expedient to overcome spatial uncertainty of parameters is including probabilistic approaches in PBDMs, thus leading to hybrid solutions. There are several valid examples in literature, such as SINMAP [
59], GEOTOP-Fs [
60], HIRESSS [
61], SlideForMap [
62] and FSLAM [
63] that include these aspects at different complexity rates, but in this paper it was preferred to focus on physically-based distributed models that include only deterministic input parameters and output results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S.; methodology, G.S. and R.V..; resources, G.S., M.Bo. and R.V.; writing—original draft preparation, G.S.; writing—review and editing, G.S., M.B., C. M., F.T.; supervision, R.V and M. Bo. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is co-funded by the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MUR) and the European Union through the REACT-EU program.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Meena, V.; Kumari, S.; Shankar, V. Physically based modelling techniques for landslide susceptibility analysis: A comparison. IOP Conf. Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1032. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., & Duan, W. Decoding vegetation’s role in landslide susceptibility mapping: An integrated review of techniques and future directions. Biogeotechnics, 2023, 100056. [CrossRef]
- Greco, R.; Marino, P.; Bogaard, T.A. Recent advancements of landslide hydrology. WIREs Water 2023, 10. [CrossRef]
- Murgia, I.; Giadrossich, F.; Mao, Z.; Cohen, D.; Capra, G.F.; Schwarz, M. Modeling shallow landslides and root reinforcement: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 181. [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Werner, A.D.; Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Tan, Z. Root-induced changes of soil hydraulic properties – A review. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125203. [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Leung, A.; Ng, C. Modelling effects of root growth and decay on soil water retention and permeability. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 56, 1049–1055. [CrossRef]
- Arce-Mojica, T.d.J.; Nehren, U.; Sudmeier-Rieux, K.; Miranda, P.J.; Anhuf, D. Nature-based solutions (NbS) for reducing the risk of shallow landslides: Where do we stand? Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 41, 101293. [CrossRef]
- Vicarelli, M.; Sudmeier-Rieux, K.; Alsadadi, A.; Shrestha, A.; Schütze, S.; Kang, M.M.; Leue, M.; Wasielewski, D.; Mysiak, J. On the cost-effectiveness of Nature-based Solutions for reducing disaster risk. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 947, 174524. [CrossRef]
- DiBiagio, A.; Capobianco, V.; Oen, A.; Tallaksen, L.M. State-of-the-art: parametrization of hydrological and mechanical reinforcement effects of vegetation in slope stability models for shallow landslides. Landslides 2024, 1–30. [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Hong, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, J. A modelling study of rainfall-induced shallow landslide mechanisms under different rainfall characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 790–801. [CrossRef]
- Gofar, N.; Rahardjo, H. Saturated and unsaturated stability analysis of slope subjected to rainfall infiltration. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 101, 05004. [CrossRef]
- Ridley, A. M. Soil suction—what it is and how to successfully measure it. In FMGM 2015: Proceedings of the Ninth Symposium on Field Measurements in Geomechanics, 2015, 27-46. Australian Centre for Geomechanics. [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D. G. Unsaturated soil mechanics in engineering practice. Journal of geotechnical and geoenvironmental engineering, 2006, 132(3), 286-321. [CrossRef]
- Bittelli, M.; Valentino, R.; Salvatorelli, F.; Pisa, P.R. Monitoring soil-water and displacement conditions leading to landslide occurrence in partially saturated clays. Geomorphology 2012, 173-174, 161–173. [CrossRef]
- Godt, J.W.; Baum, R.L.; Lu, N. Landsliding in partially saturated materials. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [CrossRef]
- van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, M.; Meisina, C.; Valentino, R.; Lu, N.; Bittelli, M.; Chersich, S. Hydrological factors affecting rainfall-induced shallow landslides: From the field monitoring to a simplified slope stability analysis. Eng. Geol. 2015, 193, 19–37. [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.; Garg, A.; Ng, C.W.W. Effects of plant roots on soil-water retention and induced suction in vegetated soil. Eng. Geol. 2015, 193, 183–197. [CrossRef]
- Farthing, M.W.; Ogden, F.L. Numerical Solution of Richards’ Equation: A Review of Advances and Challenges. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 1257–1269. [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Yang, J.; Zeng, J.; Tso, C.M.; Zeng, W.; Shi, L. Review of numerical solution of Richardson–Richards equation for variably saturated flow in soils. WIREs Water 2019, 6. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xia, J.; Xu, C.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Sobkowiak, L.; Long, C. Evapotranspiration estimation methods in hydrological models. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 359–369. [CrossRef]
- Gerke, H.H. Preferential flow descriptions for structured soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2006, 169, 382–400. [CrossRef]
- Montrasio, L., Valentino, R., & Losi, G. L. Rainfall infiltration in a shallow soil: a numerical simulation of the double-porosity effect. Electron. J. Geotechnol. Eng, 2011, 16, 1387-1403.
- Shao, W.; Yang, Z.; Ni, J.; Su, Y.; Nie, W.; Ma, X. Comparison of single- and dual-permeability models in simulating the unsaturated hydro-mechanical behavior in a rainfall-triggered landslide. Landslides 2018, 15, 2449–2464. [CrossRef]
- Rawls, W.J.; Brakensiek, D.L.; Miller, N. Green-ampt Infiltration Parameters from Soils Data. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 62–70. [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.E. Prediction of shallow landslide by surficial stability analysis considering rainfall infiltration. Eng. Geol. 2017, 231, 126–138. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Dai, T.; Li, S. Review and Comparative Analysis of Factor of Safety Definitions in Slope Stability. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2024, 42, 4263–4283. [CrossRef]
- Milledge, D.G.; Griffiths, D.V.; Lane, S.N.; Warburton, J. Limits on the validity of infinite length assumptions for modelling shallow landslides. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2012, 37, 1158–1166. [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Godt, J. Infinite slope stability under steady unsaturated seepage conditions. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, Z.; He, S. Modeling the landslide-generated debris flow from formation to propagation and run-out by considering the effect of vegetation. Landslides 2020, 18, 43–58. [CrossRef]
- Masi, E.B.; Tofani, V.; Rossi, G.; Cuomo, S.; Wu, W.; Salciarini, D.; Caporali, E.; Catani, F. Effects of roots cohesion on regional distributed slope stability modelling. CATENA 2023, 222. [CrossRef]
- Raia, S.; Alvioli, M.; Rossi, M.; Baum, R.L.; Godt, J.W.; Guzzetti, F. Improving predictive power of physically based rainfall-induced shallow landslide models: a probabilistic approach. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 495–514. [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Dietrich, W.E. A physically based model for the topographic control on shallow landsliding. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1153–1171. [CrossRef]
- O’Loughlin, E.M. Prediction of Surface Saturation Zones in Natural Catchments by Topographic Analysis. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 794–804. [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Sidle, R.C. A Distributed Slope Stability Model for Steep Forested Basins. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2097–2110. [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.; Bathurst, J.C. Physically based modelling of shallow landslide sediment yield at a catchment scale. Environ. Geol. 1998, 35, 89–99. [CrossRef]
- Abbott, M. B., Bathurst, J. C., Cunge, J. A., O’Connell, P. E., & Rasmussen, J. An introduction to the European Hydrological System—Systeme Hydrologique Europeen,“SHE”, 1: History and philosophy of a physically-based, distributed modelling system. Journal of hydrology, 1986, 87(1-2), 45-59. [CrossRef]
- Iverson, R.M. Landslide triggering by rain infiltration. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 1897–1910. [CrossRef]
- Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.; Sosio, R. Approaches for defining thresholds and return periods for rainfall-triggered shallow landslides. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 1444–1460. [CrossRef]
- Baum, R. L., Savage, W. Z., & Godt, J. W. TRIGRS: a Fortran program for transient rainfall infiltration and grid-based regional slope-stability analysis, version 2.0. Reston, VA, USA: US Geological Survey, 2008.
- Viet, T.T.; Lee, G.; Thu, T.M.; An, H.U. Effect of Digital Elevation Model Resolution on Shallow Landslide Modeling Using TRIGRS. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2017, 18. [CrossRef]
- Montrasio, L.; Valentino, R.; Corina, A.; Rossi, L.; Rudari, R. A prototype system for space–time assessment of rainfall-induced shallow landslides in Italy. Nat. Hazards 2014, 74, 1263–1290. [CrossRef]
- Montrasio, L.; Gatto, M.P.A.; Miodini, C. The role of plants in the prevention of soil-slip: the G-SLIP model and its application on territorial scale through G-XSLIP platform. Landslides 2023, 20, 1149–1165. [CrossRef]
- Capparelli, G.; Versace, P. FLaIR and SUSHI: two mathematical models for early warning of landslides induced by rainfall. Landslides 2010, 8, 67–79. [CrossRef]
- Arnone, E.; Noto, L.; Lepore, C.; Bras, R. Physically-based and distributed approach to analyze rainfall-triggered landslides at watershed scale. Geomorphology 2011, 133, 121–131. [CrossRef]
- Lepore, C.; Arnone, E.; Noto, L.V.; Sivandran, G.; Bras, R.L. Physically based modeling of rainfall-triggered landslides: a case study in the Luquillo forest, Puerto Rico. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 3371–3387. [CrossRef]
- Arnone, E.; Caracciolo, D.; Noto, L.V.; Preti, F.; Bras, R.L. Modeling the hydrological and mechanical effect of roots on shallow landslides. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 8590–8612. [CrossRef]
- Milledge, D.G.; Bellugi, D.; McKean, J.A.; Densmore, A.L.; Dietrich, W.E. A multidimensional stability model for predicting shallow landslide size and shape across landscapes. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 2481–2504. [CrossRef]
- Cislaghi, A.; Chiaradia, E.A.; Bischetti, G.B. Including root reinforcement variability in a probabilistic 3D stability model. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2017, 42, 1789–1806. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.; Schwarz, M. Tree-root control of shallow landslides. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2017, 5, 451–477. [CrossRef]
- Lizárraga, J.J.; Buscarnera, G.; J. J. Lizárraga*xJ. J. LizárragaSearch for articles by this author G. Buscarnera*xG. BuscarneraSearch for articles by this author *Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA.; Nadimi, S.; Fonseca, J.; Tamagnini, R.; Wheeler, S.J.; Sharma, R.S.; Buisson, M.S.R. Safety factors to detect flowslides and slips in unsaturated shallow slopes. Geotech. 2018, 68, 442–450. [CrossRef]
- Lizárraga, J.J.; Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.B.; Buscarnera, G. Regional-scale modelling of shallow landslides with different initiation mechanisms: Sliding versus liquefaction. Eng. Geol. 2017, 228, 346–356. [CrossRef]
- Lann, T.; Bao, H.; Lan, H.; Zheng, H.; Yan, C.; Peng, J. Hydro-mechanical effects of vegetation on slope stability: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 926, 171691. [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Leung, A.; Ng, C.; Shao, W. Modelling hydro-mechanical reinforcements of plants to slope stability. Comput. Geotech. 2018, 95, 99–109. [CrossRef]
- Sannino, G.; Tomei, F.; Bittelli, M.; Bordoni, M.; Meisina, C.; Valentino, R. Implementation of a slope stability method in the CRITERIA-1D agro-hydrological modeling scheme. Landslides 2024, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Glenn, E.P.; Huete, A.R.; Nagler, P.L.; Nelson, S.G. Relationship Between Remotely-sensed Vegetation Indices, Canopy Attributes and Plant Physiological Processes: What Vegetation Indices Can and Cannot Tell Us About the Landscape. Sensors 2008, 8, 2136–2160. [CrossRef]
- Zieher, T.; Schneider-Muntau, B.; Mergili, M. Are real-world shallow landslides reproducible by physically-based models? Four test cases in the Laternser valley, Vorarlberg (Austria). Landslides 2017, 14, 2009–2023. [CrossRef]
- Pack, R. T., Tarboton, D. G., & Goodwin, C. N. The SINMAP approach to terrain stability mapping. 1998.
- Simoni, S.; Zanotti, F.; Bertoldi, G.; Rigon, R. Modelling the probability of occurrence of shallow landslides and channelized debris flows using GEOtop-FS. Hydrological Processes: An International Journal 2007, 22, 532–545. [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Catani, F.; Leoni, L.; Segoni, S.; Tofani, V. HIRESSS: a physically based slope stability simulator for HPC applications. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 151–166. [CrossRef]
- van Zadelhoff, F.B.; Albaba, A.; Cohen, D.; Phillips, C.; Schaefli, B.; Dorren, L.; Schwarz, M. Introducing SlideforMAP: a probabilistic finite slope approach for modelling shallow-landslide probability in forested situations. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 2611–2635. [CrossRef]
- Medina, V.; Hürlimann, M.; Guo, Z.; Lloret, A.; Vaunat, J. Fast physically-based model for rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility assessment at regional scale. CATENA 2021, 201. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).